Development and Validation of Multiplex-PCR Assay for β-Carotene hydroxylase and γ-Tocopherol methyl transferase Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins in Maize for Its Application in Genomics-Assisted Breeding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of Functional Marker for crtRB1 Gene
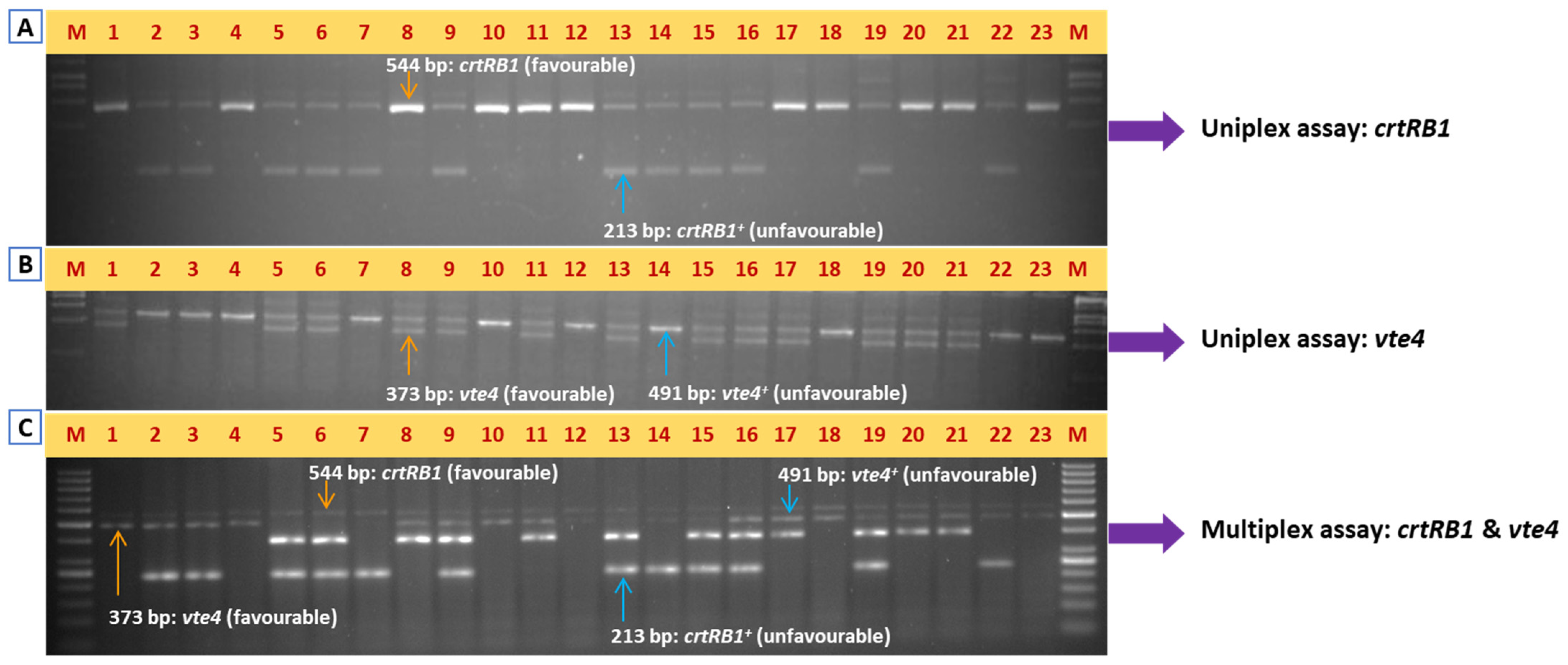
2.2. Uniplex-PCR Assay for crtRB1 Gene
2.3. Uniplex-PCR for vte4 Gene
2.4. Multiplex-PCR Assay for crtRB1 and vte4 Genes
3. Discussion
3.1. Functional Polymorphism of crtRB1 and vte4 Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins
3.2. Reproducibility of Markers for Genotyping crtRB1 and vte4 Genes
3.3. Potentiality of Multiplex-PCR Assay
3.4. Effectiveness of Genotyping Cost and Time Between Uniplex- and Multiplex-PCR Assays
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Development of Segregating Population for crtRB1 and vte4 Genes
4.2. Functional Markers for crtRB1 and vte4 Genes
4.3. Primer Synthesis and DNA Isolation for Genotyping
4.4. Uniplex-PCR Assay for crtRB1 and vte4 Genes
4.5. Multiplex-PCR Assay
4.6. Resolving and Visualization of Amplicons
4.7. Analysis of Cost and Time of Genotyping
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katral, A.; Hossain, F.; Zunjare, R.U.; Mishra, S.J.; Ragi, S.; Kasana, R.K.; Chhabra, R.; Thimmegowda, V.; Vasudev, S.; Kumar, S.; et al. Enhancing kernel oil and tailoring fatty acid composition by genomics-assisted selection for dgat1-2 and fatb genes in multi-nutrient-rich maize: New avenue for food, feed and bioenergy. Plant J. 2024, 119, 2402–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadava, D.K.; Hossain, F.; Mohapatra, T. Nutritional security through crop biofortification in India: Status & future prospects. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhijith, K.P.; Muthusamy, V.; Chhabra, R.; Dosad, S.; Bhatt, V.; Chand, G.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Zunjare, R.U.; Vasudev, S.; Yadava, D.K.; et al. Development and validation of breeder-friendly gene-based markers for lpa1-1 and lpa2-1 genes conferring low phytic acid in maize kernel. 3Biotech 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Menkir, A.; Dhliwayo, T.; Ndhlela, T.; San Vicente, F.; Nair, S.K.; Vivek, B.S.; et al. Molecular breeding for nutritionally enriched maize: Status and prospects. Front Genet. 2020, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Fact-Sheet. 2024. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Mehta, B.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Baveja, A.; Chauhan, H.S.; Chhabra, R.; Singh, A.K.; Hossain, F. Biofortification of sweet corn hybrids for provitamin-A, lysine and tryptophan using molecular breeding. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Mishra, S.J.; Chand, G.; Bhatt, V.; Bhat, J.S.; Das, A.K.; Chauhan, H.S.; et al. Enhancement of nutritional quality in maize kernel through marker-assisted breeding for vte4, crtRB1, and opaque2 genes. J. Appl. Genet. 2023, 64, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunjare, R.U.; Chhabra, R.; Hossain, F.; Baveja, A.; Muthusamy, V.; Gupta, H.S. Molecular characterization of 5′ UTR of the lycopene epsilon cyclase (lcyE) gene among exotic and indigenous inbreds for its utilization in maize biofortification. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Muthusamy, V.; Hossain, F.; Baveja, A.; Chhabra, R.; Jha, S.K.; Yadava, D.K.; Zunjare, R.U. Analysis of genetic variability for retention of kernel carotenoids in sub-tropically adapted biofortified maize under different storage conditions. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouis, H.E. Reducing mineral and vitamin deficiencies through biofortification: Progress under HarvestPlus. In Hidden Hunger: Strategies to Improve Nutrition Quality; Biesalski, H.K., Birner, R., Eds.; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 118, pp. 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mene-Saffrane, L.; Pellaud, S. Current strategies for vitamin E biofortification of crops. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Chauhan, H.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Bhat, J.S.; Guleria, S.K.; Saha, S.; Hossain, F. Genetic variability, genotype× environment interactions-and combining ability-analyses of kernel tocopherols among maize genotypes possessing novel allele of γ-tocopherol methyl transferase (ZmVTE4). J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Chhabra, R.; Katral, A.; Chand, G. Vitamin E: Pioneering the Shift from Stability to Elevated Oil Quality. In Biofortification: Nutrients; Garg, M., Sharma, S., Tiwari, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G.; Sies, H. Vitamin E in humans: Demand and delivery. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Baveja, A.; Chauhan, H.S.; Bhat, J.S.; Guleria, S.K.; Kumar, B.; Saha, S.; Hossain, F. Genetic variability for kernel tocopherols and haplotype analysis of γ-tocopherol methyl transferase (vte4) gene among exotic-and indigenous-maize inbreds. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020, 88, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for α-tocopherol transfer protein as a determinant of the biological activities of vitamin E analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide association studies identified three independent polymorphisms associated with α-tocopherol content in maize kernels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maman, S.; Hossain, F.; Katral, A.; Zunjare, R.U.; Gain, N.; Reddappa, S.B.; Kasana, R.K.; Sekhar, J.C.; Neeraja, C.N.; Yadava, D.K.; et al. Influence of storage duration on retention of kernel tocopherols in vte4-based biofortified maize genotypes. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2023, 123, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Prasanna, B.M.; Hellin, J.; Banziger, M. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Sekhar, J.C.; Gupta, H.S. Analyzing the role of sowing and harvest time as factors for selecting super sweet (-sh2sh2) corn hybrids. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2017, 77, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixley, K.; Rojas, N.P.; Babu, R.; Mutale, R.; Surles, R.; Simpungwe, E. Biofortification of maize with provitamin A carotenoids. In Carotenoids and Human Health; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.; Hossain, F.; Nepolean, T.; Saha, S.; Agrawal, P.K.; Guleria, S.K.; Gupta, H.S. Genetic variability and interrelationship of kernel carotenoids among indigenous and exotic maize (Zea mays L.) inbreds. Cereal Res. Commun. 2015, 43, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunjare, R.U.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Baveja, A.; Chauhan, H.S.; Bhat, J.S.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Saha, S.; Gupta, H.S. Development of biofortified maize hybrids through marker-assisted stacking of β-carotene hydroxylase, lycopene-ε-cyclase and opaque2 genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Kandianis, C.B.; Harjes, C.E.; Bai, L.; Kim, E.H.; Yang, X.; Skinner, D.J.; Fu, Z.; Mitchell, S.; Li, Q.; et al. Rare genetic variation at Zea mays crtRB1 increases β-carotene in maize grain. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.; Rojas, N.P.; Gao, S.; Yan, J.; Pixley, K. Validation of the effects of molecular marker polymorphisms in LcyE and CrtRB1 on provitamin-A concentrations for 26 tropical maize populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.; Hossain, F.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Choudhary, M.; Saha, S.; Bhat, J.S.; Prasanna, B.M.; Gupta, H.S. Development of β-carotene rich maize hybrids through marker-assisted introgression of β-carotene hydroxylase allele. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.; Zunjare, R.U.; Khan, S.; Baveja, A.; Muthusamy, V.; Hossain, F. Marker-assisted introgression of rare allele of β-carotene hydroxylase (crtRB1) gene into elite quality protein maize inbred for combining high lysine, tryptophan and provitamin-A in maize. Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunjare, R.U.; Chhabra, R.; Hossain, F.; Muthusamy, V.; Baveja, A.; Gupta, H.S. Development and validation of multiplex-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of rare alleles of crtRB1 and lcyE governing higher accumulation of provitamin-A in maize kernel. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, M.; Nepolean, T.; Hossain, F.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, H.S. Sequence variation in 3′UTR region of crtRB1 gene and its effect on β-carotene accumulation in maize kernel. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.; Hossain, F.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Saha, S.; Agrawal, P.K.; Gupta, H.S. Genetic analyses of kernel carotenoids in novel maize genotypes possessing rare allele of β-carotene hydroxylase gene. Cereal Res. Commun. 2016, 44, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Gowda, M.M.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Chauhan, H.S.; Baveja, A.; Bhatt, v.; Chand, G.; Bhat, J.S.; Guleria, S.K.; et al. Development of maize hybrids with enhanced vitamin-E, vitamin-A, lysine, and tryptophan through molecular breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 659381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, N.; Chhabra, R.; Chandra, S.; Zunjare, R.U.; Dutta, S.; Chand, G.; Sarika, K.; Devi, E.L.; Kumar, A.; Madhavan, J.; et al. Variation in anthocyanin pigmentation by R1-navajo gene, development and validation of breeder-friendly markers specific to C1-Inhibitor locus for in-vivo haploid production in maize. Mol. Bio Rep. 2023, 50, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henegariu, O.; Heerema, N.A.; Dlouhy, S.R.; Vance, G.H.; Vogt, P.H. Multiplex PCR: Critical parameters and step-by-step protocol. Biotechniques 1997, 23, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katral, A.; Hossain, F.; Zunjare, R.U.; Chhabra, R.; Duo, H.; Kumar, B.; Karjagi, C.G.; Jacob, S.R.; Pandey, S.; Neeraja, C.N.; et al. Multilocus functional characterization of indigenous and exotic inbreds for dgat1-2, fatb, ge2 and wri1a genes affecting kernel oil and fatty acid profile in maize kernels. Gene 2024, 895, 148001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baveja, A.; Chhabra, R.; Panda, K.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Hossain, F. Development and validation of multiplex-PCR assay to simultaneously detect favourable alleles of shrunken2, opaque2, crtRB1 and lcyE genes in marker-assisted selection for maize biofortification. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesha, S.; Avinash, P. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous identification of Ralstoniasolanacearum and Xanthomonasperforans. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, G.J.; Chhabra, R.; Singh, M. Multiplex PCR-based simultaneous amplification of selectable marker and reporter genes for the screening of genetically modified crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5167–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Kumar, P.; Patra, J.K.; Bajpai, V.K. Current perspectives on genetically modified crops and detection methods. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.M.; Huo, N.; Gu, Y.Q.; Luo, M.C.; Ma, Y.; Hane, D.; Lazo, G.R.; Dvorak, J.; Anderson, O.D. BatchPrimer3: A high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer Set | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size and Condition | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Favorable Allele(s) | Unfavorable Allele(s) | |||||
| crtRB1 | Set 1 | S1F | F: TGTGGCCCTTCTTCTTTTGT | 175 bp (S1F-S1R1: no insertion) | 171 bp (S1F-S1R2: 325 bp or 1250 bp insertion), 500 bp (S1F-S1R1: 325 bp insertion), 1096 bp (S1F-S1R2: 1250 bp insertion), and 1425 bp (S1F-S1R1: 1250 bp insertion) | Designed in the present study |
| S1R1 | R1: CAGCTCCATGTACGAATCCA | |||||
| S1R2 | R2: TTTCTTCTCCTGCGTCTTCA | |||||
| Set 2 | S2F | F: GGCCCTTCTTCTTTTGTCCT | 471 bp (S2F-S2R1: no insertion) | 171 bp (S2F-S2R2: 325 bp or 1250 bp insertion), 796 bp (S2F-S2R1: 325 bp insertion), 1096 bp (S2F-S2R2: 1250 bp insertion), and 1721 bp (S2F-S2R1: 1250 bp insertion) | ||
| S2R1 | R1: AACAGCAATACAGGGGACCA | |||||
| S2R2 | R2: TCTTTTCTTCTCCTGCGTCTTC | |||||
| Set 3 | S3F | F: GCAGATACACCACATGGACAA | 544 bp (S3F-S3R1: no insertion) | 213 bp (S3F-S3R2: 325 bp or 1250 bp insertion), 869 bp (S3F-S3R1: 325 bp insertion), 1138 bp (S3F-S3R2: 1250 bp insertion), and 1749 bp (S3F-S3R1: 1250 bp insertion) | ||
| S3R1 | R1: AGCAATACAGGGGACCAGAA | |||||
| S3R2 | R2: TTCACTCACCGGACTGCTAA | |||||
| vte4 | InDel118 | InDel118_F | F: AAAGCACTTACATCATGGGAAAC | 373 bp | 491 bp | Li et al. [18] |
| InDel118_R | R: TTGGTGTAGCTCCGATTTGG | |||||
| S. No. | Activity | Uniplex-PCR for crtRB1 | Uniplex-PCR for vte4 | Multiplex-PCR for crtRB1 + vte4 (INR) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INR | USD | INR | USD | INR | USD | ||
| 1. | DNA isolation | 13.00 | 0.16 | 13.00 | 0.16 | 13.00 | 0.16 |
| 2. | Primer synthesis | 16.512 | 0.21 | 23.39 | 0.29 | 44.66 | 0.56 |
| 3. | PCR plate | 231.80 | 2.90 | 231.80 | 2.90 | 231.80 | 2.90 |
| 4. | Master Mix | 1056.00 | 13.21 | 1056.00 | 13.21 | 1315.00 | 16.45 |
| 5. | Micro tips | 93.10 | 1.16 | 93.10 | 1.16 | 93.10 | 1.16 |
| 6. | Gel electrophoresis | 300 | 3.75 | 300 | 3.75 | 300 | 3.75 |
| 7. | Sub-total | 1710.41 | 21.39 | 1717.29 | 21.48 | 1997.56 | 24.99 |
| 8. | Total cost | 3427.70 INR/42.87 USD | 1997.56 | 24.99 | |||
| Percent (%) reduction | 41.72 | ||||||
| S. No. | Activity | Uniplex-PCR for crtRB1 (Hour) | Uniplex-PCR for vte4 (Hour) | Multiplex-PCR for crtRB1 + vte4 (Hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of PCR | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 2. | Completion of PCR run | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.3 |
| 3. | Completion of gel electrophoresis | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| 4. | Sub-total | 4.5 | 4.5 | 5.8 |
| 5. | Total time | 9.0 | 5.8 | |
| Percent (%) reduction | 35.56 | |||
| Parentage | N | Uniplex | Multiplex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crtRB1 | |||||
| PMI-PV1 (crtRB1crtRB1 & vte4+vte4+) × MGU-vte4-23 (crtRB1+crtRB1+ & vte4vte4) | 141 | CC | Cc | CC | Cc |
| 82 | 59 | 82 | 59 | ||
| vte4 | |||||
| PMI-PV1 (crtRB1crtRB1 & vte4+vte4+) × MGU-vte4-23 (crtRB1+crtRB1+ & vte4vte4) | 141 | VV | Vv | VV | Vv |
| 77 | 64 | 77 | 64 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gowda, M.M.; Muthusamy, V.; Chhabra, R.; Duo, H.; Pal, S.; Gain, N.; Katral, A.; Kasana, R.K.; Zunjare, R.U.; Hossain, F. Development and Validation of Multiplex-PCR Assay for β-Carotene hydroxylase and γ-Tocopherol methyl transferase Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins in Maize for Its Application in Genomics-Assisted Breeding. Plants 2025, 14, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14010142
Gowda MM, Muthusamy V, Chhabra R, Duo H, Pal S, Gain N, Katral A, Kasana RK, Zunjare RU, Hossain F. Development and Validation of Multiplex-PCR Assay for β-Carotene hydroxylase and γ-Tocopherol methyl transferase Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins in Maize for Its Application in Genomics-Assisted Breeding. Plants. 2025; 14(1):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14010142
Chicago/Turabian StyleGowda, Munegowda Manoj, Vignesh Muthusamy, Rashmi Chhabra, Hriipulou Duo, Saikat Pal, Nisrita Gain, Ashvinkumar Katral, Ravindra K. Kasana, Rajkumar U. Zunjare, and Firoz Hossain. 2025. "Development and Validation of Multiplex-PCR Assay for β-Carotene hydroxylase and γ-Tocopherol methyl transferase Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins in Maize for Its Application in Genomics-Assisted Breeding" Plants 14, no. 1: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14010142
APA StyleGowda, M. M., Muthusamy, V., Chhabra, R., Duo, H., Pal, S., Gain, N., Katral, A., Kasana, R. K., Zunjare, R. U., & Hossain, F. (2025). Development and Validation of Multiplex-PCR Assay for β-Carotene hydroxylase and γ-Tocopherol methyl transferase Genes Governing Enhanced Multivitamins in Maize for Its Application in Genomics-Assisted Breeding. Plants, 14(1), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14010142





