Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screening and Identification of KSB
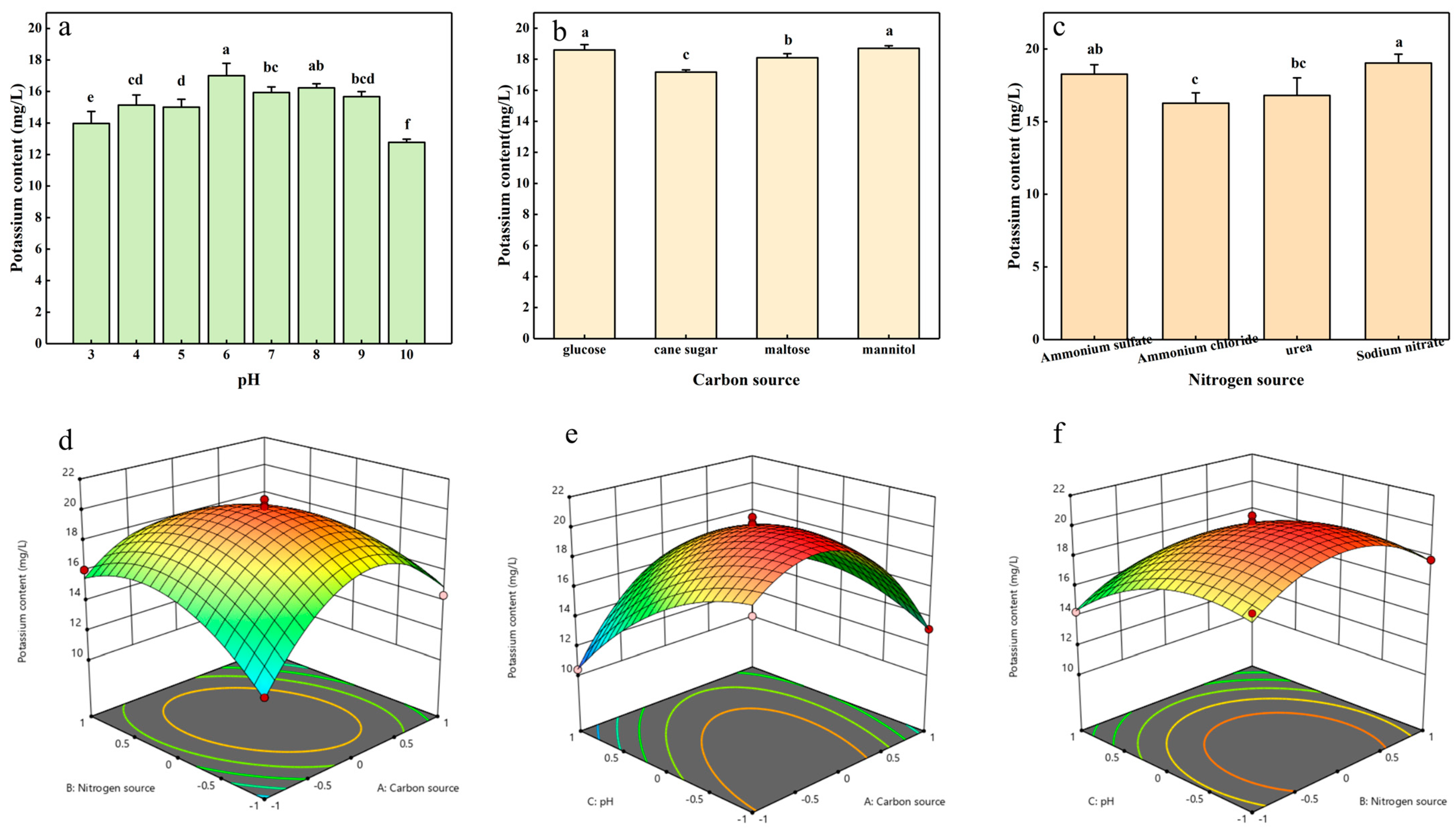
2.2. Optimization of Potassium-Solubilizing Conditions of Strain ZHS-1
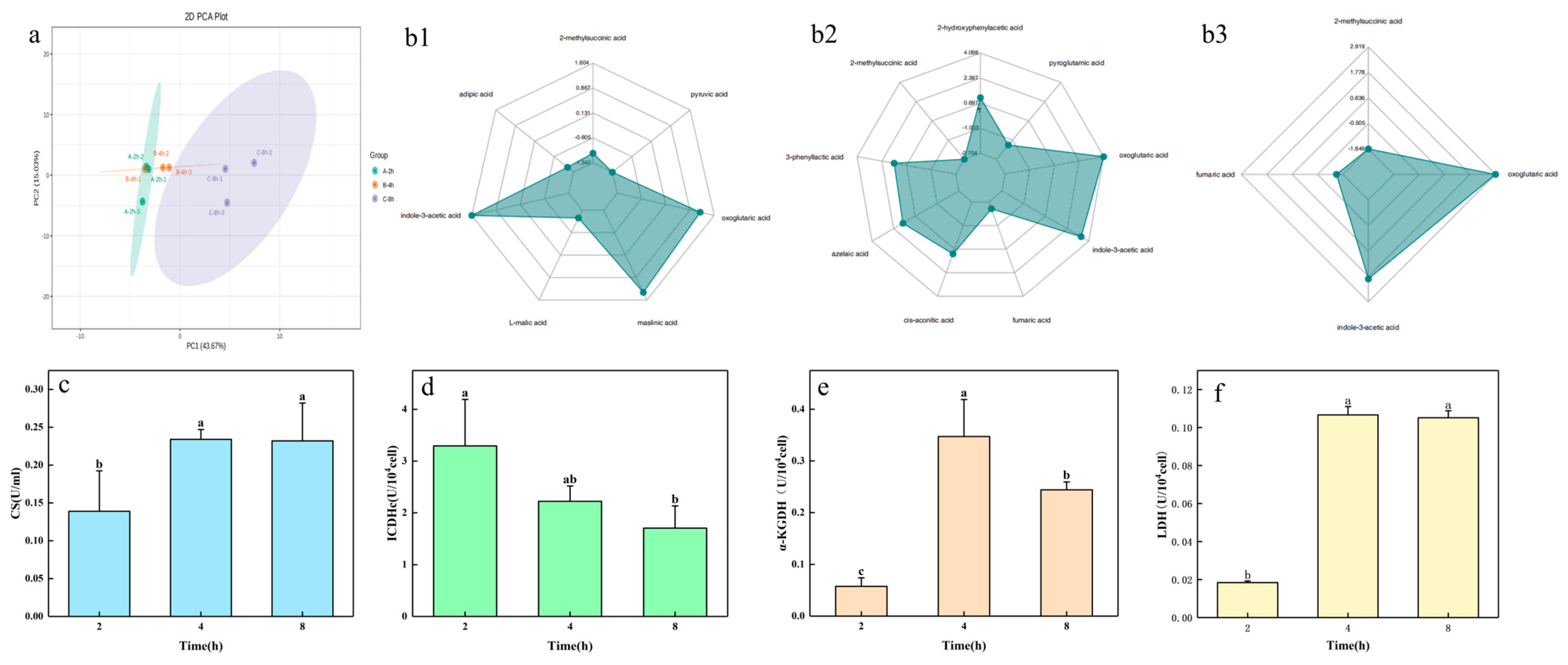
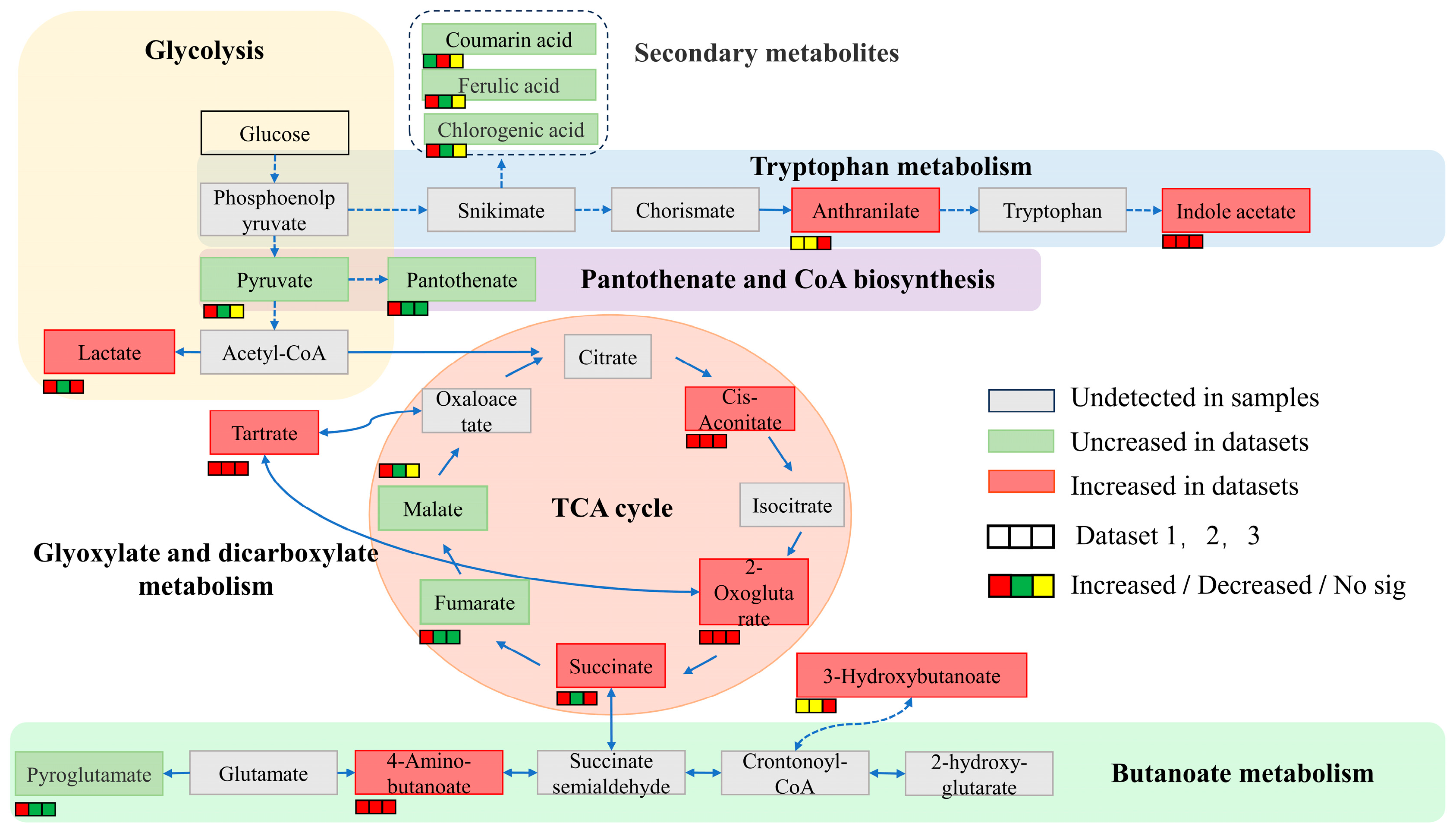
2.3. Changes in Organic Acid Content and Key Enzyme Activity in the Process of Potassium
2.4. Growth-Promoting Effect of ZHS-1 on Rice Plants
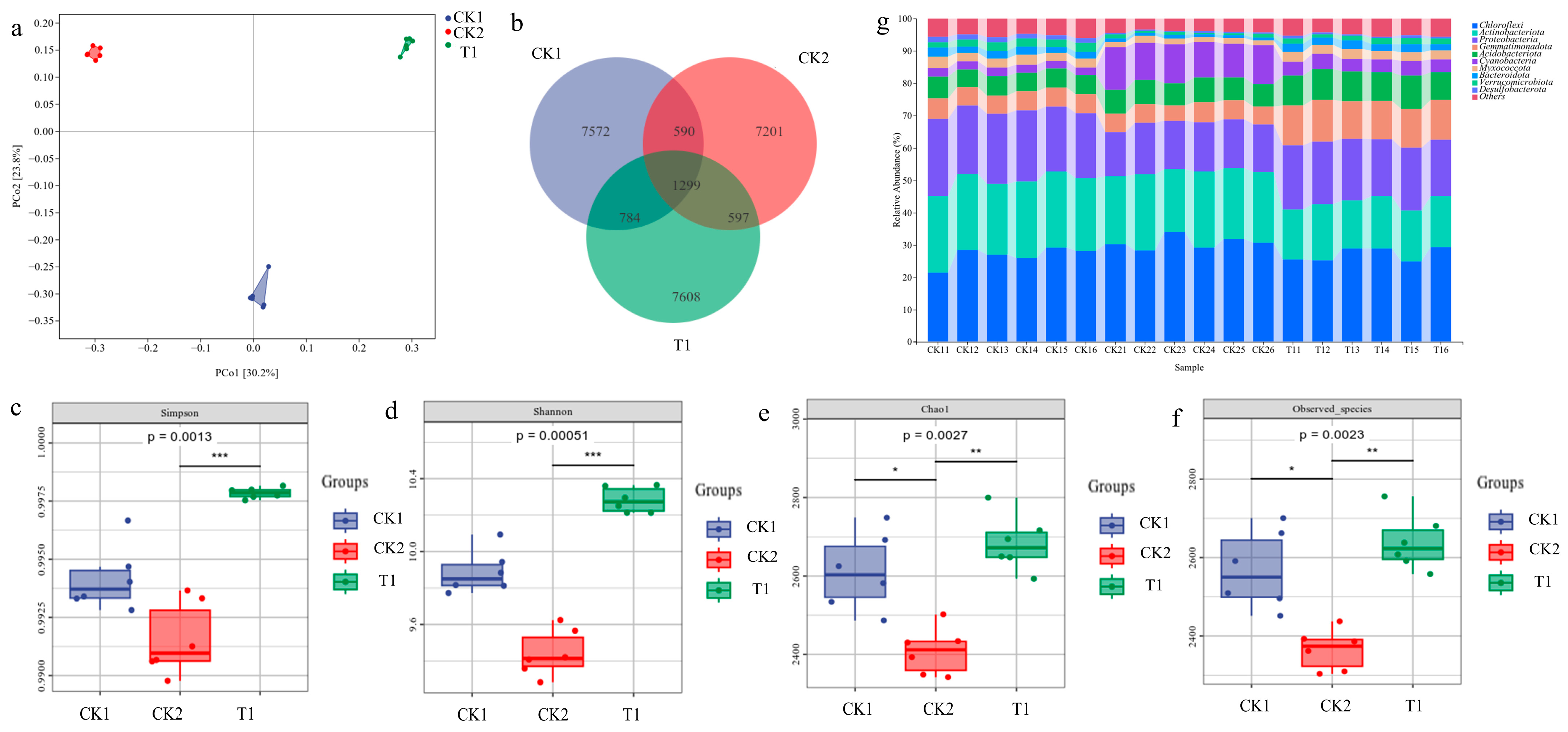
2.5. Changes in the Microbial Community in Rice Rhizosphere Soil
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Soil Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation and Identification of KSB
4.3. Determination of the Multifunctional Ability of KSB
4.3.1. Determination of Potassium Dissolving Capacity
4.3.2. Determination of Phosphate-Solubilizing Capacity
4.3.3. Determination of Indoleacetic Acid Yield
4.4. Response Surface Optimization of Potassium-Solubilizing Bacteria
4.5. Organic Acid Metabolomics Analysis
LC-MS/MS Detection of Organic Acids
4.6. Determination of Key Enzyme Activity in the Process of Organic Acid Production
4.7. Study on the Growth-Promoting Effect of KSB on Rice
4.7.1. Cultivation and Sampling of Rice PLANTS
4.7.2. Sequencing of Soil Microbial Diversity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabiei, B.; Bahador, S.; Kordrostami, M. The expression of monoterpene synthase genes and their respective end products are affected by gibberellic acid in Thymus vulgaris. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 230, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulet, J.M.; Porcel, R.; Yenush, L. Modulation of potassium transport to increase abiotic stress tolerance in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5989–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Lv, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C.; Xu, Q.; Yan, H.; Fu, J.; Liu, X. Differences in Distribution of Potassium-Solubilizing Bacteria in Forest and Plantation Soils in Myanmar. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, D.; Manning, D.A.; Allanore, A. Historical and technical developments of potassium resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, P.; Wani, M.R.; Azooz, M.M.; Tran, L.S.P. Improvement of Crops in the Era of Climatic Changes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Andrade, L.A.; Santos, C.H.B.; Frezarin, E.T.; Sales, L.R.; Rigobelo, E.C. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Agricultural Production. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Pirdashti, H.; Lendeh, K.S. Phosphate and potassium-solubilizing bacteria effect on the growth of rice. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Rahimian, H.; Pirdashti, H.; Nematzadeh, G.A. Evaluation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on the growth and grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cropped in northern Iran. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.; Thangavelu, M. Isolation and screening of potassium solubilizing bacteria from saxicolous habitat and their impact on tomato growth in different soil types. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3147–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Su, Y. Invasive Chloroplast Population Genetics of Mikania micrantha in China: No Local Adaptation and Negative Correlation between Diversity and Geographic Distance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.S.; Maurya, B.R.; Verma, J.P.; Aeron, A.; Kumar, A.; Kim, K.; Bajpai, V.K. Potassium solubilizing rhizobacteria (KSR): Isolation, identification, and K-release dynamics from waste mica. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Maurya, B.R.; Meena, V.S.; Bahadur, I.; Kumar, A. Identification and characterization of potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) from Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraja, R.; Muthukumar, T. Co-inoculation of halotolerant potassium solubilizing Bacillus licheniformis and Aspergillus violaceofuscus improves tomato growth and potassium uptake in different soil types under salinity. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Shen, Z.; Ye, J. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Potassium-Solubilizing Mechanism of Bacillus aryabhattai SK1-7. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 722379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiana, D.; Janet, L.; Cheryl, L.P.; David, R.; Bernard, R.G. Indole-3-acetic acid in plant-microbe interactions. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 85–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbendieck, R.M.; Straight, P.D. Multifaceted Interfaces of Bacterial Competition. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Gu, J.; Zhen, L.; Lv, R.; Chang, F.; Jia, F. Influences of potassium solubilizing bacteria and K-feldspar on enzyme activities and metabolic activities of the bacterial communities in kiwifruit planting soil. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayansina Segun, A.; Olubukola Oluranti, B.; Oluwole Samuel, A. Bioflocculant production and heavy metal sorption by metal resistant bacterial isolates from gold mining soil. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Kaur, T.; Yadav, N.R.; Halder, S.K.; Yadav, A.N.; Sachan, S.G.; Saxena, A.K. Potassium solubilizing and mobilizing microbes: Biodiversity, mechanisms of solubilization, and biotechnological implication for alleviations of abiotic stress. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luziatelli, F.; Ficca, A.G.; Cardarelli, M.T.; Melini, F.; Cavalieri, A.; Ruzzi, M. Genome Sequencing of Pantoea agglomerans C1 Provides Insights into Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Plant Growth-Promotion and Tolerance to Heavy Metals. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Mackiewicz, B.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Golec, M.; Milanowski, J. Pantoea agglomerans: A mysterious bacterium of evil and good. Part IV. Beneficial effects. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2016, 23, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.; Yasmin, S.; Yahya, M.; Breitkreuz, C.; Tarkka, M.; Reitz, T. The wheat growth-promoting traits of Ochrobactrum and Pantoea species, responsible for solubilization of different P sources, are ensured by genes encoding enzymes of multiple P-releasing pathways. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Rahimian, H.; Pirdashti, H.; Nematzadeh, G.A. Phosphate solubilization potential and modeling of stress tolerance of rhizobacteria from rice paddy soil in northern Iran. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Huang, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, D.; Hu, H.; Ye, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H. Variation of Potassium-Solubilizing Bacteria in Red Soil under Long-term Fertilization and Its Driving Factors. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Meena, M.C.; Das, T.K.; Sepat, S.; Verma, R.K. System productivity and economics influenced by residue and potassium management in maize (Zea mays)-wheat (Triticum aestivum) rotation. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 90, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ranea-Robles, P.; Houten, S.M. The biochemistry and physiology of long-chain dicarboxylic acid metabolism. Biochem. J. 2023, 480, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fait, A.; Fromm, H.; Walter, D.; Galili, G.; Fernie, A.R. Highway or byway: The metabolic role of the GABA shunt in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luziatelli, F.; Ficca, A.G.; Bonini, P.; Muleo, R.; Gatti, L.; Meneghini, M.; Tronati, M.; Melini, F.; Ruzzi, M. A Genetic and Metabolomic Perspective on the Production of Indole-3-Acetic Acid by Pantoea agglomerans and Use of Their Metabolites as Biostimulants in Plant Nurseries. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Yu, X.; Ye, Z. Biosynthetic Pathways and Functions of Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraby, E.J.; Agisha, V.N.; Dhandapani, S.; Sng, Y.H.; Lim, S.H.; Naqvi, N.I.; Sarojam, R.; Yin, Z.; Park, B.S. Plant growth promotion under phosphate deficiency and improved phosphate acquisition by new fungal strain, Penicillium olsonii TLL1. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1285574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. The critical role of potassium in plant stress response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7370–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadam Khani, A.; Enayatizamir, N.; Norouzi Masir, M. Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on different forms of soil potassium under wheat cultivation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Jiang, X.; Tian, C.; Cao, F.; Li, J. Effects of Bradyrhizobium Co-Inoculated with Bacillus and Paenibacillus on the Structure and Functional Genes of Soybean Rhizobacteria Community. Genes 2022, 13, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El, S., II; Abdel-Megeed, A. Impact of rock materials and biofertilizations on P and K availability for maize (Zea maize) under calcareous soil conditions. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Nachimuthu, G.; Mason, S.; McLaughlin, M.J.; McNeill, A.; Bell, M.J. Comparison of soil analytical methods for estimating wheat potassium fertilizer requirements in response to contrasting plant K demand in the glasshouse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, M.; Dai, Z.C.; Hussain, S.; Tariq, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, I.U.; Qi, S.S.; Du, D. The soil pH and heavy metals revealed their impact on soil microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, H.; Feng, Z.; Yan, Z.; Song, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhang, W.; Yao, M.; et al. Integrated organic and inorganic fertilization and reduced irrigation altered prokaryotic microbial community and diversity in different compartments of wheat root zone contributing to improved nitrogen uptake and wheat yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Qiu, C.; Hong, J. Effects of coal-derived compound fertilizers on soil bacterial community structure in coal mining subsidence areas. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1187572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, B.; Yin, Y.; Liang, F.; Xie, D.; Han, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, B.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Impact of biocontrol microbes on soil microbial diversity in ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5537–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieck, E.; Spohn, M.; Wendt, K.; Bock, E.; Shively, J.; Frank, J.; Indenbirken, D.; Alawi, M.; Lücker, S.; Hüpeden, J. Extremophilic nitrite-oxidizing Chloroflexi from Yellowstone hot springs. ISME J. 2020, 14, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, G.R.; Matharu, J.K.; Kumar, D. The Nitrogen Fixation Capability of Cyanobacteria–A Natural Source as a Bio–Fertilizer ForArachis Hypogaea. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2011, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.U.; Jie, C.; Guangwei, Z.; Boqiang, Q.; Yunlin, Z. Effect of concentrations of phosphorus and nitrogen on the dominance of Cyanobacteria. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth. Plants 2024, 13, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141945
Tian S, Xu Y, Zhong Y, Qiao Y, Wang D, Wu L, Yang X, Yang M, Wu Z. Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth. Plants. 2024; 13(14):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141945
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Shiqi, Yufeng Xu, Yanglin Zhong, Yaru Qiao, Dongchao Wang, Lei Wu, Xue Yang, Meiying Yang, and Zhihai Wu. 2024. "Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth" Plants 13, no. 14: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141945
APA StyleTian, S., Xu, Y., Zhong, Y., Qiao, Y., Wang, D., Wu, L., Yang, X., Yang, M., & Wu, Z. (2024). Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth. Plants, 13(14), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141945






