Developmental Stage and Shape of Embryo Determine the Efficacy of Embryo Rescue in Introgressing Orange/Yellow Color and Anthocyanin Genes of Brassica Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Interspecific Hybridization Followed by Hand Emasculation
2.3. Embryo Rescue and Plant Regeneration
2.4. Chromosome Doubling, Selection of F1 and Amphidiploids Plants
2.5. Cytological Observation
2.6. Estimation of Total Anthocyanin and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
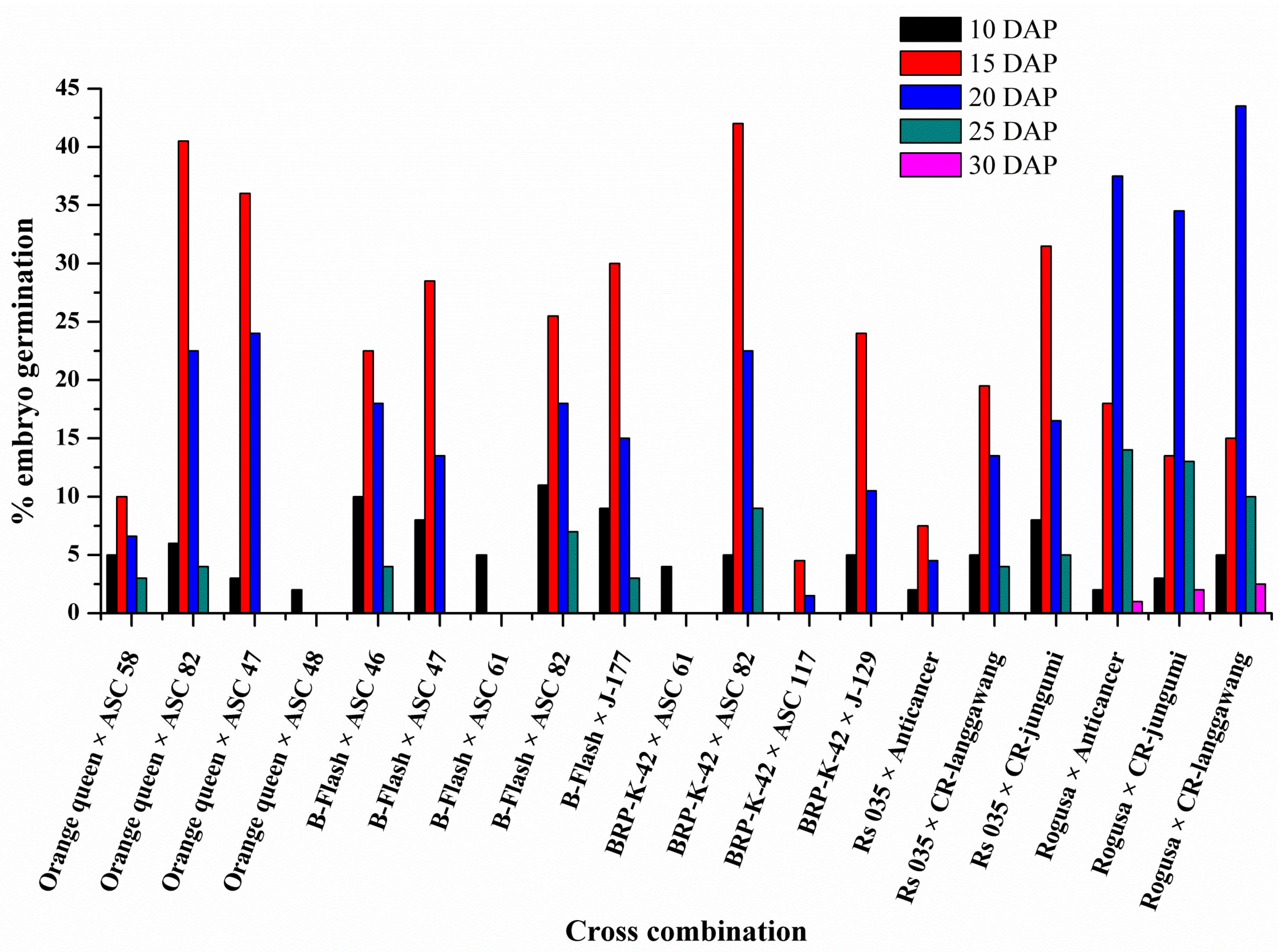
3.1. Days after Pollination (DAP) Contributes to the Success of Embryo Rescue
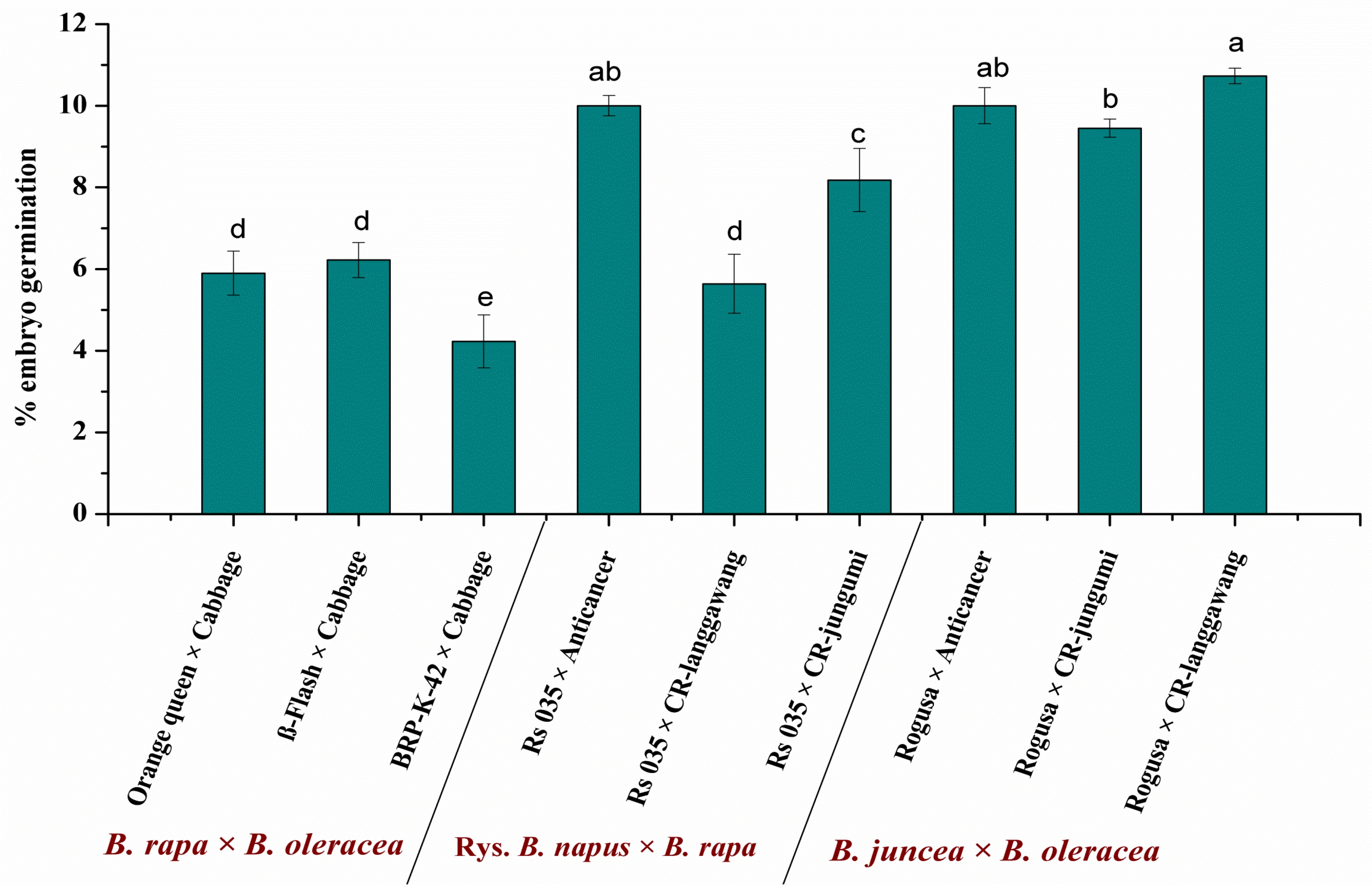
3.2. Genotypes Contribute to the Success of Embryo Rescue of Interspecies Crosses
3.3. Effect of Embryo Shape on Plant Regeneration from Rescued Embryo
3.4. Confirmation of Embryo-Rescued Hybrid Plants
3.5. Determination of Orange Color and Anthocyanin in BC1 and BC2 Progeny
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gómez-Campo, C. Morphology and Morpho-Taxonomy of the Tribe Brassiceae. Brassica Crops Wild Allies, Biology Breeding; Japan Scientific Societies Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1980; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Mandáková, T.; Wu, J.; Xie, Q.; Lysak, M.A.; Wang, X. Deciphering the diploid ancestral genome of the mesohexaploid Brassica rapa. Plant Cell 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, A.; Lunn, T. Trends and perspectives of vegetable Brassica breeding world-wide. In Proceedings of the WCHR-World Conference on Horticultural Research, Rome, Italy, 17–20 June 1998; Volume 495, pp. 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Genome triplication drove the diversification of Brassica plants. Horticult. Res. 2014, 1, 14024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Wickett, N.J.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Chanderbali, A.S.; Landherr, L.; Ralph, P.E.; Tomsho, L.P.; Hu, Y.; Liang, H.; Soltis, P.S. Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature 2011, 473, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, N.H. The role of hybridization in evolution. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, J.; Olender, M.; Wojciechowski, A.; Tomkowiak, A. Interspecific hybridization between Brassica napus and Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis genotypes through embryo rescue and their evaluation for crossability. J. Biotechnol. Comput. Biol. Bionanotechnol. 2015, 96, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhou, W.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z. Studies on distant hybridization in Brassica plants. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2001, 29, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Genetics and Breeding of Oilseed Rape; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, I. The scope and problems involved in synthesising new amphi-diploid and autotetraploid fodder brassicas in the group B. napus L., B. campestris L. and B. oleracea L. Rec. Scott. Plant Breed. Stn. Pentlandfleld Rosl. Midlothian 1963, 1963, 48–68. [Google Scholar]
- Agnihotri, A.; Lakshmikumaran, M.; Prakash, S.; Jagannathan, V. Embryo rescue of B. napus × Raphanobrassica hybrids. Crucif. Newsl. 1991, 14, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, K. Embryo rescue in plants—A review. Euphytica 1996, 89, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, Y.; Bang, S.W. Interspecific and intergeneric hybridization and chromosomal engineering of Brassicaceae crops. Breed. Sci. 2014, 64, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, L.; Yin, J.; Frauen, M.; Li, J.; Qian, W. Genomic relationships between wild and cultivated Brassica oleracea L. with emphasis on the origination of cultivated crops. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2010, 57, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, J.; Kaczmarek, J.; Wojciechowski, A.; Olejniczak, J.; Jędryczka, M. Hybrids within the genus Brassica and chemical mutants of Brassica napus–the potential sources of resistance to clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae) Formy mieszańcowe w obrębie rodzaju Brassica i mutanty chemiczne Brassica napus jako potencjalne źródła odporności na kiłę kapusty (Plasmodiophora brassicae). Prog. Plant Protect. 2015, 55, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Niemann, J.; Wojciechowski, A.; Janowicz, J. Broadening the variability of quality traits in rapeseed through interspecific hybridization with an application of immature embryo culture. BioTechnol. J. Biotechnol. Comput. Biol. Bionanotechnol. 2012, 93, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, K.C. Application of Tissue Culture Techniques to Horticultural Crops. In Tissue Culture Techniques for Horticultural Crops; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Inomata, N. Embryo rescue techniques for wide hybridization. In Breeding Oilseed Brassicas; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; pp. 94–107. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, S. Differentiation of Brassica crops in Asia and the breeding of ‘Hakuran’, a newly synthesized leafy vegetable. In Brassica Crops Wild Allies, Biology and Breeding; Japanese Science Society Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1980; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, D.; Bajaj, Y. Hybridization in Brassica juncea × Brassica campestris through ovary culture. Euphytica 1988, 37, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhou, W.; Gu, H.; Song, W.; Momoh, E. Plant regeneration from the hybridization of Brassica juncea and B. napus through embryo culture. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2003, 189, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; Yuan, Y.; Gen, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, G. Studies on artificially synthesized B. napus L. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2001, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, G.; Song, W.; Zhou, W. Resynthesizing Brassica napus from interspecific hybridization between Brassica rapa and B. oleracea through ovary culture. Euphytica 2004, 140, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. Optimum age of siliques for rescue of hybrid embryos from crosses between Brassica oleracea, B. rapa and B. carinata. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 84, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V.; Srivastava, P. Embryo culture. In Experimental Embryology of Vascular Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982; pp. 195–230. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Heneen, W.; Jönsson, R. Resynthesis of Brassies napus L. through Interspecific Hybridization between B. alboglabra Bailey and B. campestris L. with Special Emphasis on Seed Colour. Plant. Breed. 1988, 101, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.H. Interspecific hybrids between Brassica napus L. and B. oleracea L. developed by embryo culture. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1988, 75, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, W.; Wand, S.; Holcroft, D.; Jacobs, G. Anthocyanins in vegetative tissues: A proposed unified function in photoprotection. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Wang, K.; Bolitho, K.; Grafton, K.; Kortstee, A.; Karunairetnam, S.; McGhie, T.K.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nisar, N.; Li, L.; Lu, S.; Khin, N.C.; Pogson, B.J. Carotenoid metabolism in plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, G.; Kay, C.D.; Cottrell, T.; Holub, B.J. Absorption of anthocyanins from blueberries and serum antioxidant status in human subjects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7731–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Anthocyanin accumulation, antioxidant ability and stability, and a transcriptional analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple heading Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 64, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomasset, S.; Teller, N.; Cai, H.; Marko, D.; Berry, D.P.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Do anthocyanins and anthocyanidins, cancer chemopreventive pigments in the diet, merit development as potential drugs? Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 64, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Sola, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Concepción, M. Carotenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis: A colorful pathway. In The Arabidopsis Book; American Society of Plant Biologists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Fei, Z.; Pogson, B.J.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Molecular characterization and transcriptome analysis of orange head Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Planta 2015, 241, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Gao, J. Transcriptome analysis of orange head Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) and molecular marker development. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.-C.; Byun, D.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.O.; Sung, S.H.; Yang, T.-J. Association of molecular markers derived from the BrCRISTO1 gene with prolycopene-enriched orange-colored leaves in Brassica rapa. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-M.; Chung, W.-H.; Chung, H.; Kim, N.; Park, B.-S.; Lim, K.-B.; Yu, H.-J.; Mun, J.-H. Comparative analysis of the radish genome based on a conserved ortholog set (COS) of Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1975–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizawa, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyamura, T.; Matsuura, S. Simple procedure of DNA isolation from human serum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H. Fine mapping and characterization of the OR gene in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp pekinensis). Genet. Mol. Res. GMR 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D. Experiment of Genetics; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrtens, F.; Kranz, H.; Bednarek, P.; Weisshaar, B. The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB12 is a flavonol-specific regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant. Physiol. 2005, 138, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, J.; Kotlarski, S.; Wojciechowski, A. The evaluation of self-incompatibility and crossability in choosen Brassica species based on the observation of pollen tubes growth and seed set. Acta Sci. Polonorum. Agric. 2014, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wojciechowski, A. Obtained interspecific hybrid of B. napus and B. oleracea var. italica by embryo and ovule in vitro culture. J. Huazhong (Cent. China) Agric. Univ. 2000, 19, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, Y.; Mahajan, S.; Labana, K. Interspecific hybridization of Brassica napus and B. juncea through ovary, ovule and embryo culture. Euphytica 1986, 35, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.; Wilson, J.; Kuo, I.; Lülsdorf, M.; Mallikarjuna, N.; Kuo, J.; Siddique, K. Embryo rescue and plant regeneration in vitro of selfed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and its wild annual relatives. Plant. Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2006, 85, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Lakshmi, S.; Saraswathi, M.; Akbar, A.; Mustaffa, M. Embryo rescue and plant regeneration in banana (Musa spp.). Plant. Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. (PCTOC) 2011, 105, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, G.; Hagberg, P. Efficient production of doubled haploid plants by immediate colchicine treatment of isolated microspores in winter Brassica napus. Plant. Growth Regul. 2002, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhou, W.; Hagberg, P. High frequency spontaneous production of doubled haploid plants in microspore cultures of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Euphytica 2003, 134, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.-H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schranz, M.E.; Lysak, M.A.; Mitchell-Olds, T. The ABC’s of comparative genomics in the Brassicaceae: Building blocks of crucifer genomes. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigareva, M.; Earle, E. Direct transfer of a cold-tolerant Ogura male-sterile cytoplasm into cabbage (Brassica oleracea ssp. capitata) via protoplast fusion. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygulla, W.; Snowdon, R.; Eynck, C.; Koopmann, B.; Von Tiedemann, A.; Lühs, W.; Friedt, W. Broadening the genetic basis of Verticillium longisporum resistance in Brassica napus by interspecific hybridization. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Cross Type | Cross Combination | Embryo Shape | No. of Embryos Cultured | No. of Plants Regenerated | Rate of Plant Regeneration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. rapa × B. oleracea | Orange queen × Cabbage | Torpedo | 30 | 18 | 60.00 b |
| Irregular | 25 | 10 | 40.00 c | ||
| Cotyledonary | 35 | 29 | 82.80 a | ||
| Globular | 40 | 33 | 82.50 a | ||
| β-Flash × Cabbage | Torpedo | 40 | 27 | 67.50 b | |
| Irregular | 55 | 22 | 40.00 c | ||
| Cotyledonary | 48 | 36 | 75.00 b | ||
| Globular | 28 | 20 | 71.50 a | ||
| BRP-K-42 × Cabbage | Torpedo | 20 | 11 | 55.00 b | |
| Irregular | 25 | 12 | 48.00 c | ||
| Cotyledonary | 28 | 20 | 71.43 a | ||
| Globular | 20 | 15 | 75.00 a | ||
| Rys. B. napus × B. rapa | Rs 035 × Anticancer | Torpedo | 10 | 7 | 70.00 b |
| Irregular | 15 | 9 | 60.00 c | ||
| Cotyledonary | 12 | 9 | 75.00 b | ||
| Globular | 18 | 15 | 83.33 a | ||
| Rs 035 × CR-langgawang | Torpedo | 8 | 3 | 37.50 c | |
| Irregular | 7 | 3 | 42.86 c | ||
| Cotyledonary | 10 | 7 | 70.00 b | ||
| Globular | 6 | 5 | 83.33 a | ||
| Rs 035 × CR-jungumi | Torpedo | 7 | 4 | 57.14 c | |
| Irregular | 10 | 3 | 30.00 d | ||
| Cotyledonary | 16 | 12 | 75.00 b | ||
| Globular | 12 | 10 | 83.33 a | ||
| B. juncea × B. rapa | Rogusa × Anticancer | Torpedo | 10 | 4 | 40.00 b |
| Irregular | 20 | 8 | 40.00 b | ||
| Cotyledonary | 15 | 12 | 80.00 a | ||
| Globular | 10 | 8 | 80.00 a | ||
| Rogusa × CR-jungumi | Torpedo | 11 | 5 | 45.45 b | |
| Irregular | 15 | 6 | 40.00 b | ||
| Cotyledonary | 12 | 10 | 83.33 a | ||
| Globular | 14 | 11 | 78.57 a | ||
| Rogusa × CR-langgawang | Torpedo | 4 | 1 | 25.00 b | |
| Irregular | 20 | 6 | 30.00 b | ||
| Cotyledonary | 20 | 16 | 80.00 a | ||
| Globular | 15 | 12 | 80.00 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pen, S.; Nath, U.K.; Song, S.; Goswami, G.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, H.-J.; Kim, H.-T.; Park, J.-I.; Nou, I.-S. Developmental Stage and Shape of Embryo Determine the Efficacy of Embryo Rescue in Introgressing Orange/Yellow Color and Anthocyanin Genes of Brassica Species. Plants 2018, 7, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040099
Pen S, Nath UK, Song S, Goswami G, Lee J-H, Jung H-J, Kim H-T, Park J-I, Nou I-S. Developmental Stage and Shape of Embryo Determine the Efficacy of Embryo Rescue in Introgressing Orange/Yellow Color and Anthocyanin Genes of Brassica Species. Plants. 2018; 7(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040099
Chicago/Turabian StylePen, Sreyvatey, Ujjal Kumar Nath, Samnang Song, Gayatri Goswami, Ji-Hee Lee, Hee-Jeong Jung, Hoy-Taek Kim, Jong-In Park, and Ill-Sup Nou. 2018. "Developmental Stage and Shape of Embryo Determine the Efficacy of Embryo Rescue in Introgressing Orange/Yellow Color and Anthocyanin Genes of Brassica Species" Plants 7, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040099
APA StylePen, S., Nath, U. K., Song, S., Goswami, G., Lee, J. -H., Jung, H. -J., Kim, H. -T., Park, J. -I., & Nou, I. -S. (2018). Developmental Stage and Shape of Embryo Determine the Efficacy of Embryo Rescue in Introgressing Orange/Yellow Color and Anthocyanin Genes of Brassica Species. Plants, 7(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040099




