Raindrop-Removal Image Translation Using Target-Mask Network with Attention Module
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The proposed model utilizes two networks to separate the raindrop-mask network and raindrop-removal network.
- The raindrop-mask network serves as an attention module to accurately represent the location, size, and brightness of raindrops. The raindrop-mask network is based on U-Net and learns the raindrop-mask area in the raindrop image by training on the difference between the raindrop image and clean image.
- The raindrop-removal network is based on GAN, and the attention mechanisms are applied to the input and the internal layers of the generator. The input attention of the generator is the raindrop mask, while the internal attention is the residual convolution block attention module (RCBAM). These two modules contribute to enhancing the performance of the raindrop-removal network.
2. Related Works
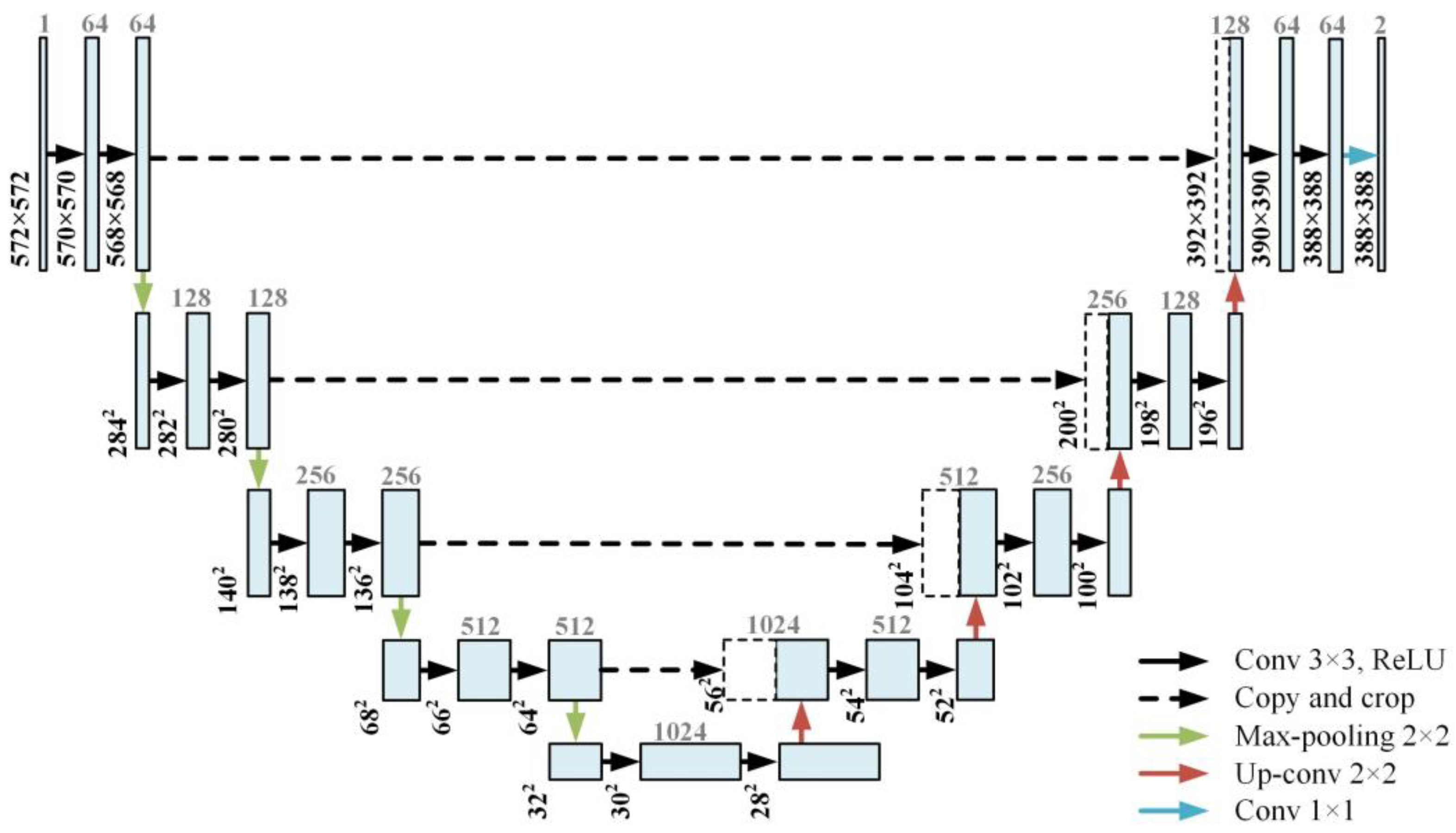
2.1. U-Net
2.2. Convolution Block Attention Module
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Raindrop-Mask Network
3.3. Raindrop-Removal Network
3.3.1. Generator
3.3.2. Discriminator
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Qualitative Evaluation
4.2. Quantitatiive Evaluation
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, R.; Tan, R.T.; Yang, W.; Su, J.; Liu, J. Attentive Generative Adversarial Network for Raindrop Removal from A Single Image. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2482–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Alletto, S.; Carlin, C.; Rigazio, L.; Ishii, Y.; Tsukizawa, S. Adherent Raindrop Removal with Self-Supervised Attention Maps and Spatio-Temporal Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, Y.; Ji, H. Deep Learning for Seeing through Window with Raindrops. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Meng, D. Selective generative adversarial network for raindrop removal from a single image. Neurocomputing 2021, 426, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Barnes, N.; Petersson, L. Attention-Based Real Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.D. Restoring Raindrops Using Attentive Generative Adversarial Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Lan, Y.; Song, S.; Li, H. Raindrop Removal from a Single Image Using a Two-Step Generative Adversarial Network. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lai, Z.; Qian, Y. Image Raindrop Removal Method for Generative Adversarial Network Based on Difference Learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1544, 012099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gao, J.; Wen, Q.; Wang, B. Generative Adversarial Network for Image Raindrop Removal of Transmission Line Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Inspection. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 6668771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Torbunov, D.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Yoo, S.; Lin, M.; Viren, B.; Ren, Y. UVCGAN: UNet Vision Transformer Cycle-Consistent GAN for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, M. Feature-Attention Module for Context-Aware Image-to-Image Translation. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Naiel, M.A.; Wong, A.; Lamm, M.; Fieguth, P. RUNet: A Robust UNet Architecture for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, E.M.; Bahrami, N.; Hsiao, A. Deep Learning Single-Frame and Multiframe Super-Resolution for Cardiac MRI. Radiology 2020, 295, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Tao, H.; Wang, H. A Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Low-Illumination Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 16–18 August 2019; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Dual UNet Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Attention Mechanism. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 24707–24742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Xu, L.; Yang, W.; Tan, R.T. Feature-Aligned Video Raindrop Removal With Temporal Constraints. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3440–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–19. ISBN 978-3-030-01234-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-T.; Huang, Z.-K.; Tsai, C.-C.; Yang, H.-H.; Ding, J.-J.; Kuo, S.-Y. Learning Multiple Adverse Weather Removal via Two-Stage Knowledge Learning and Multi-Contrastive Regularization: Toward a Unified Model. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 17632–17641. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Li, J.; Fu, X. No-Reference Quality Assessment of Contrast-Distorted Images Using Contrast Enhancement. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08879. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “Completely Blind” Image Quality Analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. GANs Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilibrium. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]


















| Model | SSIM↑ | PSNR↑ | CEIQ↑ | NIQE↓ | FID↓ | LPIPS↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pix2Pix | 0.770 | 23.621 | 3.332 | 2.499 | 47.490 | 0.114 |
| ATTGAN | 0.830 | 26.266 | 3.344 | 2.442 | 25.994 | 0.062 |
| R2Net | 0.835 | 26.160 | 3.338 | 3.015 | 26.319 | 0.071 |
| TUM | 0.663 | 23.757 | 3.269 | 2.908 | 26.995 | 0.136 |
| Proposed | 0.832 | 26.165 | 3.351 | 2.224 | 20.837 | 0.059 |
| Image Resolution | Pix2Pix | ATTGAN | TUM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 720 × 480 | 0.0473 s | 0.0391 s | 0.0466 s | 0.1169 s |
| Model | Module | Loss | Metric | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCBAM | MASK | SSIM↑ | PSNR↑ | CEIQ↑ | NIQE↓ | FID↓ | LPIPS↓ | |||||
| Case 1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.822 | 25.768 | 3.334 | 2.476 | 25.592 | 0.070 | |||
| Case 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.824 | 25.794 | 3.358 | 2.426 | 27.857 | 0.073 | ||
| Case 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.829 | 25.948 | 3.354 | 2.355 | 22.110 | 0.061 | |
| Case 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.828 | 25.796 | 3.361 | 2.288 | 23.102 | 0.063 | |
| Proposed | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.832 | 26.165 | 3.351 | 2.224 | 20.837 | 0.059 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H. Raindrop-Removal Image Translation Using Target-Mask Network with Attention Module. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153318
Kwon H-J, Lee S-H. Raindrop-Removal Image Translation Using Target-Mask Network with Attention Module. Mathematics. 2023; 11(15):3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153318
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Hyuk-Ju, and Sung-Hak Lee. 2023. "Raindrop-Removal Image Translation Using Target-Mask Network with Attention Module" Mathematics 11, no. 15: 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153318
APA StyleKwon, H.-J., & Lee, S.-H. (2023). Raindrop-Removal Image Translation Using Target-Mask Network with Attention Module. Mathematics, 11(15), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153318






