Effects of Modified Biochar on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Brassica chinensis L. in Cadmium Contaminated Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Modified Biochar
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Measurement Methods
2.3.1. Soil Analysis
2.3.2. Plant Parameters
2.3.3. Nutrition Contents in Plants
2.3.4. Plant Quality
2.3.5. Cadmium Content in Plants
2.4. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Physicochemical Properties and Cd Bioavailability in Soils
3.2. Growth of Pakchoi
3.2.1. Effects of Modified Biochar on Chlorophyll Contents in Pakchoi
3.2.2. The Effects of Modified Biochar on Plant Height, Root Length and Biomass of Pakchoi
3.3. Contents of Macronutrients in Pakchoi
3.4. Nutritional Quality of Pakchoi
3.4.1. Effects of Modified Biochar on Soluble Protein Contents in Pakchoi
3.4.2. Effects of Modified Biochar on Nitrate Content in Pakchoi
3.4.3. Effects of Modified Biochar on Soluble Sugar Contents in Pakchoi
3.4.4. Effects of Modified Biochar on Vitamin C Content in Pakchoi
3.5. Effects of Modified Biochar on Cd Accumulation in Pakchoi
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.F.; Gao, B.; Hao, H.; Zhou, H.D.; Lu, J.; Sun, K. Lead Contamination in Sediments in the Past 20 Years: A Challenge for China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lamb, D.; Paneerselvam, P.; Choppala, G.; Bolan, N.; Chung, J.W. Role of Organic Amendments on Enhanced Bioremediation of Heavy Metal (loid) Contaminated Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, H.A.; Li, X.; Jeyakumar, P.; Wei, L.; Huang, L.X.; Huang, Q.; Kamran, M.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hou, D.Y.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Influence of Biochar and Soil Properties on Soil and Plant Tissue Concentrations of Cd and Pb: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Z.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.X.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils by Biochar: Mechanisms, Potential Risks and Applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Fu, R.B.; Wang, J.X.; Shi, Y.X.; Guo, X.P. Chemical Stabilization Remediation for Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils on the Latest Decade: Available Stabilizing Materials and Associated Evaluation Methods—A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, U.; Qayyum, M.F.; Shah, M.H.R.; Danish, S.; Shahzad, A.N.; Malik, S.A.; Mahmood, S. Growth, Survival, and Heavy Metal (Cd and Ni) Uptake of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) and Fenugreek (Trigonella corniculata) in a Biochar-Amended Sewage-Irrigated Contaminated Soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.J.; Lamb, D.; Naidu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Yan, Y.B.; Ok, Y.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Choppala, G. Cadmium Solubility and Bioavailability in Soils Amended with Acidic and Neutral Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Jaoude, L.; Castaldi, P.; Nassif, N.; Pinna, M.V.; Garau, G. Biochar and Compost as Gentle Remediation Options for the Recovery of Trace Elements-Contaminated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.R.; Mulder, J.; Hale, S.E.; Martinsen, V.; Schmidt, H.P.; Cornelissen, G. Biochar Improves Maize Growth by Alleviation of Nutrient Stress in a Moderately Acidic Low-Input Nepalese Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.W.; Yin, S.J.; Suo, F.Y.; Xu, Z.C.; Chu, D.P.; Kong, Q.X.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, Y.Q.; Liu, L. Biochar and Fertilizer Improved the Growth and Quality of the Ice Plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) Shoots in a Coastal Soil of Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 144893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.L.; Yang, D.X.; Luo, J.; Williams, P.N. Rice Rhizospheric Effects on the Bioavailability of Toxic Trace Elements during Land Application of Biochar. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7344–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, A.F.; Li, T.; Wu, X.X. Effects of Passivators on Artemisia selengensis Yield and Cd Stabilization in a Contaminated Soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunovic, B.; Gonzales, H.B.; Ravi, S.; Sharratt, B.S.; Mohanty, S.K. Dynamic Effects of Biochar Concentration and Particle Size on Hydraulic Properties of Sand. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Tan, W.K.; Du, Y.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Liang, X.; Lei, J.J.; Striegel, L.; Weber, N.; Rychlik, M.; Ong, C.N. Nutritional Metabolites in Brassica Rapa Subsp. Chinensis Var. Parachinensis (Choy sum) at Three Different Growth Stages: Microgreen, Seedling and Adult Plant. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Guo, H.T.; Ma, Y.B.; Wang, L.Q.; Wei, D.P.; Hua, L.O. Genotypic Variations in the Accumulation of Cd Exhibited by Different Vegetables. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.J.; Lu, X.; Yang, Z.Q.; Chen, B.F.; Geng, S.F.; Fan, G.P.; Gao, Y.; Ying, X.L. Adsorption Characteristics of Composite Modified Biochar and Its Passivation Effect on Farmland Soil with Light to Moderate Cadmium Pollution. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 40, 457–468. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.S.; Tian, L.; Chang, C.L.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.J.; Tran, L.S.P.; Tian, C.J. Grass and Maize Vegetation Systems Restore Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.J.; Zhou, W.X.; Wang, S.F.; Li, Y.T.; Cao, Y.G. The Influence of Soil Erodibility and Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity on Soil Nutrients in the Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23739-2009; Soil Quality—Analysis of Available Lead and Cadmium Contents in Soils—Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, china, 2009.
- Pandey, V.; Patel, A.; Patra, D.D. Biochar Ameliorates Crop Productivity, Soil Fertility, Essential Oil Yield and Aroma Profiling in Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Duigan, S.P.; Berlyn, G.P. An Evaluation of Noninvasive Methods to Estimate Foliar Chlorophyll Content. New Phytol. 2002, 153, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, C.A.; Sword, G.A.; Lenhart, P.A.; Burkness, E.; Hutchison, W.D.; Behmer, S.T. Quantifying Plant Soluble Protein and Digestible Carbohydrate Content, Using Corn (Zea mays) as an Exemplar. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, e58164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neata, G.; Hoza, G.; Teodorescu, R.I.; Basaraba, A.; Petcuci, A.; Sima, R. Phosphorus, Potassium and Nitrate Contents in Fruit of Pickling Cucumbers Grown in a High Tunnel. Notul. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca. 2016, 44, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salehi, A.; Tasdighi, H.; Gholamhoseini, M. Evaluation of Proline, Chlorophyll, Soluble Sugar Content and Uptake of Nutrients in the German Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) under Drought Stress and Organic Fertilizer Treatments. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.; Buret, M.; Garchery, C.; Carretero, Y.; Causse, M. Technique for Rapid, Small-Scale Analysis of Vitamin C Levels in Fruit and Application to a Tomato Mutant Collection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6159–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 5009.15-2023; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Cadmium in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Rees, F.; Simonnot, M.O.; Morel, J.L. Short-Term Effects of Biochar on Soil Heavy Metal Mobility Are Controlled by Intra-Particle Diffusion and Soil pH Increase. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2014, 65, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Q.L.; Hu, H.Q. Cadmium Mobility, Uptake and Anti-Oxidative Response of Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatic) under Rice Straw Biochar, Zeolite and Rock Phosphate as Amendments. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Ren, L.H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.L.; Chen, A.W. Physicochemical Features, Metal Availability and Enzyme Activity in Heavy Metal-Polluted Soil Remediated by Biochar and Compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Hussain, Q.; Hayat, R.; Ahmad, M.; Azeem, M.; Alvi, S.; Chaudhry, A.N.; Masood, S.; Khalid, R.; Jehan, S.; et al. Deashed Biochar as N-Carrier Extended the N-Release by Inhibiting N-Losses in Calcareous Soils. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2023, 13, 9549–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Dai, K. Ecological Restoration of an Acidic Cd Contaminated Soil Using Bamboo Biochar Application. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, X.D. Effect of KOH-Enhanced Biochar on Increasing Soil Plant-Available Silicon. Geoderma 2018, 321, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Park, J.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.D.; Zhao, Z.P.; Song, F.M.; Tang, B. Pyrolysis Temperature Affects Dissolved Phosphorus and Carbon Levels in Alkali-Enhanced Biochar and Its Soil Applications. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Su, L.Z.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L. Effect of Different Types of Phosphate Fertilizer on Phosphorus Absorption and Desorption in Acidic Red Soil of Southwest China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.M.; Li, J.X.; Pei, H.H.; Li, Q.H.; Cheng, D.M.; Zhou, J.; Pei, G.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, F.W. Effective Remediation and Phytotoxicity Assessment of Oxytetracycline and Cd Co-Contaminated Soil Using Biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A. Photosynthesis, Grain Yield, and Nitrogen Utilization in Rice and Wheat. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.Y.; Yang, F.; Cen, R.; Liu, J.; Qu, Z.Y.; Miao, Q.F.; Chen, H.Y. Effects of Straw Biochar Application on Soil Temperature, Available Nitrogen and Growth of Corn. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Wirth, S.; Halwani, M.; Ibrahim, M.F.M.; El Azab, I.H.; El-Mogy, M.M.; Elkelish, A. Growth Response of Ginger (Zingiber officinale), Its Physiological Properties and Soil Enzyme Activities after Biochar Application under Greenhouse Conditions. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudari, A.; Mayane, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Colinet, G.; Oukarroum, A. Photosynthetic Performance and Nutrient Uptake under Salt Stress: Differential Responses of Wheat Plants to Contrasting Phosphorus Forms and Rates. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1038672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciri, R.; Chtouki, M.; Oukarroum, A. Mechanisms of Cadmium Mitigation in Tomato Plants under Orthophosphate and Polyphosphate Fertilization Regimes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battie-Laclau, P.; Laclau, J.P.; Beri, C.; Mietton, L.; Muniz, M.R.A.; Arenque, B.C.; Piccolo, M.D.C.; Jordan-Meille, L.; Bouillet, J.P.; Nouvellon, Y. Photosynthetic and Anatomical Responses of Eucalyptus grandis Leaves to Potassium and Sodium Supply in a Field Experiment. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbna, G.H.D.; She, D.L.; Liu, Z.P.; Elshaikh, N.A.; Shao, G.C.; Timm, L.C. Effects of Deficit Irrigation and Biochar Addition on the Growth, Yield, and Quality of Tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 222, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, L.X.; Sun, Y.X. Effects of Copper and Florfenicol on nirS- and nirK-Type Denitrifier Communities and Related Antibiotic Resistance in Vegetable Soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguntunde, P.G.; Abiodun, B.J.; Ajayi, E.A.; van de Giesen, N. Effects of charcoal production on soil physical properties in Ghana. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Ma, F.; Tankpa, V.; Bai, S.S.; Guo, X.M.; Wang, X. Mechanisms and reutilization of modified biochar used for removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.S.; Hur, J. Biochar-induced priming effects in soil via modifying the status of soil organic matter and microflora: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, U.; Saliba-Colombani, V.; Loudet, O.; Belluomo, P.; Moreau, L.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Morot-Gaudry, J.F.; Maselaux-Daubresse, U. Leaf yellowing and anthocyanin accumulation are two genetically independent strategies in response to nitrogen limitation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H.Y. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J. A handful of carbon. Nature 2007, 447, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebdelfar, N.; Khorasani, R.; Astaraei, A. Effect of some additives on heavy metals behavior and phytoavailability in municipal solid waste compost-amended soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, C.H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, B. Temperature- and duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: Characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern China. Soil. Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.N.H.; Hasan, M.; Uddain, J.; Subramaniam, S. Impact of application of Trichoderma and biochar on growth, productivity and nutritional quality of tomato under reduced N-P-K fertilization. AOAS 2020, 65, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Kumari, P.; Yadav, S.; Brestic, M.; Rastogi, A. Phytohormone priming: Regulator for heavy metal stress in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterumici, C.M.; Rosso, D.; Montoneri, E.; Ginepro, M.; Baglieri, A.; Novotny, E.H.; Kwapinski, W.; Negre, M. Processed vs. non-processed biowastes for agriculture: Effects of post-harvest tomato plants and biochar on radish growth, chlorophyll content and protein production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8826–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhan, L.P.; Xu, X.T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.B.; Yan, X.Y.; Xiong, Z.Q. Biochar and organic substitution improved net ecosystem economic benefit in intensive vegetable production. Biochar 2022, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlamynck, R.; de Souza, M.F.; Bog, M.; Leenknegt, J.; Eeckhout, M.; Meers, E. Effect of the growth medium composition on nitrate accumulation in the novel protein crop Lemna minor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Tabatabaei, Z.; Rigi, A.M.; Shahsavani, S.; Shahsavani, E.; Derakhshan, Z.; Khaneghah, A.M. Nitrate levels in Iranian potatoes and tomatoes: Application of deterministic and probabilistic approaches potential health risks. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A.Q. One-pot fabrication of multifunctional superparamagnetic attapulgite/Fe3O4/polyaniline nanocomposites served as an adsorbent and catalyst support. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Huang, D.L.; Wan, J.; Xue, W.J.; Lei, L.; Wen, X.F.; Liu, X.G.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Chloro-phosphate impregnated biochar prepared by co-precipitation for the lead, cadmium and copper synergic scavenging from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Soteriou, G.A.; Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y. The occurrence of nitrate and nitrite in Mediterranean fresh salad vegetables and its modulation by preharvest practices and postharvest conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Cao, L.P.; Luo, X.; Xiong, J.H.; Ruan, R.G. Assessment of potential nitrite safety risk of leafy vegetables after domestic cooking. Foods 2021, 10, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivelli, A.R.; Libutti, A. Effect of biochar and inorganic or organic fertilizer co-application on soil properties, plant growth and nutrient content in swiss chard. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, T.S.; Babalar, M. The effect of nitrate and plant size on nitrate uptake and in vitro nitrate reductase activity in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa cv. Selva). Sci. Hortic. 2007, 112, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xiong, J.; Tao, L.X.; Cao, Z.Z.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J.P.; Yu, X.Y.; Fu, G.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Lu, Y.L. Regulatory mechanisms of nitrogen (N) on cadmium (Cd) uptake and accumulation in plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 35186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marousek, J.; Kolár, L.; Vochozka, M.; Stehel, V.; Marousková, A. Biochar reduces nitrate level in red beet. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18200–18203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Ning, L.F.; Xun, M.; Feng, F.; Li, P.; Yue, S.Q.; Song, J.F.; Zhang, W.W.; Yang, H.Q. Biochar can increase nitrogen use efficiency of Malus hupehensis by modulating nitrate reduction of soil and root. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2019, 135, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble sugars: Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Li, B.S.; Zhang, J.L.; Christie, P.; Li, X.L. Organic fertilizer application and Mg fertilizer promote banana yield and quality in an Udic Ferralsol. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.P.; Wang, J.Z.; Han, X.P.; Chen, R.; Xue, X.M. Effects of spraying calcium fertilizer on photosynthesis, mineral content, sugar-acid metabolism and fruit quality of Fuji apples. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Hengeler, C.; Marschner, H. Changes in phloem export of sucrose in leaves in response to phosphorus, potassium and magnesium-deficiency in bean-plants. J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakourou, M.C.; Taoukis, P.S. Effect of alternative preservation steps and storage on vitamin C stability in fruit and vegetable products: Critical review and kinetic modelling approaches. Foods 2021, 10, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.W.; Ding, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.Z. Effects of biochar application on soil organic carbon composition and enzyme activity in paddy soil under water-saving irrigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.R.; Zheng, W.; Lei, T.; Liu, X.S.; Hui, M.X. The effect of different soil amendments on soil properties and on the morphological and physiological characteristics of Chinese cabbage. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.Z.; Cizer, Ö.; Pontikes, Y.; Heath, A.; Patureau, P.; Bernal, S.A.; Marsh, A.T.M. Advances in alkali-activation of clay minerals. Cement Concrete. Res. 2020, 132, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dai, J.H.; Wang, L.J.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. First principles study of structural stability against the distribution of Mg and Al atoms and adsorption behaviors of heavy metals of attapulgite. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 169, 109106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Q. Effects of ionized brackish water and polyacrylamide application on infiltration characteristics and improving water retention and reducing soil salinity. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 101, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Teng, L.L.; Wei, S.Q.; Deng, L.L.; Luo, Z.B.; Chen, Y.P.; Flanagan, D.C. Application of polyacrylamide to reduce phosphorus losses from a Chinese purple soil: A laboratory and field investigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Ok, Y.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of polyacrylamide, biopolymer and biochar on the decomposition of 14C-labelled maize residues and on their stabilization in soil aggregates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, B.; Jiao, L.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, B.X.; Sun, H.W. Preparation of ball-milled phosphorus-loaded biochar and its highly effective remediation for Cd- and Pb-contaminated alkaline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Farhangi-Abriz, S. Biochar related treatments improved physiological performance, growth and productivity of Mentha crispa L. plants under fluoride and cadmium toxicities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 194, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard—Limits of Contaminants in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
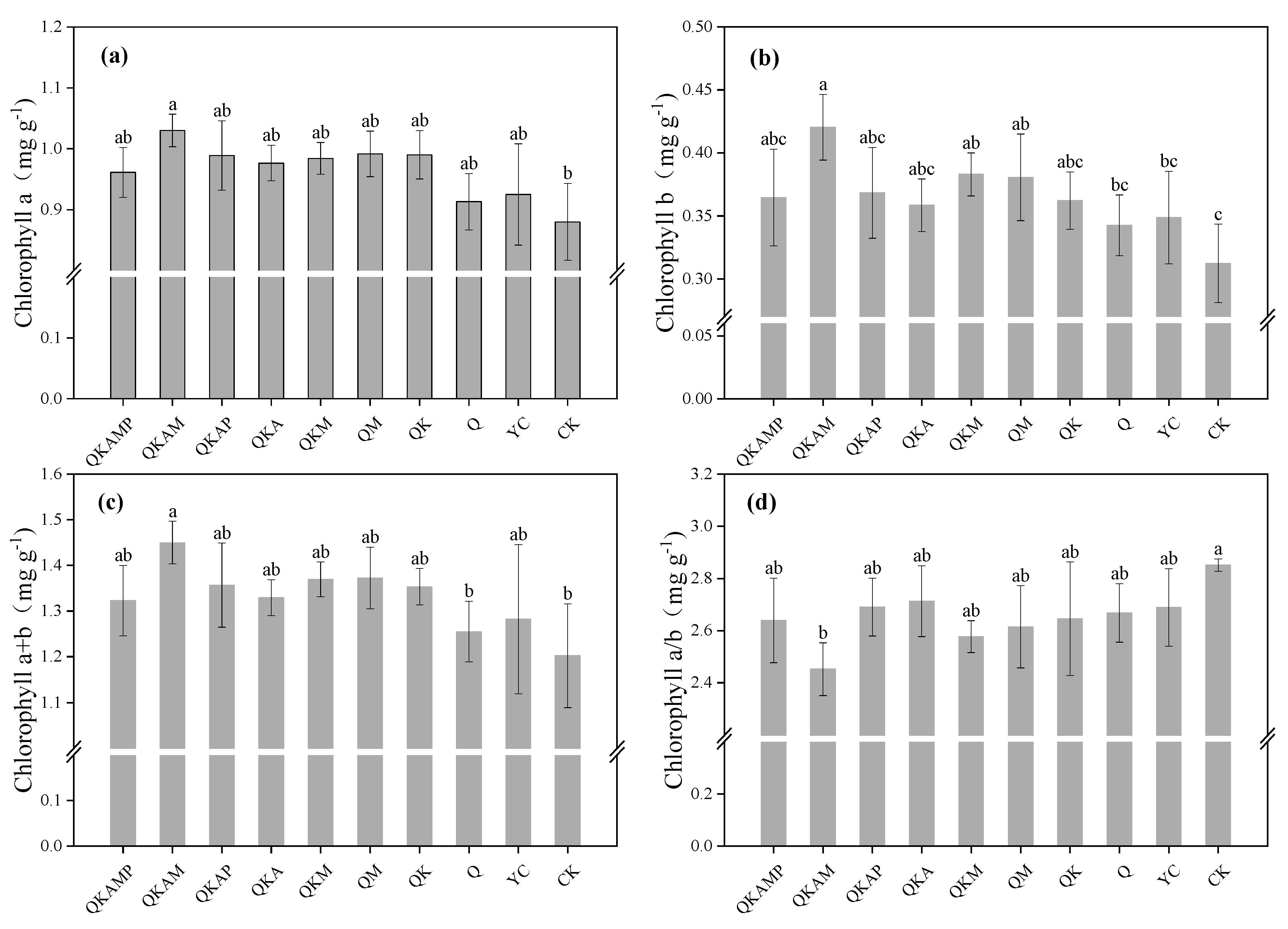
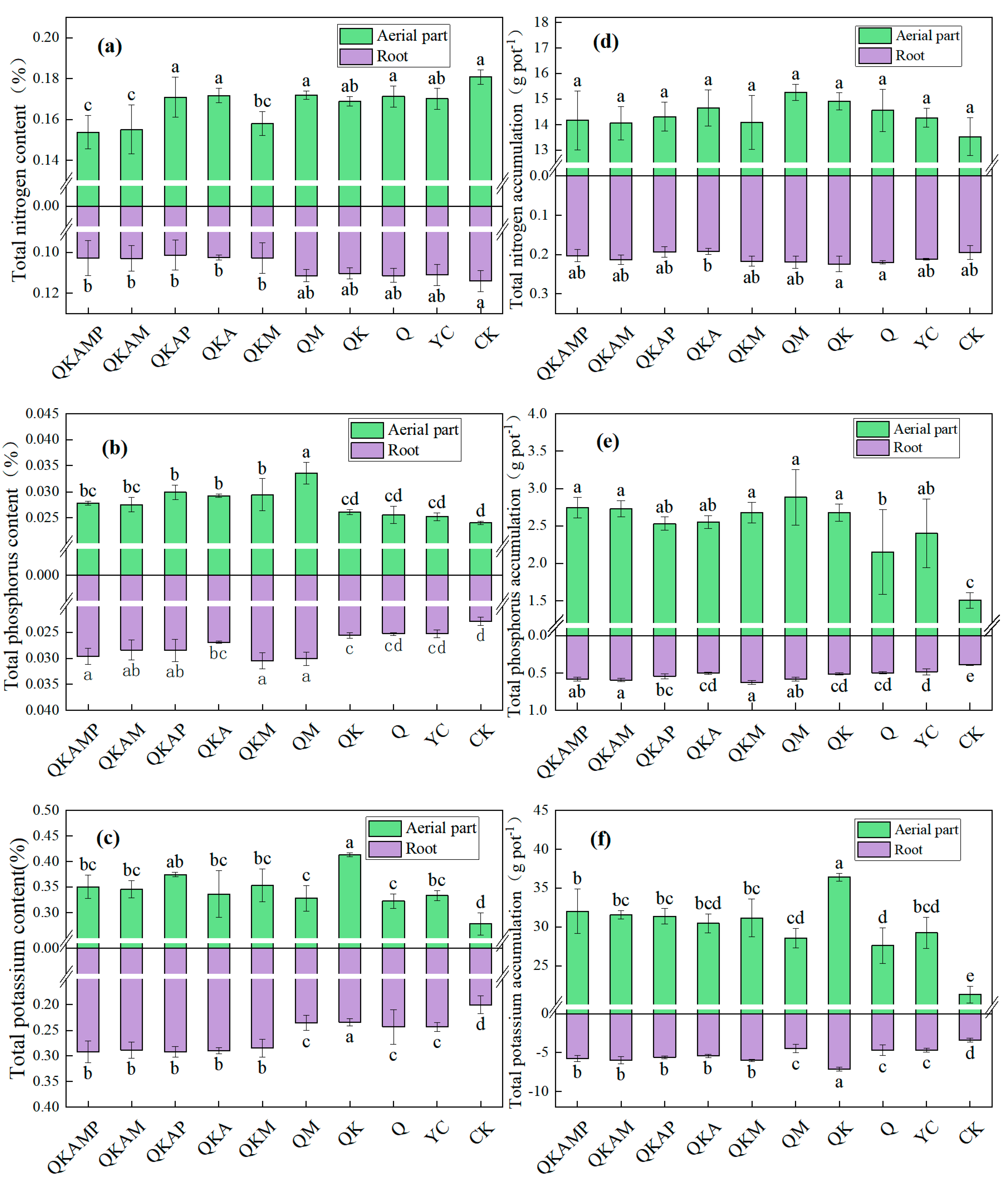
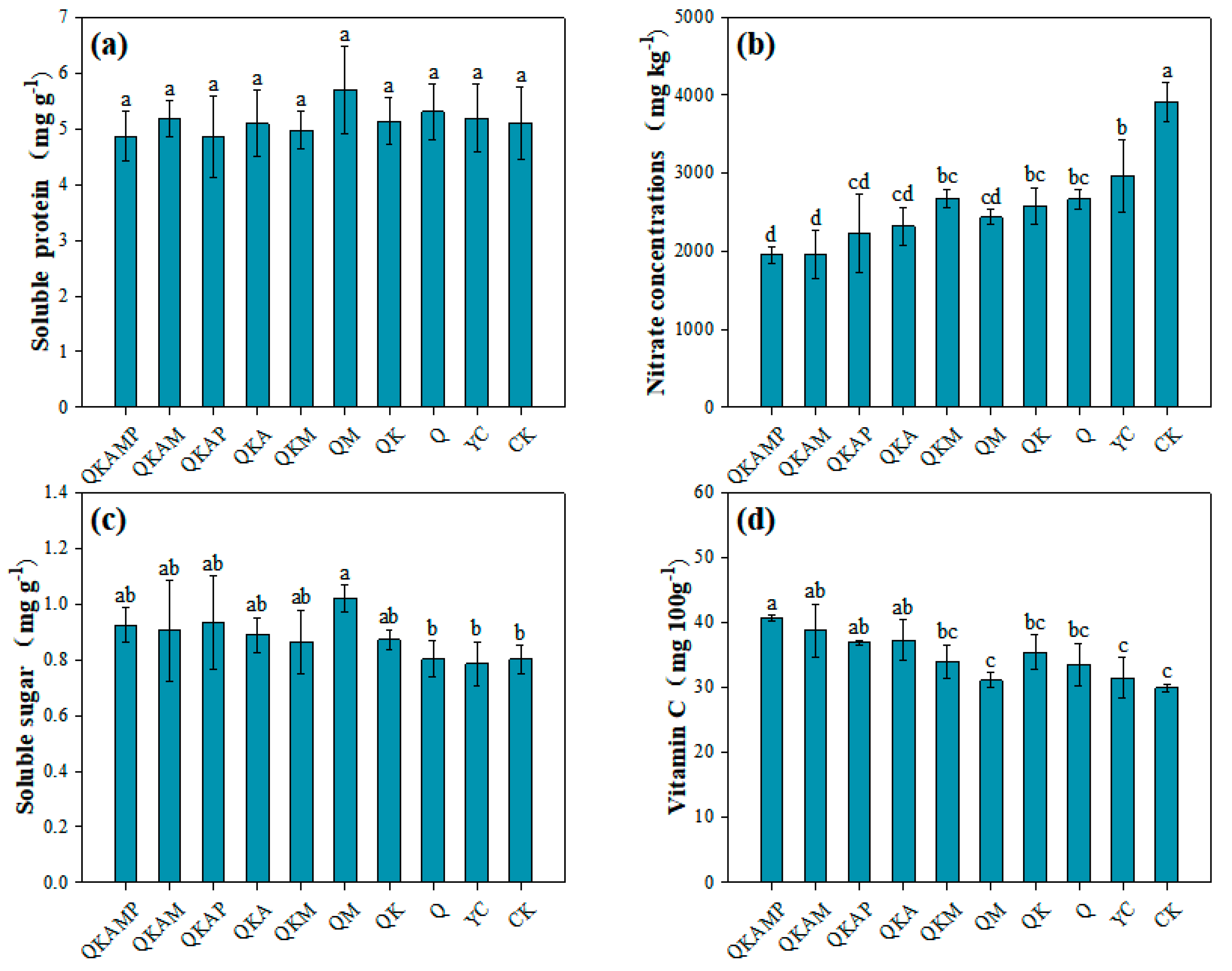
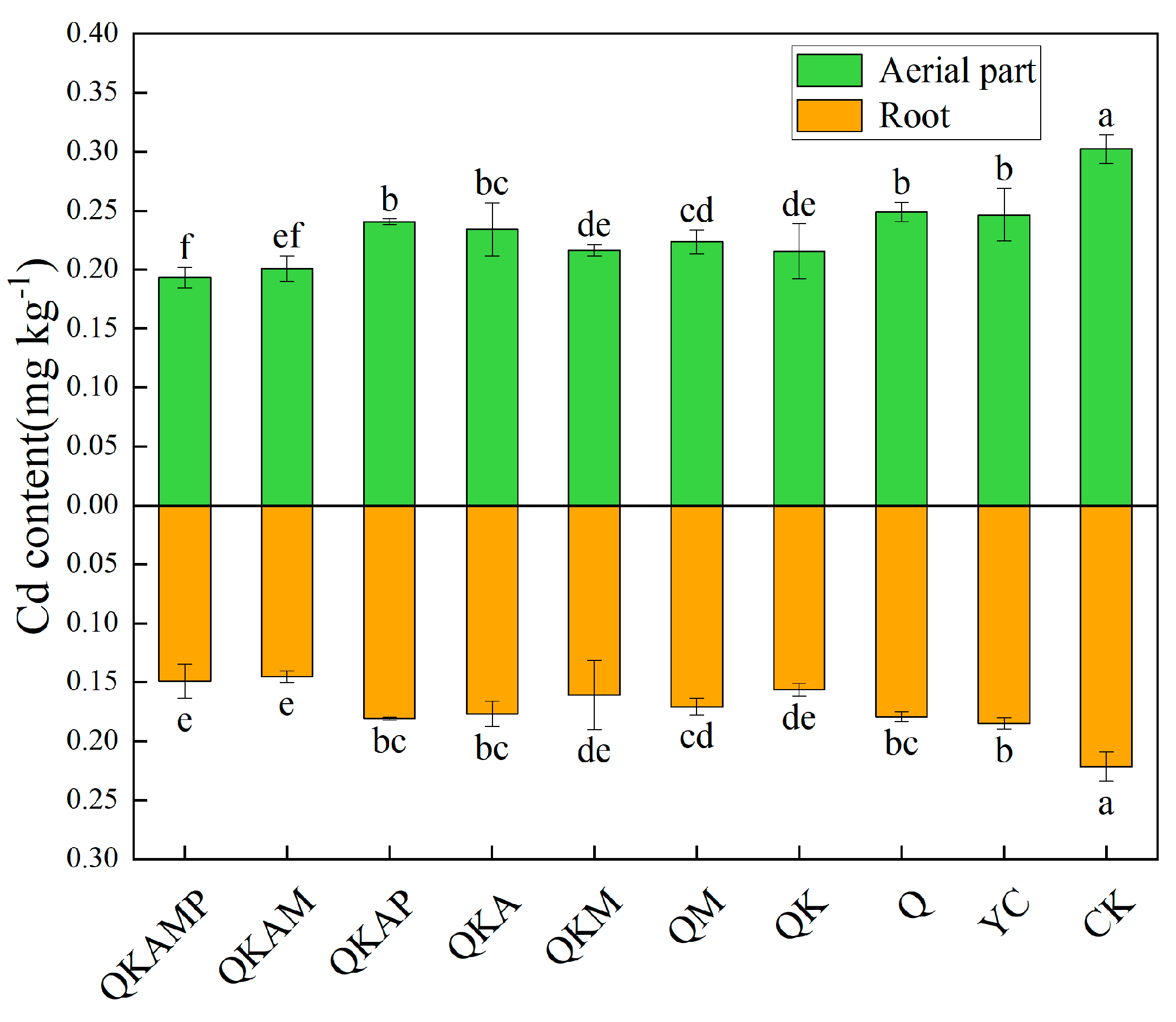
| Treatment | Biochar Modification Ratio (Mass Ratio) | Treatment Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated soil | - | CK |
| Bulk Biochar (unmodified) | 10:0 | YC |
| Biochar (ball-milled modified) | 10:0 | Q |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide modified by ball milling | 10:1 | QK |
| Biochar + Calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer modified by ball milling | 10:1 | QM |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide + Attapulgite modified by ball milling | 10:0.5:0.5 | QKA |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide + Calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer modified by ball milling | 10:0.5:0.5 | QKM |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide + Attapulgite + Calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer modified by ball milling | 10:0.5:0.3:0.2 | QKAM |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide +Attapulgite + Polyacrylamide (PAM1200-) modified by ball milling | 10:0.5:0.5:0.005 | QKAP |
| Biochar + Potassium hydroxide +Attapulgite + Calcium magnesium phosphate + Polyacrylamide (PAM1200-) Modified by ball milling | 10:0.5:0.3:0.2:0.005 | QKAMP |
| Treatments | pH | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Cadmium (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QKAMP | 7.78 a | 1.98 ab | 77.09 b | 257.13 b | 42.10 c | 0.83 f |
| QKAM | 7.72 ab | 1.99 a | 76.00 b | 258.22 b | 42.63 c | 0.85 ef |
| QKAP | 7.46 d | 1.99 a | 78.48 ab | 246.25 b | 38.38 de | 0.88 ef |
| QKA | 7.49 d | 1.98 a | 76.47 b | 253.26 b | 38.99 d | 0.88 de |
| QKM | 7.71 b | 1.99 a | 79.86 ab | 255.67 b | 52.26 b | 0.87 de |
| QM | 7.63 c | 1.94 b | 82.65 a | 90.50 c | 58.18 a | 0.87 de |
| QK | 7.76 ab | 1.97 ab | 78.87 ab | 362.50 a | 35.93 ef | 0.90 d |
| Q | 7.25 e | 1.97 ab | 78.93 ab | 83.00 c | 35.82 ef | 0.95 c |
| YC | 7.28 e | 1.99 a | 80.21 ab | 91.00 c | 35.05 f | 1.00 b |
| CK | 7.07 f | 1.84 c | 33.58 c | 74.00 c | 35.41 f | 1.11 a |
| Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | Root Length (cm) | Arial Part Fresh Weight (g pot−1) | Root Fresh Weight (g pot−1) | Aerial Part Dry Weight (g pot−1) | Root Dry Weight (g pot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QKAMP | 21.42 ± 0.91 a | 10.55 ± 0.35 a | 111.85 ± 5.59 ab | 12.54 ± 0.15 b | 9.14 ± 0.57 a | 1.97 ± 0.03 ab |
| QKAM | 21.20 ± 0.62 ab | 10.33 ± 1.06 a | 109.56 ± 3.15 ab | 13.78 ± 0.42 a | 9.09 ± 0.45 a | 2.07 ± 0.13 ab |
| QKAP | 21.54 ± 0.61 a | 10.06 ± 0.84 a | 110.34 ± 8.35 ab | 12.68 ± 0.30 b | 8.42 ± 0.36 a | 1.91 ± 0.11 abc |
| QKA | 20.89 ± 0.18 ab | 10.16 ± 1.01 a | 107.13 ± 3.14 b | 12.81 ± 0.33 b | 8.49 ± 0.35 a | 1.87 ± 0.08 bc |
| QKM | 21.32 ± 0.26 a | 9.56 ± 0.49 ab | 108.73 ± 2.79 ab | 13.69 ± 0.54 a | 8.92 ± 0.57 a | 2.11 ± 0.16 a |
| QM | 21.35 ± 0.48 a | 10.17 ± 0.58 a | 116.73 ± 4.18 a | 12.75 ± 0.30 b | 8.80 ± 0.47 a | 1.97 ± 0.13 ab |
| QK | 21.20 ± 0.43 ab | 9.75 ± 0.73 ab | 108.26 ± 5.54 ab | 13.23 ± 0.29 ab | 8.77 ± 0.24 a | 2.03 ± 0.12 ab |
| Q | 21.35 ± 0.48 a | 9.51 ± 0.67 ab | 110.93 ± 3.77 ab | 12.80 ± 0.40 b | 8.55 ± 0.47 a | 1.97 ± 0.09 ab |
| YC | 21.28 ± 1.50 a | 8.48 ± 1.00 bc | 106.53 ± 4.17 b | 12.73 ± 0.29 b | 8.72 ± 0.43 a | 1.91 ± 0.12 abc |
| CK | 19.70 ± 0.35 b | 7.96 ± 0.49 c | 96.70 ± 3.79 c | 11.76 ± 0.33 c | 7.46 ± 0.55 b | 1.71 ± 0.08 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, G.; Geng, S.; Wang, L.; Xing, J.; Fan, G.; Gao, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Modified Biochar on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Brassica chinensis L. in Cadmium Contaminated Soils. Plants 2025, 14, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040524
Pan G, Geng S, Wang L, Xing J, Fan G, Gao Y, Lu X, Zhang Z. Effects of Modified Biochar on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Brassica chinensis L. in Cadmium Contaminated Soils. Plants. 2025; 14(4):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040524
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Guojun, Shufang Geng, Liangliang Wang, Jincheng Xing, Guangping Fan, Yan Gao, Xin Lu, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Modified Biochar on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Brassica chinensis L. in Cadmium Contaminated Soils" Plants 14, no. 4: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040524
APA StylePan, G., Geng, S., Wang, L., Xing, J., Fan, G., Gao, Y., Lu, X., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Effects of Modified Biochar on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Brassica chinensis L. in Cadmium Contaminated Soils. Plants, 14(4), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040524







