Abstract
Dynamic compressors are widely used in many industrial sectors, such as air, land, and marine vehicle engines, aircraft environmental control systems (ECS), air-conditioning and refrigeration, gas turbines, gas compression and injection, etc. The data-driven formulas of mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency of dynamic compressors are required for the design, energy analysis, performance simulation, and control- and/or diagnosis-oriented dynamic simulation of such compressors and the related systems. This work develops data-driven models for predicting the performance of dynamic compressors, including empirical models for mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency, which have high prediction accuracy and broad application range. The performance maps of two multi-stage axial compressors of an aero engine and a centrifugal compressor of an aircraft ECS were chosen for evaluation of the existing empirical formulas and testing of the new models. There are 16 empirical models of mass flow rate and 14 empirical models of isentropic efficiency evaluated, and the results show that it is necessary to develop highly accurate empirical formulas both for mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency. With the data-driven method, two empirical models for mass flow rate and one for isentropic efficiency are developed. They are in general form, with some terms removable to make them simple while enhancing their applicability and prediction accuracy. The new models have much higher prediction accuracy than the best existing counterparts. The new mass flow rate models predict for the three compressors a mean absolute relative deviation (MAD) not greater than 1.3%, while the best existing models all have MAD > 2.0%. The new efficiency model predicts for the three compressors an MAD of 1.0%, 0.4%, and 1.9%, respectively, while the best existing model predicts for the three compressors an MAD of 1.8%, 0.8%, and 3.2%, respectively.
1. Introduction
Dynamic compressors are widely used in many industrial sectors, such as air, land, and marine vehicle engines, aircraft environmental control systems (ECSs), air-conditioning and refrigeration, gas turbines, turbochargers, gas compression and injection, air compression for producing compressed air, pipeline compression for gas transport, electric power generation applications for industrial power plants, and combined heat and power systems for buildings, and they are also used in oil refineries, chemical and petro-chemical plants, and natural gas processing plants [1,2,3,4,5].
The mathematical models of isentropic efficiency (also called efficiency or adiabatic efficiency) and mass flow rate of compressors are necessary for performance study, energy analysis, and control- and/or diagnosis-oriented dynamic simulation of systems including compressors. These models may be built by a mechanism analysis method, a data-based method, or a hybrid method.
The mechanism analysis method is based on theoretical analysis and studies the intrinsic mechanism of the physical object, building a mathematical model from the physical laws of mass, energy and momentum conservation. The obtained model is called the mechanism model. Dynamic compressors are thermal fluid components, for which the mechanism analysis method is generally based on the conservation laws of mass, energy, and momentum in thermal fluid mechanics, yielding a model usually with some form of the Navier–Stokes equation. Solving this kind of mechanism models involves complex numerical operations, such as the computational fluid mechanics (CFD) manipulation [6,7,8], which is so computationally intensive and inefficient that it is unfit for control- and/or diagnosis-oriented dynamic simulation and less attractive than data-driven counterparts.
The data-based method may be classified into the data-driven, the graphical, and the tabular methods. The graphical method usually models compressors using performance maps, and the tabular method uses look-up tables. Due to the difficulty of data-driven modeling for dynamic compressors, the graphical and tabular methods were widely used in early modeling and simulation [9,10], and are still frequently used today [11,12]. Yang et al. [11] used the Ansys CFX software to obtain turbine and compressor performance maps for the performance simulation and analysis of a reversed bootstrap ECS. Jennings et al. [12] used performance maps to calculate the performance of the compressor and turbine in the modeling and simulation of the B737-800 passenger aircraft ECS.
Data-driven methods are based on available data, discovering correlations and mathematical relationships between the variables among the data, and then expressing these relationships mainly in the form of a mathematical formula or artificial neural network. The former is often referred to as an empirical formula, empirical model, or correlation. An empirical formula is also called a mean value model in some literature regarding turbochargers and land vehicle engines [13,14,15].
The main categories of the data-driven methods include the regression analysis method, the artificial intelligence method, and the curve fitting method [16,17,18]. The regression analysis method includes linear regression, nonlinear regression, and Gaussian process regression, etc. The artificial intelligence method includes artificial neural networks (ANN), machine learning, and genetic algorithms, etc. In the actual modeling process, these methods are often used interchangeably. For example, Zhang and Duraisamy [17] used multi-scale Gaussian process regression and neural network methods in machine learning based modeling. In addition, different literature may have inconsistent definitions or different names for a certain method. For example, Ahmad et al. [18] use the terms of the regression analysis method and the statistical modeling method alternately.
Among data-driven modeling methods, the regression analysis is the most widely used, and can be used alone or in combination with other methods. Using the regression analysis method, Pulpeiro Gonzalez and Hall [19] obtained the empirical formulas representing the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency maps of turbine and compressor. Using the non-parametric regression method, Sun et al. [20] obtained the health indices for ECS health management based on the ECS flight parameters detected onboard. Regression analysis methods are often used in conjunction with other methods. For example, Fang et al. [21,22] first used the Taylor expansion method to obtain the basic model for the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency of cooling turbines, and then determined the number of terms and constants using regression analysis methods based on experimental data.
In the artificial intelligence method, ANN and machine learning methods are most commonly used, and machine learning methods are often aided by other methods, such as ANN and regression analysis. Nikiforov et al. [23] established a mathematical model using an ANN method to replace the performance maps of a centrifugal compressor. Fei et al. [24] proposed an artificial intelligence method combining the feedforward backpropagation neural network and the Gaussian kernel function to predict the performance maps of a multi-stage axial compressor and compared it with the feedforward backpropagation neural network method and the support vector machine method. Zhang and Duraisamy [17] attempted to add terms to the turbulent Reynolds averaged equation to improve its accuracy and applicability. The added items were obtained using a machine learning method called supervised learning. Uzun et al. [25] used a deep machine learning method and an ANN method to establish an aircraft fuel consumption model based on the given meteorological and flight data.
The least squares method is commonly used in curve fitting methods. Tu and Chen [26] used it to obtain the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency formulas based on a compressor performance map for a MAN Diesel & Turbo TCA88 turbocharger from Augsburg, Germany. Li et al. [27] used a partial least squares curve fitting method to obtain the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency formulas for a variable geometry compressor in a diesel engine.
The hybrid modelling method is the combination of the mechanism analysis method and the data-driven method. It utilizes the mechanism analysis method to establish a basic mathematical model of the system through appropriate simplification and uses the data-driven method to determine the constants and terms in the model, and the resultant model is also known as a semi-empirical formula, or simply called an empirical formula. Due to the use of the data-driven method in the modeling process, the hybrid method is also categorized as a data-driven method in some literature. Using the hybrid modelling method, Yang and Yang [28] established an equation for the number of transfer units (NTU) in ECS heat exchangers, with the heat transfer coefficient in the NTU equation determined based on experimental data. Chen et al. [29] obtained the basic performance models of a centrifugal compressor through theoretical analysis, with the constants in the models to be determined using the genetic algorithm based on experimental data.
In the above data-driven modelling methods, regression analysis, curve fitting, and hybrid methods yield empirical formulas, which are the dominant models for dynamic compressors because they are compact and time-efficient in design, analysis and performance simulation and favorite for control- and/or diagnose-oriented dynamic simulation among such compressors and systems [30,31].
There are a number of empirical formulas for compressor mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency for turbochargers and land and marine vehicle engines [13,14,15,26,30,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. However, for dynamic compressors used in aero engines and aircraft ECSs, the empirical formulas of the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency are rare, with only two papers [42,43] found presenting the empirical formulas for aero engine compressors and two articles [44,45] found for the empirical formulas for aircraft ECS compressors. In addition, our systematic review and evaluation show that the prediction accuracy of the existing empirical models for mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency is not satisfactory for the dynamic compressors of aero engines and aircraft ECSs, and thus new models with a high accuracy need to be developed [1,31,44,45].
The purpose of the present paper is to meet the above needs, developing the empirical formulas of mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency that have high prediction accuracy and broad application range for dynamic compressors, with an emphasis on their application to aero engines and aircraft ECSs. For this purpose, the empirical models of mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency for existing dynamic compressors are reviewed, and the reviewed models are evaluated with the performance data of aero engine and aircraft ECS compressors. Then, new empirical formulas for the mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency of dynamic compressors are developed using data-driven methods. Considering that most of the existing models have fixed terms, which may be accurate for the authors’ own data, but usually experience large deviation when applied to data from other sources, the new models are in general form, with some terms removable to simplify them while enhancing their applicability and prediction accuracy. Several data-driven methods are tested to select one which produces the best result.
2. Existing Empirical Models of Compressor Mass Flow Rate and Isentropic Efficiency
2.1. Basic Parameters of Dynamic Compressors
- Parameters regarding mass flow rate
For a dynamic compressor, the mass flow rate G may be indirectly expressed as the normalized mass flow rate parameter ϕ and the corrected mass flow rate ϕcorr.
where G is the mass flow rate; d is the blade wheel diameter; U is the blade tip speed; ρ, p and T are the air density, pressure, and temperature, respectively; and the subscripts in and ref denote the inlet and reference point, respectively. The reference point is usually set at T = 288.15 K and p = 101,325 Pa. The compressor tip speed U is defined as
where n is the compressor rotational speed. Other useful parameters regarding the compressor rotational speed are the rotational speed parameter nt, the corrected rotational speed ncorr, and the rotational speed ratio nr, as defined below:
where nref is the compressor rotational speed at the reference point, usually the design point.
Some researchers [13,14] have related the mass flow rate to the dimensionless head parameter ψ, which is defined as
where cp is the gas specific heat at constant pressure, k is the isentropic exponent, and πc is the compressor compression ratio.
Some researchers [39,43] correlate the mass flow rate indirectly by setting the compression ratio as the function instead of the mass flow rate.
- 2.
- Compressor isentropic efficiency
The compressor isentropic efficiency η (sometimes called adiabatic efficiency, or simply efficiency) is defined as
where Ws and W are the compressor isentropic compression work and actual compression work, respectively.
Substituting Equations (10) and (11) into Equation (9) yields
2.2. Existing Empirical Formulas for Compressor Mass Flow Rate
The available existing empirical formulas for compressor mass flow rate are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Existing empirical models for compressor mass flow rate.
2.3. Existing Empirical Formulas for Compressor Efficiency
The available existing empirical formulas for compressor efficiency are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Existing empirical models for compressor efficiency.
3. Evaluation of the Reviewed Models for Applications to Aero Engine and ECS Compressors
The above-mentioned models were evaluated against dynamic compressors of an aero engine and an aircraft ECS to find the clue for proposing highly accurate new mass flow and isentropic efficiency models.
3.1. Criteria for Evaluation
Two commonly-used criteria are chosen for the evaluation, which are the mean absolute relative deviation (MAD) and the corrected coefficient of determination Rc2 [1,31]. The former provides the direct information of the average deviation of the model predictions from the sample data set, and the latter is a statistical index that gives some information about the goodness of fit of a model. In most cases, the two criteria yield the same sorting of the compared models in prediction accuracy. However, if two models have close values of MAD and Rc2 or there is a big difference between the numbers of predictors, the orders ranked by these two criteria may be different.
The MAD is chosen for the primary criterion and Rc2 is used as auxiliary because the deviation of the model predictions from the real data is more concerning in engineering practice.
where yexp and ypred are the experimental and predicted values, respectively, and N is the number of the sample data.
where ymean is the mean experimental value, R2 is the coefficient of determination, s2 is the residual mean square, and m is the number of predictors. For example, m = 15 in the efficiency model of Tu and Chen [26].
The coefficient of determination R2 is also a statistical index that gives some information about the goodness of fit of a model. However, for a particular model, its value tends to increase when the sample size is reduced and the model thus becomes closer to being saturated. Rc2 corrects this overestimation problem by considering the number of predictors in the model, and thus it is generally considered superior to R2, especially when comparing models with different numbers of predictors.
3.2. Description of Dynamic Compressors
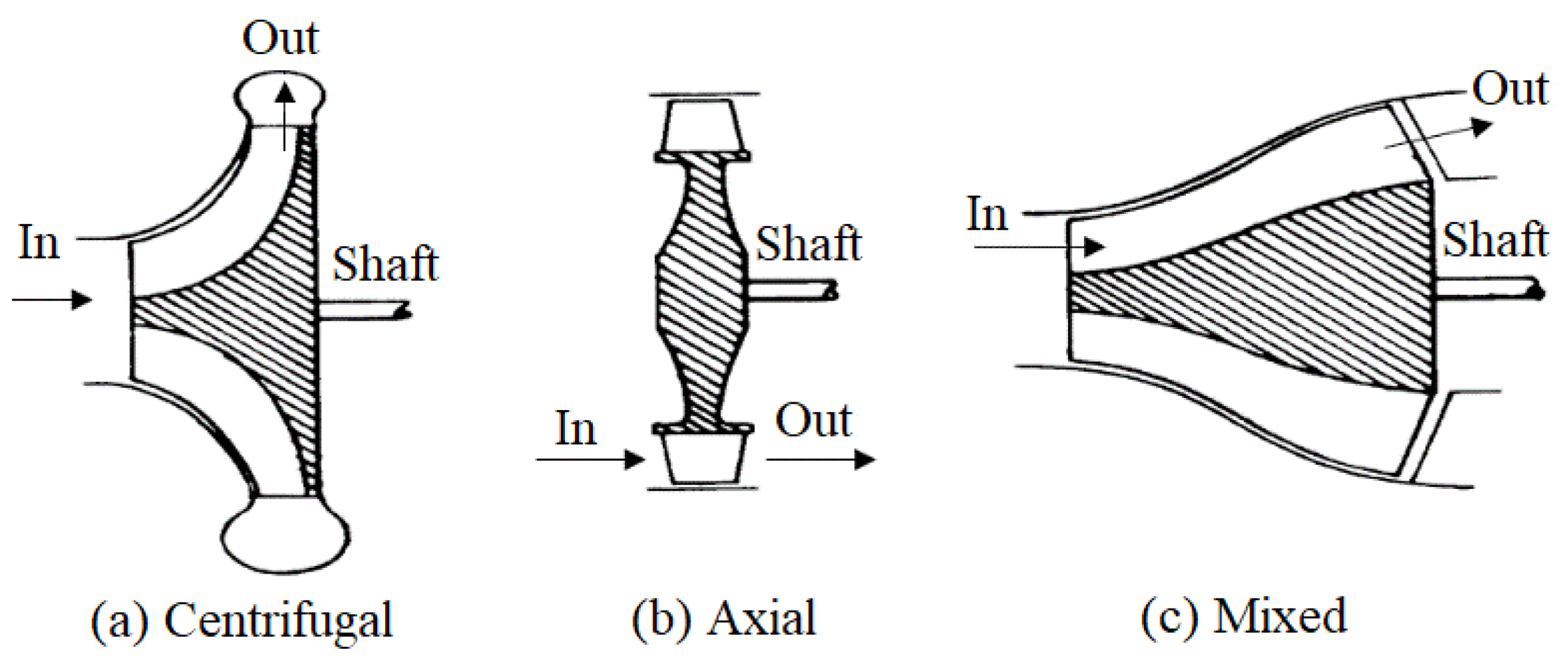
A dynamic compressor is a rotary machine that inputs energy continuously on the gas to compress the fluid by inducing a change of angular momentum to it as it flows through the compressor blading. According to fluid flow directions when entering and leaving compressors, dynamic compressors have three categories: centrifugal, axial, and mixed, as shown in Figure 1, where all compressors are single stage.
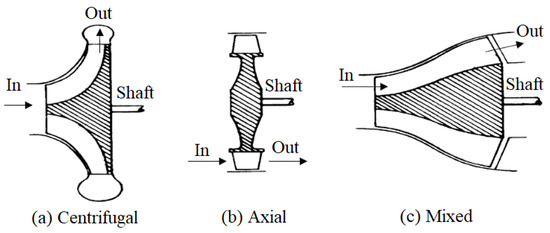
Figure 1.
Types of dynamic compressors.
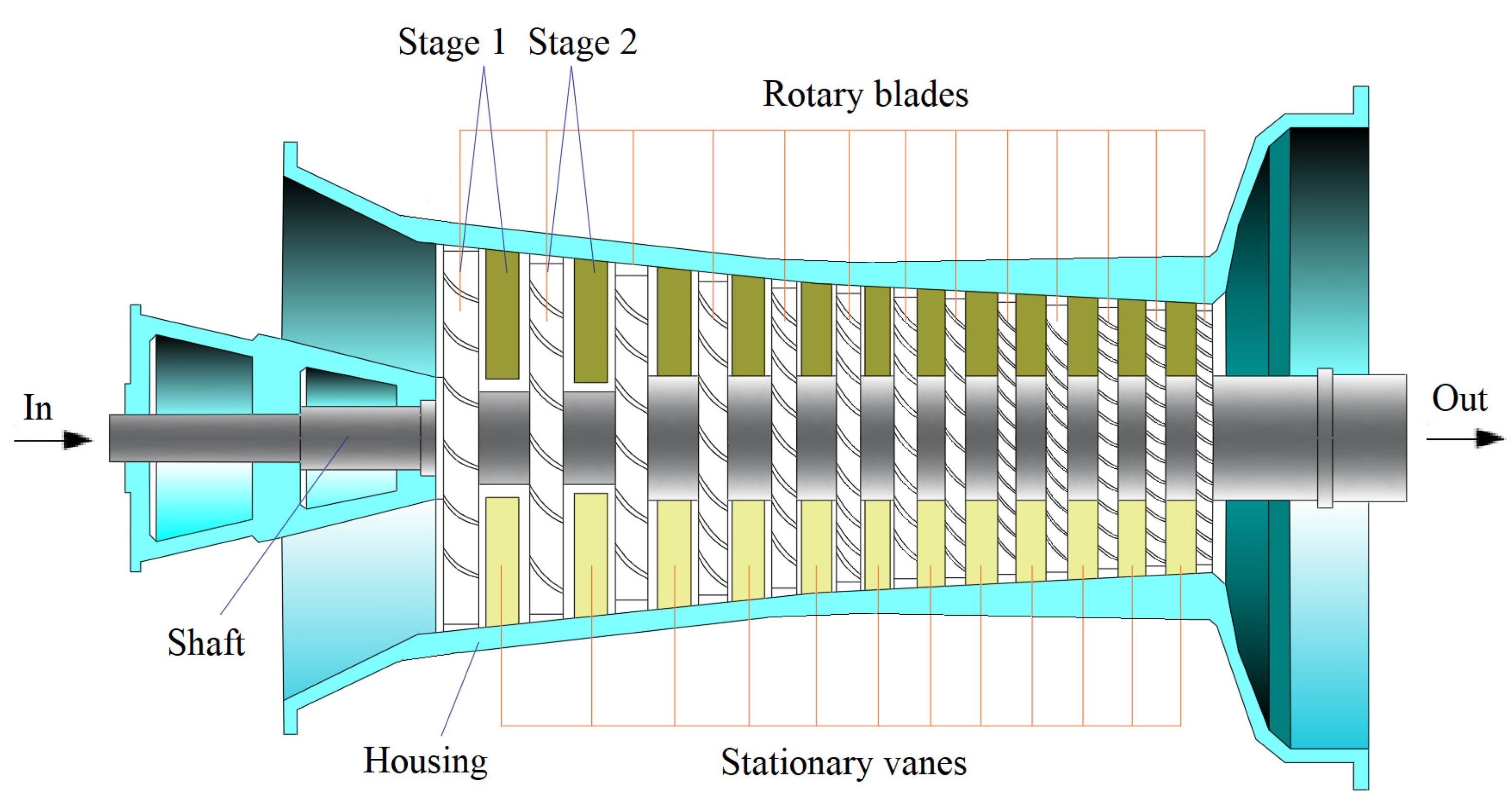
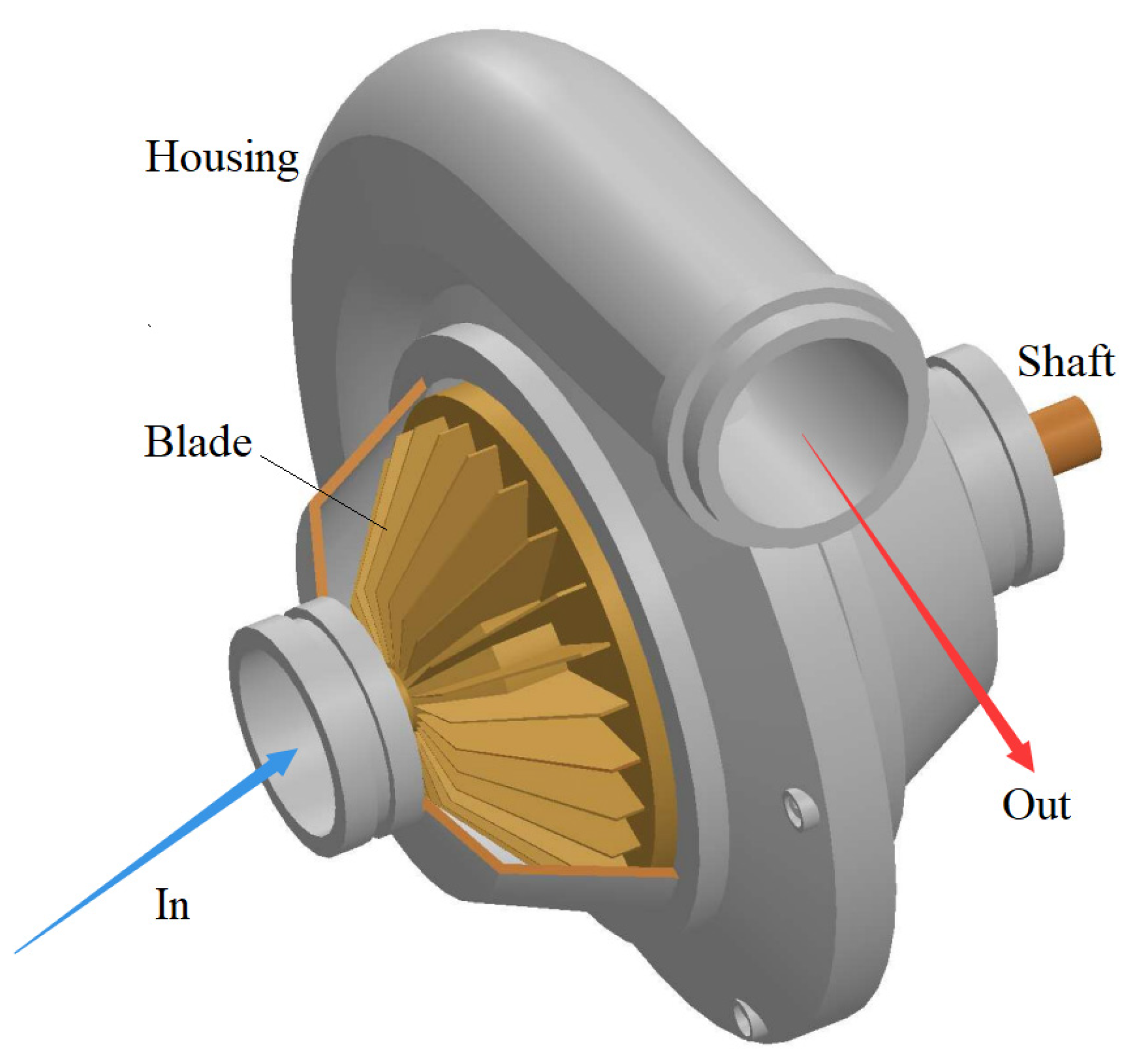
For a centrifugal compressor, gas enters it parallel to the shaft and leaves the blades radially. For an axial compressor, gas enters it and leaves the blades both parallel to the shaft. If gas enters a compressor parallel to the shaft and leaves the blades at an angle greater than 0° but less than 90° to the shaft, it is a mixed type. Figure 2 shows schematically a multi-stage axial compressor. Figure 3 shows schematically a single-stage centrifugal compressor.
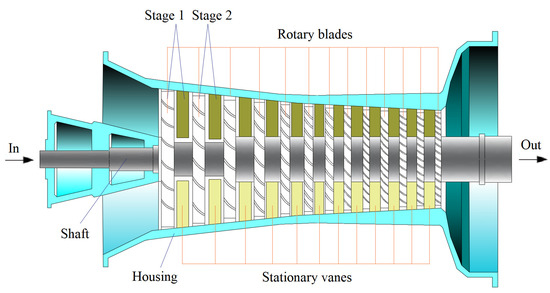
Figure 2.
Schematics of an axial dynamic compressor.
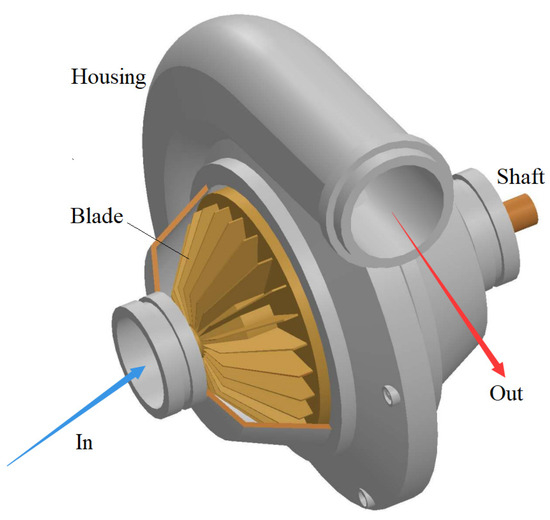
Figure 3.
Schematics of a single-stage centrifugal dynamic compressor.
3.3. Performance Maps of Dynamic Compressors
Three dynamic compressors are chosen for this study, with two from a civil turbofan engine named BIGFAN and the third from an airliner three-wheel high pressure water separator (HPWS) ECS. The BIGFAN engine compressors are multi-stage axial compressors, a commonly seen type in aero engines. The BIGFAN engine is a civil turbofan engine simulated in NLR’s Gas turbine Simulation Program (GSP) version 11 [46]. The ECS compressor is a single-stage centrifugal compressor used in Fokker 100 airliner, a regional jet that was produced by Fokker in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Single-stage centrifugal compressors are a commonly seen type of compressors used in aircraft ECS.
3.3.1. Performance Maps of BIGFAN Compressors
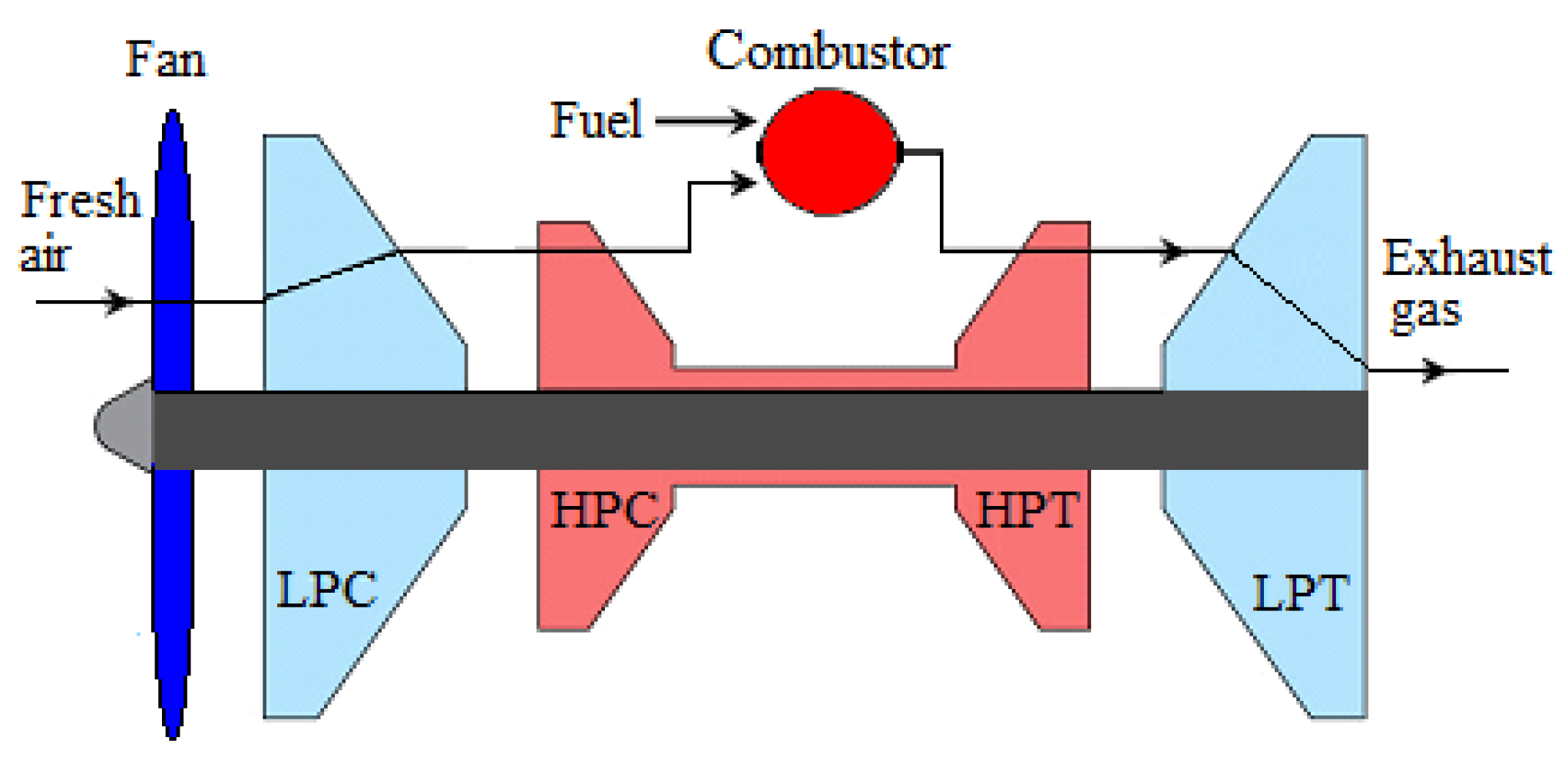
The main components of a BIGFAN include, in air flow direction, a fan, a low-pressure compressor (LPC), a high-pressure compressor (HPC), a combustor, a high-pressure turbine (HPT), and a low-pressure turbine (LPT) [46,47,48], as shown in Figure 4. The LPC is mounted on one shaft driven by the LPT, and the HPC is mounted on the high-pressure shaft driven by the HPT.
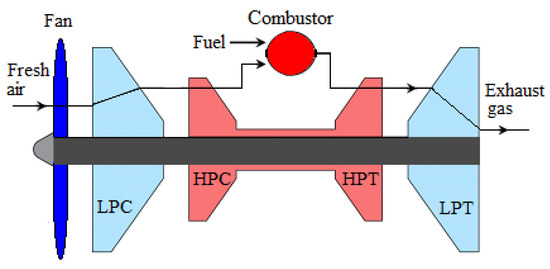
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of turbofan engine (BIGFAN).
The fan delivers the compressed air to the compressors, where air pressure is increased gradually, coming out of the HPC as high-pressure hot air. The high-pressure hot air enters the combustor, or combustion chamber, where fuel is added. The air temperature increases remarkably in the combustor due to the combustion of air–fuel mixture, and then it enters the HPT and LPT in sequence, where it expands, producing the needed power.
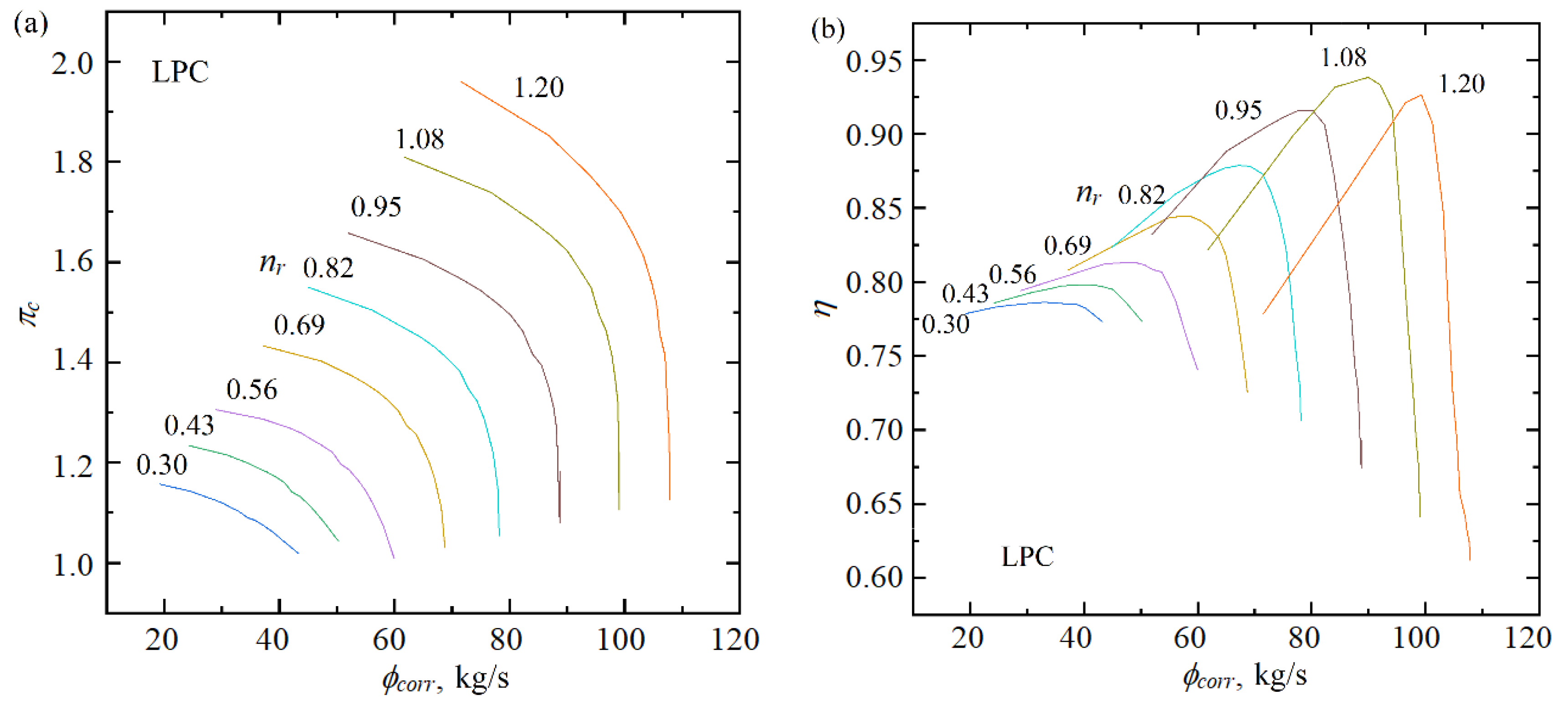
The performance maps of the BIGFAN compressors were generated using the NLR’s GSP version 11 [46,47]. The performance map of the BIGFAN LPC is shown in Figure 5. The parameter ranges are the compression ratio πc from 1.07 to 1.96, the corrected mass flow rate ϕcorr from 19.2 to 107.8 kg/s, the isentropic efficiency η from 0.62 to 0.94, and the rotational speed ratio nr from 0.3 to 1.2.
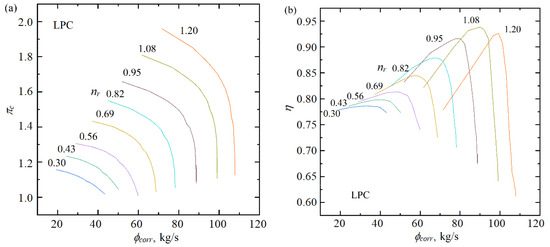
Figure 5.
Performance map of the BIGFAN LPC [47]. (a) Performance map of mass flow rate. (b) Performance map of isentropic efficiency.
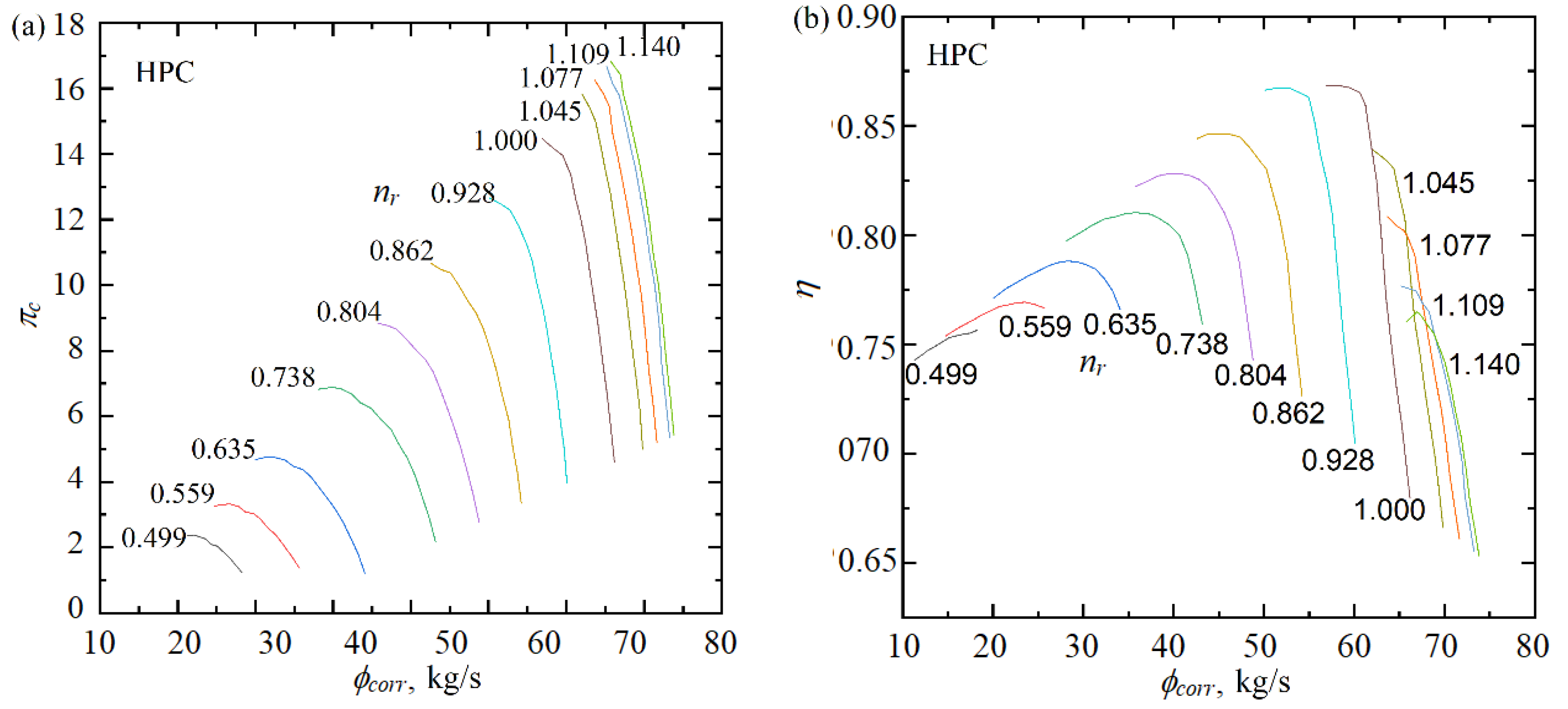
The performance map of the BIGFAN HPC is shown in Figure 6. The parameter ranges are the compression ratio πc from 1.21 to 16.82, the corrected mass flow rate ϕcorr from 20 to 65.7 kg/s, the isentropic efficiency η from 0.65 to 0.87, and the rotational speed ratio nr from 0.5 to 1.14.
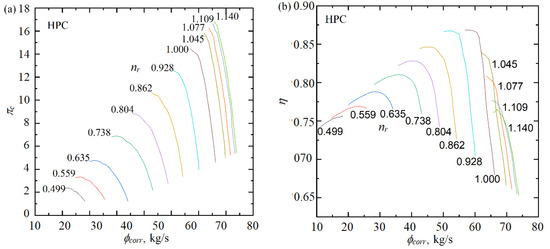
Figure 6.
Performance map of the BIGFAN HPC [47]. (a) Performance map of mass flow rate. (b) Performance map of isentropic efficiency.
3.3.2. Performance Map of Aircraft ECS Compressor
For aircraft ECSs, dynamic compressors are used in air cycle machines (ACMs), vapor cycle refrigeration systems, and electric-driven air sources [2]. An ACM, which is composed of one or two cooling turbines with a compressor, a fan, or both on the same shaft to utilize the turbine work [49,50,51], is the key component of an air cycle ECS. The compressor of an ACM is either centrifugal, axial, or mixed dynamic, with the centrifugal type dominant.
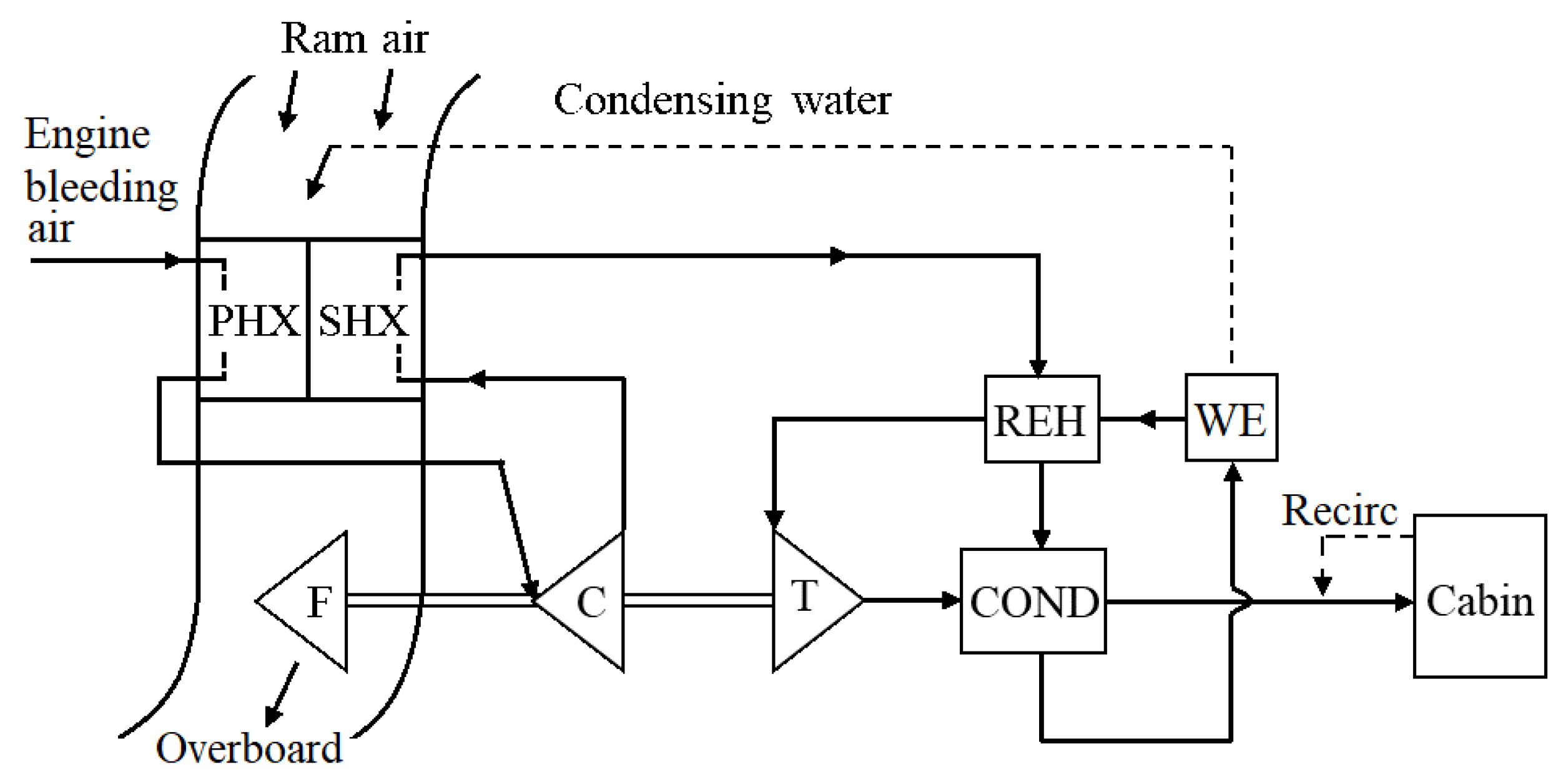
An airliner HPWS ECS with a three-wheel ACM is shown schematically in Figure 7, which utilizes main engine bleed air as the pressurized air source and ram air as the heat sink [2]. The HPWS contains a condenser (COND), a reheater (REH), and a water extractor (WE). The bleed air passes through the primary heat exchanger (PHX), where it is cooled down. Then, it enters the ACM compressor (C), where its pressure is boosted. Leaving the compressor, the air is further cooled by the secondary heat exchanger (SHX). Coming out the SHX, it sequentially passes through the RHE hot side, the COND hot side, the WE, the RHE cold side, the ACM turbine (T), and the COND cold side, becoming cold air. The cold air mixes with the recirculation air from the cabin, and then the mixture enters the cabin, and eventually discharged overboard.
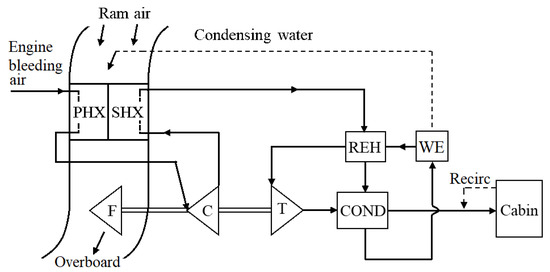
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of three-wheel HPWS ECS [2].
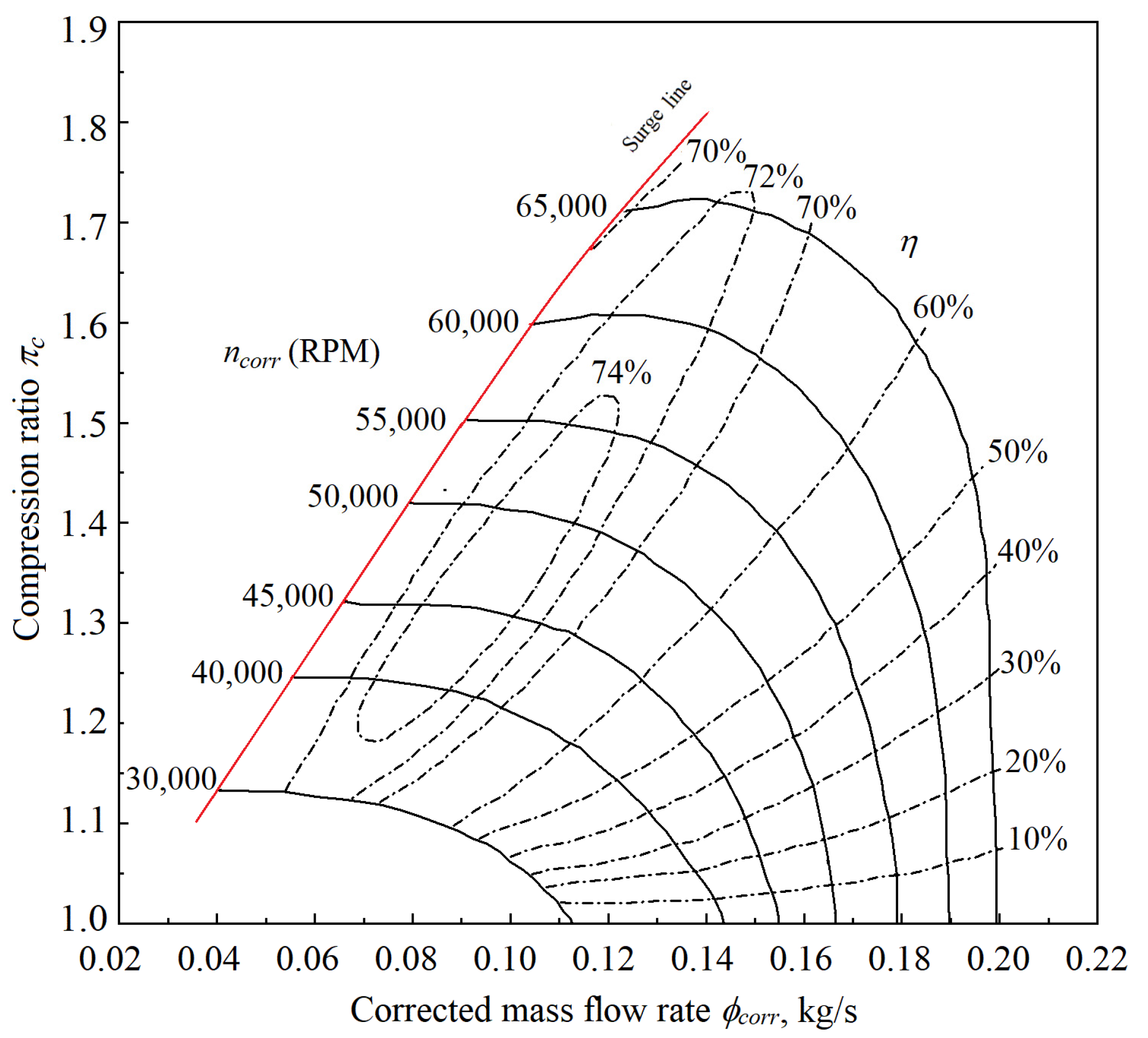
The performance map of an airliner ECS compressor is taken from [45], as shown in Figure 8. The data were read from the map using a computer software. The parameter ranges are the compression ratio πc from 1.02 to 1.73, the corrected mass flow rate ϕcorr from 0.04 to 0.2 kg/s, the isentropic efficiency η from 0.1 to 0.75, and the corrected rotational speed ncorr from 30,000 to 65,000 RPM.
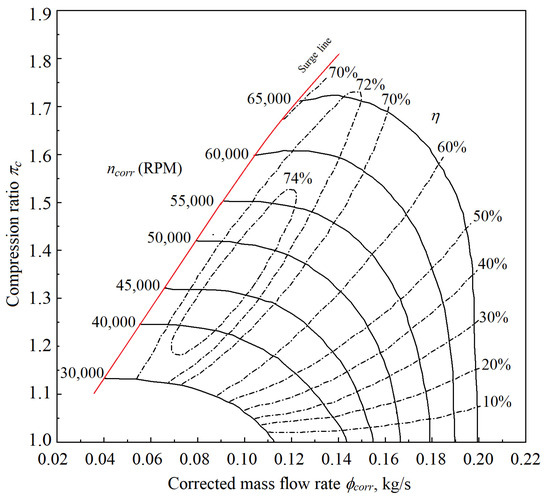
Figure 8.
Performance map of the ECS compressor [45].
3.4. Evaluation of the Existing Mass Flow Models
The evaluation results of the above-reviewed mass flow models against the BIGFAN LPC, the BIGFAN HPC, and the ECS compressor are shown in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5, respectively, where only the models with MAD < 15% are listed.

Table 3.
Mass flow models applied to the BIGFAN LPC.

Table 4.
Mass flow models applied to the BIGFAN HPC.

Table 5.
Mass flow models applied to the ECS compressor.
- None of the evaluated existing mass flow models has an MAD less than 2.0%, indicating the need to develop new models with high accuracy.
- The Tian [44] model has the highest prediction accuracy for the BIGFAN LPC and the ECS compressor, with MADs of 2.0% and 2.4%, respectively, while it predicts poorly for the BIGFAN HPC, with an MAD of 11.0%. The Orkisz and Stawarz [42] model has the highest prediction accuracy for the BIGFAN HPC, with MAD = 2.1%, and a moderate prediction accuracy for the BIGFAN LPC, with an MAD of 3.5%, while it predicts poorly for the ECS compressor, with an MAD of 15%.
- The BIGFAN LPC is a multi-stage axial compressor, with ϕcorr = 19.2–107.8 kg/s and πc = 1.07–1.96. The BIGFAN HPC is a multi-stage axial compressor, with ϕcorr = 20–65.7 kg/s and πc = 1.21–16.82. The ECS compressor is a centrifugal compressor, with ϕcorr = 0.04–0.2 kg/s and πc = 1.02–1.73. Comparing the compressor type, mass flow rate, and the compression ratio, from the prediction accuracy of the Tian [44] model and the Orkisz and Stawarz [42] model to the three compressors, it may be reasoned that, among the three factors, the compression ratio and the compressor type rank in the first and the second places as to the effect on model applicability, and a single mass flow rate model may not be adequate to variety of applications.
- For evaluating the applicability of compressors, the MAD is much better than Rc2. This can be seen by comparing the prediction accuracy of the Tian [44] model and that of Jensen et al. [13]. For the BIGFAN LPC and the ECS compressor, the Jensen et al. [13] model has higher Rc2 values than the Tian [44] model, but actually the predictions of the Jensen et al. [13] model has much larger deviation from the map values than the Tian [44] model has.
3.5. Evaluation of the Existing Isentropic Efficiency Models
The evaluation results of the above-reviewed efficiency models against the BIGFAN LPC, the BIGFAN HPC, and the ECS compressor are shown in Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8, respectively, where only the models with MAD < 15% are listed.

Table 6.
Isentropic efficiency models applied to the BIGFAN LPC.

Table 7.
Isentropic efficiency models applied to the BIGFAN HPC.

Table 8.
Isentropic efficiency models applied to the ECS compressor.
All the mass flow rates in the efficiency maps of the BIGFAN LPC, the BIGFAN HPC, and the ECS compressor are given in the corrected mass flow parameter ϕcorr, with the inlet temperature Tin and inlet pressure pin not available, while the Tu and Chen [26] model uses volume flow rate Q, and thus it is not applicable theoretically and does not appear in the tables.
- The Tian [44] model has the highest prediction accuracy for all the three compressors, with MAD = 1.8% for the BIGFAN LPC, MAD = 0.8% for the BIGFAN HPC, and MAD = 3.2% for the ECS compressor, suggesting that it is possible to propose a single efficiency model for a wide range of applications.
- For the ECS compressor, the highest prediction accuracy of the existing models is MAD = 3.2% and, for the BIGFAN LPC, the highest prediction accuracy of the existing models is MAD = 1.8%, indicating a need to develop a highly accurate efficiency model.
4. Development of New Empirical Models for Dynamic Compressor Performance
The above-mentioned three performance maps of the dynamic compressors are used to test and tune the basic forms.
4.1. New Empirical Models of Mass Flow Rate
4.1.1. Developing New Models
Several data-driven methods are tried to develop new empirical models of mass flow rate, among which two effective examples are introduced below.
Method 1
The performance maps of the three compressors show that the corrected mass flow parameter ϕcorr is the function of the compression ratio πc and the corrected rotational speed ncorr, or πc is the function of the ϕcorr and ncorr. Thus, it follows that
or
Assuming that f(πc, ncorr) is the function of the product of the sub-function f1(πc, ncorr), f2(πc, ncorr), …, fk(πc, ncorr), Equation (17) becomes
where fi(πc, ncorr) (i = 1, 2, …, k) have very complicated forms due to the complicated compressor configurations and the flow fields in compressor channels.
So far, it is impossible to derive an explicit equation for fi(πc, ncorr) through theoretical analysis, and thus data-driven methods have to be used to find the right forms. Generally, a variety of the basic forms of empirical correlations need to be constructed and then tested through computation based on the available compressor performance data. The following steps are adopted to determine mass flow rate model forms:
- Choose a k value. For example set k = 3.
- Construct sub-functions f1(πc, ncorr), f2(πc, ncorr), and f3(πc, ncorr). The simplest practice is to use polynomial forms.
- Based on the above-mentioned three performance maps of mass flow rate, conduct extensive computational trial and error using different data-driven methods. Those yielding superior results are selected to refine the sub-functions in the next step. In this step, the tested data-driven methods include the Levenberg–Marquardt method, the Powell Optimization method, the Quasi-Newton method, the Simplex method, the Gold Rush Optimizer, the Python curve fit tool, and the Genetic Algorithm (GA). The Levenberg–Marquardt method, the Python curve fit tool, and GA show superior performance, and are selected to refine the sub-functions in the next step.
- Use MAD as the criterion to tune the sub-functions using the data-driven methods selected in the above step. In this step, add or remove terms in the sub-functions one by one to determine which terms should be included. If removing a term does not increase MAD, this term should be removed. If adding a term does not reduce MAD, this term should not be added. The general model form include all terms for the three compressors.
- If the result obtained in the above step is unsatisfactory, go to step 1 and repeat the processes of trial and error in steps 1–4, until a satisfied result is obtained.
Regarding the use of GA, the initial number of populations is 300–500, the number of iterations is 2000–4000, the crossover probability is 0.85, and the variance probability is 0.1. The sub-generation of individuals with the smallest MAD without Rc2 deterioration is the optimal one after the iteration. The data is split into two groups, one with 75% of the total data, and the other with 25%, similar to the training set and test set in machine learning. The training set, which contains 75% of the total data, is used to obtain the model, and then the model is used to predict the test set. The resultant MAD is the weighted arithmetic mean of the MADs of the two data sets.
The final general model yielded by this method is of the form
where ai (i = 1, 2, …, 16) are the constants to be determined by the available data.
Mention should be made of the fact that the above equation is a general form for the mass flow rate of dynamic compressors. Some terms may be removed to simplify the form for a given compressor. It is suggested to remove as many terms as possible to simplify the model for a given compressor. The suggest methodology is as follows.
At first, remove one term, if necessary, from the general form. Test each term in the general form by removing it while keeping all the other terms to calculate the MAD and the Rc2 of the reduced model. Divide all the terms into three categories: strong relevant terms, weak relevant terms, and little relevant terms. A term is strong relevant if the MAD increases remarkably when removing it from the model, a term is weak relevant if the MAD increases noticeably when removing it from the model, and a term is little relevant if the MAD increases very little or does not increase when removing it from the model. Among the little relevant terms, the one yielding the smallest MAD and the greatest or almost greatest Rc2 when removed should be deleted from the general form. For convenience, the model yielded in this round is called the first-generation model. Generally, for a given compressor, at least one term can be removed from the general form.
Secondly, test each term of the above-mentioned weak relevant and little relevant terms remaining in the first-generation model by removing it while keeping all the other terms to calculate the MAD and the Rc2 of the further reduced model, and classify them into strong relevant terms, weak relevant terms, and little relevant terms. Among the little relevant terms, if any, the one yielding the smallest MAD and the greatest or almost greatest Rc2 when removed may be deleted from the first-generation model. The model yielded in this round is called the second-generation model. Please note that a strong relevant term, no matter in which round it is yielded, remains as a strong relevant term in the next round, and all strong relevant terms are kept in the model, exempt from testing.
In the second round, if there is no little relevant term, the first-generation model is the final result. If not, try to reduce the second-generation model using the same method as that when reducing the first-generation model. Repeat this method until no term can be removed.
With this approach, the final mass flow rate model and accuracy for the three compressors are obtained, as listed in Table 9, where the terms with the constants in the “Terms removed from Equation (20)” column are removed from Equation (20).

Table 9.
Final mass flow rate model form and accuracy for the three compressors.
Method 2
Equation (20) has very high accuracy for the BIGFAN LPC and BIGFAN HPC, but it falls short of predicting the ECS compressor satisfactorily. Therefore, a need exists to develop another mass flow rate model with high prediction accuracy for the ECS compressor, which is of the centrifuge type and operates at low compression ratio.
Observing the ECS compressor performance map in Figure 8, it is found that, for a given corrected rotational speed ncorr, the compression ratio πc is the exponential function of the corrected mass flow parameter ϕcorr, and thus it follows that
where A, B, and C can be expressed as the function of corrected rotational speed ncorr.
Through extensive computer test, the polynomial function for A, B, and C yields preferable results. The obtained final form of mass flow rate is as follows:
where the constants ai,j (i = 1, 2, 3, and j = 1, 2, 3) are to be determined by the available data.
The prediction ability of Equation (21) for the three compressors is shown in Table 10. It is seen that this model has a high prediction accuracy for the ECS compressor, and its prediction ability for the BIGFAN LPC is fairly good.

Table 10.
Prediction ability of Equation (21).
From the compressor type, it is reasoned that Equation (20) may be better for multi-stage axial compressors and Equation (21) may be better for centrifugal compressors. However, for a given compressor, it is suggested that careful computer tests should be conducted to determine which model is better.
4.1.2. Comparison of the New Models with the Best Existing Models
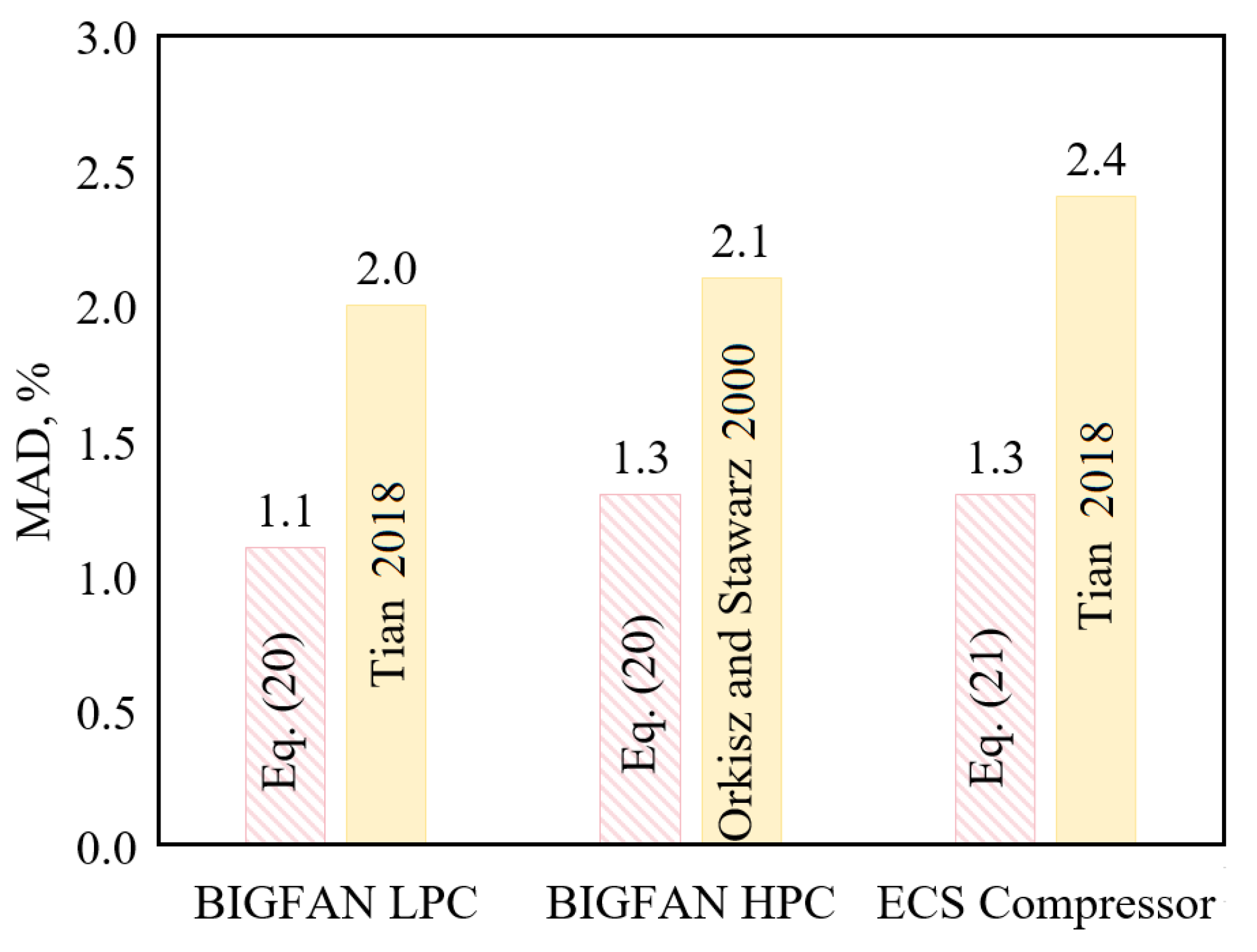
Figure 9 shows the comparison of the prediction errors (MAD) of the new mass flow models with the best existing ones in prediction accuracy, where Equations (20) and (21) are the new models, and Tian [44] and Orkisz and Stawarz [42] are the best existing models for the specified compressors. It is seen that the new models predict the three compressors with MAD ≤ 1.3%, while the best existing models all have MAD > 2.0%, indicating that the new models improve the prediction accuracy greatly.
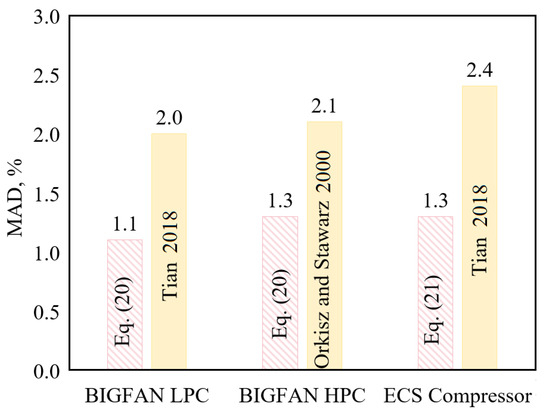
Figure 9.
Prediction MAD: New mass flow models vs. the best existing ones (Tian [44] for BIGFAN LPC and ECS compressor, Orkisz and Stawarz [42] for BIGFAN HPC).
4.2. New Empirical Model of Isentropic Efficiency
4.2.1. Developing New Model
From the evaluation of the isentropic efficiency models of dynamic compressors, it is seen that the Tian [44] model gives satisfied prediction results for the BIGFAN LPC and HPC, while no model predicts well for the ECS compressor. In practice, the available performance dada of aero engine and ECS compressors are usually given in the corrected mass flow rate ϕcorr or the mass flow rate parameter ϕ without giving Tin and pin information, leaving the volume flow rate Q unknown. Since Tin and pin vary in real operation processes, it is necessary to propose a compressor efficiency model with ϕcorr or ϕ instead of Q.
In order to find more clues for developing a said new efficiency model, the Tu and Chen [26] efficiency model was evaluated against the above-mentioned three efficiency maps by assuming that Tin and pin are constant, from which the volume flow rate Q is calculated. The results show that the Tu and Chen [26] has very high prediction accuracy for the BIGFAN LPC and BIGFAN HPC, though its prediction accuracy is not high for the ECS compressor. By assuming that Tin and pin are constant, the prediction accuracy of the Tu and Chen [26] model is overestimated.
Based on the above evaluation and analysis, several basic efficiency model forms were constructed. Through extensive computer testing, it is found that the best basic efficiency model form for a dynamic compressor is as follows:
It should be mentioned that, for a given compressor, some terms in the above general form may be removed with little increase in MAD. In other words, some terms in Equation (22) may be removed to simplify the efficiency model for a given compressor. It is suggested to remove as many terms as possible for a given compressor as long as the Rc2 value does not noticeably deteriorate.
The prediction accuracy of the new model for the BIGFAN LPC, the BIGFAN HPC, and the ECS compressor is listed in Table 11, where the terms with the constants in the “Terms removed from Equation (22)” column are removed from Equation (22).

Table 11.
Prediction accuracy of the new efficiency model.
4.2.2. Comparison of the New Model with the Best Existing Models
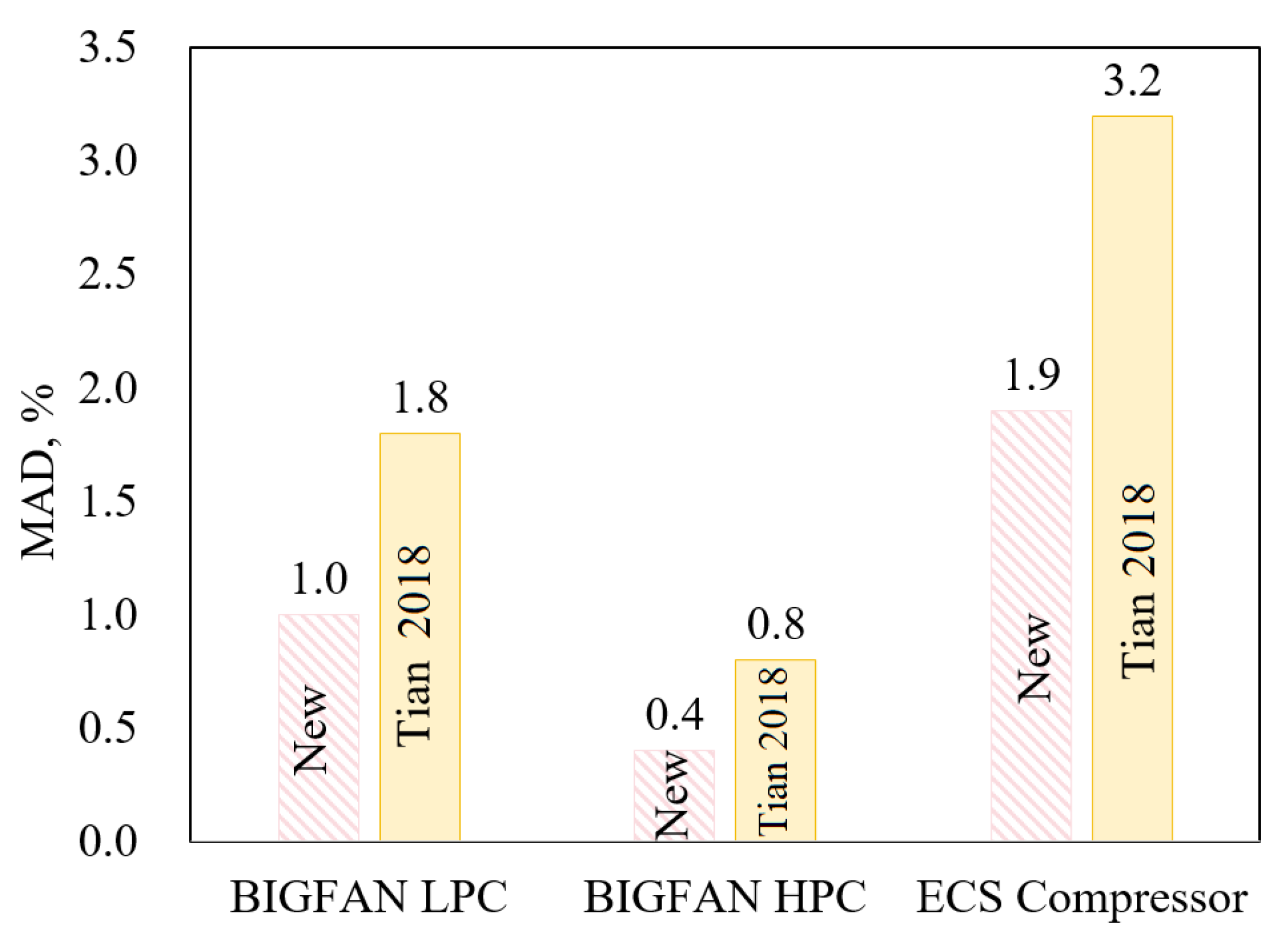
Figure 10 shows the comparison of the prediction errors (MAD) of the new isentropic efficiency model with the best existing model in prediction accuracy, where New means Equation (22) and Tian [44] denotes the Tian [44] compressor efficiency model, which predicts best for all of the three compressors. It is seen that the new model has a much higher prediction accuracy (much lower MAD) than the best existing model.
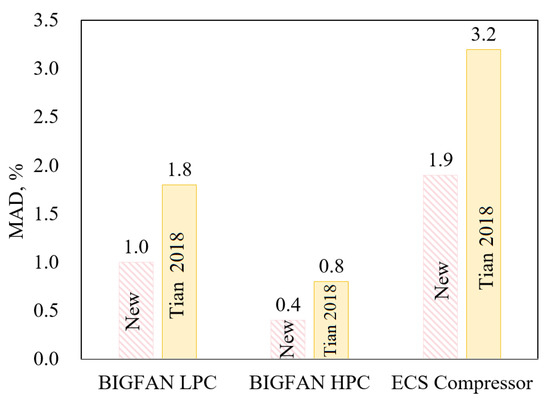
Figure 10.
Prediction MAD: New efficiency model vs. the best existing one (Tian [44]).
5. Conclusions and Discussion
The existing empirical formulas for dynamic compressors, including 16 mass flow rate models and 14 isentropic efficiency models, were evaluated against the performance data of two multi-stage axial compressors used in an aero engine and a centrifugal compressor used in an aircraft ECS. Two empirical formulas for mass flow rate and one for isentropic efficiency of dynamic compressors are proposed. The following conclusions are obtained:
- For three dynamic compressors, none of the existing empirical models of mass flow rate has an MAD less than 2.0%, and the smallest MAD of the existing isentropic efficiency models is 3.4%, indicating the need to develop new models with high accuracy.
- As to the effect on the applicability of mass flow rate models, compression ratio and compressor type rank in the first and the second places among the three factors of compressor type, mass flow rate, and the compression ratio. A single mass flow rate model may not be adequate to a variety of applications.
- A compressor efficiency model is less sensitive to compressor type, mass flow rate, and the compression ratio than a mass flow rate model. The Tian [44] model was developed for aircraft ECS centrifugal compressors with low compression ratio and small mass flow rate, but it has the highest prediction accuracy for multi-stage axial compressors in wide ranges of compression ratio and mass flow rate among the existing models.
- The data-driven method is used to develop new models of mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency for dynamic compressors, for which two empirical formulas (Equations (20) and (21)) for the mass flow rate and one (Equation (22)) for the isentropic efficiency are developed.
- The new models have much higher prediction accuracy than the best existing models. The new mass flow rate models predict the three compressors with MAD ≤ 1.3%, while the best existing models all have MAD > 2.0%. The new efficiency model predicts the BIGFAN LPC, BIGFAN HPC, and ECS compressor, with MAD of 1.0%, 0.4%, and 1.9%, respectively, while the best existing one predicts the BIGFAN LPC, BIGFAN HPC, and ECS compressor with MAD of 1.8%, 0.8%, and 3.2%, respectively.
- For evaluating the applicability of compressors, the criterion MAD is much better than Rc2, while Rc2 is preferred to refining a general form, with some terms needing to be removed or added.
- Most of the existing empirical models of mass flow rate and isentropic efficiency of dynamic compressors relate to dimensional parameters, which limits the model robustness. Modeling the characteristics by relying on the fundamentals of the theory of dynamic compressors may have potential to solve the problem.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.F.; Methodology, X.F. and Y.Y.; Software, B.Y.; Validation, X.F., Y.F. and Z.H.; Formal analysis, X.F. and Y.F.; Investigation, X.F., Y.F. and Y.Y.; Resources, X.F. and B.Y.; Data curation, Y.F., Y.Y. and Z.H.; Writing—original draft, X.F.; Funding acquisition, X.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yang Yang was employed by the company Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China, Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| ai | constant (i = 0, 1, 2, …) |
| bi | constant (i = 0, 1, 2, …) |
| cp | constant pressure specific heat, J/kg K |
| d | blade wheel diameter, m |
| G | mass flow rate, kg/s |
| k | isentropic exponent |
| Ma | Mach number |
| n | rotational speed, rev/s (RPS) |
| ncorr | corrected rotational speed, , RPS |
| nr | non-dimensional speed, n/nref |
| nt | rotational speed parameter, , rev/s K1/2 |
| p | pressure, Pa |
| Q | volume flow rate, m3/s |
| R | gas constant, J/kg K |
| R2 | coefficient of determination |
| Rc2 | corrected coefficient of determination |
| s2 | residual mean square |
| T | temperature, K |
| U | blade tip speed, m/s |
| W | compression work, W |
| Z | coefficient of relative stability margin |
| Greek symbols | |
| γ | polytropic exponent |
| η | isentropic efficiency |
| πc | compression ratio |
| ρ | density, kg/m3 |
| ϕ | normalized mass flow rate |
| ϕcorr | corrected mass flow parameter, kg/s |
| ψ | dimensionless head parameter |
| Subscripts | |
| corr | corrected parameter |
| exp | experimental |
| in | inlet |
| max | maximum |
| out | outlet |
| pred | predicted |
| ref | value at a reference point |
| top | maximum value on a speedline |
| s | isentropic |
References
- Yang, B.; Fang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, F.; Bi, M.; Chen, C.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Applicability of empirical models of isentropic efficiency and mass flow rate of dynamic compressors to jet engines. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 106, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X. Aircraft Environmental Control and Refrigeration; Beihang Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Meira, R.L.; Costa, G.M.N.; Kalid, R.A.; Martins, M.A.F. Improving the centrifugal compressor map through rigorous thermodynamic modeling: An analysis on a natural gas compression station pipeline. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 92, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molière, M. The fuel flexibility of gas turbines: A review and retrospective outlook. Energies 2023, 16, 3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Hooman, K.; Yang, X. Assessment evaluation of a trigeneration system incorporated with an underwater compressed air energy storage. Appl. Energy 2021, 303, 117648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, X.; Gu, C.; Li, Y. Experiment and numerical simulation of the performance on scaled compressor cascade and development of a prediction model. Int. J. Heat. Fluid. Flow. 2024, 105, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Agarwal, R.K. Numerical simulations and design optimization of compressor cascade flow using one equation and Wray-Agarwal turbulence model. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2022, 36, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, V.; Sdanghi, G.; Mozet, K.; Schaefer, S.; Maranzana, G.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Numerical simulation of a thermally driven hydrogen compressor as a performance optimization tool. Appl. Energy 2022, 323, 119628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, G.S. Digital Controlled Closed Loop Air Cycle Development; SAE 851319; Society of Automobile Engineers, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhao, J.Q.; Sun, W. Dynamic simulation of bootstrap air cycle refrigeration components for aircraft environmental control system. J. Syst. Simul. 2004, 16, 727–729. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Sheng, C.; Xie, H.; Luo, G.; Hou, Y. Study on coupling performance of turbo-cooler in aircraft. Energy 2021, 224, 120029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennions, I.; Ali, F.; Miguez, M.E.; Escobar, I.C. Simulation of an aircraft environmental control system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 172, 114925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.P.; Kristensen, A.F.; Sorenson, S.C.; Houbak, N.; Hendricks, E. Mean Value Modeling of a Small Turbocharged Diesel Engine; SAE 910070; Society of Automobile Engineers, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M. Mean Value Modeling of Turbocharged Spark Ignition Engines. Master′s Thesis, DTU, Kgs Lyngby, Denmark, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Canova, M.; Midlam-Mohler, S.; Guezennec, Y.; Rizzoni, G. Mean value modeling and analysis of HCCI diesel engines with external mixture formation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2009, 131, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. A digital twin modeling method for turbofan engine real-time test data analysis and performance monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Prognostics and System Health Management (PHM-2020), Virtual Meeting, 16–18 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Duraisamy, K. Machine learning methods for data-driven turbulence modeling. In Proceedings of the 22nd AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. A comprehensive overview on the data driven and large scale based approaches for forecasting of building energy demand: A review. Energy Build. 2018, 165, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulpeiro Gonzalez, J.; Hall, C. Equation-Based Compressor and Turbine Modeling for Variable Geometry Turbochargers; SAE Technical Paper 2018-01-0966; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, C.; Liu, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, R. A data-driven health indicator extraction method for aircraft air conditioning system health monitoring. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Dai, Q. Modeling of turbine mass flow rate performances using the Taylor expansion. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xu, Y. Development of an empirical model of turbine efficiency using the Taylor expansion and regression analysis. Energy 2011, 36, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, A.; Popova, D.; Soldatova, K. A network application for modeling a centrifugal compressor performance map. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 232, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Zhao, N.; Shi, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z. Compressor performance prediction using a novel feed-forward neural network based on Gaussian kernel function. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, M.; Demirezen, M.U.; Inalhan, G. Physics guided deep learning for data-driven aircraft fuel consumption modeling. Aerospace 2021, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Chen, H. Modeling of a compressor’s performance map by fitting function methodology. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 779–780, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. A prediction model of compressor with variable-geometry diffuser based on elliptic equation and partial least squares. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, C. Application of scaling-endoreversible thermodynamic analysis model to aircraft environmental control system-methodology development. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 112, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zuo, S.; Wu, Z. Aerodynamic performance modeling of the centrifugal compressor and stability analysis of the compression system for fuel cell vehicles. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2021, 3, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canova, M. Development and validation of a control-oriented library for the simulation of automotive engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2004, 5, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y. Empirical models for efficiency and mass flow rate of centrifugal compressors. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 41, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P. Air Charge Estimation in Turbocharged Spark Ignition Engines. Ph.D. Thesis No. 989, Department of Electrical Engineering, Linkoping University, Linkoping, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmanovsky, I.V.; Moraal, P.E.; van Nieuwstadt, M.J.; Criddle, M.; Wood, P. Modeling and Identification of a 2.0 L Turbocharged DI Diesel Engine; Ford Internal Technical Report SR-97-039; Ford: Dearborn, MI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Moraal, P.; Kolmanovsky, I. Turbocharger modeling for automotive control application. SAE Trans. 1999, 108, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoutsanis, E.; Meskin, N.; Benammar, M.; Khorasani, K. A component map tuning method for performance prediction and diagnostics of gas turbine compressors. Appl. Energy 2014, 135, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsanis, E.; Meskin, N.; Benammar, M.; Khorasani, K. Transient gas turbine performance diagnostics through nonlinear adaptation of compressor and turbine maps. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2015, 137, 091201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteus, J. Mean Value Engine Model of a Heavy Duty Diesel Engine; LITH-ISY-R-2666; Department of Electrical Engineering, Linkopings Universitet: Linkoping, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, L.; Nielsen, L.; Brugard, J.; Bergstriim, J.; Pettersson, F.; Andersson, P. Modeling of a turbocharged SI engine. Annu. Rev. Control. 2002, 26, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzella, L.; Amstutz, A. Control of diesel engines. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 1998, 18, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Ai, F. Performance prediction of the centrifugal compressor based on a limited number of sample data. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5954128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Park, I.; Min, K.; Sunwoo, M. Model-based feedforward control of the VGT in a diesel engine based on empirical models of compressor and turbine efficiencies. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2015, 16, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkisz, M.; Stawarz, S. Modeling of turbine engine axial-flow compressor and turbine characteristics. J. Propuls. Power 2000, 16, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieros, G.; Stamatis, A.; Mathioudakis, K. Jet engine component maps for performance modeling and diagnosis. J. Propuls. Power 1997, 13, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Research on Mathematical Modeling of Fault Prediction of Aircraft Environmental Control System. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Simulation Research on Mean Value Model of Air Circulation Machine and Aircraft Environmental Control System. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NLR. Program GSP 11; National Aerospace Laboratory NLR: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B. Research on Adaptive Control of Turbofan Engine Based on Data Driven. Ph.D. Thesis, Beihang University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Fang, X.; Zhuang, F.; Chen, C.; Shang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B. Evaluation of applicability of empirical models of turbine performance to aircraft engine. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 117, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Claeys, H. The Continuing Evolution of the C-130 Environmental Control System; SAE 1999-01-2163; Society of Automobile Engineers, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, S.K. F-15 Environmental System Improvements; SAE 901235; Society of Automobile Engineers, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C.; Bullick, B.A.; Catt, J.A.; Hamstra, J.W.; Walker, G.P.; Wurth, S. F-35 air vehicle technology overview. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Atlanta, GA, USA, 25–29 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).