Abstract
This paper presents the findings from a systematic review of 29 websites and 13 frameworks that provide STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) educational resources for parents, educators, and children (birth–8 years of age). Our theoretical approach is rooted within a social semiotic perspective that has indicated that multimodality enables children to use different types of expression to communicate a message or share an idea. Using the PRISMA methodology and the narrative document analysis approach, the themes that emerged included how the content and resources available on the websites addressed whether multimodality supported STEM engagement in an inclusive manner. The findings revealed that there were scarce multimodal resources that engaged children with fun, interactive, and meaningful opportunities to be autonomous learners (e.g., children had agency) (n = 11 out of 29), moving between the digital and hands-on physical spaces (n = 8 out of 29), employing gamification for deep learning (n = 4 out of 29), and piquing children’s imagination, inquiry, and creativity, and links to everyday STEM scenarios were hardly present (n = 10 out of 29). The implications lie in addressing early STEM engagement by considering children’s learning abilities and agency, bearing in mind parents/educators’ sociocultural backgrounds, confidence in STEM awareness, and multimodal avenues for communicating STEM learning and inquiry.
1. Introduction
As part of the National STEM School Education Strategy, the Australian Government Department of Education [1] invested AUD64.6 million in initiatives to enhance STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) learning opportunities, among which three were for young children: Little Scientists, Let’s Count, and the Early Learning STEM Australia project. Nevertheless, early-childhood educators and parents/carers from educationally disadvantaged backgrounds continue to face challenges in accessing high-quality evidence-based resources for building children’s STEM learning trajectories from an early age. Research is also grappling with effective means of providing parents, educators, and children with authentic and meaningful STEM learning resources that are inclusive and accessible to all [2,3]. Moreover, emerging research shows how children engaging in multimodal STEM activities from early childhood begin to learn skills such as communication, social-emotional skills, scientific literacy, and inquiry about the world and scientific phenomena around them [4,5]. Regardless of socioeconomic status (SES), sociocultural background, ethnicity, and gender, it is important to build parents’ and educators’ capacity to support children’s STEM learning trajectories [6] to be able to tackle the declining pattern of children maintaining their positive attitudes towards science, mathematics, and engineering as they age [7].
Research alerts us to the arguably more important notion of focusing on children’s intrinsic interest in STEM content areas while they are in their early years of schooling, which can be scaffolded through teachers’ play-based teaching practices [2,3]. This paper presents the findings from a systematic review analysis of 29 websites and 13 frameworks that provide STEM educational resources for parents, educators, and children (birth–8 years of age). The research question for this paper is to examine the nature of the role of multimodal learning resources in promoting STEM engagement for children. This systematic review is timely in addressing inclusivity (e.g., sociocultural) in STEM engagement, and understanding the role of the multimodal learning experiences (e.g., apps, games, digital stories, virtual worlds) that educators and parents/carers can meaningfully use for building young children’s (birth–8 years of age) STEM engagement. Given that STEM education is a priority for both Australian national and state governments, it is important to gain insight into the value that existing digital and/or multimodal educational resources in early childhood attach to STEM education and those that address inclusivity in STEM engagement.
Building children’s foundation of STEM knowledge and skills such as scientific experimentation, inquiry skills, and design- and technology-related skills is a national priority [5]. Internationally, STEM education is regarded as critical and the one significant arm of education that effectively prepares future young generations for the jobs of tomorrow that need skills such as communication, scientific thinking, inquiry, and becoming digitally competent [1,8]. Recently, Australia’s Chief Scientist [9] and the Education Council’s National STEM School Education Strategy 2016–2026 report (currently under national consultation) stressed the importance of a kind of STEM learning that is inclusive in incorporating the growing number of girls engaged in STEM-related careers, in line with preparing Australia’s future workforce (spanning both vocational and university education and training credentials). The report recommends ensuring that all students finish school with a strong foundational knowledge in the disciplines of STEM and the related skills needed for 75% of future jobs (e.g., mathematics, analytical thinking, digital literacy, problem-solving skills). It then becomes critical to support parents and educators such as early-childhood professionals at the forefront of the national priority agenda by providing them with access to quality evidence-based resources to become confident in the early engagement of children in STEM education and adapt an inclusive approach in achieving so. In this systematic review paper, we analyse and discuss 29 websites and 13 frameworks to gain insights into the value of existing digital and/or multimodal educational resources for children’s inclusive STEM engagement.
2. Inclusive STEM Engagement—State of the Art
In present times, young children are multimodal learners and communicators [10]. Learning should occur in a context where every child, regardless of their sociocultural background and ability, has an opportunity to participate in STEM education, such as, for example, via text, visual, kinaesthetic, aural, and spatial modalities. Multimodal playspaces allow children to manoeuvre and manipulate artefacts available to them in both digital and physical spaces [11]. For example, technology-mediated tools as part of multimodal playspaces allow children to take advantage of new modalities and effectively reach new ways of making meaning of scientific concepts [12] and maths learning [6] through activities related to their immediate interests and real-life scenarios. Research such as the botSTEM project and their underpinning didactical framework address STEM teaching as an inclusive pedagogy that makes use of inquiry, engineering design methodology, collaborative work, and robotic technologies. Yelland [3] suggests that STEM teaching and learning encourage children to think beyond one modality while exploring their everyday world, make interconnections, and rationalise choices about which modality, or combination of modalities, communicates their message most effectively. Thus, STEM engagement should be inclusive for all children and give them the opportunity to become agentic learners via STEM education.
Recent empirical research is now emerging that addresses young children’s STEM engagement via technology-constructed resources [12]. For example, studies have examined the critical role of the teacher and the importance of child–adult interactions during STEM experiences that are technology-mediated in early-childhood settings: Fleer [13], on using iPads for digital storytelling; Kewalramani et al. [14], on using the Internet of Toys (IoToys); games-based learning, both in formal and informal home-based environments to support children’s STEM and social-emotional learning; Undheim [15], on digital stories and literacy learning; and Lowrie and Larkin’s study [6], employing maths learning apps for early STEM learning. These types of studies show us that STEM can be incorporated into educators’ teaching practice to create rich learning opportunities in an early-childhood environment where children and teachers can learn and explore technologies together as part of the repertoire of multimodal learning and interactions.
While considering the technologies constructed and the multimodal teaching and learning practices in early-childhood education (ECE), it is also important to look at the seminal ways in which digital learning has been positioned in the research. For example, Prensky [16] distinguished the quality of digital learning activities in the following categories:
- Well-designed activities provide powerful interactive experiences that can enhance young children’s learning, foster cognitive skills’ development, and promote healthy development.
- Poorly designed activities are simple sedentary activities that contribute little to children’s learning, skills’ development, or healthy development while being potentially associated with obesity and poor physical conditions.
Neumann [17] has found that, when studies involving preschool children are being examined, it is critical to correlate the benefits of using digital activities in different areas of children’s learning and development such as emergent literacy and experiences that are well-designed to motivate and encourage learning rather than traditional teaching methods. Co-operative social interactions among children and adults should also be promoted when playing digital activities [8,18].
Supportive materials for STEM play and learning (including digital activities) are designed to indulge the interests and abilities of children, as well as their instinct to learn. In such cases, children are more likely to develop and strengthen their initiative, attention, industriousness, and love for learning [19]. However, not all digital activities are developmentally appropriate and/or inclusive or meticulously designed to enhance how children learn in the 21st century’s digital era. While much of the available literature on digital technologies in ECE focuses on the role and use of computers by young children [20], during the past few years, there has been an increase in research and descriptive literature about the use of other kinds of technologies. This includes focusing on the rising popularity of smart mobile technologies and mobile applications (apps) [19], as well as addressing cultural inclusion in STEM participation.
An important development of digital technologies has been the ability to intuitively interact with devices such as tablets or robots. The ability to draw on a screen with a digital pen or fingers, drag and swipe on a screen, or program a robotic toy as part of everyday play that is multimodal has allowed a new generation of users to move from being consumers to actively constructing while using these technologies [3,12]. This ability to construct using digital devices is consistent with constructivist principles that emphasise the importance of children actively constructing representations of their own understanding (e.g., drawing or creating a scene using playdoh) rather than consuming another person’s representation (e.g., watching a YouTube clip). This is apparent in disciplines such as science, where children can use arrows to indicate the direction of forces or computational thinking and represent their understanding of the movement of a Beebot through a course. This construction using digital technologies further enhances learning by providing children with the opportunity of having multimodal experiences where the technologies allow immediate audio-visual or tactile feedback in response to input by the user (e.g., programming a robot and then allowing it to move as part of everyday play).
3. Theoretical Perspectives
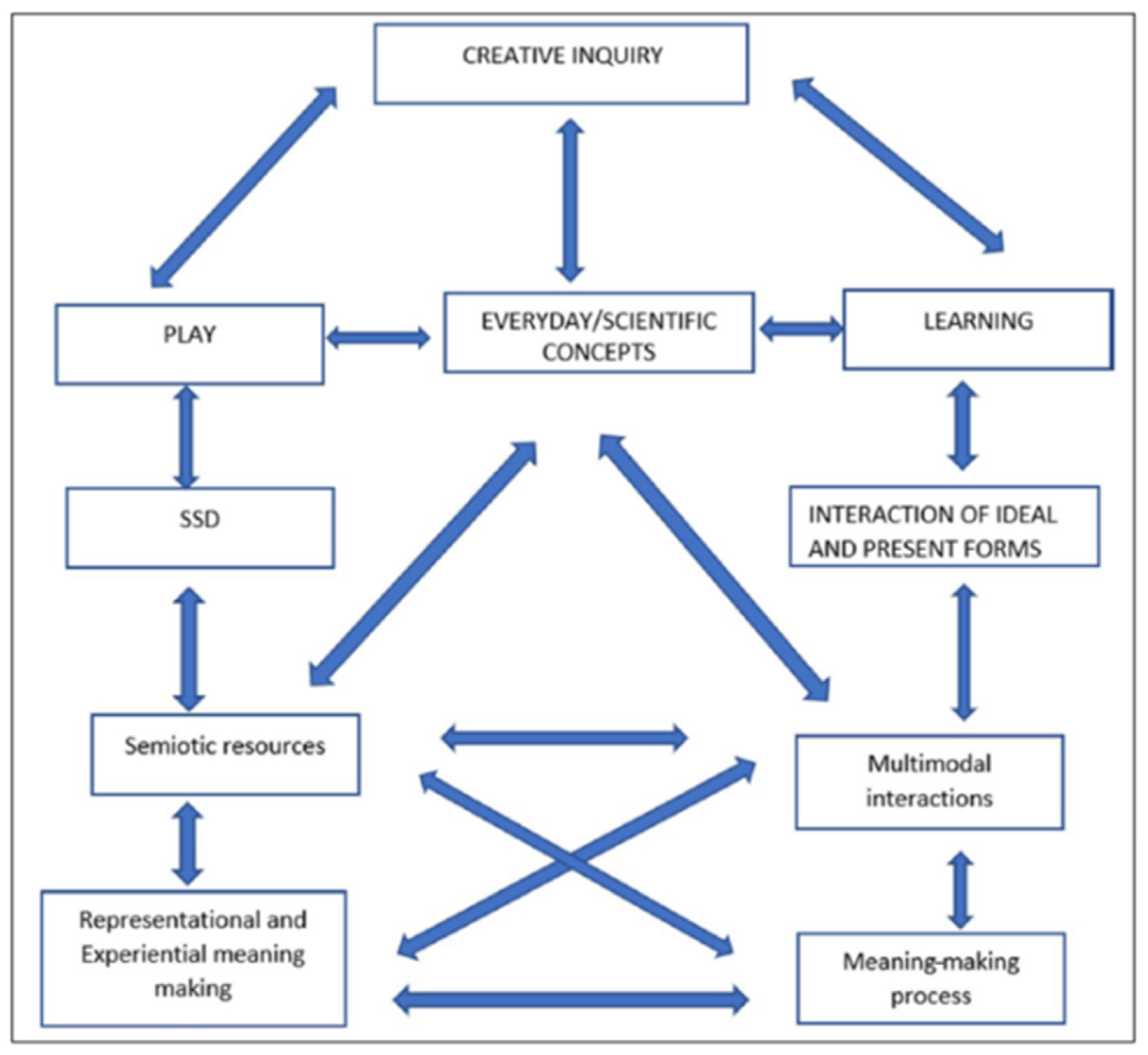
Our theoretical approach is rooted within a social semiotic perspective. Kress [21] have indicated that multimodality enables children to use different types of expression to communicate a message or share an idea, thus making their different perspectives visible to the adults and peers in their learning environment. Multimodality enhances learning experiences by fostering curiosity, engaging children in inquiry-based learning, and allows children to explore ideas by exploring multimodal representations and engage in meaning-making by constructing their own [18,22]. In addition, sociocultural perspectives also harness the Vygotskian concept of mediation [23], whereby multimodal resources are viewed as mediating means and learning as a mediating action, and where resources are important for building up children’s schema, interests, creativity, and inquiry. In this paper, a multimodal resource is described as a semiotic resource that aids in the making of meanings and includes not only meanings made with language but other meaning-making systems such as gestures, actions, movement, aural/sound, haptics/touch, and symbols that are significant in a child’s social learning environment [14]. Hence, frameworks derived from a social semiotic perspective assume that meaning-making does not occur in isolation but in social situations or activities within a learning environment (e.g., physical, digital). One such framework is Kewalramani and Veresov’s [12] multimodal creative inquiry (MCI) approach (Figure 1), which underpins the use of semiotic resources for STEM learning and engagement which has been adapted in this paper as the analytical framework. We explain our analytical approach in the next section.
Figure 1.
Multimodal creative inquiry approach [12].
4. Analytical Framework Employed
Research into STEM education has focused on studying how learning is expressed and developed through social semiotic resources such as verbal and written text and language [24]. With the rapid advent of innovative technologies and online learning, especially in primary and secondary schooling, e.g., [3,10], researchers have recently widened the scope to include the use of digital resources besides text, language, and physical artefacts such as apps, games, diagrams. However, there are very few in the early-childhood context that afford children’s engagement with STEM-related games that are multimodal in nature, offer open-ended exploration, and allow for children’s creativity and agency [9,11,15]. Our analytical approach draws upon the MCI approach, which is rooted within a social semiotic perspective. Learning resources are defined as multiple modes, and the concept of multimodality is employed to draw attention to the use of several modes in a certain learning situation, such as generating inquiry and curiosity for STEM learning and engagement using multimodal representations [12,24]. The idea of MCI is developed as a framework to analyse not only STEM subject-specific terminology but also because STEM concepts are often more abstract and information-dense. The development of multimodal resources illustrating scientific content, for example, using different means (text, sound, touch, aural, haptic) might be a way to support early learning and agency in STEM engagement, regardless of the children’s cultural backgrounds, gender, and abilities.
For children to establish early and sustainable ways and means to engage in STEM learning, it is essential that they are exposed to a variety of multimodal texts, pictures, games, and interactive books that include technology-constructed learning tools, particularly those which provoke children’s creative inquiry. For example, digital stories, picture books, and games within different communicative contexts can augment children’s science learning from an early preschool age [19], as a potential way of sparking a young child’s belonging to STEM.
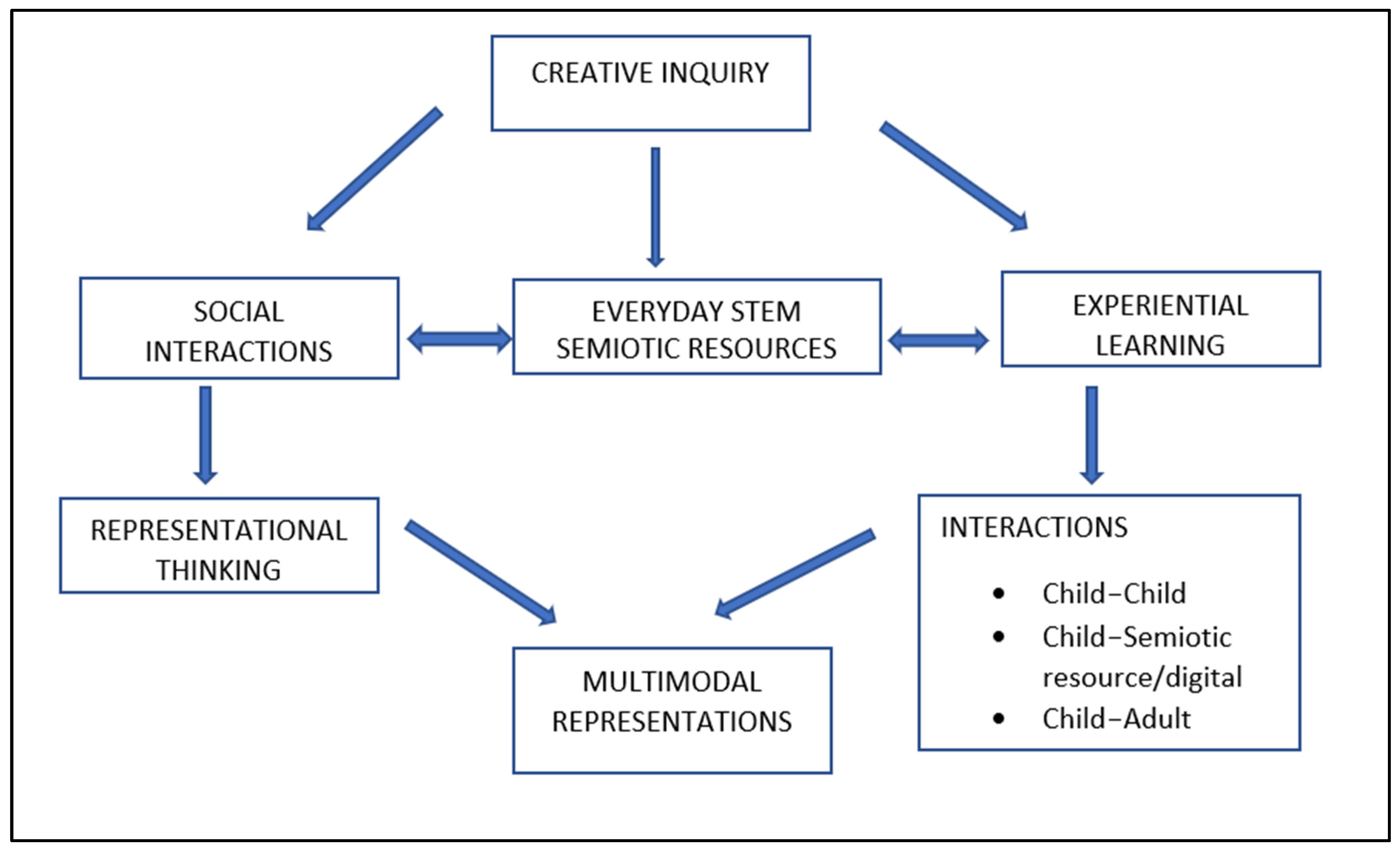
The multimodal representation approach considers creative inquiry as a collectively created way of introducing STEM to young children through three types of multimodal interactions: child–adult, child–child, child–semiotic resource/digital tool interactions and communication. These interactions do not solely rely on verbally reproduced ideas that a child might respond to when prompted by a teacher/parent’s question without showing creativity and independent thinking. Rather, we have adapted the MCI approach to develop a “multimodal representation” approach as an opportunity to enhance multimodal learning from “concept-centred” to “child-centred” and “development-focused”, particularly the one which allows STEM learning and engagement within children’s everyday environments to become “creativity-focused”, “experientially focused”, and “representationally focused” via multimodal interactions which children can draw upon within social learning environments. Figure 2 depicts the multimodal representation analytical approach we have employed to analyse the websites and frameworks for children’s inclusive STEM engagement.
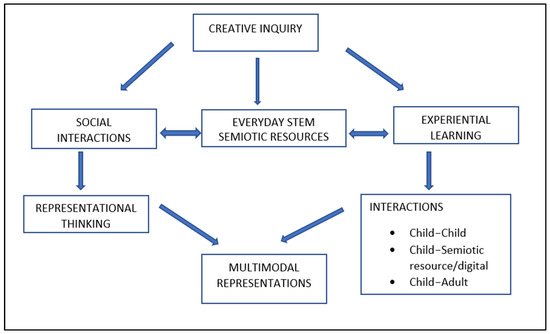
Figure 2.
Multimodal representation analytical framework for inclusive STEM engagement.
The premise for our analysis was to examine STEM websites that required performing things away from technology: that is, the idea of constructing multimodal representations via experiential learning and types of multimodal interactions. As noted by Larkin et al. [25], when technologies and similar means are employed, for example, for young children’s mathematics learning, experiences need to be thoughtfully designed to enable positive and meaningful play experiences. Larkin et al.’s [25] study used representations to design STEM apps that supported the development of logical reasoning using the four conceptual blocks of decoding, encoding, conditionals, and debugging. Although research has shown that representations and representational learning and thinking demonstrate a range of skills—such as how children might process information [20,21,22], design, build, and create, our study analysis looks at the lens of multimodal representations for understanding the nature of multimodal and technology-constructed learning experiences for children’s STEM learning. As seen in Figure 2, the three types of interactions can account for “real” hands-on and “messy play” types of experiential learning. Multimodal representations account for using physical and virtual spaces as a seamless continuum of a child’s STEM engagement and, rather than offering monomodal experiences, offer opportunities for children to converge meaning of abstract STEM concepts and develop imaginary situations [19] within both digital and non-digital playspaces, leading to cognitive thinking and creative reasoning. The interactions move across different playspaces due to the tactile nature of the digital tools available to children; thus, the interactions do not remain static but blend between the virtual and physical spaces, to provide children with representational fluency. Children’s ability to move between representations fosters 2D artefacts to become 3D-created artefacts and representations highlighting experiential STEM learning and representational thinking.
Given the seminal research around ensuring a child-centred approach while designing technology-constructed STEM learning experiences [10,20], we were also cautious about considering the broader ecology of childhood play. In that sense, multimodal representations should position children’s interests and STEM concepts prevalent within their everyday environments (formal and informal learning). Secondly, the design of learning experiences must promote the child as an active user and manipulator of the semiotic resources available to them in both digital and non-digital playspaces, rather than as a passive consumer. The next section discusses the state of the art of inclusive STEM engagement and research around the use of technologies for children’s STEM learning.
5. Methodology
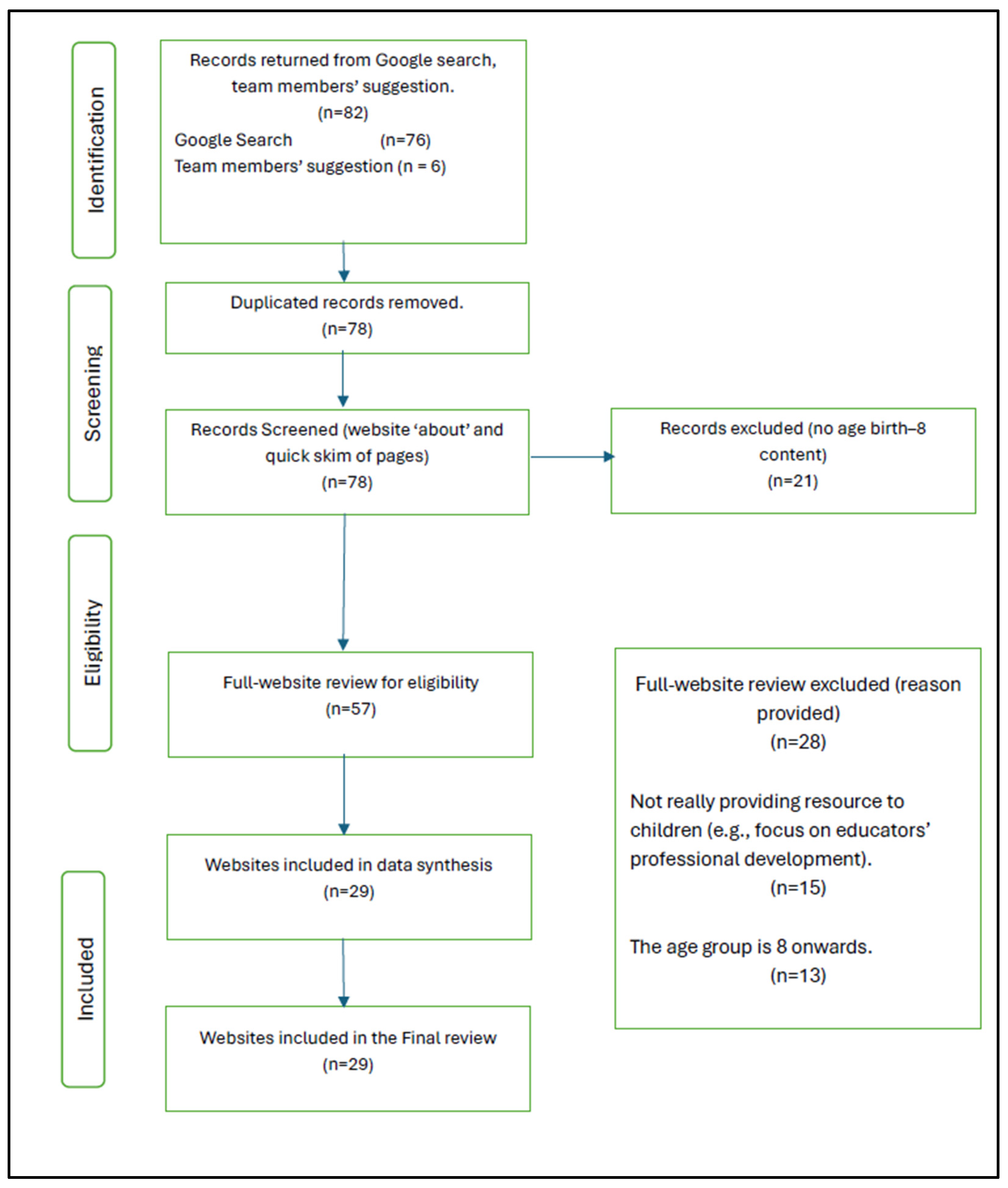
Using the PRISMA methodology [26], a systematic review of 29 websites and 13 frameworks (see Figure 3) that supported children’s inclusive STEM engagement was conducted. Initially, 82 websites that supported children’s STEM engagement were scanned. Data were obtained from (1) targeted websites, (2) internet search engines, and (3) international government documents. The inclusion criteria were the following: learning resources to cater to educators, parents/carers, and children aged birth–8 years, policies, guidelines, and frameworks that support children’s STEM engagement, and learning trajectories in digital and/or multimodal ways. Online resources/websites that promoted STEM for children above eight years of age were excluded.
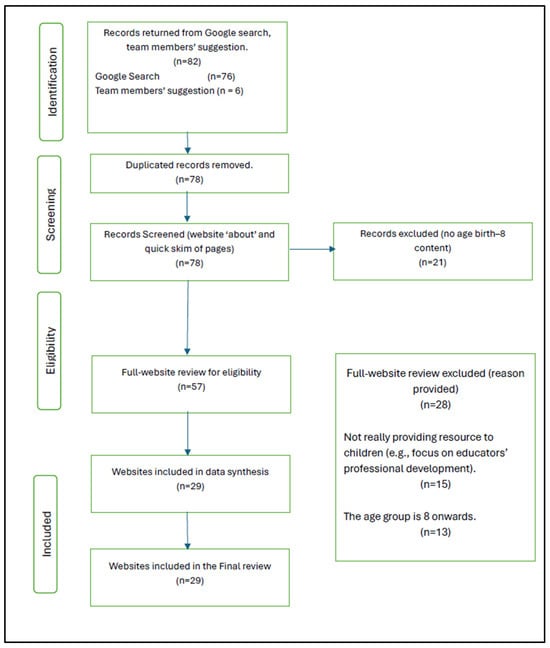
Figure 3.
PRISMA chart.
Using a narrative document analysis approach [27], the themes that emerged included how the content and resources available on the website addressed whether multimodality supported STEM engagement and children’s STEM learning trajectories, especially looking at the inclusion of girls and children from underrepresented communities and inclusivity issues. This study’s analytical framework (Figure 2) was used to deduce the themes.
6. Data Analysis
The search terms and synonyms included the following: (STEM, multimodal, digital, inclusive) AND (experiential, representation) AND (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics guideline or procedure or framework or governance). For the general Google search, the first set of search results were restricted to content from Australia to ensure that we captured Australian-context research around STEM educational websites and the available resources. Subsequently, the filter for Australia was removed, and the international search results were reviewed.
Eighty-two websites for documents and learning resources were initially screened for relevance by title, “who we are”/“about us” webpages, research summaries, or tabs/webpages. An Excel spreadsheet was constructed, and a synthesis was conducted initially by the research assistant and the first author, as per the recommendations for systematic searches using the PRISMA method [26,28]. Full-text documents and resources were then read to ensure that the documents and learning materials met the inclusion criteria. Duplicate documents were removed. The first four authors screened a sample of eligible websites (n = 29) and achieved a good agreement (90%). They subsequently screened the remaining websites to ensure that validity and reliability were achieved and that no resources were left behind that might have met the inclusion criteria. The included governance documents available on the observed websites were synthesised (see Table 1) in a narrative review, and the results were crosschecked by the research working group (co-authors named in this paper). The narrative review themes included how the content and resources available on the website aligned with the early-childhood content (catering to children from birth to 8 years of age), addressed diversity and inclusion for engaging children in STEM and whether multimodality supported STEM learning and engagement.

Table 1.
Twenty-nine websites and their related frameworks analysed for a systematic review.
7. Results
In this study, 29 websites were included as part of the systematic review. The websites were based on STEM content, aimed at groups of children from birth to 8 years of age, and we analysed whether the websites provided resources for children’s STEM learning. For instance, some websites focused on teachers’ planning, professional development, and networking; hence, these were not included in the findings. Aligning with this study’s analytical framework (Figure 2), while analysing the data, we found that the content regarding accessing STEM resources in home-based environments and addressing cultural diversity and inclusivity issues is considerably underrepresented in STEM learning website resources. While early-childhood education content is well-represented, the content explicitly for children aged from birth to five years is still lacking. Resources for guiding teachers/educators’ STEM practices are usually word-dense (difficult to digest). Multimodal resources that can be spontaneously and autonomously played by children (e.g., games, manipulatives) are scarce. Easy-to-read frameworks and guidelines for supporting educators/teachers’ STEM practices are under-developed. When considering the importance of girls in STEM, the information for educators and parents is generally text-based. Websites (e.g., the Finnish StarT programme for project-based learning) provide teachers with specific guidance/tips to create a STEM classroom. Website content that approaches the broad issue of inclusivity and gender is rare, with the following websites being the exceptions (e.g., Conceptual PlayWorlds; botSTEM). A detailed explanation of the findings has been provided and summarised in Table 2 and Table 3, with two broad themes emerging: “multimodal representations and links to everyday STEM learning” and “consideration of children’s learning abilities and diversity”.

Table 2.
Theme 1: multimodal representations and links to everyday STEM learning.

Table 3.
Theme 2: Consideration of children’s learning abilities and diversity.
7.1. Theme 1: Multimodal Representations and Links to Everyday STEM Learning
An exemplary website of the botSTEM project and the didactical framework addresses teacher pedagogy and content. It is a gender-inclusive pedagogy that uses inquiry, engineering design methodology, collaborative work, and robotic technologies. The botSTEM toolkit provides teachers and preservice teachers with assorted teaching practices. The resources also highlight how important it is for young children to first engage, notice, wonder, and question. This, in turn, depends on how educators and parents provide the time and space for children to play in a scientifically stimulating environment. The role of the adult (teachers in the case of the botSTEM project) becomes critical in scaffolding children’s STEM conceptualisations, which subsequently informs how children are “hooked” to engaging with multimodal resources. The focus then becomes to ensure that educators support children’s agency and STEM identity formation, which peaks children’s connections to STEM.
Another project website, the Conceptual PlayWorlds (CPW) Model [4], demonstrates how teachers create drama-based and roleplay scenarios for the exploration of science topics, such as sound, and educators’ scaffolding of children, including toddlers, to imagine objects tied to the narrative experience of science in a story and motivate children to think more visually about their world. While it is not possible from toddlers’ language to determine their conceptual understandings, it is possible to notice their actions and how they enter play and solve problems. However, the CPW does not construct the play experiences for parents/educators using technology-constructed tools; rather, it relies on the premise of imaginary play and tools available in children’s everyday environments, particularly scientific phenomena. Next, we explain how the following key ideas emerged in our data as part of multimodal representations and links to everyday STEM learning.
7.1.1. Scarcely Presented Resources That Engage Children with Fun, Interactive, and Meaningful Opportunities to Be Autonomous Learners (Children Have Agency and Are Autonomous Learners)
Only 11 websites contained online interactive resources that allowed children to autonomously explore, whereas only online screen-based games were present on websites such as ABC Education and Matific. As Gee [29] stated, digital games integrate multiple representations (e.g., visual image, music, actions), which could provide students with a multimodal text learning environment. Other forms include simulation (e.g., Luma website) and coding programs (e.g., Code and Scratch junior). Simulation can offer experientially realistic learning experiences to children, as it provides students with opportunities to visualise or interact with the phenomenon being explored that cannot be easily seen or are not safe to try in the real world (e.g., molecular structures, chemical reactions). Similar to interactive games, simulation is a multimodal learning environment. A major difference between simulation and games is that games usually have a goal to play, whereas a simulation does not have the same approach. For coding and applying critical thinking skills, the modular programming software is the main approach to teaching children computational thinking and programming. Children can try various combinations of function modules, and they can see immediate feedback based on their actions, which constitutes a multimodal learning context.
7.1.2. Moving between Digital and Hands-On Interactions
When considering whether the websites moved between the digital to the physical environments, only eight websites contained both online interactive resources and offline physical activities. These eight websites could be grouped into two categories. First, websites like ELSA and Code had online resources and interconnected offline activities. For instance, ELSA provided a range of apps for students to play with and freely explore. It also offered a variety of related offline activities that allowed students to extend their experiences with apps further. In this sense, children were exposed to multiple representations (online digital and offline concrete) of relevant STEM concepts, enriching their learning experiences. Similarly, programming learning websites such as Code, on top of providing traditional online programming experiences, offered offline paper-based activities to analogise the algorithm and programming process on the computer. Second, websites such PBS Learning and Let’s Count provided online and offline resources in a parallel way. That is, the online and offline resources were separate and not relevant to one another, just like a library for various resources.
When exploring websites with games as a tool for learning STEM concepts, only four websites provided online gameplay (e.g., LUMA Centre Finland’s StarT-programme and Code). Both the LUMA and Code websites allowed students to create games themselves by encouraging coding. Another website, The Smithsonian Science Education Center, did not include online games; however, it recommended a few game apps that could be downloaded from the Apple Appstore.
7.1.3. Links to Everyday STEM and Experiential Learning
Only twelve websites provided home-friendly activity resources; nine websites provided activities utilising everyday home materials (e.g., kitchen, garden). For instance, everyday learning for STEM had a strong focus on how to conduct STEM activities based on home resources, such as plants, soil, cooking, and ice. Similarly, Science Buddies provided rich home-friendly activities, such as, for example, activities exploring the biology of plants and experiments in the kitchen.
Only 10 websites focused on conducting STEM activities as part of sensory play experiences in children’s everyday settings and learning environment. This meant that these websites provided resources that could be easily implemented in everyday home or early-learning centre (ELC) settings, and STEM concepts were embedded in these activities. For instance, Science Buddies offered a variety of activities that were suitable for families, such as making ice cream and flower dissection. Alternatively, CPW mainly targeted ELCs and provided a conceptual play framework that enabled ELCs to integrate STEM content into children’s everyday play in centres. The common feature of these activities, whether for home or ELC settings, was that they utilised existing accessible materials in the home or ELC and could easily fit into the everyday routine at home or in ELCs. This meant that they did not require additional time and extra resources, which were two main challenges for sustainable STEM education in the early-childhood context. It appears that websites focusing on everyday STEM heavily overlap with the websites offering home-friendly activities.
7.2. Theme 2: Consideration of Children’s Learning Abilities and Diversity
In this systematic review, none of the included STEM websites catered for different learning abilities or being culturally inclusive, such as catering to specific cultural diversity, Indigenous knowledge, or low socioeconomic and diverse cultural backgrounds. Websites such as the Digital Technology Hub mentioned neurodivergent children’s learning, and Primary Connections included elements of Indigenous cultural perspectives; however, these websites were excluded from our analysis due to our scope only being birth–8 years of age in terms of age groups.
All websites had easy-to-use resources. Online interactives on these websites were easy to navigate and operate. Offline activities were collated with clear guidance and a list of materials. However, some websites, such as Matific and ELSA, required a subscription to obtain full access to the resources, and whether the user had to pay for the resources was unclear. Only one website, Ask Dr Universe, enabled children to communicate ideas and wonderings. On this particular website, children could ask questions as a form of post. The majority of websites that provided platforms such as blogs were not for children’s communication but for that of parents and teachers.
In the review of the websites, it was found that 12 websites (such as Science Buddies and PBS Learning) included both parent and educator resources. However, it appears that all these websites presented parent and educator resources in silos rather than having a connection between the parent and educator roles, considering the contextual needs and acknowledging that STEM learning could be diverse based on the needs of parents and educators and children’s interests. Especially, based on the Australian National Innovation and Science Agenda [5], where sparking girls’ interests in STEM has become a national priority, addressing children’s agency to become autonomous learners early-on is critical. The role of the adult and resources that supported and encouraged adults to engage and interact with children in STEM activities were also missing in the presentation of the 29 websites. Hence, our systematic review recognised a gap in STEM resources being able to capitalise on the opportunity to extend or develop STEM learning across both formal and informal home-based learning environments. The consideration of children’s learning abilities and diverse needs is an important factor to consider while fostering children’s creative inquiry and the provision of multimodal avenues of communicating STEM learning.
In creating resources which appeal to culturally and ethnically diverse backgrounds, the resources presented in, for example, the “Let’s Count” and Luma Centre Finland websites somewhat considered children/parents/educators’ local contexts to anchor STEM as an everyday learning experience, rather than being reduced to seeing STEM as learnt and/or taught in siloes and monomodal ways or as text-centric subjects which are based on speculation and assumptions of how one might want to learn or engage in STEM. The systematic review found that there were scarce resources that accounted for capitalising and valuing children’s agency and their preferred learning styles by providing multiple means of meaning-making: for example, the Luma Centre Finland resources, where students observed the environment to carry out their own investigations related to their own interests. Such STEM resources on an online learning platform may be beneficial to users of diverse cultural and ability groups, enabling children to make choices via differentiated learning methods.
8. Discussion
The research question for this paper was to examine the role of multimodal learning resources in promoting inclusive STEM engagement for children. Our study findings revealed there were scarce multimodal resources that engaged children with fun, interactive, and meaningful opportunities to be autonomous learners (e.g., children had agency) (n = 11 out of 29), moving between digital and hands-on physical spaces (n = 8 out of 29; e.g., the Early Learning STEM Australia website), employing gamification for deep learning (n = 4 out of 29), and peaking children’s imagination, inquiry, and creativity, and links to everyday STEM scenarios were hardly present (n = 10 out of 29).
With the advent of the digital era, STEM learning resources are becoming more and more available on digital platforms. However, making STEM connections with resources available in a digital environment is not an easy task, requiring early-childhood educators and parents of young children to be educated and aware of how to use resources and how well said resources align with their teaching philosophies and cultural backgrounds [28]. Further, building adults’ confidence in STEM teaching and allowing them to have access to resources and multimodal tools that allow children to explore and have first-hand lived experiences in how STEM knowledge is applied to real-world problems are needed. Achieving so is necessary to make STEM a personalised journey where each child, regardless of gender and ability, sees a space for them as part of everyday STEM.
The findings suggest that, while there are many STEM-focused digital platforms for children, educators, and families to use, none offers all the elements required for a comprehensive, multimodal, and inclusive approach to STEM learning. Multimodal resources that allow children to have agency have been known, both through theoretically rooted and pedagogical practices, to promote deep meaning-making. Through experiential and creative inquiry approaches, children engage in STEM with gestures, actions, movement, aural/sounds, and haptics/touch in social learning environments [21,25,30]. However, in the digital platforms examined in this research, we found that the websites were limited in their multimodal approaches, such as providing text-heavy content with some sounds and haptics to encourage STEM learning. In addition, these platforms targeted the older age range of children, aged 4–8 years, using text as the main form of interaction.
Few websites encouraged movement between the digital and physical spaces, and fewer sites used games to support STEM learning. Ideally, moving from digital to physical spaces would involve educators or parents supporting STEM learning. Kewalramani and Veresov [12] have suggested that a social semiotic perspective assumes that meaning-making does not occur in isolation but is situated in social situations or activities within a learning environment. This cements the importance of delivering STEM concepts in a manner that can move from the digital to the physical with connections to the social environment, which could also include games and digital books. Hence, it highlights the importance of promoting social interactions between children and families/educators as well as digital elements.
A limited number of platforms provided the opportunity for children’s imagination, inquiry, and creativity and links to everyday STEM scenarios. This highlights the need for digital platforms that can bring STEM concepts into the everyday lives and environments of children, educators, and families. More importantly, no digital platform considered children with differing abilities, gender, or low socioeconomic backgrounds, hence disengaging with what is considered the “everyday”. Unilateral platforms with the vision of one type of learner limit the opportunity to successfully support STEM learning for all learners.
The analysis and findings of this review found a gap in digital platforms that offered multimodal representation with a social semiotic perspective, games, and everyday STEM for children in an inclusive manner from birth to 8 years of age, their families, and their educators. The websites explored were shown to have covered only one or two elements. Future research should include exploring the longitudinal outcomes of educators, families, and children engaging with multimodal STEM resources. A deep dive into whether educators, families, and children build knowledge, language, understanding, and confidence when approaching STEM would be beneficial to research in finding ways to connect multimodal learning and engagement in the everyday context. Additionally, there is a need to explore, within online learning platforms, what types of modes of representation and digital interactions support STEM learning with young children and parents/educators from diverse sociocultural backgrounds. In the next section, we provide recommendations for the future development of multimodal STEM resources that address the gaps found in this review.
9. Conclusions and Recommendations
9.1. Representation
This analysis has indicated how limited representations of the world are present on the websites analysed. For children to effectively engage with STEM ideas and practices, it is critical that they see themselves actively represented in the images on the websites. It is recommended that websites sharing STEM-related content include a range of representations of children (of all colours, abilities, and cultural backgrounds) engaging with STEM ideas and practices and seek input from relevant practitioners and curriculum framework stakeholders to ensure that such representations are accurate and not based on biased stereotypes.
It is recommended that research should explore some of the various reasons postulated by diverse communities for the ways in which they prefer to learn and be involved in children’s STEM education early-on and the rate at which they resonate with STEM. There needs to be not only a multimodal but also an inclusive environment, especially for underrepresented communities, to allow innovation and belonging to flourish and persist in learning STEM, as one might find the practices of existing educational structures, systems, and beliefs to be challenging and beyond their level [31,32]. To achieve gender equity in STEM, we need to incorporate diverse perspectives and priorities, expanding knowledge and attempting to reduce gaps in understanding girls agency in STEM, for example, while simultaneously pushing to discover which STEM practices and values can be included in and become foundational to Australia’s STEM workforce development [33,34]. Our review findings insinuate the need to start by engaging young children early-on, and further research on the nature of evidence-based multimodal resources can address cultural, gender, and socioeconomic diversity.
9.2. Multimodal Representations
This analysis has indicated that text is the most common form of communication on websites. It is acknowledged that this is likely due to textual information being cheaper and easier to create and the facts that websites have been created to prefer the sharing of text and that search engine optimisation (SEO) engines find it more straightforward to track text on websites, leading to higher ranks on said search engines. However, this can bias websites against children who may have difficulties with written languages (typically only in English) due to factors including not having learned to read yet (relevant for early-childhood audiences), learning difficulties, or English as an additional language.
Another factor is that text is not always the most appropriate way to communicate STEM ideas and practices to young children. Certain everyday words and experiences (e.g., floating and sinking) might be understandable as children may use them at home or school. However, relying on text-only representations with more abstract concepts (e.g., force, gravity) or phenomena that cannot be observed (e.g., photosynthesis, travelling light) may, at best, lead to a limited understanding or, at worst, the learning of incorrect concepts.
For these reasons, it is recommended that STEM websites use a range of multimodal representations, such as videos with subtitles, visual images which engage young children, and, where appropriate, models or representations which add to children’s understandings of STEM ideas and processes (e.g., the use of arrows to demonstrate the direction of forces). Additionally, representations that can be manipulated (e.g., simulations and interactive games which are adaptive based on children’s abilities) to allow children to explore their developing understanding of STEM ideas in fun and engaging ways would be even more beneficial.
9.3. Educational Advantage and STEM-Related Careers
The analysis of websites provided in this paper highlighted the need for greater representation for a broad range of students and their families. The role of multimodal resources for inclusive STEM engagement was the focus of this study, with an aim of children being able to see themselves represented in STEM education and related pathways from their early years and onwards. It is also important for the families and caregivers of young children to be aware that there are STEM careers available within their everyday contexts that they may have not previously considered. Similarly, the findings of the current study can provide direction to educators who may not be aware of the depth and range of STEM careers that are potentially relevant to their students. While careers in the early years of children are not often focused on, programs such as the Australian Government’s Little Ripples [35] (https://www.yourcareer.gov.au/resources/little-ripples, accessed on 15 March 2023) highlight the importance of positivity and support for students developing a sense of who they are. Similarly, the seminal concept of science capital [34] highlights the importance of children being able to see themselves in science- and STEM-related careers, which is related to cultural capital and gender equity in accessing STEM. Multimodality and multimodal representations are one way for young children to be able to express their ideas, creative inquiry, and scientific thinking [3,30,32]. Additionally, children are more likely to aspire to a science or STEM career when they can see positive representations in the people around them, such as in the media, popular culture, and everyday STEM concepts they can engage with—resources which support children’s developing interests and enable life-long belonging to STEM. Knowing the nuanced differences between careers such as those of a botanist, a gardener, and an agriculturalist could help motivate students and their caregivers. Hence, future research should consider the use of additional resources that involve multimodal representations and options in light of generating children’s future interests and careers.
While it was not an explicit part of our systematic review research question, it would be beneficial for STEM websites for early-childhood children to refer to careers explicitly, particularly while thinking of supporting parents’ and educators’ knowledge about the range of “everyday” STEM careers. Typically, STEM careers are associated with higher-education degrees [9]. However, in reality, these disciplines and skills are fundamental to a range of everyday careers, including, but not limited to, houses and construction (e.g., electricians need to have a critical understanding of electricity and the nature of materials), food and hospitality (e.g., bakers require a unique applied understanding of chemistry and biology), or gardening or food production (e.g., gardeners need to have an understanding of chemistry and mathematics and utilise problem-solving skills). It would be exhaustive for any website to list these careers, but it is recommended that STEM websites work towards unpacking how a range of careers utilise the concepts and everyday learning dispositions catering to young children within each discipline, but also how often they can be integrated and build on one another.
Returning to the representations discussed earlier and given that this review only analysed 29 websites (aimed at children from birth to 8 years of age), it would be recommended that people from careers in everyday STEM and TAFE/VET sectors be highlighted, but that the examples of these people should be from a range of genders, cultures, socioeconomic groups, and physical abilities. Again, representations that go beyond being “multimodal” are critical so that young children might “see” examples of people who are like them in their everyday lives and aspire to engage in STEM-related educational trajectories from early childhood and onwards.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, S.K., G.A. and J.S.; methodology, J.S.; validation, G.A., J.S., G.R. and L.H.; formal analysis, S.K., G.A., J.S. and G.R.; resources and data curation, L.X., L.H., J.S., B.D., B.V.L. and V.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K., G.A., J.S. and G.R.; writing—review and editing, S.K., G.A., J.S., G.R., L.H. and L.X.; project management, B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Invergowrie Foundation, Victoria, Australia.
Informed Consent Statement
No ethical approval was needed for this study as all data are available publicly.
Data availability statements
The data were derived from the resources available in the public domain (see Table 1 for the list of the 29 websites and frameworks).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the generous funding provided by The Invergowrie Foundation, Victoria, Australia, for supporting this research and funding research assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data, the writing of the manuscript, and the decision to publish the results.
References
- Australian Government Department of Education. National STEM School Education Strategy. 2022. Available online: https://www.education.gov.au/education-ministers-meeting/resources/national-stem-school-education-strategy (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Lowrie, T.; Larkin, K. Experience, represent, apply (ERA): A heuristic for digital engagement in the early years. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 51, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelland, N. A pedagogy of multiliteracies: Young children and multimodal learning with tablets. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2018, 49, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleer, M. Scientific Playworlds: A model of teaching science in play-based settings. Res. Sci. Educ. 2019, 49, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government Department of Education. School and Early Learning STEM Initiatives. 2022. Available online: https://www.education.gov.au/australian-curriculum/resources/early-learning-stem-multimodal-learning-21st-century (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainable Development Goals. 2020. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/education/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Australian Government Department of Education. Early Learning Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM). 2022. Available online: https://www.education.gov.au/australian-curriculum/support-science-technology-engineering-and-mathematics-stem (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Early Childhood Australia. Statement on Young Children and Digital Technologies. 2018. Available online: https://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/our-work/submissions-statements/eca-statement-young-children-digital-technologies/ (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- National Science and Technology Council. National Science and Technology Council: Sixteenth Meeting. 2023. Available online: https://www.chiefscientist.gov.au/news-and-media/national-science-and-technology-council-sixteenth-meeting (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Arnott, L.; Yelland, N. Multimodal lifeworlds: Pedagogies for play inquiries and explorations. J. Early Child. Educ. Res. 2020, 9, 124–146. Available online: https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/71967/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Dorouka, P.; Papadakis, S.; Kalogiannakis, M. Tablets and apps for promoting robotics, mathematics, STEM education and literacy in early childhood education. Int. J. Mob. Learn. Organ. 2020, 14, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewalramani, S.; Veresov, N. Multimodal Creative Inquiry: Theorising a new approach for children’s science meaning-making in Early Childhood Education. Res. Sci. Educ. 2021, 52, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleer, M. Digital pop-ups: Studying digital pop-ups and theorising digital pop-up pedagogies for preschools. Eur. Early Child. Educ. Res. J. 2020, 28, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewalramani, S.; Palaiologou, I.; Dardanou, M. The Integration of Internet of Toys in Early Childhood Education: Research from Australia, Norway, and England; Routledge: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undheim, M. The Process Is Not Enough: Children and Teachers Creating Multimodal Digital Stories in Kindergarten. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensky, M. Brain Gain: Technology and the Quest for Digital Wisdom. St. Martin’s Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, M.M. Using tablets and apps to enhance emergent literacy skills in young children. Early Child. Res. Q. 2018, 42, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, L.; Palaiologou, I.; Gray, C. Internet of toys across home and early childhood education: Understanding the ecology of the child’s social world. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2019, 28, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, K. Digital technology in early STEM education: Exploring its supportive role. In STEM, Robotics, Mobile Apps in Early Childhood and Primary Education: Technology to Promote Teaching and Learning; Papadakis, S., Kalogiannakis, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Murcia, K.; Campbell, C.; Aranda, G. Trends in early childhood education practice and professional learning with digital technologies. Pedagogika 2018, 68, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, G. Multimodality: A Social Semiotic Approach to Contemporary Communication; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hubber, P.; Tytler, R.; Haslam, F. Teaching and learning about force with a representational focus: Pedagogy and teacher change. Res. Sci. Educ. 2010, 40, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygotsky, L. Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Mental Process; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Prain, V.; Tytler, R. Theorising learning in science through integrating multimodal representations. Res. Sci. Educ. 2022, 52, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, K.; Lommatsch, C.; Resnick, I.; Lowrie, T. The design and use of a digital tool to support the development of preschool children’s logical reasoning. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022, 55, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, G. Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qual. Res. J. 2009, 9, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.P. What Video Games Have to Teach Us about Learning and Literacy; Palgrave/Macmillan: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Delgado, C.; Moje, E.B. An integrative framework for the analysis of multiple and multimodal representations for meaning-making in science education. Sci. Educ. 2014, 98, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, M.; McSkimming, B.M. Of microscopes and meeting places: A literature review examining barriers to Indigenous participation in STEM. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, B. Integration of digital games in learning and e-learning environments: Connecting experiences and context. In Digital Games and Mathematics Learning: Potential, Promises and Pitfalls; Lowrie, T., Jorgensen, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 35–53. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Páez, T.; Aguilera, D.; Perales-Palacios, F.J.; Vílchez-González, J.M. What are we talking about when we talk about STEM education? A review of the literature. Sci. Educ. 2019, 103, 799–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moote, J.; Archer, L.; DeWitt, J.; MacLeod, E. Science capital or STEM capital? Exploring relationships between science capital and technology, engineering, and maths aspirations and attitudes among young people aged 17/18. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2020, 57, 1228–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commonwealth of Australia Department of Education, Skills and Employment. Little Ripples. 2021. Available online: https://www.yourcareer.gov.au/get-career-resources/little-ripples (accessed on 30 March 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).