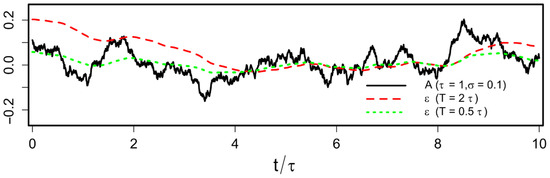
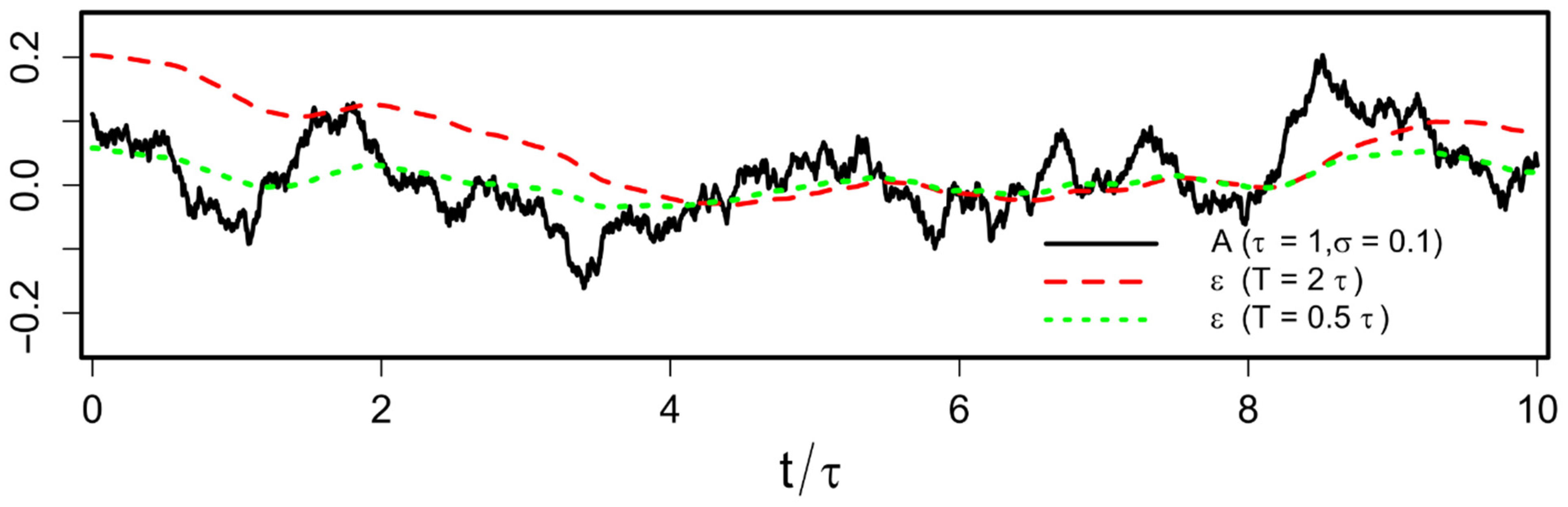
Abstract
Population dynamics is affected by environmental fluctuations (such as climate variations), which have a characteristic correlation time. Strikingly, the time scale of predictability can be larger for the population dynamics than for the underlying environmental fluctuations. Here, we present a general mechanism leading to this increase in predictability. We considered colored environmental fluctuation acting on a population close to equilibrium. In this framework, we derived the temporal auto and cross-correlation functions for the environmental and population fluctuations. We found a general correlation time hierarchy led by the environmental-population correlation time, closely followed by the population autocorrelation time. The increased predictability of the population fluctuations arises as an increase in its autocorrelation and cross-correlation times. These increases are enhanced by the slow damping of the population fluctuations, which has an integrative effect on the impact of correlated environmental fluctuations. Therefore, population fluctuation predictability is enhanced when the damping time of the population fluctuation is larger than the environmental fluctuations. This general mechanism can be quite frequent in nature, and it largely increases the perspectives of making reliable predictions of population fluctuations.
Keywords:
population dynamics; predictability; anomalies; environmental fluctuations; population fluctuations; correlation times; temporal correlation; colored noise; colored environmental fluctuations MSC:
92B05
1. Introduction
Population dynamics is frequently affected by the randomness of the environmental fluctuations requiring the use of stochastic dynamics equations [1,2]. Environmental fluctuations have different sources including variability in resources needed by a population (e.g., food) [3]; unpredictability in weather or climate [4,5]; and natural disasters [6], which are usually considered extreme cases of environmental fluctuations [7]. Environmental fluctuations can alter the dynamics of a population, significantly impacting population fluctuations and their predictability [8], and even causing the extinction of otherwise stable populations [6,9,10]. Random environmental fluctuations can have an appreciable time correlation, requiring models with colored (temporally correlated) noise instead of white noise. Accurate prediction of the population dynamics requires using appropriate colored noise (i.e., with the correct correlation time function) to simulate the environmental fluctuations [11,12]. The color (or temporal correlation) of the environmental fluctuations has been shown to have relevant consequences for population dynamics and the population extinction risk [13,14,15,16,17]. The impact of colored noise on the dynamics has also been experimentally observed [11,18,19].
The environmental variability is especially critical in some species. For example, ectotherms are particularly sensitive to changes in temperature [20,21]. Ectotherms suffer important changes in growth [22] and development [23] depending on the circumstances given by the environment, and a study of the underlying mechanism describing the general effect of environmental variability can help to understand ectotherms’ dynamics.
Here we are interested in using stochastic population dynamics models to obtain further insight into the predictability of the population fluctuations. It has been reported that the predictability of the population fluctuations can be larger than the underlying environmental fluctuations [11,24]. In particular, primary production fluctuations have been found to be predictable at larger time scales than the underlying sea surface temperature anomalies (environmental fluctuations) [25]. In the context of the study of the impact of El Niño teleconnections on the European climate variability, it was found that the predictability of the crop yield was higher than that of the underlying atmospheric variables affecting crop yield [26]. Analogous results have been found for the predictability of Malaria in Africa [27]. Similarly, higher predictability has been found for the Pacific fisheries anomalies than for the underlying Pacific sea surface temperatures (SSTs) when exploiting the Atlantic-Pacific teleconnection [28].
Here, we aim to apply stochastic population dynamics with colored environmental noise to understand population fluctuation predictability and its relations with environmental fluctuation predictability. In terms of temporal correlations, we aim to understand how the dynamics transform the temporal correlations of the environmental fluctuations into temporal correlations of the population fluctuations.
In Section 2, we present the population dynamics model (for small fluctuations around equilibrium) driven by colored environmental noise. In Section 3, we compute and compare the auto and cross-correlation functions between the environmental fluctuations and the population fluctuations. We compute their maxima and characteristic times, establishing their hierarchies, which provide insight into the propagation of the amplitude and temporal correlation of the fluctuations. Finally, the results are discussed in Section 4.
3. Temporal Autocorrelations and Cross-Correlations
Once we have seen the behavior of the evolution before, our target is to calculate temporal correlations for a single species in the presence of temporally autocorrelated noise. We want to calculate environmental (noise) autocorrelation, species autocorrelation, and environmental-species correlation, as well as a correlation time.
The correlation between two magnitudes and in two instants separated by a delay is given by the correlation function
where means expected value. This correlation indicates how good is as a predictor of . Therefore, to understand the predictability of the population fluctuations, we have computed the correlations functions of the environmental fluctuations and of the population fluctuations . See Appendix A for the detail of the computations. The correlation functions are
where is the dimensionless ratio between the characteristic damping time of the population fluctuations and the correlation time of the environmental fluctuations . We have represented these correlation functions in Figure 2A.
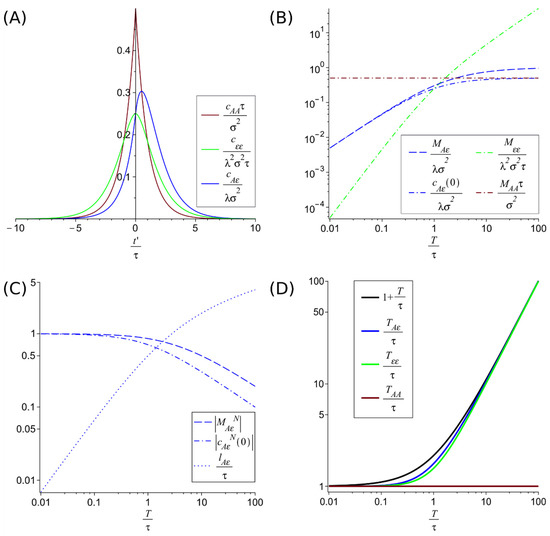
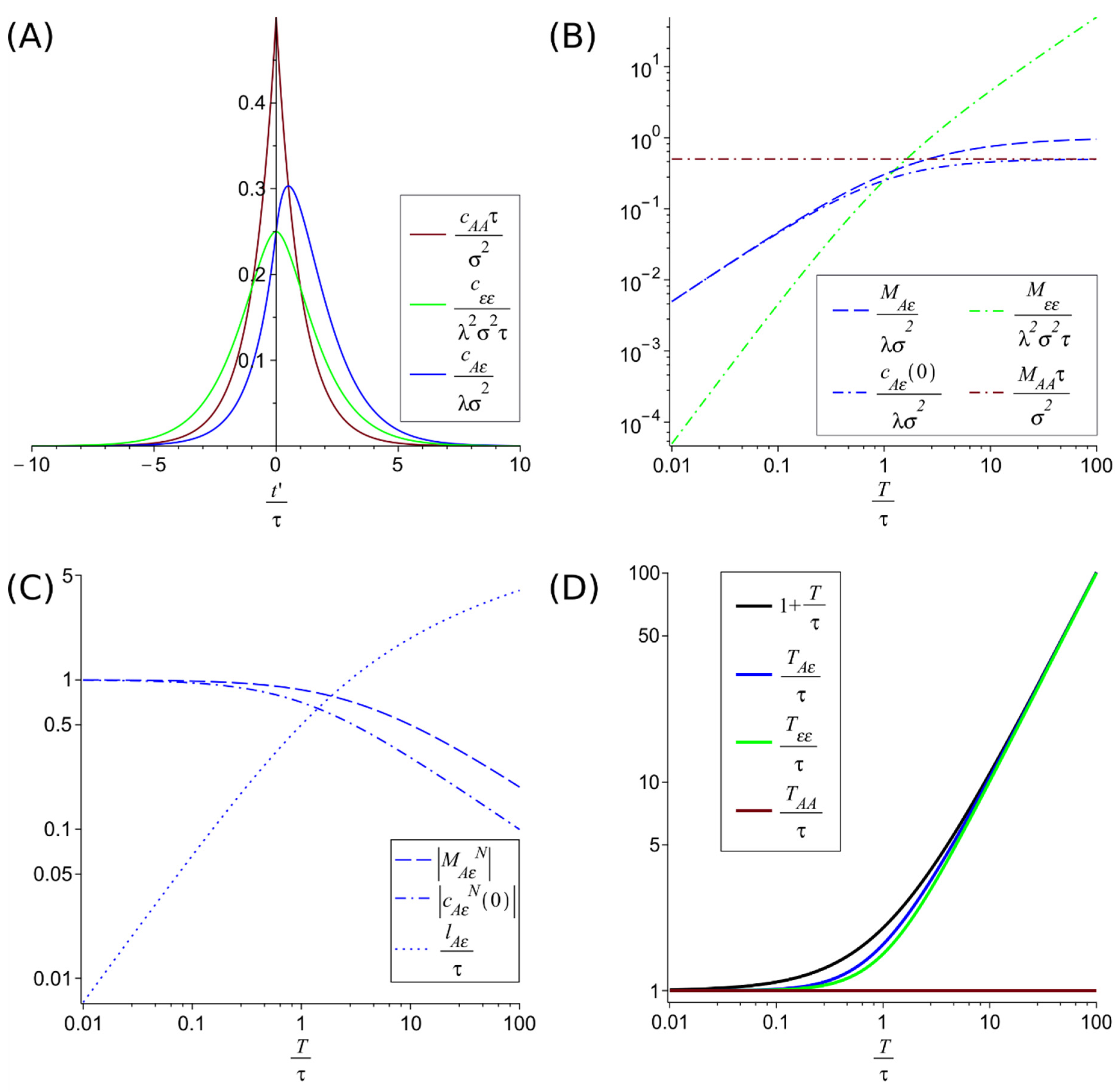
Figure 2.
Correlation functions with their maximums and their values at t′ = 0 and correlation times. (A) represents the adimensionalized correlation functions (green), (red) and (blue) adimensionalized for the case . (B) compares the adimensionalized maxima of the autocorrelations function and (which coincide with the value at of the respective autocorrelation) with the maxima of the adimensionalized crosscorrelation function and its value at zero delay . Their normalized values, and are shown in (C), with the delay of the cross-correlation maximum . (D) compares the correlations times , and . These plots illustrate the hierarchies for temporal correlations and for the maxima of the correlations discussed in the main text. In particular, it shows that for low damping (large ) the crosscorrelation time increases, allowing longer-term predictions, despite the decrease in accuracy that can be seen from the decay of the normalized maximum of the crosscorrelation .
3.1. Maxima of the Correlation Functions
The autocorrelation function of the environmental fluctuations and the autocorrelation function of the species , which are symmetric, have their maximum at the origin, ,
The cross-correlation , has a value at the origin of
But the cross-correlation has a lagged maximum (a minimum for negative coupling ), see Figure 2A, situated at a time displacement (
This lag means that the population is more affected by the fluctuation after a certain time instead of instantly. Because of the basic property of correlations , the correlation function has the maximum in . This maximum is at for any , and approaches the origin (smaller lag) as decreases. This dependence on causes the lag to tend to zero if the characteristic time of return to equilibrium of the population is very short.
The cross-correlation at this maximum located at has a value
It can be shown that the maximum correlation at most doubles the correlation at the origin , i.e., .
The maxima values can be adimensionalized and compared as in Figure 2B. This shows the following hierarchy
This hierarchy means that when the characteristic time scale of population fluctuations damping is greater than the environmental fluctuations correlation time the magnitude of the adimensionalized maxima increases as the fluctuation propagates (from the environment to the population). Conversely, when the population fluctuations dampen faster than the environmental fluctuations correlations time (), the maxima decrease as the fluctuation propagates. Only in this later regime and when (i.e., on the constant environmental fluctuation limit) the normalized environment-population cross-correlation maximum reaches full correlation (but at zero delay, ). See Figure 2C. The normalized environment-population cross-correlation maximum and value at the origin are given by
3.2. Temporal Correlations
The characteristic time of temporal correlations gives the time extension of the predictability. For simple exponential decays of the correlation, the correlation time is just given by the characteristic decay factor in the exponential. For more general cases, we define the correlation time as
The absolute value allows incorporating the effects of negative correlations as predictors. For the autocorrelations and cross-correlations, we get
In Figure 2D, these correlation times are plotted as functions of , the ratio between the damping time of the population fluctuations and the correlation time of the environmental fluctuations . Figure 2D suggests a hierarchy of correlation times that can be proven from the previous expressions, i.e., Equations (17)–(19).
The difference between the last two is bounded by .
This hierarchy of correlation times implies a longer correlation time, and therefore a larger scale of predictability, for population fluctuations than for environmental fluctuations.
4. Discussion
We aimed to understand the predictability of population fluctuations compared to environmental fluctuation predictability. To obtain an insight into the question, we computed the correlation functions of a population close to an equilibrium state in the presence of environmental colored noise. This computation allowed us to compute the correlation times and the maxima of the correlation functions, finding hierarchies for them, which gives general relations.
We found that the predictability of the population fluctuations is always higher than for the environmental fluctuations. Because of this, we have determined that the correlation time of the population fluctuations is always greater than the correlation time of the environmental fluctuations. The difference in correlation time increases with increased characteristic damping time of population fluctuations . For example, for we have and ; we also have that the maximum of the population-environment cross-correlation is at with a normalized correlation , showing a clear increase with respect to the correlation time for the environmental fluctuations . The underlying mechanism is analogous to the one described by Hasselmann for the integration of the fast weather components leading to the slow climate dynamics [30]. Our model stresses that the mechanism is general and time-scale independent. In practical cases times scales can range from days (for prey populations in agriculture) to years (for large species or ecosystems).
This study was inspired by our previous results on spatial population synchrony [31,32,33,34] and motivated by the findings that population fluctuations showed larger predictability than the underlying environmental variables. This was shown to happen for a wide range of systems: primary production in oceans [25], crop yield [26], malaria [27] and fisheries [28]. This higher predictability increases the prospects of predicting climatic variability effects on populations [26,27,28,35,36,37].
The determination of the effective equilibrium can be challenging in practical cases [24]. In general, the effective equilibrium is obtained from the time-average of the data in long-enough time series. However, sometimes the equilibrium can have seasonal oscillations or long-term trends. In this case, these variations in the equilibrium have to be taken into account, substracting them to obtain the correct fluctuations around equilibrium. Several model extensions are possible to obtain an insight into the scope of the results. The results have been obtained for a single-environmental variable acting on a single-species in the small fluctuation regime, which allows the linearization of the dynamical equations around the equilibrium. This model can be extended, including several interacting species and several environmental variables (which may also interact as wind stress and sea surface temperature). Another extension is including the division of species populations into distinct life stages, with some of them particularly affected by environmental fluctuations [38]. Our model considers small enough environmental fluctuations (which implies the population is close to equilibrium). This can be extended by studying larger environmental fluctuations in particularly relevant ecological models, which would clarify how the results in the present work are affected by the presence of nonlinearities.
The present study raises the question of how the propagation of fluctuations through the food webs impacts the predictability of the different species’ population fluctuations. This more profound understanding of the population predictability will help to design improved conservation policies, particularly useful for species especially sensitive to environmental variability (represented in our model with great couplings ), such as ectotherms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J.C.-G.; Methodology, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Software, R.C.-M.; Validation, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Formal analysis, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Investigation, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Resources, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Data curation, R.C.-M.; Writing-original draft preparation R.C.-M.; Writing-rewiew and editing, R.C.-M. and F.J.C.-G.; Visualization, R.C.-M.; Supervision, F.J.C.-G.; Project administration, F.J.C.-G.; Funding adquisition, F.J.C.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by 817578 TRIATLAS project of the Horizon 2020 Programme (EU) and RTI2018-095802-B-I00 of Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (Spain) and Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER, EU).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge early conversation with Emilia Sánchez (CERFACS) on predictability and temporal correlations, in relation with our previous results on spatial synchrony. We also acknowledge Belén Rodríguez-Fonseca and Iñigo Gómara for conversations on further applications of the presented framework.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Computation of Temporal Correlation Functions and Times
As the dynamics are time invariant, the asymptotic time correlations are stationary. The stationarity condition is
where and . The application of this stationary condition provides relationships between time correlation, which allow computing them.
Appendix A.1. Wiener Process Temporal Autocorrelation
The temporal autocorrelation of the Wiener process (whose derivative gives the white noise) is known to be
Appendix A.2. Wiener—Colored-Noise Temporal Cross-Correlation
We now that is zero for , as there is no fluctuation propagation to the past. Therefore, we just have to make the computation for positive time displacement.
We compute for , , , …
These results allow us to get the general expression
In the large limit, we get the exponential expression
Therefore, we have
Appendix A.3. Wiener—Population Temporal Cross-Correlation
There is no propagation of the fluctuations to the past. Thus, is zero for , and we only have to compute the correlation for positive time displacement.
The same procedure used for allows obtaining
The later expression gives, when
while for
(Note that in the limit the results for are recovered, indicating the continuity of the solution on .)
Therefore, we have the temporal correlation
Appendix A.4. Colored-Noise Autocorrelations
The computation of this (and the following) temporal correlations relies on the time invariance of the dynamics, which leads to the stationarity of the asymptotic temporal correlations.
We begin calculating the temporal autocorrelation for the environmental autocorrelations, , whose stationary condition implies
Expanding up to the first order in we get
which gives the equation
As we have shown that and [Equations (A2) and (A3)], which indicates that there are still terms of second order in the previous equation. Keeping only the first order terms in and using , the equation becomes
This later equation gives , in terms of the cross-correlations of the white noise with the colored noise and with the population fluctuations.
Substituting Equation (A2), we get environmental autocorrelation
Appendix A.5. Colored-Noise—Population Cross-Correlation
We continue with the environment-species temporal cross-correlation , whose stationary condition gives
Again, up to the first order in , we get
resulting in the second relation,
Recalling again that and , fewer terms are of the first order in , leading to
Substituting Equations (A3) and (A4), we can calculate the environmental-population fluctuations cross-correlation
while .
Appendix A.6. Autocorrelations of the Population Fluctuations
We finally compute the temporal autocorrelation for the population fluctuations of the species , whose stationary condition implies
Keeping terms up to first order in dt, we obtain the following expression:
In terms of correlations and using the relation , we have
Substituting Equation (A5), we get for the population fluctuations autocorrelation
Appendix A.7. Maxima
The environmental noise autocorrelation and of the population fluctuations autocorrelation have their maximum at the origin . The environment-population cross-correlation has a lagged maximum at a time with
with a magnitude given by
These expressions are also given in the main text in terms of , the ratio of the population relaxation time and the correlation time of environmental fluctuations .
Appendix A.8. Correlation Times
The previous explicit expression for the time correlation function allows computing their respective correlation times
where is the ratio of the population relaxation time and the correlation time of environmental fluctuations .
References
- Gotelli, N.J. A Primer of Ecology, 4th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lande, R.; Engen, S.; Saether, B.-E. Stochastic Population Dynamics in Ecology and Conservation. In Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, M.; Takada, T. Environmental Stochasticity. eLS 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, P.; Bonelli, S.; Barbero, F.; Balletto, E. Relative Importance of Density-Dependent Regulation and Environmental Stochasticity for Butterfly Population Dynamics. Oecologia 2009, 161, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltz, D.; Rubenstein, D.I.; White, G.C. The Impact of Increased Environmental Stochasticity Due to Climate Change on the Dynamics of Asiatic Wild Ass. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangel, M.; Tier, C. Dynamics of Dynamics of Metapopulations with Demographic Stochasticity and Environmental Catastrophes. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1993, 44, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, M. Minimum Viable Populations: Coping with Uncertainty. In Viable Populations for Conservation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, A.D.; Douglass, R.J.; Mills, J.N.; Bjørnstad, O.N. Environmental Fluctuations Lead to Predictability in Sin Nombre Hantavirus Outbreaks. Ecology 2015, 96, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.J. Interactive Effects of Temporal Correlations, Spatial Heterogeneity and Dispersal on Population Persistence. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo-Miguel, R.; Jarillo, J.; Cao-García, F.J. Dispersal-induced resilience to stochastic environmental fluctuations in populations with Allee effect. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 014413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L. Environmental Colour Affects Aspects of Single-Species Population Dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2000, 267, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, J.M. Ecology, Evolution and 1f-Noise. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripa, J.; Lundberg, P. Noise Colour and the Risk of Population Extinctions. Proc. R. Soc. London 1996, 263, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, M.; Ripa, J.; Kaitala, V. Extinction Risk under Coloured Environmental Noise. Ecography 2000, 23, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenman, J.V.; Benton, T.G. The Amplification of Environmental Noise in Population Models: Causes and Consequences. Am. Nat. 2003, 161, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamenev, A.; Meerson, B.; Shklovskii, B. How Colored Environmental Noise Affects Population Extinction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 268103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanio, T.; Hidalgo, J.; A Muñoz, M. Impact of Environmental Colored Noise in Single-Species Population Dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, J.; Löytynoja, K.; Kaitala, V. Environmental Noise and Population Dynamics of the Ciliated Protozoa Tetrahymena Thermophila in Aquatic Microcosms. Oikos 2003, 102, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuman, D.C.; Costantino, R.F.; Desharnais, R.A.; Cohen, J.E. Colour of Environmental Noise Affects the Nonlinear Dynamics of Cycling, Stage-Structured Populations. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Moses, M.E.; West, G.B.; Hou, C.; Brown, J.H. A General Model for Effects of Temperature on Ectotherm Ontogenetic Growth and Development. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2011, 279, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaijmans, K.P.; Heinig, R.L.; Seliga, R.A.; Blanford, J.I.; Blanford, S.; Murdock, C.C.; Thomas, M.B. Temperature Variation Makes Ectotherms More Sensitive to Climate Change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D. Temperature and Organism Size—A Biological Law for Ectotherms? Adv. Ecol. Res. 1994, 25, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, G.; van der Have, T.M. Temperature Dependence of Development Rate, Growth Rate and Size: From Biophysics to Adaptation. In Phenotypic Plasticity of Insects: Mechanisms and Consequence; Science Publishers, Inc.: Plymouth, UK, 2009; pp. 461–526. [Google Scholar]
- Pimm, S.L.; Redfearn, A. The Variability of Population Densities. Nature 1988, 334, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séférian, R.; Bopp, L.; Gehlen, M.; Swingedouw, D.; Mignot, J.; Guilyardi, E.; Servonnat, J. Multiyear Predictability of Tropical Marine Productivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11646–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capa-Morocho, M.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, B.; Ruiz-Ramos, M. Crop Yield as a Bioclimatic Index of El Niño Impact in Europe: Crop Forecast Implications. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 198–199, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, I.; Suárez-Moreno, R.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, B.; Caminade, C.; Wade, M.; Thiaw, W.M.; Deme, A.; Morse, A.P.; Ndione, J.-A.; Gaye, A.T.; et al. Oceanic Influence on Seasonal Malaria Incidence in West Africa. Weather Clim. Soc. 2022, 14, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómara, I.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, B.; Mohino, E.; Losada, T.; Polo, I.; Coll, M. Skillful prediction of tropical Pacific fisheries provided by Atlantic Niños. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ojalvo, J.; Sancho, J.M.; Ramírez-Piscina, L. Generation of spatiotemporal colored noise. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 4670–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K. Stochastic Climate Models Part I. Theory. Theory. Tellus 1976, 28, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarillo, J.; Saether, B.-E.; Engen, S.; Cao, F.J. Spatial Scales of Population Synchrony of Two Competing Species: Effects of Harvesting and Strength of Competition. Oikos 2018, 127, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarillo, J.; Sæther, B.-E.; Engen, S.; Cao-García, F.J. Spatial Scales of Population Synchrony in Predator-Prey Systems. Am. Nat. 2020, 195, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Jarillo, J.; Peeters, B.; Hansen, B.; Cao-García, F.; Sæther, B.; Engen, S. Population Responses to Harvesting in Fluctuating Environments. Clim. Res. 2022, 86, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Grande, M.A.; Cao-García, F.J. Spatial Scales of Population Synchrony Generally Increases as Fluctuations Propagate in a Two Species Ecosystem. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.11043. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2012/2012.11043.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Iizumi, T.; Luo, J.-J.; Challinor, A.; Sakurai, G.; Yokozawa, M.; Sakuma, H.; Brown, M.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of El Niño Southern Oscillation on the global yields of major crops. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watters, G.M.; Olson, R.J.; Francis, R.C.; Fiedler, P.C.; Polovina, J.J.; Reilly, S.B.; Aydin, K.Y.; Boggs, C.H.; E Essington, T.; Walters, C.J.; et al. Physical Forcing and the Dynamics of the Pelagic Ecosystem in the Eastern Tropical Pacific: Simulations with ENSO-Scale and Global-Warming Climate Drivers. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christensen, V.; Coll, M.; Buszowski, J.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Frölicher, T.; Steenbeek, J.; Stock, C.A.; Watson, R.; Walters, C.J. Oceanic Influence on Seasonal Malaria Incidence in West Africa. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, W.H.; Martin, T.E.; Skelly, D.K.; Woods, H.A. Metamorphosis in an Era of Increasing Climate Variability. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).