Physiological Characteristics of Photosynthesis in Yellow-Green, Green and Dark-Green Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Musil.) under Varying Light Intensities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Influence of Light Intensity on Chl a + band the Fluorescence Parameters of Chinese Kale Plants
2.2. ETR Values of Three Chinese Kale Cultivars underVariousLight Intensity Conditions
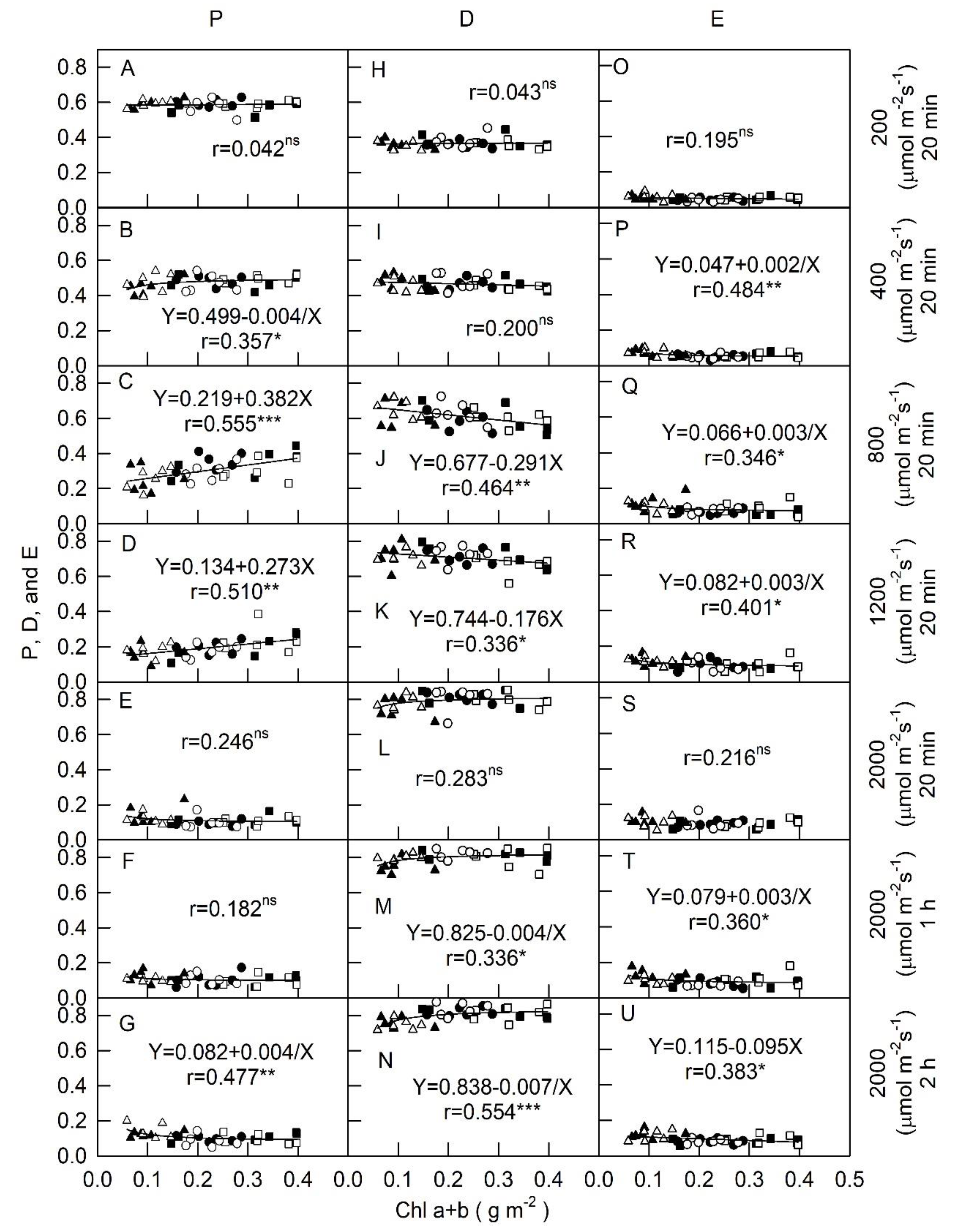
2.3. Relationships betweenChl a + b and Car/Chl a + b
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Cultural Practice
4.2. Determination of ChlFVariables
4.3. Determination of the Spectral Reflectance, Chl a + b and CarContent
Chlb = 0.02405 × OD647 − 0.004359 × OD537 − 0.005507 × OD663,
Car = [OD470 − (17.1 × (Chla + Chlb) − 9.479 × Ant)]/119.26.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Jared, J.; Stewart, I.D.; Christopher, R.; Adams, W. Optimization of Photosynthetic productivity in contrasting environments by regulons controlling plant form and function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Givnish, T.J. Adaptive radiation of photosynthetic physiology in the Hawaiian lobeliads:Dynamic photosynthetic responses. Oecologia 2008, 155, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kałużewicz, A.; Bączek-Kwinta, R.; Krzesiński, W.; Spiżewski, T.; Zaworska, A. Effect of biostimulants on chlorophyll fluorescenceparameters of broccoli (brassica oleracea var. italica)under drought stress and rewatering. Acta Sci. Pol. HortorumCultus 2018, 17, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.M. Continuous excitation chlorophyll fluorescence parameters: A review for practitioners. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Bravo, R.; Arellano, C.; Sosinski, B.R.; Fernandez, G.E. A protocol to assess heat tolerance in a segregating population of raspberry using chlorophyll fluorescence. Sci. Hort. 2011, 130, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.H.; Chien, L.F.; Jiang, C.Y.; Shih, F.C.; Chen, H.Y. A comparison between yellow-green and green cultivars of four vegetable species in pigments, ascorbate, photosynthesis, energy dissipation, and photoinhibition. Photosynthetica 2011, 49, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagwansupyakorn, C. Brassica oleracea L. cv. group Chinese kale. In Plant Resource South-East Asia No. 8: Vegetables; Siemonsma, J.S., Kasem, P., Eds.; Pudoc Scientific Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, W.; Greer, D.; Sun, O. Physiological impacts of magnesiumdeficiency in Pinus radiata: Growth and photosynthesis. New Phytol. 2000, 146, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Heskel, M.; Lu, X.; Munger, J.W.; Sun, S.; Tang, J. Chlorophyllfluorescence tracks seasonal variations of photosynthesis from leaf tocanopy in a temperate forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.W.; Zarter, C.R.; Ebbert, V.; Demmig-Adams, B. Photoprotective strategies of overwinteringevergreens. BioScience 2004, 54, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, C.B.; Grace, S.C. Perspectives on photoinhibition and photorespiration in the field: Quintessential inefficiencies of the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis? J. Exp. Bot. 1995, 46, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Adams, W.W.; Barker, D.H.; Logan, B.A.; Bowlong, D.R.; Verhoeven, A.S. Using chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the fraction of absorbed light allocated to thermal dissipation of excess excitation. Physiol. Plant 1996, 98, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakani, V.G.; Surabhi, G.K.; Reddy, K.R. Photosynthesis andfluorescence responses of C4 plant Andropogongerardii acclimatedto temperature and carbon dioxide. Photosynthetica 2008, 46, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, M.Y.; Weng, J.H. Relationship between photosynthetic CO2 uptake rate and electron transport rate in two C4 perennial grasses under different nitrogen fertilization, light and temperature conditions. Acta Physiol. Plant 2014, 36, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Fuchigami, L.H.; Breen, P.J. The relationship betweenphotosystem II efficiency and quantum yield for CO2 assimilationis not affected by nitrogen content in apple leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Torres, E.; Bravo, L.A.; Corcuera, L.J.; Johnson, G.N. Iselectron transport to oxygen an important mechanism inphotoprotection? Contrasting responses from Antarcticvascular plants. Physiol. Plant 2007, 130, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Harnly, J.M. Identification of the phenolic components of collard greens, kale, and chinese broccoli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7401–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre-González, A.; Montesinos-Pereiraa, D.; Romeroa, L.; Blascoa, B.; Ruiz, J.M. Analysis of metabolic and nutritional biomarkers in Brassica oleracea L. cv. Bronco plants under alkaline stress. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotech. 2018, 93, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, C.J.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Black, T.A.; Jarvis, P.G.; Walthall, C.L.; Grace, J.; Hall, F.G. Remote sensing of photosynthetic-light-use efficiency of boreal forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 101, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Li, X.P.; Niyogi, K.K. Non-photochemical quenching: A response to excess light energy. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schansker, G.; Tóth, S.Z.; Strasser, R.J. Dark recovery of the Chl a fluorescence transient (OJIP) after light adaptation: The qT-component of non-photochemical quenching is related to an activated photosystem I acceptor side. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollastrini, M.; Nogales, A.; Benavides, R.; Bonal, D.; Finer, L.; Radoglou, K.; Bussotti, F. Tree diversity affects chlorophyll a fluorescence andother leaf traits of tree species in a boreal forest. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lefsrud, M.G.; Kopsell, D.A.; Sams, C.E. Irradiance from distinct wavelength light-emitting diodes affect secondary metabolites in kale. HortScience 2008, 43, 2243–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polívka, T.; Frank, H.A. Molecular factors controlling photosynthetic light harvesting by carotenoids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sola, M.A.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M. Carotenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis: A colorful pathway. The Arab. Book 2012, 10, e0158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracheboud, Y.; Leipner, J. The application of chlorophyll fluorescence to study light, temperature, and drought stress. In Practical Applications of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Plant Biology; DeEll, J.R., Toivonen, P.M.A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Porcar-Castell, A.; Pfündel, E.; Korhonen, J.F.; Juurola, E. A new monitoring PAM fluorometer (MONI-PAM) to study the short- and long-term acclimation of photosystem II in field conditions. Photosynth. Res. 2008, 96, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylinski, C.; Gamon, J.; Oechel, W. Seasonal patterns of reflectance indices, carotenoid pigments and photosynthesis of evergreen chaparral species. Oecologia 2002, 131, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids, the pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar]

 ), green (
), green ( ), and dark-green (
), and dark-green ( ) foliage cultivars of Chinese kale cultivated under (A) full fertilization treatment (100 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied twice weekly) and (B) restricted fertilization treatment(50 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied once weekly). Measurements were made in different light intensities at 200, 400, 800, and 1200 μmol m−2 s−1 for 20 min, and 2000 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD conditions for 20 min (a), 1 h (b), and 2 h (c). Vertical bars indicate standard deviations (n = 6).
) foliage cultivars of Chinese kale cultivated under (A) full fertilization treatment (100 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied twice weekly) and (B) restricted fertilization treatment(50 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied once weekly). Measurements were made in different light intensities at 200, 400, 800, and 1200 μmol m−2 s−1 for 20 min, and 2000 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD conditions for 20 min (a), 1 h (b), and 2 h (c). Vertical bars indicate standard deviations (n = 6).
 ), green (
), green ( ), and dark-green (
), and dark-green ( ) foliage cultivars of Chinese kale cultivated under (A) full fertilization treatment (100 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied twice weekly) and (B) restricted fertilization treatment(50 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied once weekly). Measurements were made in different light intensities at 200, 400, 800, and 1200 μmol m−2 s−1 for 20 min, and 2000 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD conditions for 20 min (a), 1 h (b), and 2 h (c). Vertical bars indicate standard deviations (n = 6).
) foliage cultivars of Chinese kale cultivated under (A) full fertilization treatment (100 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied twice weekly) and (B) restricted fertilization treatment(50 mL of 0.1% NH4NO3 and K2HPO4 applied once weekly). Measurements were made in different light intensities at 200, 400, 800, and 1200 μmol m−2 s−1 for 20 min, and 2000 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD conditions for 20 min (a), 1 h (b), and 2 h (c). Vertical bars indicate standard deviations (n = 6).

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, K.-H.; Shih, F.-C.; Huang, M.-Y.; Weng, J.-H. Physiological Characteristics of Photosynthesis in Yellow-Green, Green and Dark-Green Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Musil.) under Varying Light Intensities. Plants 2020, 9, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080960
Lin K-H, Shih F-C, Huang M-Y, Weng J-H. Physiological Characteristics of Photosynthesis in Yellow-Green, Green and Dark-Green Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Musil.) under Varying Light Intensities. Plants. 2020; 9(8):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080960
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Kuan-Hung, Feng-Chi Shih, Meng-Yuan Huang, and Jen-Hsien Weng. 2020. "Physiological Characteristics of Photosynthesis in Yellow-Green, Green and Dark-Green Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Musil.) under Varying Light Intensities" Plants 9, no. 8: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080960
APA StyleLin, K.-H., Shih, F.-C., Huang, M.-Y., & Weng, J.-H. (2020). Physiological Characteristics of Photosynthesis in Yellow-Green, Green and Dark-Green Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Musil.) under Varying Light Intensities. Plants, 9(8), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080960






