Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
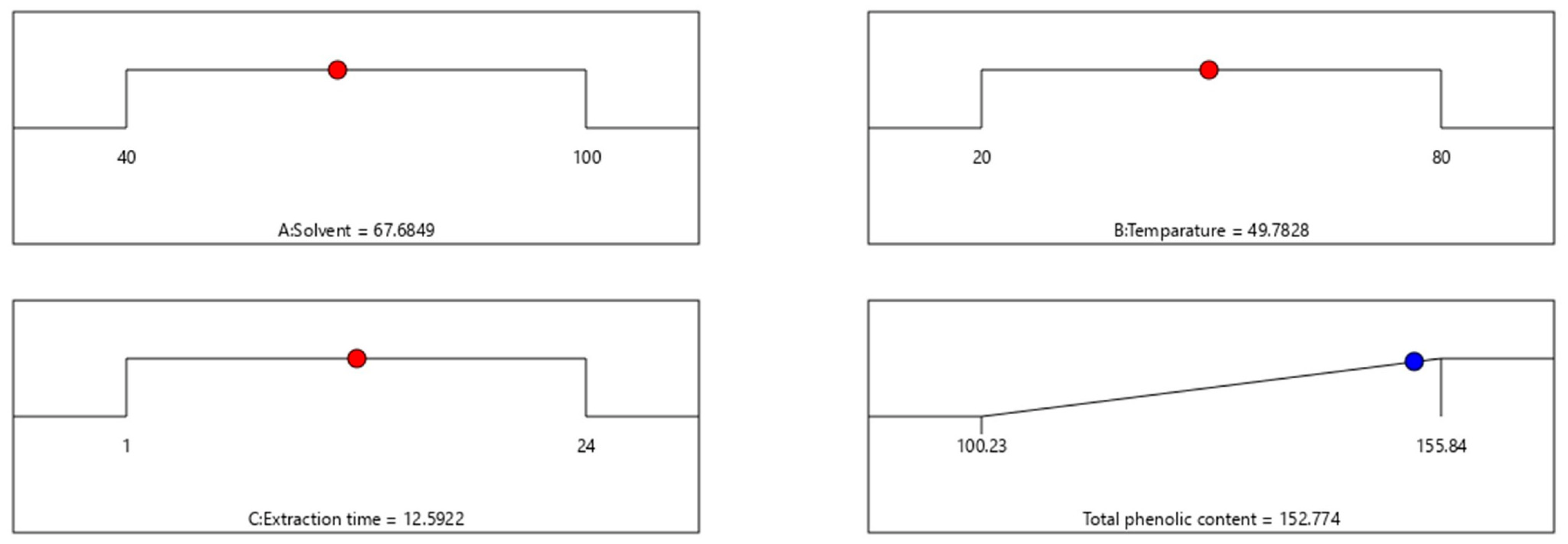
2.1. Statistical Optimisation of the Extraction Process for the Enhanced Extraction of Phenols
2.2. Quantitative Estimation of Certain Groups of Phytochemicals of the PECTS
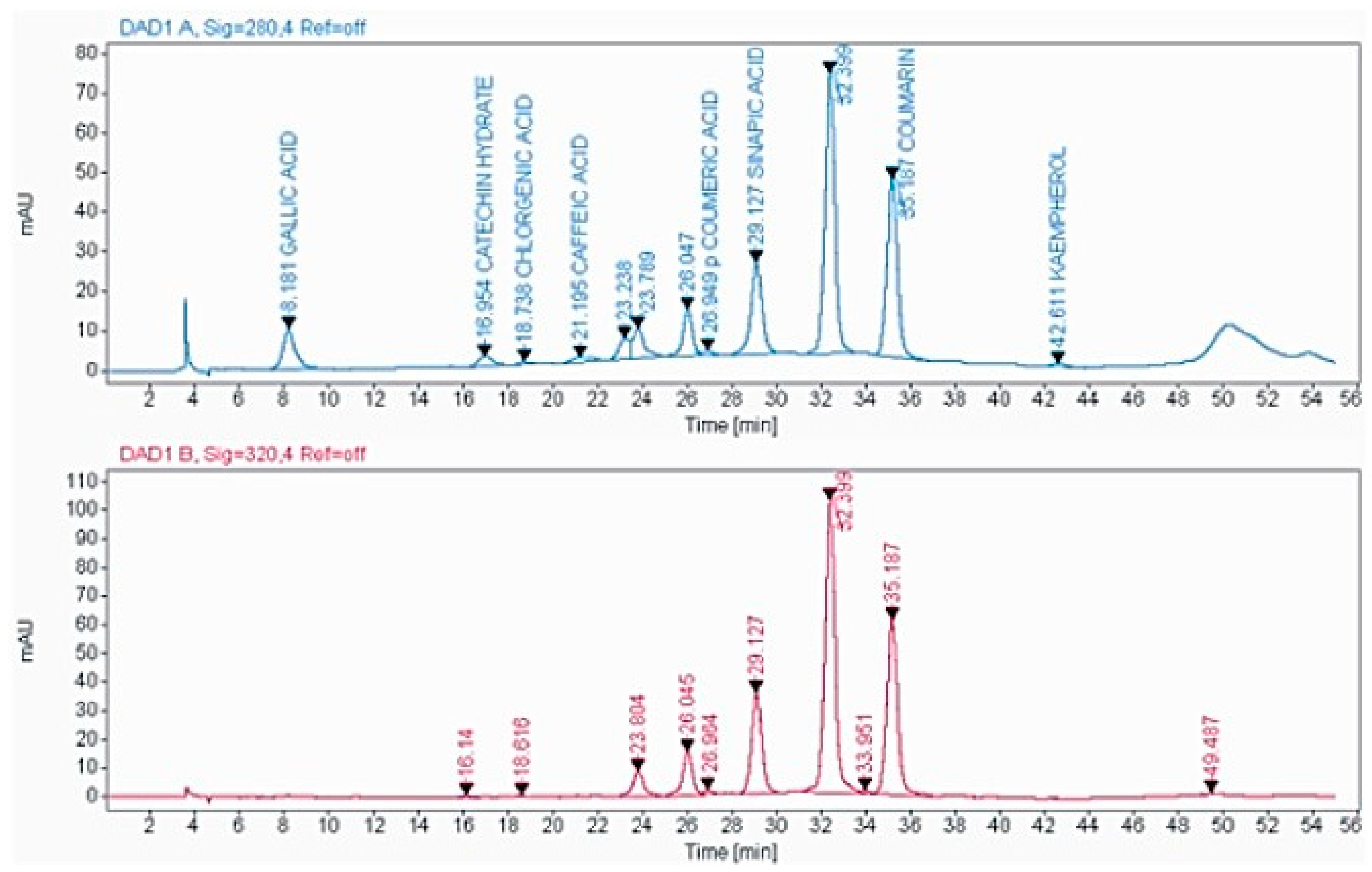
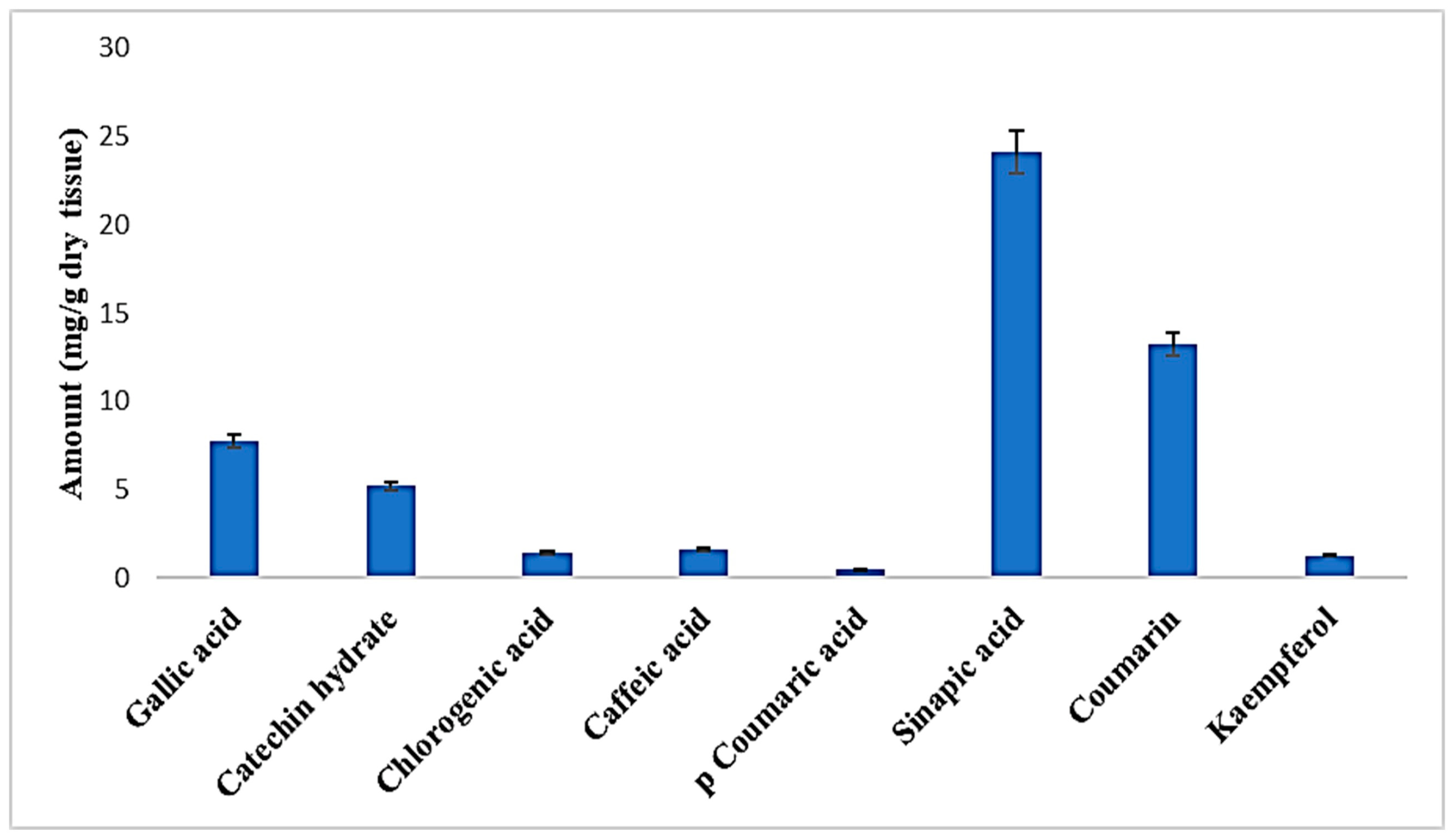
2.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of the PECTS
2.4. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis of PECTS
2.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Study of the PECTS
2.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Assay
2.5.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.4. Phosphomolybdenum Assay
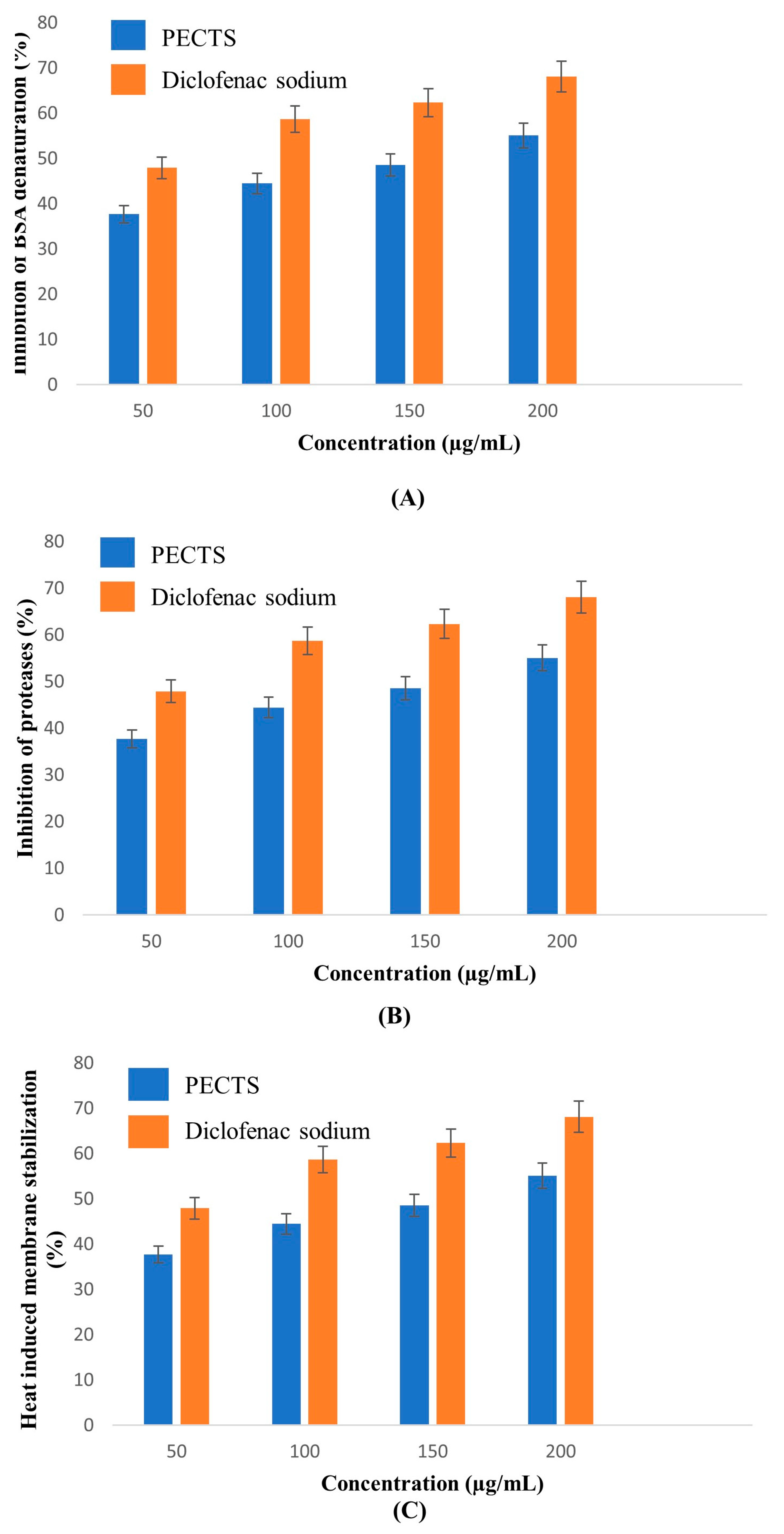
2.6. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Study of the PECTS
2.6.1. Inhibition of the Albumin Denaturation Assay
2.6.2. Antiprotease Activity
2.6.3. Membrane Stabilisation Assay
Heat-Induced Haemolysis Assay
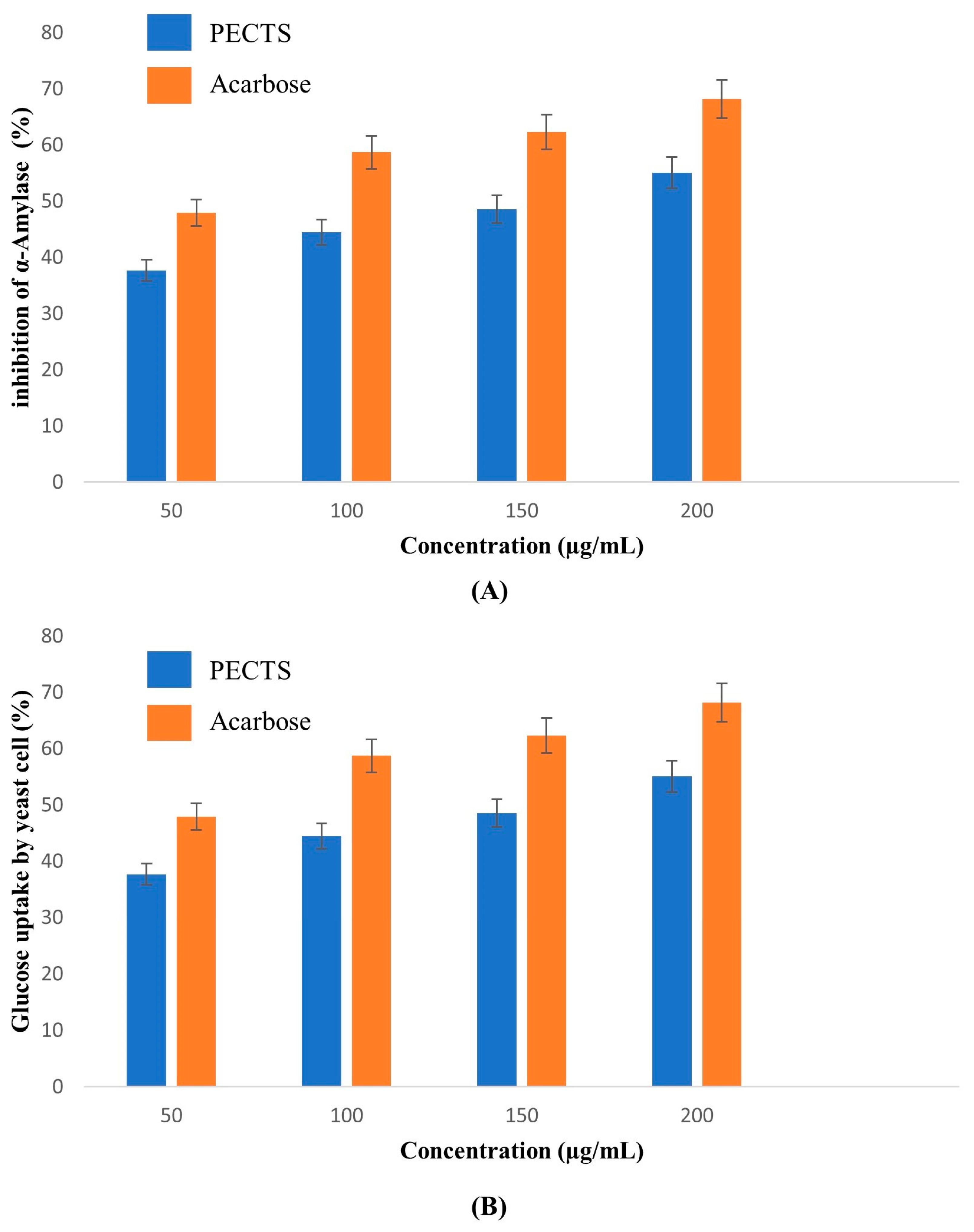
2.7. In Vitro Antidiabetic Study of the PECTS
2.7.1. α-Amylase Inhibitory Assay
2.7.2. Yeast Cell Glucose Uptake Assay
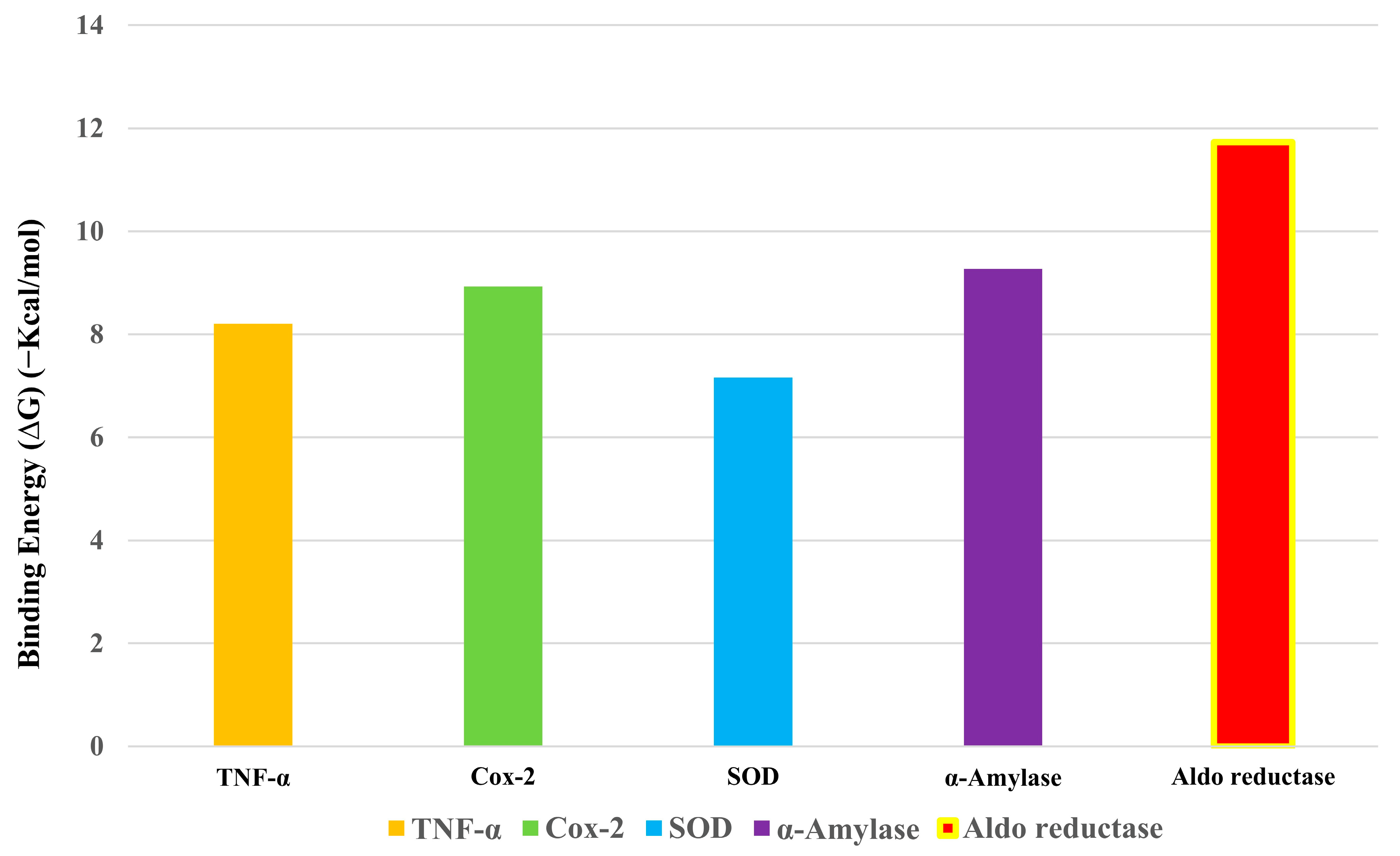
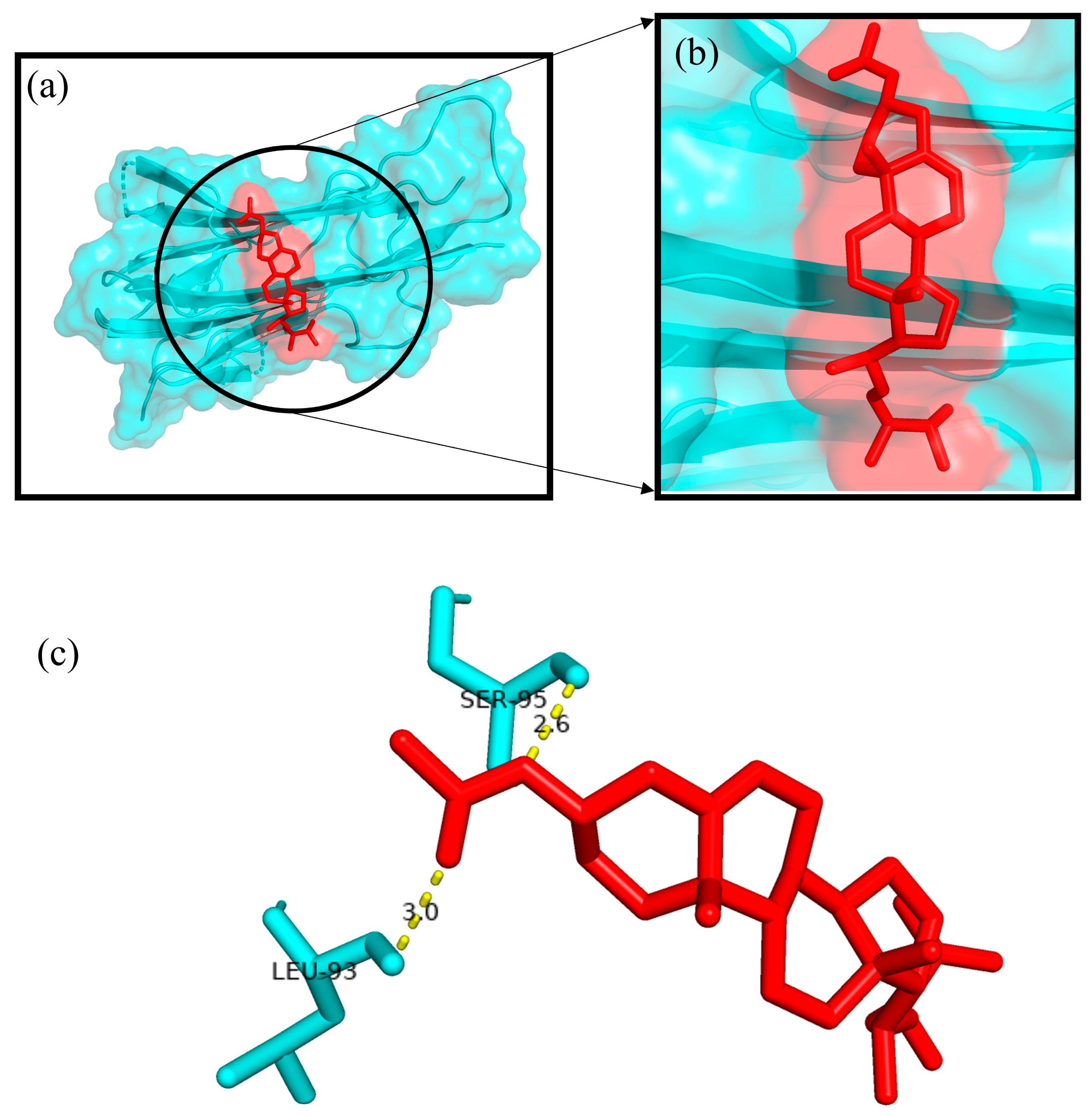
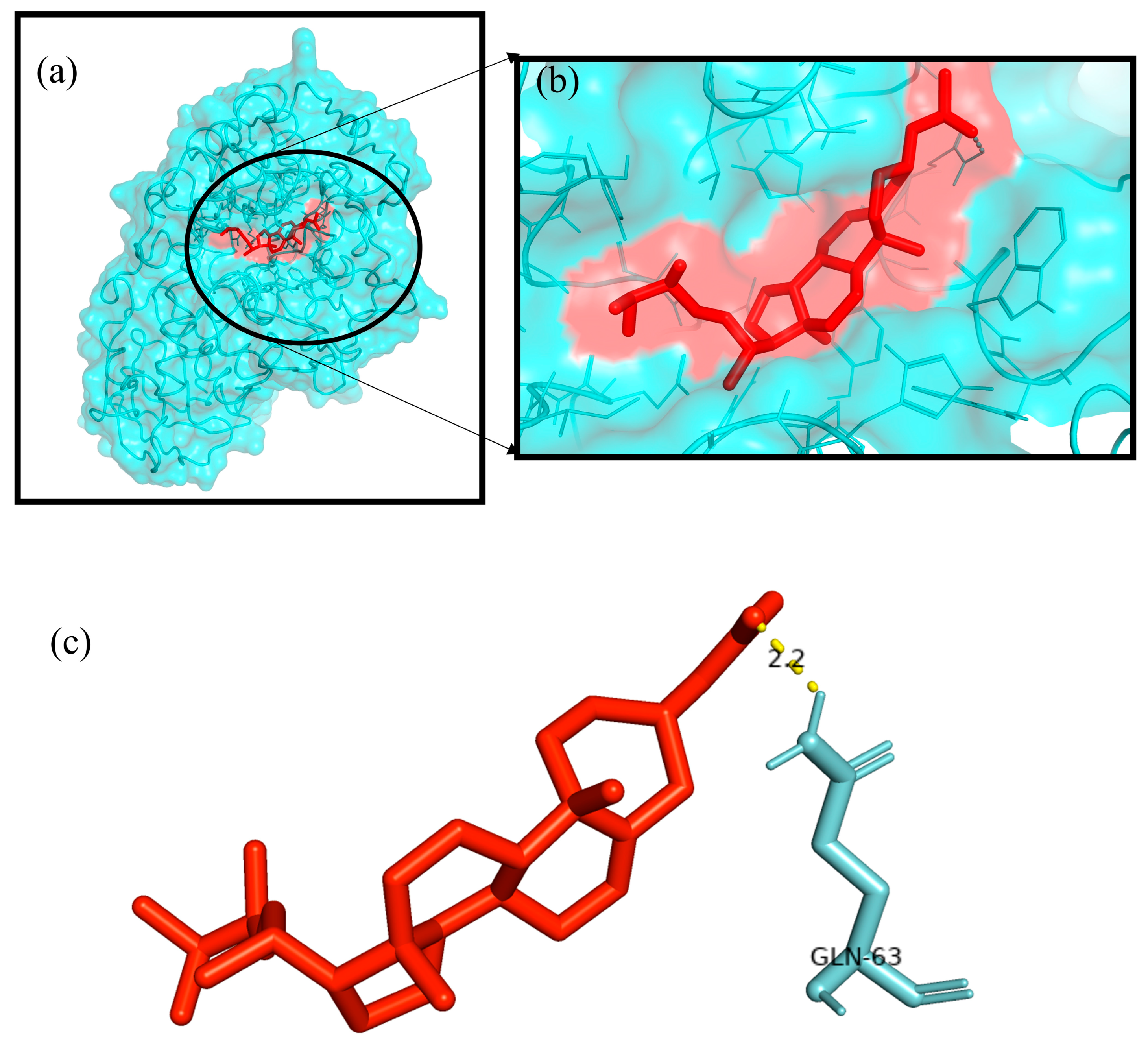
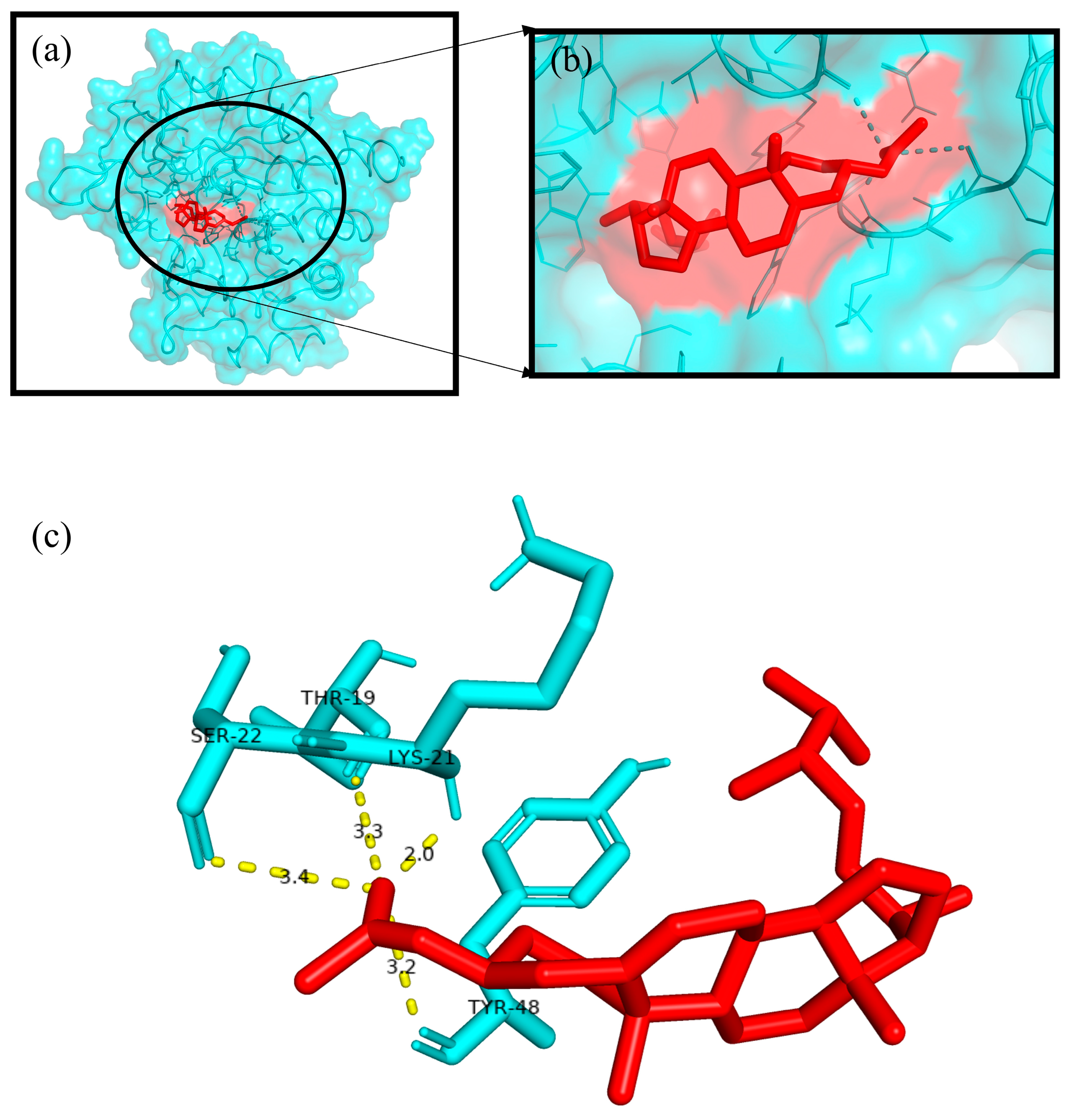
2.8. In Silico Molecular Docking Study
2.9. Toxicity Analysis of the PECTS
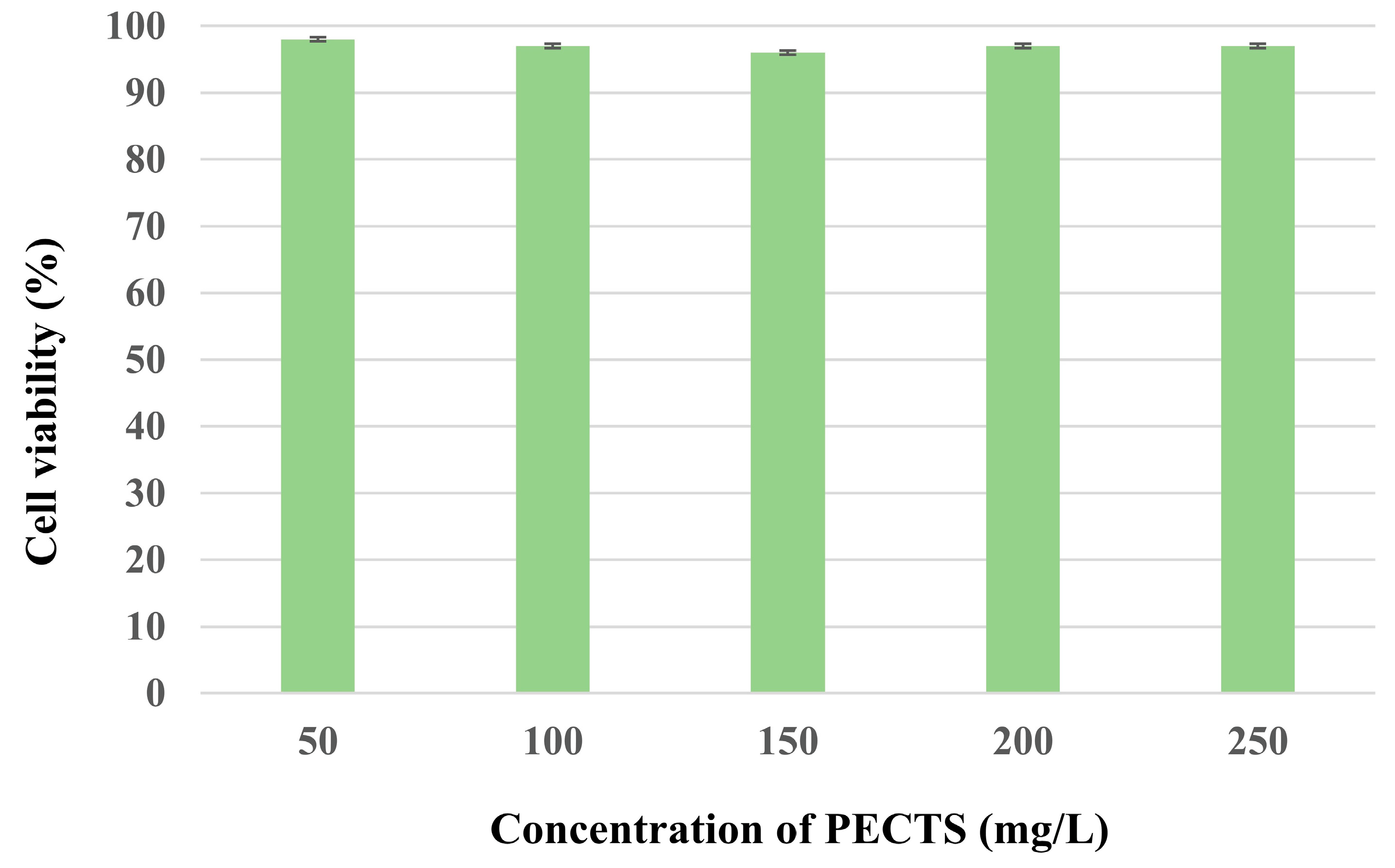
2.9.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
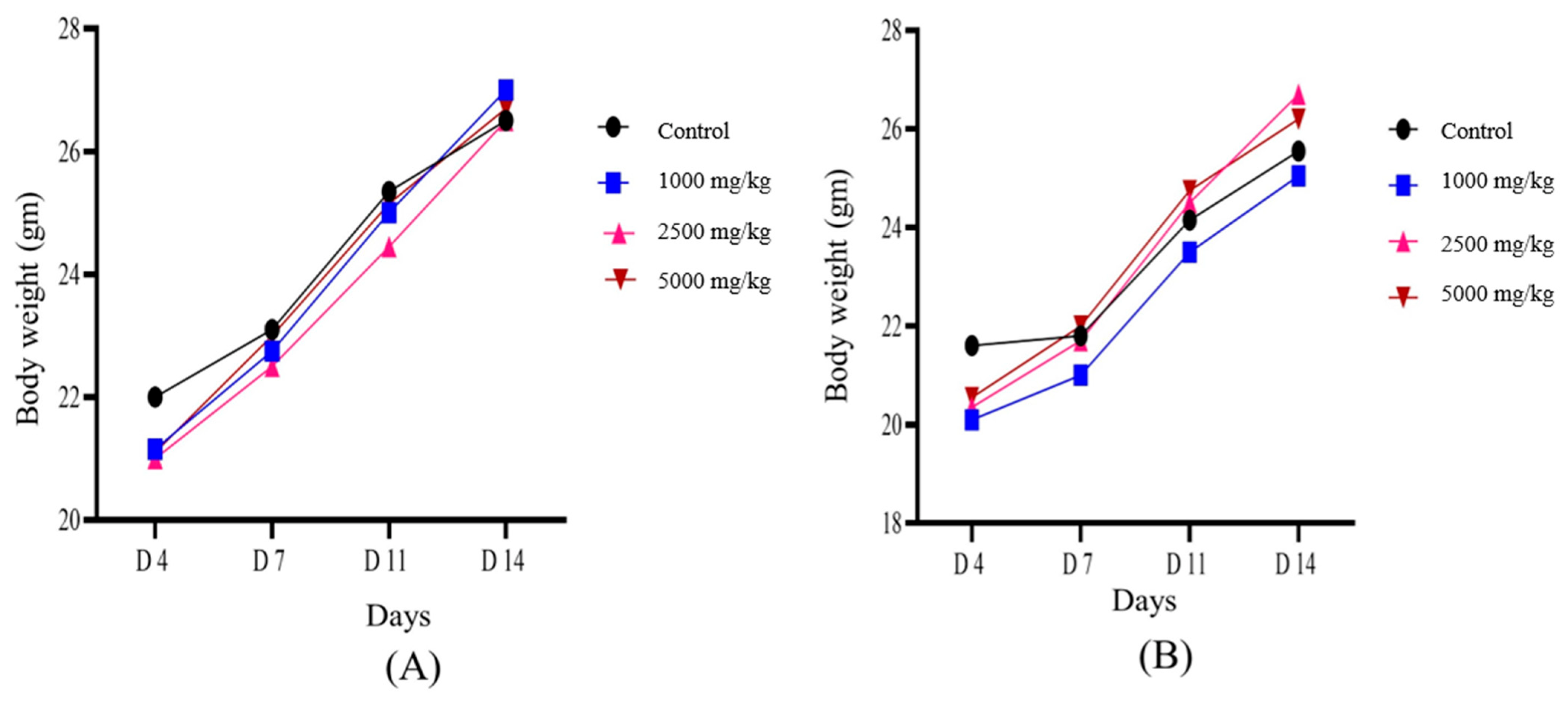
2.9.2. In Vivo Acute Toxicity Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Preparation of the Plant Materials
4.2. Statistical Optimisation of the Extraction Process for the Enhanced Extraction of Phenols
4.3. Quantitative Estimation of Certain Groups of Phytochemicals of the PECTS
4.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of the PECTS
4.5. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis of the PECTS
4.6. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Study of the PECTS
4.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
4.6.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Assay
4.6.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
4.6.4. Phosphomolybdenum Assay
4.7. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity Study of the PECTS
4.7.1. Inhibition of Albumin Denaturation Assay
4.7.2. Antiprotease Activity Assay
4.7.3. Membrane Stabilisation Assay
A. Preparation of the R.B.C. Suspension
B. Heat-Induced Haemolysis Assay
4.8. In Vitro Antidiabetic Activity Study of the PECTS
4.8.1. α-Amylase Inhibitory Assay
4.8.2. Glucose Uptake Assay Using Yeast Cells
4.9. In Silico Molecular Docking Study
4.10. Toxicity Analysis of the PECTS
4.10.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.10.2. In Vivo Acute Toxicity Study
Animals and Ethical Use
Experiment Details
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, J.; Arya, R.; Gupta, A. A review on chemical and biological properties of Cayratia trifolia Linn. (Vitaceae). Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Sharma, M. Review on Indian Medical Plants; ICMR: New Delhi, India, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 879–882. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, R.D.; Sharma, J.; Painuli, R.M. Plants used in traditional healthcare of livestock by Gujjar community of Sub-Himalayan tracts, Uttarakhand, India. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2010, 1, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Jasuja, N.D. Evaluation of Primary Metabolites and Antioxidant Potential Activity of Cayratia trifolia (Leaf and Stems). J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, C.P. Indian Medicinal Plants: An illustrated of Dictionary; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, K.; Singh, M.; Pillai, U. Ethnobotanical survey of Rajasthan-An update. Am. Eurasian J. Bot. 2008, 1, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Swarnkar, S.; Katewa, S.S. Ethnobotanical observation on tuberous plants from tribal area of Rajasthan (India). Ethnobot. Leafl. 2008, 1, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, M.I.; Susanty, S.; Fawwaz, M. Antioxidant and antidiabetic potential of galing stem extract (Cayratia trifolia Domin). Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganathan, B.; Palanisamy, C.P.; Panagal, M. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity potential of n-hexane extract of Cayratia trifolia L. Bioinformation 2021, 17, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, P.C.; Sophia, D.; Raj, C.A.; Ragavendran, P.; Starlin, T.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K. In vitro antioxidant activities and HPTLC analysis of ethanolic extract of Cayratia trifolia (L.). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2012, 2, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, S.; Perumal, P.C.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K. Chromatographic and spectrophotometric analysis of bioactive compounds from Cayratia trifolia (L.) stem. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rambo, D.F.; Biegelmeyer, R.; Toson, N.S.; Dresch, R.R.; Moreno, P.R.; Henriques, A.T. Box–Behnken experimental design for extraction optimization of alkaloids from Erythrina verna Vell. trunk barks and LC Method Validation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 133, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthal, L.K.; Dey, A.; Satyavathi, K.; Bhojaraju, P. GC-MS analysis of bio-active compounds in methanolic extract of Lactuca runcinata DC. Pharmacogn. J. 2014, 6, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Lin, P.; Cheng, F. In silico polypharmacology of natural products. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.B.; Sowemimo, A.A.; Sofidiya, M.O.; Badmos, K.B.; Fageyinbo, M.S.; Abdulkareem, F.B.; Odukoya, O.A. Sub-acute and chronic toxicity profiles of Markhamia tomentosa ethanolic leaf extract in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.; Chan, J.; Wanke, S.; Neinhuis, C.; Simmonds, M.S. Local uses of Aristolochia species and content of nephrotoxic aristolochic acid 1 and 2—A global assessment based on bibliographic sources. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 108–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlozi, S.H.; Mmongoyo, J.A.; Chacha, M. The in vivo toxicity evaluation of leaf and root methanolic extracts of Tephrosia vogelii Hook. f using animal model. Clin. Phytosci. 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauheed, A.M.; Mamman, M.; Ahmed, A.; Sani, N.I.A.; Suleiman, M.M.; Sulaiman, M.H.; Balogun, E.O. Acute, sub-acute, sub-chronic and chronic toxicity studies of four important Nigerian ethnomedicinal plants in rats. Clin. Phytosci. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Mukherjee, S.; Saini, P.; Roy, P.; Babu, S.P.S. Antifilarial effects of polyphenol rich ethanolic extract from the leaves of Azadirachta indica through molecular and biochemical approaches describing reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated apoptosis of Setaria cervi. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 136, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bandyopadhayay, B.; Basak, B.; Mandal, N.; Apurba, D.E.Y.; Mondal, B. An improved method of optimizing the extraction of polyphenol oxidase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Peel. Not. Sci. Biol. 2012, 4, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheena, S.; Chintagunta, A.D.; Dirisala, V.R.; Sampath Kumar, N.S. Extraction of bioactive compounds from Psidium guajava and their application in dentistry. AMB Express. 2019, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonato, F.R.; Santana, D.G.; de Melo, F.M.; dos Santos, G.G.L.; Brustolim, D.; Camargo, E.A.; de Sousa, D.P.; Soares, M.B.P.; Villarreal, C.F. Anti-inflammatory properties of rose oxide. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.R.; Hameed, I.H.; Ubaid, J.M. Analysis of the secondary metabolite products of Ammi majus and evaluation anti-insect activity. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2016, 8, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar]
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ahamed, M.B.; Ezzat, M.O.; Majid, A.S.; Majid, A.M. The anticancer, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the sesquiterpene β-caryophyllene from the essential oil of Aquilaria crassna. Molecules 2015, 20, 11808–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noge, K.; Becerra, J.X. Germacrene D, a common sesquiterpene in the genus Bursera (Burseraceae). Molecules 2009, 14, 5289–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.R.; Devi, P.S. Evaluation of mosquitocidal activity of essential oil and sesquiterpenes from leaves of Chloroxylon swietenia DC. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Zamora, C.M.; Torres, C.A.; Nuñez, M.B. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of essential oils from Verbenaceae species growing in South America. Molecules 2018, 23, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, G.; Hazzah, T.; Hartsel, J.A.; Eades, J.; Hickory, B. Cannabis sativa: An overview. In Nutraceuticals, 2nd ed.; Gupta, C.R., Lall, R., Srivastava, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 38, pp. 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Govindarajan, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Maggi, F. High toxicity of camphene and γ-elemene from Wedelia prostrata essential oil against larvae of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10383–10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, R.; Dey, A.; Manavalan, R.; Prakasam, K.; Jayachandra, E.; Sreenivasa, G. Inhibition of albumin denaturation and antiinflammatory activity of furfuryl substituted pyrimidinoimidazolinones. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2008, 6, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Elisha, I.L.; Dzoyem, J.P.; McGaw, L.J.; Botha, F.S.; Eloff, J.N. The anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant activity and relationships with total phenolics and total flavonoids of nine South African plants used traditionally to treat arthritis. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, R.; Ayub, H.; Nawaz, S.; Islam, Z.U.; Yasmin, T.; Bano, A.; Wakeel, A.; Zia, S.; Roberts, T.H. Antimicrobial activity, toxicity and anti-inflammatory potential of methanolic extracts of four ethnomedicinal plant species from Punjab, Pakistan. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anosike, C.A.; Obidoa, O.; Ezeanyika, L.U. Membrane stabilization as a mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of garden egg (Solanum aethiopicum). DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, W.; Krause, H.P.; Müller, L.; Schutt, H.; Sitt, R.; Thomas, G. Inhibitors of the rate of carbohydrate and lipid absorption by the intestine. Int. J. Obes. 1984, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konappa, N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Pradeep, C.K.; Chowdappa, S.; Jogaiah, S. GC–MS analysis of phytoconstituents from Amomum nilgiricum and molecular docking interactions of bioactive serverogenin acetate with target proteins. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, S.; Ray, A.S.; Rahaman, C.H. Natural Phytocompounds from Common Indian Spices for Identification of Three Potential Inhibitors of Breast Cancer: A Molecular Modelling Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, A.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Maskooki, A.; Niakousari, M.; Elhamirad, A.H. Optimization of subcritical water extraction of bioactive compounds from barberry fruit (Berberis vulgaris) by using response surface methodology. Int. J. Agri. Crop. Sci. 2013, 6, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ilaiyaraja, N.; Likhith, K.R.; Babu, G.S.; Khanum, F. Optimisation of extraction of bioactive compounds from Feronia limonia (wood apple) fruit using response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chem. 2015, 173, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.N.; Ray, A.S.; Rahaman, C.H. A comprehensive and systematic review on potential anticancer activities of eugenol: From pre-clinical evidence to molecular mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, N.; Perestrelo, R.; Marques, J.C.; Câmara, J.S. Relationship between antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of red, rosé and white wines. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Verma, R.J. Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic extract of Terminalia chebula Retzius fruits. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2016, 10, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.A.; El-Nour, M.E.M.; Yagi, S.M. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) rhizome, callus and callus treated with some elicitors. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, W.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y. Identification of phenolics in the fruit of emblica (Phyllanthus emblica L.) and their antioxidant activities. Food chem. 2008, 109, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandonien, D.; Murkovic, M. The detection of radical scavenging compounds in crude extract of borage (Borago officinalis L.) by using an on-line HPLC-DPPH method. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2002, 53, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.K.; Bonde, C.G. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of extracts of Bridelia retusa Spreng Bark: Impact of dielectric constant and geographical location. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2011, 5, 817–822. [Google Scholar]
- Agata, I. Studies on caffeic acid derivatives in medicinal plants. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 119, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajner-Czopek, A.; Gertchen, M.; Rytel, E.; Kita, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A. Study of antioxidant activity of some medicinal plants having high content of caffeic acid derivatives. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nićiforović, N.; Abramovič, H. Sinapic acid and its derivatives: Natural sources and bioactivity. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Jiang, J.G. Pharmacological and nutritional effects of natural coumarins and their structure–activity relationships. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1701073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.V.; Dutra, L.M.; de Jesus, H.C.R.; de Lima Nogueira, P.C.; de Souza Moraes, V.R.; Salvador, M.J.; de Holanda Cavalcanti, S.C.; dos Santos, R.L.C.; do Nacimento Prata, A.P. Chemical composition and antioxidant, antimicrobial, and larvicidal activities of the essential oils of Annona salzmannii and A. pickelii (Annonaceae). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1934578X1100600636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Quispe, C.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Nigam, M.; Mishra, A.P.; Konovalov, D.A.; Orobinskaya, V.; Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Zam, W.; et al. Phytosterols: From preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byju, K.; Anuradha, V.; Vasundhara, G.; Nair, S.M.; Kumar, N.C. In vitro and in silico studies on the anticancer and apoptosis-inducing activities of the sterols identified from the soft coral, Subergorgia reticulata. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. New drugs cost US$2.6 billion to develop. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2014, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.-L.; Ai, S.-M.; Liang, J.; Sang, P.; Ji, X.-L.; Liu, S.-Q. Insights into Protein–Ligand Interactions: Mechanisms, Models, and Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konc, J.; Lešnik, S.; Janežič, D. Modeling enzyme-ligand binding in drug discovery. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe-Nishimura, C. Aldose reductase in glucose toxicity: A potential target for the prevention of diabetic complications. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.H.; Martin, K.A.; Hwa, J. Aldose reductase, oxidative stress, and diabetic mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lin, J.; Xu, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J.Y. Inhibition of aldose reductase activates hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α and ameliorates hepatosteatosis in diabetic db/db mice. J. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 789730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Ramana, K.V.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of aldose reductase and oxidative damage in diabetes and the consequent potential for therapeutic options. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 26, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kador, P.F.; Kinoshita, J.H.; Sharpless, N.E. Aldose reductase inhibitors: A potential new class of agents for the pharmacological control of certain diabetic complications. J. Med. Chem. 1985, 28, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Moussaoui, A.; Bourhia, M.; Jawhari, F.Z.; Mechchate, H.; Slighoua, M.; Bari, A.; Ullah, R.; Mahmood, H.M.; Ali, S.S.; Ibenmoussa, S.; et al. Phytochemical Identification, Acute, and Sub-Acute Oral Toxicity Studies of the Foliar Extract of Withania frutescens. Molecules 2020, 25, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.K.; Lakshminarasimhan, P.; Chowdhery, H.J.; Singh, P. Flora of West Bengal, Vol-II Leguminosae-Aizoaceae; Botanical Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- POWO. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/ (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Jain, S.K.; Rao, R.R. A Handbook of Field and Herbarium Methods; Today and Tomorrows Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, T.; Hillis, W.E. The phenolic constituents of Prunus domestica. I.—The quantitative analysis of phenolic constituents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1959, 10, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.E.M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Abd El-Salam, S.M.; Omran, A.A. Biochemical changes in phenols, flavonoids, tannins, vitamin E, β–carotene and antioxidant activity during soaking of three white sorghum varieties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.S.; Mandal, S.K.; Rahaman, C.H. Pharmacognostical fingerprinting and selective bioactivity studies of Solanum glaucophyllum Desf. J. Tradit. Folk Pract. 2018, 6, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Byrne, D.H. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, R.J.; Cheng, S.J.; Klaunig, J.E. Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Pineda, M.; Aguilar, M. Spectrophotometric Quantitation of Antioxidant Capacity through the Formation of a Phosphomolybdenum Complex: Specific Application to the Determination of Vitamin E. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindappa, M.; Channabasava, R.; Sowmya, D.V.; Meenakshi, J.; Shreevidya, M.R.; Lavanya, A.; Santoyo, G.; Sadananda, T.S. Phytochemical screening, antimicrobial and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of endophytic extracts from Loranthus sp. Pharmacogn. J. 2011, 3, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansawasdi, C.; Kawabata, J.; Kasai, T. α-Amylase inhibitors from roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn.) tea. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, V.P. Mechanism of glucose transport across the yeast cell membrane. J. Bacteriol. 1962, 84, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Lin, S.R.; Yang, J.M. iGEMDOCK: A graphical environment of enhancing GEMDOCK using pharmacological interactions and post-screening analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrodinger, L.; DeLano, W. PyMol. 2020. Available online: http://www.pymol.org/pymol (accessed on 4 September 2021).
- Singh, H.; Dhole, P.A.; Saravanan, R.; Baske, P.K. Ethnomedicinal plants used in sexual disorder in Balangir and Deogarh districts, Odisha, India. Int. J. Curr. Sci. 2017, 20, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals: Acute Oral Toxicity—Acute Toxic Class Method. Test no. 423; adopted 22 March 1996, and revised method adopted 17 December 2001; OECD: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]

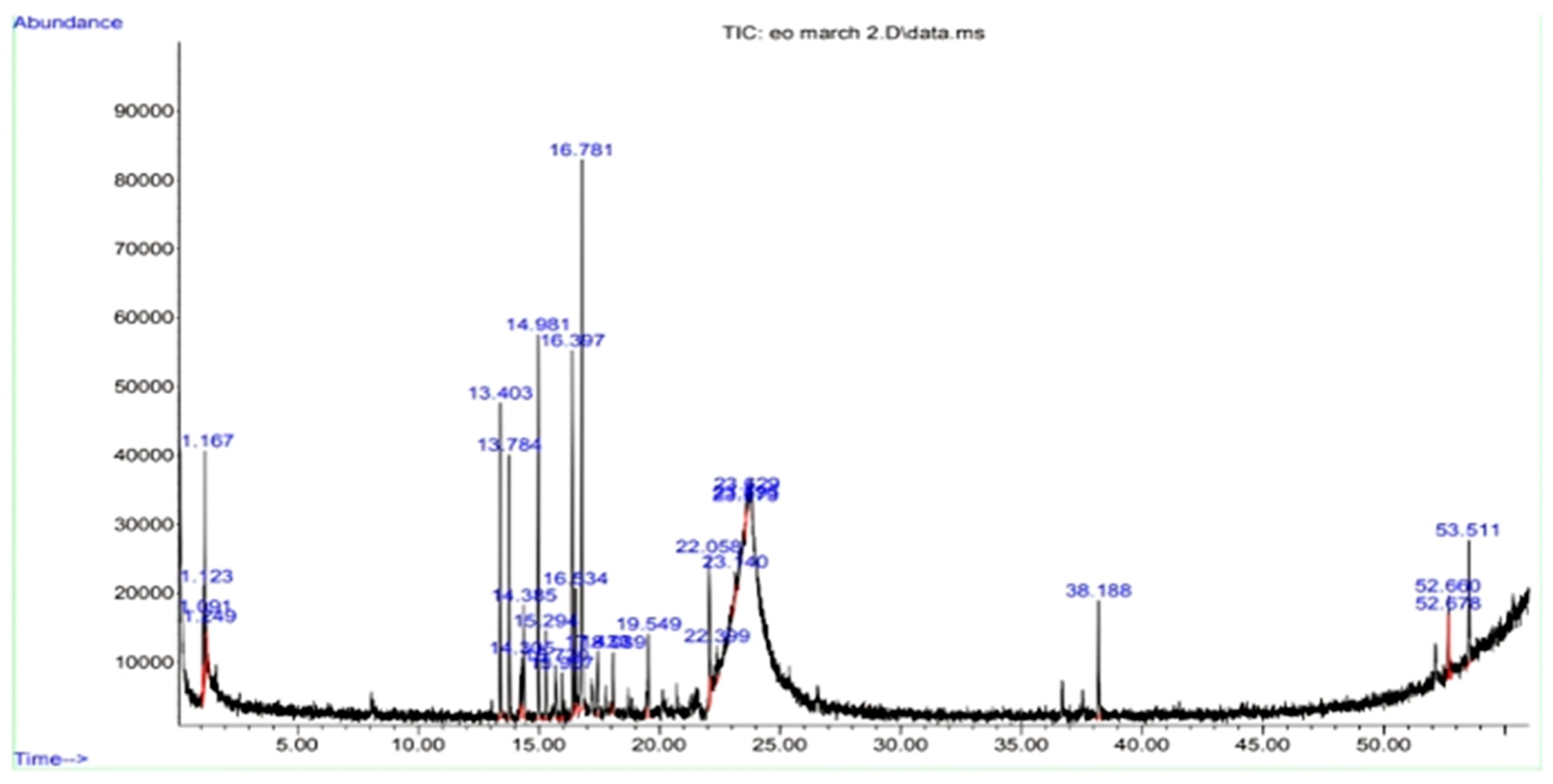
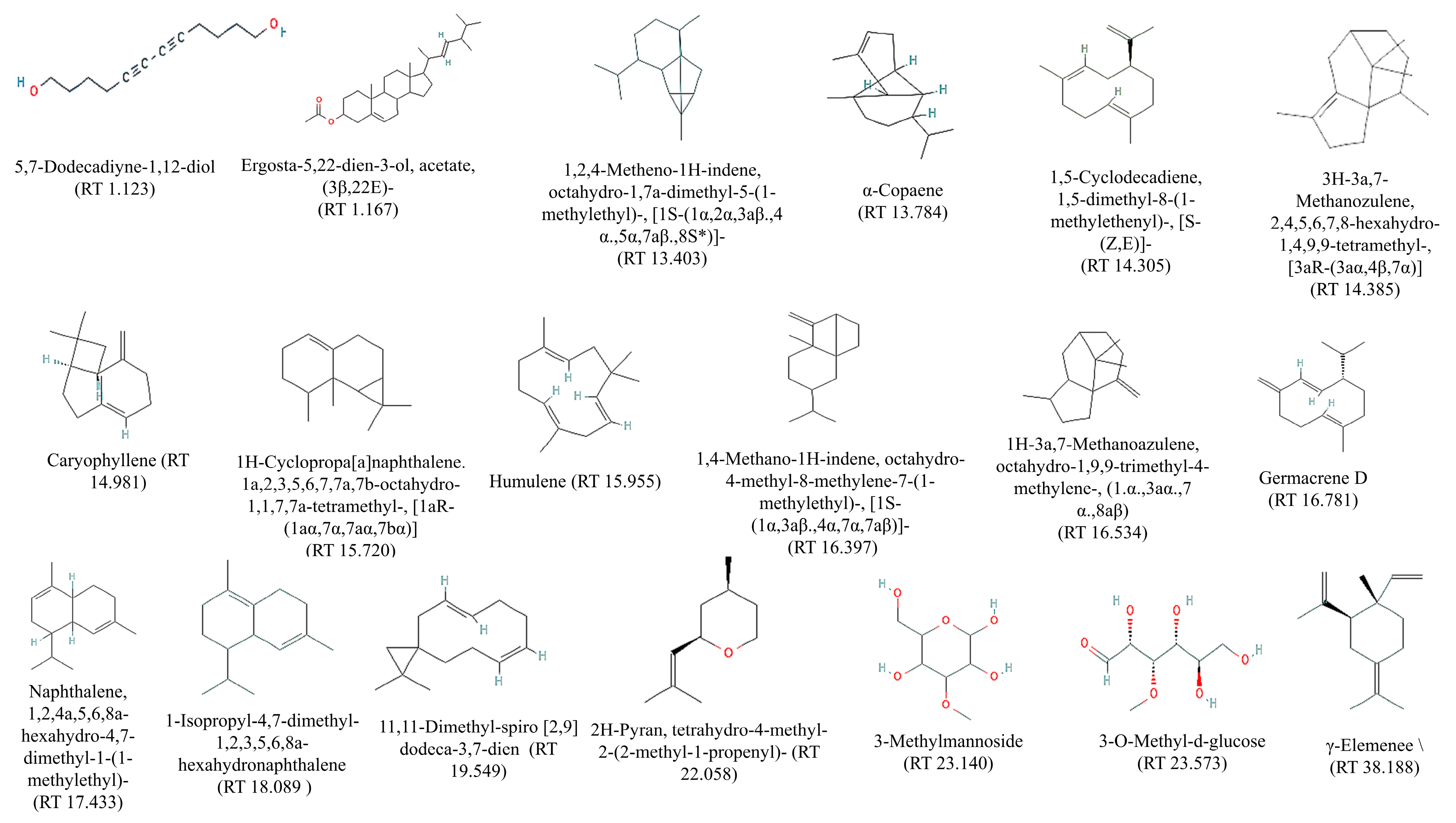



| Sl. No. | Retention Time (Minute) | PubChem CID | Compound | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Peak Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.123 | 560878 | 5,7-Dodecadiyne-1,12-diol | C12H18O2 | 194.13 | 0.979 |
| 2 | 1.167 | 5352877 | Ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, acetate, (3β,22E)- | C30H48O2 | 440.36 | 5.132 |
| 3 | 13.403 | 519960 | 1,2,4-Metheno-1H-indene, octahydro-1,7a-dimethyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-, [1S-(1α,2α,3aβ.,4 α.,5α,7aβ.,8S*)]- | C15H24 | 204.18 | 8.493 |
| 4 | 13.784 | 19725 | α-Copaene | C15H24 | 204.18 | 7.422 |
| 5 | 14.305 | 20839485 | 1,5-Cyclodecadiene, 1,5-dimethyl-8-(1-methylethenyl)-, [S-(Z,E)]- | C15H24 | 204.18 | 1.508 |
| 6 | 14.385 | 99856 | 3H-3a,7-Methanozulene, 2,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-1,4,9,9-tetramethyl-, [3aR-(3aα,4β,7α)] | C15H24 | 204.18 | 2.771 |
| 7 | 14.981 | 5281515 | Caryophyllene | C15H24 | 204.18 | 10.962 |
| 8 | 15.720 | 28481 | 1H-Cyclopropa[a]naphthalene. 1a,2,3,5,6,7,7a,7b-octahydro-1,1,7,7a-tetramethyl-, [1aR-(1aα,7α,7aα,7bα)] | C15H24 | 204.18 | 1.478 |
| 9 | 15.955 | 5281520 | Humulene | C15H24 | 204.18 | 1.268 |
| 10 | 16.397 | 530427 | 1,4-Methano-1H-indene, octahydro-4-methyl-8-methylene-7-(1-methylethyl)-, [1S-(1α,3aβ.,4α,7α,7aβ)]- | C15H24 | 204.18 | 10.288 |
| 11 | 16.534 | 521302 | 1H-3a,7-Methanoazulene, octahydro-1,9,9-trimethyl-4-methylene-, (1.α.,3aα.,7 α.,8aβ) | C15H24 | 204.18 | 3.045 |
| 12 | 16.781 | 5317570 | Germacrene D | C15H24 | 204.18 | 16.755 |
| 13 | 17.433 | 101708 | Naphthalene, 1,2,4a,5,6,8a-hexahydro-4,7-dimethyl-1-(1-methylethyl)- | C15H24 | 204.18 | 2.023 |
| 14 | 18.089 | 10223 | 1-Isopropyl-4,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,5,6,8a-hexahydronaphthalene | C15H24 | 204.18 | 1.505 |
| 15 | 19.549 | 5367333 | 11,11-Dimethyl-spiro [2,9] dodeca-3,7-dien | C14H22 | 190.17 | 2.921 |
| 16 | 22.058 | 6432154 | 2H-Pyran, tetrahydro-4-methyl-2-(2-methyl-1-propenyl)- | C10H18O | 154.13 | 5.438 |
| 17 | 23.140 | 247323 | 3-Methylmannoside | C7H14O6 | 194.07 | 0.870 |
| 18 | 23.573 | 8973 | 3-O-Methyl-d-glucose | C7H14O6 | 194.07 | 0.286 |
| 19 | 38.188 | 6432312 | γ-Elemene | C15H24 | 204.18 | 3.857 |
| Sl. No. | Compound | Chemical Group | Chemical Structure | Biological Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,2,4-Metheno-1H-indene, octahydro-1,7a-dimethyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-, [1S-(1α,2α,3aβ.,4 α.,5α,7aβ.,8S*)]- | Sesquiterpene | CC(C)C1CCC2(C3C1C4C2(C4C3)C)C | Antiproliferative, genotoxic, and oxidant activities | [21] |
| 2 | 1,4-Methano-1H-indene, octahydro-4-methyl-8-methylene-7-(1-methylethyl)-, [1S-(1α,3aβ.,4α,7α,7aβ)] | Sesquiterpene | CC©C1CCC2(C3C1C(C2=C)CC3)C | Not reported | |
| 3 | 11,11-Dimethyl-spiro [2,9] dodeca-3,7-dien | Spiro compound | CC1(CC12CCC=CCCC=CC2)C | Not reported | |
| 4 | 1H-3a,7-Methanoazulene, octahydro-1,9,9-trimethyl-4-methylene-, (1.α.,3aα.,7 α.,8aβ) | Sesquiterpene | CC1CCC23C1CC©(C)C)CCC3=C | Not reported | |
| 5 | 1H-Cyclopropa[a]naphthalene. 1a,2,3,5,6,7,7a,7b-octahydro-1,1,7,7a-tetramethyl-, [1aR-(1aα,7α,7aα,7bα)]- | Sesquiterpene | CC1CCC=C2C1(©(C3(C)C)CC2)C | Antibacterial | [21] |
| 6 | 1-Isopropyl-4,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,5,6,8a-hexahydronaphthalene | Sesquiterpene | CC1=CC2C(CCC(=©C1)C)C(C)C | Not reported | |
| 7 | 2H-Pyran, tetrahydro-4-methyl-2-(2-methyl-1-propenyl) | Monoterpene | CC©OC(C1)C=C(C)C | Anti-inflammatory | [22] |
| 8 | 3H-3a,7-Methanozulene, 2,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-1,4,9,9-tetramethyl-, [3aR-(3aα,4β,7α)] | Sesquiterpene | CC1CC©C3=C(CCC13C2(C)C)C | Not reported | |
| 9 | 3-Methylmannoside | Carbohydrate | COC1C(C(OC(C1O)O)CO)O | Not reported | |
| 10 | 3-O-Methyl-d-glucose | Carbohydrate | COC(C(C=O)O)C(C(CO)O)O | Anticancer and anti-inflammatory | [23] |
| 11 | 5,7-Dodecadiyne-1,12-diol | Fatty acid | C(CCO)CC#CC#CCCCCO | Not reported | |
| 12 | 1,5-Cyclodecadiene, 1,5-dimethyl-8-(1-methylethenyl)-, [S-(Z,E)]- | Terpenoid | CC1=CCCC(=CCC(CC1)C(=C)C)C | Not reported | |
| 13 | Caryophyllene | Sesquiterpene | CC1=C©(=C)C2CC(C2CC1)(C)C | Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial | [24] |
| 14 | Ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, acetate, (3β,22E)- | Sterol | CC(C)C(C)C=CC(C)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2CC=C4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)C | Not reported | |
| 15 | Germacrene D | Sesquiterpene | CC1=CCCC(=C)C=CC(CC1)C(C)C | Mosquitocidal and repellent activity against aphids and ticks | [25,26,27] |
| 16 | Humulene | Sesquiterpene | CC1=CCC(C=CCC(=CCC1)C)(C)C | Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antineoplastic | [28] |
| 17 | Naphthalene, 1,2,4a,5,6,8a-hexahydro-4,7-dimethyl-1-(1-methylethyl)- | Sesquiterpene | CC1=CC2C(CC1)C(=CCC2C(C)C)C | Not reported | |
| 18 | α-Copaene | Sesquiterpene | CC1=CCC2C3C1C2(CCC3C(C)C)C | Antiproliferative and antioxidant | [21] |
| 19 | γ-Elemene | Sesquiterpene | CC(=C1CCC(C(C1)C(=C)C)(C)C=C)C | Insecticidal | [29] |
| Phytocompound | Target Proteins | Binding Energy (∆G) (Kcal/mol) | Ligand Efficiency | Inhibition Constant ((Ki) (nM)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, acetate, (3β,22E) | TNF-α | −8.21 | −0.26 | 964.03 |
| Cox-2 | −8.93 | −0.28 | 282.86 | |
| Superoxide dismutase | −7.16 | −0.22 | 5.62 | |
| α-Amylase | −9.27 | −0.29 | 161.19 | |
| Aldo reductase | −11.73 | −0.37 | 2.53 |
| Symbols | Independent Variables | Unit | Coded Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 (Low) | 0 (Medium) | +1 (High) | |||
| A | Methanol concentration | % | 40 | 70 | 100 |
| B | Temperature | °C | 20 | 50 | 80 |
| C | Extraction duration | Hours | 1 | 12.5 | 24 |
| Dependent variable/response variable | Goal | ||||
| Y1 | Total phenolic content | mg GAE/g dry tissue | Maximise | ||
| Run | Solvent (%) | Temperature (°C) | Extraction Duration (Hours) | Total Phenolic Content (Mg GAE/g Dry Tissue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70 | 20 | 24 | 100.24 |
| 2 | 70 | 20 | 1 | 108.45 |
| 3 | 100 | 50 | 24 | 103.88 |
| 4 | 70 | 50 | 12.5 | 154.35 |
| 5 | 70 | 50 | 12.5 | 151.25 |
| 6 | 70 | 50 | 12.5 | 155.84 |
| 7 | 40 | 50 | 24 | 108.68 |
| 8 | 70 | 80 | 24 | 105.34 |
| 9 | 70 | 80 | 1 | 100.23 |
| 10 | 40 | 50 | 1 | 105.22 |
| 11 | 100 | 80 | 12.5 | 100.55 |
| 12 | 70 | 50 | 12.5 | 150.44 |
| 13 | 70 | 50 | 12.5 | 151.33 |
| 14 | 40 | 80 | 12.5 | 116.45 |
| 15 | 40 | 20 | 12.5 | 111.22 |
| 16 | 100 | 20 | 12.5 | 107.45 |
| 17 | 100 | 50 | 1 | 102.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hazra, S.; Ray, A.S.; Das, S.; Das Gupta, A.; Rahaman, C.H. Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot. Plants 2023, 12, 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071495
Hazra S, Ray AS, Das S, Das Gupta A, Rahaman CH. Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot. Plants. 2023; 12(7):1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071495
Chicago/Turabian StyleHazra, Samik, Anindya Sundar Ray, Swetarka Das, Arunava Das Gupta, and Chowdhury Habibur Rahaman. 2023. "Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot" Plants 12, no. 7: 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071495
APA StyleHazra, S., Ray, A. S., Das, S., Das Gupta, A., & Rahaman, C. H. (2023). Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot. Plants, 12(7), 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071495







