SLIM1 Transcription Factor Promotes Sulfate Uptake and Distribution to Shoot, Along with Phytochelatin Accumulation, Under Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
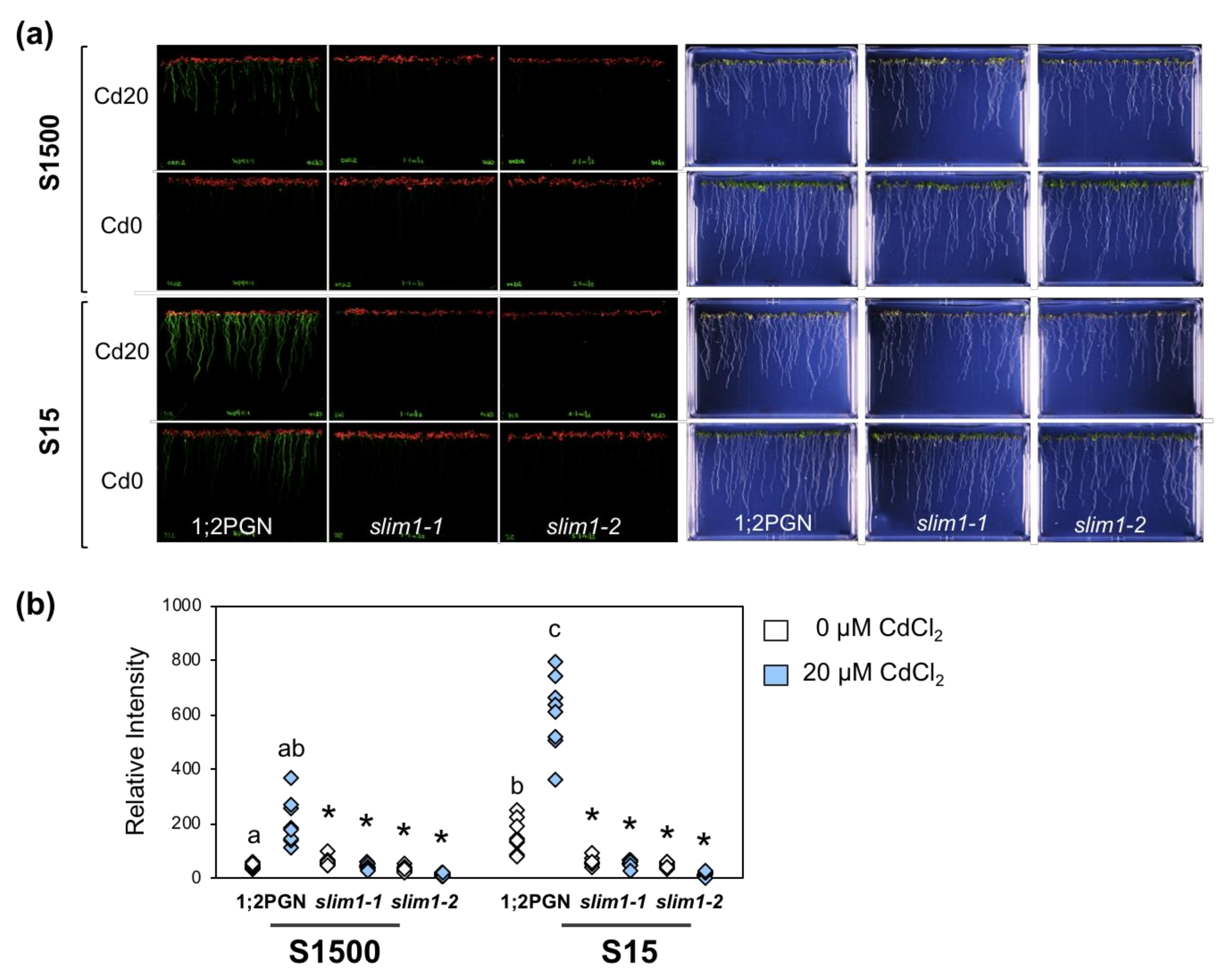
2.1. The slim1 Mutant Was More Sensitive to Cd and Accumulated Less Cd Than the Parental Line 1;2PGN
2.2. Cd-Induced Increases of Sulfate Uptake, Sulfate Transport to Shoots, and Sulfate Content in Shoots Were Diminished in slim1–2
2.3. Cd-Inducible Expression of SULTR1;2 Was Moderated in slim1–2
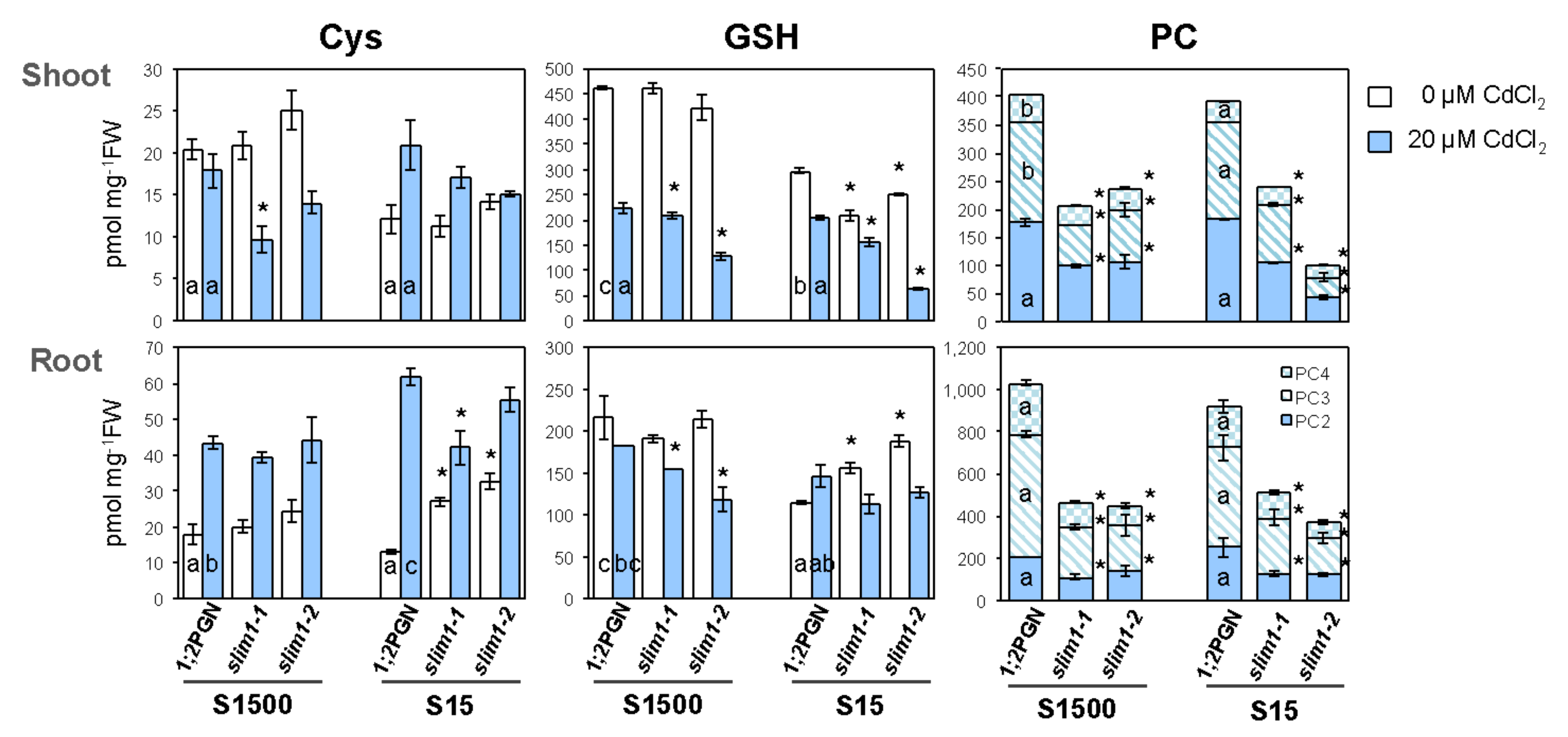
2.4. Accumulation of GSH and PC Was Diminished in slim1–2
2.5. Cd Treatment and−S Additively Increased SULTR1;2 Expression and Sulfate Uptake, which Depended on SLIM1
2.6. SLIM1 Increases PC Levels in Response to Cd Treatment Even in Combination with−S
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Cd Analysis
4.3. Sulfate Uptake and Translocation Activity
4.4. Measurements of Sulfate, Thiols (Cys, GSH, and PCs), and Total S Levels
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Imaging and Quantification of GFP Fluorescence
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nawrot, T.; Plusquin, M.; Hogervorst, J.; Roels, H.A.; Celis, H.; Thijs, L.; Vangronsveld, J.; Van Hecke, E.; Staessen, J.A. Environmental exposure to cadmium and risk of cancer: A prospective population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Järup, L.; Akesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomine, S.; Wang, R.; Ward, J.M.; Crawford, N.M.; Schroeder, J.I. Cadmium and iron transport by members of a plant metal transporter family in Arabidopsis with homology to Nramp genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4991–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic Heavy Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Crop Plants and Foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 29, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, R.; Bashir, K.; Ishimaru, Y.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. The role of heavy-metal ATPases, HMAs, in zinc and cadmium transport in rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujimaki, S. Route and Regulation of Zinc, Cadmium, and Iron Transport in Rice Plants (Oryza sativa L.) during Vegetative Growth and Grain Filling: Metal Transporters, Metal Speciation, Grain Cd Reduction and Zn and Fe Biofortification. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2015, 16, 19111–19129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.F.; Aarts, M.G. The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3187–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choppala, G.; Saifullah Bolan, N.; Bibi, S.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Rengel, Z.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Ashwath, N.; Sik Ok, Y. Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2014, 33, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S. Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C.; Schat, H. Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. South African J. Bot. 2010, 76, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chmielowska-Bąk, J.; Gzyl, J.; Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M.; Deckert, J. The new insights into cadmium sensing. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobbett, C.S.; May, M.J.; Howden, R.; Rolls, B. The glutathione-deficient, cadmium-sensitive mutant, cad2-1, of Arabidopsis thaliana is deficient in gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Plant J. 2002, 16, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, C.S.; Remans, T.; Keunen, E.; Jozefczak, M.; Gielen, H.; Opdenakker, K.; Weyens, N.; Vangronsveld, J.; Cuypers, A. Phytoextraction of toxic metals: A central role for glutathione. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salt, D.E.; Rauser, W.E. MgATP-Dependent Transport of Phytochelatins Across the Tonoplast of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.C. Glutathione Synthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1830, 3143–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobbett, C.; Goldsbrough, P. Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vatamaniuk, O.K.; Mari, S.; Lu, Y.P.; Rea, P.A. Mechanism of heavy metal ion activation of phytochelatin (PC) synthase: Blocked thiols are sufficient for PC synthase-catalyzed transpeptidation of glutathione and related thiol peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31451–31459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbette, S.; Taconnat, L.; Hugouvieux, V.; Piette, L.; Magniette, M.L.; Cuine, S.P.; Auroy, P.; Richaud, P.; Forestier, C.; Bourguignon, J.; et al. Genome-wide transcriptome profiling of the early cadmium response of Arabidopsis roots and shoots. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1751–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenk, M.H. Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants-a review. Gene 1996, 179, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Nishikori, S.; Shiraki, K.; Hirata, K.; Takagi, M. Chelation of cadmium ions by phytochelatin synthase: Role of the cysteine-rich C-terminal. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howden, R.; Goldsbrough, P.B.; Andersen, C.R.; Cobbett, C.S. Cadmium-sensitive, cad1 mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana are phytochelatin deficient. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobbett, C.S.; May, M.J.; Howden, R.; Rolls, B. The glutathione-deficient, cadmium- sensitive mutant, cad2-1, of Arabidopsis thaliana is deficient in gamma- glutamylcysteine synthetase. Plant J. 1998, 16, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.B.; Smith, A.P.; Howden, R.; Dietrich, W.M.; Bugg, S.; O’Connell, M.J.; Goldsbrough, P.B.; Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatin synthase genes from Arabidopsis and the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leustek, T. Sulfate metabolism. Arabidopsis Book 2002, 1, e0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K. Sulfur assimilatory metabolism. The long and smelling road. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Kopriva, S.; Giordano, M.; Saito, K.; Hell, R. Sulfur assimilation in photosynthetic organisms: Molecular functions and regulations of transporters and assimilatory enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.R.; Kahn, M.; Seefeldt, L.; Tsay, Y.F.; Kopriva, S. Chapter 16 nitrogen and sulfur. In Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants; Buchanan, B.B., Gruissem, W., Jones, R.L., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 746–768. [Google Scholar]
- Davidian, J.C.; Kopriva, S. Regulation of sulfate uptake and assimilation—the same or not the same? Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.F.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, L.N.; He, S.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, Z.A.; He, S.G.; Liu, H. Effects of exogenous sulfur on alleviating cadmium stress in tartary buckwheat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, L.; Kang, J.; Pang, H.; Li, Q.; Du, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Lv, J. Sulfur Protects Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Seedlings against Cadmium Stress by Regulating Ascorbate-Glutathione Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.A.; Asgher, M.; Per, T.S.; Masood, A.; Fatma, M.; Khan, M.I. Ethylene Potentiates Sulfur-Mediated Reversal of Cadmium Inhibited Photosynthetic Responses in Mustard. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matraszek, R.; Hawrylak-Nowak, B.; Chwil, S.; Chwil, M. Interaction Between Cadmium Stress and Sulphur Nutrition Level on Macronutrient Status of Sinapis alba L. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaid, A.; Bhat, J.A.; Wani, S.H.; Masoodi, K.Z. Role of Nitrogen and Sulfur in Mitigating Cadmium induced Metabolism Alterations in Plants. J. Plant Res. 2019, 35, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Smith, F.W.; Blake-Kalff, M.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Saito, K. The role of three functional sulfate transporters involved in uptake and translocation of sulfate in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2000, 23, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kataoka, T.; Hayashi, N.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Root-to-shoot transport of sulfate in Arabidopsis: Evidence for the role of SULTR3;5 as a component of low-affinity sulfate transport system in the root vasculature. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 4198–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Inoue, E.; Yamaya, T.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H. Sulfur-responsive elements in the 3′-nontranscribed intergenic region are essential for the induction of SULFATE TRANSPORTER 2;1 gene expression in Arabidopsis roots under sulfur deficiency. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Wirtz, M.; Hell, R.; Oliver, D.J.; Xiang, C.B. SULTR3;1 is a chloroplast- localized sulfate transporter in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2013, 73, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, H.; Davidian, J.C.; Aubert, G.; Aime, D.; Belghazi, M.; Lugan, R.; Heintz, D.; Wirtz, M.; Hell, R.; Thompson, R.; et al. The seed composition of Arabidopsis mutants for the group 3 sulfate transporters indicates a role in sulfate translocation within developing seeds. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N. Chapter 13 Sulfur Assimilation and Glutathione Metabolism in Plants. In Glutathione in Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Tolerance; Hossain, M.A., Mostofa, M.G., Diaz-Vivancos, P., Burritt, D.J., Fujita, M., Tran, L.-S.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, T.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Ohnishi, M.; Mimura, T.; Buchner, P.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Vacuolar sulfate transporters are essential determinants controlling internal distribution of sulfate in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, C.; Oliver, D.J. Glutathione metabolic genes coordinately respond to heavy metals and jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harada, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Koizumi, N.; Sano, H. Cadmium stress induces production of thiol compounds and transcripts for enzymes in involved in sulfur assimilation pathways in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocito, F.F.; Pirovano, L.; Cocucci, M.; Sacchi, G.A. Cadmium-induced sulfate uptake in maize roots. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nocito, F.F.; Lancilli, C.; Crema, B.; Fourcroy, P.; Davidian, J.C.; Sacchi, G.A. Heavy metal stress and sulfate uptake in maize roots. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Du, Z.; Qi, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, W.; Zhao, Z. RNA-sequencing analysis reveals transcriptional changes in the roots of low-cadmium-accumulating winter wheat under cadmium stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouached, H.; Wirtz, M.; Alary, R.; Hell, R.; Arpat, A.B.; Davidian, J.C.; Fourcroy, P.; Berthomieu, P. Differential regulation of the expression of two high-affinity sulfate transporters, SULTR1.1 and SULTR1.2, in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibagaki, N.; Rose, A.; McDermott, J.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Hayashi, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Davies, J.P. Selenate-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana identify Sultr1;2, a sulfate transporter required for efficient transport of sulfate into roots. Plant J. 2002, 29, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, C.; Takimoto, Y.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N.; Hokura, A.; Shinano, T.; Nakamura, T.; Suyama, A.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A. Effects of cadmium treatment on the uptake and translocation of sulfate in Arab. Thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 2353–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Inoue, E.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Transcriptome profiling of sulfur-responsive genes in Arabidopsis reveals global effect on sulfur nutrition on multiple metabolic pathways. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tohge, T.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H. Arabidopsis SLIM1 is a central transcriptional regulator of plant sulfur response and metabolism. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besson-Bard, A.; Gravot, A.; Richaud, P.; Auroy, P.; Duc, C.; Gaymard, F.; Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.P.; Pugin, A.; Wendehenne, D. Nitric oxide contributes to cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis by promoting cadmium accumulation in roots and by up-regulating genes related to iron uptake. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. A novel regulatory pathway of sulfate uptake in Arabidopsis roots: Implication of CRE1/WOL/AHK4-mediated cytokinin-dependent regulation. Plant J. 2004, 38, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, C.G.; Yoshimoto, N.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Tsuchiya, Y.N.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H.; Dalmay, T. Sulphur starvation induces the expression of microRNA-395 and one of its target genes but in different cell types. Plant J. 2009, 57, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancilli, C.; Giacomini, B.; Lucchini, G.; Davidian, J.C.; Cocucci, M.; Sacchi, G.A.; Nocito, F.F. Cadmium exposure and sulfate limitation reveal differences in the transcriptional control of three sulfate transporter (Sultr1;2) genes in Brassica juncea. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, C.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A. Sulfate Transporters Involved in Cd-Induced Changes of Sulfate Uptake and Distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana. In Sulfur Metabolism in Higher Plants—Fundamental. Environmental and Agricultural Aspects; De Kok, L.J., Hawkesford, M.J., Haneklaus, S.H., Schnug, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Sasakura, N.; Watanabe, A.; Leustek, T.; Engler, J.A.; Engler, G.; Van Montagu, M.; Saito, K. Regulation of sulfur assimilation in higher plants: A sulfate transporter induced in sulfate starved roots plays a central role in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11102–11107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidmar, J.J.; Tagmount, A.; Cathala, N.; Touraine, B.; Davidian, J.E. Cloning and characterization of a root specific high-affinity sulfate transporter from Arabidopsis thaliana. Febs Lett. 2000, 475, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, N.; Takahashi, H.; Smith, F.W.; Yamaya, T.; Saito, K. Two distinct high-affinity sulfate transporters with different inducibilities mediate uptake of sulfate in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J. 2002, 29, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, N.; Inoue, E.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H. Posttranscriptional regulation of high-affinity sulfate transporters in Arabidopsis by sulfur nutrition. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, Y.; Ushiwatari, T.; Suyama, A.; Tominaga-Wada, R.; Wada, T.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A. Contribution of root hair development to sulfate uptake in Arabidopsis. Plants 2019, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wu, F.H.; Li, J.X.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, W.H.; Hu, W.J.; Gao, L.J.; Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Glutathione homeostasis and Cd tolerance in the Arabidopsis sultr1;1-sultr1;2 double mutant with limiting sulfate supply. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A. Metabolic changes sustain the plant life in low-sulfur environments. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, M.N.; Kahn, L.M.; Leustek, T.; Long, R.S. Chapter 16 Nitrogen and Sulfur. In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants; Buchanan, B.B., Wilhelm, G., Jones, R.L., Eds.; American Society of Plant Physiologists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 658–710. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Song, W.Y.; Ko, D.; Eom, Y.; Hansen, T.H.; Schiller, M.; Lee, T.G.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. The phytochelatin transporters AtABCC1 and AtABCC2 mediate tolerance to cadmium and mercury. Plant J. 2012, 69, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Regulation of high-affinity sulphate transporters in plants: Towards systematic analysis of sulphur signalling and regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Pasini, R.; Dan, H.; Joshi, N.; Zhao, Y.; Leustek, T.; Zheng, Z.L. Aberrant gene expression in the Arabidopsis SULTR1;2 mutants suggests a possible regulatory role for this sulfate transporter in response to sulfur nutrient status. Plant J. 2014, 77, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.L.; Zhang, B.; Leustek, T. Transceptors at the boundary of nutrient transporters and receptors: A new role for Arabidopsis SULTR1;2 in sulfur sensing. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirai, M.Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Awazuhara, M.; Kimura, T.; Noji, M.; Saito, K. Global expression profiling of sulfur-starved Arabidopsis by DNA macroarray reveals the role of O-acetyl-l-serine as a general regulator of gene expression in response to sulfur nutrition. Plant J. 2003, 33, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, L.; Parmar, S.; Błaszczyk, A.; Hesse, H.; Hoefgen, R.; Hawkesford, M.J. O-Acetylserine and the regulation of expression of genes encoding components for sulfate uptake and assimilation in potato. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubberten, H.M.; Klie, S.; Caldana, C.; Degenkolbe, T.; Willmitzer, L.; Hoefgen, R. Additional role of O-acetylserine as a sulfur status-independent regulator during plant growth. Plant J. 2012, 70, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Silbermann, M.; Speiser, A.; Forieri, I.; Linster, E.; Poschet, G.; Allboje Samami, A.; Wanatabe, M.; Sticht, C.; Teleman, A.A.; et al. Sulfur availability regulates plant growth via glucose-TOR signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 27, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H.; Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Song, G.; Zhou, H.; Ma, H. Sulfate application decreases translocation of arsenic and cadmium within wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Hirai, M.Y.; Chino, M.; Komeda, Y.; Naito, S. Effects of sulfur nutrition on expression of the soybean seed storage protein genes in transgenic petunia. Plant Physiol. 1992, 99, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, M.Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Chino, M.; Naito, S. Effects of sulfate concentrations on the expression of a soybean seed storage protein gene and its reversibility in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995, 36, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmani, R.; Modareszadeh, M.; Kim, D.; Hwang, S. Overexpression of tobacco UBQ2 increases Cd tolerance by decreasing Cd accumulation and oxidative stress in tobacco and Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 166, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, N.; Kataoka, T.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Takahashi, H. Measurement of uptake and root-to-shoot distribution of sulfate in Arabidopsis seedlings. Bio-Protocol 2016, 6, e1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minocha, R.; Thangavel, P.; Dhankher, O.P.; Long, S. Separation and quantification of monothiols and phytochelatins from a wide variety of cell cultures and tissues of trees and other plants using high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1207, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaguchi, C.; Khamsalath, S.; Takimoto, Y.; Suyama, A.; Mori, Y.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A. SLIM1 Transcription Factor Promotes Sulfate Uptake and Distribution to Shoot, Along with Phytochelatin Accumulation, Under Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2020, 9, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020163
Yamaguchi C, Khamsalath S, Takimoto Y, Suyama A, Mori Y, Ohkama-Ohtsu N, Maruyama-Nakashita A. SLIM1 Transcription Factor Promotes Sulfate Uptake and Distribution to Shoot, Along with Phytochelatin Accumulation, Under Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2020; 9(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaguchi, Chisato, Soudthedlath Khamsalath, Yuki Takimoto, Akiko Suyama, Yuki Mori, Naoko Ohkama-Ohtsu, and Akiko Maruyama-Nakashita. 2020. "SLIM1 Transcription Factor Promotes Sulfate Uptake and Distribution to Shoot, Along with Phytochelatin Accumulation, Under Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 9, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020163
APA StyleYamaguchi, C., Khamsalath, S., Takimoto, Y., Suyama, A., Mori, Y., Ohkama-Ohtsu, N., & Maruyama-Nakashita, A. (2020). SLIM1 Transcription Factor Promotes Sulfate Uptake and Distribution to Shoot, Along with Phytochelatin Accumulation, Under Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 9(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020163




