Effect and Mechanism of Roughness on the Performance of a Five-Stage Axial Flow Compressor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of Research Methods
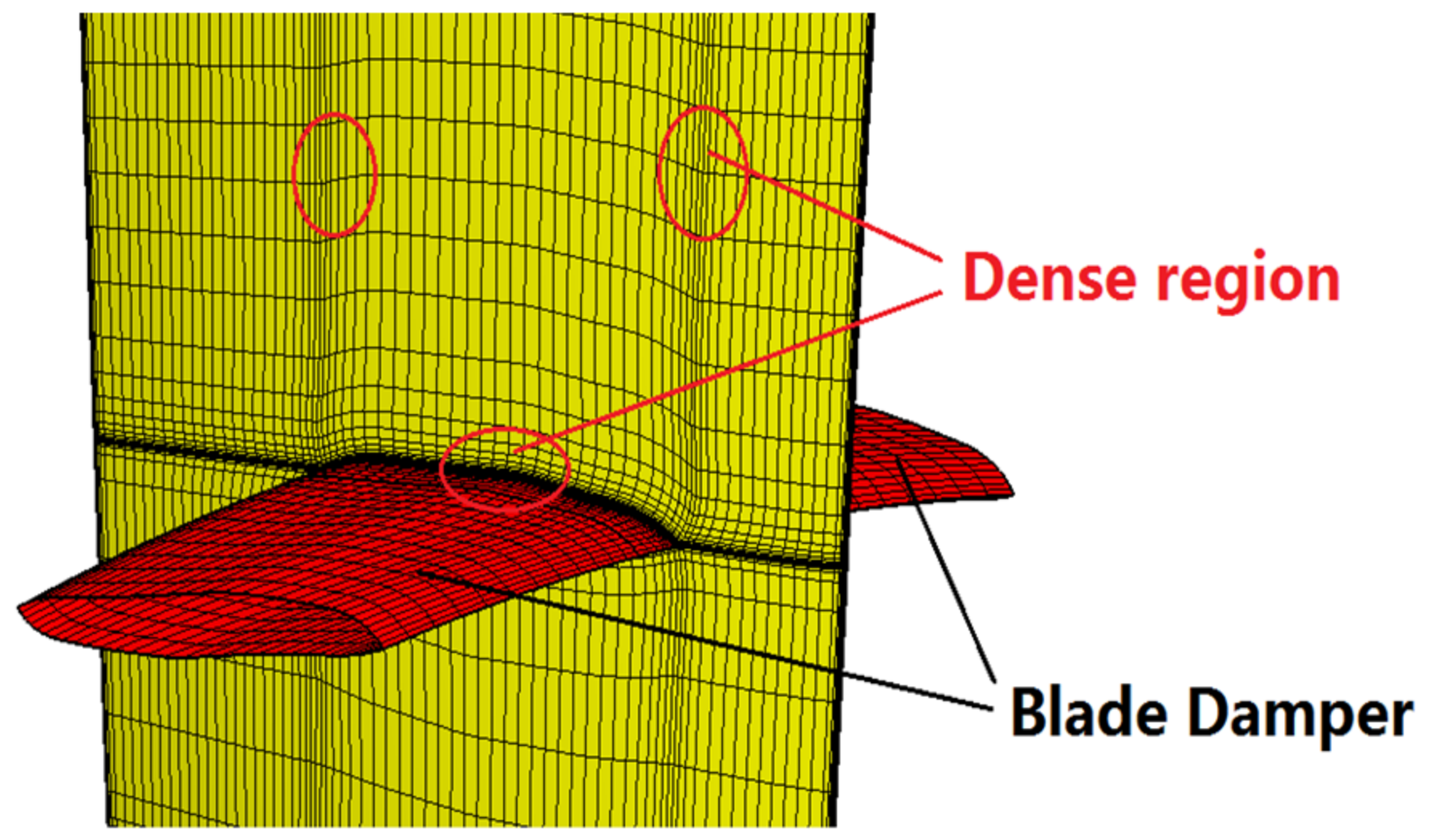
2.1. Research Object
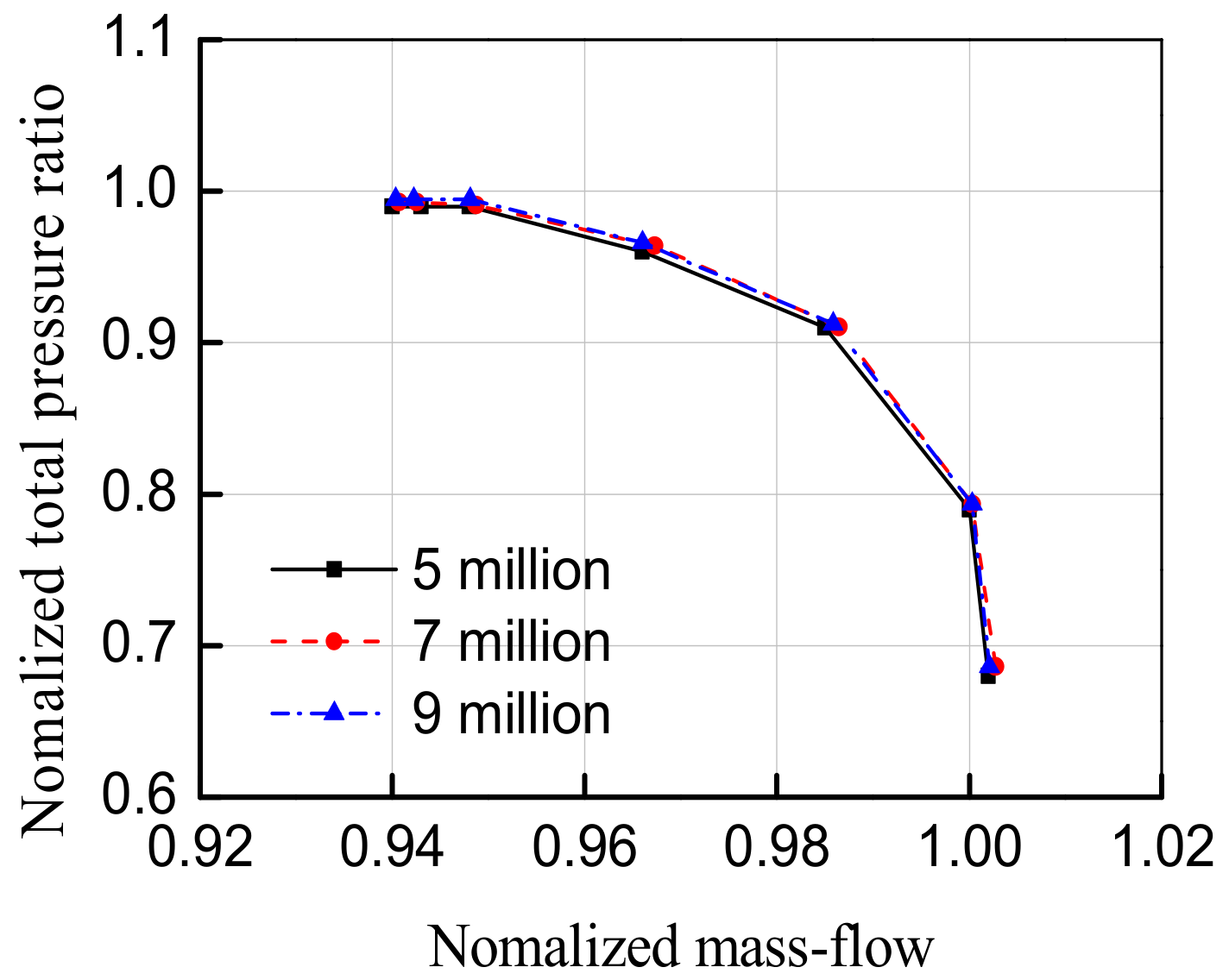
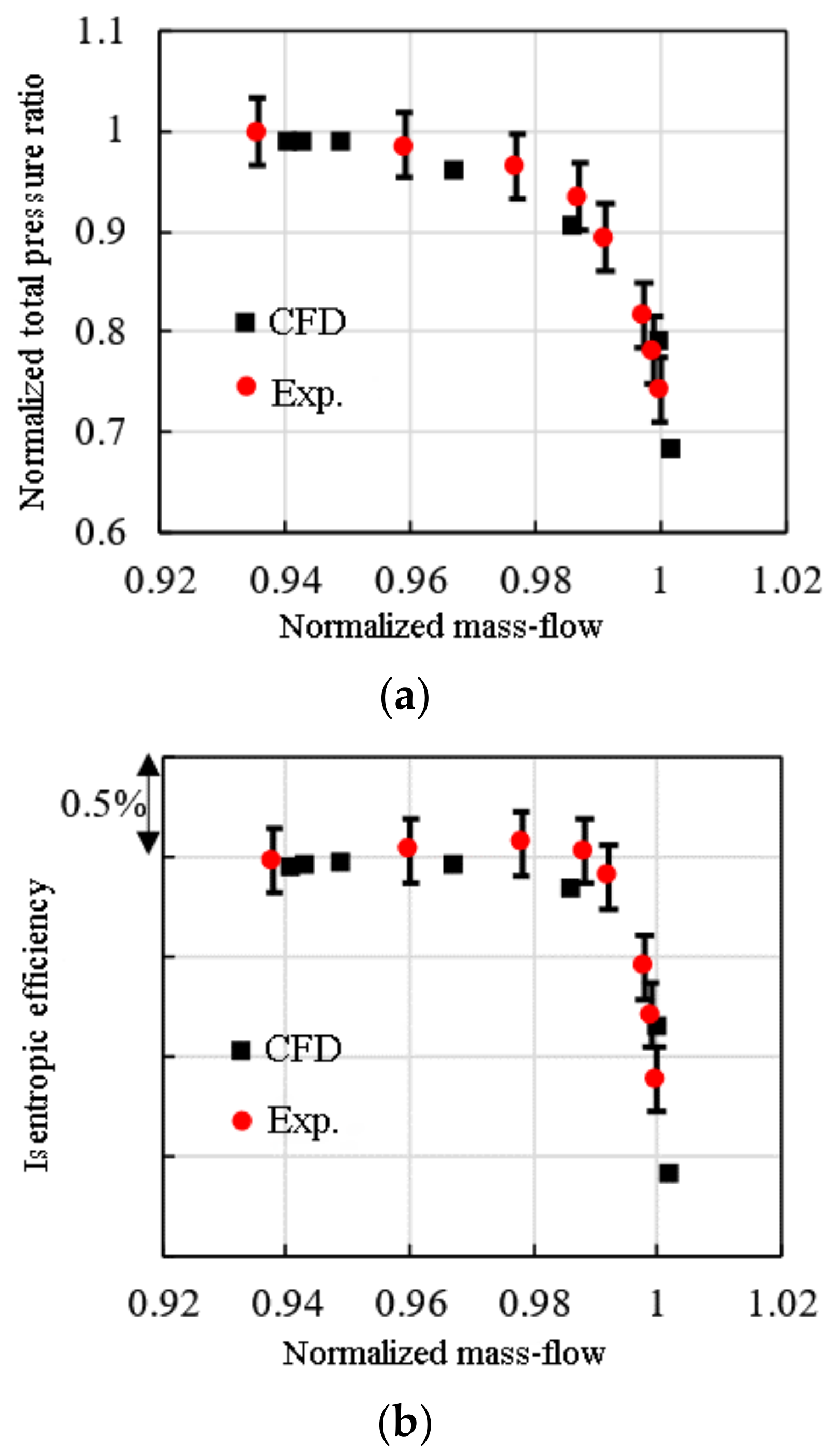
2.2. Validations of Numerical Schemes
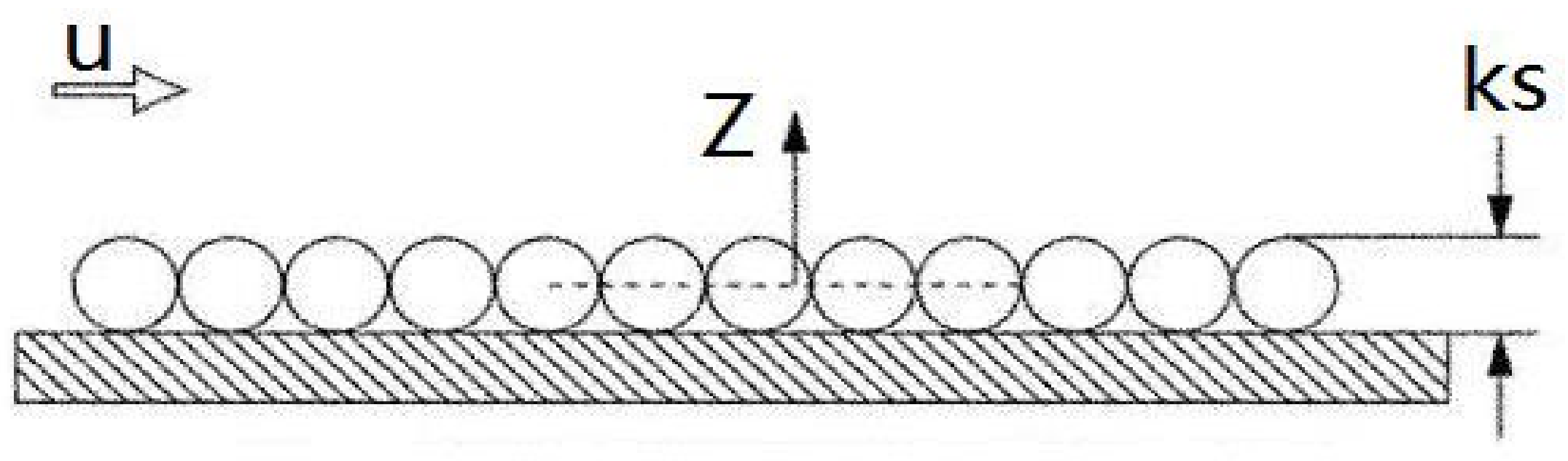
2.3. Equivalent Gravel Roughness Model
3. Results and Discussion
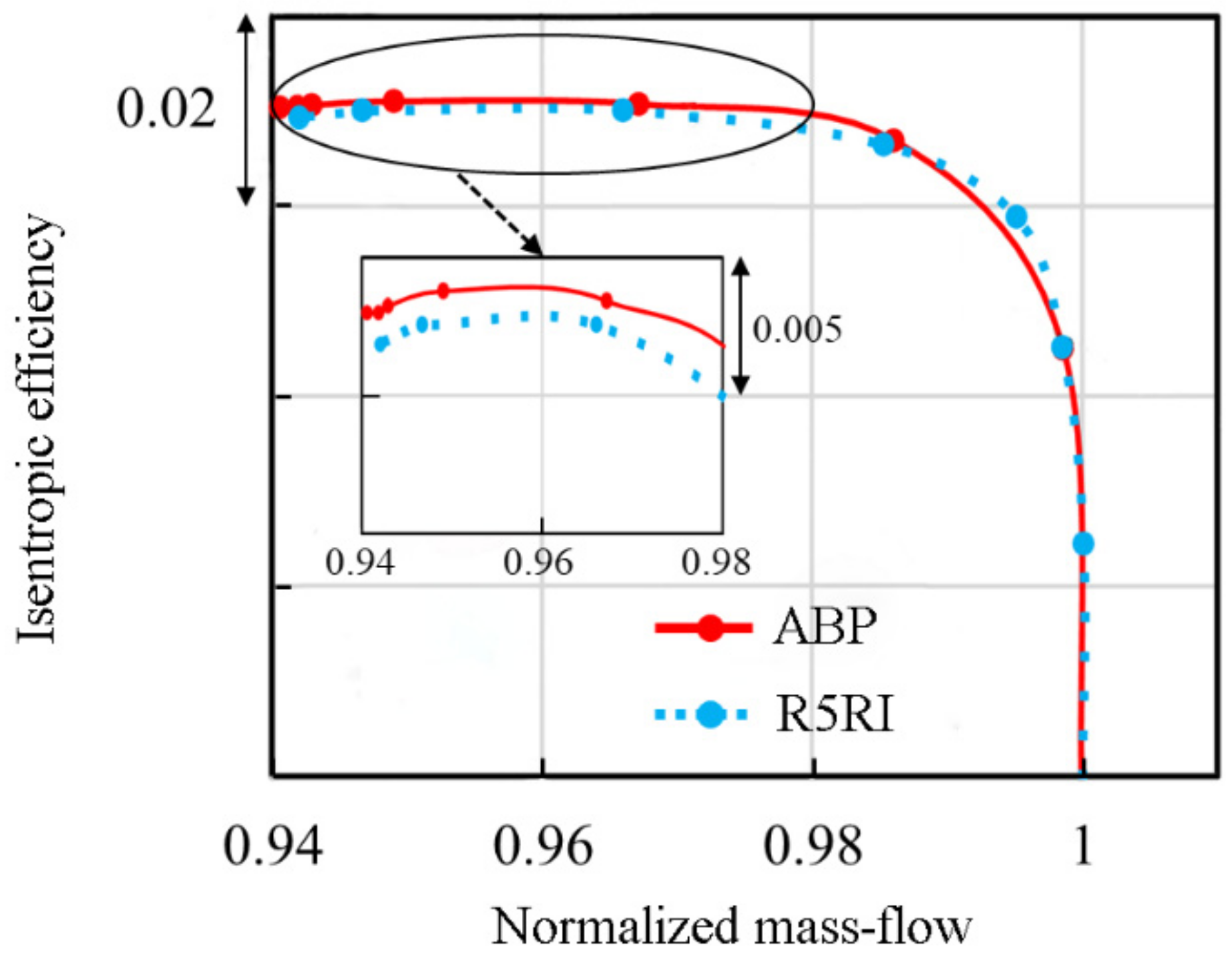
3.1. Influence of Roughness Variation on Compressor Overall Performance
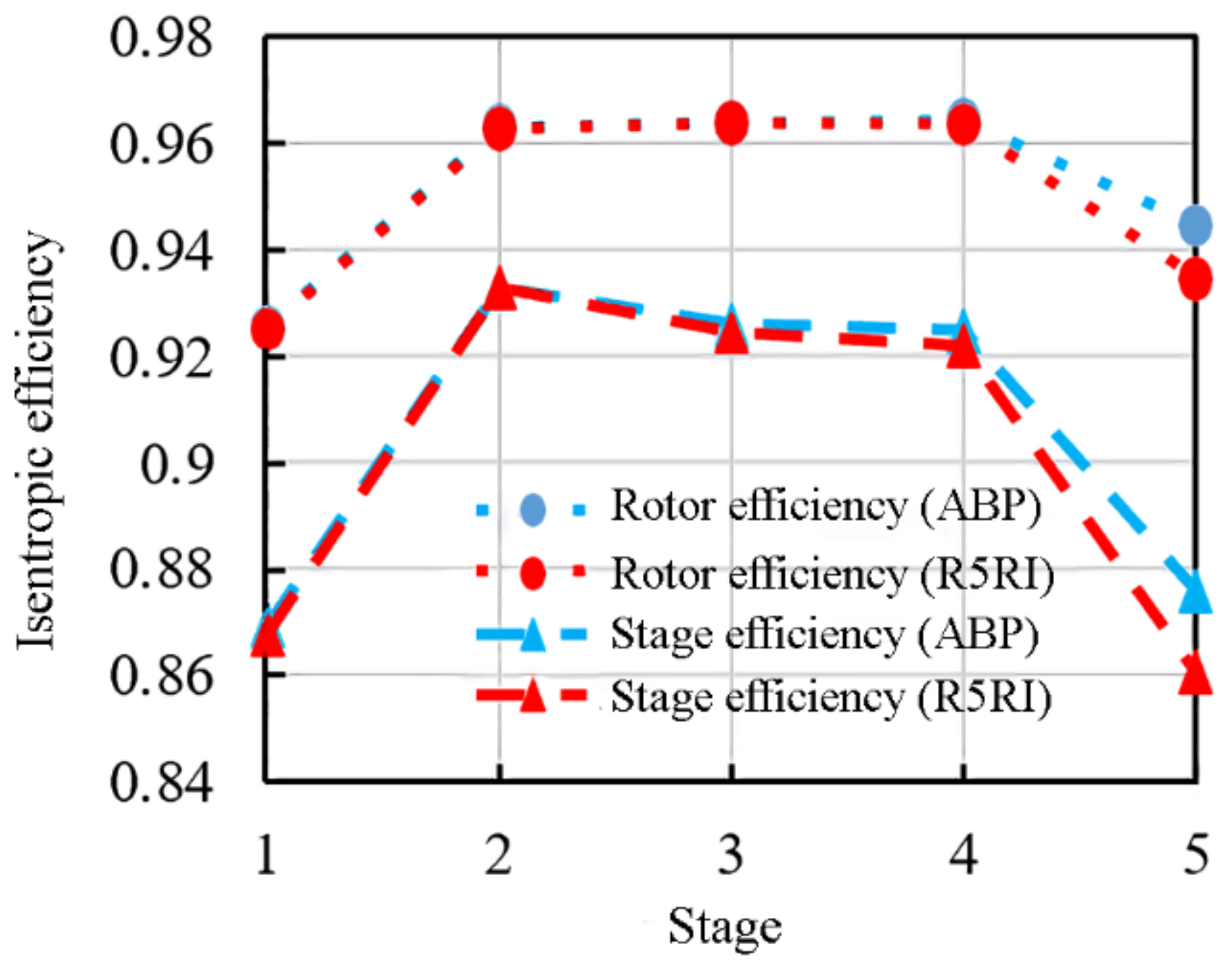
3.2. Influence of Roughness Variation on Compressor Stage Performance
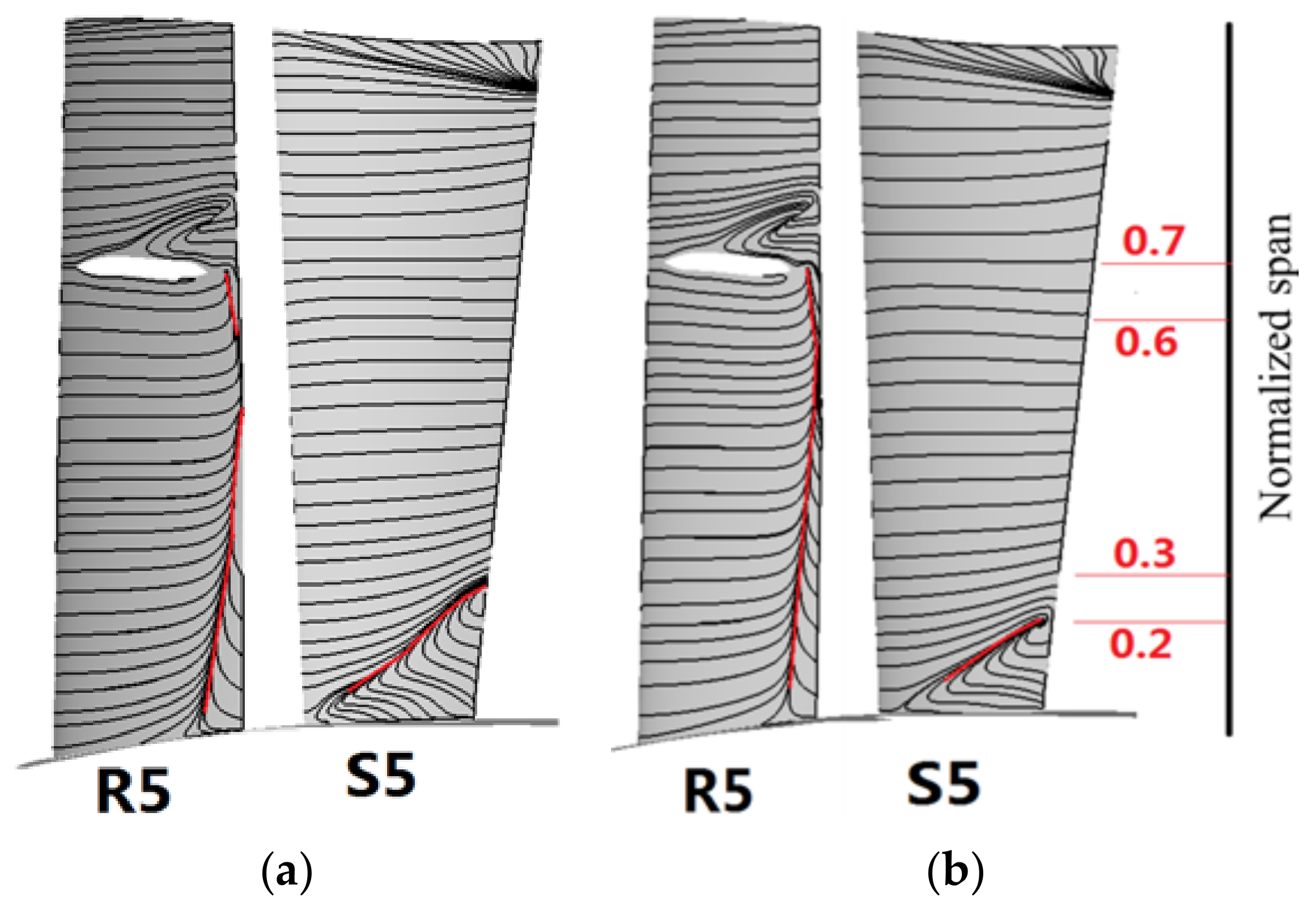
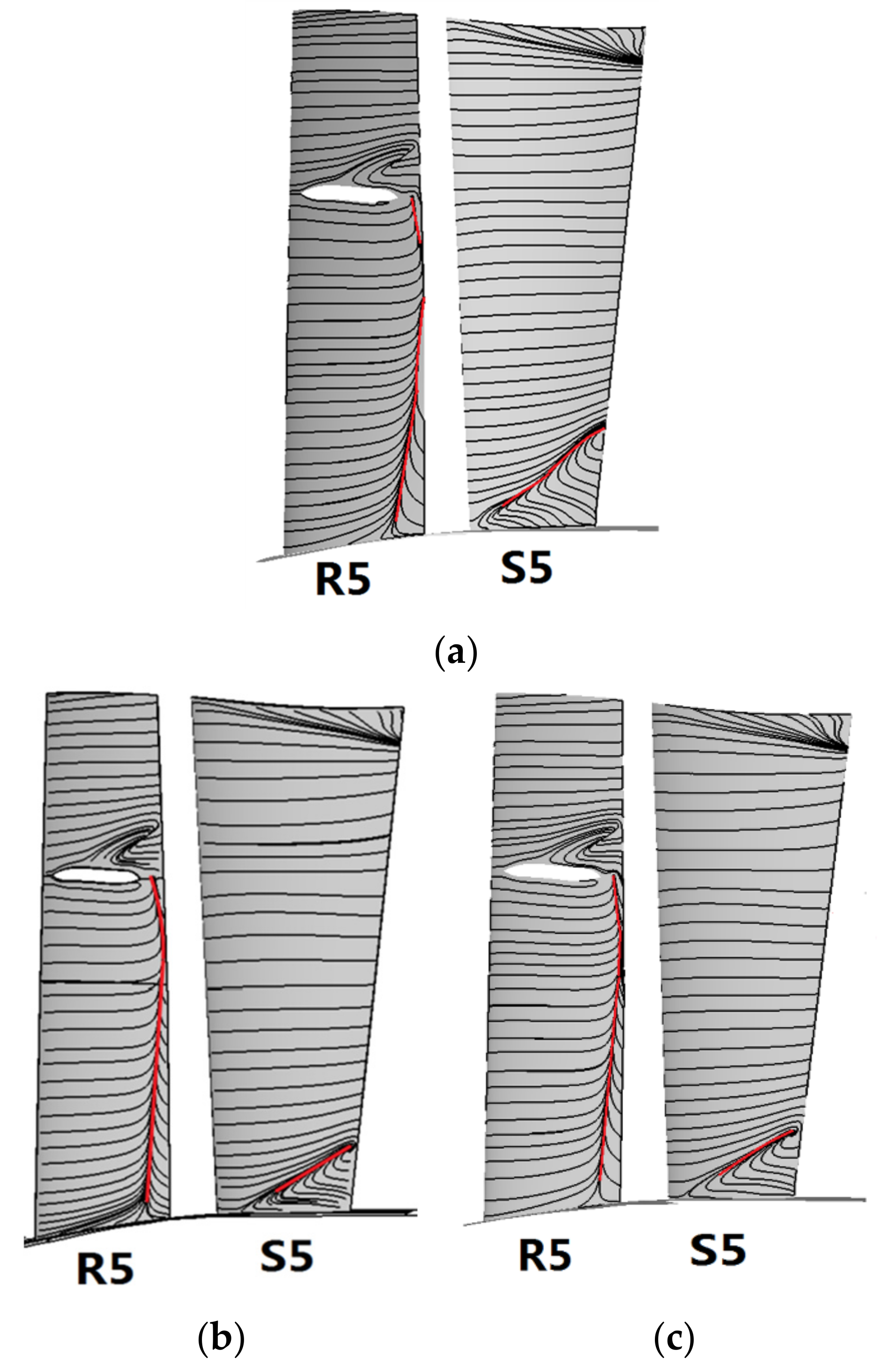
3.3. Influence of Roughness Variation in the Fifth Stage on Compressor Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diakunchak, I.S. Performance Deterioration in Industrial Gas Turbines. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1992, 114, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Piomelli, U. Roughness Effects on the Reynolds Stress Budgets in Near-Wall Turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 760, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meneveau, C. Large Eddy Simulations and Parameterisation of Roughness Element Orientation and Flow Direction Effects in Rough Wall Boundary Layers. J. Turbul. 2016, 17, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, A.J.; Mckeon, B.J.; Marusic, I. High–Reynolds Number Wall Turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 43, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Samtaney, R. Wall-Modelled Large-Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flow Past Airfoils. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 873, 174–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vanna, F.; Cogo, M.; Bernardini, M.; Picano, F.; Benini, E. Unified Wall-Resolved and Wall-Modeled Method for Large-Eddy Simulations of Compressible Wall-Bounded Flows. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2021, 6, 034614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, M.; Pirozzoli, S.; Orlandi, P. Compressibility Effects on Roughness-Induced Boundary Layer Transition. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 35, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redford, J.A.; Sandham, N.D.; Roberts, G.T. Compressibility Effects on Boundary-Layer Transition Induced by an Isolated Roughness Element. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 2818–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammert, K.; Milsch, R. Boundary Layers on Rough Compressor Blades; ASME Paper GT1972-48; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Back, S.C.; Hobson, G.V.; Song, S.J.; Millsaps, K.T. Effects of Reynolds Number and Surface Roughness Magnitude and Location on Compressor Cascade Performance. J. Turbomach. 2012, 134, 051013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suder, K.L.; Chima, R.V.; Strazisar, A.J.; Roberts, W.B. The Effect of Adding Roughness and Thickness to a Transonic Axial Compressor Rotor. J. Turbomach. 1995, 117, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, M.; Pinelli, M.; Spina, P.R.; Venturini, M. Numerical Analysis of the Effects of Nonuniform Surface Roughness on Compressor Stage Performance. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2011, 133, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldi, N.; Morini, M.; Pinelli, M.; Spina, P.R.; Suman, A.; Venturini, M. Numerical Analysis of the Effects of Surface Roughness Localization on the Performance of an Axial Compressor Stage. Energy Procedia 2014, 45, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldi, N.; Morini, M.; Pinelli, M.; Spina, P.R.; Suman, A.; Venturini, M. Performance Evaluation of Non-Uniformly Fouled Axial Compressor Stages by Means of Computational Fluid Dynamic Analyses. J. Turbomach. 2014, 136, 021016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Geng, S.; Zhang, H.; Nie, C. Experimental Study for Effects of Surface Roughness on Compressor Cascade Loss Characteristics. J. Propuls. Technol. 2016, 37, 1263–1270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Chu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, L. Effectiveness of Blade Surface Roughness on 3D Corner Separation and Loss in Compressor Cascades. J. Propuls. Technol. 2019, 40, 504–514. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y. The Control Mechanism for the Boundary Layer of a High Subsonic Compressor Airfoil by Surface Roughness Under Different Reynolds Numbers. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2019, 40, 504–514. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Hui, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Study on the Impact of Fouling on Axial Compressor Stage; ASME Paper GT2012-68041; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Benini, E. Three-Dimensional Multi-Objective Design Optimization of a Transonic Compressor Rotor. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.N.; Afzal, A.; D’ Souza, L.V.; Ansari, Z.; Mohammed Samee, A.D. Computational Fluid Dynamics in Turbomachinery: A Review of State of the Art. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2017, 24, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, X. Review of Design Optimization Methods for Turbomachinery Aerodynamics. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 93, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braembussche, R.A. Numerical Optimization for Advanced Turbomachinery Design. In Optimization and Computational Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 147–189. [Google Scholar]
- De Vanna, F.; Bof, D.; Benini, E. Multi-Objective RANS Aerodynamic Optimization of a Hypersonic Intake Ramp at Mach 5. Energies 2022, 15, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, A.; Zhang, H.; Chu, W. Method of Improving Stability of a Highly-Loaded Axial Compressor Stage by Coupling Different Casing Treatments. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2022, 15, 645–657. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H. Experimental Investigation of the Problem of Surface Roughness. Tech. Rep. Arch. Image Libr. 1936, 7, 747–748. [Google Scholar]
- Goodhand, M.N.; Walton, K.; Blunt, L.; Lung, H.W.; Miller, R.J.; Marsden, R. The Limitations of “Ra” to Describe Surface Roughness; ASME Paper GT2015-43329; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bons, J.P. A Review of Surface Roughness Effects in Gas Turbines. J. Turbomach. 2010, 132, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M. Viscous Fluid Flow; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, D. Principle of Centrifugal Compressor; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


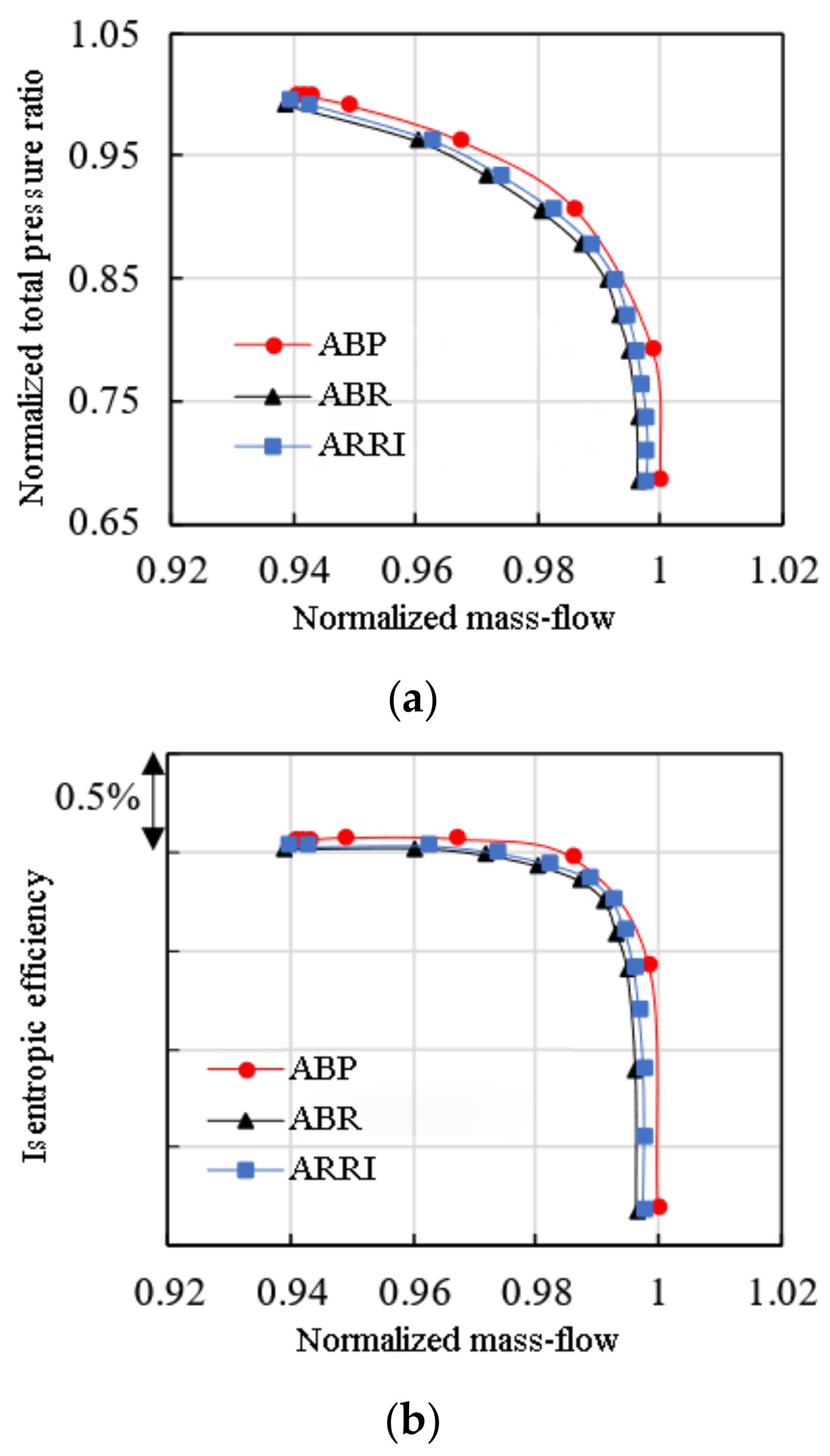
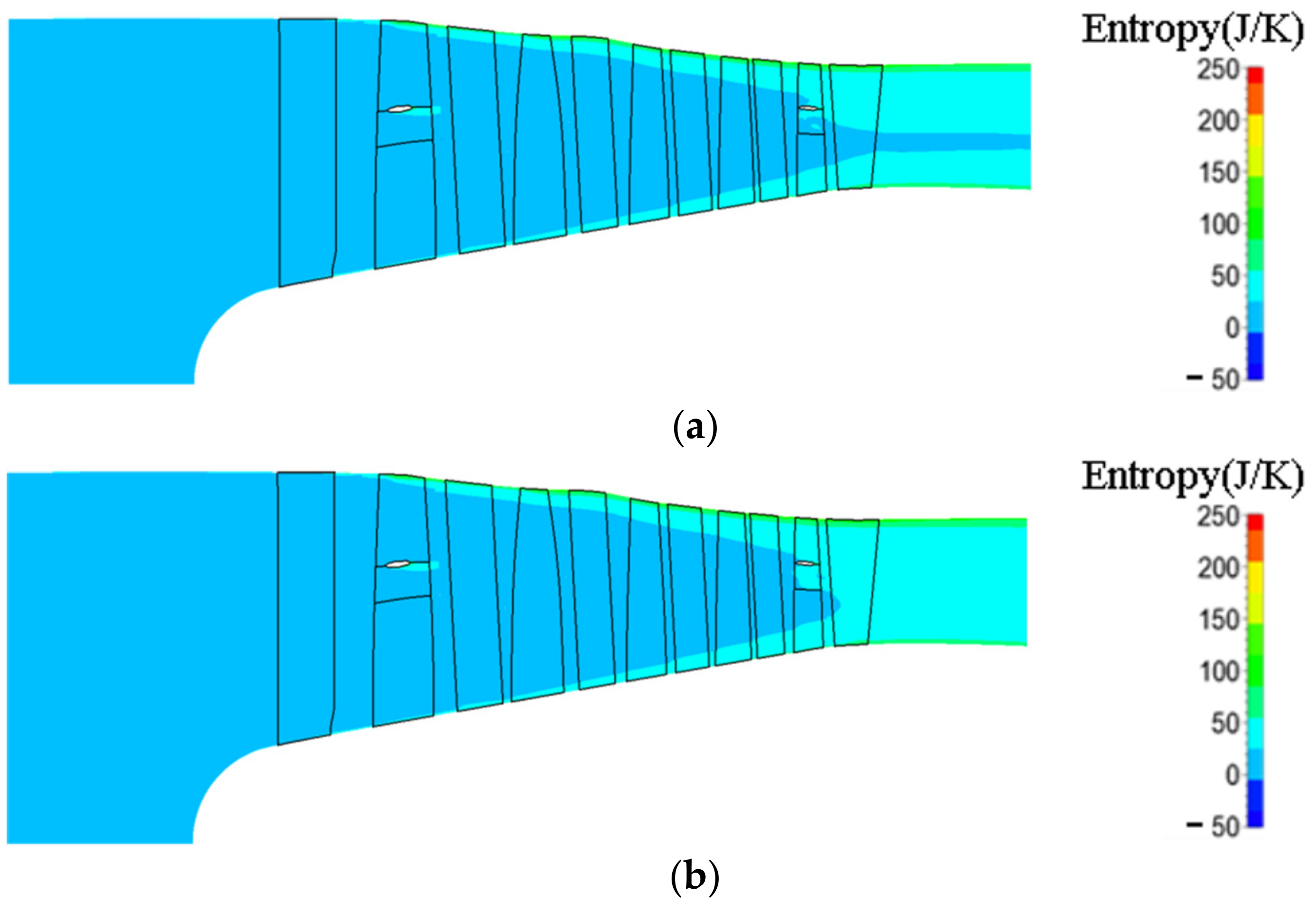
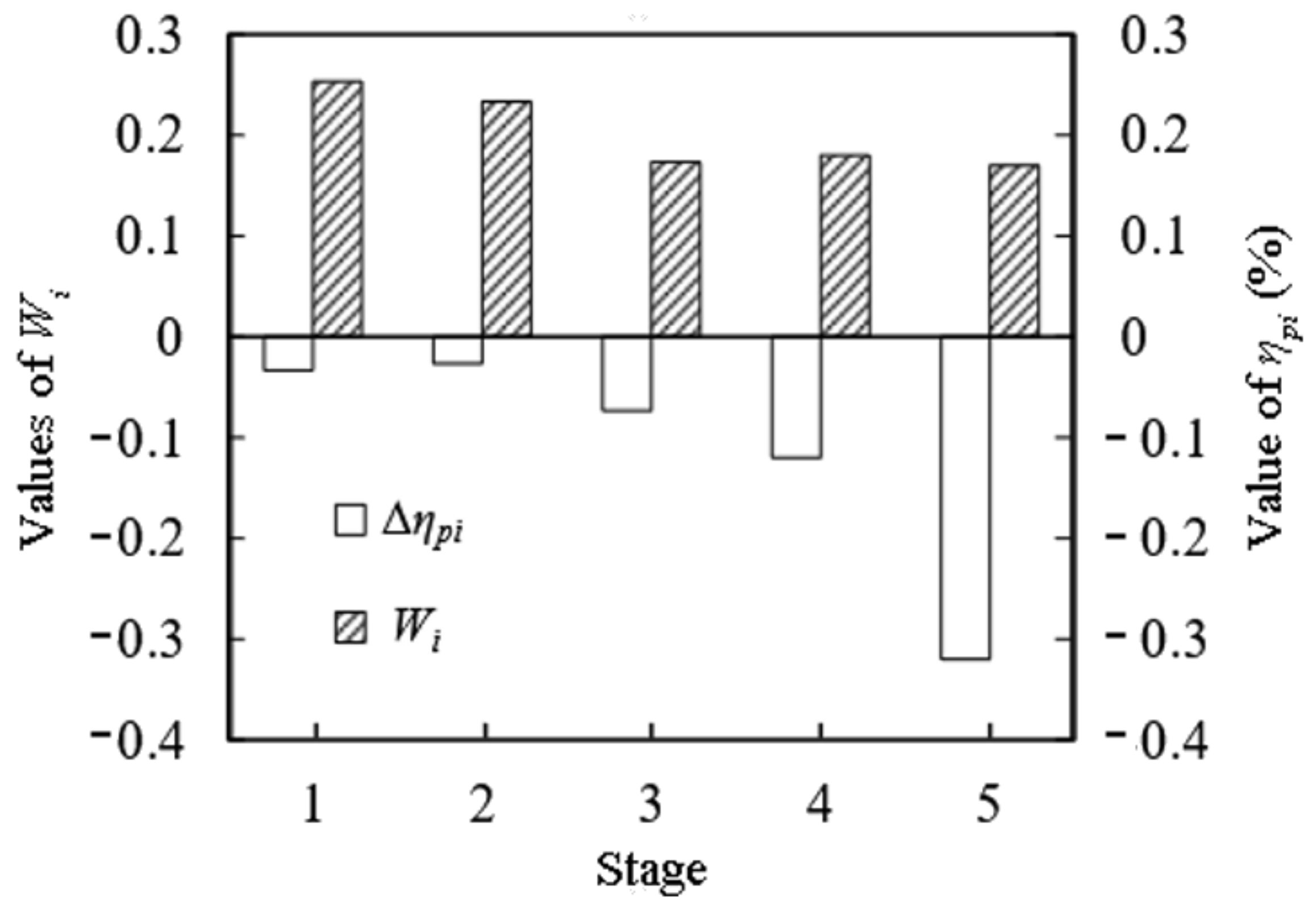
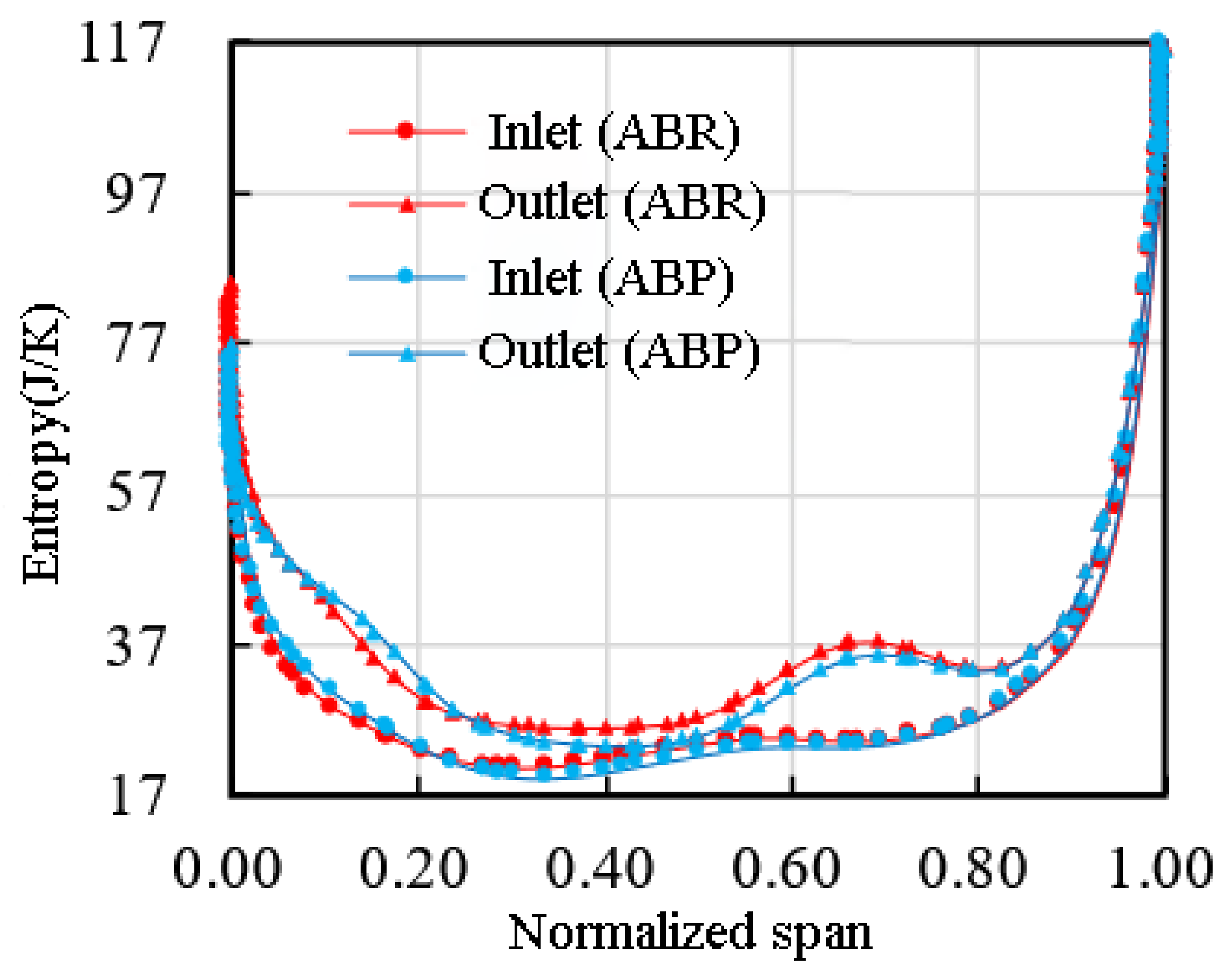
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Design rotational speed | 7952 r/min |
| Total pressure ratio | 2.95 |
| Pressure ratio of 1st stage | 1.29 |
| Pressure ratio of 2nd stage | 1.30 |
| Pressure ratio of 3rd stage | 1.21 |
| Pressure ratio of 4th stage | 1.22 |
| Pressure ratio of 5th stage | 1.20 |
| Suction Surface μm | Pressure Surface μm | |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | 14.35 | 10.39 |
| R5 | 8.75 | 7.59 |
| Rest rotors | 10.45 | 8.49 |
| All stators | 9.37 | 7.26 |
| Roughness Condition | Decrease Amount | Decrease Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| ABR | 0.67% | 100% |
| ARRI | 0.44% | 65.7% |
| R5RI | 0.27% | 40.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Gao, C.; Chu, W. Effect and Mechanism of Roughness on the Performance of a Five-Stage Axial Flow Compressor. Aerospace 2022, 9, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9080428
Chen Y, Gao C, Chu W. Effect and Mechanism of Roughness on the Performance of a Five-Stage Axial Flow Compressor. Aerospace. 2022; 9(8):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9080428
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yan, Chunxiang Gao, and Wuli Chu. 2022. "Effect and Mechanism of Roughness on the Performance of a Five-Stage Axial Flow Compressor" Aerospace 9, no. 8: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9080428
APA StyleChen, Y., Gao, C., & Chu, W. (2022). Effect and Mechanism of Roughness on the Performance of a Five-Stage Axial Flow Compressor. Aerospace, 9(8), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9080428






