Abstract
Undaria pinnatifida can effectively deal with organotin pollution through its excellent accumulation and degradation capabilities found under laboratory conditions. However, nothing is known regarding its accumulation, degradation performance, and related impact factors in the wild farming area. In this study, we monitored triphenyltin chloride (TPTCL) contents and degradation products in different algal parts (blades, stipes, sporophylls, and holdfasts) of cultivated U. pinnatifida from December 2018 to May 2019. Our results showed that sporophytes had an accumulation and degradation capacity for TPTCL. The TPTCL contents and degradation products varied with the algal growth stages and algal parts. TPTCL accumulated in the blades at the growth stage and the blades, stipes, sporophylls, and holdfasts at the mature stage. The TPTCL content among algal parts was blades (74.92 ± 2.52 μg kg−1) > holdfasts (62.59 ± 1.42 μg kg−1) > sporophylls (47.24 ± 1.41 μg kg−1) > stipes (35.53 ± 0.55 μg kg−1). The primary degradation product DPTCL accumulated only in the blades at any stage, with a concentration of 69.30 ± 3.89 μg kg−1. The secondary degradation product MPTCL accumulated in the blades at the growth stage and in the blades, stipe, and sporophyll at the mature stage. The MPTCL content among algal parts was blades (52.80 ± 3.48 μg kg−1) > sporophylls (31.08 ± 1.53 μg kg−1) > stipes (20.44 ± 0.85 μg kg−1). The accumulation pattern of TPTCL and its degradation products seems closely related to nutrient allocation in U. pinnatifida. These results provide the basis for applying cultivated U. pinnatifida in the bioremediation of organotin pollution and the food safety evaluation of edible algae.
1. Introduction
Triphenyltin chloride (TPTCL) is an artificial synthetic compound with the composition of tin atoms and phenyl [1,2], and is widely used in wood preservatives, antifouling coatings, and agricultural pesticides [3,4]. Industrial and domestic wastewater are two principal pathways of bringing TPTCL into the marine ecosystem and, therefore, antifouling, causing significant damage to marine organisms due to its powerful biocidal characteristics [5,6,7]. For marine animals, TPTCL has mainly led to biomorphological changes in oysters [8], imposex in gastropods [9,10,11], and neurobehavioral toxicity in fish [12]. For marine microalgae, TPTCL forces the alteration of physiological processes through membrane lipid interactions destroying internal photosynthetically active lamellae or inhibiting nitrate reductase activity [13,14]. Nevertheless, there have been a limited number of investigations regarding the physiological responses of marine macroalgae to TPTCL stress.
Undaria pinnatifida (Laminariales; Phaeophyceae) is a forest-forming brown macroalga indigenous to the Northwestern Pacific area [15,16,17] and has recently established a presence across temperate rocky coasts worldwide [18,19,20]. This species plays an important role in the maintenance of coastal water environments by removing excessive nutrients [21,22] and alleviating chemical pollution [23]. Additionally, U. pinnatifida has been maricultured on a large scale in East Asia [24,25,26] because of its great commercial value in foodstuffs [27,28], pharmaceuticals, and agriculture [29,30,31,32]. In recent years, coastal chemical pollutants have constituted a major environmental threat to seaweed farming [33]. Our previous study showed that high TPTCL concentrations negatively influenced the survival, growth, and enzyme activities of cultivated sporophytes of U. pinnatifida, promoting a decline in yield and quality [34]. Additionally, U. pinnatifida sporophytes exhibited excellent TPTCL accumulation and degradation capabilities under controlled laboratory conditions. Therefore, it was considered an appropriate candidate for bioremediation [35]. Nevertheless, TPTCL’s accumulation and degradation patterns in the species as well as the relative impact factors have not been investigated under field cultivation conditions.
In the present study, we investigated changes in TPTCL and its degradation products in cultivated U. pinnatifida at different life stages and parts within sporophytes. These study results are expected to provide important information for assessing the seawater purification potential of this high-value species in China. These results are expected to help evaluate the food safety of this commercial species.
2. Results
2.1. Seasonal Variation in Water Temperature and Nutrient Concentration
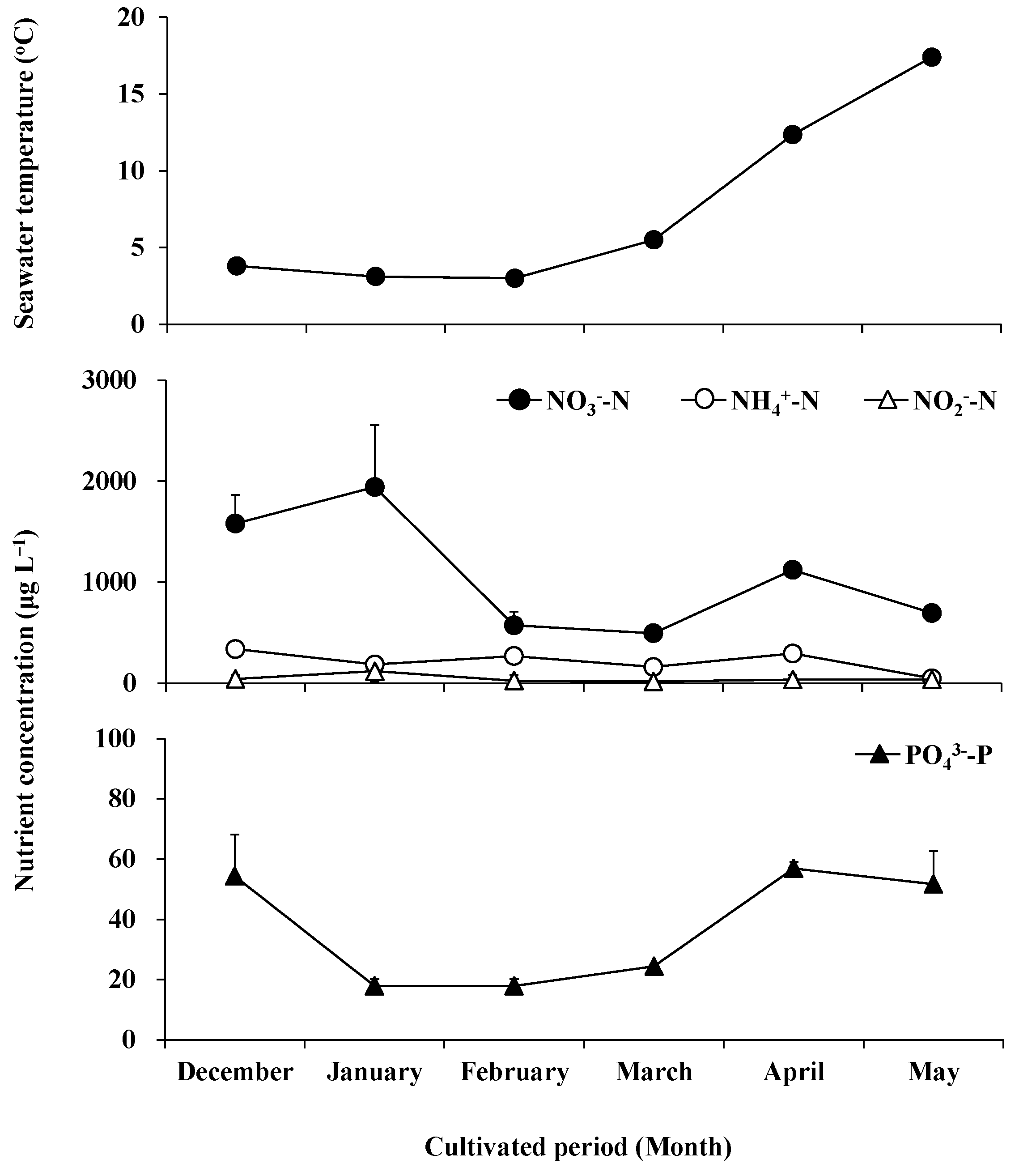
The water temperature varied slightly from 3 °C to 5.5 °C from December to March, and rose rapidly in April and May, reaching 12.4 °C and 17.4 °C, respectively (Figure 1). The fluctuation of NO3−-N concentration was greater than that of NO2−-N, NH4+-N, and PO43−-P (Figure 2). The NO3--N concentration increased from December to January, reaching an annual maximum of 1942.51 μg L−1 in January, decreased from 494.63 μg L−1 to 573.44 μg L−1 in February and March, recovered to 1121.87 μg L−1 in April, and decreased again to 695.67 μg L−1 in May. The NO2−-N concentration was maintained between 19.49 μg L−1 and 44.56 μg L−1 in months other than January, where its concentration reached a maximum of 120.70 μg L−1. The NH4+-N concentration maintained a range of 185.98 μg L−1–337.96 μg L−1 from December to April and decreased to a minimum of 47.47 μg L−1 in May. The PO43--P concentration was 54.41 μg L−1 in December, decreased from 18.01 μg L−1 to 24.49 μg L−1 between January and March, and returned to 51.69 μg L−1–56.87 μg L−1 in April and May.

Figure 1.
The water temperature and concentrations of nitrate (solid circle), ammonium (clear circle), nitrite (clear triangle), and orthophosphate (solid triangle) in seawater during field cultivation from December 2018 to May 2019.
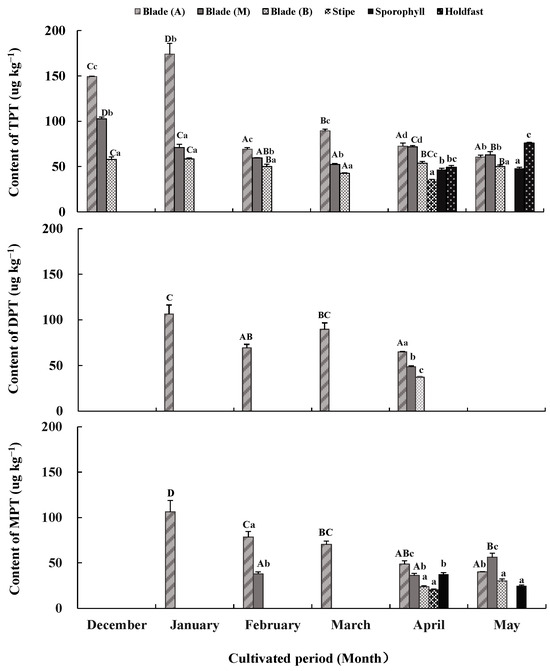
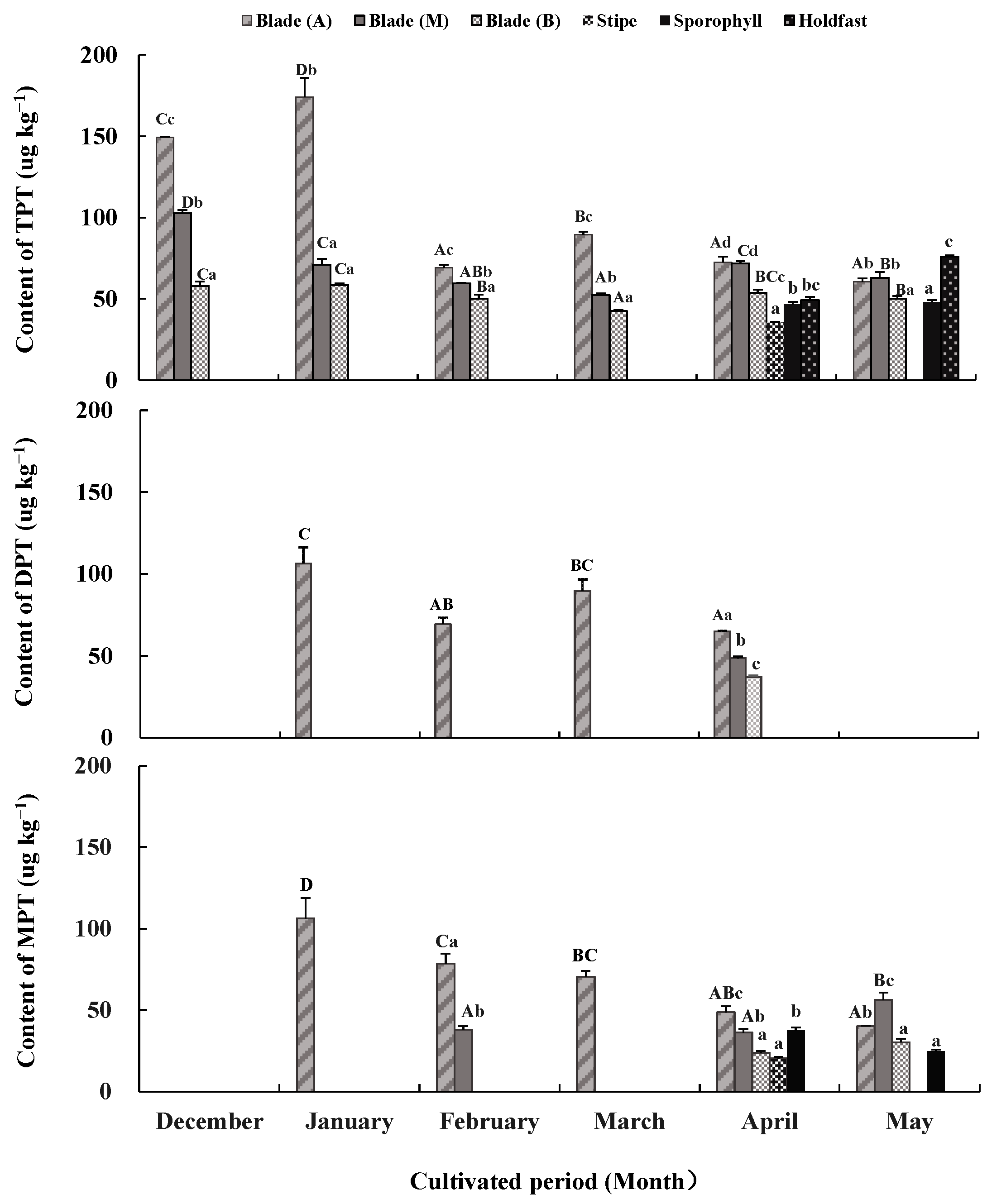
Figure 2.
Triphenyltin chloride (TPTCL) content and its degradation products diphenyltin dichloride (DPTCL) and monophenyltin trichloride (MPTCL) in Undaria pinnatifida tissues during field cultivation. Different capital and lowercase letters represent significant differences among algal parts and cultivated periods, respectively, at p < 0.05.
2.2. Seasonal Morphological Characteristics of U. pinnatifida
Table 1 shows the morphological characteristics (length, width, and fresh weight) of blades, stipes, and sporophylls in cultivated U. pinnatifida. Significant growth was shown in the morphological features of blades and stipes from December 2018 to February 2019 (p < 0.05). The length and width values increased and reached a peak of 138.33 ± 27.06 cm and 22.54 ± 5.99 cm at the blades and 38.96 ± 10.78 cm and 1.86 ± 0.29 cm at the stipes in February. Afterward, these values decreased in March, slightly rebounded in April, and in May reached another peak of 101.88 ± 20.97 cm and 36.89 ± 9.39 cm at the blades and 247.36 ± 133.77 cm and 36.61 ± 8.37 cm at the stipes. Changes in fresh weight were similar to those of length and width. The fresh weight of the blades and stipes reached a maximum of 247.36 ± 133.77 g and 93.73 ± 32.10 g in May after experiencing fluctuations in December and April. Sporophylls appeared in February, and their length, width, and fresh weight gradually increased and reached a maximum of 28.02 ± 11.70 cm, 6.49 ± 1.62 cm, and 105.95 ± 72.5 g, respectively, in May.

Table 1.
Seasonal morphological characteristics of U. pinnatifida during field cultivation. Different lowercase letters represent significant differences in morphological characteristics among months.
2.3. TPTCL and Its Degradation Products in Seawater and in Sporophytic Tissues from Different Parts
TPTCL and its degradation products DPTCL and MPTCL were not detected in the seawater samples but were detected in sporophytic tissues (Figure 2). TPTCL, DPTCL, and MPTCL concentrations varied across algal tissues and the cultivated periods (p < 0.05).
From December to March, TPTCL was only detected in blade tissue. Its content was generally higher in apical tissue (69.22 μg kg−1–174.08 μg kg−1), followed by middle tissue (52.29 μg kg−1–102.70 μg kg−1), and basal tissue (42.52 μg kg−1–58.46 μg kg−1) (p < 0.05). In April and May, TPTCL was detected in almost all algal tissues, except for stipes in May. The order of TPTCL content from large to small in each algae tissue was apical and middle blade tissues (71.74 μg kg−1–72.52 μg kg−1) > basal blade tissue, holdfasts and sporophylls (46.57 μg kg−1–53.71 μg kg−1) > stipes (35.53 μg kg−1) in April, and holdfasts (75.84 μg kg−1) > apical and middle blade tissues (60.72 μg kg−1–63.01 μg kg−1) > basal blade tissue and sporophylls (47.90 μg kg−1–50.23 μg kg−1) in May (p < 0.05). Compared to the values from December to March, the gap among the tissue of different algal parts was reduced in April and May. There was also a significant difference in the TPTCL content between the cultivated periods. The TPTCL content in the apical blade tissue fluctuated greatly, reaching its maximum in January (174.08 μg kg−1), followed by December (149.29 μg kg−1) and March (89.49 μg kg−1), and remaining low in other months (60.72 μg kg−1–72.52 μg kg−1) (p < 0.05). The TPTCL content in the middle and basal blade tissues decreased from December to March and rebounded slightly in April and May (p < 0.05); however, its fluctuation was not as significant as that of the apical blade tissue. TPTCL content in the stipe tissue still existed in April but disappeared in May, whereas TPTCL content in the holdfast increased from April to May.
DPTCL, the primary degradation product of TPTCL, was detected only in apical blade tissue from January to March and in minor amounts in all blade tissues in April. DPTCL content in January (106.28 μg kg−1) was the highest, followed by that in March (89.74 μg kg−1), with the lowest in February and April (37.03 μg kg−1–69.35 μg kg−1) (p < 0.05). The average DPTCL content during the cultivated period was 69.30 ± 3.89 μg kg−1 in blade tissue.
MPTCL, the secondary degradation product of TPTCL, only appeared in apical or middle blade tissues from January to March. It also appeared in nearly all test tissues in April and May. The TPTCL content in the apical and middle blade tissues was always higher than in other tissues (p < 0.05). The maximum MPTCL content was in January in the apical blade tissue (106.23 μg kg−1), and this value decreased gradually until May (40 μg kg−1) (p < 0.05). The MPTCL content in the middle blade tissue was kept low in February and April but increased significantly in May (56.19 μg kg−1) (p < 0.05). The MPTCL content in other tissues fluctuated in the range of 20.44 μg kg−1–37.51 μg kg−1. The average MPTCL content was 52.80 ± 3.48 μg kg−1 in blade tissue, followed by 31.08 ± 1.53 μg kg−1 in sporophylls and 20.44 ± 0.85 μg kg−1 in stipes.
3. Discussion
3.1. Accumulation of TPTCL by Cultivated U. pinnatifida
TPTCL content was detected in most sporophyte parts of U. pinnatifida throughout the cultivated period, although it was not detected in the seawater collected in the cultivation area. TPTCL content accumulated only in the blades from December to March and in most algal parts from April to May. The average TPTCL content throughout the cultivated period was 74.92 ± 2.52 μg kg−1 in the blades, followed by 62.59 ± 1.42 μg kg−1 in holdfasts, 47.24 ± 1.41 μg kg−1 in sporophylls, and 35.53 ± 0.55 μg kg−1 in stipes. These results suggested that U. pinnatifida has a remarkable bioaccumulation capability for TPTCL. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) is an important indicator for describing the magnitude of bioaccumulation of organic compounds in organisms [36]. Unfortunately, it failed to obtain accurate BCFs of U. pinnatifida from TPTCL because TPTCL content in seawater could not be detected. To compare the BCFs between different algal parts and species, we estimated the BCFs of U. pinnatifida using the detection limit we established for TPTCL in seawater samples. The BCFs of TPTCL between different parts of U. pinnatifida were approximately >386.02 in blades (>528.36 in apical blades, >360.83 in middle blades, and >268.88 in basal blades), >322.44 in holdfasts, >243.35 in sporophylls and >183.07 in stipes. In this study, the BCFs of TPTCL by U. pinnatifida were much lower than those previously reported in microalgae and macroalgae. The BCFs of TPT by the freshwater green microalga Tetradesmus obliquus (formerly alga Scenedesmus obliquus) were 1.14 × 105. The BCFs of TBT by T. obliquus and the mixed microalgae Dunaliella salina and D. viridis were >3.32 × 105 and >3.48 × 105, respectively, after a 7-day exposure to TPT [37]. The BCFs of TBT by marine microalgae Chaetoceros neogracilis (formerly Chaetoceros gracilis) (Mediophyceae), Platymonas sp. (Chlorophyta), and Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae) were 4.53 × 105, 5.9 × 104, and 9.1 × 104, respectively, when exposed to TBT for 72 h [38]. The TBT and TPT concentrations in the phytoplankton of Otsuchi Bay, Japan, were 240 μg kg−1–980 μg kg−1 and 20 μg kg−1–670 μg kg−1 dry weight; the BCFs were 3.0 × 103–1.32 × 105 and 2.2 × 103–7.44 × 104, respectively [39]. There were few reports on TPT and TBT accumulations by macroalgae except for our previous study. TPTCL and TBTCL content in the young sporophytes of U. pinnatifida reached a maximum of 1659.87 μg kg−1 and 2973.84 μg kg−1 after 3 days of exposure to 5.0 μg L−1 of TPTCL and TBTCL; the BCFs were >8.55 × 103 and >2.97 × 104, respectively. TPTCL and TBTCL concentrations in the matured sporophytes of U. pinnatifida were 1704.17 μg kg−1 and 1650.63 μg kg−1; the BCFs were >8.78 × 103 and >8.25 × 103, respectively [35]. BCFs can be affected by pollutant properties (type, concentration, structure, and existence form), biological characteristics of algae (species, size, sex, organ, growth and development stage), and environmental conditions (temperature, salinity, water hardness, dissolved oxygen concentration, and light conditions) [40]. In water, suspended particles and sediments have strong adsorption of all kinds of trace contaminants, affecting their existence, form, bioavailability, and bioaccumulation [1]. Microalgae, a type of suspended particle, have a higher ratio of surface area to volume and more advantages in surface adsorption and organotin uptake than macroalgae [38]; therefore, they have more BCFs than macroalgae. U. pinnatifida cultured in the laboratory exhibits higher BCFs of TPTCL than U. pinnatifida cultivated in the field because of the high initial concentration of TPTCL and stable culture conditions in the laboratory, including temperature, light and water velocity, and nutrient supply [35]. Although the BCFs of cultivated U. pinnatifida were not as high as microalgae, they are still expected to accumulate a large amount of TPTCL from seawater in the cultivation process because of its huge production (an output of 225,600 tons of fresh weight in 2021) [41] and long cultivation period (from October to May every year). These results suggest that cultivated U. pinnatifida has great potential as a bioremediation tool for removing organotin compounds from natural seawater, especially in waters with severe organotin pollution.
3.2. Degradation of TPTCL by Cultivated U. pinnatifida
In February, there was a sharp reduction (about 30~55%) in TPTCL content in the blades, especially in the apical part of the blades. Afterward, the TPTCL content in the algal parts remained at relatively low levels until May. Subsequently, DPTCL, the primary degradation product of TPTCL, appeared in the blades from January to April, and its content gradually decreased. MPTCL, the secondary degradation product of TPTCL, appeared in the blades and other parts from January to May, but its content gradually reduced. DPTCL and MPTCL appeared one month later than TPTCL, whereas DPTCL disappeared one month earlier than MPTCL. Furthermore, the appearance of both DPTCL and MPTCL was accompanied by a decrease in TPTCL, indicating that DPTCL and MPTCL appeared with the gradual degradation of TPTCL by U. pinnatifida. DPTCL and MPTCL appeared simultaneously and reached their maximum concentrations in January. However, only TPTCL and MPTCL were retained in the algal tissues in May. These results revealed that TPTCL degradation by U. pinnatifida was more efficient at the growth stage than at the mature stage.
Previous studies on organotin degradation by algae mainly focused on TBT rather than TPT. Fifty percent of TBT was degraded to DBT, MBT, and inorganic tin by a green alga Ankistrodesmus falcatus when exposed to a certain TBT concentration for 4 weeks [42]. Chaetoceros neogracilis degraded 5% TBT into DBT and MBT after exposure to 0.4 μg L−1 of TBT for 72 h [38]. Chlorella vulgaris degraded 27% and 41% of TBT into DBT and MBT, whereas Chlorella sp. only degraded 26% of TBT into DBT when exposed to 100 μg L−1 and 30 μg L−1 of TBT for 14 days [43]. The four microalgae, Chlorella miniata, C. sorokiniana, Tetradesmus dimorphus (formerly Scenedesmus dimorphus), and Comasiella arcuata var. platydisca (formerly Scenedesmus platydiscus) degraded TBT into DBT and MBT inside the cells. TBT-specific uptake and degradation by Chlorella was higher than by Tetradesmus/Comasiella, likely due to larger cell sizes and biomass [44]. Both the microalgae Leptocylindrus danicus (Mediophyceae) and Amphidinium carterae (Dinophyceae) degraded TBT to the less toxic DBT and MBT. A. carterae transformed DBT into MBT more rapidly than L. danicus [45]. Our previous study was the first to report TPTCL and TBTCL degradation by the macroalgae U. pinnatifida [35]. U. pinnatifida exposed to TPTCL and TBTCL for 12 days absorbed 100% of TPTCL and 98% of TBTCL in the culture medium and degraded them into DPTCL and DBTCL and, subsequently, DPTCL and DBTCL into MPTCL and MBTCL. The TPTCL and TBTCL concentrations and their degradation products were MPTCL > TPTCL > DPTCL for sporophytes at any stage, TBTCL > DBTCL for the young stage, and TBTCL > DBTCL > MBTCL for the mature stage. U. pinnatifida’s ability to degrade TPTCL was higher than that of TBTCL, and its degradation capacity at the mature stage was stronger than at the growth stage. These results revealed that algae’s capacity to degrade TPTCL and TBTCL varies with algal species, growth and development stages, cell compositions, enzyme activities, and organotin forms and concentrations.
Regarding U. pinnatifida’s degradation mechanism for TPTCL and TBTCL, whether cultivated in the field or in the laboratory, no degradation products were detected in seawater, assuming that degradation occurs in the algae cells. It was acknowledged that the degradation of organotin compounds by micro-organisms mainly occurred in the cell but not on the surface of the cell wall [45,46]. TPTCL is transferred across the cell membrane through active transport and interactions with membrane lipids and proteins due to its hydrophobicity and metabolism [47], causing intracellular accumulation and biodegradation. TPTCL dephenylation may also be related to the cellular metabolism of ions, carbohydrates, and organic acids [46]. Metabolite analysis confirmed that TPTCL was degraded through the cleavage of Sn-C bonds producing diphenyltin, monophenyltin, and tin, respectively [48]. The Sn-C bonds could be effectively cleaved by cytochrome P450, which is the enzyme responsible for TPTCL degradation [49]. Unfortunately, most of TPTCL’s degradation mechanisms were obtained from micro-organisms but not from marine algae. More studies should identify TPTCL’s degradation mechanisms in marine algae.
TPT and TBT are well known for their strong toxicity and significant impact on marine environments and organisms [50]. U. pinnatifida’s strong degradation capacity for TPTCL and TBTCL guarantees its application in the bioremediation of organotin pollution. In addition, U. pinnatifida is also a commercial species for food or food additives; therefore, its food safety has also attracted more attention. In this study, the average TPTCL content in U. pinnatifida cultivated in Jiaozhou Bay from December to the following May varied between 57.99 μg kg−1 and 103.35 μg kg−1 in blades, 0 μg kg−1 and 35.53 μg kg−1 in stipes, and 47.95 μg kg−1 and 61.87 μg kg−1 in sporophylls. According to the acceptable daily intake (ADI, 0.5 μg kg−1 body weight per day) of TPTCL regulated by the FAO and WHO [51,52], a person with 60 kg of body weight should consume 0.29 kg–0.52 kg of fresh blades, or 0.84 kg–no limit of stipes, or 0.48 kg–0.63 kg of sporophylls daily. The blades appear to be more risky than other algal parts, especially in December and January. Food safety evaluations of cultivated U. pinnatifida should consider multiple factors, such as the cultivation area, organotin concentration, algal growth stage, algal parts and so on.
3.3. Temporal and Intra-Sporophyte Variations of TPTCL and Its Degradation Products in Cultivated U. pinnatifida
TPTCL accumulation and its degradation products in cultivated U. pinnatifida varied with cultivation periods and algal parts. TPTCL accumulation was more active from December to January, and DPTCL and MPTCL accumulations were more active from January to March. The presence of TPTCL and its degradation products was concentrated only in blades from December to March, and in minor amounts in blades, sporophylls, holdfasts, and stipes from April to May. TPTCL’s accumulation pattern is consistent with the allocation and storage pattern of nutrients, such as carbon and nitrogen, in U. pinnatifida. Previous reports demonstrated that TPTCL transport and stepwise transformation are metabolically mediated activities in aquatic animals [53,54]. Other results certified that TPTCL degradation by microbes was related to the cellular metabolism of ions, carbohydrates, organic acids, and enzymes [46,49]. These results suggest that TPTCL’s transportation and transformation may depend on intracellular nutrients, such as carbon and nitrogen, which help explain TPTCL’s accumulation pattern and nutrient allocation pattern. The cultivated U. pinnatifida grew rapidly from December to February. Nutrients produced through photosynthesis and nutrient uptake were mainly allocated and stored in the blades and midribs (recorded as part of the stipes) to expand productive areas and improve production. With the appearance of sporophylls in February, nutrients were mainly allocated and stored in the basal part of the blades (with meristem) and sporophylls in April and May to prepare for growth in width, thickness, and reproduction. The midway harvest of larger individuals led to a sharp reduction in March and a slow increase in April of morphological parameters and induced developmental stagnation of sporophylls and regrowth of the blades in width and thickness (Table 1). Similar growth and nutrient allocation patterns were reported in U. pinnatifida cultivated in Miyagi, Japan, after thallus excision. Thallus excision caused compensatory growth, first in the blades and then in sporophylls [55]. TPTCL and its degradation products in U. pinnatifida had similar temporal and intra-sporophyte variations to nutrients, suggesting that TPTCL can indicate nutrient allocation patterns.
In addition, some algal parts of U. pinnatifida such as holdfasts and sporophylls with no or little productivity had high TPTCL contents and degradation products, implying a long-distance transport of nutrients in these algae. To meet the meristem’s nitrogen and carbon demands, the long-distance transport of nitrogen and carbon from mature to basal blades has been reported in the brown macroalgae Saccharina japonica (formerly Laminaria japonica), Laminaria digitata, Laminaria hyperborea, and Saccharina latissima (formerly Laminaria saccharina) [56,57,58,59]. Another report noted that some brown algae in Laminariaceae, Lessoniaceae, and Alariaceae could translocate assimilates from the non-growing part toward the intercalary growing region, the stipes, and even holdfasts, to support new tissue formation and reproductive organs [60]. The sieve elements of the medulla were considered the transport route [59]. This long-distance transport mechanism may explain intra-sporophyte variations in TPTCL and its degradation products in cultivated U. pinnatifida.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Treatment
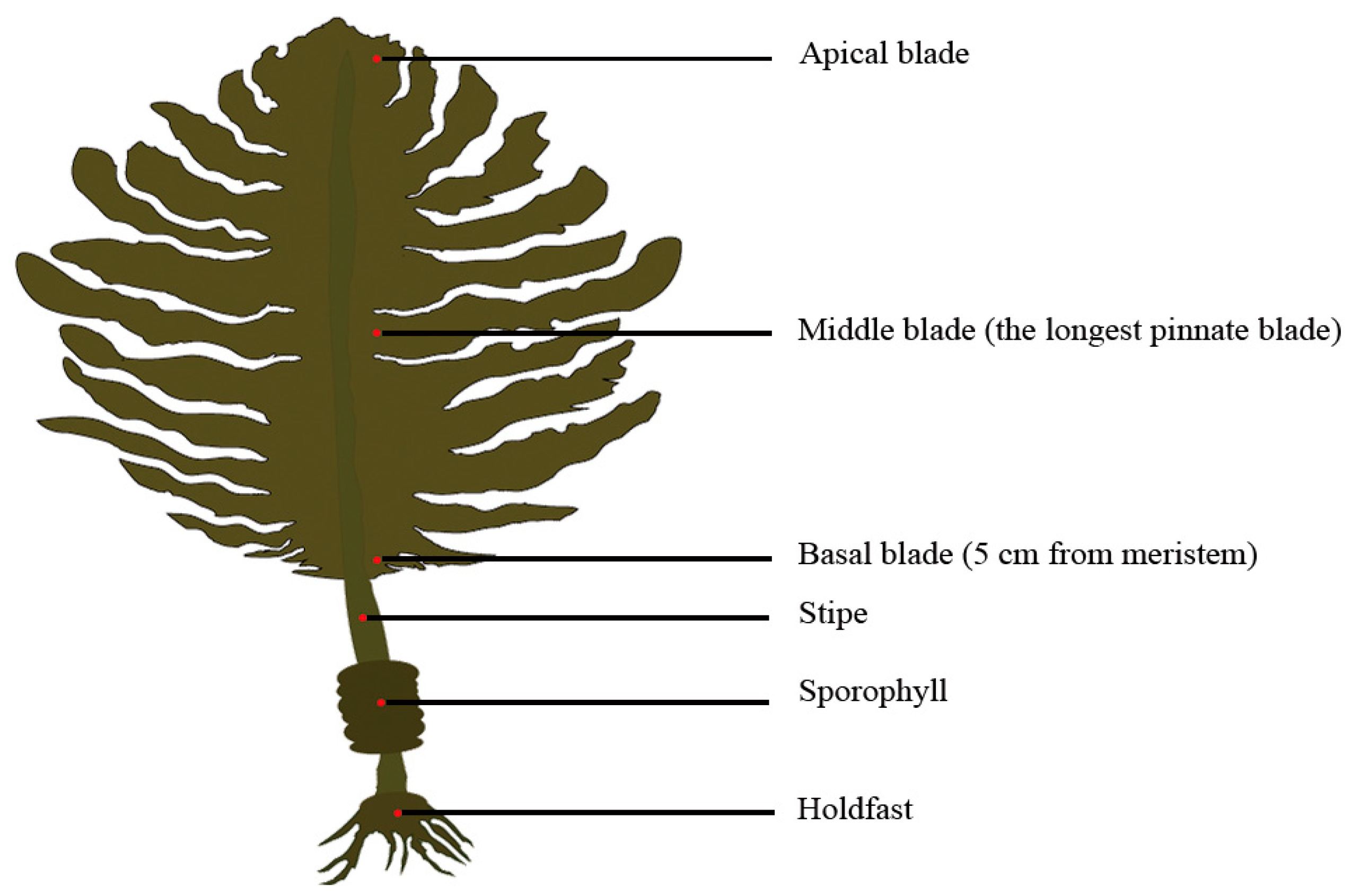
From December 2018 to May 2019, U. pinnatifida sporophytes (n = 70) were randomly collected every month from cultivated populations in Jiaozhou Bay (36° 06′ N, 120° 18′ E), Qingdao, China. At the same time, 500 mL of seawater samples were collected every month from the culture area’s surface (at a depth of 0.5 m). The seawater temperature was measured in situ with a thermometer. The algal and seawater samples were transported immediately to the laboratory in cooling boxes. Forty-five healthy sporophytes were chosen and fully rinsed with sterilized filtered seawater to remove detritus and epiphytes. There were three replicates in this investigation, with each replicate comprising 15 sporophytes. The length and width of the blades, stipes and sporophylls were measured for each sporophyte. The fresh weight of each part was measured after artificial segmentation. For each sporophyte, 5 g of fresh tissue was excised from holdfasts, sporophylls, stipes, basal blades (5 cm from meristem), middle blades (the longest pinnate blade), and apical blades, respectively (Figure 3). These algal parts and seawater samples were promptly placed in a freezer and stored at a temperature of −80 °C for subsequent experiments. In addition, concentrations of NO3−-N, NO2−-N, NH4+-N, and PO43−-P in seawater samples were determined according to the Specifications for Oceanographic Survey (GB/T 12763.4-2007) (Ministry of Natural Resources of China 2007) [61].

Figure 3.
The algal parts of Undaria pinnatifida from which sporophytic tissues were excised for the detection of TPTCL and its degradation products.
4.2. Determination of TPTCL and Its Degradation Products in Seawater and Sporophytic Tissues from Different Parts
Eight organotin chloride standards, namely triphenyltin (TPT, 95%), diphenyltin (DPT, 96%), monophenyltin (MPT, 98%), tributyltin (TBT, 99%), dibutyltin (DBT, 95%), monobutyltin (MBT, 98%), dimethyltin (DMT, 98%), and tetrabutyltin (TeBT, 95%), with internal standard tripropyltin (TPrT, 99.3%) and the derivative agent sodium tetraethylborate (NaBEt4, 98%), were purchased from Beijing Bellingway Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The concentrations of these reagents were 1000 mg (Sn) L−1 for organotin standards and 36.25 μg L−1 for TPrT, respectively. Tropolone (98%) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan), and other reagents used in analysis were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
To determine the concentrations of TPTCL and its degradation products in seawater, 20 mL of seawater and 100 μL of TPrT standard solution were poured into a 50 mL glass tube and maintained for 30 min under dark conditions. To extract TPTCL and its deg-radation products, 10 mL of acetic acid–sodium acetate buffer solution, 300 μL of NaBEt4 (2%), and 2 mL of n-hexane were added to the tube and mixed intensively using an oscillator for 5 min. The upper extract was collected. We added and further mixed 2 mL of tropolone-n-hexane (0.005%) for 2 min and the upper extract was recovered. All these extracts were mixed and evaporated into 1 mL.
Before extracting TPTCL and its degradation from sporophytic tissues, lyophilized seaweed samples were ground into a powder and filtered through a 40-mesh sieve (380 μm). After fully mixing, 0.3 g dry powder and 100 μL TPrT standard solution were placed in flasks and maintained overnight under dark conditions. To extract TPTCL and its degradation products, 5 mL of NaCl solution (20%) and 15 mL of HCL-ethyl acetate (0.3 mol L−1) were added to flasks and mixed intensively using an ultrasonic treatment for 15 min at 32 kHz. We added and stirred 20 mL of tropolone-n-hexane (0.01%) for 40 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 min and the upper extract was collected. Subsequently, 15 mL of n-hexane was added to the remaining deposit and stirred for 20 min for the second extraction. We added 20 mL of acetic acid–sodium acetate buffer solution, 300 μL of NaBEt4 (2%), and 1.5 mL of n-hexane to the extracts and stirred for 30 min. These extracts were mixed and evaporated into 1 mL.
After passing through the 0.22 μm organic system filter membrane, the organic phases were prepared for loading onto a gas spectrum. A gas chromatograph (SCION 456-GC, Bruker Daltonic Inc., Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with a pulsed flame photometric detector and a 394 nm sulfur filter was used to analyze TPTCL concentrations and their degradation products in samples. An HP-5 capillary column (30 m × 320 μm, 0.25 μm, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used for separation. The injection volume was 1.0 μL and the injection port temperature was 250 °C. The chromatographic column temperature was set to 45 °C for 3 min, increased to 120 °C at a rate of 15 °C min−1 and held for 2 min, then ramped up to 150 °C at a rate of 5 °C min−1 and held for 2 min, further rose to 220 °C at a rate of 10 °C min−1 and held for 2 min, and eventually reached 240 °C at a rate of 10 °C min−1 and held for 3 min. The carrier gas was nitrogen (purity ≥ 99.999%) at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min. The detection temperature was 280 °C. The make-up gas was hydrogen—(14 mL min−1) and air (27 mL min−1). The signal delay time was 4.0 ms and the pulse width was 20.0 ms.
For seawater samples, the recovery, relative standard deviation (RSD), and detection limit were 80.54–115.59%, 3.42–8.51%, and 194.1 ng L−1 for TPTCL, 72.94–87.30%, 4.40–13.20%, and 76.5 ng L−1 for DPTCL, and 79.57–118.48%, 1.23–10.98%, and 156 ng L−1 for MPTCL, respectively. For seaweed samples, the recovery, relative standard deviation (RSD), and detection limit were 102.89–107.98%, 6.58–8.24%, and 0.012 mg kg−1 for TPTCL, 73.12–76.14%, 0.68–8.47%, and 0.017 mg kg−1 for DPTCL, and 76.69–110.25%, 2.74–5.23%, and 0.010 mg kg−1 for MPTCL, respectively.
4.3. Statistical Analysis
The Kruskal–Wallis and Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison tests were used to analyze significant differences in the contents of TPTCL and their degradation products across different algal parts in each month and across cultivation periods, as not every dataset showed a normal distribution and homogeneous variance. Differences were considered significant at a probability of 5% (p < 0.05). All analyses were conducted using SPSS software (Version 26.0, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the sporophyte of cultivated Undaria pinnatifida had an accumulation and degradation capacity for TPTCL. TPTCL contents and degradation products varied with the algal growth stages and algal parts. TPTCL accumulated in the blades at the growth stage and the blades, stipes, sporophylls, and holdfasts at the mature stage. The TPTCL content among algal parts was blades > holdfasts > sporophylls > stipes. The primary degradation product DPTCL accumulated only in the blades at any stage, and the secondary degradation product MPTCL accumulated in the blades at the growth stage and in the blades, stipe, and sporophyll at the mature stage. The MPTCL content among algal parts was blades > sporophylls > stipes. The accumulation pattern of TPTCL and its degradation products seems closely related to nutrient allocation in U. pinnatifida. Due to the limited data in this study, further studies are needed to identify TPTCL’s accumulation and degradation mechanisms in marine algae, especially with more attention paid to the functions of some key substances such as alginic acid.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, J.L.; Writing–original draft preparation, X.R.; Writing–review and editing, J.L. and X.G.; Project administration and funding acquisition, J.L. and X.G.; Investigation, formal analysis, and data curation, Y.Z. and X.R.; Validation and resources, Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201328), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 842212015), the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202211067) and the Dongying Marine Ecological Restoration Project (20230389).
Data Availability Statement
The data of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Liyan Ma and Jingming Li of China Agricultural University for guiding the analysis of organotin compounds and providing analytical instruments. We also thank Benshan Wang for providing the cultivated algal materials. We wish to express our gratitude to all the reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions on this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hoch, M. Organotin compounds in the environment—An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 719–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.; Tsai, C.; Su, C.; Wang, Y. Environmental dissipation of fungicide triphenyltin acetate and its potential as a groundwater contaminant. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2001, 49, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigarick, A.A.; Webster, R.K.; Meyer, R.P.; Zalom, F.G.; Smith, K.A. Effect of pesticide treatments on nontarget organisms in California rice paddies: I. Impact of triphenyltin hydroxide; II. Impact of diflubenzuron and triflumuron. Hilgardia 1990, 58, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, G.; Song, Z. Immobilization of Spirulina subsalsa for removal of triphenyltin from water. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2002, 30, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K. Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1996, 26, 3–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Takayanagi, K.; Tateishi, M.; Tagata, H.; Ikeda, K. Organotin compounds and polychlorinated biphenyls of livers in squid collected from coastal waters and open oceans. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 96, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.A.; Argese, E.; Tagliapietra, D.; Bettiol, C.; Ghirardini, A.V. Toxicity of tributyltin and triphenyltin to early life-stages of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Alzieu, C.; Sanjuan, J.; Deltreil, J.; Borel, M. Tin contamination in Arcachon Bay: Effects on oyster shell anomalies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1986, 17, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, T.; Shiraishi, H.; Shimizu, M.; Morita, M. Effects of triphenyltin chloride and five other organotin compounds on the development of imposex in the rock shell, Thais clavigera. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 95, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.M.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; Vieira, M.N.; Solé, M. Triphenyltin and tributyltin, single and in combination, promote imposex in the gastropod Bolinus brandaris. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjeiro, F.; Sánchez-Marín, P.; Barros, A.; Galante-Oliveira, S.; Moscoso-Pérez, C.; Fernández-González, V.; Barroso, C. Triphenyltin induces imposex in Nucella lapillus through an aphallic route. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 175, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Z.; Zhong, L. Effects of low concentrations of triphenyltin on neurobehavior and the thyroid endocrine system in zebrafish. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Song, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W. Toxic effect of triphenyltin chloride on the alga Spirulina subsalsa. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, M.; Mak, N.K.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y. Triphenyltin chloride induced growth inhibition and antioxidative responses in the green microalga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.K. Common Seaweeds of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, C.H.; Shin, H.C. Growth and size distribution of some large brown algae in Ohori, east coast of Korea. Hydrobiologia 1989, 204–205, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Nishihara, G.N.; Tokunaga, S.; Terada, R. The effect of irradiance and temperature responses and the phenology of a native alga, Undaria pinnatifida (Laminariales), at the southern limit of its natural distribution in Japan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.D. Review of Research on Undaria pinnatifida in New Zealand and Its Potential Impacts on the Eastern Coast of the South Island; Department of Conservation: Wellington, New Zealand, 2004; pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- James, K.; Kibele, J.; Shears, N.T. Using satellite-derived sea surface temperature to predict the potential global range and phenology of the invasive kelp Undaria pinnatifida. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 3393–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, G.; Smale, D.A. Undaria pinnatifida: A case study to highlight challenges in marine invasion ecology and management. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 8624–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4311–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.I.; Gil, M.N.; Esteves, J.L. Nutrient uptake rates by the alien alga Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyta) (Nuevo Gulf, Patagonia, Argentina) when exposed to diluted sewage effluent. Hydrobiologia 2004, 520, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, C. Biosorption of Heavy Metal Ions by Brown Seaweeds from Southern Coast of Korea. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 2012, 17, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Akiyama, K. Cultivation and utilization of Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame) as food. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.K.; Hwang, I.K.; Park, E.J.; Gong, Y.G.; Park, C.S. Development and cultivation of F2 hybrid between Undariopsis peterseniana and Undaria pinnatifida for abalone feed and commercial mariculture in Korea. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.F.; Pang, S.J.; Li, J.; Gao, S.Q. Breeding of an elite cultivar Haibao no. 1 of Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyceae) through gametophyte clone crossing and consecutive selection. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, N.; Vallorani, L.; Milanovic, N.; Stocchi, V. Evaluation of marine algae wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and kombu (Laminaria digitata japonica) as food supplements. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhasankar, P.; Ganesan, P.; Bhaskar, N.; Hirose, A.; Stephen, N.; Gowda, L.R.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Edible Japanese seaweed, wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) as an ingredient in pasta: Chemical, functional and structural evaluation. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Novel antiviral fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida (Mekabu). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T. Suppression of Th2 immune responses by mekabu fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 137, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmingson, J.A.; Falshaw, R.; Furneaux, R.H.; Thompson, K. Structure and antiviral activity of the galactofucan sulfates extracted from Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2006, 18, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeeshani, H.; Hassouna, A.; Lu, J. Proteins extracted from seaweed Undaria pinnatifida and their potential uses as foods and nutraceuticals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 6187–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, W.; Han, M. Biosorption of nickel and copper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): Application of isotherm and kinetic models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Gao, X.; Li, J. Physiological and ultrastructural responses of the brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida to triphenyltin chloride (TPTCL) stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Gao, X. Accumulation and degradation of organotin compounds in cultivated sporophytes of the brown alga Undaria pinnatifida. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, L.Q. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Bai, Z.; Dai, S.; Xie, Q. Accumulation and toxic effect of organometallic compounds on algae. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 7, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. Removal and transformation of tributytin in seawater by three marine microalgae. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 1994, 3, 341–348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harino, H.; Fukushima, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawai, S.; Miyazaki, N. Contamination of butyltin and phenyltin compounds in the marine environment of otsuchi bay, Japan. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 101, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y. Bioaccumulation and Influential Mechanisms of Heavy Metals in Offshore Seafood. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, China, June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Fisheries and Fisheries Administration, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, PRC. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook 2022; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 22–23.
- Maguire, R.J.; Wong, P.T.S.; Rhamey, J.S. Accumulation and metabolism of tri-n-butyltin cation by a green alga, Ankistrodesmus falcatus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.K.; Lau, P.S.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Biodegradation capacity of tributyltin by two chlorella species. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 105, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Chong, A.M.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Removal of tributyltin (TBT) by live and dead microalgal cells. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. A study on biosorption and biodegradation of tributyltin by two red tide microalgae. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Ye, J.; Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Huang, J. Biosorption and biodegradation of triphenyltin by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and their influence on cellular metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Teruel, J.A.; Aranda, F.J. Effect of triorganotin compounds on membrane permeability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1720, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ye, J.; Ma, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, X. Triphenyltin biosorption, dephenylation pathway and cellular responses during triphenyltin biodegradation by Bacillus thuringiensis and tea saponin. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Yang, K.; Ye, J.; Long, Y.; Ke, J.; Ou, H. Triphenyltin degradation and proteomic response by an engineered Escherichia coli expressing cytochrome P450 enzyme. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.F.; Li, J. The Contaminative Status of Organic Tin Compounds and its Reproductive Toxicity. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2005, 22, 549–551. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 13: Triphenyltin Compounds. Available online: https://www.inchem.org/documents/cicads/cicads/cicad13.htm (accessed on 2 May 1999).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Pesticide Residues in Food 1991. In Proceedings of the FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper Report of Joint FAO/Who Meeting on Pesticide Residues in Food 1991, Geneva, Switzerland, 16–25 September 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Takayanagi, K. Bioconcentration and elimination of bis (tributyltin) oxide (TBTO) and triphenyltin chloride chloride (TPTC) in several marine fish species. Wat. Res. 1992, 26, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Oshima, Y.; Sei, I.; Miyazaki, N. Metabolism of tributyltin and triphenyltin by Dall’s porpoise hepatic microsomes. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Endo, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Agatsuma, Y. Combined effects of seawater temperature and nutrient condition on growth and survival of juvenile sporophytes of the kelp Undaria pinnatifida (Laminariales; phaeophyta) cultivated in northern honshu, japan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüning, K.; Schmitz, K.; Willenbrink, J. CO2 fixation and translocation in benthic marine algae. III. Rates and ecological significance of translocation in Laminaria hyperborea and L. saccharina. Mar. Biol. 1973, 23, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.S.; Jones, R.G.; Hunt, R.D. A seasonal carbon budget for a laminarian population in a Scottish sea-loch. Helgoländer Wiss. Meeresunters 1977, 30, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, H.; Maita, Y.; Kuwada, K. Nitrogen recycling mechanism within the thallus of Laminaria japonica (Phaeophyceae) under the nitrogen limitation. Fish. Sci. 1994, 60, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, I.R.; Stewart, W.D.P. Occurrence and significance of nitrogen transport in the brown alga Laminaria digitata. Mar. Biol. 1983, 77, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.; Lobban, C.S. A survey of translocation in Laminariales (Phaeophyceae). Mar. Biol. 1976, 36, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 12763.4-2007; Part 4: Survey of Chemical Parameters in Seawater. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 13–23.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).