Genome Size and Chromosome Number Evolution in Korean Iris L. Species (Iridaceae Juss.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chromosome Numbers and Karyotype Analysis
2.3. Genome Size Measurement by Flow Cytometry (FCM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromosome Numbers and Karyotypes of Iris L.
3.1.1. Iris L. Subgenus Limniris Spach Section Limniris Spach
3.1.2. Iris L. Subgenus Limniris Spach Section Ioniris Spach
3.1.3. Iris L. Subgenus Pardanthopis (Hance) Baker
3.1.4. Sisyrinchium rosulatum E.P.Bicknell.
3.2. Genome Size Variation in Iris L.
3.3. Evolution of Chromosome Numbers and Genome Sizes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lysak, M.A.; Berr, A.; Pecinka, A.; Schmidt, R.; McBreen, K.; Schuber, I. Mechanisms of chromosome number reduction in Arabidopsis thaliana and related Brassicaceae species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5224–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, I. Chromosome evolution. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Schneeweiss, G.M. Karyotype diversity and evolutionary trends in angiosperms. In Plant Genome Diversity 2: Physical Structure, Behaviour and Evolution of Plant Genomes; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.D.; Leitch, I.J. Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms: Targets, trends and tomorrow. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 467–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Blöch, C.; Turner, B.; Villaseñor, J.L.; Stuessy, T.F.; Schneeweiss, G.M. The promiscuous and the chaste: Frequent allopolyploid speciation and its genomic consequences in American Daisies (Melampodium sect. Melampodium; Asteraceae). Evolution 2012, 66, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.S.; McCann, J.; Parker, J.S.; Takayama, K.; Hong, S.P.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H. rDNA loci evolution in the genus Glechoma (Lamiaceae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, T.S.; Parker, J.S.; Emadzade, K.; Temsch, E.M.; Leitch, A.R.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H. Multiple origins and nested cycles of hybridization result in high tetraploid diversity in the monocot Prospero. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róis, A.S.; Castro, S.; Loureiro, J.; Sádio, F.; Rhazi, L.; Guara-Requena, M.; Caperta, A.D. Genome sizes and phylogenetic relationships suggest recent divergence of closely related species of the Limonium vulgare complex (Plumbaginaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2018, 304, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone, A.B.; López, A.; Hojsgaard, D.H.; Giussani, L.M. A novel indicator of karyotype evolution in the tribe Leucocoryneae (Allioideae, Amaryllidaceae). J. Plant Res. 2018, 131, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Yang, S.; Song, J.H.; Jang, T.S. Karyotype and genome size variation in Ajuga L. (Ajugoideae-Lamiaceae). Nord. J. Bot. 2019, 37, e02337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.A.S.; Filho, J.R.M.; Vasconcelos, S.; Gitaí, J.; Campos, J.S.; Viccini, L.F.; Zizka, G.; Leme, E.M.C.; Brasileiro-Vidal, A.C.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M.B. Genome size evolution and chromosome numbers of species of the cryptanthoid complex (Bromelioideae, Bromeliaceae) in a phylogenetic framework. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 192, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, A.; Gouja, H.; Vallés, J.; Garnatje, T.; Buhagiar, J.; Neffati, M. Chromosome number and genome size in Atriplex mollis from southern Tunisia and Atriplex lanfrancoi from Malta (Amaranthaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2020, 306, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, I.J.; Leitch, A.R. Genome size diversity and evolution in land plants. In Plant Genome Diversity 2: Physical Structure, Behaviour and Evolution of Plant Genomes; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 307–322. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, I.; Vu, G.T.H. Genome stability and evolution: Attempting a holistic view. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, J.; Leitch, I.J. The plant DNA C-values database (release 7.1): An updated online repository of plant genome size data for comparative studies. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblatt, P.; Walbot, V.; Zimmer, E. Estimation of genome size (C-value) in Iridaceae by cytophotometry. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 1984, 71, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.; Glick, L.; Abadi, S.; Einhorn, M.; Kopelman, N.M.; Salman-Minkov, A.; Mayzel, J.; Chay, O.; Mayrose, I. The chromosome counts database (CCDB): A community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, P.; Manning, J.C.; Rudall, P.J. Iridaceae. In The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants. Vol. 3, Flowering Plants. Monocotyledons: Lilianae (Except Orchidaceae); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 295–333. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Noltie, H.J.; Mathew, B. Iridaceae. In Flora of China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 24, pp. 297–313. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.A. Patterns of evolution in characters that define Iris subgenera and sections. Aliso 2006, 22, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wilson, C.A. Molecular phylogeny of crested Iris based on five plastid markers (Iridaceae). Syst. Bot. 2013, 38, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionenko, G.I. The Genus Iris; Academy of Science USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, B. The Iris; Batsford: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.A. Subgeneric classification in Iris re-examined using chloroplast sequence data. Taxon 2011, 60, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.K. Iridaceae Juss. In The Genera of Vascular Plants of Korea; Academy Publ. Co.: Seoul, Korea, 2007; pp. 1326–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.B. Colored Flora of Korea; Hyangmunsa: Seoul, Korea, 2003; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, J.K.; Park, H.D.; Park, S.J. Phylogenetic study of Korean Iris (Iridaceae) based on nrDNA ITS sequences. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2002, 32, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kim, Y.D.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.I. Endangered vascular plants in the republic of Korea. In Korean Red List of Threatened Species, 2nd ed.; National Institute of Biological Resources: In-Cheon, Korea, 2014; pp. 137–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, S.J. A phylogenetic study of Korean Iris L. based on plastid DNA (psbA-trnH, trnL-F) sequences. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2013, 43, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, O.; Son, S.W.; Suh, G.U.; Park, S.J. Natural hybridization of Iris species in Mt. Palgong-san, Korea. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2015, 45, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Park, Y.W.; Yoon, P.S.; Choi, H.W.; Bang, J.W. Karyotype analysis of eight Korean native species in the genus Iris. Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci. 2004, 12, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, T.S. Micromorphological and cytological comparisons between Youngia japonica and Y. longiflora using light and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MicroMeasure 3.3 Program. Available online: https://micromeasure.software.informer.com/3.3 (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Temsch, E.M.; Greilhuber, J.; Krisai, R. Genome size in liverworts. Preslia 2010, 82, 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Greilhuber, J.; Ebert, I. Genome size variation in Pisum sativum. Genome 1994, 37, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Oldiges, H.; Gohde, W.; Jain, V.K. Flow cytometric measurement of nuclear DNA content variations as a potential in vivo mutagenicity test. Cytometry 1981, 2, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Vargas, P.; Luceño, M.; Cuadrado, Á. Evolution of Iris subgenus Xiphium based on chromosome numbers, FISH of nrDNA (5S, 45S) and trnL-trnF sequence analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 289, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljak-Yakovlev, S.; Pustahija, F.; Šolić, E.M.; Bogunić, F.; Muratović, E.; Bašić, N.; Catrice, O.; Brown, S.C. Towards a genome size and chromosome number database of Balkan Flora: C-values in 343 taxa with novel values for 242. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2010, 3, 190–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, N.A.; Dagher-Kharrat, M.B.; Hidalgo, O.; Zein, R.E.; Douaihy, B.; Siljak-Yakovlev, S. Unlocking the karyological and cytogenetic diversity of Iris from Lebanon: Oncocyclus section shows a distinctive profile and relative stasis during its continental radiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160816. [Google Scholar]
- Emadzade, K.; Jang, T.S.; Macas, J.; Kovařík, A.; Novák, P.; Parker, J.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H. Differential amplification of satellite PaB6 in chromosomally hypervariable Prospero autumnale complex (Hyacinthaceae). Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Leitch, A.R.; McCann, J.; Jang, T.S.; Macas, J. Employing next generation sequencing to explore the repeat landscape of the plant genome. In Next Generation Sequencing in Plant Systematics. Regnum Vegetabile 157; Koeltz Scientific Books: Königstein, Germnay, 2015; Volume 158, pp. 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Macas, J.; Novák, P.; Pellicer, J.; Čížková, J.; Koblížková, A.; Neumann, P.; Fuková, I.; Doležel, J.; Kelly, L.J.; Leitch, I.J. In depth characterization of repetitive DNA in 23 plant genomes reveals sources of genome size variation in the legume tribe Fabeae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, J.; Jang, T.S.; Macas, J.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Matzke, N.J.; Novák, P.; Stuessy, T.F.; Villaseñor, J.L.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H. Dating the species network: Allopolyploidy and repetitive DNA evolution in American Daisies (Melampodium sect. Melampodium, Asteraceae). Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarevitch, I.; Golovnina, K.; Scherbik, S.; Blinov, A. Phylogenetic relationships of the Siberian Iris species inferred from noncoding chloroplast DNA sequences. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.A. Phylogenetic relationships among the recognized series in Iris section Limniris. Syst. Bot. 2009, 34, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Huang, Z.; Liao, J.Q.; Song, H.X.; Luo, X.M.; Gao, S.P.; Lei, T.; Jiang, M.Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Q.B.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Iris L. from China on chloroplast trnL-F sequences. Biologia 2018, 73, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.A. Phylogeny of Iris based on chloroplast matK gene and trnK intron sequence data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, P.; Takei, M. Chromosome cytology of Iridaceae—Patterns of variation, determination of ancestral base numbers, and modes of karyotype change. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 1997, 84, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.Y.; Matyasek, R.; Kovařík, A.; Leitch, A.R. Parental origin and genome evolution in the allopolyploids Iris versicolor. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jersáková, J.; Trávníček, P.; Kubátová, B.; Krejčíková, J.; Urfus, T.; Liu, Z.J.; Lamb, A.; Ponert, J.; Schulte, K.; Curn, V.; et al. Genome size variation in Orchidaceae subfamily Apostasioideae: Filling the phylogenetic gap. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 172, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmarda, P.; Bureš, P.; Horová, L.; Leitch, I.J.; Mucina, L.; Pacini, E.; Tichý, L.; Grulich, V.; Rotreklová, O. Ecological and evolutionary significance of genomic GC content diversity in monocots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Taxon; Collection Number | Locality; GPS Coordinate; Collector | Chromosome Number (2n) | Genome Size 1 C ± S.D. (pg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iris | |||
| Subgenus Limniris section Limniris | |||
| Iris ensata Thunb. | 7.76 4 | ||
| IMHAE103 | Yang-Yang, Kangwon; N38°05′44″, E128°39′15″, 154 m; TS, SK, CM | 24 | 7.86 ± 0.022 |
| IMHAE117 | Pyeong-Chang, Kangwon; N37°41′34.03″, E128°45′25.79″, 889 m; TS, SK, CM | 24 | 7.66 ± 0.011 |
| I. koreana Nakai 1, 2 | 7.29 4 | ||
| sck00042 | Byeonsanbando National Park Endangered Species Botanical Garden (Cult.); SS, RI, CB, SK | 50 | 7.22 ± 0.068 |
| sck00043 | Byeonsanbando National Park Endangered Species Botanical Garden (Cult.); SS, RI, CB, SK | 50 | 7.35 ± 0.029 |
| I. laevigata Fisch. 1 | 7.12 4 | ||
| Jebi-2 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 32 | 7.06 ± 0.010 |
| Jebi-3 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 32 | 7.18 ± 0.046 |
| I. minutoaurea Makino | 3.85 4 | ||
| Gasan_8 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′41″, E128°34′12″, 733 m; TS, CB, HJ | 22 | 3.92 ± 0.008 |
| JCKCK193269 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′35″, E128°34′36″, 675 m; TS, CB, SK, YM | 22 | 3.71 ± 0.171 |
| JCKCK193273-1 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′26″, E128°34′26″, 779 m; TS, CB, SK, YM | 22 | 3.71 ± 0.024 |
| JCKCK193273-2 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′26″, E128°34′26″, 779 m; TS, CB, SK, YM | 22 | 3.72 ± 0.006 |
| JC041913 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′44″, E128°33′51″, 629 m; TS, YM | 22 | 4.09 ± 0.042 |
| JCKC1932211-2 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′28″, E128°34′18″, 806 m; TS, CB, SK, YM | 22 | 3.79 ± 0.019 |
| JCKC1932211-3 | Gasan, Kyungsang; N36°02′28″, E128°34′18″, 806 m; TS, CB, SK, YM | 22 | 3.70 ± 0.003 |
| I. odaesanensis Y.N.Lee 1, 3 | 3.72 4 | ||
| YSG18-66_1 | Gangwon; YS | 28 | 3.67 ± 0.012 |
| YSG18-66_2 | Gangwon; YS | 28 | 3.68 ± 0.011 |
| YSG18-66_4 | Gangwon; YS | 28 | 3.70 ± 0.019 |
| BKC928 | Kyungsang; CB, YC | 28 | 3.79 ± 0.007 |
| JCKC1932271 | Kyungsang; TS, CB, KS, YM | 28 | 3.76 ± 0.021 |
| JC041904 | Kyungsang; TS, YM | 28 | 3.74 ± 0.042 |
| JC041903 | Kyungsang; TS, YM | 28 | 3.67 ± 0.015 |
| JC041940 | Kyungsang; TS, YM | 28 | 3.73 ± 0.018 |
| I. oxypetala Bunge | 6.08 4 | ||
| CC0621-50 | Ga-Gokri, Chungnam; N37°01′21″, E126°34′30″, 4 m; CB, CM | 40 | 6.38 ± 0.014 |
| CC20190621-58 | Ga-Gokri, Chungnam; N37°01′17″, E126°34′32″, 3 m; CB, CM | 40 | 6.06 ± 0.010 |
| CC20190621-64 | Ga-Gokri, Chungnam; N37°01′24″, E126°34′26″, 4 m; CB, CM | 40 | 6.00 ± 0.017 |
| JCCMH025 | Gang-Wha, Incheon; N37°45′37″, E126°14′29″, 80 m; TS, CB, CM | 40 | 5.90 ± 0.005 |
| I. pseudacorus L. | 5.89 4 | ||
| Keumjeong-34 | Mt. Keumjeong, Busan; N35°14′ 5.5″, E129°03′24.6″, 455 m; CB, YK, YC | 34 | 5.82 ± 0.012 |
| Chungdae_2 | Sinseong-dong, Daejeon; N36°22′44.8″, E127°20′35.5″, 83 m; CB | 34 | 5.87 ± 0.017 |
| CC20190621-1 | Is. Hwangdo, Chungnam; N36°35′58.2″, E126°22′42.5″, 14 m; CB | 34 | 5.87 ± 0.024 |
| CC20190621-48 | Dangjin, Chungnam; N37°01′21″, E126°34′30″E, 4 m; CB, CM | 34 | 5.98 ± 0.011 |
| J20190616-1 | Nogokjae, Kimchoen; N36°04′04″, E128°12′50″, 242 m; TS, KS, CB | 34 | 6.02 ± 0.026 |
| BKC910 | Mt. Keumjeong, Busan; N35°14′06″, E129°03′28″, 459 m; CB, YK, YC | 34 | 5.77 ± 0.009 |
| CC20190621-57 | Ga-Gokri, Chungnam; N37°01′21″, E126°34′30″, 4 m; CB, CM | 34 | 5.91 ± 0.009 |
| I. rossii Baker | 3.73 4 | ||
| SJH1830 | Mt. Cheon-Gwan, Jeon-Ra; N34°32′39.4″, E126°55′40.8″, 225 m; SJH | 32 | 3.69 ± 0.014 |
| Pusanuni_2 | Mt. Keumjeong, Busan; N35°14′23.8″, E129°4′27.23″, 169 m; CB, YK | 32 | 3.72 ± 0.005 |
| J513 | Mun-San, Kyung-Gi; N37°57′55″, E126°56′13″, 58 m; TS | 32 | 3.85 ± 0.010 |
| J514 | Mun-San, Kyung-Gi; N37°57′55″, E126°56′11″, 74 m; TS | 32 | 3.67 ± 0.013 |
| Jeokseong_2 | Mun-San, Kyung-Gi; N37°57′55″, E126°56′13″, 58 m; TS | 32 | 3.66 ± 0.005 |
| Keumjeong_8 | Mt. Keumjeong, Busan; N35°14′23.8″ E129°4′27.23″, 169 m; CB, CM | 32 | 3.79 ± 0.018 |
| JCK05_7 | Mt. Saeng-Aeng; N36°19′21.9″, E126°30′45.7″, 110 m; TS, CB, SK | 32 | 3.74 ± 0.033 |
| JCKC190512 | Mojioreum, Jeju; N33°23′42″, E126°45′58″, 247 m; TS, CB, SK, CM | 32 | 3.75 ± 0.003 |
| SCK00021 | Mt. Bong-Wha, Chungnam; N36°47′08″, E126°26′20″, 79 m; CB, SK | 32 | 3.71 ± 0.003 |
| I. sanguinea Hornem. | 5.23 4 | ||
| K02-41 | Mt. Hwa-Ak, Kyung-Gi; N38°00′16.60″, E127°52′51.93″, 1097 m; SK | 28 | 5.22 ± 0.012 |
| Hwaya_1 | Mt. Hwa-Ya, Kyung-Gi; N36°56′24.5″, E127°16′46.8″, 162 m; TS | 28 | 5.30 ± 0.009 |
| K025-04-01 | Yeon-Cheon, Gangwon; N38°09′97.95″, E127°11′28.64″, 129 m; SK | 28 | 5.42 ± 0.021 |
| K025-04-04 | Yeon-Cheon, Gangwon; N38°09′97.95″, E127°11′28.64″, 129 m; SK | 28 | 5.18 ± 0.022 |
| Munsan_1 | Mun-San, Kyung-Gi; N37°57′55″, E126°56′13″, 58 m; TS | 28 | 5.12 ± 0.009 |
| Cheonma-3 | Mt. Cheon-Ma, Kyung-Gi; N37°41′24″, E127°24′36″, 157 m; YS, SJH | 28 | 5.11 ± 0.011 |
| JC041939 | Dae-Gu, Kyungsang; N35°54′44″, E128°38′46″, 629 m; TS, YM | 28 | 5.25 ± 0.020 |
| I. setosa Pall. ex Link 1 | 5.63 4 | ||
| Ga-3 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 38 | 5.55 ± 0.012 |
| Ga_4-1 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 38 | 5.64 ± 0.007 |
| Ga-7 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 38 | 5.57 ± 0.004 |
| Seo-2 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 38 | 5.78 ± 0.016 |
| Ga-5 | Gangwon; TS, CB | 38 | 5.59 ± 0.035 |
| Subgenus Limniris section Ioniris | |||
| I. ruthenica Ker Gawl. 1 | 2.42 4 | ||
| Mo_2 | Jeju; YS, SJH | 42 | 2.45 ± 0.004 |
| J1-1(SSK) | Incheon; SS | 42 | 2.42 ± 0.002 |
| BKC939 | Busan; CB, YM | 42 | 2.45 ± 0.006 |
| JC532 | Daegu; TS, CM | 42 | 2.39 ± 0.001 |
| JC352-1 | Daegu; TS, CM | 42 | 2.43 ± 0.006 |
| JC534-1 | Daegu; TS, CM | 42 | 2.42 ± 0.017 |
| SCK00032 | Chungnam; SS, CB, SK | 42 | 2.42 ± 0.001 |
| BKC937 | Busan; CB | 42 | 2.40 ± 0.001 |
| JCCMH004 | Incheon; TS, CB, CM | 42 | 2.43 ± 0.002 |
| I. uniflora Pall. ex Link | 2.46 4 | ||
| JCK2019-77 | Mt. Sorak, Gangwon; N38°09′27″, E128°29′19″, 790 m; TS, CB, SK | 42 | 2.48 ± 0.002 |
| JCK2019-78 | Mt. Sorak, Gangwon; N38°09′27″, E128°29′19″, 790 m; TS, CB, SK | 42 | 2.44 ± 0.003 |
| JCK2019-79 | Mt. Sorak, Gangwon; N38°09′27″, E128°29′19″, 790 m; TS, CB, SK | 42 | 2.46 ± 0.003 |
| Subgenus Pardanthopsis (Hance) Baker | |||
| Iris dichotoma Pall. 1 | 3.34 4 | ||
| SS03-1 | Cheonripo Arboretum (regenerated individual from a wild population); SS | 32 | 3.35 ± 0.004 |
| SS20-1 | Cheonripo Arboretum (regenerated individual from a wild population); SS | 32 | 3.35 ± 0.008 |
| SS20-2 | Cheonripo Arboretum (regenerated individual from a wild population); SS | 32 | 3.32 ± 0.011 |
| SS20-3 | Cheonripo Arboretum (regenerated individual from a wild population); SS | 32 | 3.34 ± 0.006 |
| I. domestica (L.) Goldblatt & Mabb. | |||
| Beom_1 | Busan (cult.); CB, YK | 32 | 4.75 ± 0.010 |
| Sisyrinchium rosulatum E.P.Bicknell. | 0.91 4 | ||
| JCKC190515 | Hyomyeong, Jeju; N33°19′25″, E126°35′39″, 327 m; TS, CB, SK, CM | 32 | 0.91 ± 0.001 |
| JCKC190451 | Gujwa, Jeju; N33°27′05″, E126°48′06″, 244 m; TS, CB, SK, CM | 32 | 0.90 ± 0.001 |
| Taxon (Collection Number) | Chromosome Length (µm) | AsI 2 (%) | RI 3 | Figure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest (Mean ± S.D.) | Smallest (Mean ± S.D.) | Total HKL 1 (Mean ± S.D.) | ||||
| Iris | ||||||
| Subgenus Limniris section Limniris | ||||||
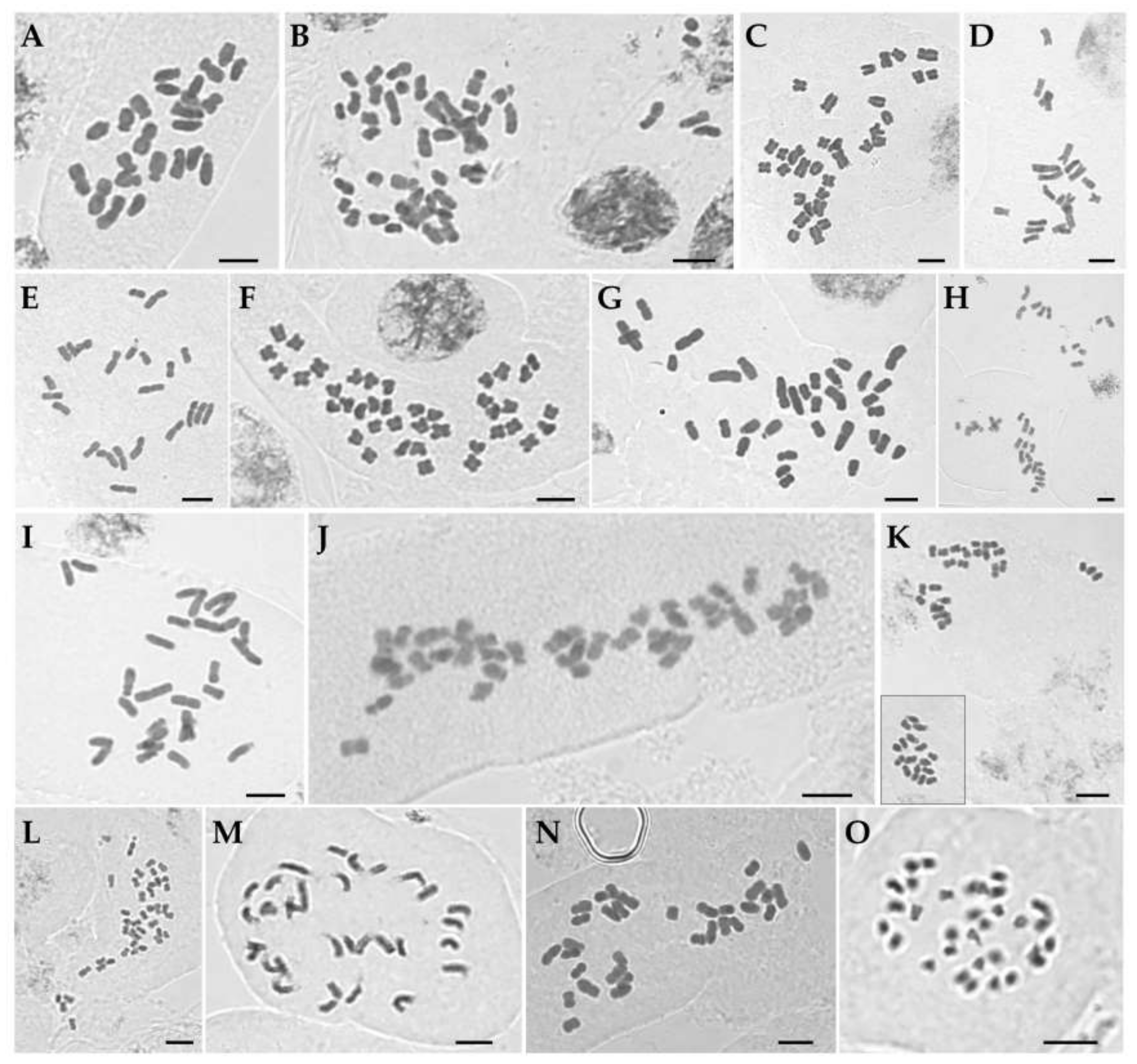
| Iris ensata (IMHAE117) | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 82.5 ± 1.7 | 66.7 | 1.69 | 1A, 2A |
| I. koreana (sck00043) | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 141.7 ± 9.9 | 61.9 | 3.51 | 1B, 2B |
| I. laevigata (Jebi-2) | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 81.8 ± 1.7 | 61.9 | 1.85 | 1 C, 2C |
| I. minutoaurea (Cheonma-2) | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 75.8 ± 2.4 | 58.3 | 2.58 | 1D, 2D |
| I. odaesanensis (YSG18-66_2) | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 86.3 ± 2.4 | 59.5 | 2.19 | 1E, 2E |
| I. oxypetala (CC0621-50) | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 86.4 ± 3.8 | 59.1 | 1.72 | 1F, 2F |
| I. pseudacorus (CC20190621-57) | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 107.1 ± 4.2 | 62.0 | 2.34 | 1G, 2G |
| I. rossii (Keumjeong_8) | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 100.5 ± 3.0 | 60.9 | 2.08 | 1H, 2H |
| I. sanguinea (Hwaya_1) | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 87.2 ± 2.8 | 62.5 | 2.09 | 1I, 2I |
| I. setosa (Seo-2) | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 122.9 ± 6.9 | 61.6 | 2.11 | 1J, 2J |
| Subgenus Limniris section Ioniris | ||||||
| I. ruthenica (JC534-1) | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 78.3 ± 4.3 | 58.0 | 2.52 | 1K, 2K |
| I. uniflora (JCK2019-79) | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 61.9 ± 1.9 | 58.3 | 1.95 | 1L, 2L |
| Subgenus Pardanthopsis | ||||||
| I. dichotoma (SS20-3) | 4.6 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 97.0 ± 4.4 | 61.9 | 2.19 | 1M, 2M |
| I. domestica (Beom_1) | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 92.8 ± 4.2 | 59.7 | 1.76 | 1N, 2N |
| Sisyrinchium rosulatum (JCKC190515) | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 43.4 ± 1.9 | 59.9 | 1.84 | 1O, 2O |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, B.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Temsch, E.M.; So, S.; Myeong, H.-H.; Jang, T.-S. Genome Size and Chromosome Number Evolution in Korean Iris L. Species (Iridaceae Juss.). Plants 2020, 9, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101284
Choi B, Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Temsch EM, So S, Myeong H-H, Jang T-S. Genome Size and Chromosome Number Evolution in Korean Iris L. Species (Iridaceae Juss.). Plants. 2020; 9(10):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101284
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Bokyung, Hanna Weiss-Schneeweiss, Eva M. Temsch, Soonku So, Hyeon-Ho Myeong, and Tae-Soo Jang. 2020. "Genome Size and Chromosome Number Evolution in Korean Iris L. Species (Iridaceae Juss.)" Plants 9, no. 10: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101284
APA StyleChoi, B., Weiss-Schneeweiss, H., Temsch, E. M., So, S., Myeong, H.-H., & Jang, T.-S. (2020). Genome Size and Chromosome Number Evolution in Korean Iris L. Species (Iridaceae Juss.). Plants, 9(10), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101284






