Conservation and Divergence of PEPC Gene Family in Different Ploidy Bamboos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of PEPC Members in Bamboos
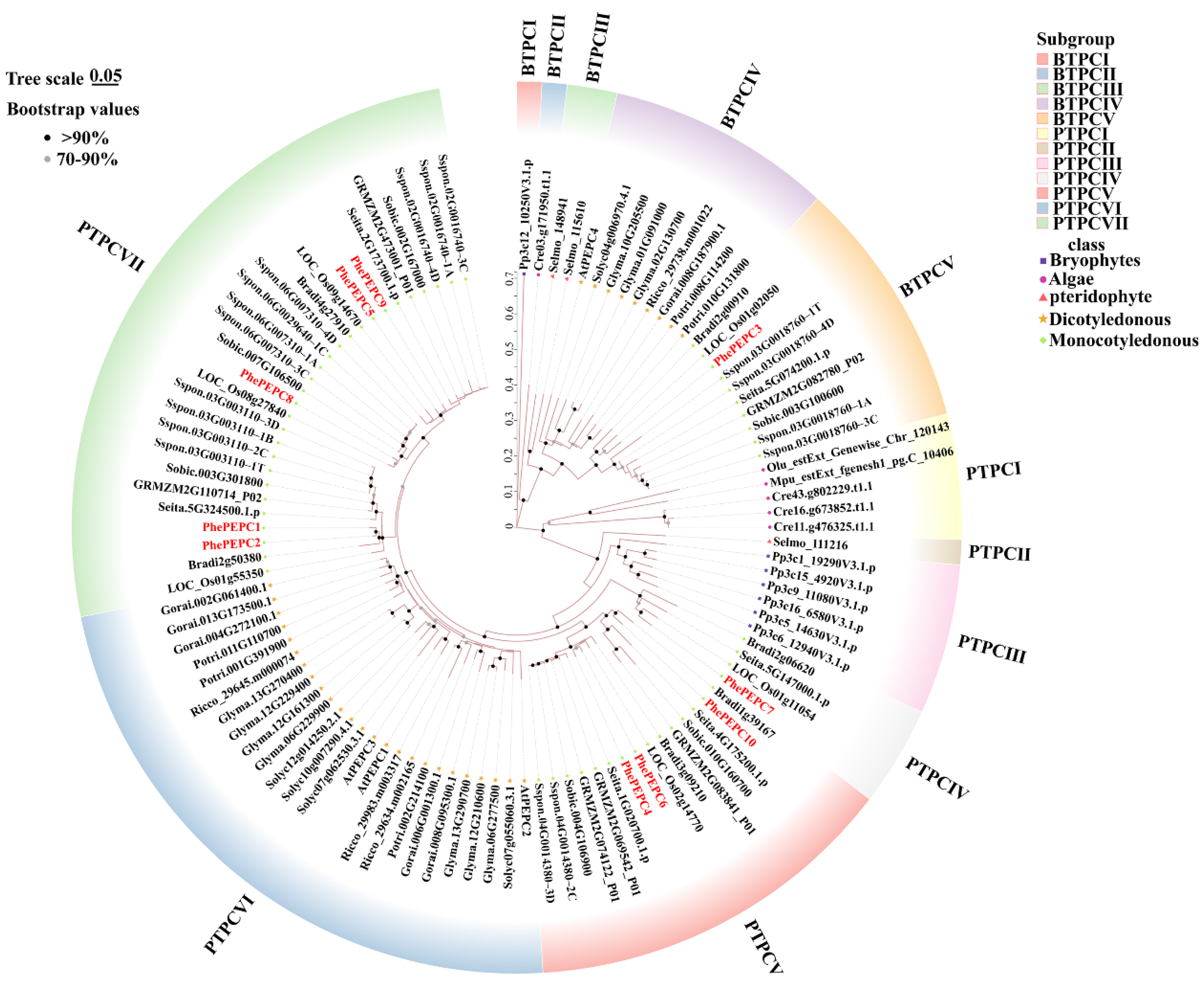
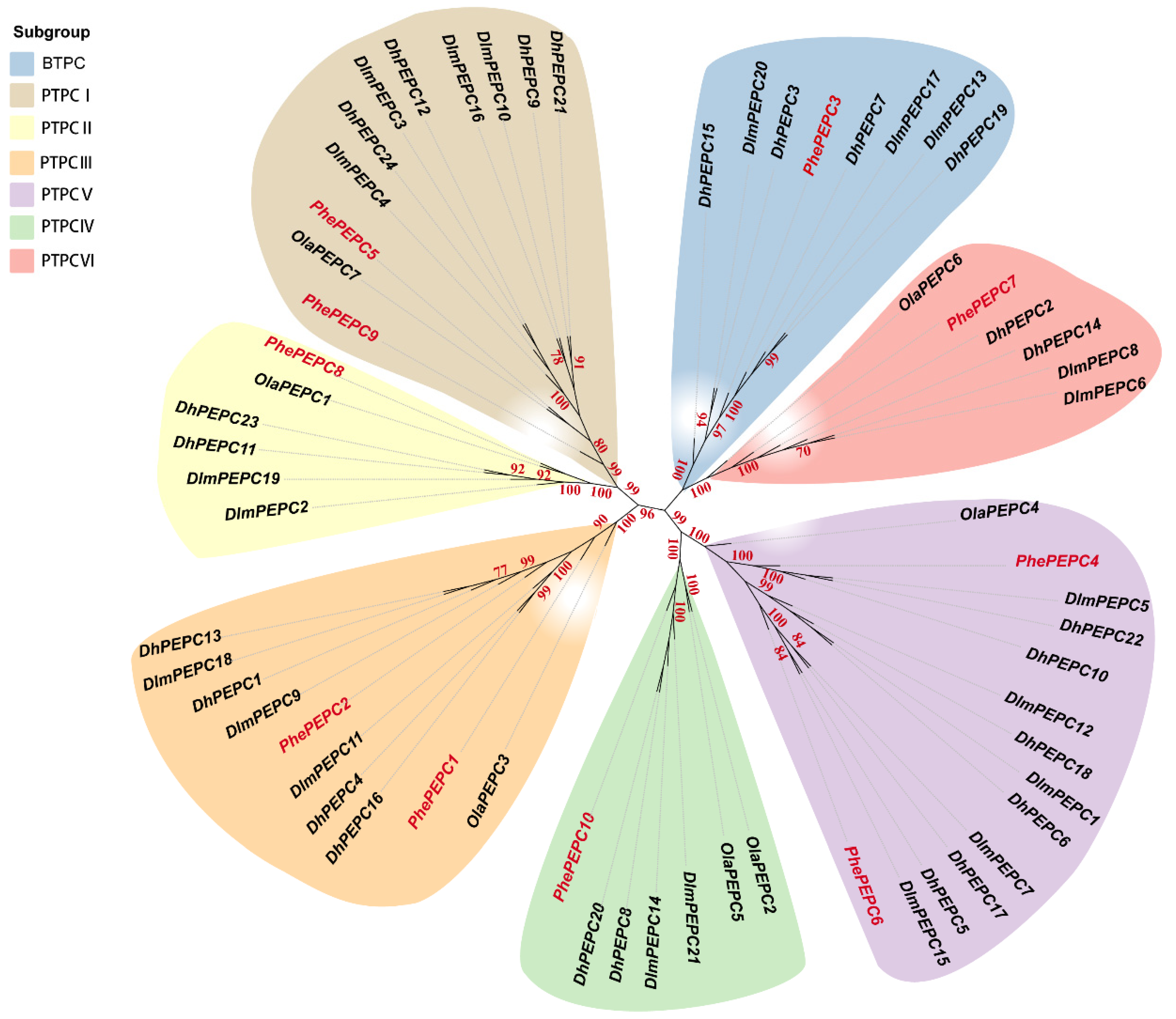
2.2. Evolutionary Analysis of PEPCs Family
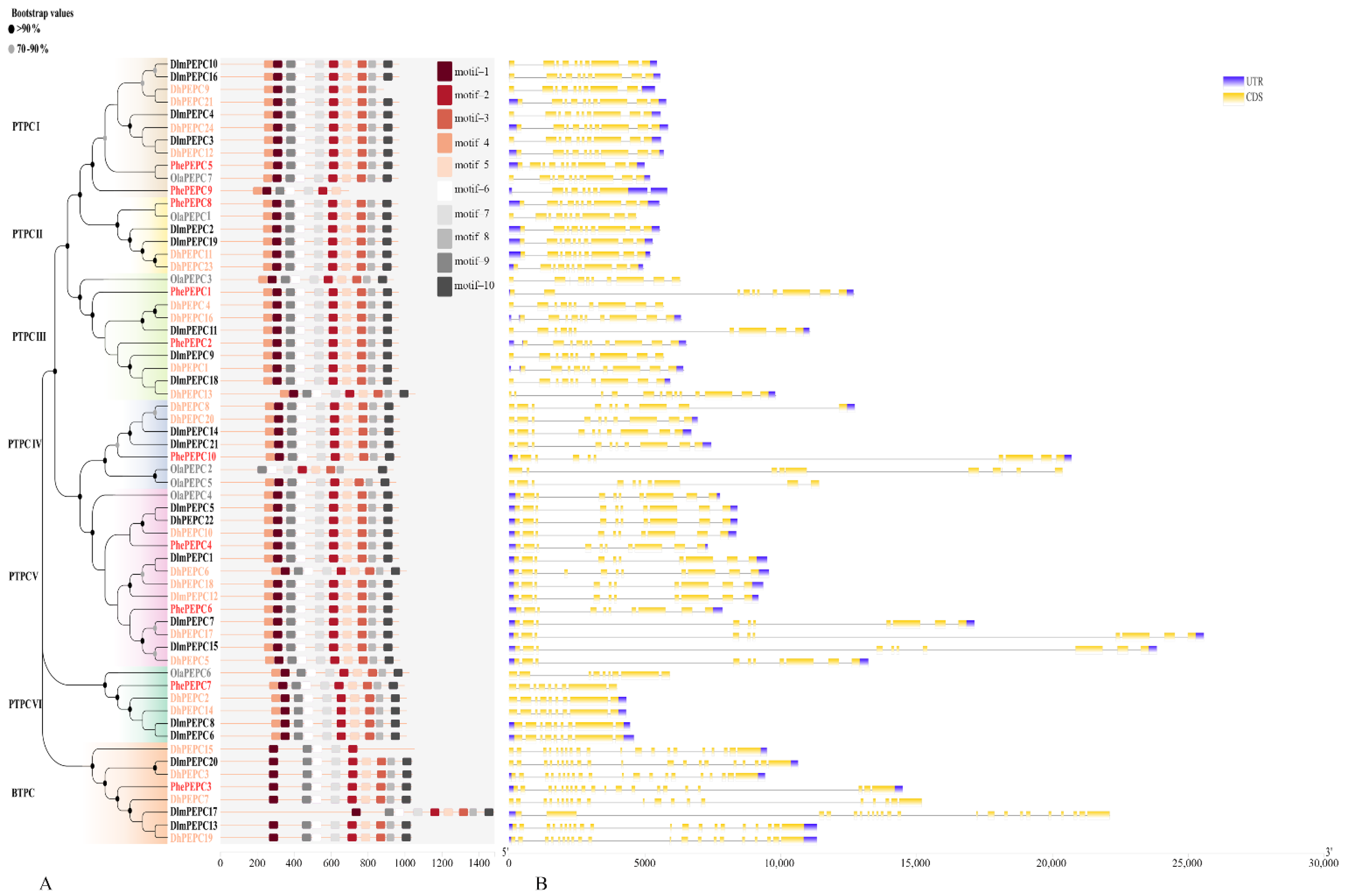
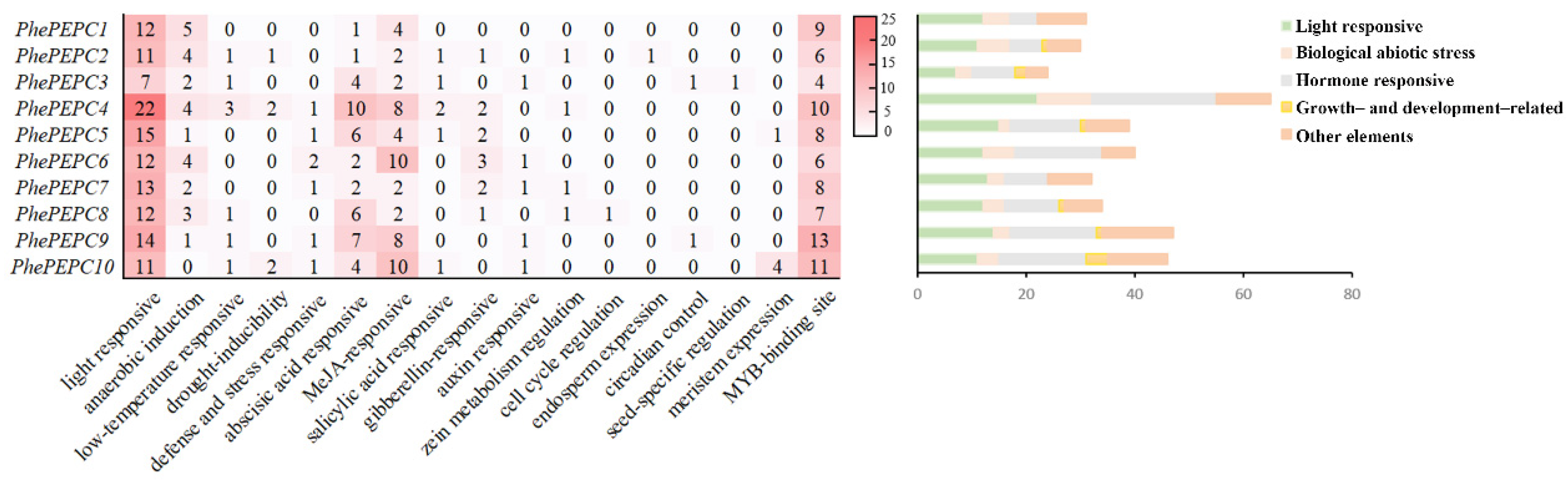
2.3. Analysis of Gene Structure, Conservative Motif and Promoter Cis-Regulatory Element
2.4. Collinearity Analysis and Evolutionary Pressure of PEPC in Bamboo
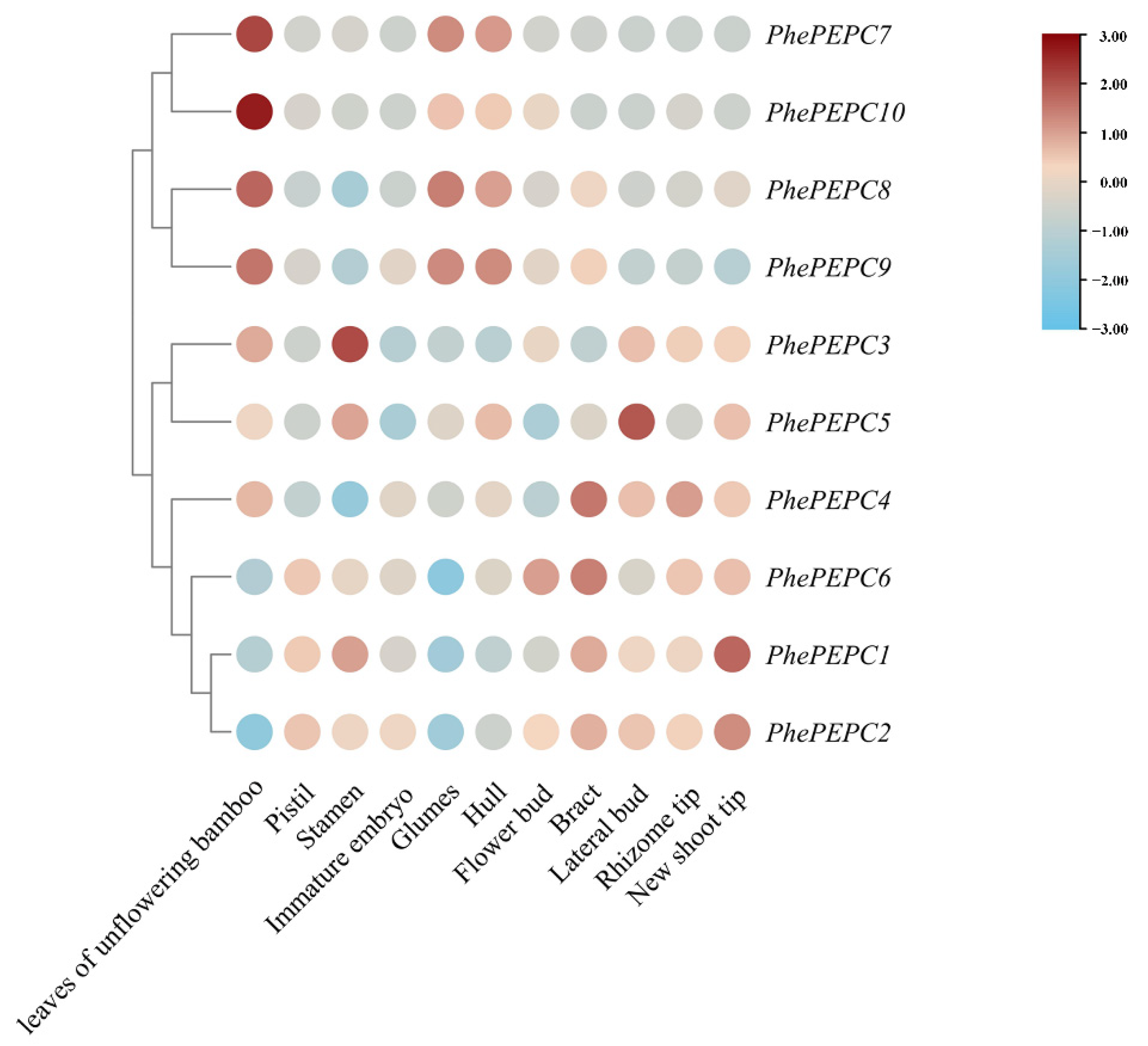
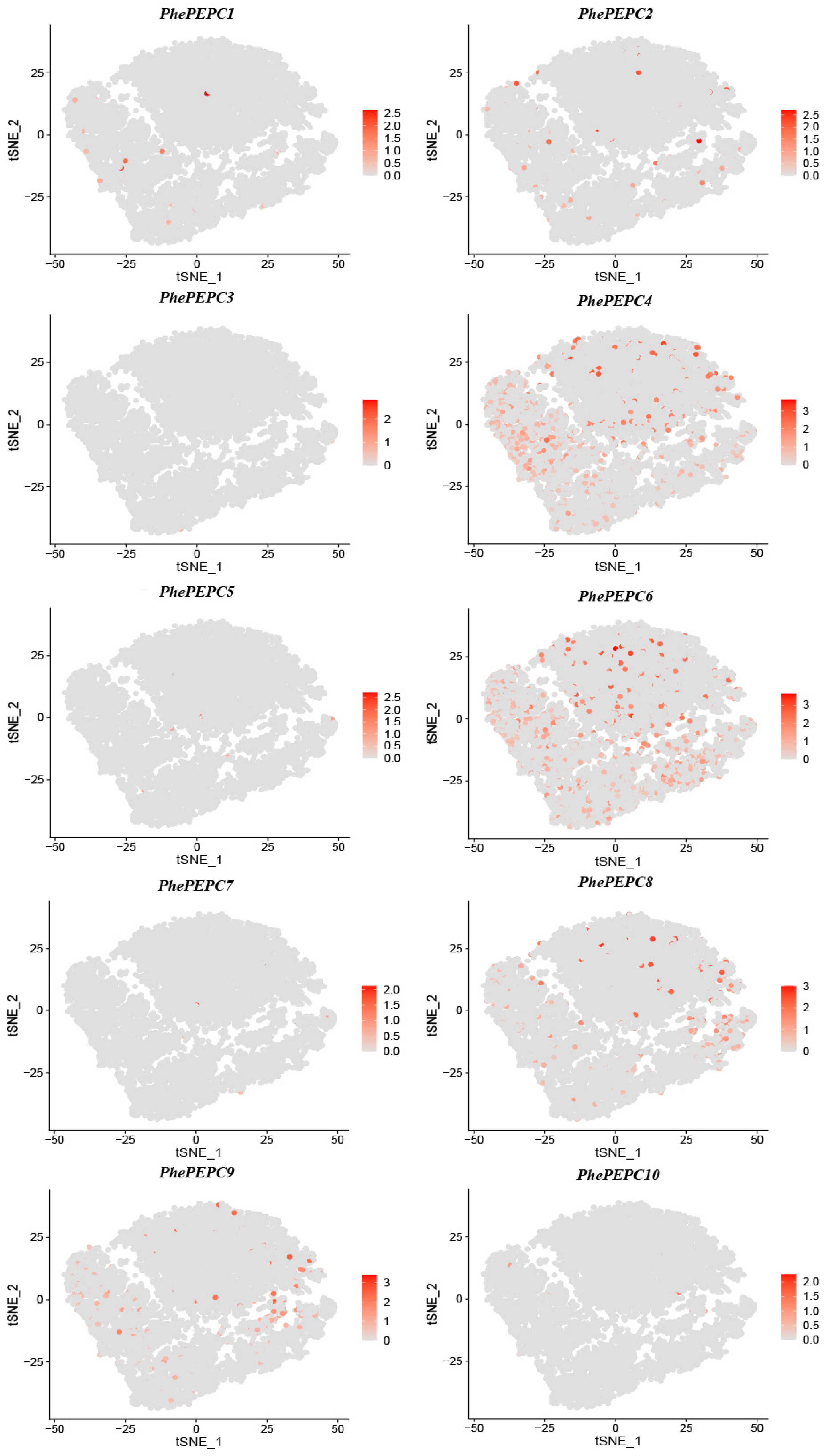
2.5. Expression Patterns of the PEPC Family in P. edulis
2.6. PhePEPCs Responds to the Exogenous GA Treatments
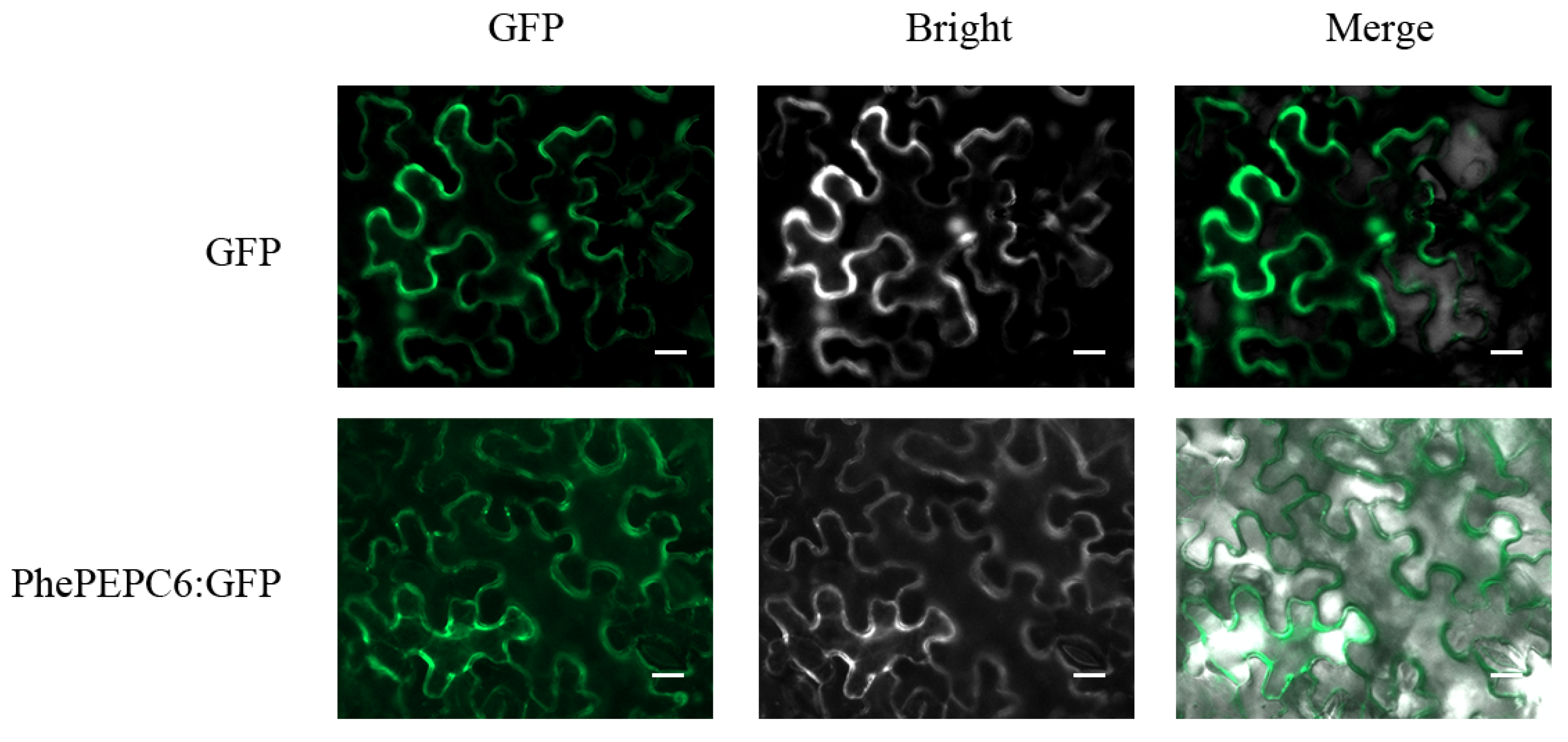
2.7. Subcellular Localizations of PhePEPC Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Characterization of PEPC in P. edulis, O. latifolia, D. latiflorus and D. brandisii
4.2. Evolutionary Analysis and Protein Multi-Sequence Alignment of PEPC in P. edulis, O. latifolia, D. latiflorus and D. brandisii
4.3. Analysis of Gene Structure, Conservative Motif and Promoter Cis-Regulatory Element
4.4. Collinearity Analysis and the Ka/Ks Ratio of P. edulis, O. latifolia, D. latiflorus and D. brandisii PEPC Genes
4.5. Analysis of Gene Expression Patterns
4.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and qRT-PCR
4.7. Subcellular Localization Experiment of PhePEPC Proteins in Moso Bamboo
4.8. Plant Material, Growth Conditions and Treatments
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Engelmann, S.; Blsing, O.; Gowik, U.; Svensson, P.; Westhoff, P. Molecular evolution of C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in the genus Flaveria—A gradual increase from C3 to C4 characteristics. Planta 2003, 217, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izui, K.; Matsumura, H.; Furumoto, T.; Kai, Y. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: A new era of structural biology. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masumoto, C.; Miyazawa, S.; Ohkawa, H.; Fukuda, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Murayama, S.; Kusano, M.; Saito, K.; Fukayama, H.; Miyao, M. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase intrinsically located in the chloroplast of rice plays a crucial role in ammonium assimilation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5226–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lang, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, R. Antisense PEP gene regulates to ratio of protein and lipid content in Brassica napus seeds. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 1999, 7, 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Blonde, J.; Plaxton, W. Structural and kinetic properties of high and low molecular mass phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase isoforms from the endosperm developing castor oilseeds. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11867–11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Echevarría, C.; Vidal, J.; Cejudo, F. Isolation and characterization of a wheat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene. Modelling of the encoded protein. Plant Sci. 2002, 162, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, H. The regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in CAM plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, B.; Park, J.; Plaxton, W. The remarkable diversity of plant PEPC (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase): Recent insights into the physiological functions and post-translational controls of non-photosynthetic PEPCs. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, A.; Baroli, I.; Badger, M.; Ivakov, A.; Lea, P.; Leegood, R.; von Caemmerer, S. The role of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase during during C4 photosynthetic isotope exchange and stomatal conductance. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysková, V.; Miedzinska, L.; Dobrá, J.; Vankova, R.; Ryslavá, H. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, NADP-malic enzyme, and pyruvate, phosphate dikinase are involved in the acclimation of Nicotiana tabacum L. to drought stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, L.; Lan, H. Cloning of PEPC-1 from a C4 halophyte Suaeda aralocaspica without Kranz anatomy and its recombinant enzymatic activity in responses to abiotic stresses. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 83, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, Y. Functions of plant Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and its applications for genetic engineering. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, R.; Cejudo, F. Identification and expression analysis of a gene encoding a bacterial-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, G.; Pinçon, G.; D’Hont, A.; Hoarau, J.; Cadet, F.; Offmann, B. Characterisation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene family in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Masuda, T.; Kawamura, T.; Hata, S.; Izui, K. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a root-form phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Zea mays: Comparison with the C4-form enzyme. Plant Cell Physiol. 1998, 39, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S. Bioinformatics Analysis of PEPC Gene Family in Pineapple. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2020, 41, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- González, M.; Sánchez, R.; Cejudo, F. Abiotic stresses affecting water balance induce phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase expression in roots of wheat seedlings. Planta 2003, 216, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhong, X.; Cong, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gai, J. Genome-wide Analysis of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase Gene Family and Their Response to Abiotic Stresses in Soybean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Gan, L.; Feng, L.; Yuan, L.; Yin, L. Bioinformatics Analysis of PEPC Gene Family in Arachis duranensis. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2018, 26, 107–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Yang, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of PEPC Gene Family in Durian (Durio zibethinus Murr.). Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 20, 76–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liese, W. Bamboo and rattan in the world. J. Bamboo Ratt. 2003, 2, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Evolutionary history of PEPC genes in green plants: Implications for the evolution of CAM in orchids. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2016, 94, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chi, W.; Jing, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, N. Molecular cloning of C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene from sorghum and cultivation of transgenic rice. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Cloning of Key Enzyme Genes (PPDK, NADP-ME) in Maize C4 Pathway and Expression Analysis of PPDK and PEPC in Arabidopsis. Ph.D. Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boxall, S.; Nirja, K.; Dever, L.; Kneová, J.; Waller, J.; Gould, P.; Hartwell, J. Kalancho PPC1 Is Essential for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism and the Regulation of Core Circadian Clock and Guard Cell Signaling Genes. Plant Cell 2020, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, B.; Fedosejevs, E.; Hill, A.; Bettridge, J.; Park, J.; Rao, S.; Leach, C.; Plaxton, W. Tissue-specific expression and post-translational modifications of plant- and bacterial-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase isozymes of the castor oil plant, Ricinus communis L. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5485–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, J.; Gandullo, J.; De, la.; Osa, C.; Feria, A.; Echevarría, C.; Monreal, J.; García-Mauriño, S. Responses to aluminum and cadmium of a RNAi sorghum line with decreased levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase 3 (PPC3). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 205, 105139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Osa, C.; Pérez-López, J.; Feria, A.; Baena, G.; Marino, D.; Coleto, I.; Pérez-Montaño, F.; Gandullo, J.; Echevarría, C.; García-Mauriño, S. Knock-down of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase 3 negatively impacts growth, productivity, and responses to salt stress in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Plant J. 2022, 111, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Ahmad, F. The phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene family identification and expression analysis under abiotic and phytohormone stresses in Solanum lycopersicum L. Gene 2019, 690, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Dai, C.; Zhou, J.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase regulation in C4-PEPC-expressing transgenic rice during early responses to drought stress. Physiol. Plant 2017, 159, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z. Progress in Bamboo Genomics Research. For. Sci. 2012, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, G. Estimation of CO2 fluxes and its seasonal variations from the effective management lei bamboo (Phyllostachys violascens). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 3434–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wen, G.; Wang, H. Change Rule of Carbon Flux and Shoots High Growth of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) during Its Fast Growth Stage. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2016, 44, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R. Changes of photosynthetic pigment and photosynthetic enzyme activity in stems of Phyllostachys pubescens during rapid growth stage after shooting. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 36, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wen, G.; Gao, R.; Zhang, R. Correlation between pigment content and reflectance spectrum of Phyllostachys pubescens stems during its rapid growth stage. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Lin, S.; Wang, S. Contents of Phosphoenolpyruvate Caboxylase (PEPC) in Bamboo Plants. J. West China For. Sci. 2015, 44, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppe, H.; Turpin, D. Integration of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in plant and algal cells. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 45, 577–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. The research progress of plant phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Territ. Nat. Resour. Study 2017, 5, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Bai, Q.; Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Gao, J. The association of hormone signalling genes, transcription and changes in shoot anatomy during Moso bamboo growth. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Mu, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Cai, M.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Fang, H.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, F. Single-cell transcriptome atlas reveals spatiotemporal developmental trajectories in the basal roots of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Yi, K.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y. Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase in Arabidopsis Leaves Plays a Crucial Role in Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ballesta, I.; Baena, G.; Gandullo, J.; Wang, L.; She, Y.M.; Plaxton, W.C.; Echevarría, C. New insights into the post-translational modification of multiple phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase isoenzymes by phosphorylation and monoubiquitylation during sorghum seed development and germination. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3523–35536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, R.; Flores, A.; Cejudo, F. Arabidopsis phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase genes encode immunologically unrelated polypeptides and are differentially expressed in response to drought and salt stress. Planta 2006, 223, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Ren, C.; Dai, C. Enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic rice over-expressing of maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene via NO and Ca2+. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 175, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Dai, C.; Zhou, J.; Yan, T.; Zhang, J. Improved short-term drought response of transgenic rice over-expressing maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase via calcium signal cascade. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 218, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Zhao, M.; Hu, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, H.; Li, Y. Physiological characteristics and metabolomics of transgenic wheat containing the maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene under high temperature stress. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Moalem, S.; Maali-Amiri, R.; Kazemi-Shahandashti, S. Effect of cold stress on oxidative damage and mitochondrial respiratory properties in chickpea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Fei, B.; Chen, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Chromosome-level reference genome and alternative splicing atlas of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Giga Sci. 2018, 7, giy115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennidakis, S.; Rao, S.; Greenham, K.; Uhrig, R.; O’Leary, B.; Snedden, W.; Lu, C.; Plaxton, W. Bacterial- and plant-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase polypeptides interact in the hetero-oligomeric Class-2 PEPC complex of developing castor oil seeds. Plant J. 2007, 52, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.; Hurley, B.; Tran, H.; Valentine, A.; She, Y.; Knowles, V.; Plaxton, W. In vivo regulatory phosphorylation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase AtPPC1 in phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, J.; Plaxton, W. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase protein kinase from developing castor oil seeds: Partial purification, characterization, and reversible control by photosynthate supply. Planta 2007, 226, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.; Garcia-Hernandez, M. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ma, P.; Yang, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xia, E.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, L.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y. Genome Sequences Provide Insights into the Reticulate Origin and Unique Traits of Woody Bamboos. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.; Eddy, S.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.; Potter, S.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A. The Pfam protein family’s database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.; Gonzales, N.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.; Geer, R.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11 Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree displays and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene features visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.; Frank, M.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van, de.; Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Gao, Z.; Lu, H.; Hu, T.; Yao, N.; Liu, K. The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.; Rinn, J.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ma, J.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, M. Selection of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR in Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.; Xu, J.; Mu, C.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, J. Conservation and Divergence of PEPC Gene Family in Different Ploidy Bamboos. Plants 2024, 13, 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172426
Cheng W, Xu J, Mu C, Jiang J, Cheng Z, Gao J. Conservation and Divergence of PEPC Gene Family in Different Ploidy Bamboos. Plants. 2024; 13(17):2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172426
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wenlong, Junlei Xu, Changhong Mu, Jutang Jiang, Zhanchao Cheng, and Jian Gao. 2024. "Conservation and Divergence of PEPC Gene Family in Different Ploidy Bamboos" Plants 13, no. 17: 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172426
APA StyleCheng, W., Xu, J., Mu, C., Jiang, J., Cheng, Z., & Gao, J. (2024). Conservation and Divergence of PEPC Gene Family in Different Ploidy Bamboos. Plants, 13(17), 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172426




