Abstract
This research aims to develop a mathematical model and a solution approach for jointly optimizing a global inventory service level and order sizes for a single-commodity supply chain network with multiple warehouses or distribution centers. The latter face stochastic demands, such as most real-world supply chains do nowadays, yielding significant model complexity. The studied problem is of high relevance for inventory management, inventory location, and supply chain network design-related literature, as well as for logistics and supply chain managers. The proposed optimization model minimizes the total costs associated with cycle inventory, safety stock, and stock-out-related events, considering a global inventory service level and differentiated order sizes for a fixed and known set of warehouses. Subsequently, the model is solved by employing the Newton–Raphson algorithm, which is developed and implemented assuming stochastic demands with a normal approximation. The algorithm reached optimality conditions and the convergence criterion in a few iterations, within less than a second, for a variety of real-world sized instances involving up to 200 warehouses. The model solutions are contrasted with those obtained with a previous widely employed approximation, where safety stock costs were further approximated and order sizes were optimized without considering stock-out-related costs. This comparison denotes valuable benefits without significant additional computational efforts. Thus, the proposed approach is suitable for managers of real-world supply chains, since they would be able to attain system performance improvements by simultaneously optimizing the global inventory service level and order sizes, thereby providing a better system cost equilibrium.
Keywords:
supply chain networks; supply chain inventory planning; system inventory service-level optimization; Newton–Raphson MSC:
90-08
1. Introduction
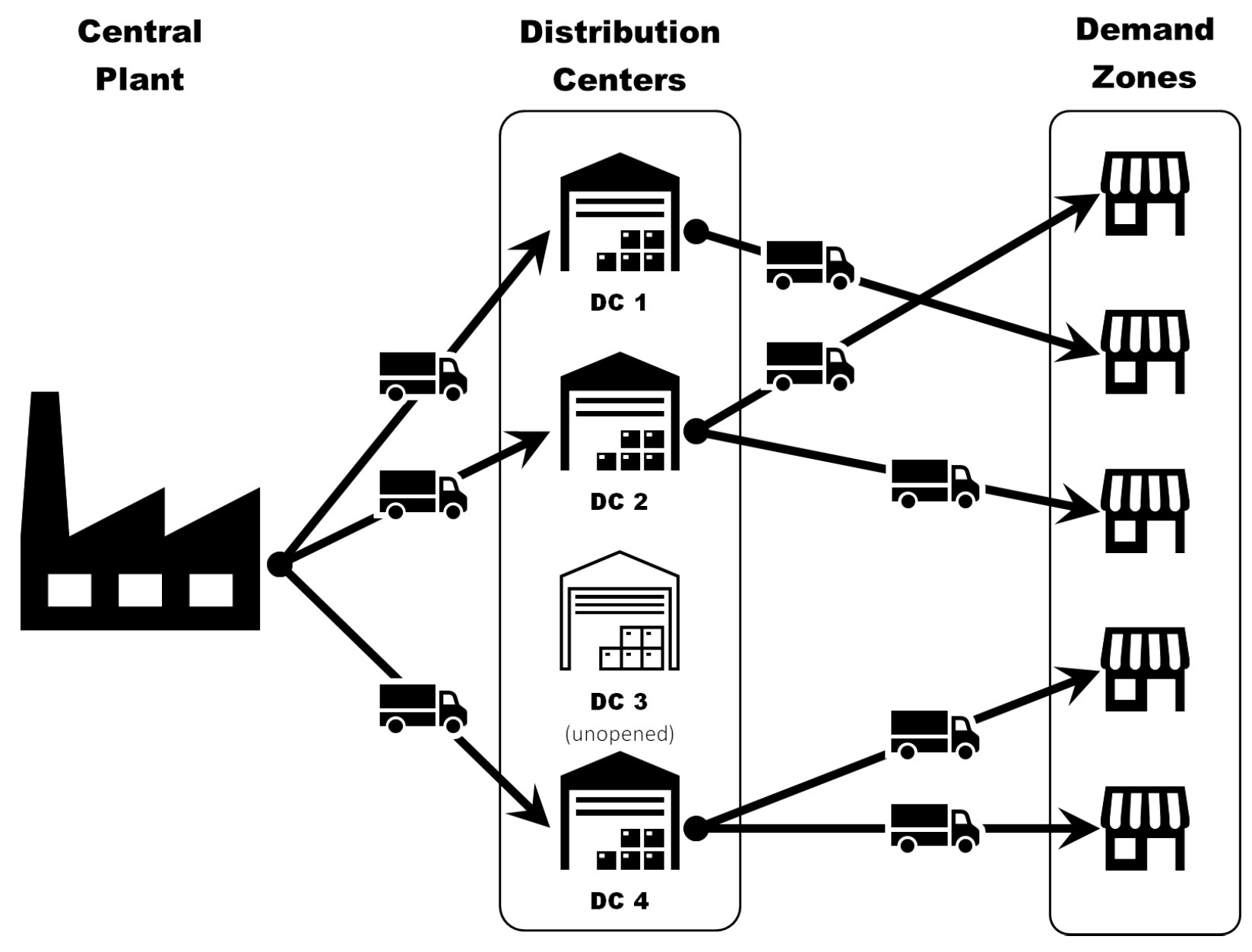
Supply chain management aims to optimize and coordinate decisions and agents to provide products and related services at the right times, quantities, and places, also aiming to minimize system-wide costs and ensuring system service-level requirements (see [1,2,3,4,5]). In this context, inventory control decisions and related costs represent key elements to be addressed, in addition to transport and warehouse operations, among other issues (see [6,7]). One of the most typical supply chain topologies comprises a set of one or more plants or suppliers that distribute products to a set of parallel warehouses or distribution centers that finally serve end customers’ demands, as shown in Figure 1 (see [3,8,9,10,11,12]). Under this topology, inventory control decisions at the warehouse level are of high significance, wherein order sizes, reorder points, and service levels represent the main decisions to be addressed. This has to be achieved while being efficient and following a number of performance indicators, such as inventory availability, stock-out probability, or demand fill rate (see [3,12,13,14]). System costs have been traditionally considered as the main objective in evaluating global performance, where obtaining even marginal savings in relative terms may generate significant improvements in the medium or long term.
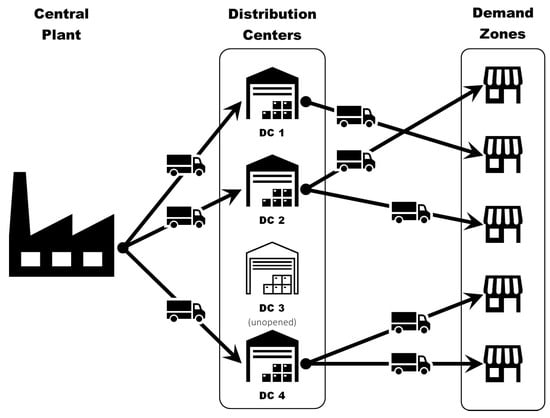
Figure 1.
Standard supply chain network topology.
From a strategic or long-term perspective, designing the underlying network is an essential problem, which typically consists of locating warehouses and plants for serving the end customers, conforming to the well-known family of facility location problems (FLPs), as shown in [15,16,17,18,19]. Traditionally, plant or warehouse locations and customer assignment decisions are made based on a sequential and hierarchical decision-making structure, where decisions belonging to higher organizational levels are made based on FLP modeling structure, without major concerns regarding the impacts on further lower-level decisions (see [3,11,12]).
Nonetheless, it is worth noticing that, when the supply chain network (SCN) is already optimized and fixed for a specific time frame (e.g., a few weeks, months, or years), the optimization of inventory-related decisions remains a relevant problem to be addressed. In this context, several research works have been developed, where Refs. [20,21] developed approaches to evaluate system performance in a two-level supply chain under different assumptions and considerations. In [22], alternative optimization approaches were developed to deal with inventory decisions, where order sizes and reorder points for a two-level supply chain were optimized. A mathematical model to optimize inventory-related decisions for a complex supply chain network was developed in [23], comprising end customers, retailers, warehouses, productive plants, and raw material suppliers, assuming a fixed service level to be ensured for end customers. Further extensions were presented in [24,25], where the first one addresses a multi-echelon supply chain system with three different demand patterns, while the second one includes product perishability and demands depending on prices and inventory levels. Other recent research works can be found in [26], which presents a deterministic supply chain inventory model involving outsourcing decisions, and [27], which addresses a deterministic single-location inventory model involving product deterioration, a supplier offering price discounts, and payment delays.
Most of the aforementioned works simultaneously optimize decisions at the warehouse level and at the plant or supplier level, consider reorder points and order sizes as decision variables, and yield different service levels for each location. Moreover, some works assume that the inventory service level is a fixed and known parameter, which should be exogenously determined by a supply chain planner or manager. In contrast, this research does not consider plant/supplier decisions and costs, and reorder points are determined through a global service-level optimization (i.e., the same service level for all warehouses). Then, reorder points are individualized for each warehouse mainly depending on lead times, served demand mean and variance, and the optimal global service level. Accordingly, this research aims to address situations in which a global service level along with order sizes are required to be optimized, in contrast to other previous related works.
As can be observed in traditional FLP-related literature, decisions related to the supply chain network design are made without considering specific impacts on inventory management ([9,10,11]). However, inventory management and strategic SCN design must take care of the impacts between each other, where the number of parallel facilities (e.g., warehouses or distribution centers) affects the total system inventory level, resulting in the well-known risk pooling effect, especially in scenarios with stochastic demands. Thus, several works show that the structure of the supply chain network directly relates to the impact that risk pooling has on system costs, conforming to the family of inventory location problems (ILPs) (see [8,9,10,11,28,29,30]), where inventory management issues are jointly addressed with SCN design decisions and costs. Subsequently, Refs. [3,12] developed reviews of ILP-related works. Furthermore, and following the basic inventory location-related aforementioned works, this kind of problem may include different relevant practical issues, such as multi-commodity and multi-period scenarios, inventory and transport capacities, alternative inventory control policies, spare parts supply chains, and supplier selection (see [31,32,33,34,35,36,37]).
In this context, the need for jointly optimizing the inventory-related service level as a problem decision variable appeared to be relevant research that needed to be addressed. Thus, Refs. [8,9] presented approximate strategies to model and solve an ILP facing customer demands with a Poisson distribution and a continuous inventory control policy. Subsequently, Ref. [38] presented the first research study with an approximate strategy to model and solve an inventory location problem with normal demands and a continuous inventory control policy. Finally, Ref. [39] presented a variation of the model in [38] and considered a heuristic solution approach.
Furthermore, Refs. [37,40] presented a generalized Benders decomposition (GBD)-based solution approach that solved an ILP at optimality with normal demands and continuous inventory control policy in competitive times. A significant contribution of this approach relies on the decomposition process, which yields a sub-problem that fully addresses all inventory-related decisions for a fixed SCN, which was previously determined to be a master problem at each algorithm iteration. These facts represent a significant potentiality, where any inventory model improvement may be integrated into an ILP, and it would be fully captured by the sub-problem following the GBD-based solution approach proposed in [37,40]. Similarly, several widely employed local search heuristics and metaheuristics may be considered to solve a related ILP with inventory service-level optimization, following [32,41,42,43,44]. For these approaches, the design of the SCN is explored by a local search algorithm (i.e., warehouse location and customer assignments), whereas solving a fixed-network inventory optimization problem (as modeled and solved in this research) may be considered a solution evaluation subroutine within the overall algorithm. Consequently, the aim of jointly optimizing order sizes and the service level for a fixed SCN gains attractiveness given the potentiality of integrating it within a broader ILP for optimizing the design of the SCN. Naturally, this and other similar integrative approaches remain as future research to be addressed.
In summary, this paper fills existing research gaps by developing a novel continuous, nonlinear optimization model to jointly optimize the global inventory service level and order sizes for a fixed supply chain network. The addressed network topology comprises multiple parallel warehouses under a normal approximation of end customer demands. A continuous inventory control policy is considered, where a common global service level for all the existing warehouses has to be observed. It worth noting that the proposed formulation involves enhancement of some well-accepted approximations in previous related literature, especially focusing on safety stock and order size optimization. Finally, a multivariate Newton–Raphson-based algorithm is developed to solve the formulated problem at optimality. This well-known method has been successfully employed in supply chain management-related research, such as in [45,46,47].
As discussed in [48], the Newton method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, is one of the most proper approaches for solving nonlinear equations and is particularly relevant when expressions for the gradient vector and the Jacobian matrix can be computed in an explicit and efficient manner. This approach involves a fine equilibrium between mathematical complexity and tractability while ensuring a quadratic convergence rate. Other approaches widely employed are variations and approximation of the Newton–Raphson approach, such as the Quasi-Newton and the Conjugate Gradient Method. Moreover, given the small- and medium-size instances considered in this research (i.e., at most 201 variables) and the possibility of having a potentially good initial guess for the order size and the global service level (as described in Section 4), an outstanding performance of the employed approach is observed.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the studied problem and the proposed model formulation, including a generic formulation and a specified one considering demands with a normal approximation. Section 3 aims to describe the solution approach developed to solve the proposed formulation, which is derived specifically for demands with a normal distribution. Subsequently, Section 4 describes the computational experimentation carried out, then presents and discusses the obtained results. Section 5 presents a further discussion of the main results obtained in the previous section, along with a brief managerial insight discussion. Finally, conclusions and future research are presented in Section 6.
2. Problem Description and Formulation
2.1. Problem Description
The problem studied in this research consists of optimizing a global inventory control service level and individual order sizes in a system comprising a single plant or supplier that fulfills incoming orders from N parallel warehouses, which finally serve demands from external customers (retailers). This topology is depicted in Figure 1. The global service level consists of a homogeneous maximum stock-out probability that must be observed at each and every warehouse. In this case, it is assumed that each warehouse faces a stochastic demand that is the aggregation of several customer demands. Particularly, following most inventory location-related literature, the aggregated demand at the warehouse level is approximated considering a normal distribution, as in [49].
Note that, although the normal distribution presents a positive probability of observing negative values (which can be considered inadequate for most demand processes), it may still be a suitable approximation in strategic problems, especially when a low variation coefficient of warehouse demands is observed, as indicated in [50]. In these cases, the probability of realizing negative demands may be considered immaterial or insignificant (see Section 5), which provides a simple simulation exercise to denote these facts. In addition, the normal distribution involves clear advantages related to its analytical properties, specially for deriving exact expressions. Moreover, ref. [50] (pp. 156–157) states that, when the variation coefficient is less than , the truncated normal distribution does not significantly differ from a normal approximation. Naturally, in cases with significant probabilities of negative demands, the normal approximation may be considered unsuitable, and other distributions or approximations should be considered, as in [49], where a truncated normal distribution was considered.
In the studied system, each warehouse i follows a continuous inventory control policy , where is the order size to be optimized, and is the reorder point, which is the critical inventory level that generates an order to the plant. The order size must be optimized according to the costs associated with the well-known Wilson model plus penalty costs associated with demands that arise during stock-out events at each warehouse. Finally, the reorder point has to be set in order to observe the global service level or stock-out probability, while the associated safety stock costs are minimized as much as possible. Thus, is set at the minimum value that guarantees the observation of the maximum stock-out probability.
2.2. Model Formulation
The studied formulation relies on the following notation and definitions:
Model parameters:
| : | Fixed order costs for each order submitted from warehouse i ($/order). | |
| : | Unit holding cost at warehouse i ($/unit-time). | |
| : | Penalty cost per unit of demand arising during stock-out events | |
| and served with a delay for each warehouse i ($/unit). | ||
| : | Lead time for the incoming orders at warehouse i. | |
| : | Demand mean per time unit (per day) at each warehouse i. | |
| : | Variance of demand per time unit at each warehouse i. |
Decision variables:
| : | Order size for each warehouse i. | |
| : | Reorder point at each warehouse i. | |
| : | Maximum stock-out probability accepted at each and every warehouse. | |
| : | Minimum probability required for not observing stock-outs (). | |
| : | Average safety stock observed at each warehouse i. | |
| : | Average demand arising during stock-out events and served with a | |
| delay at each warehouse i. |
Under the aforementioned definitions and assumptions, each warehouse faces a continuous stochastic demand during lead time , defined as , with a probability density function . Then, the problem is formulated as the following nonlinear programming model:
The first summation of the objective function in Equation (1) is the well-known Wilson model objective function, which considers order and cycle inventory costs associated with the order size at each warehouse (see [51,52]). The second term in the objective function is the expected safety stock costs at all warehouses. Finally, the third summation in (1) is the expected costs associated with demand arising during stock-out events at all warehouses. Note that it is assumed that all demands are eventually served, and these costs represent the additional expenditures of serving demands with some delay in case a stock-out event occurs (also known as backorders).
Equation (2) ensures that is set to guarantee the minimum service level or maximum stock-out probability at each warehouse. Equation (3) determines the expected safety stock just before the orders arrive at each warehouse, which is equivalent to the reorder point minus the expected demand during lead time (integrating over demand values lower than ; otherwise, it represents a stock-out). Equation (4) allows for computing the expected demand arising since stock-out is observed, until the next order arrives (i.e., it considers demand values over ; otherwise, a stock-out situation is not observed).
Assuming a normal distribution, Equation (2) allows for setting the minimum reorder point at each warehouse i, as shown in Equation (6). In addition, Equations (3) and (4) can be written as in (7) and (8), respectively (see [38]).
Note that Equation (3) assumes a minimum demand of 0, while the normal distribution is unbounded. However, the right side of the Equation (7) is obtained assuming unbounded demand (i.e., to ), representing an approximation for cases with non-negative demands. This approximation is suitable in cases where the probability of observing negative values is close to 0 and where the approximation error may not be significant.
Replacing (6)–(8) into the model, it can be written as:
It is worth mentioning that, when the penalty cost is zero , then the order size may be determined simply by following the well-known Wilson model, as shown in Expression (10) (see [51,52]). However, given the impact of the order size on the total penalty costs, as observed in the last term of Expression (9), the optimal order size does not coincide with (10). Instead, the order size is computed as Expression (11) by differentiating Equation (9) with respect to and equalizing it to zero. Moreover, it can be observed in (11) that, when the service level tends to 1, unfilled demand tends to 0, and the optimal order size converges to Expression (10).
Note that Expression (11) may represent a sort of correction to the traditional Wilson model, where penalty costs between two consecutive orders may be understood as another fixed order cost. Then, the order size computation just corrects the order costs in Expression (10) by , as observed in Expression (11).
Although it is natural to require , the derivation of optimal order sizes when served demand is non-negative naturally yields a solution that is automatically non-negative, as can be observed in (10) and (11). Otherwise, it is impossible to serve positive demands with negative order sizes. Thus, discarding negative roots in the process is enough to obtain positive order sizes for each existing warehouse with positive demands, and then is not established as a formal constraint of the problem.
3. Solution Approach
The proposed formulation is solved by searching a critical point, i.e., a solution for which the total cost gradient is zero. In other words, the algorithm searches for a solution such that , where is the total cost function defined in Equation (9), and is the decision variable vector of the problem. Then, the equation is solved by means of a root-finding problem employing the well-known multivariate Newton–Raphson method [53]. Note that all the involved expressions are explicitly developed for normally distributed demands.
The multivariate Newton–Raphson method allows us to find the approximation of a root for a vector-valued function [53]. This iterative method arises from the Taylor expansion for vector-valued functions around a point , as shown in (12), where is the Jacobian matrix.
The method is based on a linear approximation, ignoring the term. If , where , and is the current guess, then
or
Then, with an initial guess , at each iteration k, the new root approximation is
Let , , and be the order size-related costs (i.e., cycle and ordering), safety stock, and expected demand during stock-out events for the i-th warehouse, respectively. Then, for :
and, considering as the vector of the decision variables to be determined, we define:
where is the system service level. Function is considered the gradient vector of :
where:
We need to compute the optimal value of , i.e., the fixed point, where the function is minimized, which is equivalent to computing , such as .
The Newton–Raphson method will be used for addressing this computation. Let be an initial guess; then, at the k-th iteration, the current solution is given by:
where
and where is the Hessian matrix of , and
with and .
It is important to note that, to fulfill constraint (5), the following check condition is added to the updating step at the k-th iteration:
In our implementation, we consider and , with , since it is assumed that and since cannot be computed. Naturally, may consider more significant figures () up to user preferences.
The whole procedure is presented in Algorithm 1. In line 8, Equation (25) is computed in two steps. The first step is computing by solving the system . The mentioned system is solved by the routine solve of the module numpy.linalg [54]. The second step simply involves updating the current solution by computing .
| Algorithm 1 Application of Newton–Raphson Method |
The optimal order size of the Wilson model shown in Equation (10) (see [52]) is considered the initial order size for all warehouses. The initial service level is set to , the number of warehouses N depends on the instance, the tolerance of the method tol is set to and compared with the norm of the gradient vector , and the number of maximum iterations is set to 10. The input parameter params contains the demand , variance of the demand , lead time , unit holding cost , penalty cost , and fixed-order cost for each warehouse i (for more details, see Section 2.2).
4. Computational Experimentation and Numerical Results
In all of these experiments, a service level of is considered as a benchmark solution for the algorithm. In particular, the values considered are computed based on [38], which relies on a previous approximation for optimizing the system service level that assumes an approximated safety stock expression and order sizes computed as in the Wilson model’s solution.
Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 show the numerical results of the instances with , and 200 warehouses, respectively, representing a wide set of reasonable real-world sizes. For each warehouse i, all cases consider as a baseline cost parameter, and ranges within , representing a significant range of variation with respect to the holding costs, . In addition, the coefficient of variation , and for each instance, focused on high-volume, smooth demands. Thus, 9 cases or sub-instances are defined for each instance (i.e., by combining and variations). Finally, for , the order cost is determined in terms of the lead time , as , the lead time is randomly set in the range , and the average demand is considered to be in the range .

Table 1.
Results with warehouses.

Table 2.
Results with warehouses.

Table 3.
Results with warehouses.

Table 4.
Results with warehouses.

Table 5.
Results with warehouses.

Table 6.
Results with warehouses.
The columns and Base Tot. show the service level and total cost considering the Wilson order size. The columns and Op Tot. show the service level and total cost considering the order size of the presented model. The columns Diff. and %Diff. show the difference between both solutions. The last column t (sec.) shows the computational time in the execution of the presented model.
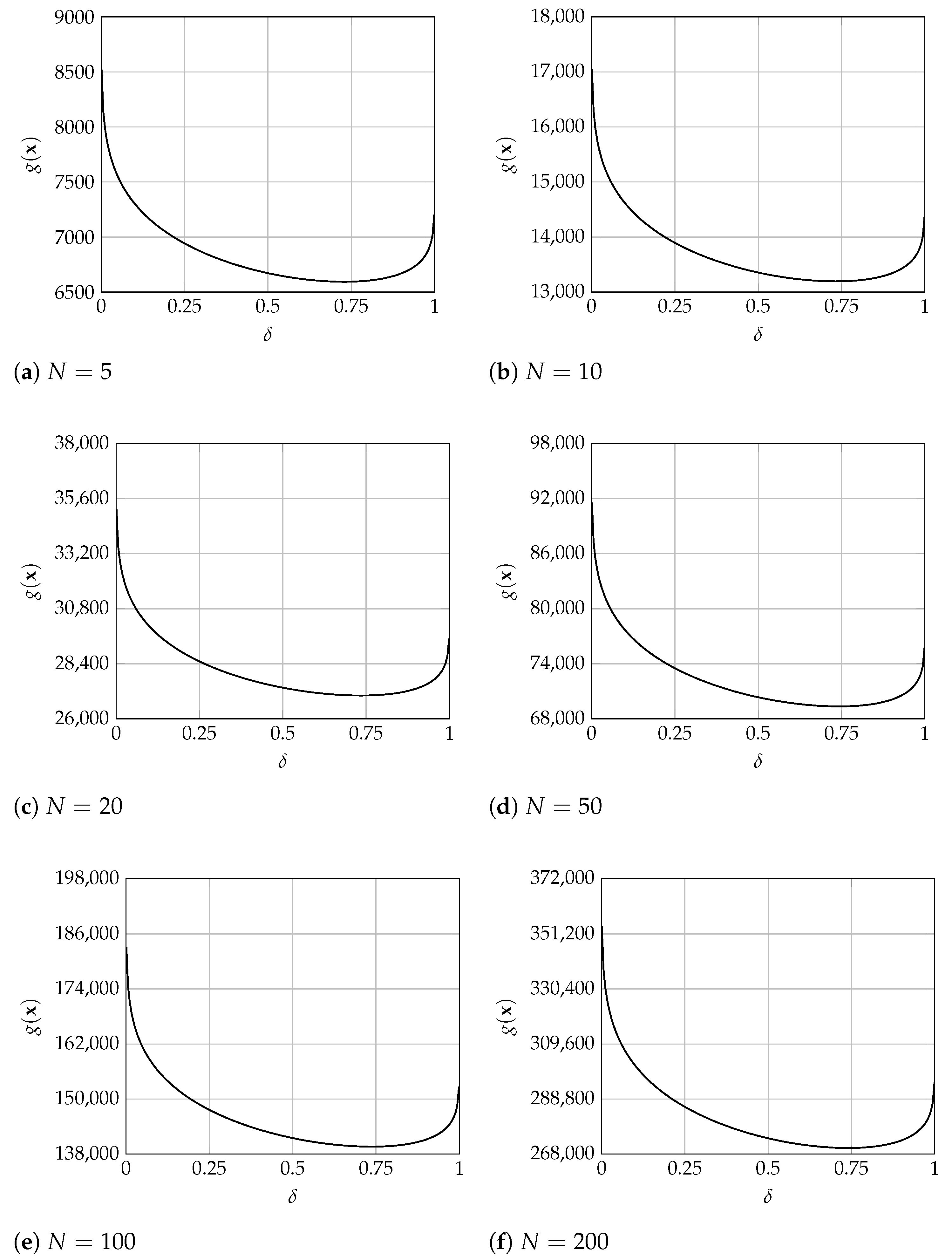
It is worth noting that the Hessian matrix of the cost function (i.e., the Jacobian matrix of the gradient vector ) at the end of the algorithm was positive definite in all tested cases. This is shown by the obtained eigenvalues that were strictly positive for all instances, as observed in Table 7 and Table 8, which show the minimum and maximum eigenvalues obtained for each instance. Therefore, it can be stated that all obtained solutions at least represent a local minimum for the studied model. In addition, merely as empirical evidence, Figure 2 shows the evolution of the total system cost for , and 200, with and , for different values of , and considering the optimal value of of expression (11) () for each fixed value of . These figures denote the existence of a single minimum for in the range . In sum, although it has not been demonstrated that the studied problem has a strictly convex objective function and a single global optimum (given the associated algebraic complexity, especially considering the relationship between and ), it is shown that all the obtained values effectively represent optimal solutions to the problem within the feasible domain of .

Table 7.
Minimum () and maximum () eigenvalues for the Hessian matrix at the approximate solution , such as , considering , and 20.

Table 8.
Minimum () and maximum () eigenvalues for the Hessian matrix at the approximate solution , such as , considering , and 200.
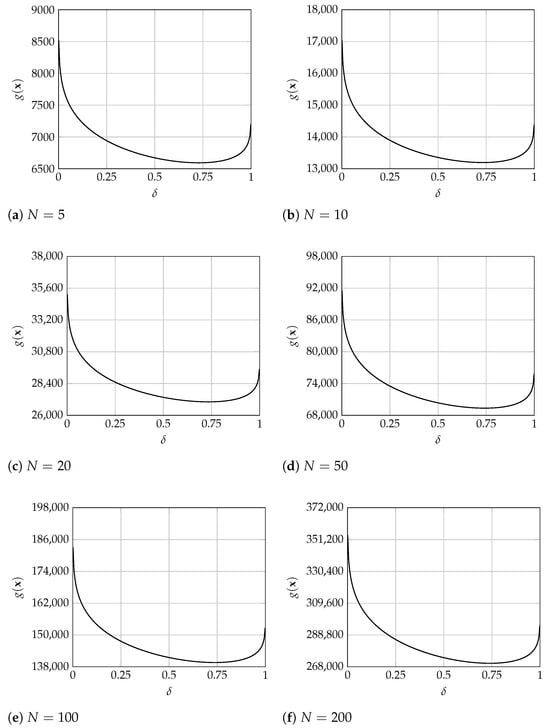
Figure 2.
Behavior of total cost for , , and , and 200.
Nevertheless, convexity may be reasonable and expected, since when the service level approaches 1, the safety stock cost tends to ∞ (i.e., the second term in Expression (1)), and the penalty cost tends to 0 (i.e., the third term in Expression (1)), thus yielding a total cost tending to ∞. In addition, the order size () converges to the Wilson model solution in Expression (10), as observed in Equation (11). This expression at the limit is independent of , and the related costs of the first term in (1) do not affect the limit of the total costs (which tends to ∞). On the contrary, when approaches 0, the safety stock cost tends to 0 and the penalty cost to ∞, again yielding a total cost approaching ∞. Moreover, the order size and related costs (the first term in Expression (1)) tends to ∞ when approaches 0.
Furthermore, it may be natural that the penalty cost is strictly and continuously increasing, whereas the safety stock cost is strictly and continuously decreasing, both with . Finally, it can be observed that order size-related costs (i.e., the first term in (1)), when order size is determined by Equation (11), are strictly and continuously decreasing from ∞ to the optimal cost of the Wilson model, given by . In sum, it may be expected that the total cost in expression (1) tends to ∞ when the service level approaches 0 or 1, creating a convex U-shaped function, when also considering that total costs are always positive when and all cost parameters are positive (i.e., 0 represents a lower bound to the total costs), as shown in Figure 2.
As can be observed for all instances in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, although the total costs for the proposed approach are slightly lower than those obtained with the benchmark approach, the system service level is significantly different when the penalty cost parameter is the lowest (i.e., ). On the contrary, when penalty cost is the highest (i.e., ) and the optimal service level tends to 1, the benchmark and the optimal service level tend to be the same. These results are explained by the fact that, when the service level is high, stock-out demands converge to 0 and order sizes tend to Wilson order size; thus, the benchmark solution becomes a very good approximation. In the same way, savings obtained when the proposed approach is employed are more significant when penalty cost parameter is the lowest. Accordingly, the proposed approach is more beneficial when is not too high and the optimal service level is not near 1. This is especially relevant from a supply chain network design perspective (as discussed in most ILP-related literature described in Section 1), where variations in the global service level may imply significant changes to the SCN configuration, such as different customer assignments or more relevant changes in warehouse locations and the number of located warehouses.
The aforementioned results are contrasted with the very low computing time required by the proposed approach, even for the largest considered instances (i.e., 200 warehouses), always being less than a second. Thus, the fact that the proposed approach has the potential to provide a better system service level, which may even impact the design of the SCN and related costs given the unsubstantial computational efforts required, supports the usage of the proposed approach instead of previous approximations.
As observed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, a significant similitude is observed in the optimal service level when varies (i.e., , , and ), while in terms of total system costs, a more significant variation is obtained when is the highest. For example, for 200 warehouses, if and , then the total savings are about , whereas when and , the total savings rise to about (i.e., more than three times in savings).
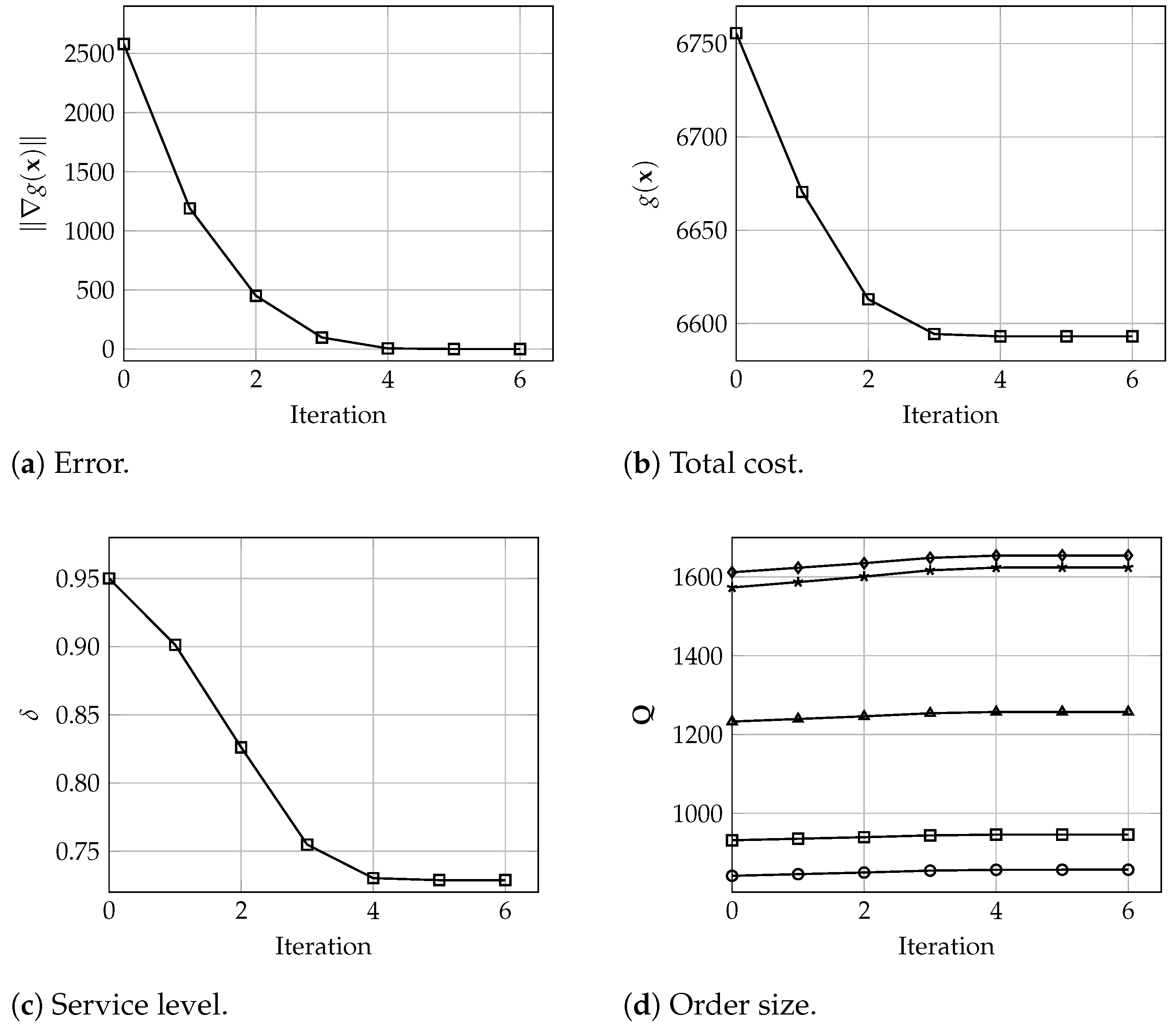
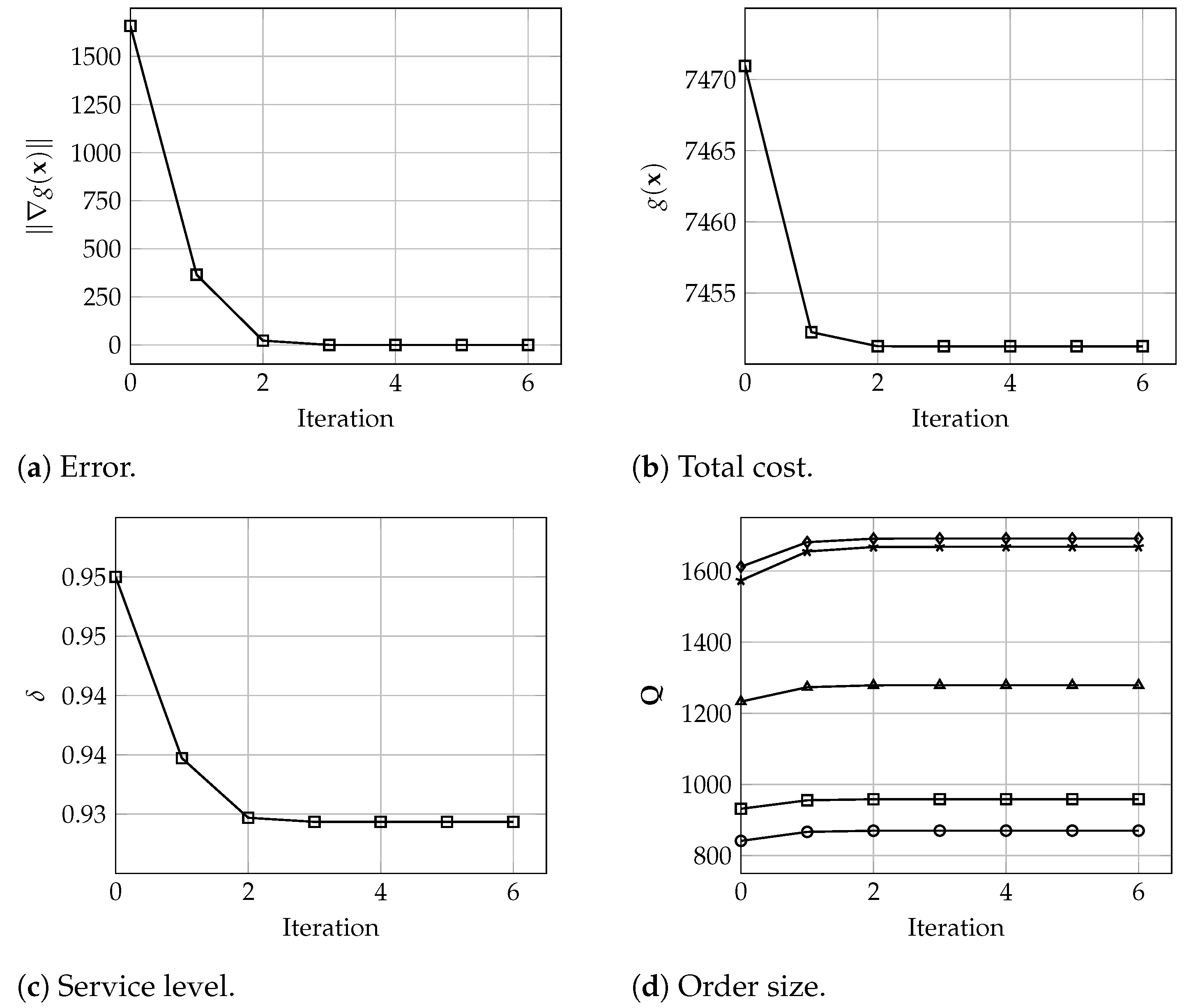
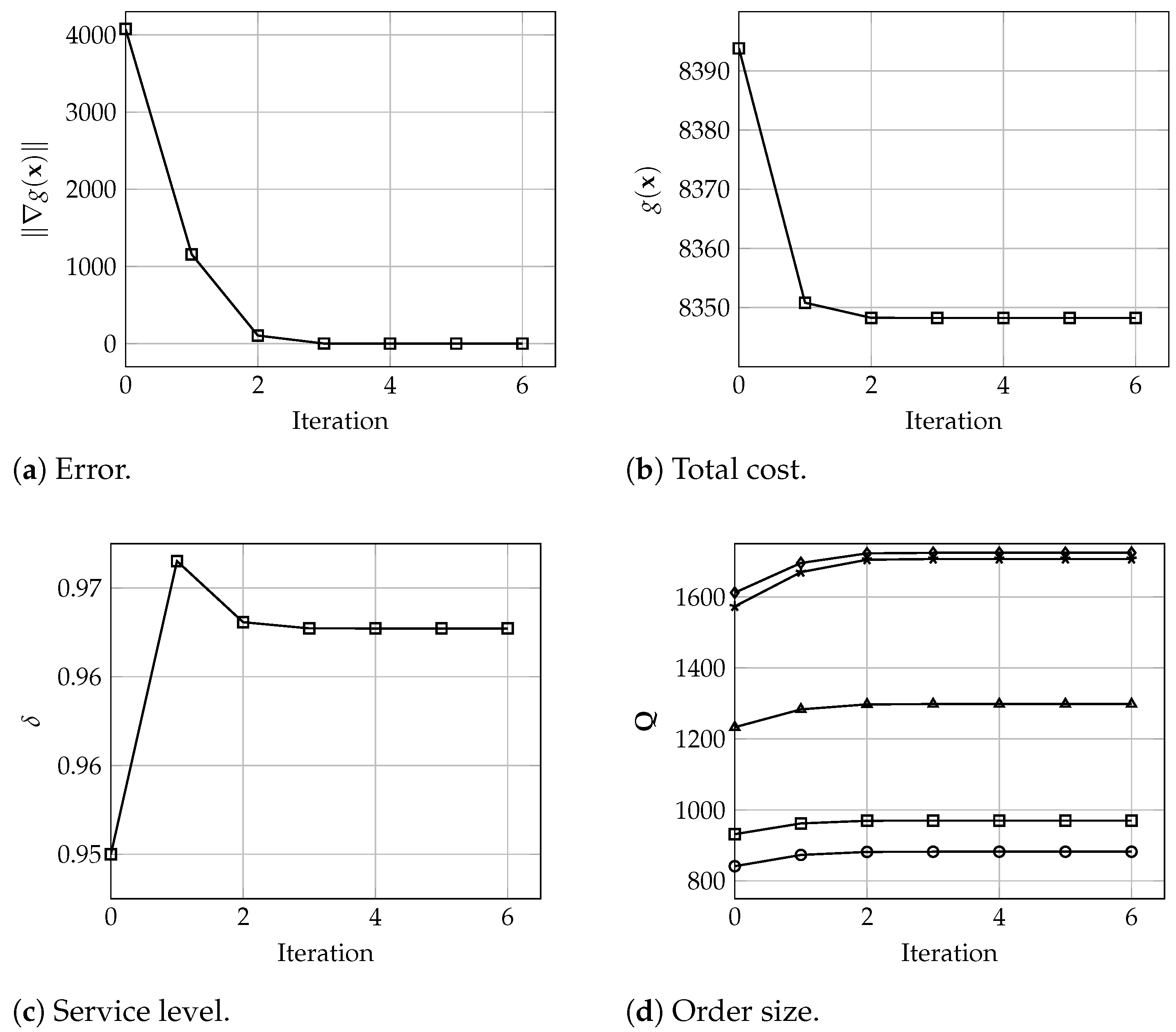
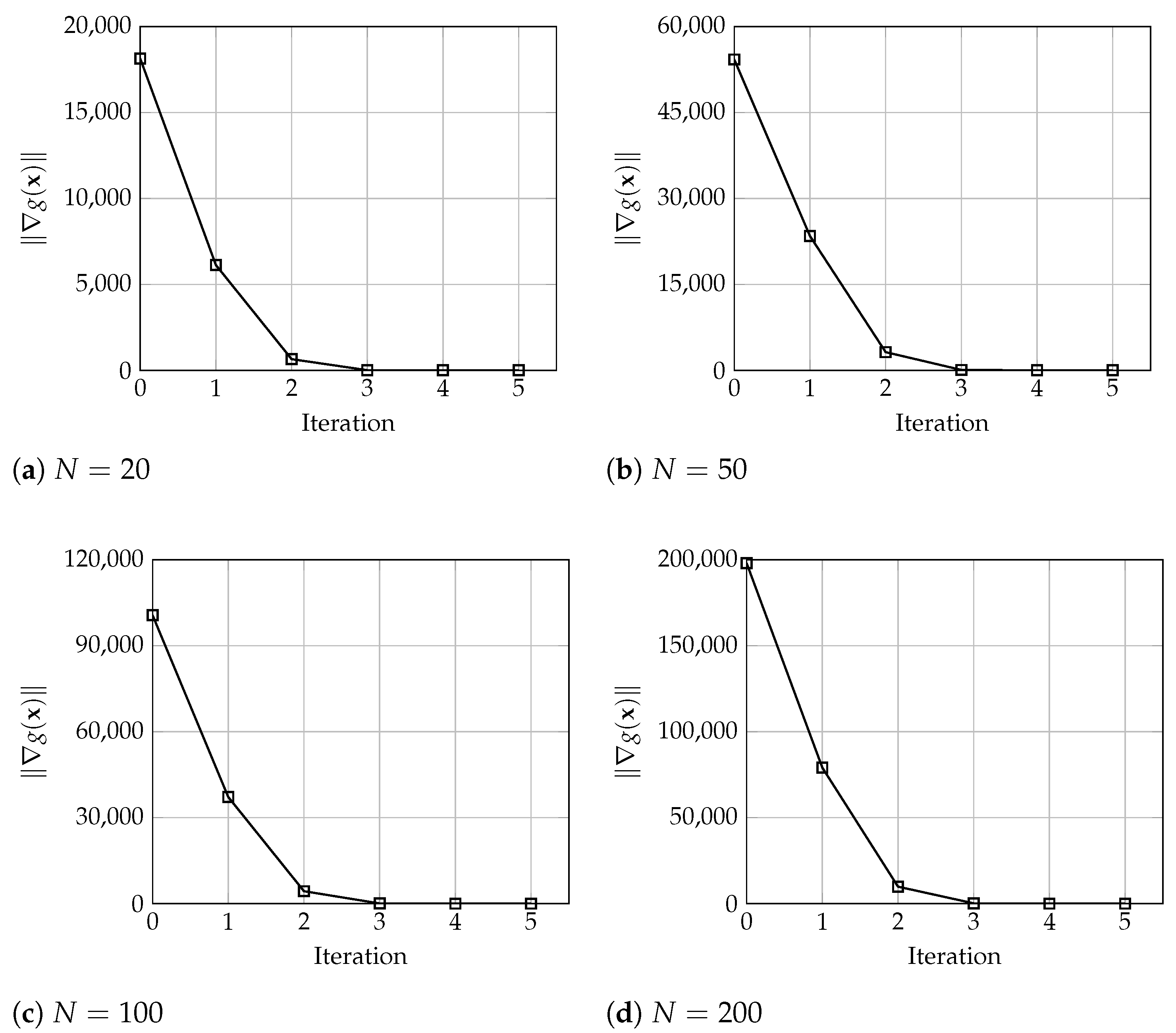
In terms of the algorithm behavior, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the number of iterations executed with warehouses and different values of and . Each graph shows the evolution of the error , total cost, i.e., the value of , the service level values , and the order size for each warehouse. These results denote the good and fast performance of the proposed algorithm, which yield optimal solutions in only 6 iterations. In particular, and in practical terms, it is observed that the solution seems to be a very good approximation of the optimal values after only 3 or 4 iterations. Analogously, these results are very similar for larger instances where, for , and 200 warehouses, the algorithm converges in 5 iterations, and the solution after 3 or 4 iterations is practically the same as the final optimal solution, all considering a tolerance of , as depicted in Figure 6.
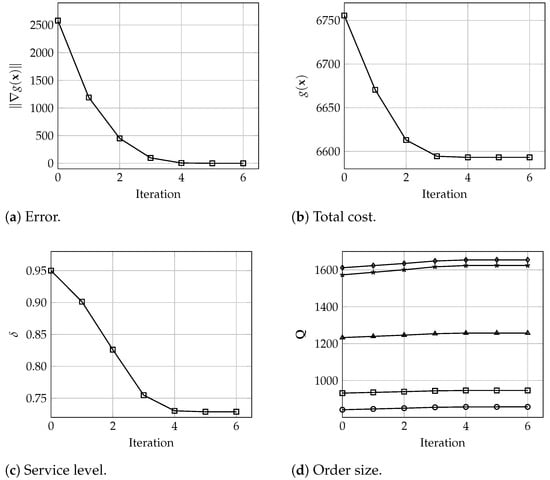
Figure 3.
Evolution of (a) the error , (b) the total cost , (c) the service level , and (d) the order size for all warehouses (), with , and 5 warehouses.
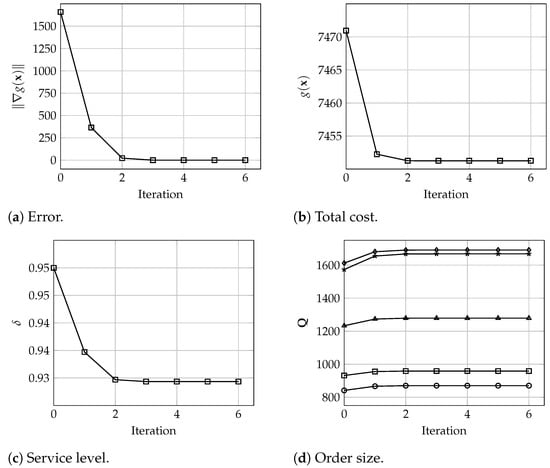
Figure 4.
Evolution of (a) the error , (b) the total cost , (c) the service level , and (d) the order size for all warehouses (), with , and 5 warehouses.
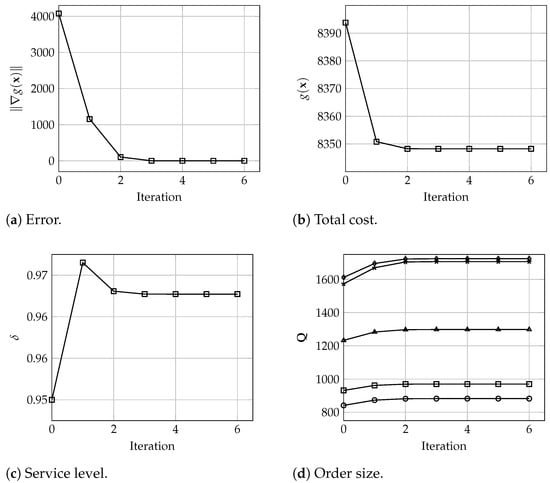
Figure 5.
Evolution of (a) the error , (b) the total cost , (c) the service level , and (d) the order size for all warehouses (), with , and 5 warehouses.
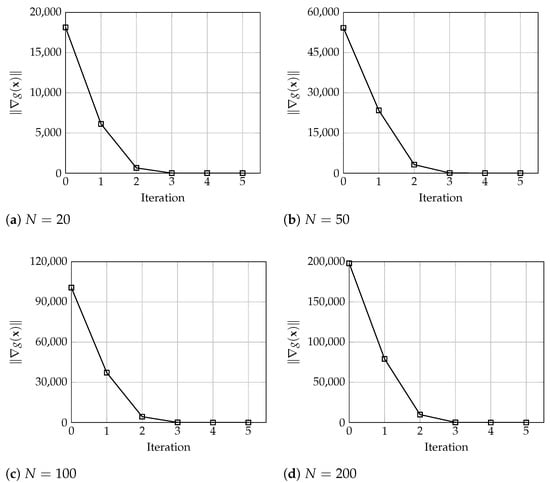
Figure 6.
Evolution of the error considering (a) 20, (b) 50, (c) 100, and (d) 200 warehouses with and .
All experiments were run on a computer with an 11th Gen Intel Core i5 processor running at GHz with 8 cores using 16 MB of RAM, running Ubuntu version . The programming language used was Python [55]. Although other programming language are suitable for this kind of studies, the selection of Python was based mainly on its free availability and easy use. In addition, the complexity and size of the studied problem and its instances are not so challenging as to require more specialize language programming, such as MATLAB or Mathematica (visited on 15 August 2024).
5. Discussion of Research Results and Managerial Insights
Given the proposed formulation and solution approach, in addition to the obtained results, several insights and implications from a scientific and practical perspective may be obtained. Firstly, this research represents a significant contribution to inventory location and supply chain inventory-related literature through an enhanced formulation along with an exact solution approach to optimizing a global inventory-related service level (i.e., stock-out probability) and order sizes for a multi-warehouse system, along with an exact solution approach based on the well-known Newton–Raphson method. Note that the proposed solution approach is analytically derived considering a normal distribution (i.e., an approximation) for warehouse demands. Nonetheless, the approach may be adapted to other distributions, while analytical derivation may result in a more complex or simpler one depending on the specific distribution considered (e.g., uniform, triangular, log-normal, truncated normal, Poisson, gamma, beta, etc.). In particular, a numerical approximation instead of an analytical derivation of the key algorithm elements (i.e., gradient vector and Jacobian matrix) may be developed considering empirical probabilistic distributions, as described in [48].
It is worth highlighting that, although normal distribution presents a positive probability of observing negative values, it may be insignificant for aggregated high-volume demands with small levels of relative variability (i.e., Coefficient of Variation, ). For example, a normal demand with a positive mean and a of implies a negative demand probability of , whereas for all experiments carried out in this research, a maximum of is considered, with a negative demand probability of . Table 9 presents the average percentage of times where negative demand values are obtained for 100 experiments, where each one involves 1000 random demand values following a normal distribution with a and (note that this experiment is independent of mean demand value, except if it is 0 or negative). It can be observed that, for a of and , negative demands are not observed, whereas for a of , only in of cases was a negative value observed. In the extreme case of considering a of , negative demands are observed in of cases. Accordingly, potential errors related to the occurrence of negative demands may be considered insignificant, and the proposed approach represents a powerful methodology for practical implementations.

Table 9.
Summary of normal demand simulation with .
In terms of the modeling structure, it is worth highlighting that previous research within inventory location-related literature fail in modeling in an exact manner both safety stock and unfilled demand costs, where the associated stock-out probability is not considered as a decision variable but as an input parameter. In our research, in contrast, the service level is considered a system decision variable to be jointly optimized, which makes the solution approach difficult. Note that if a different service level for each warehouse is assumed, then the problem may be decoupled into independent problems for each warehouse with two decision variables (i.e., the service level and the order size). On the contrary, as considered in this research, if the required service level is assumed to be the same for all warehouses, then the common system service level and the order sizes for all warehouses must be optimized simultaneously.
Based on the obtained results, it is observed that the proposed model allows for obtaining solutions with a better system performance in contrast to a natural benchmark, where the expected safety stock costs are modeled in the traditional manner observed in inventory management and inventory location literature. This simplified modeling approach yields a different suboptimal service level, slightly different order sizes for each warehouse, and a more expensive system cost compared to the proposed approach. Naturally, if a pre-fixed service level is considered near the optimal value obtained with the proposed model, then the improvements may be immaterial. On the contrary, if a pre-fixed service level is far from the optimal value obtained with our approach, then the improvements may be even more significant.
It is remarkable that the proposed model and solution approach do not imply a significant increase in computational effort, since optimal solutions are obtained after only a few iterations with very low computational times, even for the largest instances considered (i.e., 200 warehouses). Note that observing more than 10 or 20 warehouses for a single company in the real world is very infrequent, except for some global multinational companies.
Moreover, the proposed model and solution approach are particularly relevant as part of a sub-problem within further inventory location problems. This is especially significant when the generalized Benders decomposition is employed, as in [36,37,40], where the full original problem is decomposed into an MIP formulation that deals with warehouse location and customer assignment decisions (i.e., within a master problem), whereas inventory decisions are addressed by an underlying sub-problem (such as the problem addressed in this research). It is remarkable that none of the aforementioned works optimizes the service level, which is considered a fixed parameter. Accordingly, a natural future research direction consists of extending the proposed methodology to address an inventory location problem to design a supply chain network while simultaneously optimizing decisions of warehouse location, customer assignment, order sizes, and the global inventory service level, which enlarge the contributions of this research.
In terms of managerial insights, it worth highlighting that the proposed approach may definitively benefit supply chain managers by providing better solutions in terms of strategic supply chain inventory performance. These benefits may imply significant savings in the long terms. In particular, the proposed methodology (i.e., the model and the solution algorithm) may help in efficiently supporting the decision-making process related to optimally setting significant inventory decision variables in real-world supply chains, such as the global service level and warehouse order sizes. Moreover, very low computational complexity and efforts to implement the proposed approach are required, significantly facilitating its adoption and utilization in real-world settings. Finally, in relation to the existence of third-party logistic providers, they may benefit by reducing emergency shipments, given the optimal setting of the global service level and related safety stock, thus yielding reductions in related costs and improvements in terms of system sustainability and service level.
Additionally, the methodology may be used in small regions where the homogeneity of customers leads to the marketing goal of offering a homogeneous customer service level at the warehouses, since customers may perceive a service level difference or, in small regions, their communication may allow them to share this knowledge. Therefore, it is important to the company to offer the same service at different locations, since the proposed approach allows for optimizing the associated costs.
6. Conclusions and Future Research
In this research, a model to optimize inventory-related decisions for a single-commodity supply chain network comprising a set of parallel warehouses or distribution centers is developed. Inventory decisions in the model are warehouse order sizes and a common global service level consisting of a homogeneous maximum allowed stock-out probability for each warehouse, assuming stochastic demands with a generic formulation. Subsequently, a second specific formulation is derived considering a normal approximation of warehouse demands. Finally, a Newton–Raphson-based algorithm is developed to solve the problem, converging in only a few iterations and seconds for instances with up to 200 parallel warehouses.
The proposed formulation along with the developed solution approach yield significant benefits in comparison with a natural benchmark, without implying substantial additional computational efforts, thus providing significant differences in the obtained service level and lower system costs, which are contributions associated with the proposed approach.
It is worth noting that the studied problem and related variations may arise as a sub-problem within a generalized Benders decomposition for inventory location problems to optimize the supply chain network. Similarly, any two-step local search heuristic or metaheuristics may benefit from employing the proposed approach as a procedure to evaluate every SCN configuration (e.g., fitness evaluation within genetic algorithms). The above arguments enlarge the applicability and relevance of this research.
Relevant future research based on this research may increase its contributions, which involve multi-commodity and multi-period formulations, along with considering other demand distributions. Moreover, empirical distributions may be considered in which expressions involved within the algorithm are derived based on numerical approximations. A simultaneous modeling of decisions and costs at the upstream location level, such as plants or suppliers, denotes a significant extension to be addressed, following most of the literature concerning two-stage supply chain inventory management, as described in the literature review above.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L., P.A.M.-G., F.J.T.-U. and E.O.-B.; Methodology, R.L., P.A.M.-G., F.J.T.-U. and E.O.-B.; Software, R.L.; Validation, R.L., P.A.M.-G. and E.O.-B.; Formal analysis, R.L., P.A.M.-G., F.J.T.-U. and E.O.-B.; Investigation, R.L., P.A.M.-G., F.J.T.-U. and E.O.-B.; Resources, R.L.; Data curation, R.L.; Writing—original draft, R.L. and P.A.M.-G.; Writing—review & editing, R.L., P.A.M.-G., F.J.T.-U. and E.O.-B.; Visualization, R.L.; Supervision, P.A.M.-G.; Project administration, P.A.M.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was partially supported by ANID FONDECYT grant number 11230461 and “Proyecto Iniciación a la Investigación 2022” of Universidad Católica del Norte grant number VRIDT No. 055/2022.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Simchi-Levi, D.; Kaminsky, P.; Simchi-Levi, E. Designing and Managing the Supply Chain: Concepts, Strategies, and Case Studies; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Coyle, J.; Bardi, E.; Langley, J. The Management of Business Logistics: A Supply Chain Perspective; South-Western/Thomson Learning: Mason, OH, USA, 2003; p. 707. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.T.; Nickel, S.; Saldanha-da Gama, F. Facility location and supply chain management—A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 196, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dong, T.; Peng, J.; Ralescu, D. Uncertainty analysis and optimization modeling with application to supply chain management: A systematic review. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi Yazdi, A.; Tan, Y.; Spulbar, C.; Birau, R.; Alfaro, J. An approach for supply chain management contract selection in the oil and gas industry: Combination of uncertainty and multi-criteria decision-making methods. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Gu, L.; Xu, S.; Li, M. Supply Chain Inventory Management from the Perspective of “Cloud Supply Chain”—A Data Driven Approach. Mathematics 2024, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Sajadi, S.M.; Najafi, S.E.; Taghizadeh-Yazdi, M. Multi Objective and Multi-Product Perishable Supply Chain with Vendor-Managed Inventory and IoT-Related Technologies. Mathematics 2024, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozick, L.K.; Turnquist, M.A. Integrating inventory impacts into a fixed-charge model for locating distribution centers. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 1998, 34, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozick, L.K.; Turnquist, M.A. A two-echelon inventory allocation and distribution center location analysis. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2001, 37, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskin, M.; Coullard, C.; Shen, Z. An Inventory-Location Model: Formulation, Solution Algorithm and Computational Results. Ann. Oper. Res. 2002, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.A.; Garrido, R.A. Incorporating inventory control decisions into a strategic distribution network design model with stochastic demand. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2004, 40, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, R.Z.; Rashidi Bajgan, H.; Fahimnia, B.; Kaviani, M. Location-inventory problem in supply chains: A modelling review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 3769–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona, P.; Ordóñez, F.; Marianov, V. Joint location-inventory problem with differentiated service levels using critical level policy. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 83, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona, P.; Angulo, A.; Brotcorne, L.; Fortz, B.; Tapia, P. Fill-rate service level constrained distribution network design. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2024, 31, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskin, M. Network and Discrete Location: Models, Algorithms, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Drezner, Z.; Hamacher, H.W. Facility Location: Applications and Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Eiselt, H.A.; Marianov, V. Foundations of Location Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 155. [Google Scholar]
- Eiselt, H.A.; Marianov, V. Applications of Location Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 232. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, S.H.; Daskin, M.S. Strategic facility location: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 111, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axsäter, S. Exact analysis of continuous review (R, Q) policies in two-echelon inventory systems with compound Poisson demand. Oper. Res. 2000, 48, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, G.P. Exact evaluation of batch-ordering inventory policies in two-echelon supply chains with periodic review. Oper. Res. 2001, 49, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, S.C.; Willems, S.P. Optimizing strategic safety stock placement in supply chains. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2000, 2, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettl, M.; Feigin, G.E.; Lin, G.Y.; Yao, D.D. A supply network model with base-stock control and service requirements. Oper. Res. 2000, 48, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Aqlan, F.; Gao, K. Optimizing multi-echelon inventory with three types of demand in supply chain. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 107, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Gao, K.; Zheng, X. Optimizing two multi-echelon inventory systems for perishable products with price and stock dependent demand in supply chain. Sci. Iran. 2022, 29, 320–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M. Mathematical modelling of inventory and process outsourcing for optimization of supply chain management. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.J.; Liao, J.J.; Lin, S.D.; Chuang, S.T.; Srivastava, H.M. The inventory model for deteriorating items under conditions involving cash discount and trade credit. Mathematics 2019, 7, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, V. Transportation, facility location and inventory issues in distribution network design: An investigation. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1998, 18, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, S.J.; Meller, R.D. The interaction of location and inventory in designing distribution systems. IIE Trans. 2000, 32, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.J.M.; Coullard, C.; Daskin, M.S. A joint location-inventory model. Transp. Sci. 2003, 37, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.A.; Garrido, R.A. A simultaneous inventory control and facility location model with stochastic capacity constraints. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2006, 6, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Loaiza, R.E.; Olivares-Benitez, E.; Miranda Gonzalez, P.A.; Guerrero Campanur, A.; Martinez Flores, J.L. Supply chain network design with efficiency, location, and inventory policy using a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2017, 24, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero Campanur, A.; Olivares-Benitez, E.; Miranda, P.A.; Perez-Loaiza, R.E.; Ablanedo-Rosas, J.H. Design of a logistics nonlinear system for a complex, multiechelon, supply chain network with uncertain demands. Complexity 2018, 2018, 4139601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Sassi, C.; Miranda, P.A.; Paredes-Belmar, G. Lagrangian relaxation for an inventory location problem with periodic inventory control and stochastic capacity constraints. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8237925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Sassi, C.; Paredes-Belmar, G.; Gutiérrez-Jarpa, G. Multi-commodity inventory-location problem with two different review inventory control policies and modular stochastic capacity constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 143, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Ubeda, F.J.; Miranda, P.A.; Roda, I.; Macchi, M.; Durán, O. Modelling and solving spare parts supply chain network design problems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 5299–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Ubeda, F.J.; Miranda-Gonzalez, P.A.; Gutiérrez-Jarpa, G. Integrating supplier selection decisions into an inventory location problem for designing the supply chain network. J. Comb. Optim. 2024, 47, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.A.; Garrido, R.A. Inventory service-level optimization within distribution network design problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 122, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, G.R.; Fallah, A.; Davoudpour, H. A memetic algorithm for integrated location-inventory problem to optimise the total cost and customer service level. Int. J. Integr. Supply Manag. 2022, 15, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Ubeda, F.J.; Miranda, P.A.; Macchi, M. A Generalized Benders Decomposition based algorithm for an inventory location problem with stochastic inventory capacity constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, A.A.; Azad, N. Incorporating location, routing and inventory decisions in supply chain network design. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2010, 46, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiassat, A.; Diabat, A.; Rahwan, I. A genetic algorithm approach for location-inventory-routing problem with perishable products. J. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 42, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askin, R.G.; Baffo, I.; Xia, M. Multi-commodity warehouse location and distribution planning with inventory consideration. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, G.; Miranda, P.A.; Cabrera, E.; Soto, R.; Crawford, B.; Rubio, J.M.; Paredes, F. Solving a novel inventory location model with stochastic constraints and (R, s, S) inventory control policy. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 670528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Malek, L.; Montanari, R.; Meneghetti, D. The capacitated newsboy problem with random yield: The Gardener Problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 115, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An improved forecasting approach to reduce inventory levels in decentralized supply chains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 511–527. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yang, Y.; Cao, M. A New Spectral Three-Term Conjugate Gradient Method with Random Parameter Based on Modified Secant Equation and Its Application to Low-Carbon Supply Chain Optimization. J. Math. 2022, 2022, 8939770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, O.; Chakraborty, D. A single period inventory model with a truncated normally distributed fuzzy random variable demand. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2012, 43, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomopoulos, N.T. Safety Stock. In Demand Forecasting for Inventory Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, F.W. How many parts to make at once. Fact. Mag. Manag. 1913, 10, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.H. A scientific routine for stock control. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1934, 13, 116–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, T. Numerical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).