A Quantitative Trait Locus with a Major Effect on Root-Lesion Nematode Resistance in Barley
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
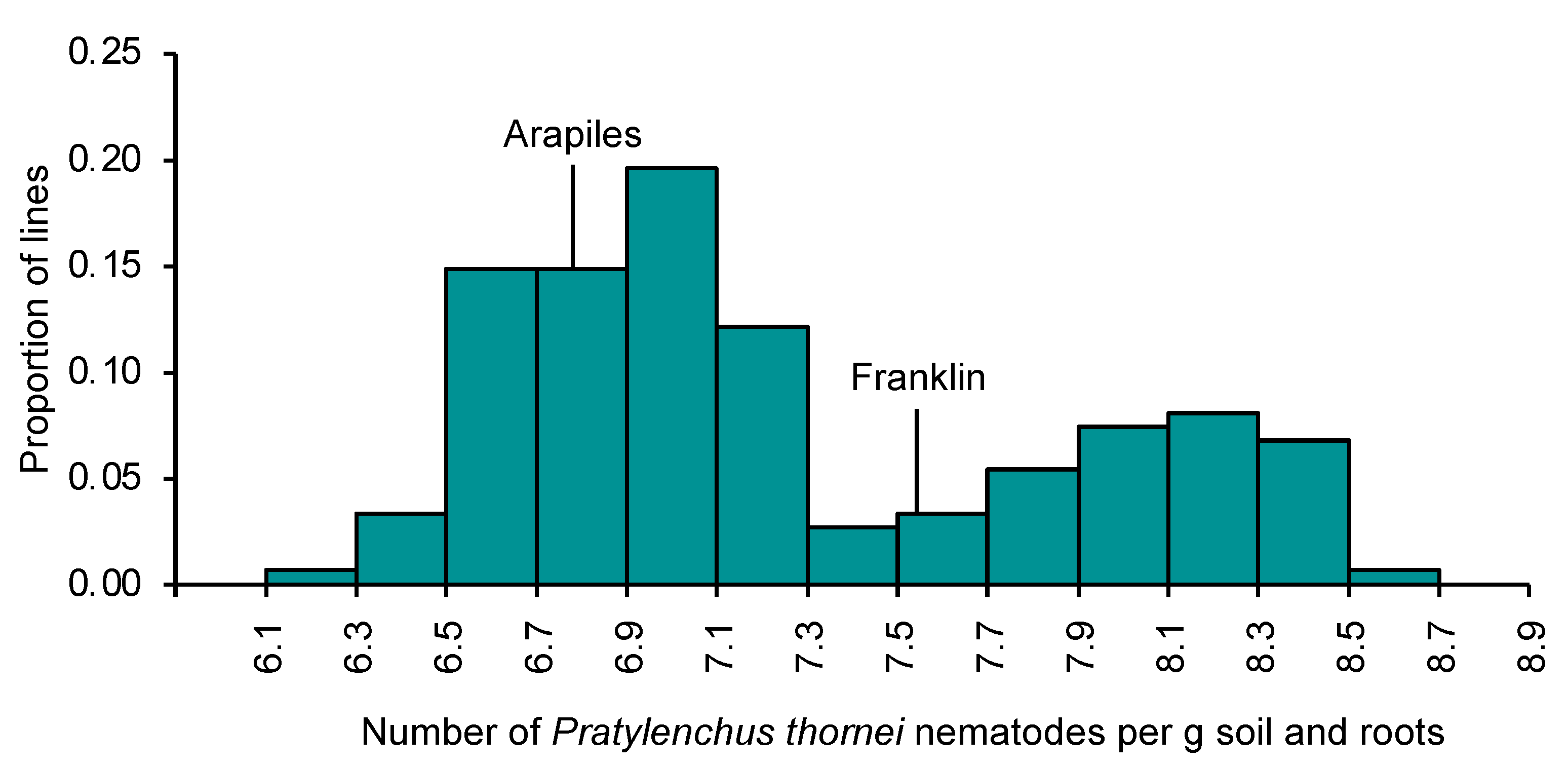
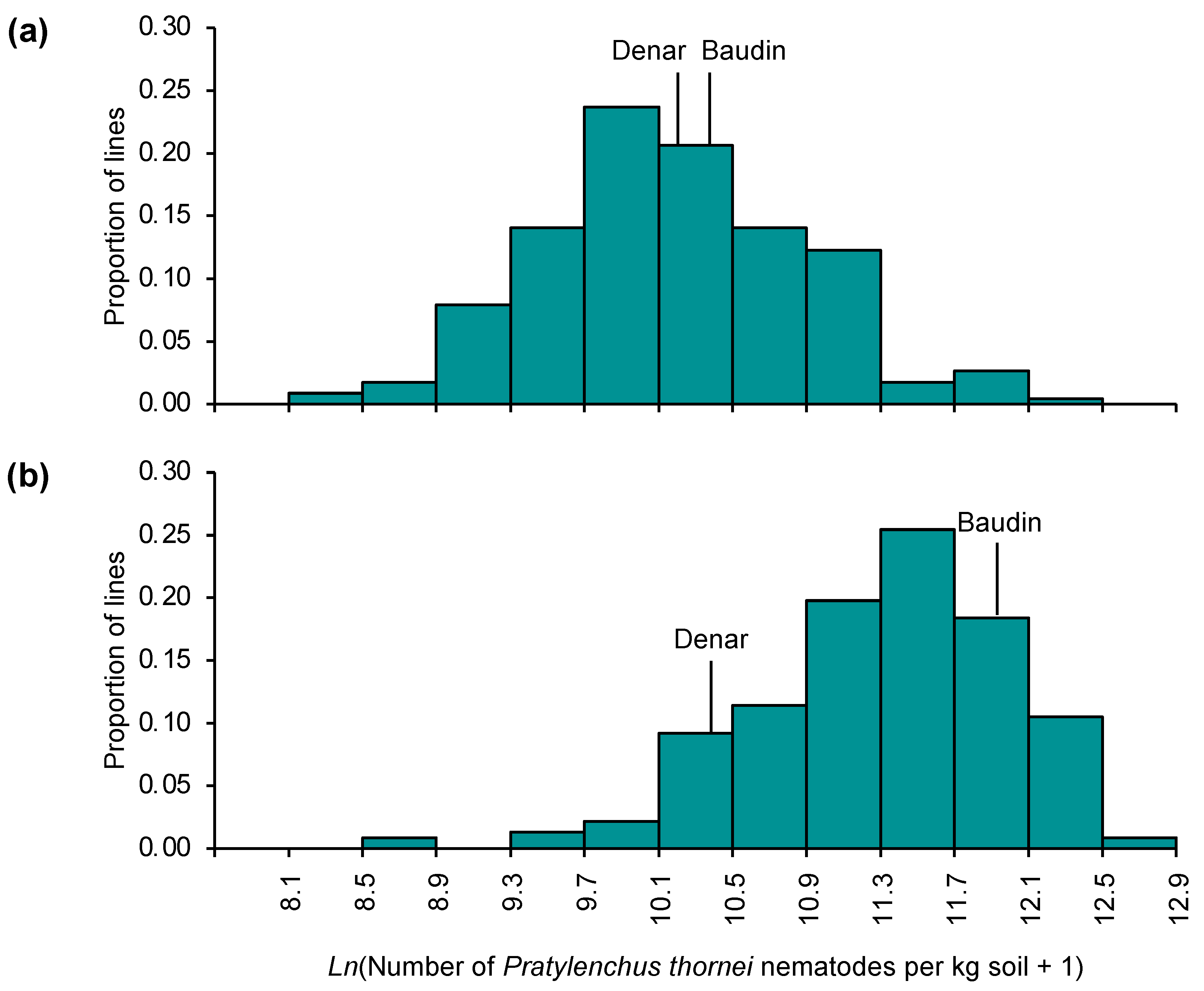
2.1. Variation for Pratylenchus thornei Resistance in Barley
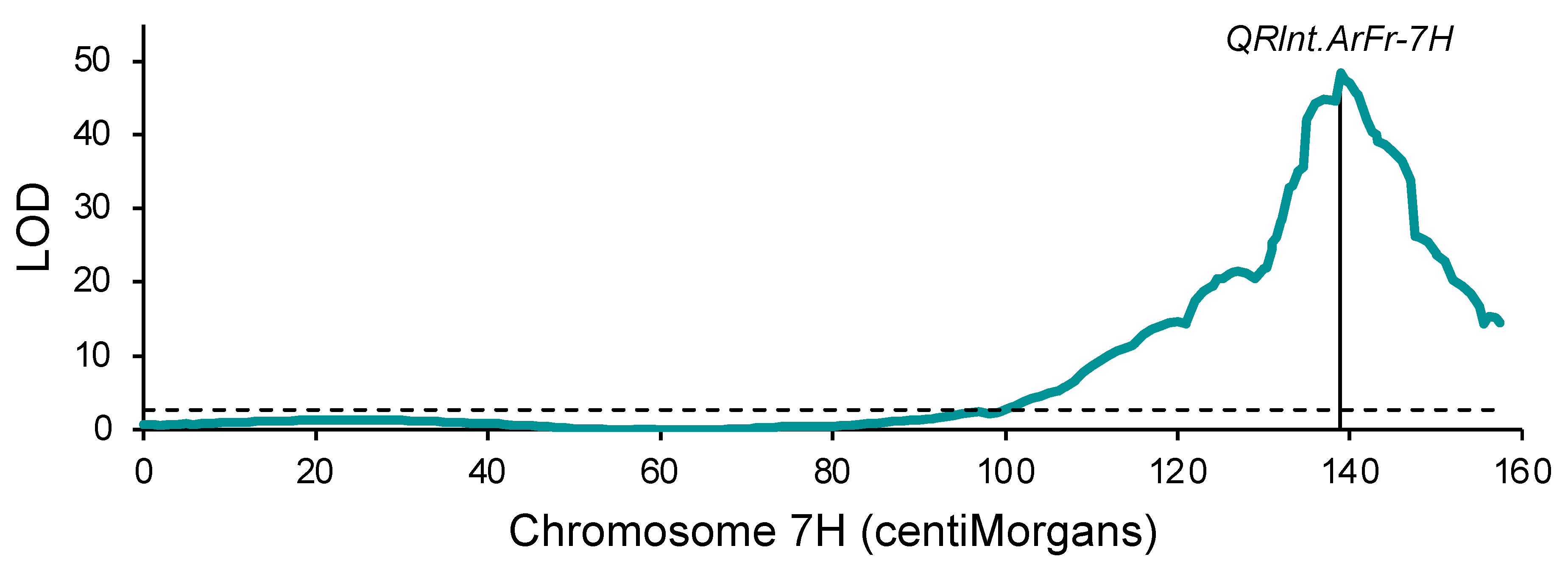
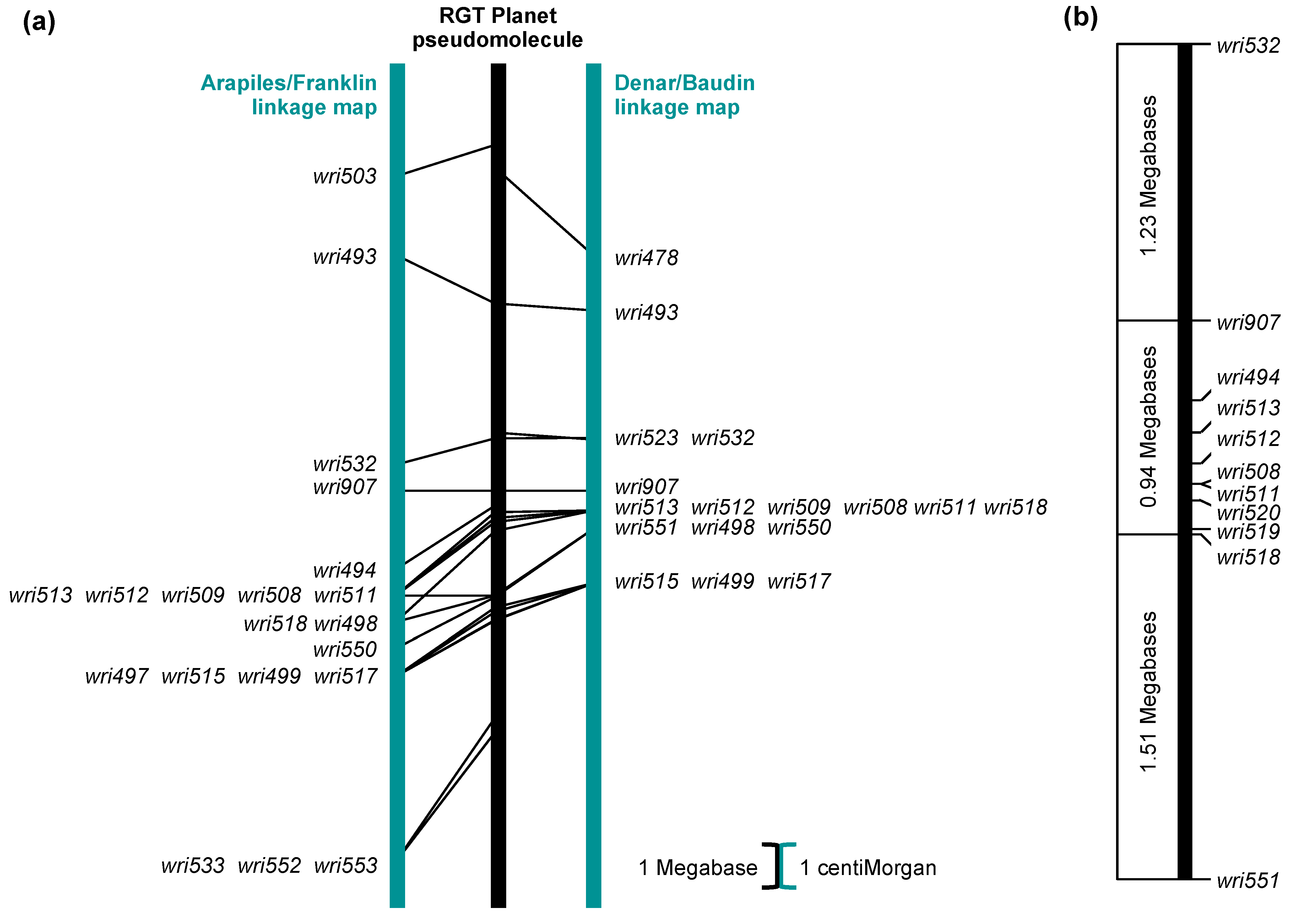
2.2. Genetic Mapping: Arapiles/Franklin
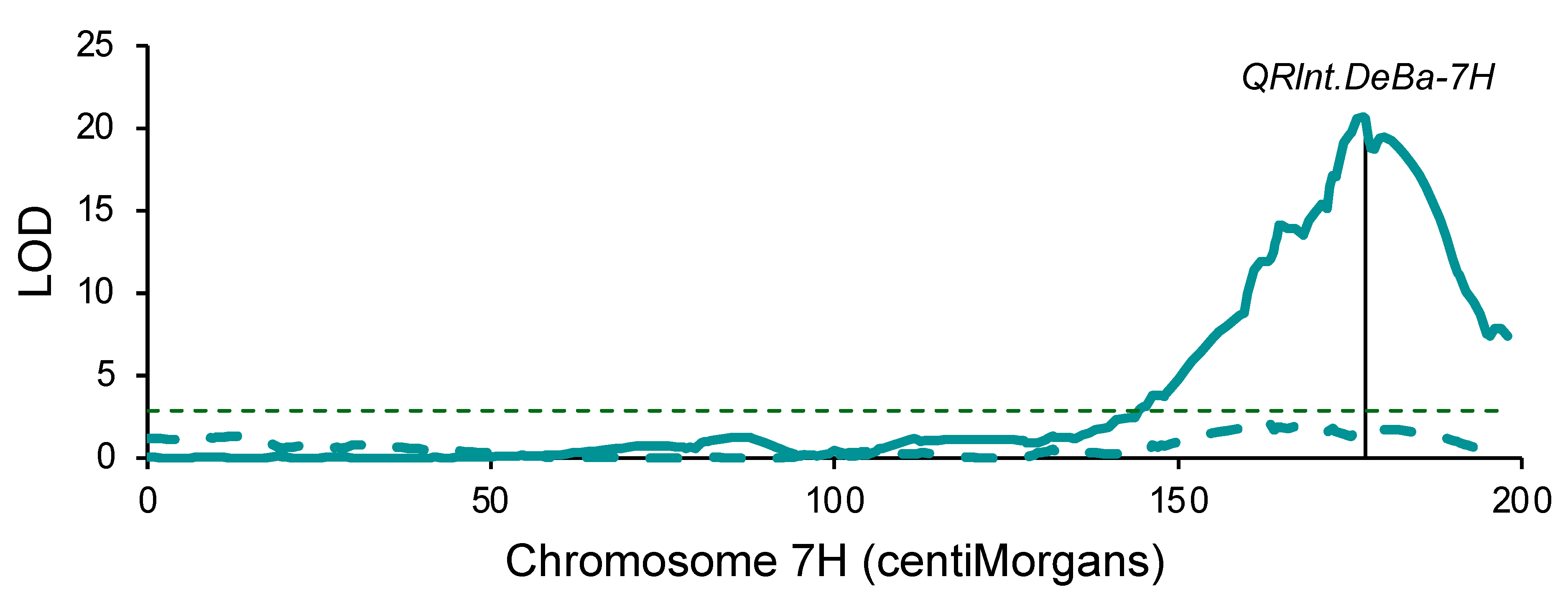
2.3. Genetic Mapping: Denar/Baudin
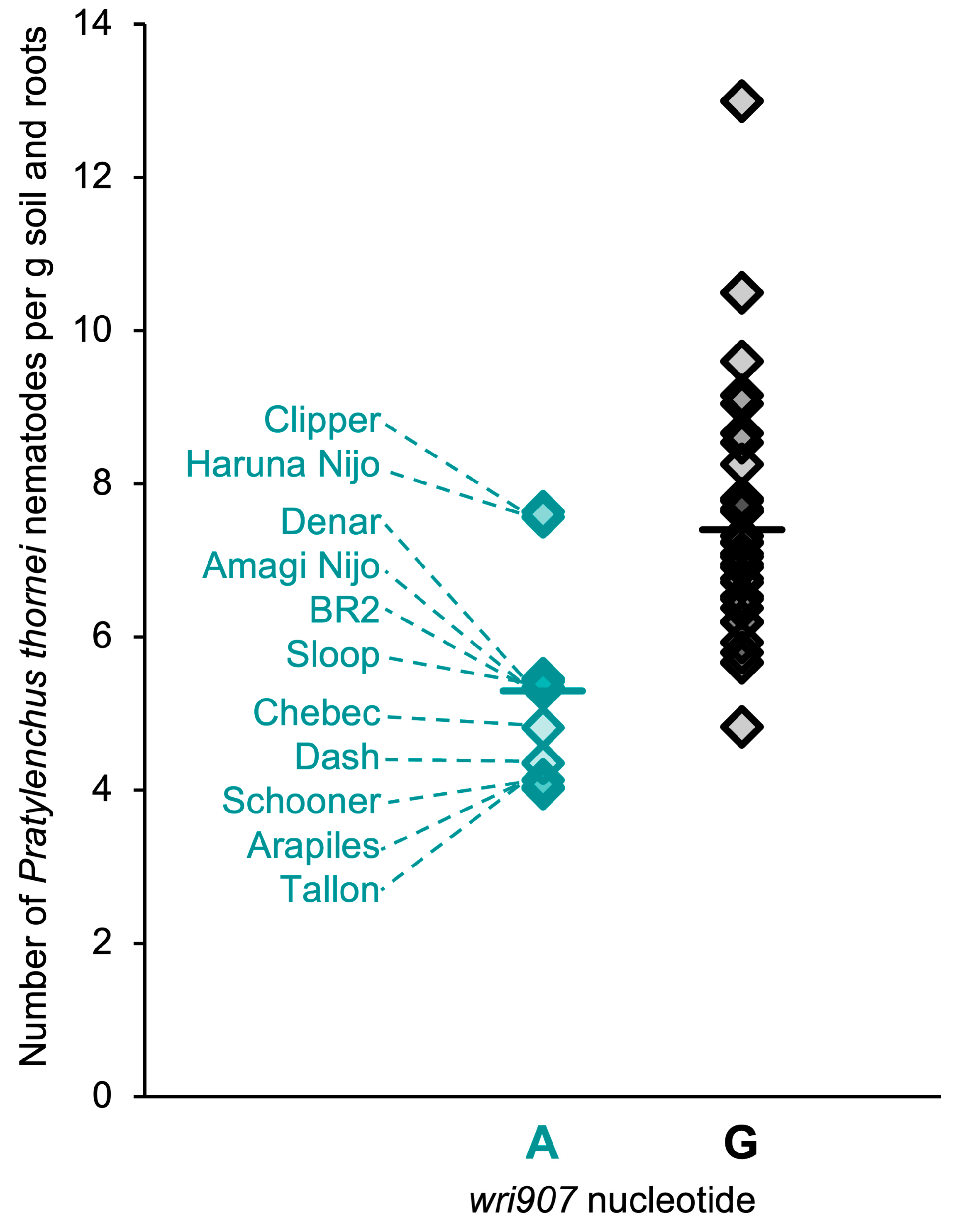
2.4. SNP Genotypes, Physical Positions and Haplotypes
3. Discussion
3.1. Mapping of a Common Quantitative Trait Locus in Two Barley Populations
3.2. Mapping of a Common Quantitative Trait Locus in Two Barley Populations
3.3. A Candidate Region and Predicted Genes on a Barley Genome Assembly
3.4. Application in Barley Breeding
3.5. Alternative Sources of Resistance
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
- (1)
- A panel of 46 barley lines (Table S1), each of which had previously been used as a parent to develop one or more mapping populations;
- (2)
- Eight varieties of bread wheat: Catalina, Chara, EGA Gregory, Estoc, Mace, Machete, Estoc, Naparoo and Yandanooka (Table S1);
- (3)
- (4)
- 225 doubled haploid lines derived from the F1 generation of a cross between Arapiles and Franklin (Table S2);
- (5)
- 235 doubled haploid lines derived from the F1 generation of a cross between Denar and Baudin (Table S4);
- (6)
4.2. Evaluation of Pratylenchus thornei Resistance in South Australia
4.3. Evaluation of Pratylenchus thornei Resistance in Queensland
4.4. Genetic Mapping, Marker Development and Genotyping
4.5. Analysis of Pan-Genomic and Pan-Transcriptomic Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, M.G.K.; Fosu-Nyarko, J. Molecular biology of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) and their interaction with host plants. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P.; Owen, K.J.; Stirling, G.R.; Bell, M.J. Root-lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus thornei and P. neglectus); a review of recent progress in managing a significant pest of grain crops in northern Australia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2008, 37, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, R.S.; Thudi, M.; Channale, S.; Manchikatia, P.K.; Varshney, R.K.; Thompson, J.P. Resistance to plant parasitic nematodes in chickpea: Current status and future perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P.; Brennan, P.S.; Clewett, T.G.; Sheedy, J.G.; Seymour, N.P. Progress in breeding wheat for tolerance and resistance to root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei. Australas. Plant Pathol. 1999, 28, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P.; O’Reilly, M.M.; Clewett, T.G. Resistance to the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei in wheat landraces and cultivars from the West Asia and North Africa WANA region. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, J.G.; Thompson, J.P. Resistance to the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei of Iranian landrace wheat. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2009, 38, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P. Resistance to root-lesion nematodes Pratylenchus thornei and P. neglectus in synthetic hexaploid wheats and their durum and Aegilops tauschii parents. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 59, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P.; Haak, M.I. Resistance to root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei in Aegilops tauschii Coss, the D-genome donor to wheat. Aust. J Agric. Res. 1997, 48, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, J.G.; Thompson, J.P.; Kelly, A. Diploid and tetraploid progenitors of wheat are valuable sources of resistance to the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei. Euphytica 2012, 186, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.P.; Reen, R.A.; Clewett, T.G.; Sheedy, J.G.; Kelly, A.M.; Gogel, B.J.; Knights, E.J. 2011 Hybridisation of Australian chickpea cultivars with wild Cicer spp. increases resistance to root-lesion nematodes Pratylenchus thornei and P. neglectus. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2011, 40, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, M.S.; Hobson, K.B.; Forknall, C.R.; Daniel, R.P.; Fanning, J.P.; Pounsett, D.D.; Simpfendorfer, S.; Moore, K.J.; Owen, K.J.; Sheedy, J.G.; et al. Highly heritable resistance to root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei in Australian chickpea germplasm observed using an optimised glasshouse method and multi-environment trial analysis. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reen, R.A.; Mumford, M.H.; Thompson, J.P. Novel sources of resistance to root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei in a new collection of wild Cicer species C. reticulatum and C. echinospermum to improve resistance in cultivated chickpea C. arietinum. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.L.; McIntyre, C.L.; Thompson, J.P.; Seymour, N.P.; Liu, C.J. Quantitative trait loci for root lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei resistance in Middle-Eastern landraces and their potential for introgression into Australian bread wheat. Austr. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 56, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, R.S.; Thompson, J.P.; Godwin, I.D. Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to two species of root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei and P. neglectus in wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 56, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, R.S.; Thompson, J.P.; Milgate, A.W.; Bansal, P.M.; Raman, H.; Bariana, H.S. QTL mapping of multiple foliar disease and root-lesion nematode resistances in wheat. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, R.S.; Thompson, J.P.; Sheedy, J.G.; Nelson, J.C. Mapping quantitative trait loci for resistance to Pratylenchus thornei from synthetic hexaploid wheat in the International Triticeae Mapping Initiative ITMI population. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 57, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsell, K.J.; Rahman, M.S.; Taylor, J.D.; Davey, R.S.; Gogel, B.J.; Wallwork, H.; Forrest, K.L.; Hayden, M.J.; Taylor, S.P.; Oldach, K.H. QTL for resistance to root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei from a synthetic hexaploid wheat source. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Linsell, K.J.; Taylor, J.D.; Hayden, M.J.; Collins, N.C.; Oldach, K.H. Fine mapping of root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei resistance loci on chromosomes 6D and 2B of wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 133, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.H.P.; Sheedy, J.G.; Taylor, J.D.; Croser, J.S.; Hayes, J.E.; Sutton, T.; Thompson, J.P.; Mather, D.E. A QTL on the CA7 chromosome of chickpea affects resistance to the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstone, V.A.; Hollaway, G.J.; Stirling, G.R. Managing nematode posts in the southern and western regions of the Australian cereal industry: Continuing progress in a challenging environment. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2008, 37, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.M.; Brennan, J.P. Estimating disease losses to the Australian barley industry. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2010, 39, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grains Research and Development Corporation National Variety Trials Disease Ratings. Available online: https://nvt.grdc.com.au/nvt-disease-ratings (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.; Kopisch-Obuch, F.J.; Keil, T.; Laubach, E.; Stein, N.; Graner, A.; Jung, C. QTL analysis of root-lesion nematode resistance in barley: 1. Pratylenchus neglectus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, A.; Sharma, S.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F.; Sharma, S.; Kopisch-Obuch, F.; Laubach, E.; Perovic, D.; Ordon, F.; Jung, C. Comparative QTL analysis of root lesion nematode resistance in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ophel-Keller, K.; McKay, A.; Hartley, D.; Herdina; Curran, J. Development of a routine DNA-based testing service for soilborne diseases in Australia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2008, 37, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, J.G.; McKay, A.C.; Lewis, J.; Vanstone, V.A.; Fletcher, S.; Kelly, A.; Thompson, J. Cereal cultivars can be ranked consistently for resistance to root-lesion nematodes Pratylenchus thornei and P. neglectus using diverse procedures. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2014, 44, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panozzo, J.F.; Eckermann, P.J.; Mather, D.E.; Moody, D.B.; Black, C.K.; Collins, H.M.; Barr, A.R.; Lim, P.; Cullis, B.R. QTL analysis of malting quality traits in two barley populations. Crop Pasture Sci. 2007, 58, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Vassos, E.; Sznajder, B.; Fox, R.; Khoo, K.H.P.; Loughman, R.; Chalmers, K.J.; Mather, D.E. A locus in barley chromosome 5H affects adult plant resistance to powdery mildew. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakodi, M.; Padmarasu, S.; Haberer, G.; Bonthala, V.S.; Gundlach, H.; Monat, C.; Lux, T.; Kamal, N.; Lang, D.; Himmelbach, A.; et al. The barley pan-genome reveals the hidden legacy of mutation breeding. Nature 2020, 588, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, R.; Guo, W.; Schreiber, M.; Marosi, V.; Bagnaresi, P.; Chalmers, K.; Chapman, B.; Dang, V.; Dockter, C.; Fiebig, A.; et al. A barley pan-transcriptome reveals layers of genotype-dependent transcriptional complexity. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channale, S.; Thompson, J.P.; Varshney, R.K.; Thudi, M.; Zwart, R.S. Multi-locus genome-wide association study of chickpea reference set identifies genetic determinants of Pratylenchus thornei resistance. Front. Plant. Sci. 2023, 14, 1139574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channale, S.; Kalavikatte, D.; Thompson, J.P.; Kudapa, H.; Bajaj, P.; Varshney, R.K. Transcriptome analysis reveals key genes associated with root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei resistance in chickpea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsell, K.J.; Riley, I.T.; Davies, K.A.; Oldach, K.H. Characterization of resistance to Pratylenchus thornei Nematoda in wheat Triticum aestivum: Attraction, penetration, motility, and reproduction. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, E.H.; Lownsbery, B.F.; Ahmed, J.M. Culture of the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus vulnus on carrot disks. J. Nematol. 1973, 5, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, A.G.; Hemming, J.R. A comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 55, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, J.R.; Marks, C.F. The determination of normalizing transformations for nematode count data from soil samples and of efficient sampling schemes. Nematologica 1975, 20, 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Broman, K.W.; Wu, H.; Sen, S.; Churchill, G.A. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 21 January 2024).
- He, C.; Holme, J.; Anthony, J. SNP genotyping: The KASP assay. In Crop Breeding. Methods in Molecular Biology; Fleury, D., Whitford, R., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1145, pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Bhat, P.R.; Close, T.J.; Lonardi, S. Efficient and accurate construction of genetic linkage maps from the minimum spanning tree of a graph. PLoS Genet. 2008, 10, e1000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Butler, D. R Package ASMap: Efficient genetic linkage map construction and diagnosis. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 79, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyam, A.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Rai, V.; Moghul, I.; Munagala, A.; Ter, F.; Chowdhary, H.; Pieniak, I.; Maynard, L.J.; Gibbins, M.A.; et al. Sequenceserver: A modern graphical user interface for custom BLAST databases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2922–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GrainGenes BLAST Service. Available online: https://wheat.pw.usda.gov/blast/ (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Tzioutziou, N.A.; Stephen, G.; Milne, I.; Calixto, C.P.; Waugh, R.; Brown, J.W.S.; Zhang, R. 3D RNA-seq: A powerful and flexible tool for rapid and accurate differential expression and alternative splicing analysis of RNA-seq data for biologists. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| RGT Planet Gene | PanBaRT20 Gene ID | Mean TPM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene ID | Description | ||
| PLANET_7H01G664900 | Carbonic anhydrase | PanBaRT20_7H77511 | 120.52 |
| PLANET_7H01G657100 | WRKY transcription factor | PanBaRT20_7H78604 | 79.51 |
| PLANET_7H01G657200 | WRKY transcription factor | PanBaRT20_7H78606 | 171.32 |
| PLANET_7H01G657500 | PanBaRT20_7H78609 | 6.04 | |
| PLANET_7H01G658100 | Aldehyde oxidase, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78620 | 5.59 |
| PLANET_7H01G658300 | Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase | PanBaRT20_7H78624 | 2.79 |
| PLANET_7H01G658600 | 50S ribosomal protein L35 | PanBaRT20_7H78626 | 6.39 |
| PLANET_7H01G659700 | 50S ribosomal protein L35 | PanBaRT20_7H78646 | 4.49 |
| PLANET_7H01G660900 | PanBaRT20_7H78652 | 32.41 | |
| PLANET_7H01G661100 | PanBaRT20_7H78658 | 60.94 | |
| PLANET_7H01G661600 | Kinase, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78661 | 4.19 |
| PLANET_7H01G661800 | Homeobox protein knotted-1, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78662 | 102.55 |
| PLANET_7H01G661900 | Kinase family protein | PanBaRT20_7H78663 | 16.81 |
| PLANET_7H01G662100 | Indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase-like | PanBaRT20_7H78670 | 72.89 |
| PLANET_7H01G662400 | NHL domain-containing protein, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78676 | 332.46 |
| PLANET_7H01G664400 | PanBaRT20_7H78691 | 2.96 | |
| PLANET_7H01G664500 | PanBaRT20_7H78695 | 8.51 | |
| PLANET_7H01G665100 | Methyltransferase-like | PanBaRT20_7H78700 | 4.91 |
| PLANET_7H01G665200 | Ribonuclease 3-like protein 3 | PanBaRT20_7H78702 | 18.89 |
| PLANET_7H01G666100 | Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein | PanBaRT20_7H78705 | 22.02 |
| PLANET_7H01G666300 | Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 1 | PanBaRT20_7H78707 | 19.99 |
| PLANET_7H01G666400 | XH/XS domain-containing family protein | PanBaRT20_7H78709 | 28.05 |
| PLANET_7H01G666500 | Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 1 | PanBaRT20_7H78710 | 21.36 |
| PLANET_7H01G666600 | Transmembrane protein | PanBaRT20_7H78711 | 23.57 |
| PLANET_7H01G666900 | PanBaRT20_7H78714 | 1.82 | |
| PLANET_7H01G667300 | NF-X1-type zinc finger protein NFXL1 | PanBaRT20_7H78717 | 3.95 |
| PLANET_7H01G667400 | Isoleucine–tRNA ligase | PanBaRT20_7H78719 | 70.82 |
| PLANET_7H01G667500 | Mis12 protein | PanBaRT20_7H78720 | 26.22 |
| PLANET_7H01G667900, PLANET_7H01G668100 | PanBaRT20_7H78730 | 353.53 | |
| PLANET_7H01G668200 | PanBaRT20_7H78735 | 42.43 | |
| PLANET_7H01G668400 | Amino acid transporter-like protein | PanBaRT20_7H78741 | 23.33 |
| PLANET_7H01G668500 | WD40 repeat-like protein | PanBaRT20_7H78742 | 31.70 |
| PLANET_7H01G668800 | S-acyltransferase | PanBaRT20_7H78743 | 26.43 |
| PLANET_7H01G668900 | Pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar | PanBaRT20_7H78744 | 183.49 |
| RGT Planet Gene | PanBaRT20 Gene ID | Number of Lines with Lower Expression than RGT Planet 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene ID | Description | ||
| PLANET_7H01G664900 | Carbonic anhydrase | PanBaRT20_7H77511 | 4 |
| PLANET_7H01G657100 | WRKY transcription factor | PanBaRT20_7H78604 | 9 |
| PLANET_7H01G657200 | WRKY transcription factor | PanBaRT20_7H78606 | 7 |
| PLANET_7H01G659700 | Kinase family protein | PanBaRT20_7H78646 | 1 |
| PLANET_7H01G660900 | PanBaRT20_7H78652 | 11 | |
| PLANET_7H01G661100 | PanBaRT20_7H78658 | 11 | |
| PLANET_7H01G661600 | Kinase, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78661 | 16 |
| PLANET_7H01G661800 | Homeobox protein knotted-1, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78662 | 1 |
| PLANET_7H01G662100 | Indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase-like | PanBaRT20_7H78670 | 2 |
| PLANET_7H01G662400 | NHL domain-containing protein, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78676 | 7 |
| PLANET_7H01G664400 | PanBaRT20_7H78691 | 2 | |
| PLANET_7H01G664500 | PanBaRT20_7H78695 | 7 | |
| PLANET_7H01G666600 | Transmembrane protein | PanBaRT20_7H78711 | 7 |
| PLANET_7H01G667900 PLANET_7H01G668100 | PanBaRT20_7H78730 | 14 | |
| PLANET_7H01G668900 | Pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar membrane proton pump | PanBaRT20_7H78744 | 2 |
| RGT Planet Gene | PanBaRT20 Gene ID | Number of Lines with Higher Expression than RGT Planet 1 | Absolute Value of log2 Fold-Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene ID | Description | Maximum | Median 2 | ||
| PLANET_7H01G664900 | Carbonic anhydrase | PanBaRT20_7H77511 | 1 | 1.56 | 1.56 |
| PLANET_7H01G657100 | WRKY transcription factor | PanBaRT20_7H78604 | 2 | 1.23 | 1.21 |
| PLANET_7H01G657500 | PanBaRT20_7H78609 | 4 | 1.16 | 1.04 | |
| PLANET_7H01G658100 | Aldehyde oxidase, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78620 | 8 | 2.90 | 1.67 |
| PLANET_7H01G658200 | Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase | PanBaRT20_7H78622 | 9 | 3.66 | 1.93 |
| PLANET_7H01G658300 | Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase | PanBaRT20_7H78624 | 1 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| PLANET_7H01G660900 | PanBaRT20_7H78652 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.25 | |
| PLANET_7H01G662100 | Indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase-like | PanBaRT20_7H78670 | 2 | 1.37 | 1.24 |
| PLANET_7H01G662400 | NHL domain-containing protein, putative | PanBaRT20_7H78676 | 1 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| PLANET_7H01G664400 | PanBaRT20_7H78691 | 1 | 1.07 | 1.07 | |
| PLANET_7H01G663800 PLANET_7H01G664600 | Glycosyltransferase | PanBaRT20_7H78697 | 5 | 1.82 | 1.54 |
| PLANET_7H01G666900 | PanBaRT20_7H78714 | 1 | 1.02 | 1.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mather, D.; Vassos, E.; Sheedy, J.; Guo, W.; McKay, A. A Quantitative Trait Locus with a Major Effect on Root-Lesion Nematode Resistance in Barley. Plants 2024, 13, 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13121663
Mather D, Vassos E, Sheedy J, Guo W, McKay A. A Quantitative Trait Locus with a Major Effect on Root-Lesion Nematode Resistance in Barley. Plants. 2024; 13(12):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13121663
Chicago/Turabian StyleMather, Diane, Elysia Vassos, Jason Sheedy, Wenbin Guo, and Alan McKay. 2024. "A Quantitative Trait Locus with a Major Effect on Root-Lesion Nematode Resistance in Barley" Plants 13, no. 12: 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13121663
APA StyleMather, D., Vassos, E., Sheedy, J., Guo, W., & McKay, A. (2024). A Quantitative Trait Locus with a Major Effect on Root-Lesion Nematode Resistance in Barley. Plants, 13(12), 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13121663







