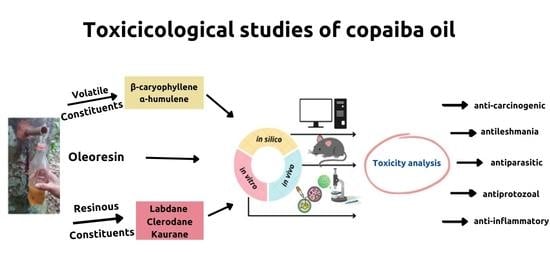
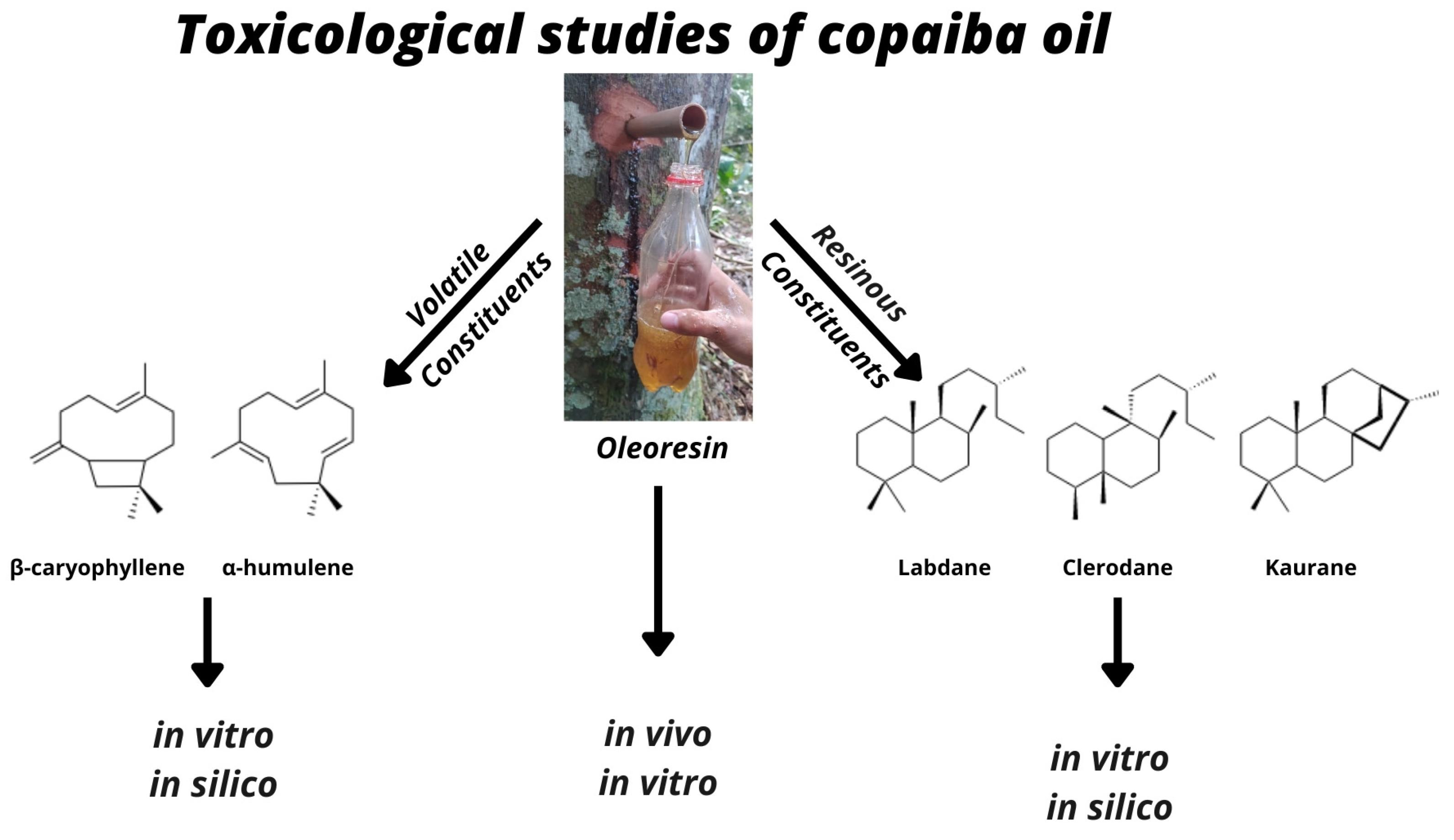
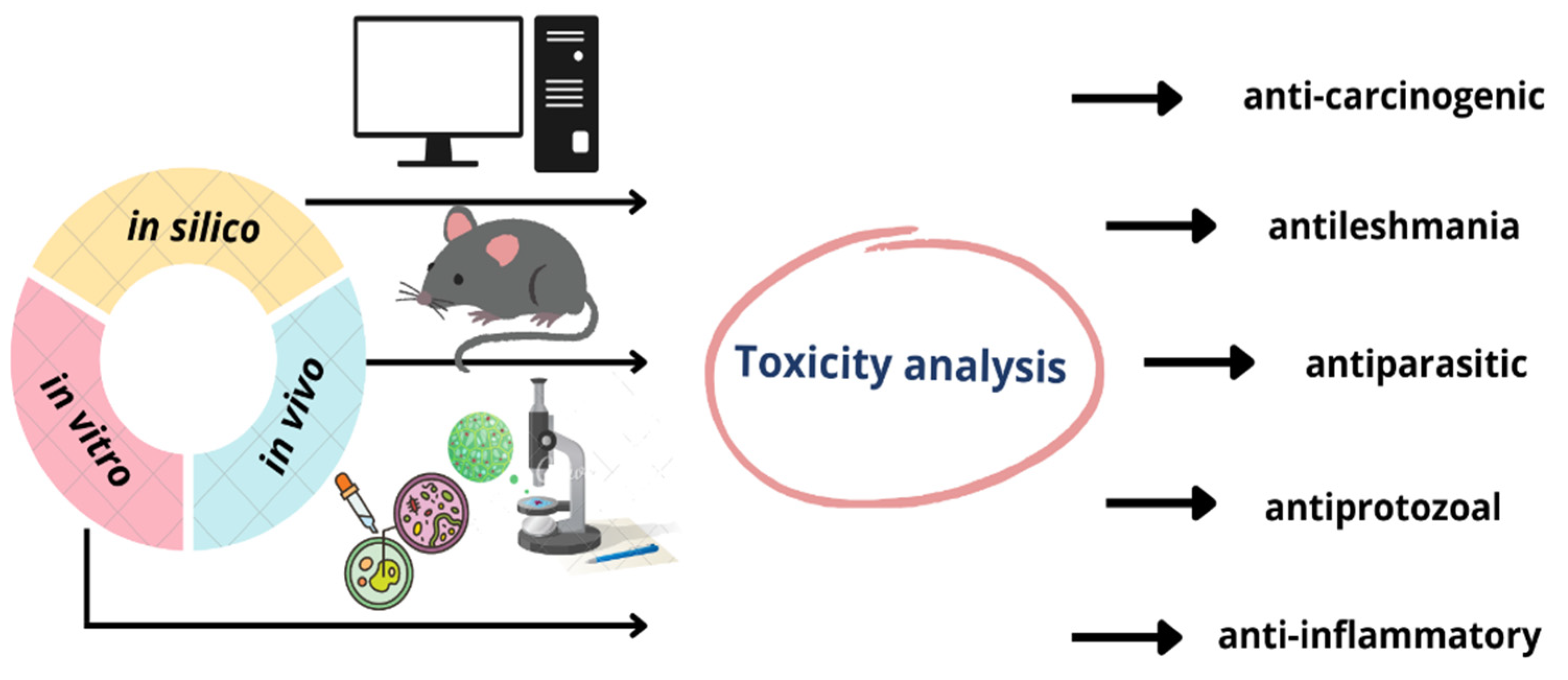
Toxicological Effects of Copaiba Oil (Copaifera spp.) and Its Active Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity Assays Usually Performed in Natural Substances
3.2. In Vivo Toxicological Analyses of the Copaiba Oil and Its Constituents
3.3. In Vitro Toxicological Analyses of the Copaiba Oil and Its Constituents
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity (Normal Cells)
3.3.2. Cytotoxicity (Cancer Cells)
| Copaifera spp. | Material | Cytotoxic Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. paupera | Methyl copalate | IC50 = 2.5 g/mL (P-388–murine lymphoma), IC50 = 5 g/mL (A549–human lung carcinoma), IC50 = 5 g/mL (HT-29–human colon carcinoma); IC50 = 10 g/mL (MEL-28–human melanoma). | [48] |
| Copaifera sp. | Kaurenoic acid | IC50 = 84.2 μM (MCF-7–human breast tumor, 45% growth inhibition) and IC50 = 44.7 μM (HCT8–human colon tumor, 45% growth inhibition). | [55] |
| C. multijuga Hayne | Oleoresin | IC50 = 457 μg/mL (B16F10–murine melanoma). | [47] |
| - | α-humulene | IC50 = 55 to 73 μM (MCF-7–human breast tumor), (PC-3–prostate tumor), (A549–lung tumor), (DLD-1–colorectal adenocarcinoma), (M4BEU–melanoma) and (CT-26–fibroblast). | [56] |
| - | β-caryophyllene oxide | IC50 = 3.95 µM (HepG2–hepatocyte carcinoma); IC50 = 12.6 µM (AGS–gastric adenocarcinoma); IC50 = 13.55 µM (HeLa–human cervical adenocarcinoma); IC50 = 16, 79 µM (SNU-1–gastric carcinoma); IC50 = 27.39 µM (SNU-16–gastric carcinoma). | [57] |
| C. multijuga Hayne | Kaurenoic, copalic, 3-hydroxy-copalic, 3-acetoxy-copalic and hardwickiic acids and kolavenic acid methyl ester | IC50 = 20 μM (AGP01–human gastric cancer), with 13% growth inhibition; IC50 = 20 μM (SF-295–human glioblastoma), with 18% growth inhibition. | [39] |
| Copaifera sp. | Copalic acid | IC50 = 68.3 μg/mL (MO59J–human glioblastoma); IC50 = 44.0 μg/mL (HeLa–human cervical adenocarcinoma). | [9] |
| - | β-caryophyllene oxide | IC50 = 8.94 × 10−3 mg/mL (A-2780–human ovarian cancer cell lineage). | [58] |
| - | β-caryophyllene oxide, α-humulene, trans-nerolidol and valencene | β-caryophyllene oxide with IC50 = 57.7 μg/mL, α-humulene with IC50 = 24.1 μg/mL, valencene with IC50 = 38.1 μg/mL and trans-nerolide with IC50 = 28.7 μg/mL (CaCo-2–human colorectal adenocarcinoma). | [59] |
| - | β-caryophyllene oxide; β-caryophyllene | IC50 = 28 µg/mL (HCT116–human colon tumor); IC50 = 32 µg/mL (PANC-1–pancreatic carcinoma); IC50 = 79 µg/mL (PC-3–prostate tumor); IC50 = 110 µg/mL (MCF-7–human breast tumor). | [37] |
3.3.3. In Silico Toxicological Analyses of the Copaiba Oil and Its Constituents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leandro, L.M.; Vargas, F.S.; Barbosa, P.C.S.; Neves, J.K.O.; Silva, J.A.; Veiga-Junior, V.F. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Terpenoids from Copaiba (Copaifera spp.) Oleoresins. Molecules 2012, 17, 3866–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga Junior, V.F.; Pinto, A.C. The Copaifera, L. genus. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azani, N.; Babineau, M.; Bailey, C.D.; Banks, H.; Barbosa, A.R.; Pinto, R.B.; Boatwright, J.S.; Borges, L.M.; Brown, G.K.; Bruneau, A.; et al. A new subfamily classification of the Leguminosae based on a taxonomically comprehensive phylogeny—The Legume Phylogeny Working Group (LPWG). Taxon 2017, 66, 44–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, C.; Mejía, J.A.A.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Borges, C.H.G.; Martins, C.H.G.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Bastos, J.K. Occurrence, chemical composition, biological activities and analytical methods on Copaifera genus—A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.; Ferrari, A.S.; da Cunha, D.C.; da Silva, J.K.; Cazarin, C.B.B.; Correa, L.C.; Prado, M.A.; de Carvalho-Silva, L.B.; Esteves, E.A.; Júnior, M.R.M. Polyphenols, antioxidants, and antimutagenic effects of Copaifera langsdorffii fruit. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.C.F.; Ribeiro, R.; Almeida e Silva, J.E.; dos Santos Tavares, S.S.; de Araujo, Y.C.D.; da Veiga-Junior, V.F. Chemistry, Biological Activities, and Uses of Copaiba Oil Resins. In Gums, Resins and Latexes of Plant Origin: Chemistry, Biological Activities and Uses; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- Sachetti, C.G.; Fascineli, M.L.; Sampaio, J.A.; Lameira, O.A.; Caldas, E.D. Avaliação da toxicidade aguda e potencial neurotóxico do óleo-resina de copaíba (Copaifera reticulata Ducke, Fabaceae). Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2009, 19, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachetti, C.G.; Carvalho, R.R.; Paumgartten, F.J.R.; Lameira, O.A.; Caldas, E.D. Developmental toxicity of copaiba tree (Copaifera reticulata Ducke, Fabaceae) oleoresin in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrão, F.; Costa, L.D.D.A.; Alves, J.M.; Senedese, J.M.; de Castro, P.T.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Bastos, J.K.; Tavares, D.C.; Martins, C.H.G. Copaifera langsdorffii oleoresin and its isolated compounds: Antibacterial effect and antiproliferative activity in cancer cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardají, D.K.R.; da Silva, J.J.M.; Bianchi, T.C.; Eugênio, D.D.S.; de Oliveira, P.F.; Leandro, L.F.; Rogez, H.L.G.; Venezianni, R.C.S.; Ambrosio, S.R.; Tavares, D.C.; et al. Copaifera reticulata oleoresin: Chemical characterization and antibacterial properties against oral pathogens. Anaerobe 2016, 40, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Baird, A.W.; Blaauboer, B.J.; Ripoll, J.V.C.; Corvi, R.; Dekant, W.; Dietl, P.; Gennari, A.; Gribaldo, L.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. The assessment of repeated dose toxicity in vitro: A proposed approach: The report and recommendations of ECVAM workshop 56. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2006, 34, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coecke, S.; Blaauboer, B.J.; Elaut, G.; Freeman, S.; Freidig, A.; Gensmantel, N.; Hoet, P.; Kapoulas, V.M.; Ladstetter, B.; Langley, G.; et al. Toxicokinetics and metabolism. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005, 33 (Suppl. S1), 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyan, M.O.; Adeyipo, T.F.; Oyemitan, I.A.; Okwuese, P.B.; Ekundina, V.O.; Akanmu, M.A. In vivo and in silico studies of Dennettia tripetala essential oil reveal the potential harmful effects of habitual consumption of the plant seed. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.; Santos, C.; Gonçalves, L.; Braga, F.; Almeida, J.; Lima, C.; Brasil, D.; Silva, C.; Hage-Melim, L.; Santos, C. Molecular Modeling of the Major Compounds of Sesquiterpenes Class in Copaiba Oil-resin. Br. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.; Oliveira, C.S.; dos Santos, W.J.O.; Oliveira, V.X.; Antar, G.M.; Lago, J.H.G.; Cerchiaro, G. Selective cytotoxicity of ent -kaurene diterpenoids isolated from Baccharis lateralis and Baccharis retusa (Asteraceae). Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, 2200083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.; de Medeiros, B.; Favacho, H.; dos Santos, K.; de Oliveira, B.; Taglialegna, J.; da Costa, E.; de Campos, K.; Carvalho, J. Pre-clinical validation of a vaginal cream containing copaiba oil (reproductive toxicology study). Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.S.; Silva, U.D.D.A.E.; Góes, L.D.M.; Hyacienth, B.M.D.S.; Carvalho, H.D.O.; Fernandes, C.P.; Castro, A.N.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Non-clinical toxicity study of the oil-resin and vaginal cream of Copaiba (Copaifera duckei, Dwyer). Cogent Biol. 2017, 3, 1394510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.C.; dos Anjos Melo, D.F.; de Oliveira, S.A.M.; Cruz, A.D.C.; da Conceição, E.C.; de Paula, J.R.; Junior, R.D.S.L.; da Cunha, L.C. Acute and a 28-repeated dose toxicity study of commercial oleoresin from Copaifera sp. in rodents. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2021, 22, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachetti, C.G.; Fascineli, M.L.; Caldas, E.D. Developmental toxicity of copaiba oil-resin (Copaifera reticulata) in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 196, S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.S.; Silva, J.R.; Gomes, C.L.; Nery, M.B.; Navarro, D.M.; Santos, G.K.; Silva-Neto, J.C.; Costa-Silva, J.H.; Araújo, A.V.; Wanderley, A.G. Effects of the oral treatment with Copaifera multijuga oil on reproductive performance of male Wistar rats. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.G.G.; Jorge, A.T.; Pereira, L.D.F.; Furtado, R.A.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Bastos, J.K.; Ramos, S.B.; Chahud, F.; Dias, L.G.G.G.; Honsho, C.D.S.; et al. Use of Copaifera multijuga for acute corneal repair after chemical injury: A clinical, histopathological and toxicogenetic study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.R.; Darin, J.D.C.; Hernandes, L.C.; Ramos, M.F.S.; Antunes, L.M.G.; Freitas, O. Genotoxicity assessment of Copaiba oil and its fractions in Swiss mice. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.O.; Costa, M.A.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias-Filho, B.P.; da Veiga-Júnior, V.F.; Lima, M.M.D.S.; Nakamura, C.V. Leishmania amazonensis: Effects of oral treatment with copaiba oil in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 129, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.K.C.; Yamaki, V.N.; Yasojima, E.Y.; Brito, M.V.H. Effect of copaiba oil in hepatic damage induced by acetaminophen in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2013, 28, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brito, M.V.H.; Costa, F.D.; De Vasconcelos, D.M.; Costa, L.A.V.; Yasojima, E.Y.; Teixeira, R.K.C.; Yamaki, V.N. Attenuation of copaiba oil in hepatic damage in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2014, 29, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghizoni, C.V.C.; Ames, A.P.A.; Lameira, O.A.; Amado, C.A.B.; Nakanishi, A.B.S.; Bracht, L.; Natali, M.R.M.; Peralta, R.M.; Bracht, A.; Comar, J.F. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Actions of Copaiba Oil Are Related to Liver Cell Modifications in Arthritic Rats. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 3409–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucca, L.G.; De Matos, S.P.; Kreutz, T.; Teixeira, H.F.; Veiga, V.F.; De Araújo, B.V.; Limberger, R.P.; Koester, L.S. Anti-inflammatory Effect from a Hydrogel Containing Nanoemulsified Copaiba oil (Copaifera multijuga Hayne). AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2017, 19, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, D.J.S., Jr.; Carvalho, L.T.F.; Rocha, I.R.O.; Brito, C.N.; Moreira, R.A.; Barros, C.A.V. Effects of Copaiba oil in the healing process of urinary bladder in rats. IBJU Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames-Sibin, A.P.; Barizão, C.L.; Castro-Ghizoni, C.V.; Silva, F.M.S.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; Bracht, L.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Marçal-Natali, M.R.; Bracht, A.; Comar, J.F. β-Caryophyllene, the major constituent of copaiba oil, reduces systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in arthritic rats. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 10262–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalenogare, D.P.; Ferro, P.R.; De Prá, S.D.T.; Rigo, F.K.; Antoniazzi, C.T.D.D.; de Almeida, A.S.; Damiani, A.P.; Strapazzon, G.; Sardinha, T.T.D.O.; Galvani, N.C.; et al. Antinociceptive activity of Copaifera ofcinalis Jacq. L oil and kaurenoic acid in mice. Infammopharmacology 2019, 27, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, A.C.S.; Alves, L.D.B.; Goldemberg, D.C.; Melo, A.C.; Antunes, H.S. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing effect of Copaiba oleoresin on the oral cavity: A systematic review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.O.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias Filho, B.P.; Veiga Junior, V.F.; Pinto, A.C.; Nakamura, C.V. Effect of Brazilian copaiba oils on Leishmania amazonensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Rosas, E.C.; Carvalho, M.V.; Henriques, M.G.M.O.; Pinto, A.C. Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of copaiba oils from Copaifera cearensis Huber ex Ducke, Copaifera reticulata Ducke and Copaifera multijuga Hayne—A comparative study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, K.L.; Feuser, P.E.; Valério, A.; Cordeiro, A.P.; de Oliveira, C.I.; Assolini, J.P.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Sayer, C.; Araújo, P.H.H. Diethyldithiocarbamate loaded in beeswax-copaiba oil nanoparticles obtained by solventless double emulsion technique promote promastigote death in vitro. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 176, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kian, D.; Lancheros, C.A.C.; Assolini, J.P.; Arakawa, N.S.; Veiga-Júnior, V.F.; Nakamura, C.V.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Conchon-Costa, I.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Yamada-Ogatta, S.F.; et al. Trypanocidal activity of copaiba oil and kaurenoic acid does not depend on macrophage killing machinery. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Andrade, T.A.M.; Leite, S.N.; Frade, M.A.C. Cytotoxicity and wound healing properties of Copaifera langsdorffii oleoresin in rabbits. Int. J. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2013, 3, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ahamed, M.B.K.; Ezzat, M.O.; Majid, A.S.A.; Majid, A.M.S.A. The Anticancer, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of the Sesquiterpene β-Caryophyllene from the Essential Oil of Aquilaria crassna. Molecules 2015, 20, 11808–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crentsil, J.A.; Yamthe, L.R.T.; Anibea, B.Z.; Broni, E.; Kwofie, S.K.; Tetteh, J.K.A.; Osei-Safo, D. Leishmanicidal Potential of Hardwickiic Acid Isolated From Croton sylvaticus. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.D.S.; de Almeida, P.D.O.; Aranha, E.S.P.; Boleti, A.P.D.A.; Newton, P.; de Vasconcellos, M.C.; Veiga Junior, V.F.; Lima, E.S. Biological Activities and Cytotoxicity of Diterpenes from Copaifera spp. Oleoresins. Molecules 2015, 20, 6194–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, C.A.C.G.; Conde, N.C.D.O.; Venâncio, G.N.; Milério, P.S.L.L.; Bandeira, M.F.C.L.; Veiga Júnior, V.F. Antibacterial Activity of Copaiba Oil Gel on Dental Biofilm. Open Dent. J. 2016, 10, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefenbach, A.L.; Muniz, F.W.M.G.; Oballe, H.J.R.; Rösing, C.K. Antimicrobial activity of copaiba oil (Copaifera ssp.) on oral pathogens: Systematic review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, F.G.G.; Casemiro, L.A.; Martins, C.H.G.; Dias, L.G.G.G.; Pereira, L.D.F.; Nishimura, L.T.; De Souza, F.F.; Honsho, C.D.S. Endodontics pastes formulated with copaiba oil: Action on oral microbiota and dentin bridge formation in dogs. Cienc. Rural. 2015, 45, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobouti, L.T.; Martins, T.C.A.; Pereira, T.J.; Mussi, M.C.M. Antimicrobial activity of copaiba oil: A review and a call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, N.; Xavier-Júnior, F.H.; Morais, A.R.V.; Dantas, T.R.F.; Dantas-Santos, N.; Verissimo, L.M.; Rehder, V.L.G.; Chaves, G.M.; Oliveira, A.G.; Egito, E.S.T. Chemical Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Natural Oil Nanostructured Emulsions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neta, M.C.S.; Vittorazzi, C.; Guimarães, A.C.; Martins, J.D.L.; Fronza, M.; Endringer, D.C.; Scherer, R. Effects of β-caryophyllene and Murraya paniculata essential oil in the murine hepatoma cells and in the bacteria and fungi 24-h time–kill curve studies. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Masso, S.; Souza, R.R.; Moreno, M.; Moreira, E. Meta-analysis on Copaiba Oil: Its Functions in Metabolism and Its Properties as an Anti-inflammatory Agent. J. Morphol. Sci. 2018, 35, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.R.M.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Christo, H.B.; Pinto, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. In vivo andin vitro studies on the anticancer activity of Copaifera multijuga hayne and its fractions. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tincusi, B.M.; Jiménez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Moujir, L.M.; Mamani, Z.A.; Barroso, J.P.; Ravelo, A.G.; Hernández, B.V. Antimicrobial Terpenoids from the Oleoresin of the Peruvian Medicinal Plant Copaifera paupera. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiel, E.; Ofir, R.; Dudai, N.; Soloway, E.; Rabinsky, T.; Rachmilevitch, S. β-Caryophyllene, a Compound Isolated from the Biblical Balm of Gilead (Commiphora gileadensis), Is a Selective Apoptosis Inducer for Tumor Cell Lines. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 872394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Jacob, J.; Varma, K.; Gopi, S. Preparation and Characterization of Liposomal β-Caryophyllene (Rephyll) by Nanofiber Weaving Technology and Its Effects on Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) in Humans: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Crossover-Designed, and Placebo-Controlled Study. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24045–24056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sotto, A.; Irannejad, H.; Eufemi, M.; Mancinelli, R.; Abete, L.; Mammola, C.L.; Altieri, F.; Mazzanti, G.; Di Giacomo, S. Potentiation of Low-Dose Doxorubicin Cytotoxicity by Affecting P-Glycoprotein through Caryophyllane Sesquiterpenes in HepG2 Cells: An in Vitro and in Silico Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.I.; Kim, E.J.; Kwon, G.T.; Jung, Y.J.; Park, T.; Kim, Y.; Yu, R.; Choi, M.-S.; Chun, H.S.; Kwon, S.-H.; et al. β-Caryophyllene potently inhibits solid tumor growth and lymph node metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells in high-fat diet–induced obese C57BL/6N mice. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.V.S.; Silva, J.D.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Cabral, L.M.; Sousa, V.P. Development and validation of a quantification method for α-humulene and trans-caryophyllene in Cordia verbenacea by high performance liquid chromatography. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, M.; Pichette, A.; Longtin, A.; Nagau, F.; Legault, J. Essential oil analysis and anticancer activity of leaf essential oil of Croton flavens L. from Guadeloupe. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Lotufo, L.; Cunha, G.; Farias, P.; Viana, G.; Pessoa, C.; Moraes, M.; Silveira, E.; Gramosa, N.; Rao, V. The cytotoxic and embryotoxic effects of kaurenoic acid, a diterpene isolated from Copaifera langsdorffii oleo-resin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, J.; Pichette, A. Potentiating effect of β-caryophyllene on anticancer activity of α-humulene, isocaryophyllene and paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 59, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, N.J.; Mosaddik, A.; Moon, J.Y.; Jang, K.C.; Lee, D.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Cho, S.K. Cytotoxic activity of β-caryophyllene oxide isolated from Jeju Guava (Psidium cattleianum Sabine) leaf. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2011, 5, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Shahwar, D.; Ullah, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Saeed, A.; Ullah, S. Anticancer activity of Cinnamon tamala leaf constituents towards human ovarian cancer cells. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 28, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambrož, M.; Boušová, I.; Skarka, A.; Hanušová, V.; Králová, V.; Matoušková, P.; Szotáková, B.; Skálová, L. The Influence of Sesquiterpenes from Myrica rubra on the Antiproliferative and Pro-Oxidative Effects of Doxorubicin and Its Accumulation in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 15343–15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, Y.; Beaumont, C.; Workman, M.; Talbot, J.N.; Hill, D.K.; Le, T.T. Fast-Acting and Receptor-Mediated Regulation of Neuronal Signaling Pathways by Copaiba Essential Oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-R.; Nam, D.; Yun, H.-M.; Lee, S.-G.; Jang, H.-J.; Sethi, G.; Cho, S.K.; Ahn, K.S. β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth and induces apoptosis through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and ROS-mediated MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett. 2011, 312, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.L.P.; Wenzel-Storjohann, A.; Barbosa, J.D.; Zidorn, C.; Peifer, C.; Tasdemir, D.; Çiçek, S.S. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of the Copaifera reticulata oleoresin and its main diterpene acids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 233, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, M.; De Grandis, R.; Campos, M.; Bauermeister, A.; Peccinini, R.; Pavan, F.; Lopes, N.; De Moraes, N. Acid diterpenes from Copaiba oleoresin (Copaifera langsdorffii): Chemical and plasma stability and intestinal permeability using Caco-2 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Jung, J.H.; Smith, D.L.; Wood, K.V.; Mclaughlin, J.L. Cytotoxic clerodane diterpenes from Polyalthia longfolia. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.A.; Mancebo-Aracil, J.; Tangarife-Castaño, V.; Gómez, L.S.A.; Zapata, B.; Mesa-Arango, A.; Galvis, L.A.B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of (+)-labdadienedial, derivatives and precursors from (+)-sclareolide. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhara, K.V.; Singh, S.P.; Sarkar, J.; Sinha, S. Cytotoxic clerodane diterpenoids from the leaves of Polyalthia longifolia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrofa, F.; Nyoman Ehrich Lister, I.; Lie, S. Identification of Chemical Compounds to Predict In Silico Toxicity using Syzygium polyanthum Ethanol Extract. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Health, Instrumentation & Measurement, and Natural Sciences (InHeNce), Medan, Indonesia, 14–16 July 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, O.S.D.S.; Franco, C.D.J.P.; de Moraes, A.A.B.; Cruz, J.N.; da Costa, K.S.; Nascimento, L.D.D.; Andrade, E.H.D.A. In silico analyses of toxicity of the major constituents of essential oils from two Ipomoea L. species. Toxicon 2021, 195, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavinas, F.C.; Macedo, E.H.B.; Sá, G.B.; Amaral, A.C.F.; Silva, J.; Azevedo, M.; Vieira, B.A.; Domingos, T.F.S.; Vermelho, A.B.; Carneiro, C.S.; et al. Brazilian stingless bee propolis and geopropolis: Promising sources of biologically active compounds. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardinelli, C.C.; Silva, J.E.A.e.; Ribeiro, R.; Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Santos, E.P.d.; de Freitas, Z.M.F. Toxicological Effects of Copaiba Oil (Copaifera spp.) and Its Active Components. Plants 2023, 12, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051054
Cardinelli CC, Silva JEAe, Ribeiro R, Veiga-Junior VF, Santos EPd, de Freitas ZMF. Toxicological Effects of Copaiba Oil (Copaifera spp.) and Its Active Components. Plants. 2023; 12(5):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051054
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardinelli, Camila Castanho, Josiane Elizabeth Almeida e Silva, Rayssa Ribeiro, Valdir F. Veiga-Junior, Elisabete Pereira dos Santos, and Zaida Maria Faria de Freitas. 2023. "Toxicological Effects of Copaiba Oil (Copaifera spp.) and Its Active Components" Plants 12, no. 5: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051054
APA StyleCardinelli, C. C., Silva, J. E. A. e., Ribeiro, R., Veiga-Junior, V. F., Santos, E. P. d., & de Freitas, Z. M. F. (2023). Toxicological Effects of Copaiba Oil (Copaifera spp.) and Its Active Components. Plants, 12(5), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051054