Effect of Extreme Climate on Topology of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
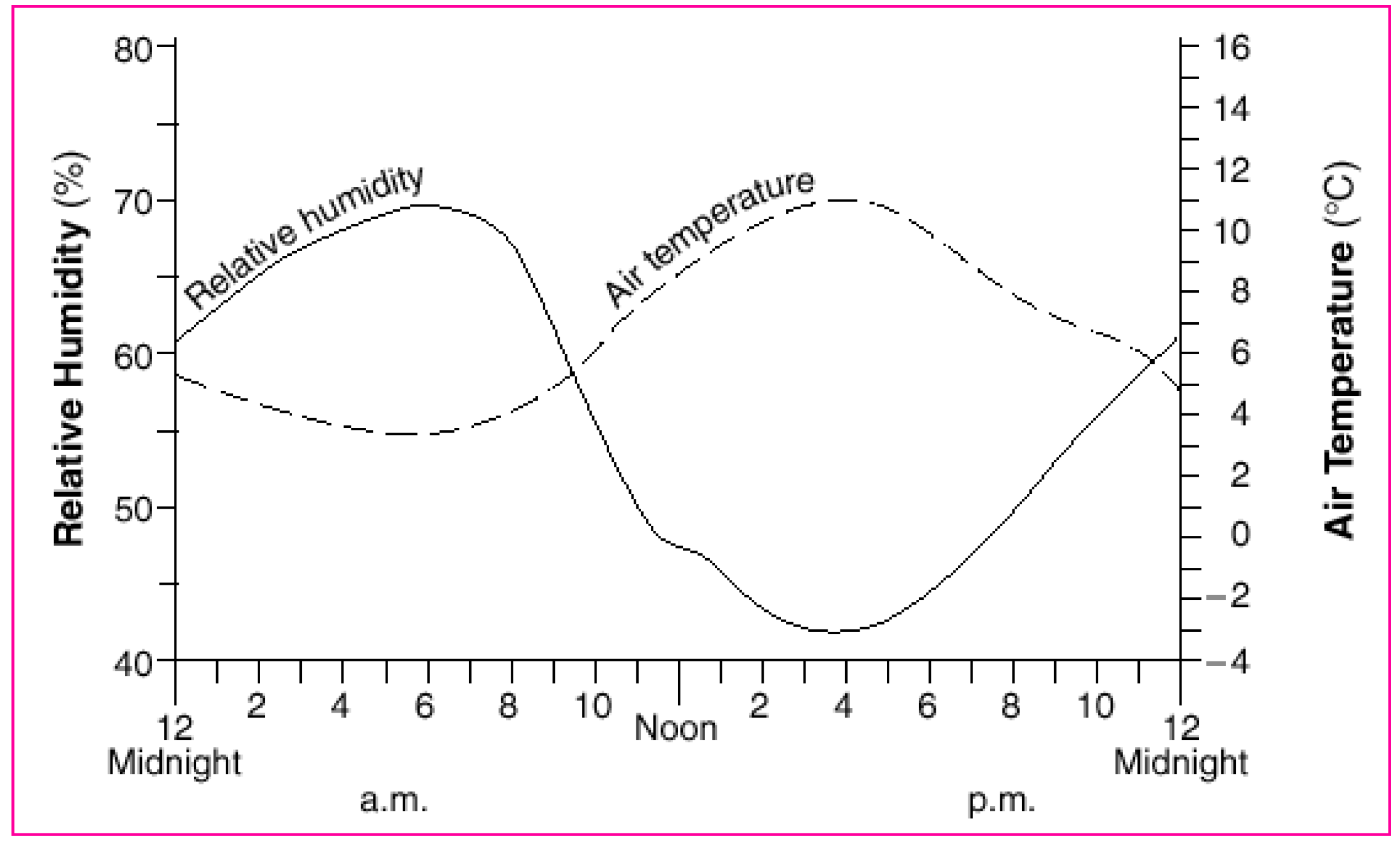
2. Global Climate Trends
3. Methodology
3.1. Creep Prediction
3.2. Shrinkage Prediction
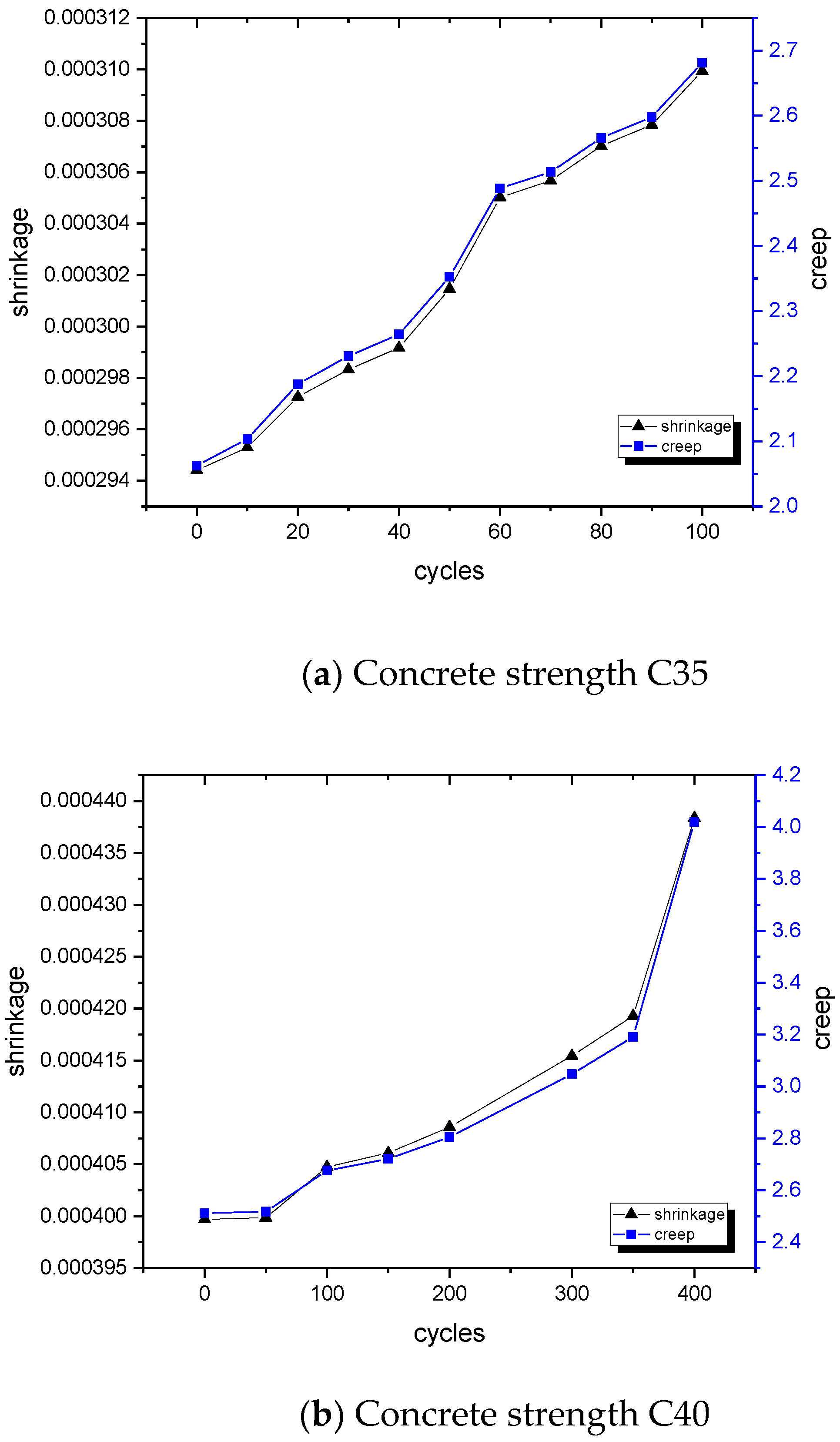
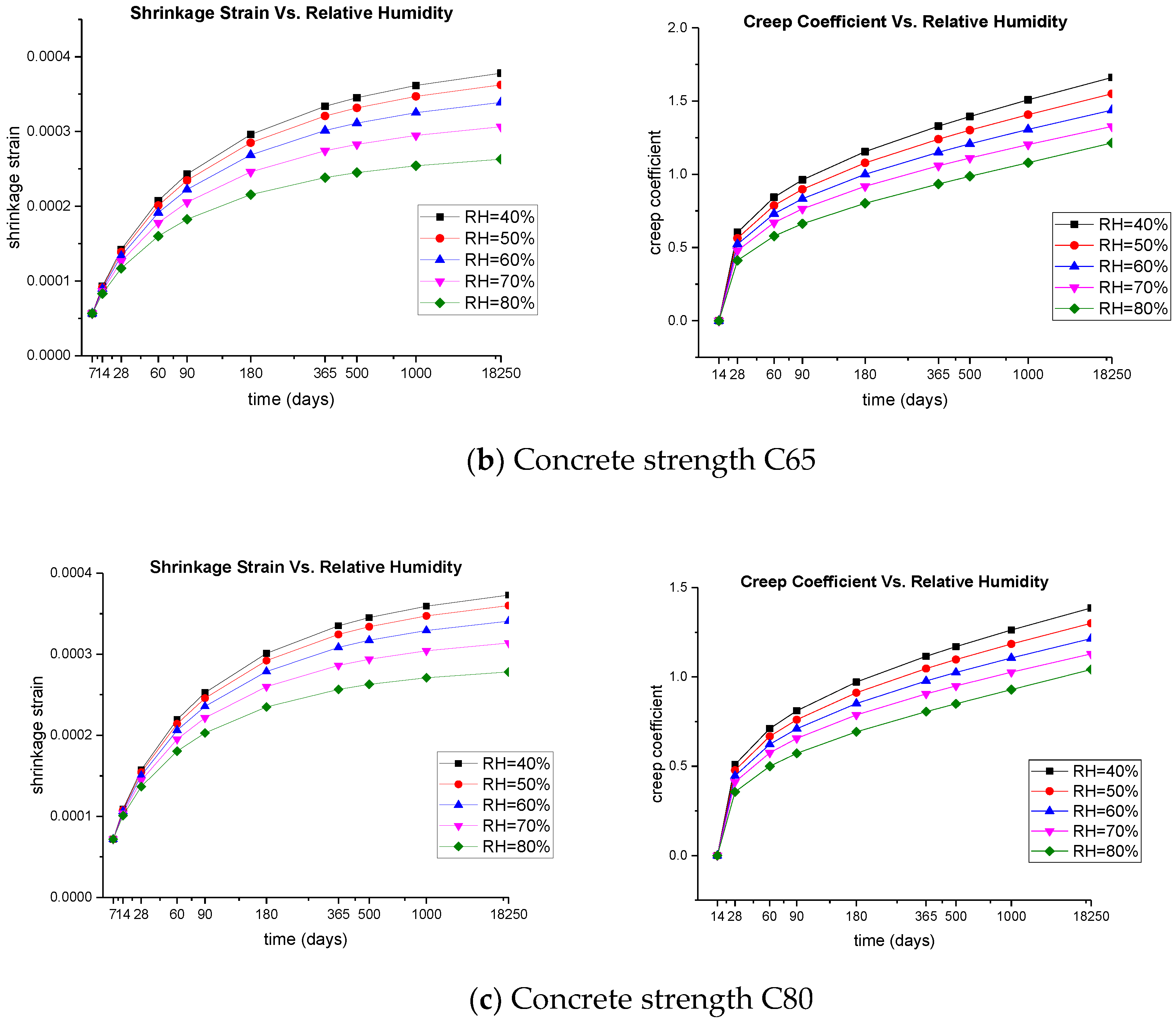
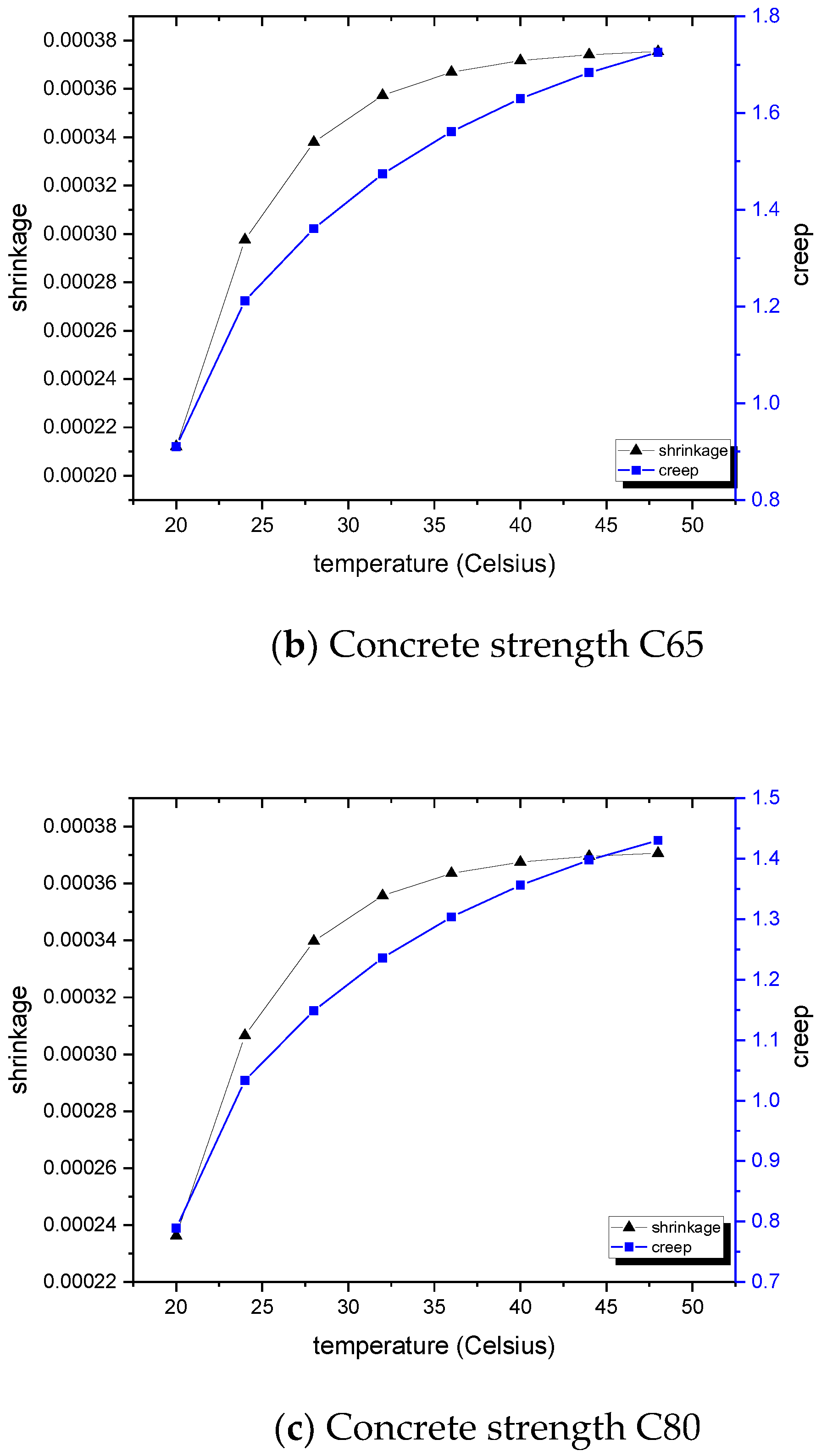
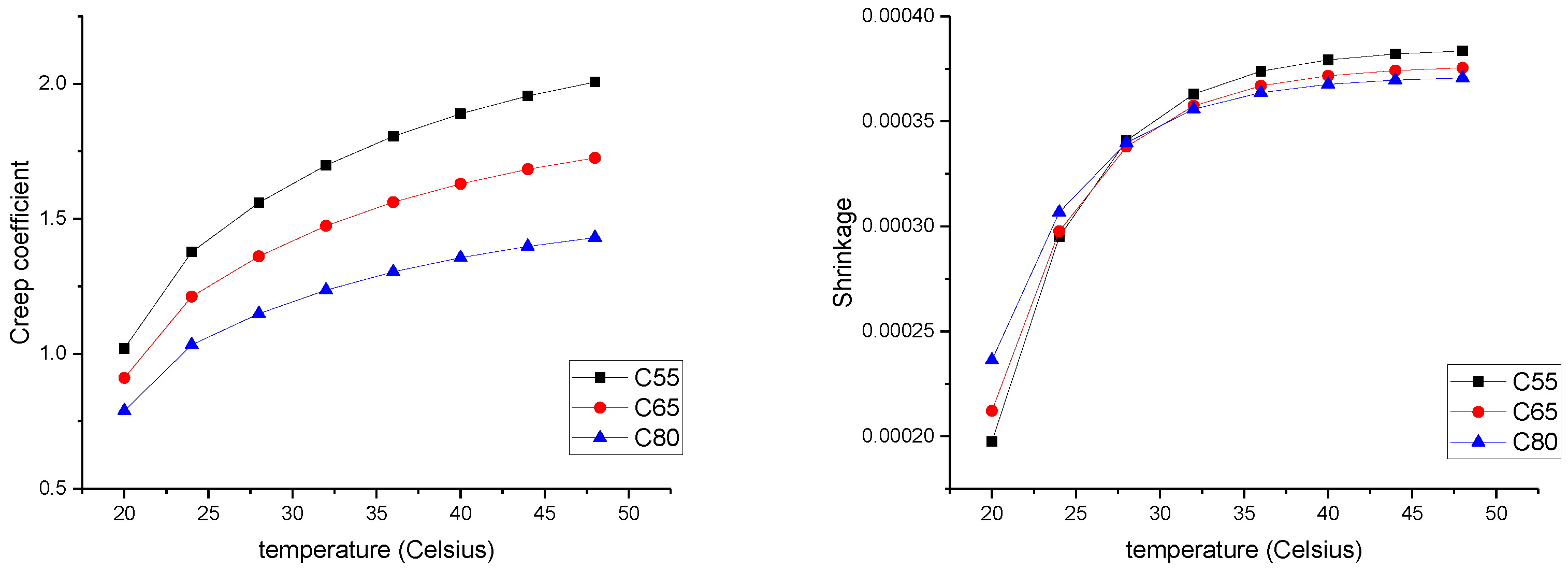
4. Results for the Effects of Climate
4.1. Extreme Temperature Impact
4.2. Extreme Humidity Impact
5. Discussion of the Effects of Climate Uncertainty
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Planton, S.; Deque, M.; Chauvin, F.; Terray, L. Expected impacts of climate change on extreme climate events. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Lopes, L.M.C.; Papaelias, M.P. Georisks in railway systems under climate uncertainties by different types of sleeper/crosstie materials. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2018, 20, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lisø, K.R.; Aandahl, G.; Eriksen, S.; Alfsn, K. Preparing for climate change impacts in Norway’s built environment. Built. Res. Inf. 2003, 31, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Ye, J.; Garcia-Leon, M.; Carcia, V.; Ortego, M.I.; Lionello, P.; Sanchez-Arcilla, A. Multivariate statistical modelling of future marine storms. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 65, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Ye, J.; Garcia-Leon, M.; Carcia, V.; Ortego, M.I.; Stanica, A.; Sanchez-Arcilla, A. Multivariate hybrid modelling of future wave-storm at the northwestern Black Sea. Water 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda Fontao, P.A.; Zacattini, J.A. Variations of rainfall rhythm in Alto Pardo Watershed, Brazil: Analysis of two specific years, a wet and dry one, and their relation with the river flow. Climate 2017, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesit, R.; Kaewunruen, S. Vibration characteristics of micro-engineered crumb rubber concrete for railway sleeper applications. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2017, 15, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Meesit, R. Sensitivity of crumb rubber particle sizes on electrical resistance of rubberised concrete. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1126937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Meesit, R.; Mondal, P. Early-age dynamic moduli of crumbed rubber concrete for compliant railway structures. J. Sustain. Cement-Based Mater. 2017, 6, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Kimani, S.K. Damped frequencies of precast modular steel-concrete composite railway track slabs. Steel Compos. Struct. 2017, 25, 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Remennikov, A.M. Effect of a large asymmetrical wheel burden on flexural response and failure of railway concrete sleepers in track systems. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2008, 15, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S. Monitoring in-service performance of fibre-reinforced foamed urethane sleepers/bearers in railway urban turnout systems. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2015, 1, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remennikov, A.M.; Kaewunruen, S. Experimental load rating of aged railway concrete sleepers. Eng. Struct. 2014, 76, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawari, H.M. Minimising Track Degradation through Managing Vehicle/Track Interaction. Ph.D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, Z. Enhancement of Dynamic Damping in Eco-Friendly Railway Concrete Sleepers Using Waste-Tyre Crumb Rubber. Materials 2018, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remennikov, A.M.; Kaewunruen, S. A review of loading conditions for railway track structures due to train and track vertical interaction. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2008, 15, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kaewunruen, S.; Robery, P.; Remennikov, A.M. Creep and shrinkage effect on railway prestressed concrete sleepers. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Rail Transportation, Chengdu, China, 10–12 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Remennikov, A.M. Progressive failure of prestressed concrete sleepers under multiple high-intensity impact loads. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 2460–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Li, D.; Ngamkhanong, C.; Janeliukstis, R.; Kaewunruen, S. Fatigue Life Assessment Method for Prestressed Concrete Sleepers. Front. Built Environ. 2017, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, É.A.; Pokropski, D.; You, R.; Kaewunruen, S. Comparison of structural design methods for railway composites and plastic sleepers and bearers. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 18, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binti Sa’adin, S.L.; Kaewunruen, S.; Jaroszweski, D. Risks of Climate Change with Respect to the Singapore-Malaysia High Speed Rail System. Climate 2016, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rail Safety and Standards Boards (RSSB). Tomorrow’s Railway and Climate Change Adaptation: Executive Report; RSSB: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krezo, S.; Mirza, O.; Kaewunruen, S.; Sussman, J.M. Evaluation of CO2 emissions from railway resurfacing maintenance activities. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 65, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Wu, L.; Goto, K.; Najih, Y.M. Vulnerability of Structural Concrete to Extreme Climate Variances. Climate 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G. Investigation of Changes in Extreme Temperature and Humidity over China through a Dynamical Downscaling Approach. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1136–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jin, S. Assessment of the Performance of Three Dynamical Climate Downscaling Methods Using Different Land Surface Information Over China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Yohe, G.; Easterling, W.; Kates, R.; Ruth, M.; Sussman, E.; Whelchel, A.; Wolfe, D.; Lipschultz, F. Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment; U.S. Global Change Research Program: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, F.E.; Brischke, C.; Meyer, L.; Isaksson, T.; Thelandersson, S.; Kavyrmaci, D. Durability of timber outdoor structures—Modelling performance and climate impacts. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering, Auckland, New Zealand, 16–19 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Solatiyan, E.; Asadi, M.; Bozorgmehrasl, M. Investigating the Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Strength Properties of Concrete Pavements in Cold Climates. Indian J. Fundam. Appl. Life Sci. 2015, 5, 2231–6345. [Google Scholar]
- Zi, G.; Moon, D.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Jang, S.C.; Kim, S.S. Investigation of a concrete sleeper failed by expansion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 26, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijen, J. Durability of Engineering Structures: Design, Repair and Maintenance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ergue, A.; Kurklu, G.; Baspinar, M.S. The effects of material properties on bond strength between reinforcing bar and concrete exposed to high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.I.; Mickleborough, N.C.; Ranzi, G. Design of Prestressed Concrete to AS3600-2009, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rusch, H.; Jungwirth, D.; Hilsdorf, H.K. Creep and Shrinkage—Their Effect on the Behaviour of Concrete Structures; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, A.M. Properties of Concrete, 4th ed.; Longman Group Limited: Harlow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, P. Prestressed Concrete Design to Eurocodes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L.; Purkiss, J. Concrete Design to EN 1992, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.S.; Yi, T.H. Freeze-thaw durability of air-entrained concrete. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 650791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.S.; Cao, W.Q.; Wang, B. Effect of fast freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of ordinary-air-entrained concrete. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 923032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ngamkhanong, C.; Kaewunruen, S. Time-dependent topology of railway prestressed concrete sleepers. In Proceedings of the World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium, Beijing, China, 24–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sussman, J.M.; Matsumoto, A. Grand Challenges in Transportation and Transit Systems. Front. Built Environ. 2016, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Kaewunruen, S. Effect of Extreme Climate on Topology of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers. Climate 2019, 7, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010017
Li D, Kaewunruen S. Effect of Extreme Climate on Topology of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers. Climate. 2019; 7(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, and Sakdirat Kaewunruen. 2019. "Effect of Extreme Climate on Topology of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers" Climate 7, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010017
APA StyleLi, D., & Kaewunruen, S. (2019). Effect of Extreme Climate on Topology of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers. Climate, 7(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010017





