Essential Oil Composition and Anti-Cholinesterase Properties of Cryptomeria japonica Foliage Harvested in São Miguel Island (Azores) in Two Different Seasons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
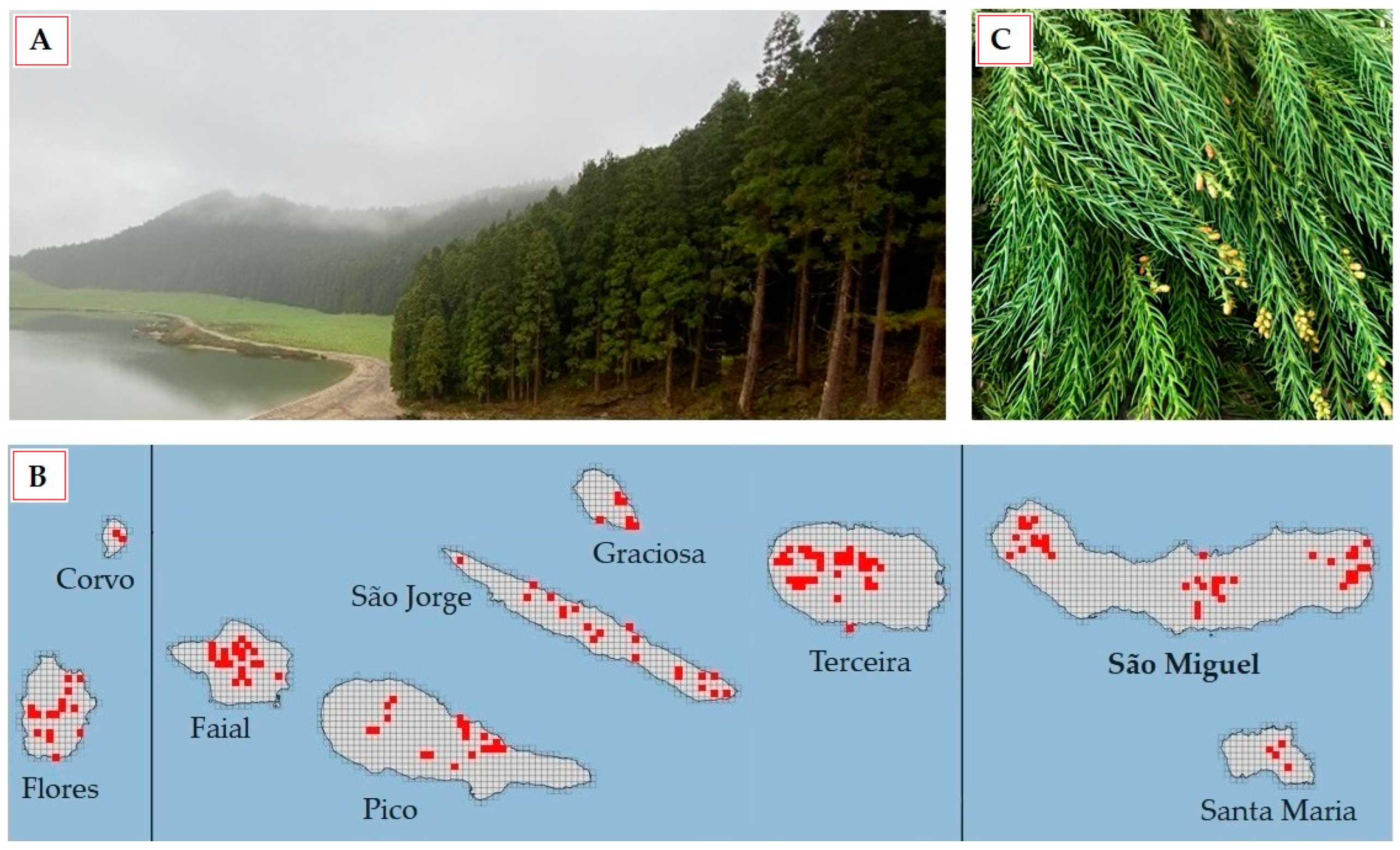
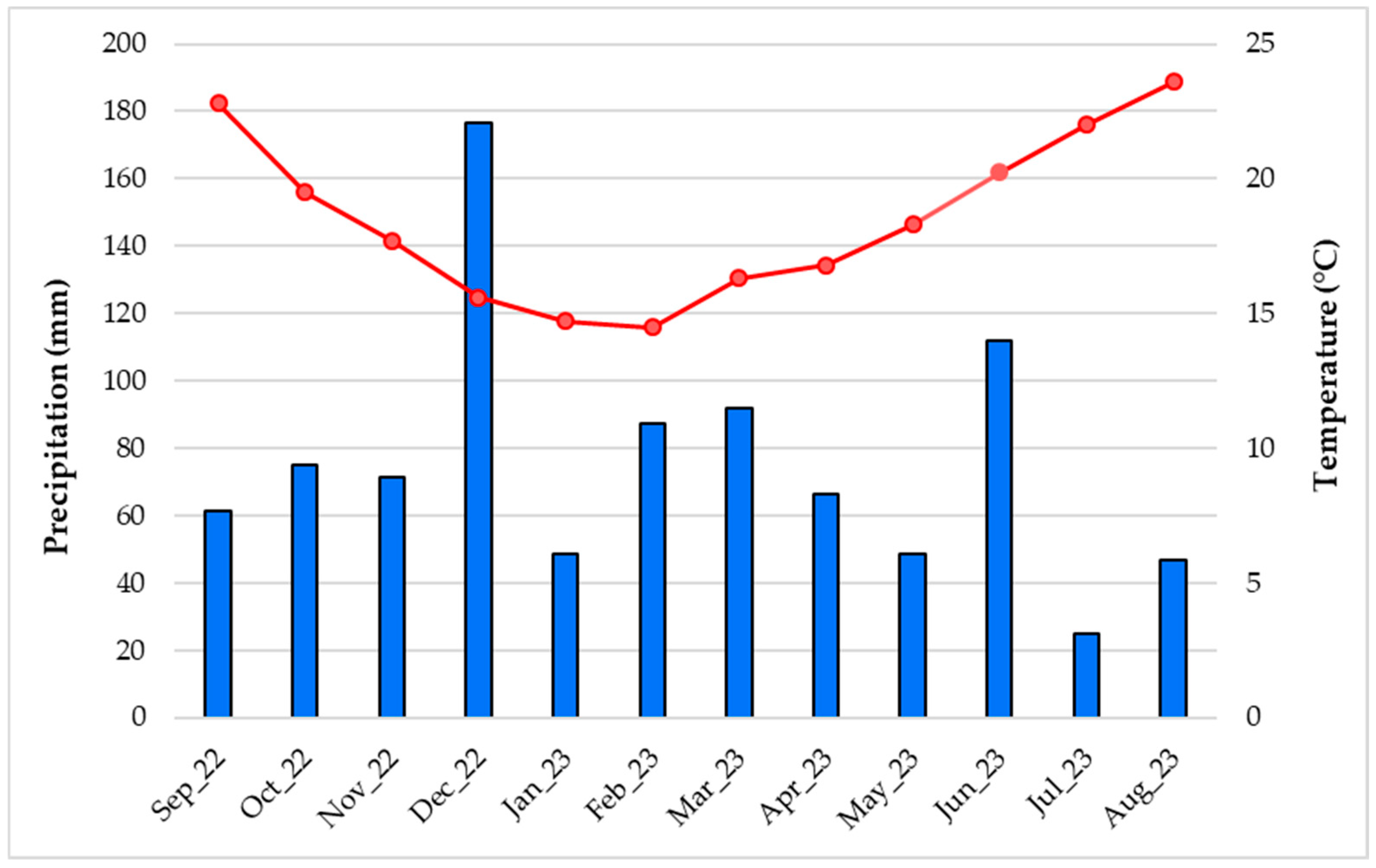
2.2. Study Area and Climatic Conditions of Season Collecting Samples
2.3. Collection and Preparation of C. japonica Foliage Samples
2.4. Extraction of Essential Oils via Hydrodistillation Process
2.5. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis of Essential Oils
2.6. Brine Shrimp Lethality Activity (BSLA) Assay
2.7. In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield, Density, Color, and Odor of Essential Oils from Azorean C. japonica Foliage Harvested in Autumn and Spring
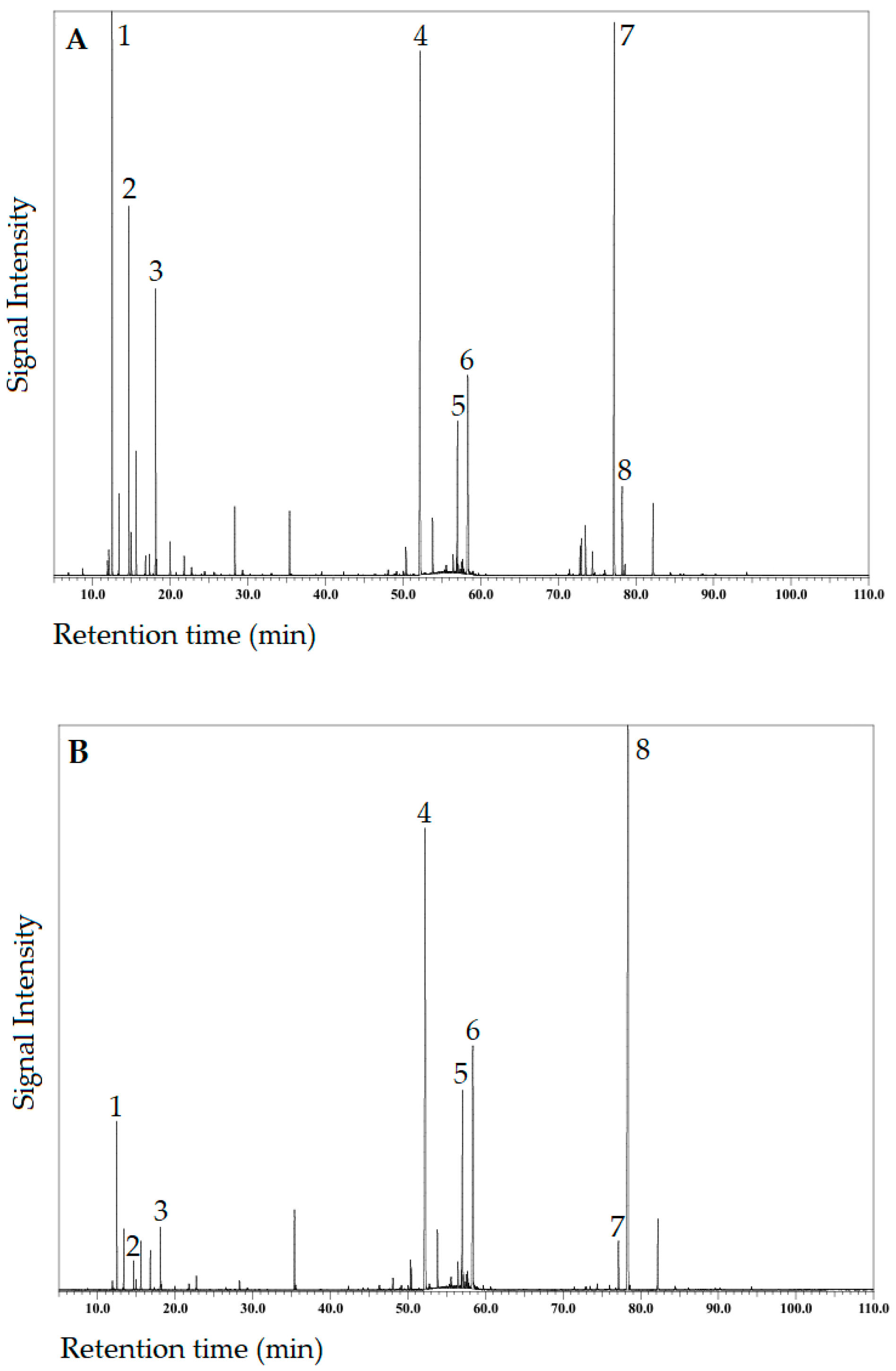
3.2. Chemical Composition of Essential Oils from Azorean C. japonica Foliage Harvested in Autumn and Spring
3.3. Brine Shrimp Lethality Activity (BSLA) of Essential Oils from Azorean C. japonica Foliage Harvested in Autumn and Spring
3.4. In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase Activity of Essential Oils from Azorean C. japonica Foliage Harvested in Autumn and Spring
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rodríguez, S.M.; Ordás, R.J.; Alvarez, J.M. Conifer biotechnology: An overview. Forests 2022, 13, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mageroy, M.H.; Nagy, N.E.; Steffenrem, A.; Krokene, P.; Hietala, A.M. Conifer defences against pathogens and pests: Mechanisms, breeding, and management. Curr. For. Rep. 2023, 9, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.-S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopaczyk, J.; Wargula, J.; Jelonek, T. The variability of terpenes in conifers under developmental and environmental stimuli. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 180, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicandri, E.; Paolacci, A.R.; Osadolor, S.; Sorgonà, A.; Badiani, M.; Ciaffi, M. On the evolution and functional diversity of terpene synthases in the Pinus species: A Review. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celedon, J.M.; Whitehill, J.G.; Madilao, L.L.; Bohlmann, J. Gymnosperm glandular trichomes: Expanded dimensions of the conifer terpenoid defense system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmkshatriya, P.P.; Brahmkshatriya, P.S. Terpenes: Chemistry, biological role, and therapeutic applications. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes, 1st ed.; Ramawat, K.G., Mèrillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 2665–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Ninkuu, V.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Fu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zeng, H. Biochemistry of terpenes and recent advances in plant protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetali, S.D. Terpenes and isoprenoids: A wealth of compounds for global use. Planta 2019, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.; Miyazaki, Y. Trends in research related to “Shinrin-yoku” (taking in the forest atmosphere or forest bathing) in Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushina, Y.; Kuriyama, I. Cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) oils. In Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety, 1st ed.; Preedy, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoo, Y. Development of pollen and female gametophytes in Cryptomeria japonica. Int. J. Plant Dev. Biol. 2007, 1, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Silva, A.S.; Atanassova, M.; Sharma, R.; Nepovimova, E.; Musilek, K.; Sharma, R.; Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Nicoletti, M.; et al. Conifers phytochemicals: A valuable forest with therapeutic potential. Molecules 2021, 26, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Woo, H.; Park, M.-J. Development of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae essential oils from forest waste in South Korea. Plants 2023, 12, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dai, M.; Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Cai, M.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wen, Y. Geographical variation reveals strong genetic differentiation in Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis. Forests 2023, 14, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Ueno, S.; Ihara-Ujino, T. Genome scanning for detecting adaptive genes along environmental gradients in the Japanese conifer, Cryptomeria Japonica. Heredity 2012, 109, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Medeiros, J.; Baptista, J.; Madruga, J.; Lima, E. Variations in essential oil chemical composition and biological activities of Cryptomeria japonica (Thunb. ex Lf) D. Don from different geographical origins: A critical review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Janeiro, A.; Medeiros, J.; Baptista, J.; Madruga, J.; Lima, E. Biological activities of organic extracts and specialized metabolites from different parts of Cryptomeria japonica (Cupressaceae): A critical review. Phytochemistry 2023, 206, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Janeiro, A.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Lima, E. Essential oils from different parts of Azorean Cryptomeria japonica (Thunb. ex Lf) D. Don (Cupressaceae): Comparison of the yields, chemical compositions, and biological properties. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavão, D.C.; Brunner, D.; Resendes, R.; Jevšenak, J.; Silva, L.B.; Silva, L. Climatic drivers and tree growth in a key production species: The case of Cryptomeria japonica (Thunb. Ex Lf) D. Don in the Azores archipelago. Dendrochronologia 2024, 85, 126204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaria Regional do Ambiente e Ação Climática, Direção Regional do Ambiente e Ação Climática. Relatório do Estado do Ambiente dos Açores. Portal do Estado do Ambiente dos Açores. Available online: https://rea.azores.gov.pt/UltimaEdicao.aspx (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Sociedade Portuguesa de Botânica (2024). Cryptomeria japonica (L.f.) D.Don: Mapa de Distribuição. Flora-On: Flora de Portugal Interactiva. Available online: http://acores.flora-on.pt/#wCryptomeria+japonica (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongnuanchan, P.; Benjakul, S. Essential oils: Extraction, bioactivities, and their uses for food preservation. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, R1231–R1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmir, J.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Sharif, K.M.; Mohamed, A.; Sahena, F.; Jahurul, M.H.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R.; Kumar, A. Review on essential oil extraction from aromatic and medicinal plants: Techniques, performance and economic analysis. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A. Factors affecting chemical variability of essential oils: A review of recent developments. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, F.; Lima, A.; Wortham, T.; Janeiro, A.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Rosa, J.S.; Lima, E. Sequential separation of essential oil components during hydrodistillation of fresh foliage from Azorean Cryptomeria japonica (Cupressaceae): Effects on antibacterial, antifungal, and free radical scavenging activities. Plants 2024, 13, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, C.Y.; Gwak, K.S.; Park, M.J.; Smith, D.; Choi, I.G. Whitening and antioxidant activities of bornyl acetate and nezukol fractionated from Cryptomeria japonica essential oil. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.J.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, T.H.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Cryptomeria japonica essential oil inhibits the growth of drug-resistant skin pathogens and LPS-induced nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.D.; Kim, J.Y. Essential oil from Cryptomeria japonica induces apoptosis in human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells via mitochondrial stress and activation of caspases. Molecules 2012, 17, 3890–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.W.; Lin, C.T.; Chu, F.H.; Chang, S.T.; Wang, S.Y. Neuropharmacological activities of phytoncide released from Cryptomeria japonica. J. Wood Sci. 2009, 55, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Park, B.J.; Kurosumi, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Evaluation of dried-wood odors: Comparison between analytical and sensory data on odors from dried sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) wood. J. Wood Sci. 2009, 55, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, E.; Kawai, S. Gender differences in the psychophysiological effects induced by VOCs emitted from Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica). Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, E.; Ohira, T. Inhalation of Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) wood odor causes psychological relaxation after monotonous work among female participants. Biomed. Res. 2018, 39, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Tanaka, K.; Akiyama, R.; Noro, I.; Nishio, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Matsumura, S.; Matsuda, H. Anti-cholinesterase activity of crude drugs selected from the ingredients of incense sticks and heartwood of Chamaecyparis obtusa. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox-Georgian, D.; Ramadoss, N.; Dona, C.; Basu, C. Therapeutic and medicinal uses of terpenes. In Medicinal Plants: From Farm to Pharmacy, 1st ed.; Joshee, N., Dhekney, S.A., Parajuli, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 333–359. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, I.; Parmar, V.M.; Mandavgane, S.A. Current trends in essential oil (EO) production. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021, 13, 15311–15334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri, P.; Salami, R.; Kouhi, S.; Kordi, M.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Hadian, J.; Astatkie, T. Applications of essential oils and plant extracts in different industries. Molecules 2022, 27, 8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungau, A.F.; Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G.; Vesa, C.M.; Tit, D.M.; Purza, A.L.; Endres, L.M. Emerging insights into the applicability of essential oils in the management of acne vulgaris. Molecules 2023, 28, 6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeiro, A.; Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Wortham, T.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Lima, E. Variations in essential oil biological activities of female cones at different developmental stages from Azorean Cryptomeria japonica (Thunb. ex Lf) D. Don (Cupressaceae). Separations 2024, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Wortham, T.; Janeiro, A.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Lima, E. Chemical compositions and in vitro antioxidant activities of the essential oils of sawdust and resin-rich bark from Azorean Cryptomeria japonica (Cupressaceae). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; Arruda, F.; Wortham, T.; Janeiro, A.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Lima, E. Chemical composition, in vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of sawdust and resin-rich bark essential oils from Azorean Cryptomeria japonica (Cupressaceae). In Proceedings of the 54th International Symposium on Essential Oils (ISEO), Balatonalmádi, Hungary, 8–11 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, E.; Medeiros, J. Terpenes as potential Anti-Alzheimer’s disease agents. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, C.; Kabra, U.D. A comprehensive review of multi-target directed ligands in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 144, 107152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.A.; Pastorinho, M.R.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A.; Sousa, A.C.A. Ecotoxicity of plant extracts and essential oils: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.V.; Freire, P.; Costa, A. Mineral waters characterization in the Azores archipelago (Portugal). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 190, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.D.; Valente, M.A.; Miranda, P.M.A.; Aguiar, A.; Azevedo, E.B.; Tomé, A.R.; Coelho, F. Climate change scenarios in the Azores and Madeira islands. World Resour. Rev. 2004, 16, 473–491. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Available online: www.ipma.pt (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Council of Europe. European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines, in European Pharmacopoeia, 7th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2010; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 7609; Essential Oils: Analysis by Gas Chromatography on Capillary Columns—General Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1985.
- Solis, P.N.; Wright, C.W.; Anderson, M.M.; Gupta, M.P.; Phillipson, J.D. A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia salina (brine shrimp). Planta Med. 1993, 59, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1987, 3, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres Jr, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, H.; Silva, F.V.M. Inhibition of enzymes important for Alzheimer’s disease by antioxidant extracts prepared from 15 New Zealand medicinal trees and bushes. J. R. Soc. N. Z. 2020, 50, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Pei, S.; Yao, L. Odor perception of aromatherapy essential oils with different chemical types: Influence of gender and two cultural characteristics. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 998612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, F.; Rosa, J.S.; Rodrigues, A.; Oliveira, L.; Lima, A.; Barroso, J.G.; Lima, E. Essential oil variability of Azorean Cryptomeria japonica leaves under different distillation methods, Part 1: Color, yield and chemical composition analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiteiro, C.; Esteves, T.; Ramalho, L.; Rojas, R.; Alvarez, S.; Zacchino, S.; Bragança, H. Essential oil characterization of two Azorean Cryptomeria japonica populations and their biological evaluations. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, F.; Lima, A.; Wortham, T.; Janeiro, A.; Rodrigues, T.; Baptista, J.; Rosa, J.S.; Lima, E. Sequential separation of essential oil components during hydrodistillation of Azorean Cryptomeria japonica foliage: Effects on yield, physical properties, and chemical composition. Separations 2023, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.C.; Moiteiro, C.; Rodrigues, M.C.S.; Almeida, A.J. Essential oil composition from Cryptomeria japonica D. Don grown in Azores: Biomass valorization from forest management. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X211038431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allures Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- NIST Chemistry WebBook, Edited by P. J. Linstrom and W. G. Mallard. Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Singh, S.; Chhatwal, H.; Pandey, A. Deciphering the complexity of terpenoid biosynthesis and its multi-level regulatory mechanism in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 3320–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, T.G.; Sahu, L.K.; Gupta, M.; Mir, B.A.; Gajbhiye, T.; Dubey, R.; Clavijo McCormick, A.; Pandey, S.K. Environmental factors affecting monoterpene emissions from terrestrial vegetation. Plants 2023, 12, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A.; Bao, H.; Shrestha, K.L.; Inoue, Y. Evaluation of light dependence of monoterpene emission and its effect on surface ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 104, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyama, T.; Tobita, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Yazaki, K.; Ueno, S.; Saito, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kitao, M.; Izuta, T. Differences in monoterpene emission characteristics after ozone exposure between three clones representing major gene pools of Cryptomeria japonica. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2018, 74, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Amagai, T.; Tani, A. Effects of soil water content and elevated CO2 concentration on the monoterpene emission rate of Cryptomeria japonica. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.N.; Niwa, S.; Mochizuki, T.; Tani, A.; Kusumoto, D.; Utsumi, Y.; Enoki, T.; Hiura, T. Seasonal variation in basal emission rates and composition of mono-and sesquiterpenes emitted from dominant conifers in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasue, M.; Ogiyama, K.; Saito, M. The diterpene hydrocarbons in the leaves of Cryptomeria japonica. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1976, 58, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasue, M.; Ogiyama, K.; Suto, S.; Tsukahara, H.; Miyahara, F.; Ohba, K. Geographical differentiation of natural Cryptomeria stands analyzed by diterpene hydrocarbon constituents of individual trees. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1987, 69, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, R.A.; McCrindle, R.; Overton, K.H. The diterpenes from the leaves of Cryptomeria japonica. Phytochemistry 1970, 9, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.; Wilde, V. Sesqui-, di-, and triterpenoids as chemosystematic markers in extant conifers: A review. Bot. Rev. 2001, 67, 141–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Hu, H.; Wei, G.; Cui, J.; Xu, J. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal differences in terpenoid and flavonoid biosynthesis in Cryptomeria fortune needles across different seasons. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 862746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logarto Parra, A.; Silva Yhebra, R.; Guerra Sardiñas, I.; Iglesias Buela, L. Comparative study of the assay of Artemia salina L. and the estimate of the medium lethal dose (LD50 value) in mice, to determine oral acute toxicity of plant extracts. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azra, M.N.; Noor, M.I.M.; Burlakovs, J.; Abdullah, M.F.; Abd Latif, Z.; Yik Sung, Y. Trends and new developments in Artemia research. Animals 2022, 12, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.R.; Andrade, F.K.; Alves, D.R.; de Morais, S.M.; Vieira, R.S. Anti-acetylcholinesterase and toxicity against Artemia salina of chitosan microparticles loaded with essential oils of Cymbopogon flexuosus, Pelargonium x ssp and Copaifera officinalis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Dos Santos, J.F.; Carvalho, M.T.B.; Picot, L.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Groult, H.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.S.S. Anticancer activity of limonene: A systematic review of target signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4957–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddin, L.B.; Jha, N.K.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Kesari, K.K.; Beiram, R.; Ojha, S. Neuroprotective potential of limonene and limonene containing natural products. Molecules 2021, 26, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, T.C.; Gomes, T.M.; Pinto, B.A.S.; Camara, A.L.; De Andrade, P.A.M. Naturally occurring acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and their potential use for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plant Material | Essential Oil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Odor | Density (g·mL−1) * | Yield (%, v/w) * | ||
| DM | FM | ||||
| Az–CJF Aut | yellow | strong aromatic-fresh smell | 0.90 ± 0.03 a | 1.37 ± 0.19 a | 0.60 ± 0.08 a |
| Az–CJF Spr | 0.91 ± 0.01 a | 1.06 ± 0.07 a | 0.47 ± 0.03 a | ||
| No. | Class | Component | RT | RIL | RIC | Relative Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aut–EO | Spr–EO | ||||||
| 1 | MH | Tricyclene | 12.03 | 921 | 918 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.06 |
| 2 | MH | α-Thujene | 12.18 | 924 | 921 | 0.51 ± 0.13 * | 0.11 ± 0.01 * |
| 3 | MH | α-Pinene | 12.61 | 932 | 929 | 11.22 ± 0.92 * | 6.51 ± 0.67 * |
| 4 | MH | α-Fenchene | 13.41 | 945 | 943 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 5 | MH | Camphene | 13.51 | 946 | 945 | 1.52 ± 0.18 | 1.58 ± 0.34 |
| 6 | MH | Sabinene | 14.80 | 969 | 967 | 8.12 ± 1.57 * | 1.60 ± 0.15 * |
| 7 | MH | β-Pinene | 15.10 | 974 | 973 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.46 ± 0.03 |
| 8 | MH | β-Myrcene | 15.73 | 988 | 984 | 2.43 ± 0.29 * | 1.46 ± 0.20 * |
| 9 | MH | α-Phellandrene | 16.81 | 1002 | 1003 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 10 | MH | δ-3-Carene | 16.95 | 1008 | 1005 | 0.34 ± 0.03 * | 1.02 ± 0.13 * |
| 11 | MH | α-Terpinene | 17.47 | 1014 | 1013 | 0.56 ± 0.22 * | 0.14 ± 0.02 * |
| 12 | MH | p-Cymene | 17.95 | 1020 | 1020 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 13 | MH | Limonene | 18.27 | 1024 | 1025 | 7.43 ± 2.16 * | 2.00 ± 0.30 * |
| 14 | MH | β-Phellandrene | 18.36 | 1025 | 1026 | 0.29 ± 0.04 * | 0.19 ± 0.03 * |
| 15 | MH | γ-Terpinene | 20.14 | 1054 | 1053 | 0.90 ± 0.35 * | 0.20 ± 0.07 * |
| 16 | OM | trans-Sabinene hydrate | 20.92 | 1060 | 1065 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 17 | MH | Terpinolene | 21.96 | 1086 | 1080 | 0.47 ± 0.11 * | 0.22 ± 0.06 * |
| 18 | OM | Linalool | 22.90 | 1095 | 1095 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.09 |
| 19 | OM | cis-Sabinene hydrate | 23.00 | 1097 | 1096 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| 20 | OM | β-Thujone | 24.17 | 1112 | 1113 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | - |
| 21 | OM | cis-p-Menth-2-en-1-ol | 24.61 | 1118 | 1119 | 0.09 ± 0.01 * | 0.02 ± 0.00 * |
| 22 | OM | trans-p-Menth-2-en-1-ol | 25.83 | 1136 | 1137 | 0.08 ± 0.02 * | 0.02 ± 0.00 * |
| 23 | OM | Camphene hydrate | 26.72 | 1145 | 1150 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| 24 | OM | Isoborneol | 27.15 | 1155 | 1155 | - | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 25 | OM | Borneol | 27.88 | 1165 | 1166 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| 26 | OM | Terpinen-4-ol | 28.50 | 1174 | 1175 | 2.01 ± 0.74 * | 0.60 ± 0.09 * |
| 27 | OM | α-Terpineol | 29.49 | 1186 | 1189 | 0.13 ± 0.02 * | 0.09 ± 0.00 * |
| 28 | OM | cis-Piperitol | 29.62 | 1195 | 1191 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | - |
| 29 | OM | trans-Piperitol | 30.45 | 1207 | 1203 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | - |
| 30 | OM | endo-Fenchyl acetate | 31.04 | 1218 | 1212 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 31 | OM | Linalyl acetate | 33.23 | 1253 | 1244 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | - |
| 32 | OM | Bornyl acetate | 35.58 | 1287 | 1278 | 1.58 ± 0.18 * | 2.50 ± 0.16 * |
| 33 | OM | Isobornyl acetate | 35.74 | 1283 | 1280 | 0.02 ± 0.00 * | 0.14 ± 0.01 * |
| 34 | OM | trans-Sabinyl acetate | 35.86 | 1289 | 1282 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | - |
| 35 | OM | Methyl thujate | 37.98 | 1318 | 1313 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 36 | SH | δ-Elemene | 39.00 | 1335 | 1329 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 37 | OM | α-Terpenyl acetate | 39.72 | 1346 | 1340 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| 38 | SH | β-Elemene | 42.54 | 1389 | 1383 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| 39 | SH | β-Caryophyllene | 44.46 | 1417 | 1412 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| 40 | SH | γ-Elemene | 45.08 | 1427 | 1422 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| 41 | SH | trans-β-Farnesene | 46.54 | 1454 | 1446 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 |
| 42 | SH | α-Humulene | 46.71 | 1452 | 1448 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 43 | SH | cis-Muurola-4(14),5-diene | 47.12 | 1465 | 1455 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 44 | SH | 10-β-H-Cadina-1(6),4-diene | 47.74 | 1461 | 1465 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 45 | SH | trans-Cadina-1(6),4-diene | 47.92 | 1475 | 1468 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 46 | SH | Germacrene D | 48.30 | 1484 | 1474 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.09 |
| 47 | SH | β-Selinene | 48.81 | 1489 | 1482 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| 48 | SH | trans-Muurola-4(14),5-diene | 48.97 | 1493 | 1484 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 49 | SH | α-Selinene | 49.20 | 1498 | 1488 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| 50 | SH | α-Muurolene | 49.38 | 1500 | 1491 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| 51 | OS | epi-Cubebol | 49.53 | 1493 | 1493 | - | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| 52 | OS | β-Dihydroagarofuran | 49.78 | 1503 | 1497 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 53 | SH | γ-Cadinene | 50.26 | 1513 | 1505 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| 54 | OS | Cubebol | 50.38 | 1514 | 1507 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 55 | SH | δ-Cadinene | 50.57 | 1514 | 1510 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 1.02 ± 0.05 |
| 56 | SH | Zonarene | 50.85 | 1526 | 1515 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 57 | SH | trans-Cadina-1,4-diene | 51.26 | 1533 | 1521 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 58 | SH | α-Cadinene | 51.67 | 1537 | 1529 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 59 | OS | Elemol | 52.39 | 1548 | 1541 | 16.00 ± 2.25 * | 20.80 ± 1.62 * |
| 60 | SH | Germacrene B | 52.98 | 1559 | 1551 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.04 |
| 61 | OS | (E)-Nerolidol | 53.09 | 1561 | 1553 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| 62 | OS | Germacrene D-4-ol | 54.02 | 1574 | 1568 | 0.97 ± 0.60 | 1.33 ± 0.04 |
| 63 | OS | Guaiol | 55.06 | 1597 | 1586 | - | 0.36 ± 0.00 |
| 64 | OS | β-Oplopenone | 55.59 | 1607 | 1595 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| 65 | OS | 5,7-di-epi-α-Eudesmol | 55.79 | 1607 | 1598 | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| 66 | OS | Eudesm-5-en-11-ol | 55.98 | 1590 | 1600 | - | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 67 | OS | Rosifoliol | 56.14 | 1600 | 1604 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | - |
| 68 | OS | 1,10-di-Epi-Cubenol | 56.28 | 1618 | 1607 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| 69 | OS | 10-epi-γ-Eudesmol | 56.68 | 1622 | 1614 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 0.70 ± 0.02 |
| 70 | OS | 1-Epi-Cubenol | 56.83 | 1627 | 1616 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| 71 | OS | Valerianol | 56.92 | 1623 | 1618 | 0.24 ± 0.00 | - |
| 72 | OS | Agaraspirol | 57.00 | 1619 | - | 0.50 ± 0.02 | |
| 73 | OS | Eremoligenol isomer | 57.15 | 1622 | 0.22 ± 0.00 | - | |
| 74 | OS | γ-Eudesmol | 57.23 | 1630 | 1623 | 3.89 ± 0.26 * | 6.04 ± 0.47 * |
| 75 | OS | Hinesol | 57.67 | 1640 | 1631 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 76 | OS | τ-Cadinol | 57.79 | 1638 | 1633 | 0.29 ± 0.03 * | 0.42 ± 0.05 * |
| 77 | OS | epi-α-Cadinol | 57.90 | 1638 | 1635 | 0.34 ± 0.04 * | 0.51 ± 0.06 * |
| 78 | OS | δ-Cadinol | 58.04 | 1644 | 1638 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.04 |
| 79/80 | OS | β-Eudesmol + α-Eudesmol | 58.42 | 1649/1652 | 1645 | 7.83 ± 0.51 * | 12.61 ± 0.81 * |
| 81 | OS | Intermedeol | 58.49 | 1636 | 1646 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 82 | OS | Selin-11-en-4-α-ol | 58.55 | 1658 | 1647 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 83 | OS | 7-epi-α-Eudesmol | 58.86 | 1662 | 1652 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| 84 | OS | Bulnesol | 59.09 | 1670 | 1656 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| 85 | OS | Elemyl acetate | 59.22 | 1659 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 86 | OS | Hedycaryol | 59.80 | 1669 | - | 0.08 ± 0.01 | |
| 87 | OS | Cryptomeridiol | 67.04 | 1813 | 1801 | - | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| 88 | OS | Oplopanonyl acetate | 69.81 | 1855 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | |
| 89 | DH | Sclarene | 71.56 | 1891 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | - | |
| 90 | DH | Isopimara-9(11),15-diene | 71.69 | 1905 | 1893 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 |
| 91 | DH | Isopimara-9(11),15-diene isomer | 71.88 | 1897 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | - | |
| 92 | DH | Rosa-5,15-diene | 73.06 | 1926 | 1921 | 0.82 ± 0.09 * | 0.03 ± 0.00 * |
| 93 | DH | Kryptomeren | 73.20 | 1924 | 0.89 ± 0.12 * | 0.28 ± 0.06 * | |
| 94 | DH | Pimaradiene | 73.75 | 1948 | 1935 | 1.21 ± 0.17 * | 0.32 ± 0.07 * |
| 95 | DH | Sandaracopimara-8(14),15-diene | 74.65 | 1968 | 1954 | 0.57 ± 0.09 | 0.30 ± 0.04 |
| 96 | DH | Isophyllocladene | 74.95 | 1966 | 1960 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 |
| 97 | OD | Manool oxide | 76.87 | 1987 | 1977 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 98 | DH | Phyllocladene | 77.43 | 2016 | 2011 | 18.92 ± 2.00 * | 5.08 ± 0.62 * |
| 99 | DH | Kaur-16-ene | 78.48 | 2042 | 2034 | 2.58 ± 0.22 * | 23.00 ± 2.07 * |
| 100 | DH | Abietatriene | 78.83 | 2055 | 2041 | 0.26 ± 0.04 * | 0.12 ± 0.02 * |
| 101 | OD | Nezukol | 82.45 | 2132 | 2120 | 1.58 ± 0.52 | 2.70 ± 0.37 |
| 102 | OD | Sandaracopimarinal | 84.68 | 2184 | 2170 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.08 ± 0.02 |
| 103 | OD | Phyllocladanol | 85.98 | 2209 | 2199 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| 104 | OD | trans-Ferruginol | 90.26 | 2297 | 2299 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | - |
| Grouped components (%) | |||||||
| Monoterpene hydrocarbons (MH) | 34.95 ± 6.07 * | 15.83 ± 2.08 * | |||||
| Oxygenated monoterpenes (OM) | 4.45 ± 1.02 | 3.89 ± 0.38 | |||||
| Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons (SH) | 1.64 ± 0.02 | 2.20 ± 0.23 | |||||
| Oxygenated sesquiterpenes (OS) | 30.76 ± 3.95 * | 44.58 ± 3.24 * | |||||
| Diterpene hydrocarbons (DH) | 25.49 ± 2.16 | 29.34 ± 2.90 | |||||
| Oxygenated diterpenes (OD) | 1.69 ± 0.62 | 2.84 ± 0.39 | |||||
| Total identified components (%) | 98.98 ± 0.40 | 98.68 ± 0.62 | |||||
| Total terpenes (%) | 62.08 ± 3.94 * | 47.37 ± 3.88 * | |||||
| Total terpenoids (%) | 36.90 ± 3.54 * | 51.31 ± 2.19 * | |||||
| Ratio terpenes/terpenoids | 1.68 ± 0.27 * | 0.92 ± 0.10 * | |||||
| EO and Compound | Anti-Cholinesterase Activity (IC50, µg·mL−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Acetylcholinesterase | Anti-Butyrylcholinesterase | |
| Aut–EO | NA | 148.33 ± 44.06 c |
| Spr–EO | NA | 83.67 ± 21.22 b |
| (–)-α-Pinene | 95.71 ± 3.65 b | 648.35 ± 22.42 d |
| Donepezil | 0.01 ± 0.003 a | 1.85 ± 0.29 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, T.; Lima, A.; Wortham, T.; Arruda, F.; Janeiro, A.; Baptista, J.; Lima, E. Essential Oil Composition and Anti-Cholinesterase Properties of Cryptomeria japonica Foliage Harvested in São Miguel Island (Azores) in Two Different Seasons. Plants 2024, 13, 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13233277
Rodrigues T, Lima A, Wortham T, Arruda F, Janeiro A, Baptista J, Lima E. Essential Oil Composition and Anti-Cholinesterase Properties of Cryptomeria japonica Foliage Harvested in São Miguel Island (Azores) in Two Different Seasons. Plants. 2024; 13(23):3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13233277
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Tânia, Ana Lima, Tanner Wortham, Filipe Arruda, Alexandre Janeiro, José Baptista, and Elisabete Lima. 2024. "Essential Oil Composition and Anti-Cholinesterase Properties of Cryptomeria japonica Foliage Harvested in São Miguel Island (Azores) in Two Different Seasons" Plants 13, no. 23: 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13233277
APA StyleRodrigues, T., Lima, A., Wortham, T., Arruda, F., Janeiro, A., Baptista, J., & Lima, E. (2024). Essential Oil Composition and Anti-Cholinesterase Properties of Cryptomeria japonica Foliage Harvested in São Miguel Island (Azores) in Two Different Seasons. Plants, 13(23), 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13233277











