Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Suppression of a Rotating Flexible Beam with Segmented Active Constrained Layer Damping Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
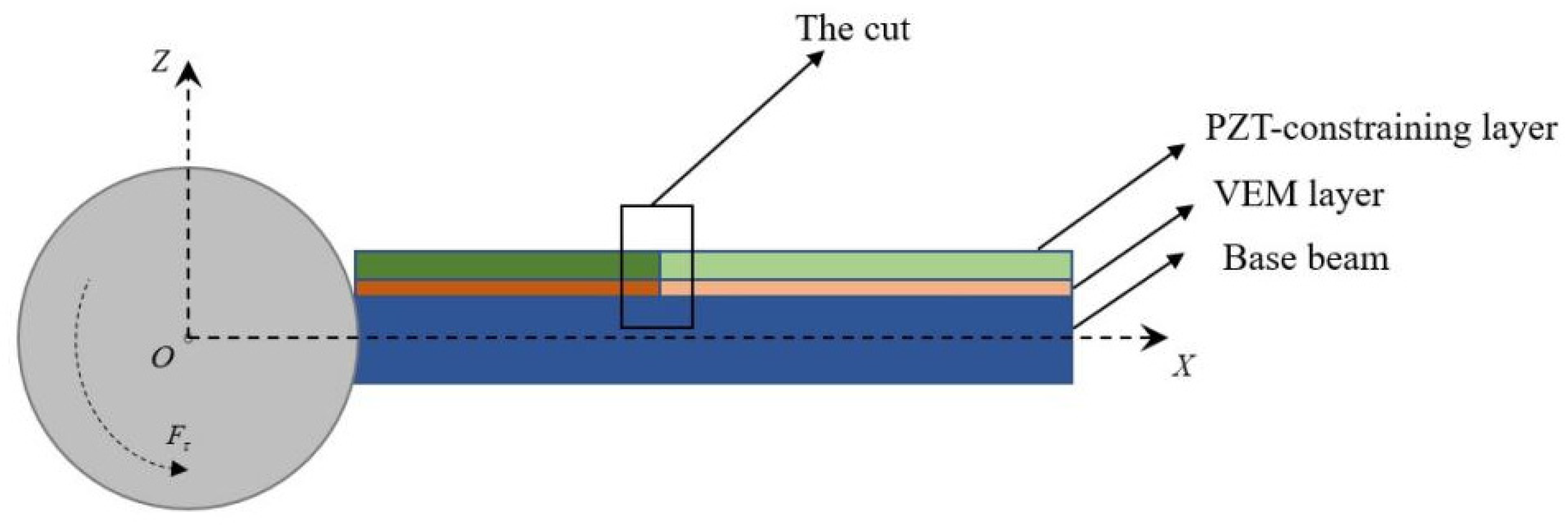
2. Dynamic Modeling
2.1. Basic Assumptions
- (1)
- The SACLD beam consists of three layers, a piezoelectric constraining layer, a viscoelastic damping layer, and a base layer, without considering the sliding between the layers;
- (2)
- The shear displacement of the piezoelectric and base layers is neglected; only the shear displacement of the viscoelastic damping layer is considered;
- (3)
- The piezoelectric layer is polarized along the thickness direction;
- (4)
- The longitudinal contraction caused by transversal displacement is considered for each beam;
- (5)
- The beam rotates on a horizontal plane, without considering the effect of gravity;
- (6)
- The transverse displacements of the three layers are considered the same.
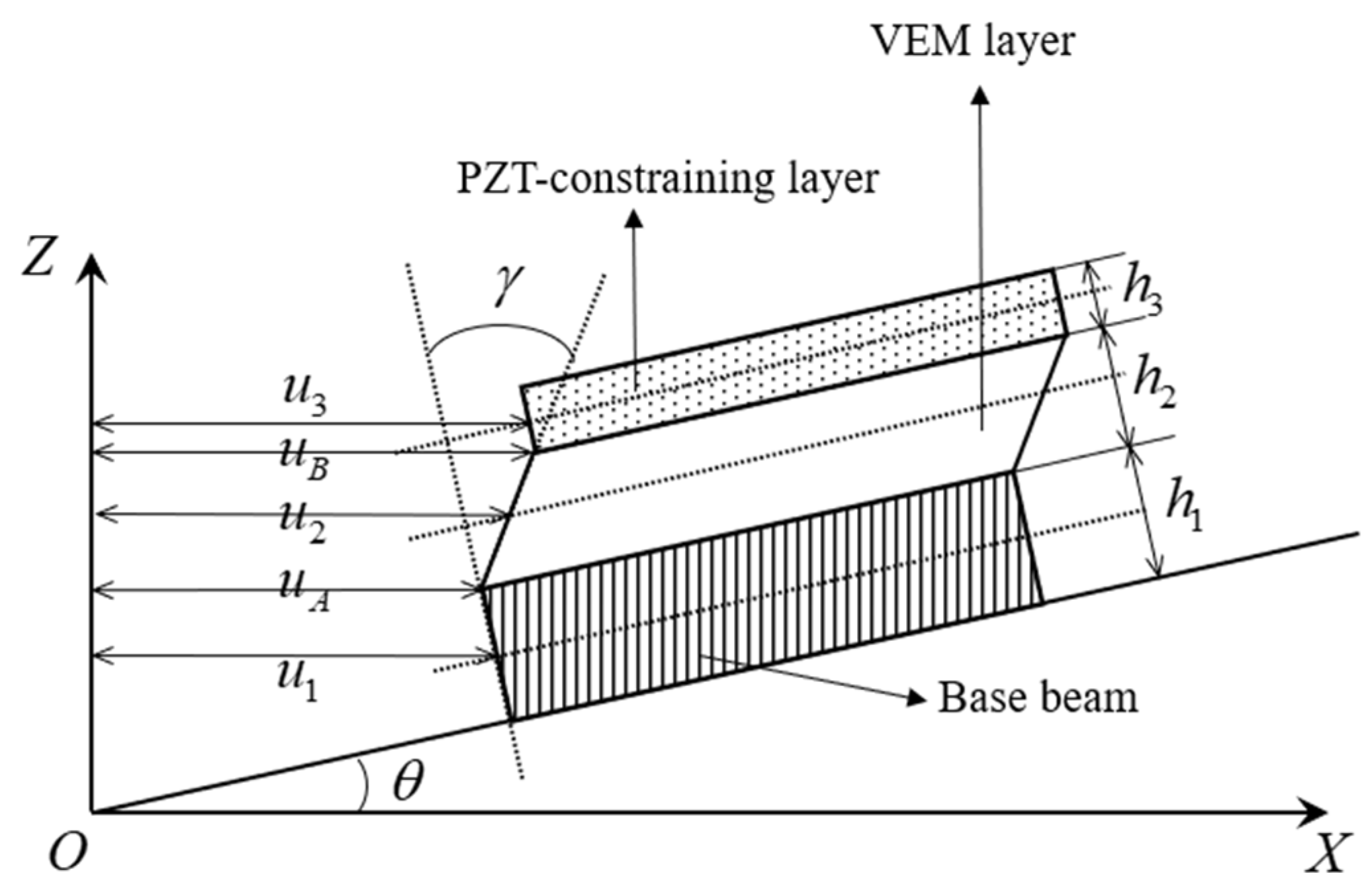
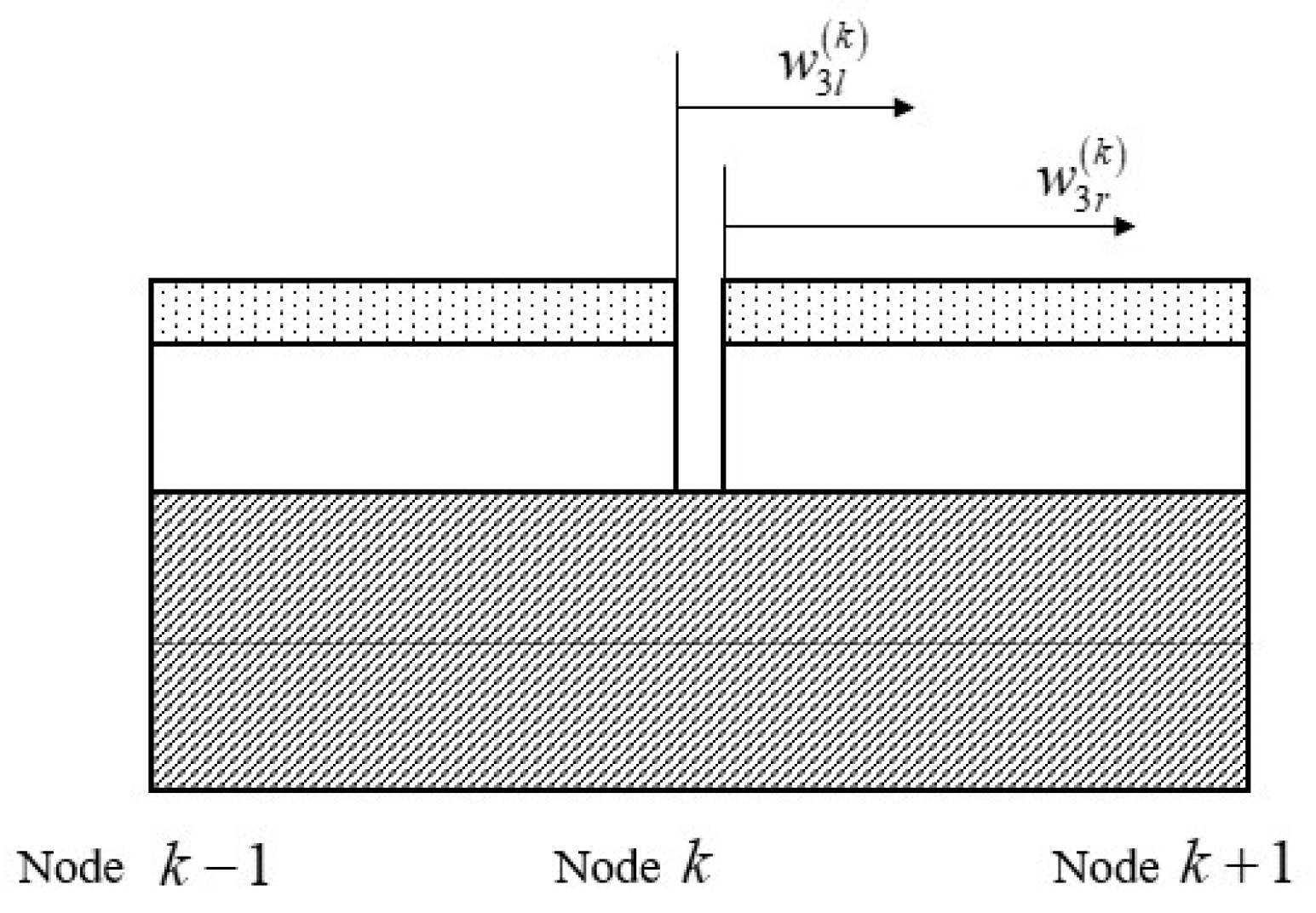
2.2. Displacement Description
2.3. Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
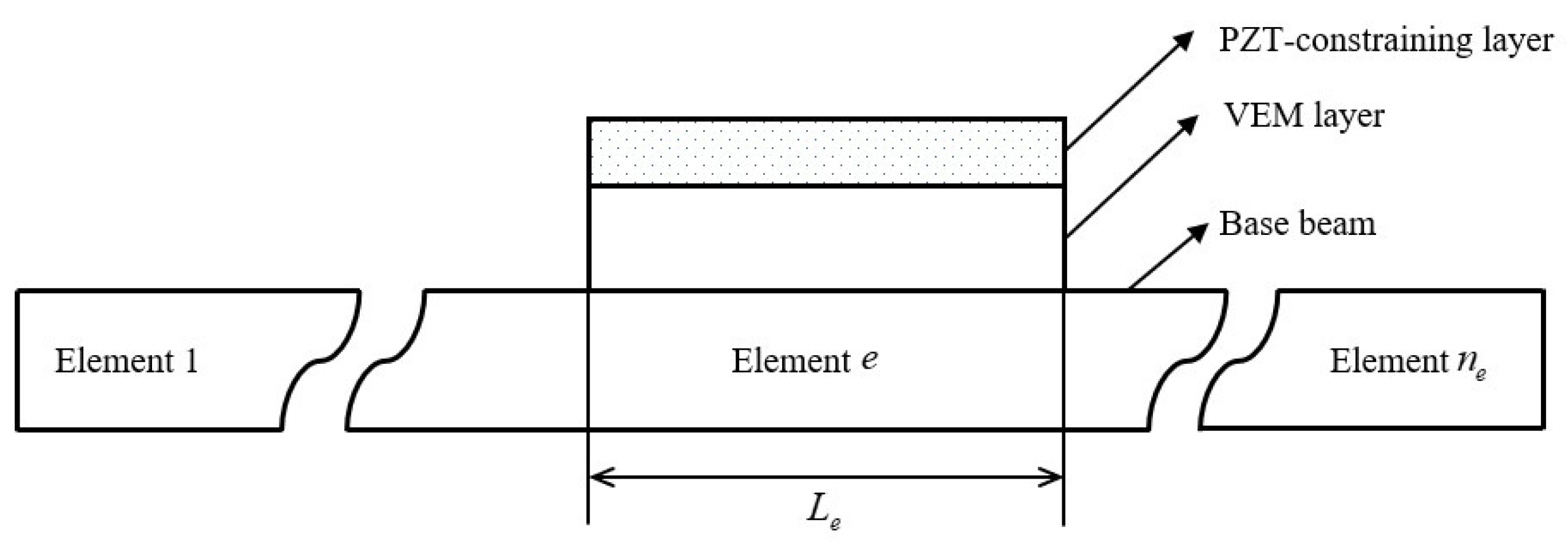
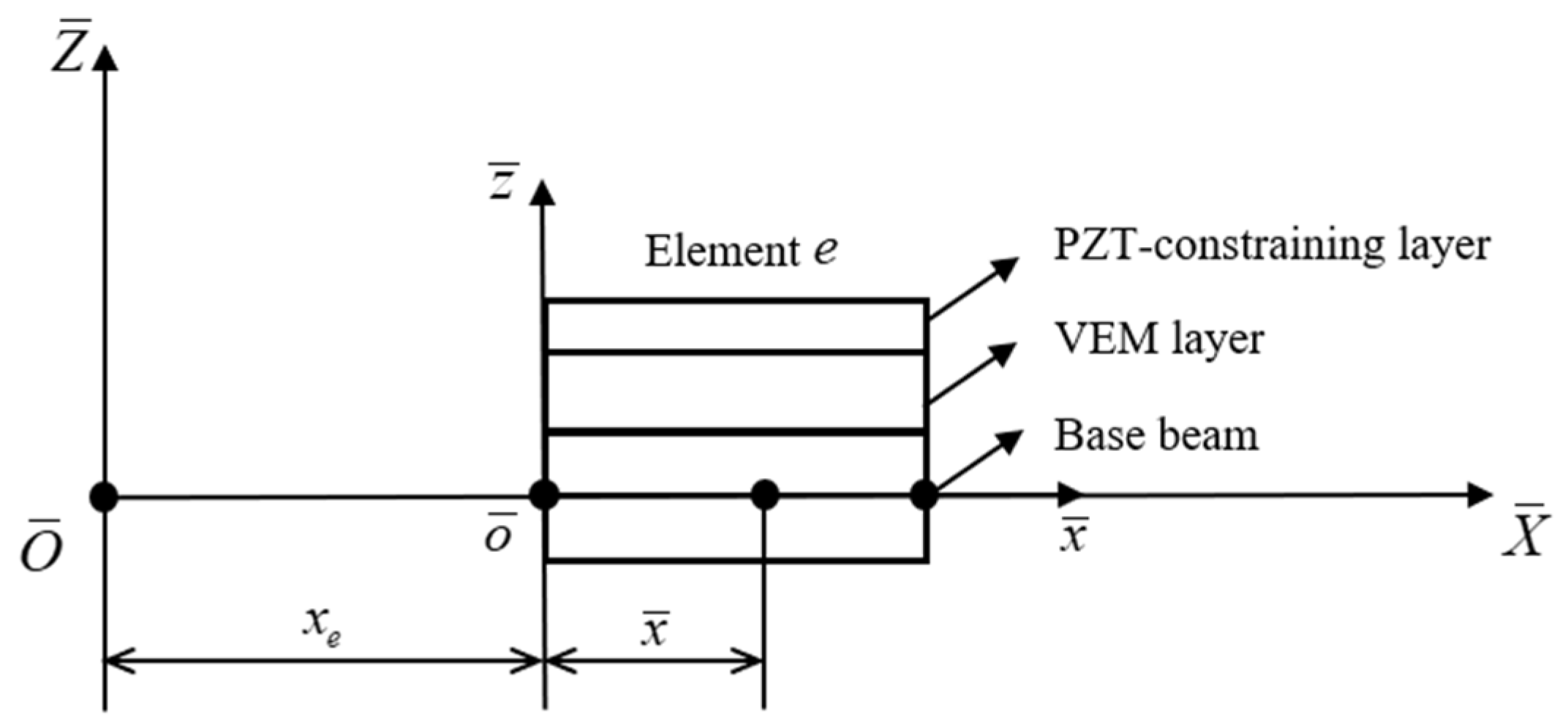
2.4. Equations of the System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validations of the Hub–SACLD Beam System
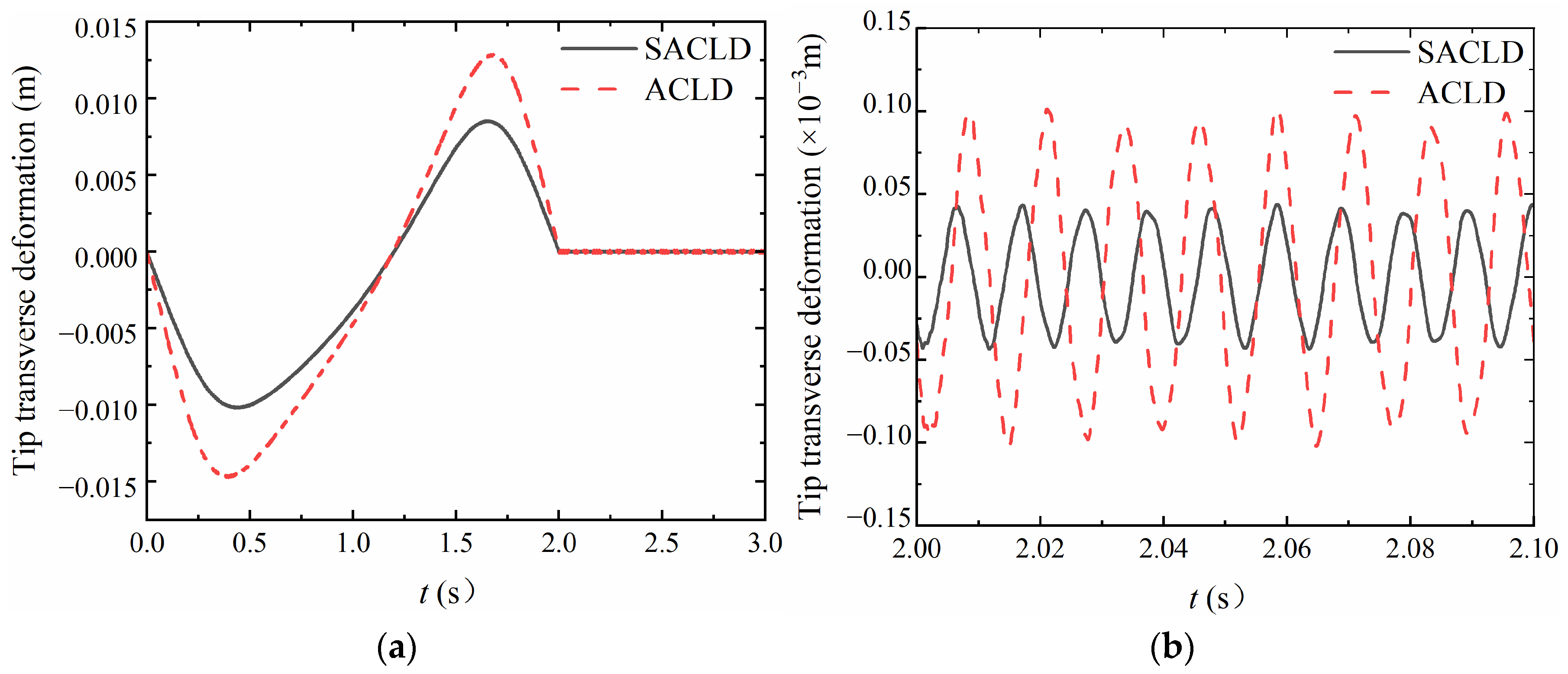
3.2. Dynamic Response Analysis
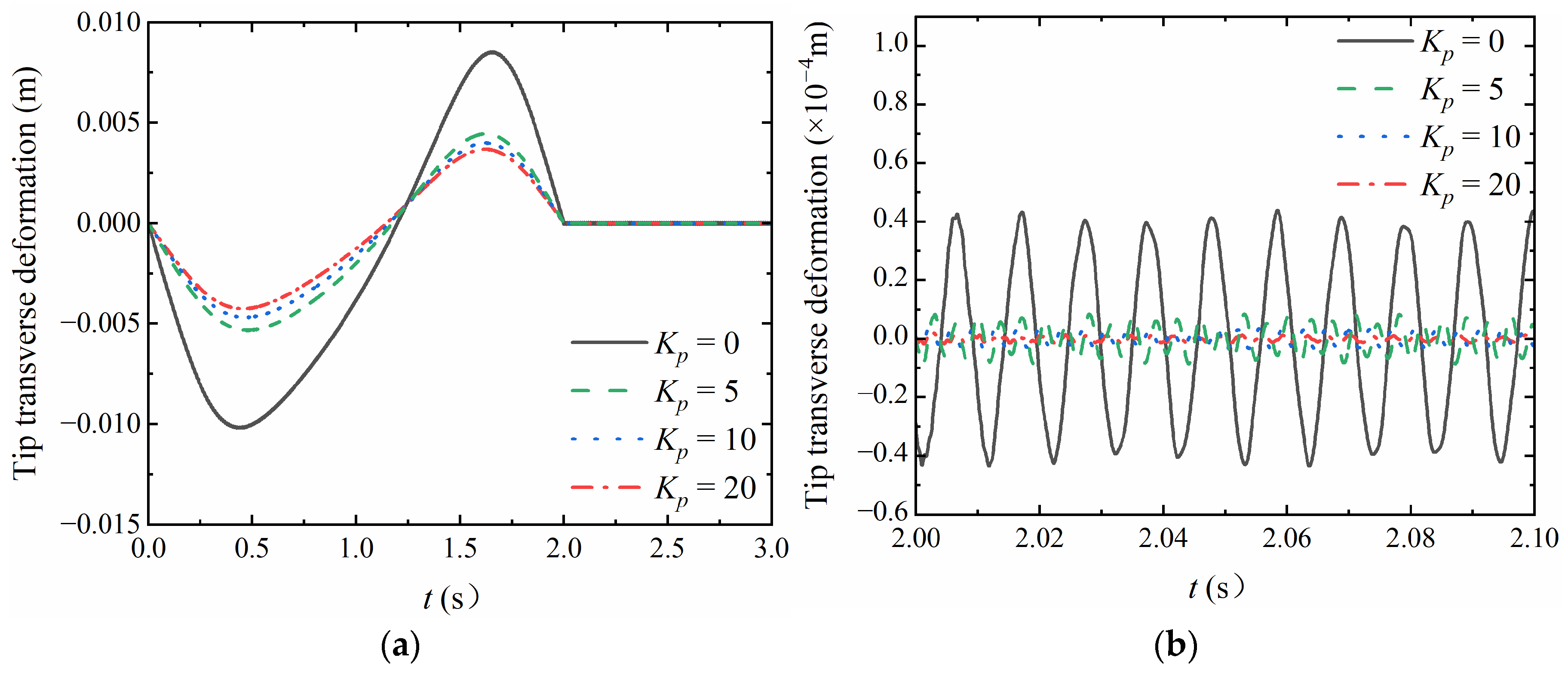
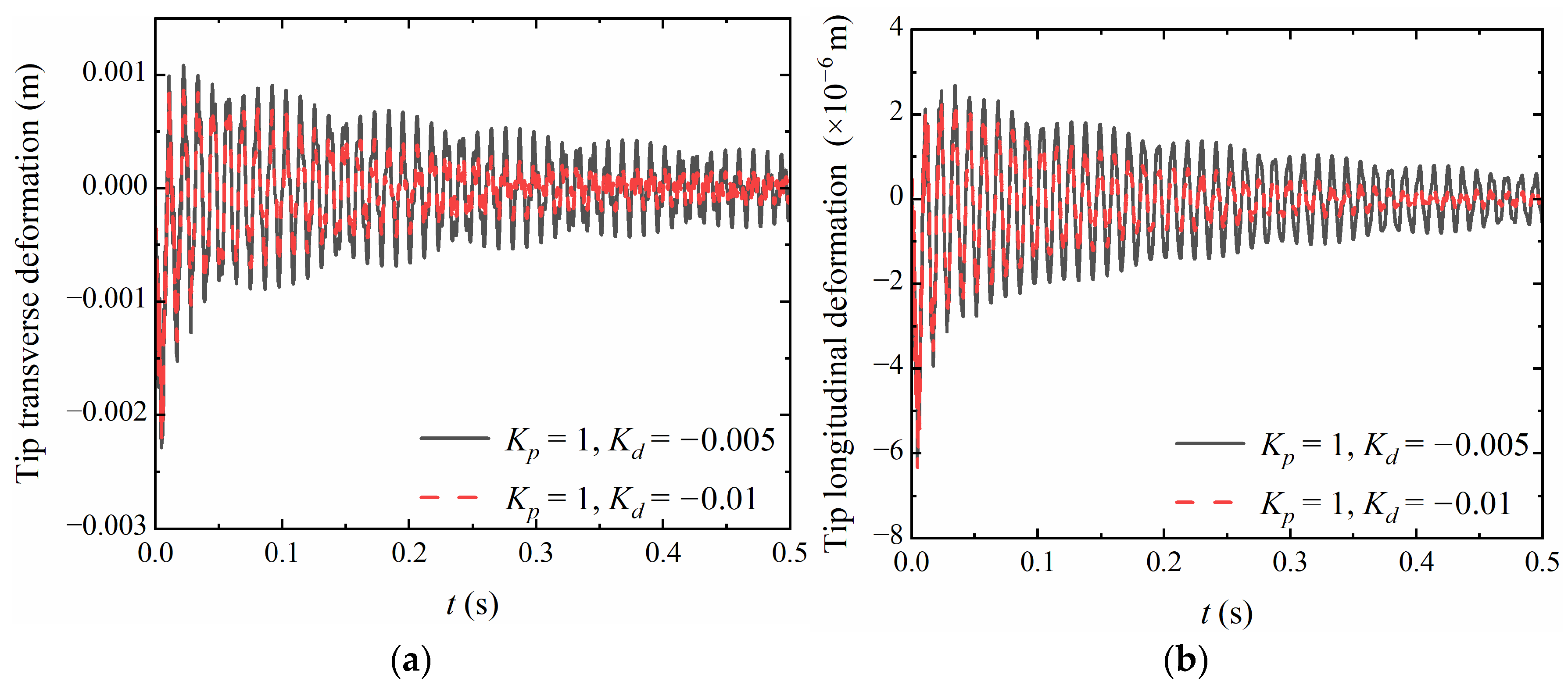
3.3. Vibration Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Matrices in Equation (30)
Appendix B. The Matrices in Equation (33)
References
- Ma, H.W.; Sun, W.; Du, D.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, H.H. Nonlinear vibration analysis of double cylindrical shells coupled structure with bolted connection and partially attached constrained layer damping. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 223, 107270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Lv, H.Y.; Zhou, Z.X.; Han, Q.K.; Liu, J.G. Nonlinear vibration analysis of fiber reinforced composite cylindrical shells with partial constrained layer damping treatment. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 157, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zheng, H.; Liu, G.R. Vibration analysis of a beam with PCLD patch. Appl. Acoust. 2004, 65, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Tan, X.M.; Cai, C. Damping analysis of beams covered with multiple PCLD patches. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2006, 48, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cai, C.; Pau, G.S.H.; Liu, G.R. Minimizing vibration response of cylindrical shells through layout optimization of passive constrained layer damping treatments. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 279, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Qiu, Q.; Wan, H.; Zhang, D.D. Damping analysis of multilayer passive constrained layer damping on cylindrical shell using transfer function method. J. Vib. Acoust. 2014, 136, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Sainsbury, M.G. The Galerkin element method applied to the vibration of rectangular damped sandwich plates. Comput. Struct. 2000, 74, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröhlich, M.; Böswald, M.; Wallaschek, J. Viscoelastic damping design—A novel approach for shape optimization of Constrained Layer Damping treatments at different ambient temperatures. J. Sound Vib. 2023, 555, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, A.; Ro, J. Optimum design and control of active constrained layer damping. J. Vib. Acoust. 1995, 117, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, A. Active and Passive Vibration Damping; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Varadan, V.V.; Lim, Y.H.; Varadan, V.K. Closed loop finite-element modeling of active/passive damping in structural vibration control. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.H.K.; Yau, D.T.W. Vibration characteristics of a rotating flexible arm with ACLD treatment. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 269, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T. Active structural acoustics control of beams using active constrained layer damping through loss factor maximization. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 287, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharnappa, N.; Ganesan, N.; Sethuraman, R. Dynamic modeling of active constrained layer damping of composite beam under thermal environment. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 305, 728–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, C.M.A.; Rodrigues, J.D. Combined feedback/feedforward active control of vibration of beams with ACLD treatments: Numerical simulation. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoud, H.; Daya, E.M.; Belouettar, S.; Duigou, L.; Potier-Ferry, M. Damping analysis of beams submitted to passive and active control. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, S.P. Vibration and damping characteristics of beams with active constrained layer treatments under parametric variations. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4162–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Theoretical and experimental vibration analysis of rotating beams with combined ACLD and Stressed Layer Damping treatment. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.K.; Nayak, B.; Sarangi, S.K. Active Vibration Control of Smart Functionally Graded Beams. Procedia Eng. 2016, 144, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, D.G.; Guo, Y.B. Dynamic modeling and analysis of a rotating flexible beam with smart ACLD treatment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 131, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.G. Dynamic modeling and vibration analysis of rotating beams with active constrained layer damping treatment in temperature field. Compos. Struct. 2019, 226, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.N.; Sarangi, S.K. Augmented active constrained layer damping of beams using graphite reinforced viscoelastic composite material. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.W. Influence analysis of control signal phase on the vibration reduction effect of active constrained layer damping. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 190, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Baz, A. Vibration control of bending modes of plates using active constrained layer damping. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 227, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liao, W.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Guo, Y.B. Vibration analysis of a free moving thin plate with fully covered active constrained layer damping treatment. Compos. Struct. 2020, 235, 111742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattimani, S.C.; Ray, M.C. Vibration control of multiferroic fibrous composite plates using active constrained layer damping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 106, 334–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.; Behera, D.K. Active constrained layer damping treatment on graphene reinforced composite plates. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 5206–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallannavar, V.; Kattimani, S. Effect of temperature on the performance of active constrained layer damping of skew sandwich plate with CNT reinforced composite core. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 5423–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wong, P.K.; Ma, X.; Xie, Z.C.; Xu, J.; Cristino, V.A. Simplification of finite element modeling for plates structures with constrained layer damping by using single-layer equivalent material properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 157, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.Y.; Li, J.W.; Wei, D.T.; Gao, P.X.; Yan, Y.Y.; Han, Q.K. Vibration control of an aero pipeline system with active constraint layer damping treatment. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, X.F.; Rong, W.C.; Gao, P.X.; Yu, T.; Han, H.W.; Xu, L.J. Vibration and damping analysis of pipeline system based on partially piezoelectric active constrained layer damping treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyas, M. Vibration control of skew magneto-electro-elastic plates using active constrained layer damping. Compos. Struct. 2019, 208, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyas, M.; Harursampath, D.; Nguyen-Thoi, T. Influence of active constrained layer damping on the coupled vibration response of functionally graded magneto-electro-elastic plates with skewed edges. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 1019–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Wang, K.W. A new active constrained layer configuration with enhanced boundary actions. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Wang, K.W. Characteristics of enhanced active constrained layer damping treatments with edge elements, Part 1: Finite element model development and validation. ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 1998, 120, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Wang, K.W. Characteristics of enhanced active constrained layer damping treatments with edge elements, Part 2: System analysis. ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 1998, 120, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.X.; Liao, W.H. Damping Characteristics of beams with enhanced self-sensing active constrained layer treatments under various boundary conditions. J. Vib. Acoust. 2005, 127, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.G.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic modeling and vibration control of a rotating space flexible arm with enhanced active constrained layer damping treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 531, 012071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liao, W.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Guo, Y.B. Dynamic modeling and analysis of rotating beams with partially covered enhanced active constrained layer damping treatment. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 455, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.G.; Chen, S.J.; Liao, W.H. Vibration suppression of a rotating functionally graded beam with enhanced active constrained layer damping treatment in temperature field. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 161, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Ray, M.C.; Patil, N.D.; Kundalwal, S.I. Dynamic modelling and analysis of smart carbon nanotube-based hybrid composite beams: Analytical and finite element study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2021, 235, 2185–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Liao, W.H.; Zhang, D.G. Vibration control of a rotating hub-plate with enhanced active constrained layer damping treatment. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Liao, W.-H. Dynamical analysis and vibration estimation of a flexible plate with enhanced active constrained layer damping treatment by combinatorial neural networks of surrogates. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 108136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, R.; Lee, C.T. Length optimization for constrained viscoelastic layer damping. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 48, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, G. Improving single-constrained-layer damping treatment by sectioning the constraining layer. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1987, 5, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lesieutre, G.A.; Lee, U. A finite element for beams having segmented active constrained layers with frequency-dependent viscoelastics. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, R.K.; Kawiecki, G. Experimental evaluation of segmented active constrained layer damping treatments. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1997, 8, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompette, P.; Fatemi, J. Damping of beams. Optimal distribution of cuts in the viscoelastic constrained layer. Struct. Optim. 1997, 3, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Gu, H.; Zhou, X. Use of segmented constrained layer damping treatment for improved helicopter aeromechanical stability. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Gu, H.Z.; Beri, R. Modeling segmented active constrained layer damping using hybrid displacement field. AIAA J. 2001, 39, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cento, P.F.; Kawiecki, G. Finite element modeling of segmented active constrained damping layers including bonding layer effect. J. Vib. Control 2002, 8, 805–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajmi, M.A.; Bourisli, R.I. Optimum design of segmented passive-constrained layer damping treatment through genetic algorithms. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2008, 15, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, L.; Gerald, K. Optimization of segmented constrained layer damping with mathematical programming using strain energy analysis and modal data. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Avinash, K.; Pravin, H. Optimization of segmented constrained layer damping literature review. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2014, 3, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.T.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Qin, C. Dimensionless analysis of segmented constrained layer damping treatments with modal strain energy method. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 8969062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinonso, O.U. Experimental Study of Segmented Constrained Layer Damping in Rectangular and Sinusoidal Beams; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]


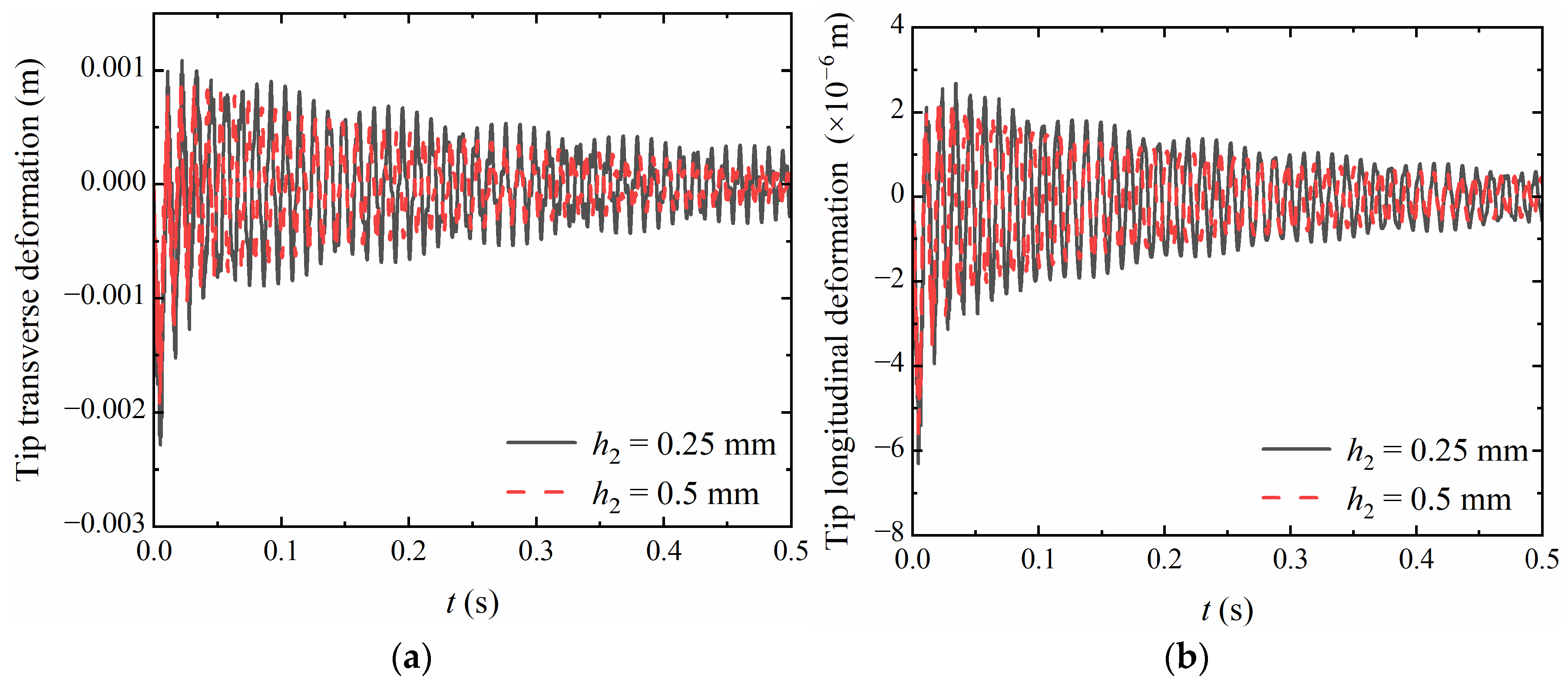
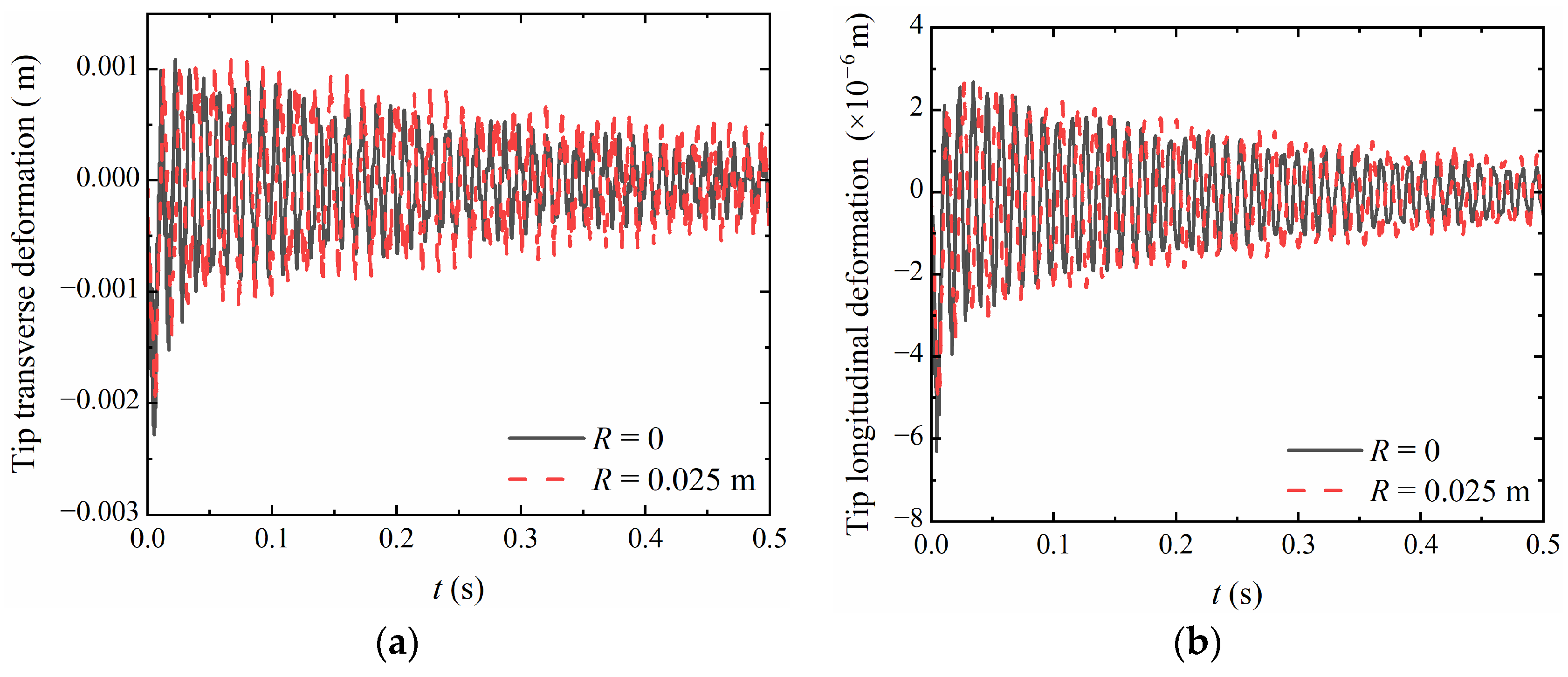
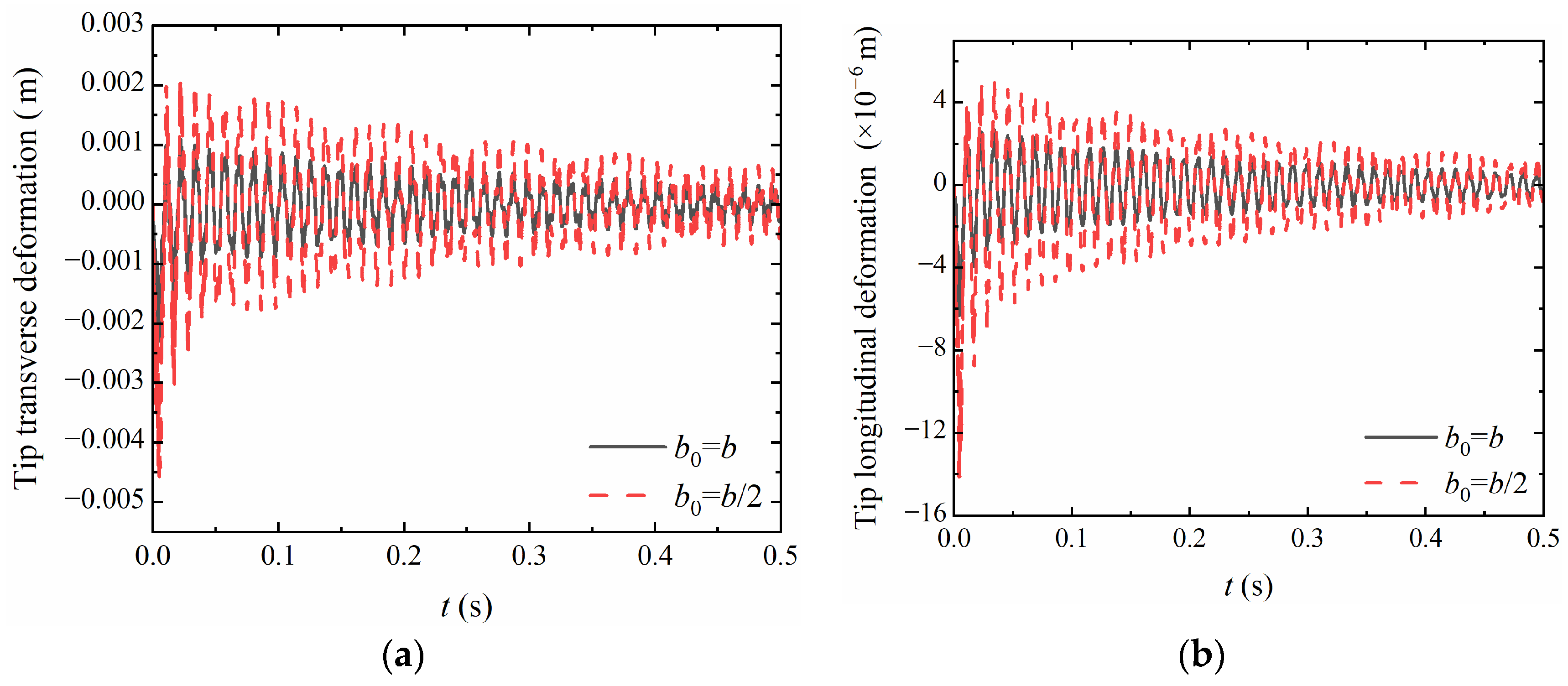
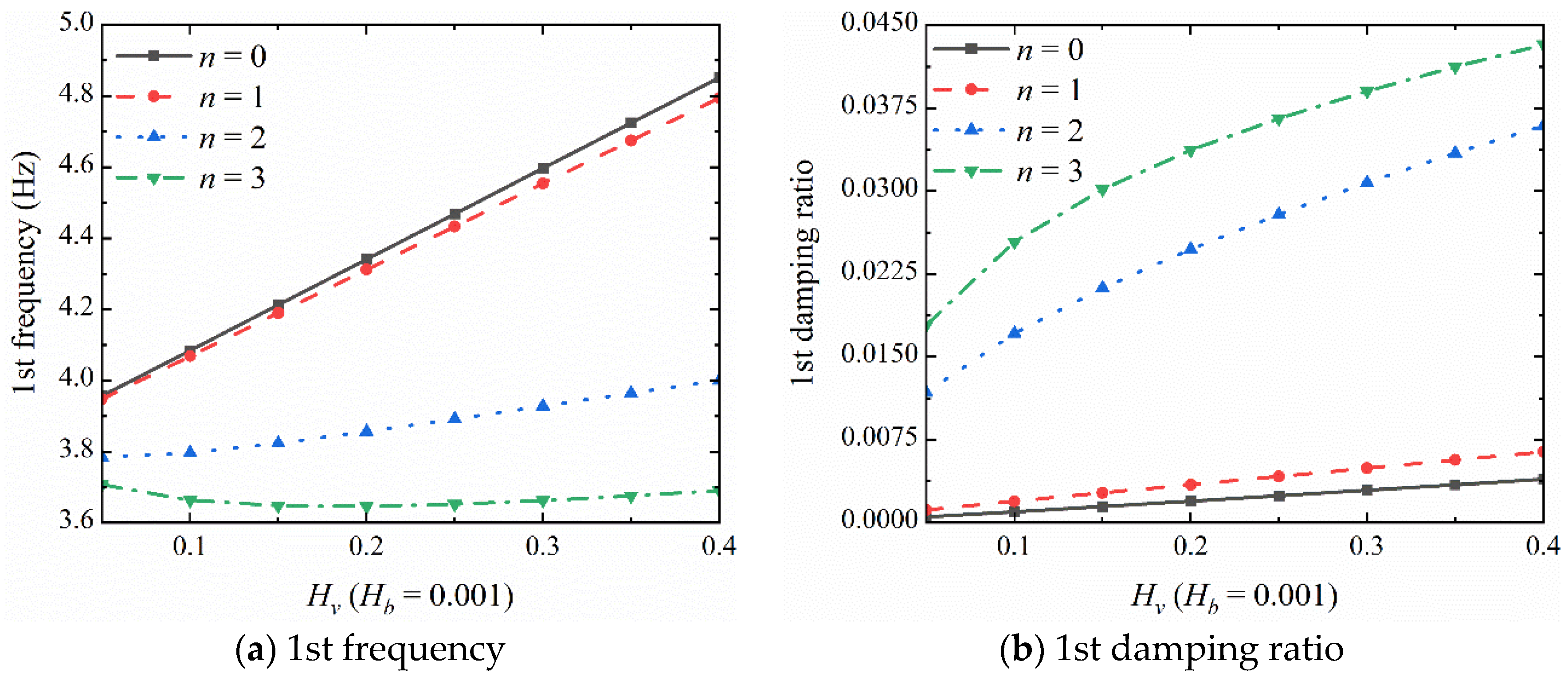
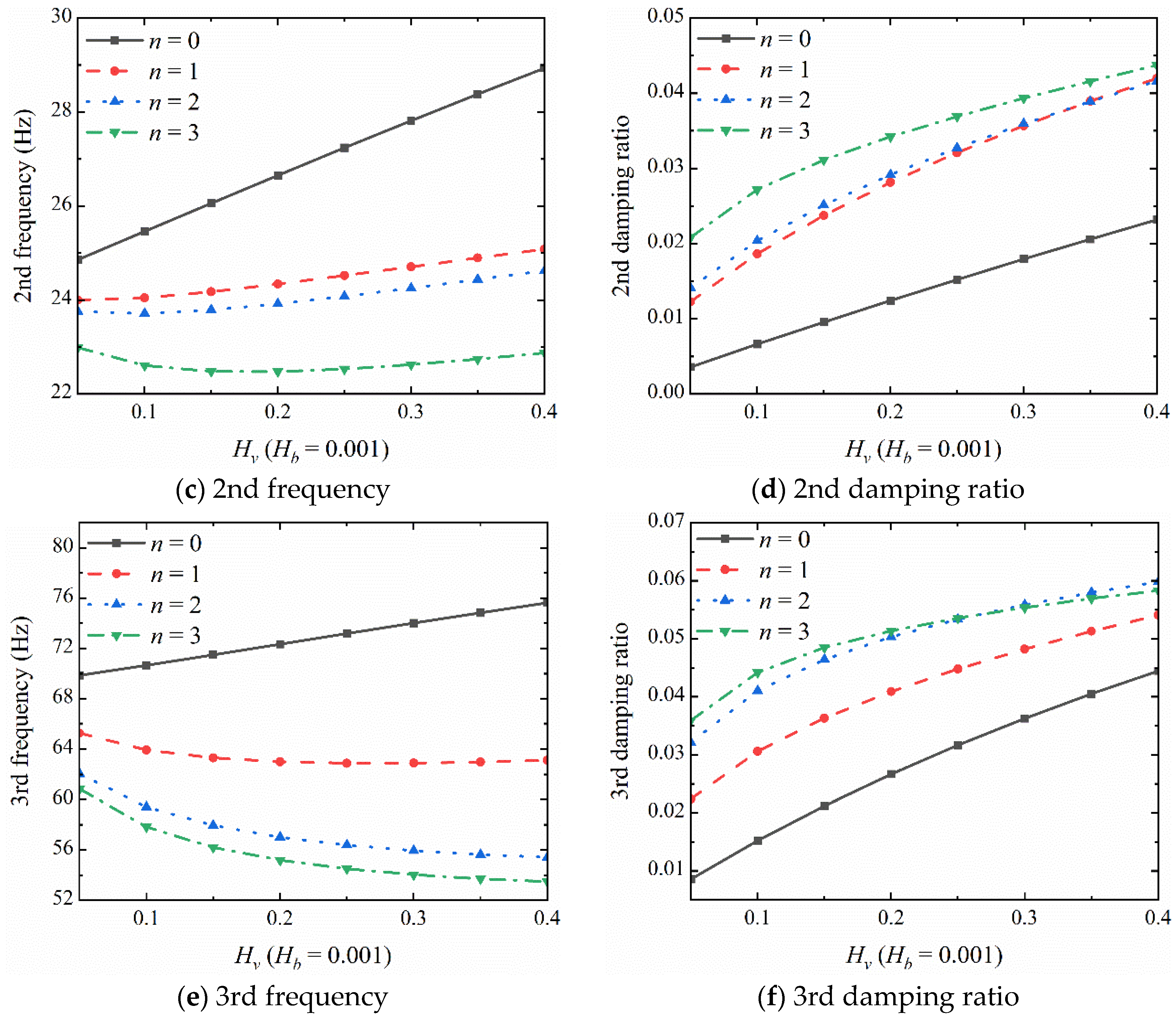
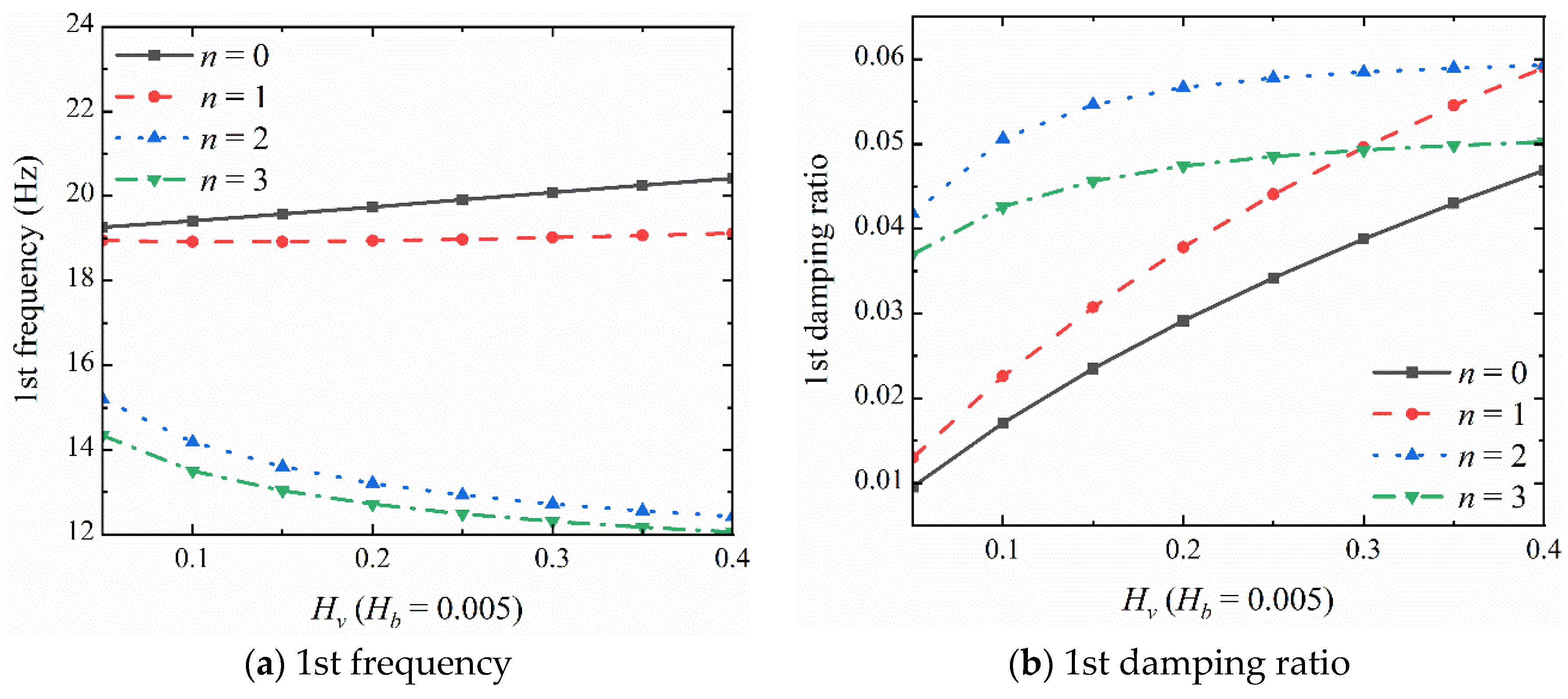
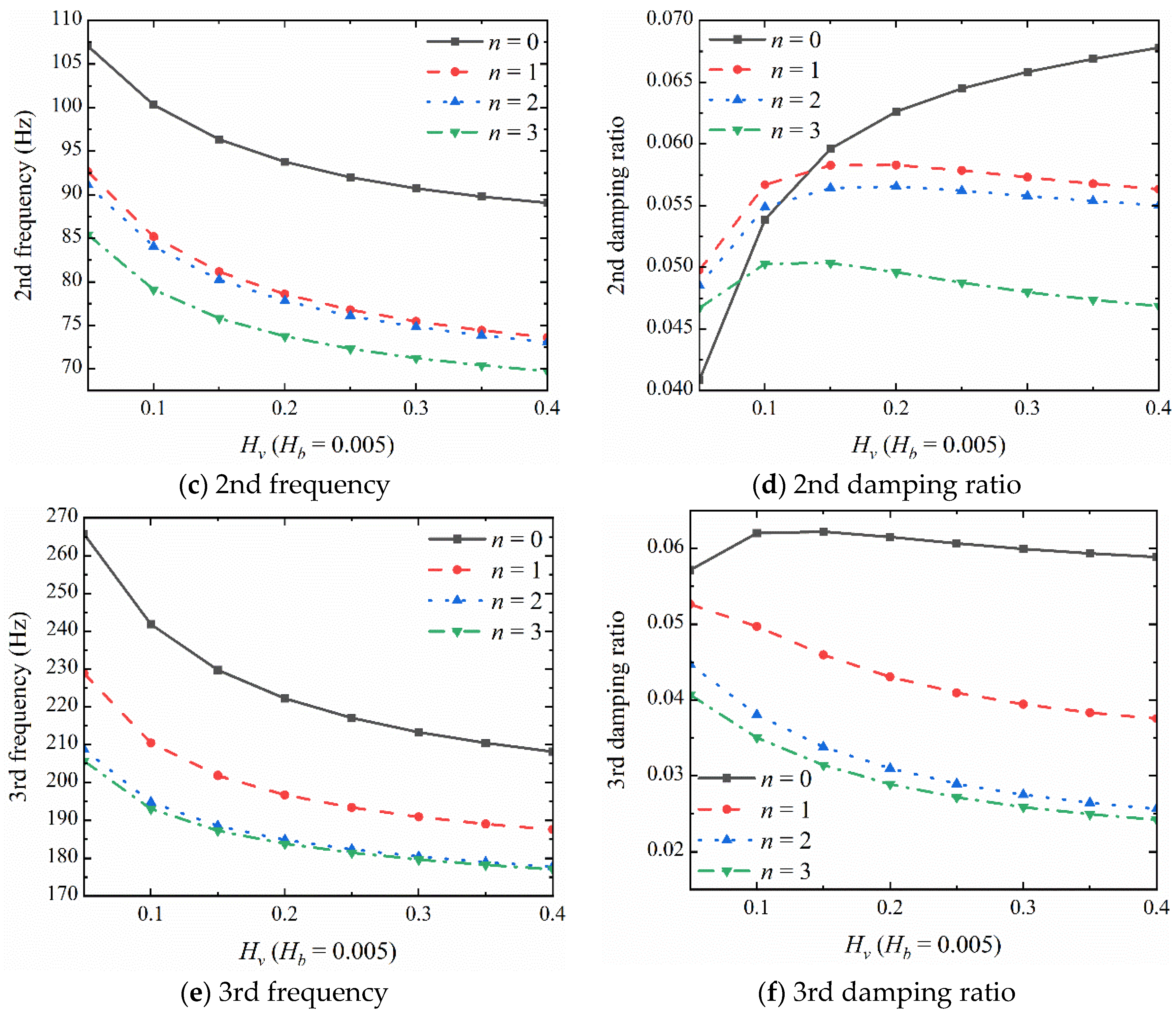
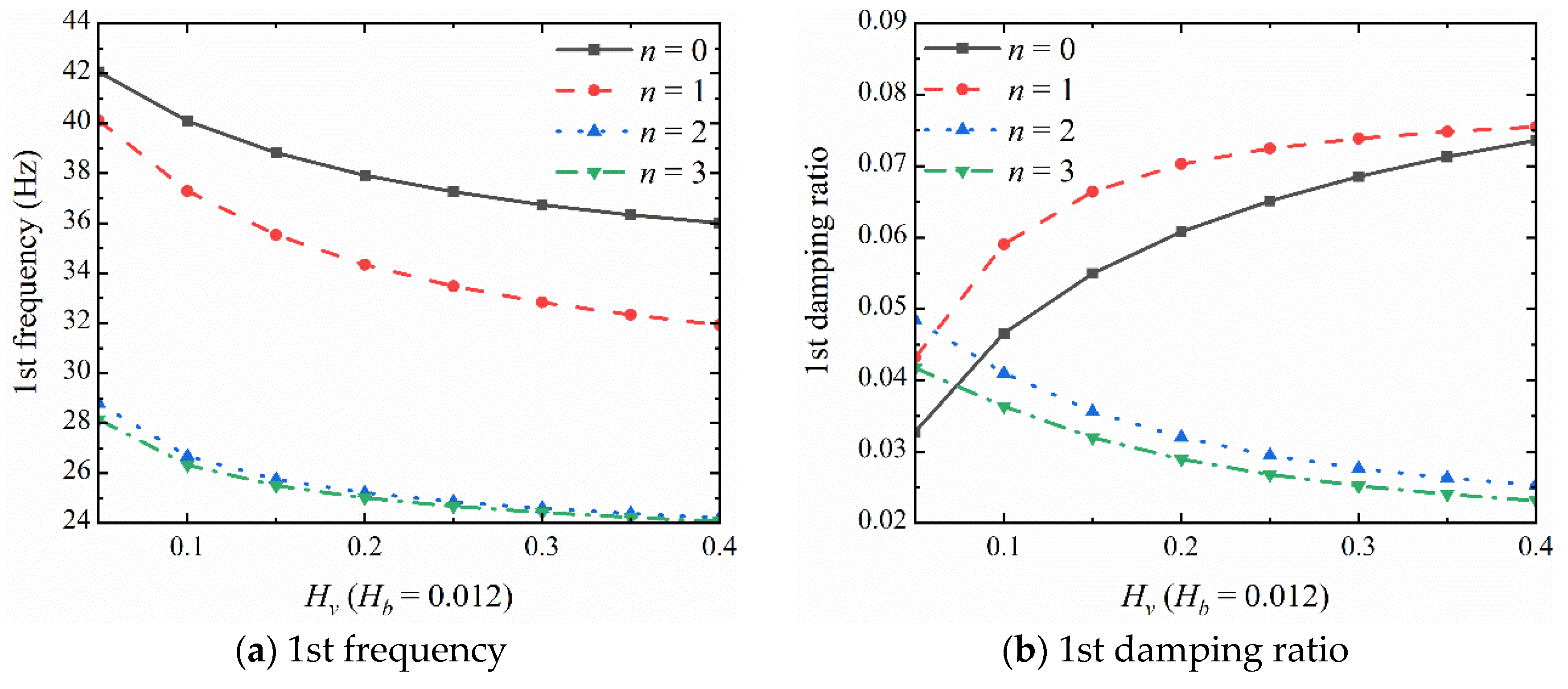
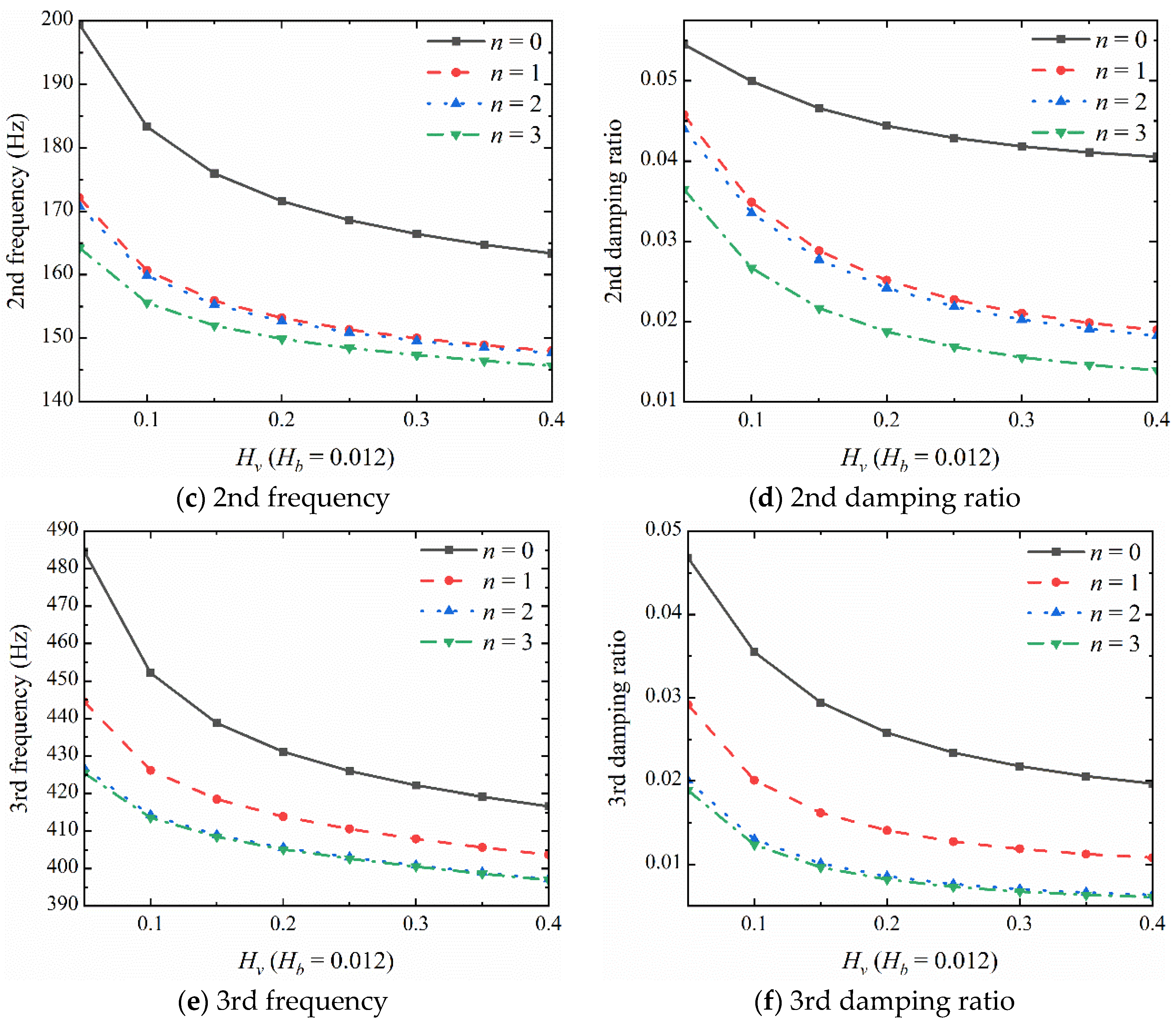

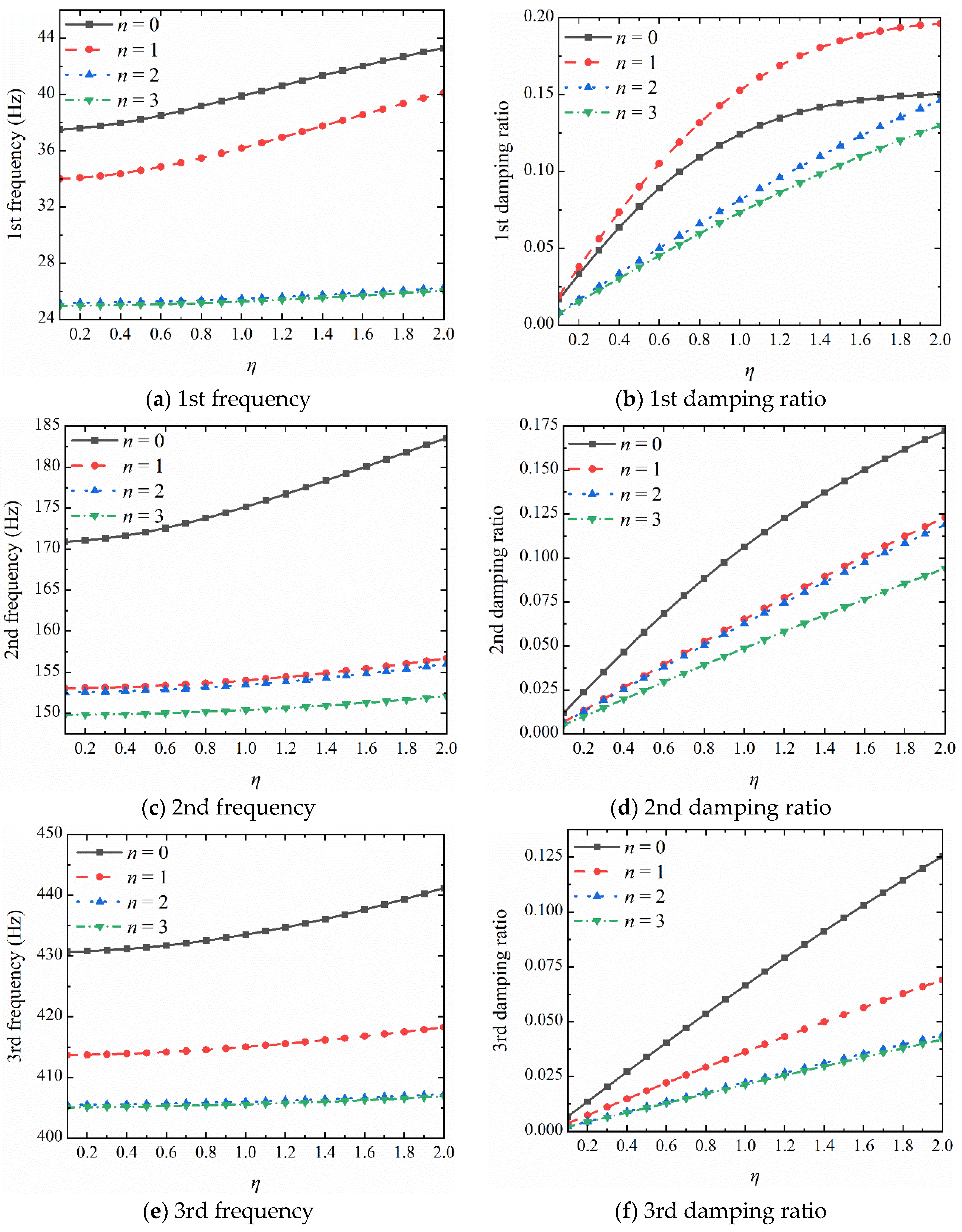

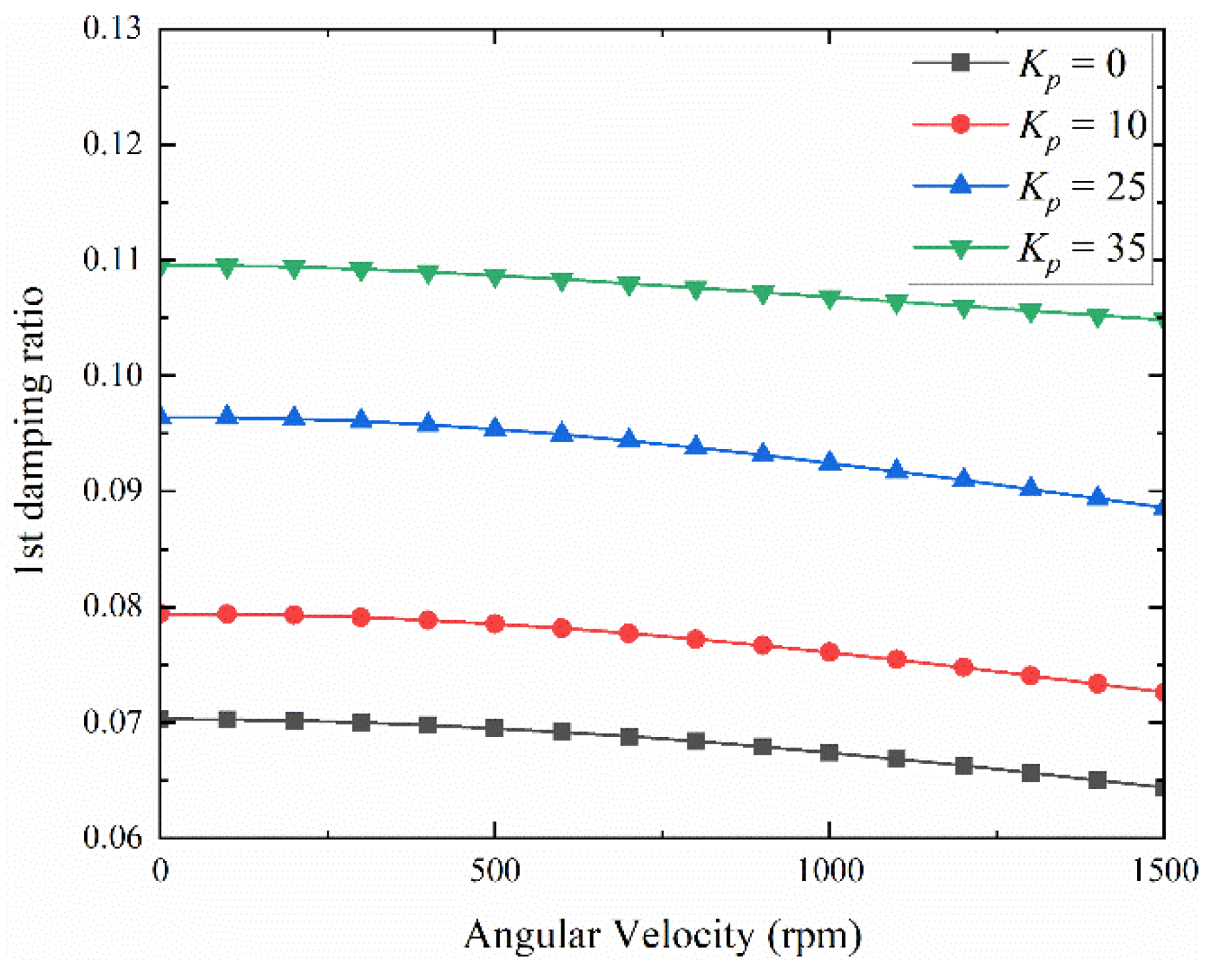
| (rpm) | Mode No. | Ref. [12] | Present | Err (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 1 | 20.21 | 20.21412 | 0.0253 |
| 2 | 104.384 | 104.4093 | 0.0242 | |
| 3 | 277.427 | 277.4587 | 0.0114 | |
| 600 | 1 | 20.5604 | 20.55981 | −0.0028 |
| 2 | 106.685 | 106.7338 | 0.0457 | |
| 3 | 280.155 | 280.1561 | 0.11 | |
| 1000 | 1 | 21.1927 | 21.19537 | 0.0126 |
| 2 | 111.178 | 111.2351 | 0.0514 | |
| 3 | 285.44 | 285.466 | 0.0091 |
| Hb | Mode No. | Ref. [55] | Present | Err (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 1 | 18.9 | 19.4 | 2.6% |
| 2 | 101 | 101.2 | 0.19% | |
| 3 | 283 | 283.8 | 0.28% | |
| 0.012 | 1 | 21.5 | 21.9 | 1.8% |
| 2 | 119 | 119.4 | 0.34% | |
| 3 | 334 | 334.8 | 0.24% | |
| 0.015 | 1 | 25.6 | 25.9 | 1.17% |
| 2 | 147 | 147.0 | 0.00% | |
| 3 | 412 | 412.4 | 0.97% |
| (rpm) | Mode No. | ACLD | SACLD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | ANSYS | Present | ANSYS | ||
| 0 | 1 | 20.16942 | 20.08 | 19.4 | 19.1 |
| 2 | 104.1151 | 104.09 | 101.2 | 101.068 | |
| 3 | 277.1195 | 277.1 | 283.8 | 283.26 | |
| 200 | 1 | 20.21412 | 20.261 | 19.47999 | 19.25 |
| 2 | 104.4093 | 105.01 | 101.5351 | 101.451 | |
| 3 | 277.4587 | 277.96 | 284.176 | 283.76 | |
| 600 | 1 | 20.55981 | 20.321 | 19.95035 | 20.047 |
| 2 | 106.7338 | 106.3 | 103.8929 | 102.732 | |
| 3 | 280.1561 | 279.27 | 286.812 | 285.63 | |
| 1000 | 1 | 21.19537 | 21.179 | 20.78848 | 20.665 |
| 2 | 111.2351 | 111.201 | 108.4595 | 107.457 | |
| 3 | 285.466 | 286.2 | 292.0034 | 291.32 | |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 0.3 m | ρ1 | 2700 kg/m3 |
| Le | 0.03 m | ρ2 | 1250 kg/m3 |
| b | 0.0127 m | ρ3 | 7600 kg/m3 |
| h1 | 1.8 × 10−3 m | G2 | 2 × 106 Pa |
| h2 | 0.25 × 10−3 m | η | 0.38 |
| h3 | 0.762 × 10−3 m | d31 | 23 × 10−12 m/V |
| E1 | 64.9 GPa | g31 | 0.216 V·m/N |
| E2 | 2(1 + η)G* | k31 | 0.12 |
| E3 | 64.9 Gpa | k3t | 12 |
| Xk | 0.7 | R | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Liao, W.-H.; Fang, J. Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Suppression of a Rotating Flexible Beam with Segmented Active Constrained Layer Damping Treatment. Aerospace 2023, 10, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121010
Wang Y, Fang Y, Li L, Zhang D, Liao W-H, Fang J. Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Suppression of a Rotating Flexible Beam with Segmented Active Constrained Layer Damping Treatment. Aerospace. 2023; 10(12):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121010
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yue, Yiming Fang, Liang Li, Dingguo Zhang, Wei-Hsin Liao, and Jianshi Fang. 2023. "Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Suppression of a Rotating Flexible Beam with Segmented Active Constrained Layer Damping Treatment" Aerospace 10, no. 12: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121010
APA StyleWang, Y., Fang, Y., Li, L., Zhang, D., Liao, W.-H., & Fang, J. (2023). Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Suppression of a Rotating Flexible Beam with Segmented Active Constrained Layer Damping Treatment. Aerospace, 10(12), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121010







