Measures of Extropy Based on Concomitants of Generalized Order Statistics under a General Framework from Iterated Morgenstern Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Distributional Characteristics of Concomitants of GOS Based on IFGM
3. JPDF of Concomitants of GOS Based on IFGM
4. Some Measures for Based on IFGM
4.1. Measure of J for Based on IFGM()
- Case 2: If and , the m-GOS become upper record values. Suppose be a sequence of bivariate RVs from a continuous distribution. If is the sequence of upper record values in the sequence of X’s, then the Y, which corresponds with the rth record value, will be referred the concomitant of the rth record value, denoted by Hence, the PDF for has been acquired (cf. [4])where and According to (17), the J measure of is
4.2. Measure of CRJ for Based on IFGM()
4.3. Measure of NCJ for Based on IFGM()
5. Empirical Measures for Based on IFGM()
5.1. Empirical NCRJ
5.2. Empirical NCJ
- 1.
- Generally, with fixed n and the values of and Var decrease as the value of increases.
- 2.
- In general, fixing n and yields and Var, which decreases as the value of increases.
- 1.
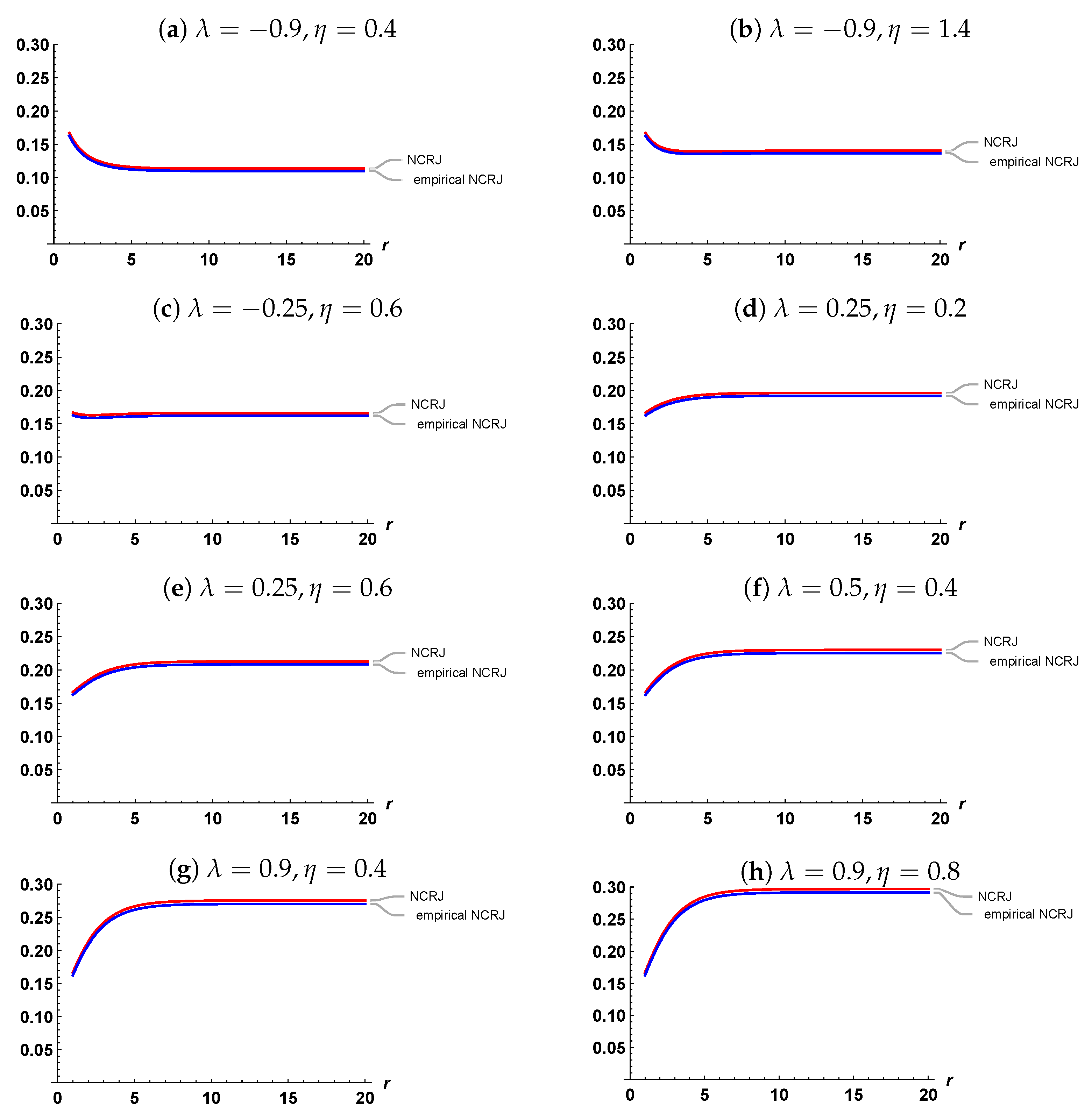
- Generally, the empirical NCRJ and NCRJ have similar values with all values of the parameter space
- 2.
- The empirical NCRJ and NCRJ increase as increases.
- 3.
- With the increase in the values of r, stability occurs in the values of both NCRJ and empirical NCRJ.
6. An Application
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDF | Cumulative distribution function |
| Probability density function | |
| GOS | Generalized order statistics |
| POS-II | Progressive type-II censored order statistics |
| J | Extropy |
| CRJ | Cumulative residual extropy |
| NCRJ | Negative cumulative residual extropy |
| NCJ | Negative cumulative extropy |
References
- Abd Elgawad, M.A.; Barakat, H.M.; Xiong, S.; Alyami, S.A. Information measures for generalized order statistics and their concomitants under general framework from Huang-Kotz FGM bivariate distribution. Entropy 2021, 23, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elgawad, M.A.; Alawady, M.A. On concomitants of generalized order statistics from generalized FGM family under a general setting. Math. Slovaca 2022, 72, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawady, M.A.; Barakat, H.M.; Abd Elgawad, M.A. Concomitants of generalized order statistics from bivariate Cambanis family of distributions under a general setting. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 2021, 44, 3129–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.M.; Nigm, E.M.; Alawady, M.A.; Husseiny, I.A. Concomitants of order statistics and record values from iterated of FGM bivariate-generalized exponential distribution. Revstat 2019, 19, 291–307. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.S.; Kotz, S. Correlation structure in iterated Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern distributions. Biometrika 1984, 71, 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Husseiny, I.A.; Barakat, H.M.; Mansour, G.M.; Alawady, M.A. Information measures in record and their concomitants arising from Sarmanov family of bivariate distributions. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 2022, 408, 114120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamps, U. A Concept of Generalized Order Statistics; Teubner: Stuttgart, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kamps, U.; Cramer, E. On distribution of generalized order statistics. Statistics 2001, 35, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H.A. Concomitants of order statistics. Bull. Int. Stat. Inst. 1973, 45, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- David, H.A.; Nagaraja, H.N. Concomitants of Order Statistics. In Handbook of Statistics; Balakrishnan, N., Rao, C.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 16, pp. 487–513. [Google Scholar]
- Alawady, M.A.; Barakat, H.M.; Xiong, S.; Abd Elgawad, M.A. Concomitants of generalized order statistics from iterated Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern type bivariate distribution. Comm. Stat. Theory Methods 2022, 51, 5488–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaspoor, Z.; Jafari, A.A.; Tahmasebi, S. Measures of extropy for concomitants of generalized order statistics in morgenstern family. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 2022, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.M.; Husseiny, I.A. Some information measures in concomitants of generalized order statistics under iterated FGM bivariate type. Quaest. Math. 2021, 44, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.M.; Nigm, E.M.; Husseiny, I.A. Measures of information in order statistics and their concomitants for the single iterated Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern bivariate distribution. Math. Popul. Stud. 2021, 28, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.I.; Ahsanullah, M. Concomitants of generalized order statistics from Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern distributions. Statist. Methodol. 2008, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohie El-Din, M.M.; Amein, M.M.; Mohamed, M.S. Concomitants of case-II of generalized order statistics from Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern distributions. J. Stat. Appl. Pro. 2015, 3, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lad, F.; Sanfilippo, G.; Agro, G. Extropy: Complementary dual of entropy. Stat. Sci. 2015, 30, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G. The extropy of order statistics and record values. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2017, 120, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Jia, K. The residual extropy of order statistics. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2018, 133, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Jia, K. Extropy estimators with applications in testing uniformity. J. Nonparametric Stat. 2018, 30, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Abdulrahman, A.T.; Almaspoor, Z.; Yusuf, M. Ordered variables and their concomitants under extropy via COVID-19 data application. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6491817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Barakat, H.M.; Alyami, S.A.; Abd Elgawad, M.A. Cumulative residual tsallis entropy-based test of uniformity and some new findings. Mathematics 2022, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Kazemi, M.R.; Keshavarz, A.; Jafari, A.A.; Buono, F. Compressive sensing using extropy measures of ranked set sampling. Math. Slovaca 2023, 73, 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanshahi, S.; Zarei, H.; Khammar, A. On cumulative residual extropy. Probab. Eng. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseiny, I.A.; Syam, A.H. The extropy of concomitants of generalized order statistics from Huang-Kotz-Morgenstern bivariate distribution. J. Math. 2022, 2022, 6385998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Toomaj, A. On negative cumulative extropy with applications. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2021, 51, 5025–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairamov, I.; Eryilmaz, S. Spacings, exceedances and concomitants in progressive type-II censoring scheme. J. Statist. Plann. Inference 2006, 136, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, K.N. The distribution and frequency of record values. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B 1952, 14, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, R. Spacings. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1965, 27, 395–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherpieny, E.A.; Muhammed, H.Z.; Almetwally, E.M. FGM bivariate Weibull distribution. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference in Statistics (53rd), Computer Science, and Operations Research, Institute of Statistical Studies and Research, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 3–5 December 2018; pp. 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Buono, F.; Longobardi, M. On weighted extropies. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2022, 51, 6250–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Akbari, M.; Raqab, M.Z. Objective Bayesian estimation for the differential entropy measure under generalized half-normal distribution. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 2023, 46, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.; Egbon, O.A.; Ramos, P.L.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Louzada, F. Objective Bayesian analysis for the differential entropy of the Gamma distribution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.14081. [Google Scholar]
- Shakhatreh, M.K.; Dey, S.; Alodat, M.T. Objective Bayesian analysis for the differential entropy of the Weibull distribution. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 89, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| for | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | |||||
| 5 | 0.5 | 0.3640 | 0.3495 | 0.2911 | 0.2796 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.1820 | 0.1747 | 0.1455 | 0.1398 |
| 5 | 2 | 0.0910 | 0.0874 | 0.0728 | 0.0700 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.3224 | 0.3109 | 0.2657 | 0.2572 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.1612 | 0.1555 | 0.1329 | 0.1286 |
| 10 | 2 | 0.8060 | 0.0777 | 0.0664 | 0.0643 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 0.3001 | 0.2919 | 0.2594 | 0.2532 |
| 15 | 1 | 0.1501 | 0.1460 | 0.1297 | 0.1266 |
| 15 | 2 | 0.070 | 0.0730 | 0.0648 | 0.0633 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.2880 | 0.2817 | 0.2580 | 0.2519 |
| 20 | 1 | 0.1440 | 0.1409 | 0.1284 | 0.1260 |
| 20 | 2 | 0.0720 | 0.0704 | 0.0642 | 0.0630 |
| for | |||||
| n | |||||
| 5 | 0.5 | 0.0391 | 0.0369 | 0.0293 | 0.0280 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.0098 | 0.0092 | 0.0073 | 0.0070 |
| 5 | 2 | 0.0024 | 0.0023 | 0.0018 | 0.0017 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.0165 | 0.0159 | 0.0137 | 0.0133 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.0041 | 0.0040 | 0.0034 | 0.0033 |
| 10 | 2 | 0.0010 | 0.0009 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 0.0103 | 0.0101 | 0.0092 | 0.0090 |
| 15 | 1 | 0.0026 | 0.0025 | 0.0023 | 0.0022 |
| 15 | 2 | 0.0006 | 0.0006 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.0075 | 0.0074 | 0.0070 | 0.0068 |
| 20 | 1 | 0.0019 | 0.0018 | 0.0017 | 0.0017 |
| 20 | 2 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| MLE Parameters Estimation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIC | BIC | |||||||
| IFGM-WD | 1.689 | 21.032 | 3.275 | 6.327 | −0.8926 | 2.363 | 371.684 | 380.288 |
| IFGM-GD | 0.2872 | 21.573 | 0.4156 | 10.698 | 0.927 | 1.496 | 342.448 | 339.40 |
| IFGM-GED | 63.57 | 0.218 | 7.136 | 0.568 | −0.592 | 3.491 | 320.32 | 317.58 |
| r | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −2.774 | −2.705 | −2.642 | −2.585 | −2.532 | −2.485 | −2.441 | −2.402 | −2.366 | −2.334 | |
| r | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| −2.305 | −2.279 | −2.255 | −2.234 | −2.216 | −2.200 | −2.186 | −2.175 | −2.165 | −2.158 | |
| r | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| −2.154 | −2.152 | −2.152 | −2.155 | −2.162 | −2.171 | −2.184 | −2.200 | −2.145 | −2.274 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Husseiny, I.A.; Alawady, M.A.; Alyami, S.A.; Abd Elgawad, M.A. Measures of Extropy Based on Concomitants of Generalized Order Statistics under a General Framework from Iterated Morgenstern Family. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061377
Husseiny IA, Alawady MA, Alyami SA, Abd Elgawad MA. Measures of Extropy Based on Concomitants of Generalized Order Statistics under a General Framework from Iterated Morgenstern Family. Mathematics. 2023; 11(6):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061377
Chicago/Turabian StyleHusseiny, Islam A., Metwally A. Alawady, Salem A. Alyami, and Mohamed A. Abd Elgawad. 2023. "Measures of Extropy Based on Concomitants of Generalized Order Statistics under a General Framework from Iterated Morgenstern Family" Mathematics 11, no. 6: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061377
APA StyleHusseiny, I. A., Alawady, M. A., Alyami, S. A., & Abd Elgawad, M. A. (2023). Measures of Extropy Based on Concomitants of Generalized Order Statistics under a General Framework from Iterated Morgenstern Family. Mathematics, 11(6), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061377







