Controlled-Release Fertilizer Improving Paddy Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Reducing Soil Residual Nitrogen and Leaching Losses in the Yellow River Irrigation Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Yield of Paddy
2.2. Nitrogen Uptake and N Use Efficiency of Paddy
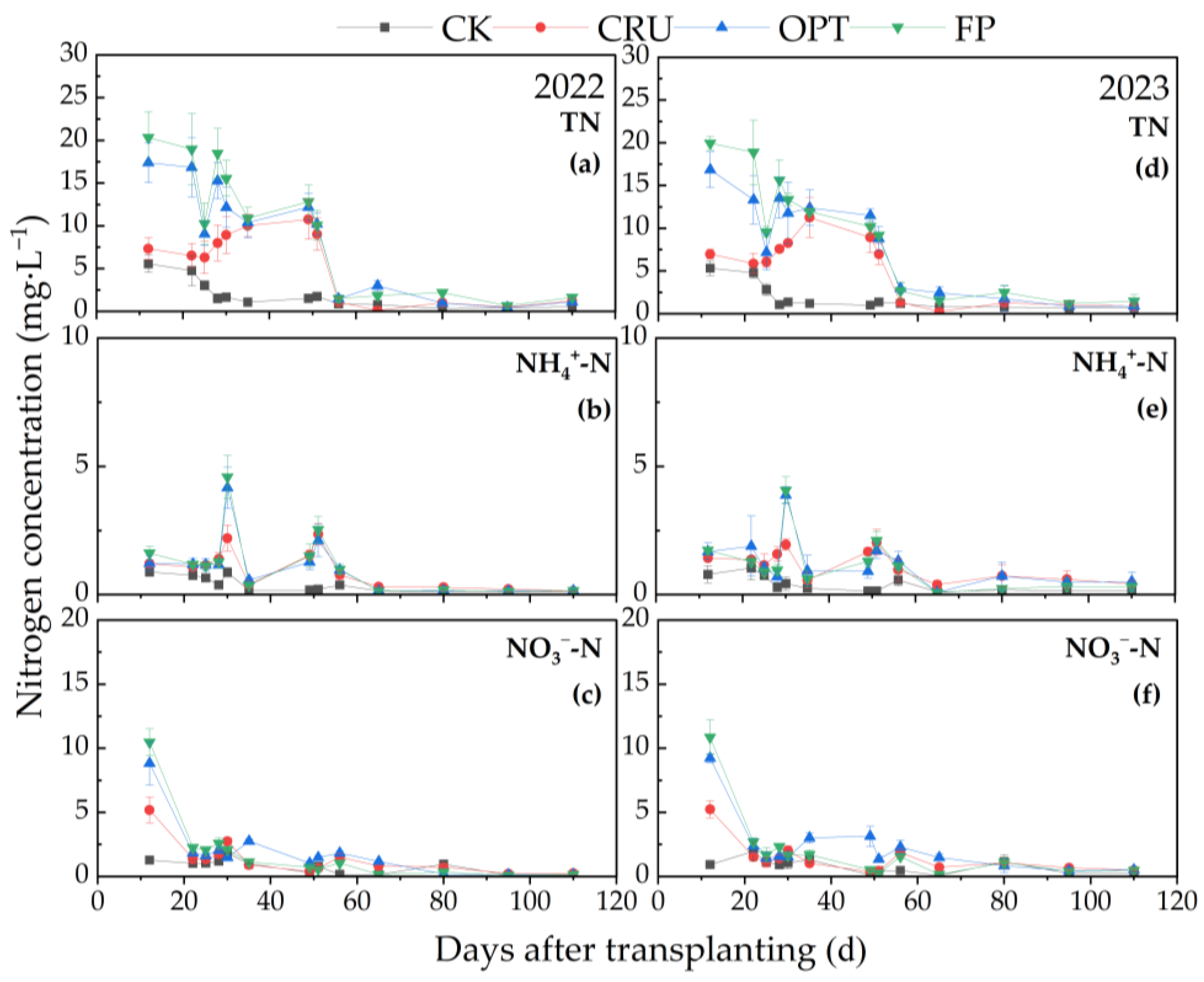
2.3. Nitrogen Concentration in the Surface and Leaching Water
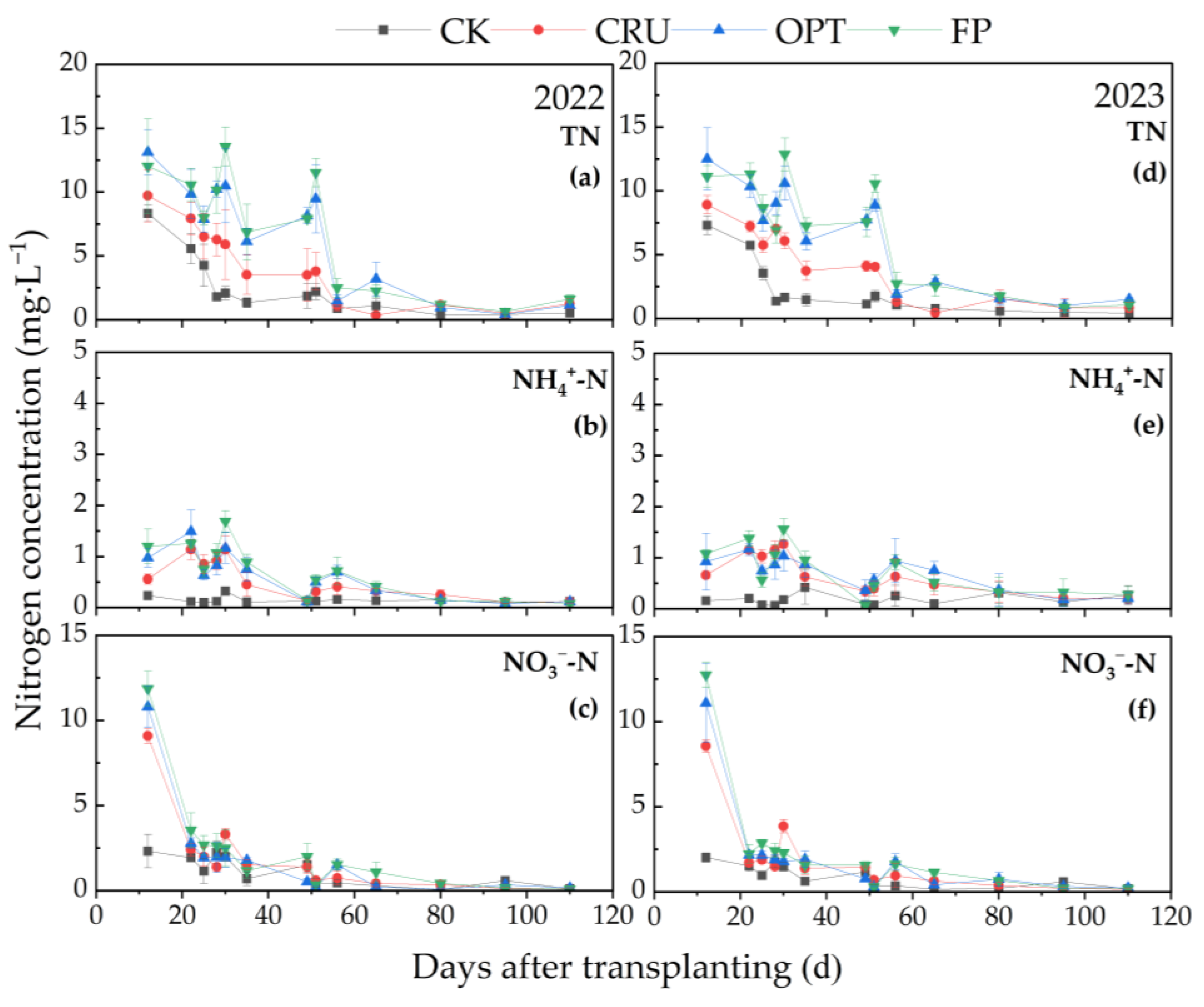
2.4. Amount of N Leached Amount and Leaching Coefficient of Paddy
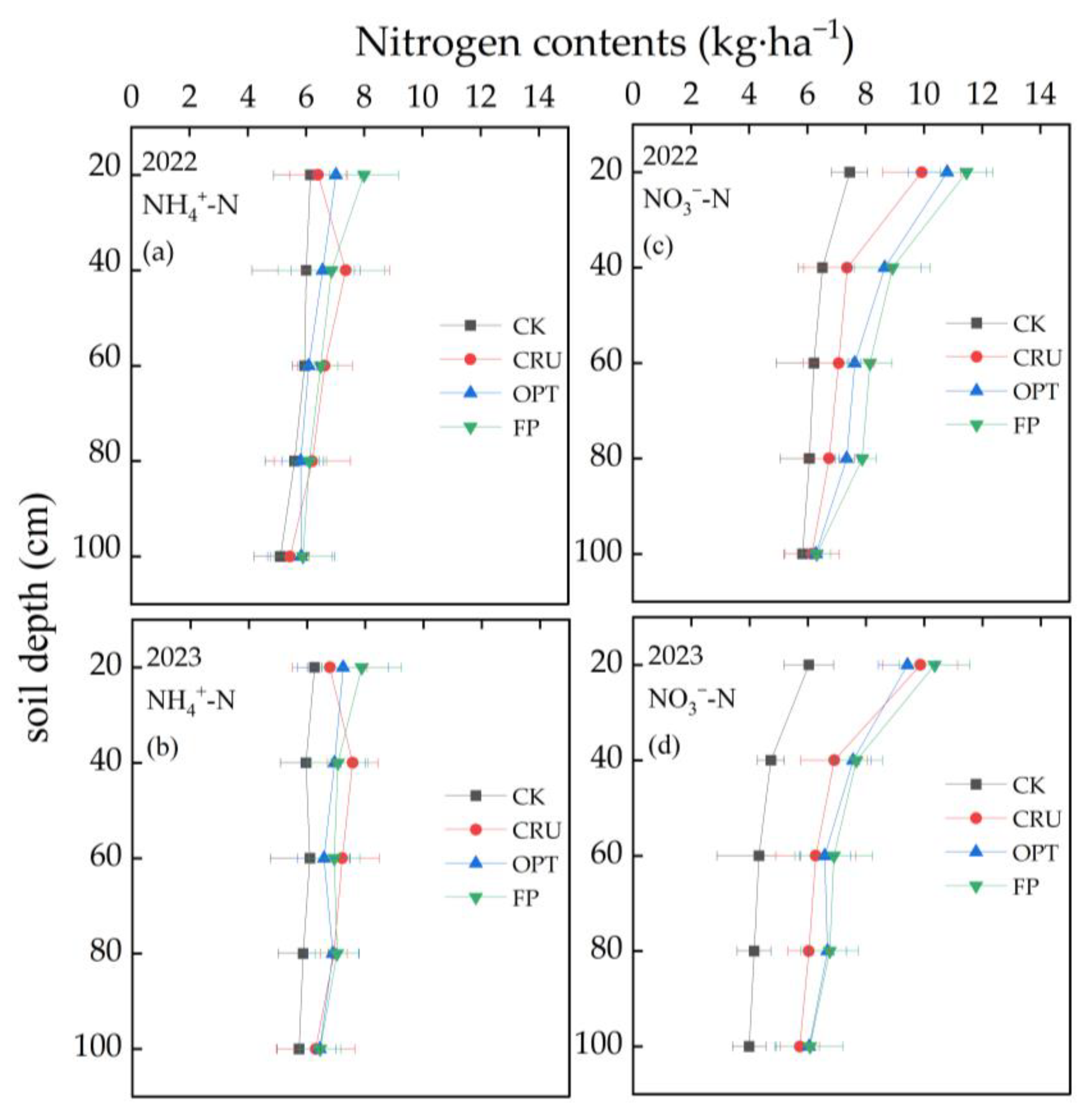
2.5. Residual NH4+-N and NO3−-N Contents in the Soil Profile
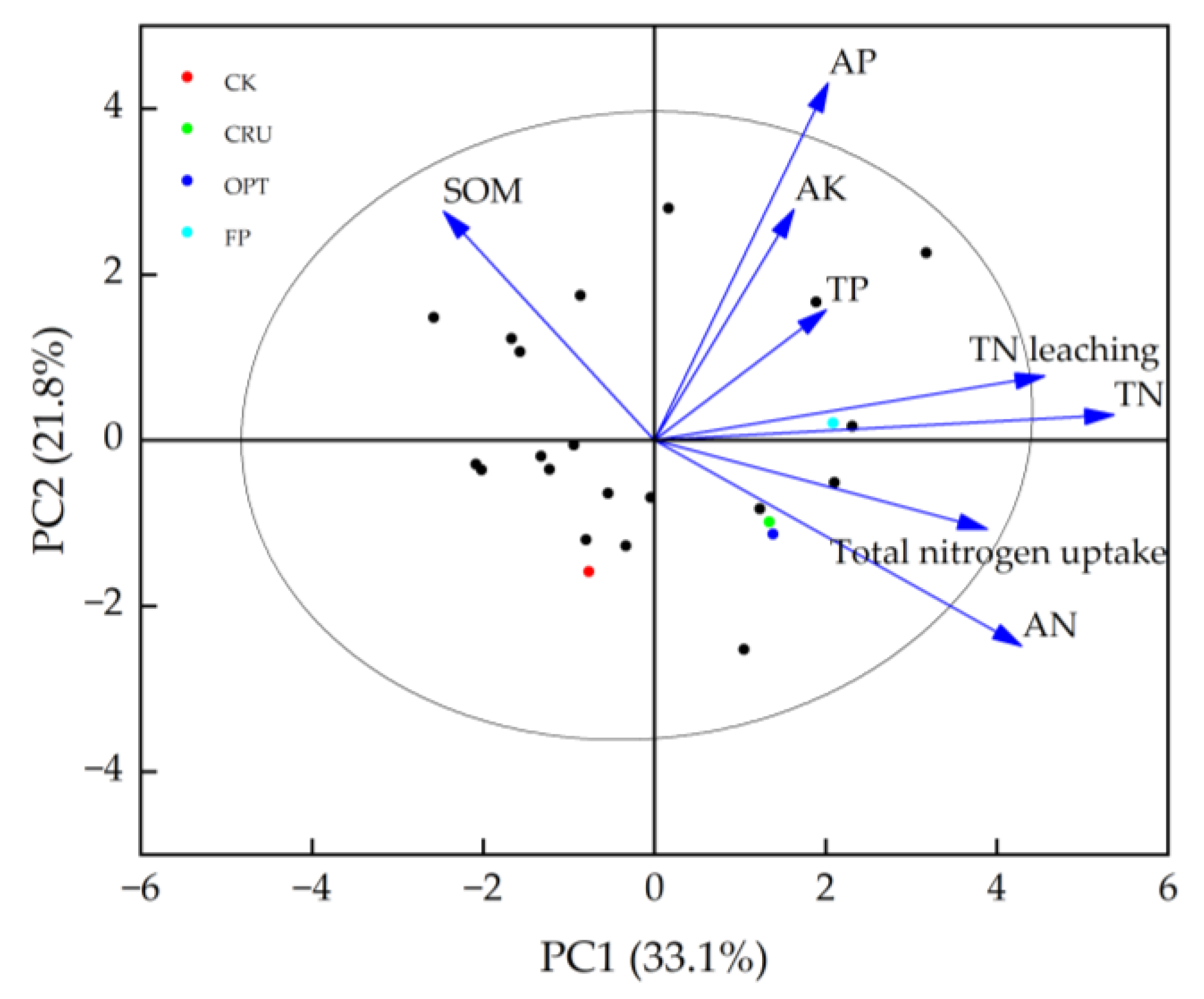
2.6. Relationships Between N Leaching and the Physical–Chemical Properties of Soil
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Optimal N Application on Paddy Yield
3.2. Effects of Optimal N Application on N Leaching Loss
3.3. Effects of Optimal N Application on N Use Efficiency
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Site
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Sampling and Measurements
4.4. Calculations
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, R.S. Effects of nitrogen application rate on rice yield and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency. Fujian Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 54, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.; Chu, C. Nitrogen use efficiency in crops: Lessons from Arabidopsis and rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, F.; Hou, T.-Y. Current status of nitrogen and phosphorus losses and related factors in Chinese paddy fields: A review. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Huo, Z. Research progress and prospect of slow and controlled release fertilizer application technology in rice. China Rice 2023, 29, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of N fertilization pattern on rice yield, N use efficiency and fertilizer–N fate in the Yangtze River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Hua, Z.; Xue, H.; Mei, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, S. Comparison of nitrogen loss weight in ammonia volatilization, runoff, and leaching between common and slow-release fertilizer in paddy field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive nitrogen loss pathways and their effective factors in paddy field in southern China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.-H.; Yu, Y.-L.; Yang, L.-Z. Nitrogen balance and environmental impact of paddy field under different N management methods in Taihu Lake region. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, H.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Q. Effects of different types of fertilizers application on rice grain quality. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 79, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoying, Z.; Qingwen, Z.; Hui, Z.; Hussain, H.A.; Shaaban, M.; Zhengli, Y. Pathways of nitrogen loss and optimized nitrogen management for a rice cropping system in arid irrigation region, northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of water saving irrigation and controlled release nitrogen fertilizer managements on nitrogen losses from paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Q.; Xie, C.; Li, M.; Huang, S. Nitrogen loss from surface runoff and ammonia volatilization from paddy field as impacted by different fertilizers and planting methods. J. Irrig. Drain. 2021, 40, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Lu, J.; Hou, W.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Khan, M.R.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Li, X. Reducing nitrogen losses through ammonia volatilization and surface runoff to improve apparent nitrogen recovery of double cropping of late rice using controlled release urea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11722–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, F.; Zhao, T.; Chen, C.; Hong, Y.; Yang, Z. Effect of postponing N application on rice yield and N losses in Yellow River irrigation area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.P.; Yang, S.Q.; YI, J.; Yang, Z.L. Analysis on current situation of water pollution and pollutant sources in Ningxia Yellow River irrigation region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y. Experimental research on variation feature of three kinds of nitrogen from paddy field in Qingtongxia irrigation area. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 790–794. [Google Scholar]
- She, D.; Hu, L.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Ma, K. Simulation of non-point source pollution losses from farmland in Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Ma, K. Evaluating agricultural non-point source pollution with high-resolution remote sensing technology and SWAT model: A case study in Ningxia Yellow River Irrigation District, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Su, W.; Lu, M. Evaluating regional mean optimal nitrogen rates in combination with indigenous nitrogen supply for rice production. Field Crops Res. 2012, 137, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staugaitis, G.; Viškelis, P.; Rimantas Venskutonis, P. Optimization of application of nitrogen fertilizers to increase the yield and improve the quality of Chinese cabbage heads. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2008, 58, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaojie, W.; Jiarong, L.; Ruolin, L.; Shichen, W.; Jing, M.; Zhenke, Z.; Guangbin, Z.; Hua, X. The impact of nitrogen application rate on rice yield and greenhouse gas emissions of ratoon rice in the Taihu Lake region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wu, L.; Chai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y. Effects of nitrogen application rates on rice grain yield, nitrogen-use efficiency, and water quality in paddy field. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Geng, Y. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, activities of leaf enzymes, and rice yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Kennedy, I. Nitrogen fertilizer losses from rice soils and control of environmental pollution problems. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yu, S.e.; Ma, T.; Ding, J.; He, P.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, G. Effects of water and nitrogen management on water productivity, nitrogen use efficiency and leaching loss in rice paddies. Water 2022, 14, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, R.; Gao, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z. Regulating N Application for Rice Yield and Sustainable Eco-Agro Development in the Upper Reaches of Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 239279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Gu, W.; Liu, H. Field analysis of water and nitrogen fate in lowland paddy fields under different water managements using HYDRUS-1D. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Ronga, X.; Xie, G.; Chang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Effectiveness of a 10-year continuous reduction of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on production, nitrogen loss and utilization of double-cropping rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z. Improving agronomic practices to reduce nitrate leaching from the rice–wheat rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yang, L.; Yan, T.; Xue, F.; Zhao, D. Rice dry matter and nitrogen accumulation, soil mineral N around root and N leaching, with increasing application rates of fertilizer. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, F.; Mao, X.; Yi, J. Controlled-release urea application and optimized nitrogen applied strategy reduced nitrogen leaching and maintained grain yield of paddy fields in Northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1033506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Xu, J.Z.; Luo, Y.F.; Hou, H.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from paddy fields with different water and nitrogen managements. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.T.; Liao, Q.J.H.; Wang, S.W. Statistical analysis and estimation of N leaching from agricultural fields in China. Soils 2011, 43, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.S.; Kou, C.L.; Wang, H.J. Effects of decreasing nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching and vegetable yield in field. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.K.; Sheng, Q.Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, F.H.; Zhong, Z.X.; Fa, S.X.; Hua, T.S.; Hui, C.G.; Fa, L.Y.; De, Z.X. Effects of controlled-release urea on yield of one season middle rice and nitrogen use efficiency. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 31, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Wang, M.-L.; Wang, B.-C.; Li, Y.-D.; Wang, S.-Q. Effects of a single basal application of polymer-coated urea to a wheat field on crop yield, nitrogen use efficiency and NH3 and N2O emissions in eastern China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Geng, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X. Controlled-release urea improved rice yields by providing nitrogen in synchrony with the nitrogen requirements of plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4183–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobermann, A.R. Nitrogen use efficiency-state of the art. Agron.-Fac. Publ. 2005, 6, 316. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Li, X.K.; Lu, J.W.; Xu, W.M.; Yang, Y.Q.; Lu, J.M. Effects of controlled-release urea on yield, nutrient uptaking and nitrogen use efficiency of rice. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2014, 33, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hussain, S.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Li, X. Nitrogen losses, use efficiency, and productivity of early rice under controlled-release urea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, T.; Chen, C.; Hong, Y. Rice yield, nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen leaching losses as affected by long-term combined applications of manure and chemical fertilizers in yellow river irrigated region of ningxia. China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 22–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fageria, N.K.; Santos, A.B.d.; Baligar, V.C. Phosphorus soil test calibration for lowland rice on an Inceptisol. Agron. J. 1997, 89, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsina, J.; Singh, U.; Badaruddin, M.; Meisner, C.; Amin, M. Cultivar, nitrogen, and water effects on productivity, and nitrogen-use efficiency and balance for rice–wheat sequences of Bangladesh. Field Crops Res. 2001, 72, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.; Gines, G.; Dizon, M.; Samson, M.; Alcantara, J. Nitrogen-use efficiency in tropical lowland rice systems: Contributions from indigenous and applied nitrogen. Field Crops Res. 1996, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Yield in 2022 (t∙ha−1) | Yield in 2023 (t∙ha−1) | Average Yield (t∙ha−1) | Ratio of Yield Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.8 ± 0.2 c | 3.0 ± 0.5 b | 3.4 ± 0.2 c | |
| CRU | 8.5 ± 0.6 a | 6.7 ± 0.6 a | 7.6 ± 0.2 a | 125.4 ± 6.1 a |
| OPT | 6.9 ± 0.6 b | 5.7 ± 0.7 a | 6.3 ± 0.5 b | 86.8 ± 15.5 b |
| FP | 7.0 ± 0.3 b | 5.7 ± 0.6 a | 6.3 ± 0.4 b | 87.9 ± 12.7 b |
| Year | Treatment | N Uptake by Paddy Straw (kg∙ha−1) | N Uptake by Paddy Grain (kg∙ha−1) | Total N Uptake (kg∙ha−1) | NUE (%) | NAE (kg∙kg−1) | NPP (kg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | CK | 22.36 ± 6.19 c | 45.23 ± 4.82 c | 67.60 ± 7.56 c | |||
| CRU | 40.53 ± 4.89 a | 98.00 ± 6.97 a | 138.53 ± 3.50 a | 39.41 ± 1.94 a | 26.45 ± 3.40 a | 47.36 ± 3.40 a | |
| OPT | 30.66 ± 2.52 ab | 80.29 ± 5.59 b | 110.95 ± 4.05 b | 20.64 ± 1.93 b | 14.87 ± 2.72 b | 32.80 ± 2.72 b | |
| FP | 32.03 ± 0.73 b | 81.38 ± 8.22 b | 114.41 ± 7.54 b | 19.51 ± 3.14 b | 13.45 ± 1.31 b | 29.13 ± 1.31 b | |
| 2023 | CK | 20.53 ± 6.06 b | 35.23 ± 6.32 b | 55.76 ± 11.93 b | |||
| CRU | 34.12 ± 1.82 a | 82.99 ± 13.77 a | 117.11 ± 15.20 a | 34.08 ± 8.45 a | 20.56 ± 3.39 a | 37.13 ± 3.39 a | |
| OPT | 29.87 ± 0.69 ab | 68.10 ± 8.05 a | 97.97 ± 7.82 a | 20.10 ± 3.72 b | 13.02 ± 3.34 b | 27.22 ± 3.34 b | |
| FP | 29.01 ± 9.78 ab | 64.95 ± 15.53 a | 93.96 ± 17.11 a | 15.91 ± 7.13 b | 11.25 ± 2.29 b | 23.68 ± 2.29 b |
| Year | Treatment | TN Leaching (kg∙ha−1) | TN Leaching Coefficient (%) | NH4+-N Leaching (kg∙ha−1) | NH4+-N Leaching Coefficient (%) | NO3−-N Leaching (kg∙ha−1) | NO3−-N Leaching Coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | CK | 20.30 ± 2.58 e | 1.31 ± 0.10 d | 8.67 ± 1.54 c | |||
| CRU | 32.91 ± 3.76 cd | 7.01 ± 2.09 b | 2.96 ± 0.55 bc | 0.92 ± 2.25 b | 17.05 ± 1.82 b | 4.66 ± 2.16 ab | |
| OPT | 44.01 ± 3.76 bc | 11.29 ± 1.79 b | 2.10 ± 0.09 cd | 0.38 ± 2.19 a | 25.60 ± 4.18 b | 8.06 ± 1.96 b | |
| FP | 48.04 ± 4.17 ab | 11.56 ± 1.74 b | 3.49 ± 0.44 b | 0.91 ± 1.68 ab | 30.11 ± 3.84 ab | 8.93 ± 1.96 b | |
| 2023 | CK | 12.30 ± 2.11 d | 1.09 ± 0.26 c | 6.33 ± 1.12 b | |||
| CRU | 25.14 ± 2.22 c | 7.13 ± 1.24 b | 2.52 ± 0.35 b | 0.79 ± 1.09 a | 14.98 ± 1.55 bc | 4.81 ± 1.46 a | |
| OPT | 35.90 ± 4.81 b | 11.24 ± 2.29 a | 2.23 ± 1.04 b | 0.54 ± 1.83 ab | 23.36 ± 3.27 c | 8.11 ± 1.11 a | |
| FP | 36.77 ± 2.75 b | 10.20 ± 1.15 ab | 3.27 ± 0.43 bc | 0.91 ± 1.21 a | 27.53 ± 2.19 b | 8.83 ± 0.94 a |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | Total Porosity (%) | Total Salt (g·kg−1) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Total N (g·kg−1) | Available N (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 1.36 | 48.7 | 0.49 | 10.74 | 1.01 | 38.66 |
| 20~40 | 1.36 | 48.8 | 0.40 | 8.71 | 0.85 | 26.98 |
| 40~60 | 1.53 | 42.3 | 0.39 | 5.26 | 0.40 | 25.12 |
| 60~80 | 1.64 | 39.0 | 0.35 | 4.41 | 0.31 | 24.31 |
| 80~100 | 1.44 | 45.4 | 0.31 | 3.15 | 0.29 | 23.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Yue, X.; Liang, X.; Hong, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, C.; Liu, R. Controlled-Release Fertilizer Improving Paddy Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Reducing Soil Residual Nitrogen and Leaching Losses in the Yellow River Irrigation Area. Plants 2025, 14, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030408
He J, Wang Y, Li H, Ma J, Yue X, Liang X, Hong Y, Wang F, Hu C, Liu R. Controlled-Release Fertilizer Improving Paddy Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Reducing Soil Residual Nitrogen and Leaching Losses in the Yellow River Irrigation Area. Plants. 2025; 14(3):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030408
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jingjing, Ying Wang, Hong Li, Junhua Ma, Xiang Yue, Xiangyu Liang, Yu Hong, Fang Wang, Chenxia Hu, and Ruliang Liu. 2025. "Controlled-Release Fertilizer Improving Paddy Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Reducing Soil Residual Nitrogen and Leaching Losses in the Yellow River Irrigation Area" Plants 14, no. 3: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030408
APA StyleHe, J., Wang, Y., Li, H., Ma, J., Yue, X., Liang, X., Hong, Y., Wang, F., Hu, C., & Liu, R. (2025). Controlled-Release Fertilizer Improving Paddy Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Reducing Soil Residual Nitrogen and Leaching Losses in the Yellow River Irrigation Area. Plants, 14(3), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030408





