Abstract
Mine ventilation is crucial for ensuring safe production in mines, as it is integral to the entire underground mining process. This study addresses the issues of high energy consumption, regulation difficulties, and unreasonable regulation schemes in mine ventilation systems. To this end, we construct an optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation using mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP), focusing on objectives such as minimizing energy consumption, optimal regulation locations and modes, and minimizing the number of regulators. We analyze the construction methods of the mathematical optimization model for both selected and unselected fans. To handle high-order terms in the MINLP model, we propose a variable discretization strategy that introduces 0-1 binary variables to discretize fan branches’ air quantity and frequency regulation ratios. This transformation converts high-order terms in the constraints of fan frequency regulation into quadratic terms, making the model suitable for solvers based on globally accurate algorithms. Example analysis demonstrate that the proposed method can find the optimal solution in all cases, confirming its effectiveness. Finally, we apply the optimization method of ventilation network regulation based on MINLP to a coal mine ventilation network. The results indicate that the power of the main fan after frequency regulation is 71.84 kW, achieving a significant energy savings rate of 65.60% compared to before optimization power levels. Notably, ventilation network can be regulated without adding new regulators, thereby reducing management and maintenance costs. This optimization method provides a solid foundation for the implementation of intelligent ventilation systems.
Keywords:
mine ventilation; ventilation network; ventilation network regulation; mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP); variable discretization MSC:
90C11; 90C20; 90C90
1. Introduction
Mine ventilation is a critical safeguard for ensuring safe production throughout the entire underground mining process. During mine production, surface air must be continuously transported to underground workplaces for personnel to breathe and to dilute and remove various toxic gases and mine dust, ensuring the health and safety of workers. Therefore, a mine ventilation system that is safe, economical, and efficient is fundamental to ensuring mine safety [1,2,3]. However, as mining progresses, the number of roadways increases, leading to an increasingly complex ventilation network. If the ventilation network is not effectively regulated, underground workplaces may not receive sufficient fresh airflow, and the concentration of mine dust and flammable gases may not be adequately controlled, potentially leading to serious incidents such as asphyxiation, explosion, and fire, thereby significantly endangering worker safety.
Moreover, the mine ventilation system is a stochastic system characterized by a complex structure and strong coupling [4], making the regulation of the ventilation network extremely challenging. Traditional ventilation system design and regulation often rely on empirical judgments and simple mathematical models, which are insufficient to effectively respond to the dynamic mine environment and increasingly complex ventilation demands. With rising energy costs and increasingly stringent safety standards for mine operations, how to realize the economic and efficient operation of the ventilation system under the premise of ensuring safety has become an urgent problem.
Therefore, the optimization of mine ventilation network regulation is not only a necessary means to improve the level of mine safety production, but also the key to reducing energy consumption and operating costs. How to ensure the safe, economical, and efficient operation of the ventilation system through scientific and reasonable means of regulation has become a key and difficult problem of mine ventilation network optimization research [5,6]. This research direction holds significant theoretical importance and demonstrates considerable potential and urgent demand in practical applications.
The regulation of mine ventilation networks is a longstanding issue. Historically, mine ventilation engineers depended on personal experience and industry or government practice guidelines to determine the optimal ventilation network regulation scheme through iterative evaluation of airflow and pressure distributions [7]. This method is time-consuming and only meets underground air requirements without ensuring a regulation scheme that provides minimum ventilation energy consumption. Consequently, many researchers have employed operations research methods to address the optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation, aiming to obtain a regulation scheme that minimizes ventilation energy consumption [8,9,10]. The optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation is a large-scale non-convex, nonlinear problem [11], the purpose of which is to determine the operating conditions of the fans, the number of regulators, and their locations to meet the underground air demand requirements and minimize the ventilation energy consumption. Some researchers use nonlinear programming methods to solve the optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation [12,13]. However, these methods often face issues such as low solution efficiency or convergence to non-optimal solutions. To simplify the scale and complexity of the mathematical optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation, Weiming Hu and Ian Longson [14] proposed dividing the problem into two sub-problems: optimal airflow allocation and optimal arrangement of regulators. This method aims to identify the optimal ventilation network regulation scheme. However, while this two-step solution method can minimize ventilation network energy consumption, the number and locations of regulators may not be globally optimal. Consequently, this method has some limitations.
With the advancement of intelligent optimization algorithms, their unique search mechanisms enable effective handling of nonlinear problems. Consequently, many researchers employ these algorithms to address the optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation. Lowndes I.S. and Yang Z.Y. [15] firstly proposed using Genetic Algorithm (GA) for the optimal design of ventilation systems in multi-layer metal mines and further analyzed the effects of coding method and population size on the performance of GA [16]. Additionally, intelligent optimization algorithms, such as the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm [17], Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm [18], Equilibrium Optimizer Algorithm [19], and Sooty Tern Algorithm [20], have been employed to address the optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation. All the above studies focus on minimizing ventilation energy consumption as the optimization objective and establish nonlinear optimization models. However, they do not evaluate the practicality of the locations and numbers of regulators, which is an important consideration in actual ventilation network regulation. Therefore, Kaiyan Cheng et al. [21] proposed an optimization method for mine ventilation network regulation utilizing an improved Differential Evolution Algorithm combined with a critical path algorithm. This method aims to achieve a regulation scheme that minimizes ventilation energy consumption while reducing the number of regulators. Additionally, many researchers have employed multi-objective intelligent optimization algorithms for mine ventilation network regulation. These methods have resulted in more diverse regulation schemes that are applicable to a wider range of scenarios [4,22,23].
For the optimization of mine ventilation network regulation, many studies focus solely on minimizing ventilation energy consumption, often neglecting the comprehensive consideration of the locations and numbers of regulators or the reasonableness of the regulation schemes. Improper placement of regulators can disrupt underground transportation and production processes, while an excessive number of regulators may significantly increase the costs associated with both regulation and maintenance of the mine ventilation system. With the widespread adoption of variable frequency fans in mines [24,25,26], it is crucial for ventilation network regulation schemes to also account for the variable frequency regulation capabilities of these fans. Additionally, while intelligent optimization algorithms significantly simplify the optimization of mine ventilation network regulation, they require substantial computational resources for large-scale, complex problems. Therefore, improvements are needed in their convergence and stability [27,28].
To address these issues, we establish a mixed-integer nonlinear programming model for mine ventilation network regulation, with objectives including ventilation energy consumption, regulation location, regulation mode, and number of regulators, so that the model can be solved by a solver that applies a globally accurate algorithm. And, for whether the mine fans have been selected, we analyze the optimization model construction methods with unselected fans and selected fans, respectively. Meanwhile, to address the high-order terms in the fan frequency regulation constraints of the optimization model for mine ventilation networks with selected fans, we propose a variable discretization strategy to simplify the solution process.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the detailed construction of the mathematical optimization models. Section 3 discusses the variable discretization strategy and case studies. Section 4 applies the proposed methodology to optimize a real operating coal mine ventilation network. Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research.
2. Construction of Optimization Model for Mine Ventilation Network
The optimal regulation scheme for the mine ventilation network must not only minimize energy consumption but also evaluate the practicality of regulation locations, modes, and the number of regulators. Therefore, we establish a multi-objective optimization mathematical model for mine ventilation network regulation based on minimum ventilation energy consumption, optimal regulation location, optimal regulation mode, and minimum number of regulators.
2.1. Optimization Objectives
2.1.1. Minimum Ventilation Energy Consumption
The objective of minimizing ventilation energy consumption can be expressed as
where is the objective of minimum ventilation energy consumption, is the weight coefficient for this objective, is the set of all fan branches , is the power of branch , W, is the air pressure of fan branch , Pa, and is the air quantity of fan branch , m3/s.
2.1.2. Optimal Regulation Location
To facilitate the mathematical description of the objective of optimal regulation location, we introduce a mixed-integer programming method and define as a 0-1 binary variable indicating whether the branch requires regulation. This binary variable must satisfy the following constraints:
where is a larger constant to ensure that , is the air pressure regulation value of the branch , Pa, and is the regulation value that allowed to be ignored in the branch , which satisfies , .
Subject to the above conditions, the binary variable is satisfied:
Thus, the objective of optimal regulation location can be expressed as
where is the objective of optimal regulation location, is the weight coefficient for this objective, is the number of branches of the ventilation network, and is the regulation level of the branch . A positive value, and the larger it is, indicates that the branch cannot be increasing resistance regulation. A negative value, and the smaller it is, indicates that the branch cannot be increasing energy regulation or decreasing resistance regulation. The regulation level is determined by the mine ventilation engineer based on the roadway properties and its adjustability.
2.1.3. Optimal Regulation Mode
To facilitate the mathematical description of the objective of optimal regulation mode, we introduce a mixed-integer programming method and define as a 0-1 binary variable, indicating whether the branch requires increasing resistance regulation, and as a 0-1 binary variable, indicating whether the branch requires increasing energy regulation or decreasing resistance regulation. These binary variables , must satisfy the following constraints:
where is a larger constant to ensure that , and is a larger constant to ensure that .
Subject to the above conditions, these binary variables , can be expressed as
Thus, the objective of optimal regulation mode can be expressed as
where is the objective of optimal regulation mode, and is the weight coefficient for this objective.
2.1.4. Minimum Number of Regulators
The objective of minimum number of regulators can be expressed as
where is the objective of minimum number of regulators, and is the weight coefficient for this objective.
2.2. Constraints
2.2.1. Air Quantity Balance Law (Kirchhoff’s Current Law)
In a ventilation network, the algebraic sum of the air quantity entering and leaving any node is zero.
where is the air quantity of the branch , m3/s, and is the basic association matrix, which represents the relationship between nodes and branches.
2.2.2. Air Pressure Balance Law (Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law)
In a ventilation network, the algebraic sum of the air pressures at each branch of any closed loop is zero.
where is the number of independent loops of the ventilation network, , is the air pressure of the branch , , is the air resistance of the branch , N*s2/m8, is the air pressure regulation value of the branch , Pa, is the fan air pressure of the branch , Pa, and is the independent loop matrix, which represents the relationship between branches and loops.
2.2.3. Mine Fans Operating Constraint
(1) When the fan model is fixed and no changes to the fan are allowed, the operating conditions can be used to determine the fan air pressure characteristic curve. The fan air pressure characteristic curve can be expressed as follows:
where , , and are the fitting coefficients of fan air pressure characteristic curve.
In actual mine ventilation networks, frequency regulation is a crucial method for adjusting the operating conditions of the mine fans [29]. According to the proportionality law of mine fans, it is known
where , are the air pressure before and after the frequency regulation of the fan , Pa, , are the air quantities before and after the frequency regulation of the fan , , is the ratio of the frequency regulation of the fan , and , , are the rotational speeds before and after the frequency regulation of the fan , r/min.
Therefore, by substituting Equations (13) and (14) into Equation (12), the expression for the air pressure characteristic curve under frequency regulation of the fan can be derived as shown in Equation (15). This frequency regulation allows for a broader operating range of the fans, which facilitates the development of a more effective optimization scheme for the mine ventilation network regulation.
Based on this, the objective of minimum ventilation energy consumption, once the fan model has been determined, can be expressed as
(2) When a fan has not yet been installed, the air pressure of the fan branch must exceed the algebraic sum of the air pressures of all branches within the same pathway. Therefore, the fan branch must satisfy the following constraints:
where is the independent pathway matrix, which represents the relationship between branches and pathways, and the number of independent pathways is equal to the number of independent loops.
2.2.4. Air Pressure Regulation Value Constraints
Branch air pressure regulation value shall be satisfied, as follows:
where is the lower limit of the air pressure regulation value of the branch , Pa, and is the upper limit of the air pressure regulation value of the branch , Pa.
2.2.5. Air Quantity Range Constraints
Branch air quantity regulation value shall be satisfied, as follows:
where is the lower limit of the air quantity of the branch , m3/s, and is the upper limit of the air quantity of the branch , m3/s.
2.3. Mathematical Optimization Model of Mine Ventilation Network Regulation
As shown in Table 1, Model I is the mathematical optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation with selected fans. Its decision variables include the frequency regulation ratio , the air pressure regulation value , the air quantity of cotree branches, and the auxiliary decision variables , , and . The air quantities of other branches can be obtained through the air quantities of the cotree branches by using Equation (20), which can greatly reduce the number of decision variables by using them as decision variables. The optimization objectives in Model I involve nonlinear functions with cubic terms, making it a mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) model. Model II, on the other hand, is the mathematical optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation without selected fan. Its decision variables are the air pressure fan branches, the air pressure regulation value , the air quantity of cotree branches, and the auxiliary decision variables , , and . The objective function and constraints in Model II involve nonlinear functions with quadratic terms, making it a mixed-integer quadratic programming (MIQP) model.
where is the air quantity of branch , m3/s, is the independent loop matrix, and is the air quantity of cotree branch , i.e., the air quantity of the independent loop , m3/s.

Table 1.
Mathematical optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation.
3. Model Solving
In the previous section, we constructed mathematical optimization models for mine ventilation network regulation, all of which are nonlinear mixed-integer programming models. Currently, the mainstream commercial solvers GUROBI and CPLEX can only solve mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) and mixed-integer quadratic programming (MIQP) models. From Section 2.3, Model II is an MIQP model, so it can be solved directly using the solvers. As for the cubic terms in Model I, we propose a variable discretization strategy to convert the cubic term in the optimization objective of minimum ventilation energy consumption (as shown in Equation (16)) into a quadratic term, so that the MINLP model with a cubic term is transformed into the MIQP model, which makes it suitable for solvers to solve in order to reduce the difficulty of solving the model.
3.1. Discretization Strategy for Fan Air Quantity and Frequency Regulation Ratio Variables
To avoid the appearance of cubic terms in the optimization objective of minimum ventilation energy consumption, we convert these cubic terms into quadratic terms by introducing 0-1 binary variables to discretize both the fan air quantity and frequency regulation ratio variables. The air quantity of the fan branch is discretized over its range based on a fixed accuracy, so that it takes the values of {}, where is the -th discrete value of the air quantity for the fan branch , . Similarly, the frequency regulation ratio of fan branch takes the values of {}, where is the -th discrete value of the frequency regulation ratio for the fan branch , .
We define the 0-1 binary variable to indicate whether the air quantity of the fan branch takes the value and the 0-1 binary variable to indicate whether the frequency regulation ratio of the fan branch takes the value ,
To restrict the values of and , the following constraints should be satisfied:
The above constraints imply that only one of the binary variables takes the value of 1, i.e., the air quantity of the fan branch must be one of {}; and only one of the binary variables takes the value of 1, i.e., the frequency regulation ratio for the fan branch must be one of {}. Furthermore, it follows from the characterization of the binary variables
Therefore, the cubic terms , , and in the optimization objective of minimum ventilation energy consumption of Model I can be simplified by transforming them into quadratic and linear terms.
Therefore, the optimization objective for minimizing ventilation energy consumption in Model I, using the discretization strategy, can be expressed as
Model I after discretization of the fan air quantity variables and the frequency regulation ratio variables is shown in Equation (27). This model is an MIQP model whose decision variables are the fan branch air quantity discrete variables , the frequency regulation ratio discrete variable , the air pressure regulation value , the air quantity of cotree branches, and the auxiliary decision variables , , and .
3.2. Example Analysis
3.2.1. Optimization of Ventilation Network Regulation with Single Fan
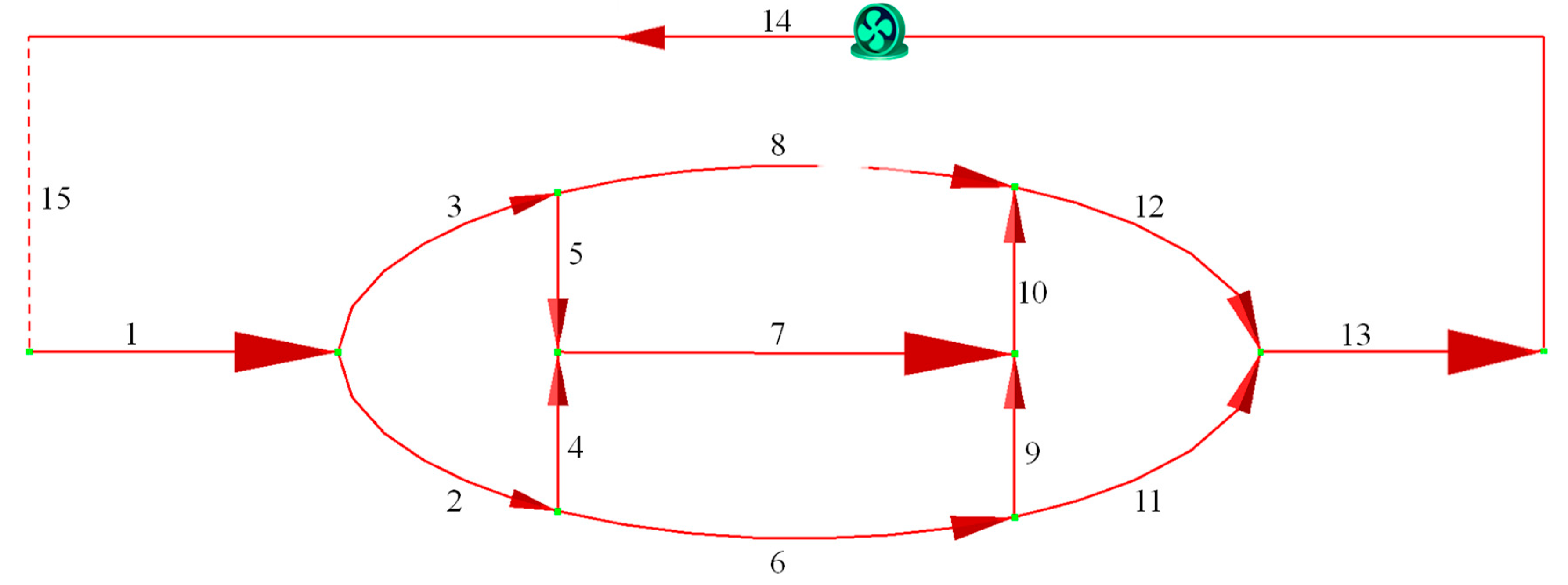
In the ventilation network with single fan shown in Figure 1, branches 6 and 7 are fixed-airflow branches with air quantities of 30 m3/s and 40 m3/s, respectively, while branch 14 is a pre-selected fan branch with an air quantity of 95 m3/s. Branches 1, 13, 14, and 15 are non-adjustable branches with a regulation level of −100, while the remaining branches can be adjusted by increasing resistance with a regulation level of −1. The solution was computed using GUROBI 10.0.1 with a runtime of 0.1 s. The parameters of both the optimized and original ventilation networks are provided in Table 2, and the optimization results are consistent with the improved Differential Evolution Algorithm combined with the critical path algorithm (IDECP) used in reference [21] and the Interior Penalty Function (IPF) method used in reference [30].
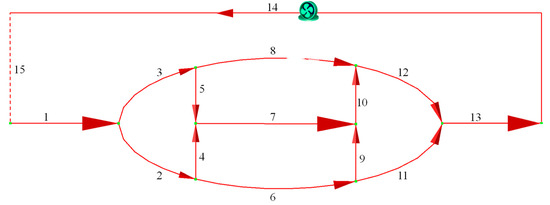
Figure 1.
Diagram of ventilation network with single fan (the number indicates the branch number).

Table 2.
Optimized and original parameters of ventilation network with single fan.
3.2.2. Optimization and Regulation of Ventilation Network Regulation with Multiple Fans
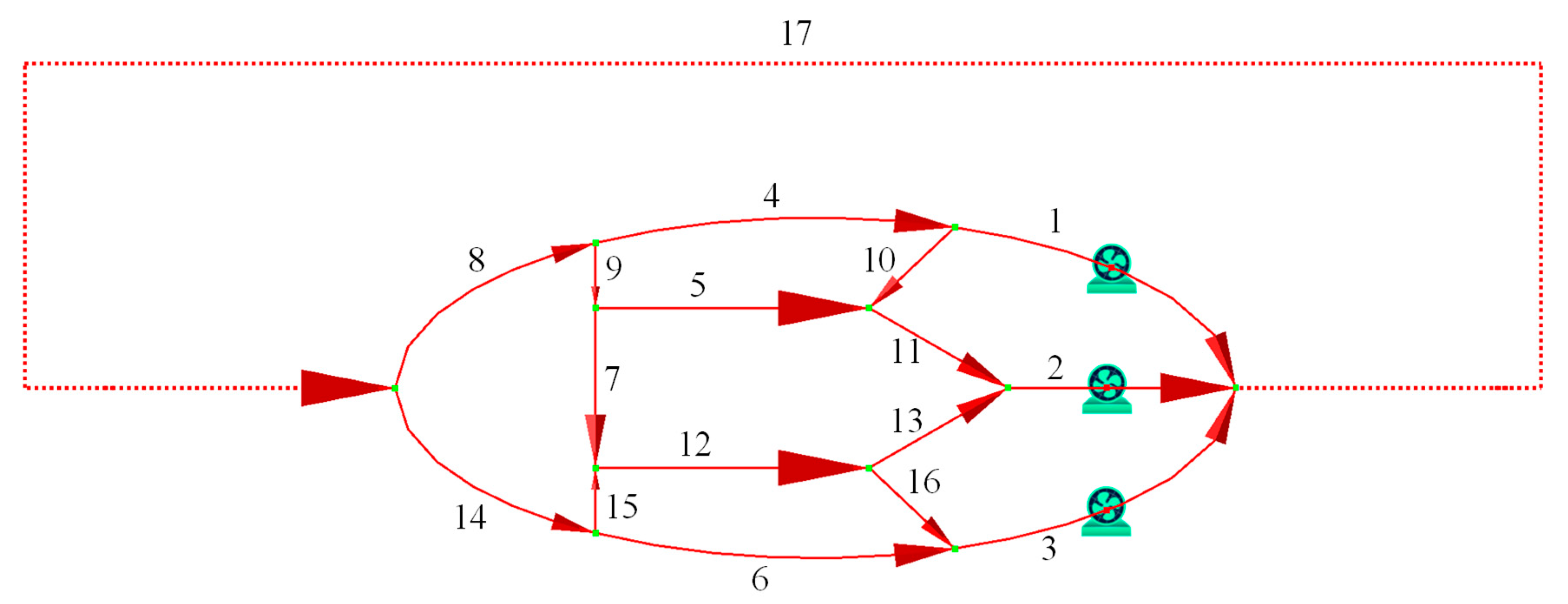
In the ventilation network with multiple fans shown in Figure 2, branch 10 is a fixed-airflow branch with air quantity of 1 m3/s. Branches 1, 2, and 3 are pre-selected fan branches with air quantities of 25 m3/s, 60 m3/s, and 35 m3/s, respectively. The fan branches are non-adjustable with a regulation level of −100, while the remaining branches can be adjusted by increasing resistance with a regulation level of −1. The solution was computed using GUROBI 11.0.1 with a runtime of 0.29 s. The parameters of both the optimized and original ventilation networks are provided in Table 3. The total power of the optimized mine fans is 250.22 kW. The optimization results are consistent with those reported in reference [21] and are superior to the results obtained using the Constrained Variable Metric (SVM) method in reference [31].
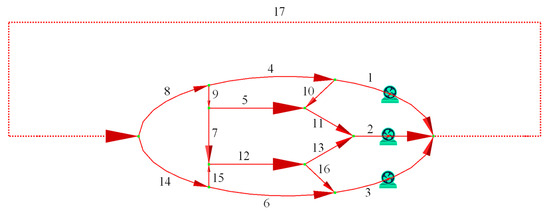
Figure 2.
Diagram of ventilation network with multiple fans (the number indicates the branch number).

Table 3.
Optimized and original parameters of ventilation network with multiple fans.
4. Case Study
4.1. Overview of the Ventilation Network of a Coal Mine
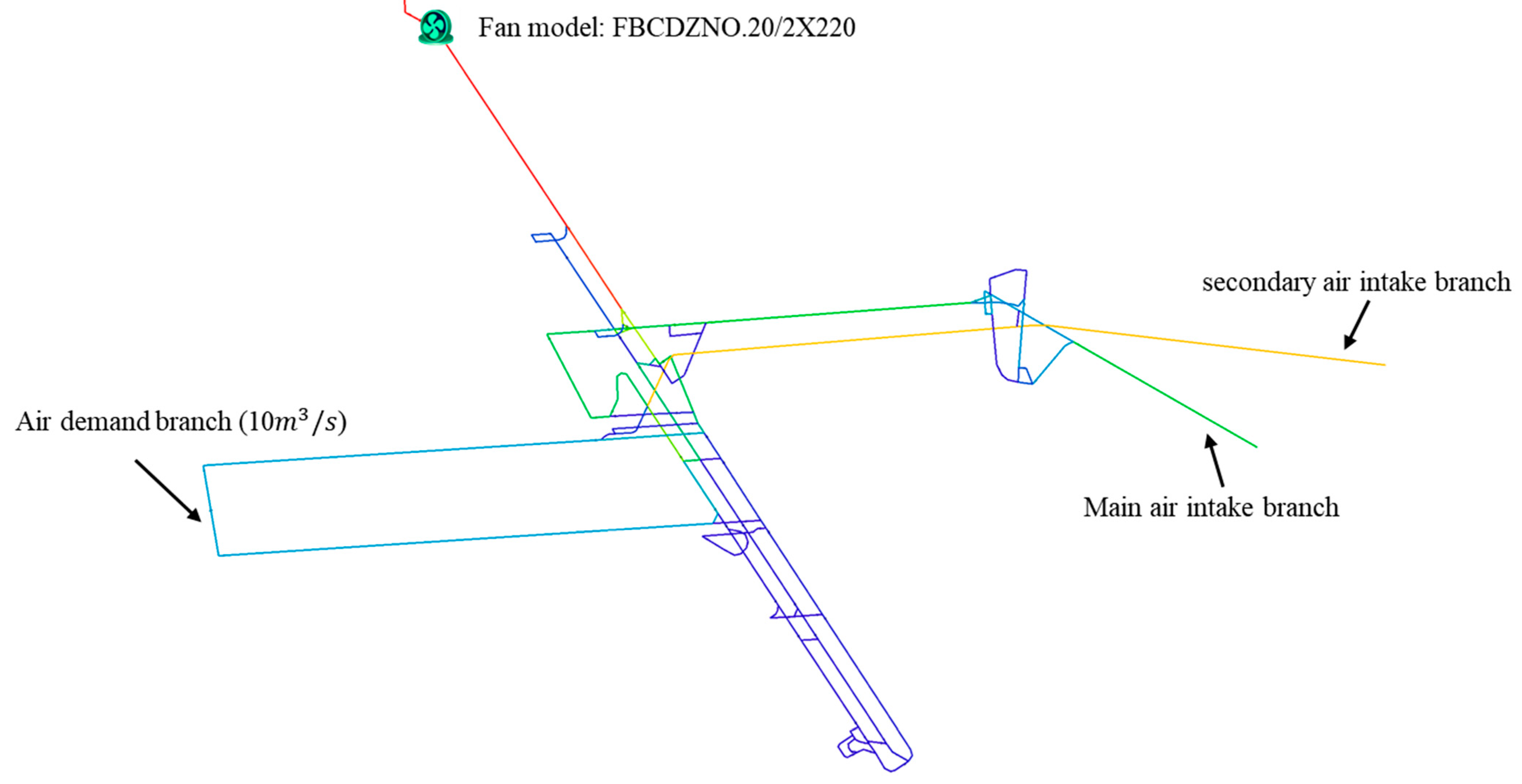
The ventilation network of a coal mine is shown in Figure 3. The ventilation network comprises 95 nodes (), 125 branches (, and 31 independent loops (). Branch 122 is an air demand branch with an air quantity of 10 m3/s. Branch 94 is a fan branch, and the main fan model is FBCDZNO.20/2X220. The air pressure characteristic curve of the main fan is , with a frequency range of 35 Hz to 50 Hz. The basic parameters of some roadways in the ventilation network are shown in Table 4. ‘Regulator’ in the roadway type indicates that the roadway is equipped with a regulation windscreen or damper.
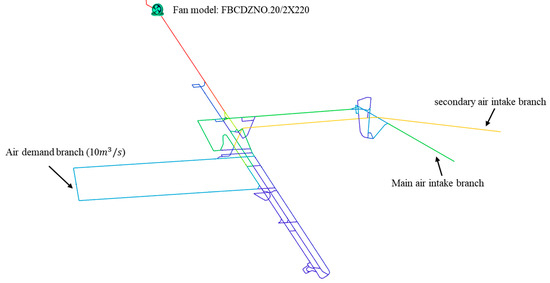
Figure 3.
Ventilation network diagram of a coal mine.

Table 4.
Basic parameters of some roadways in the mine ventilation network.
4.2. Optimization Results
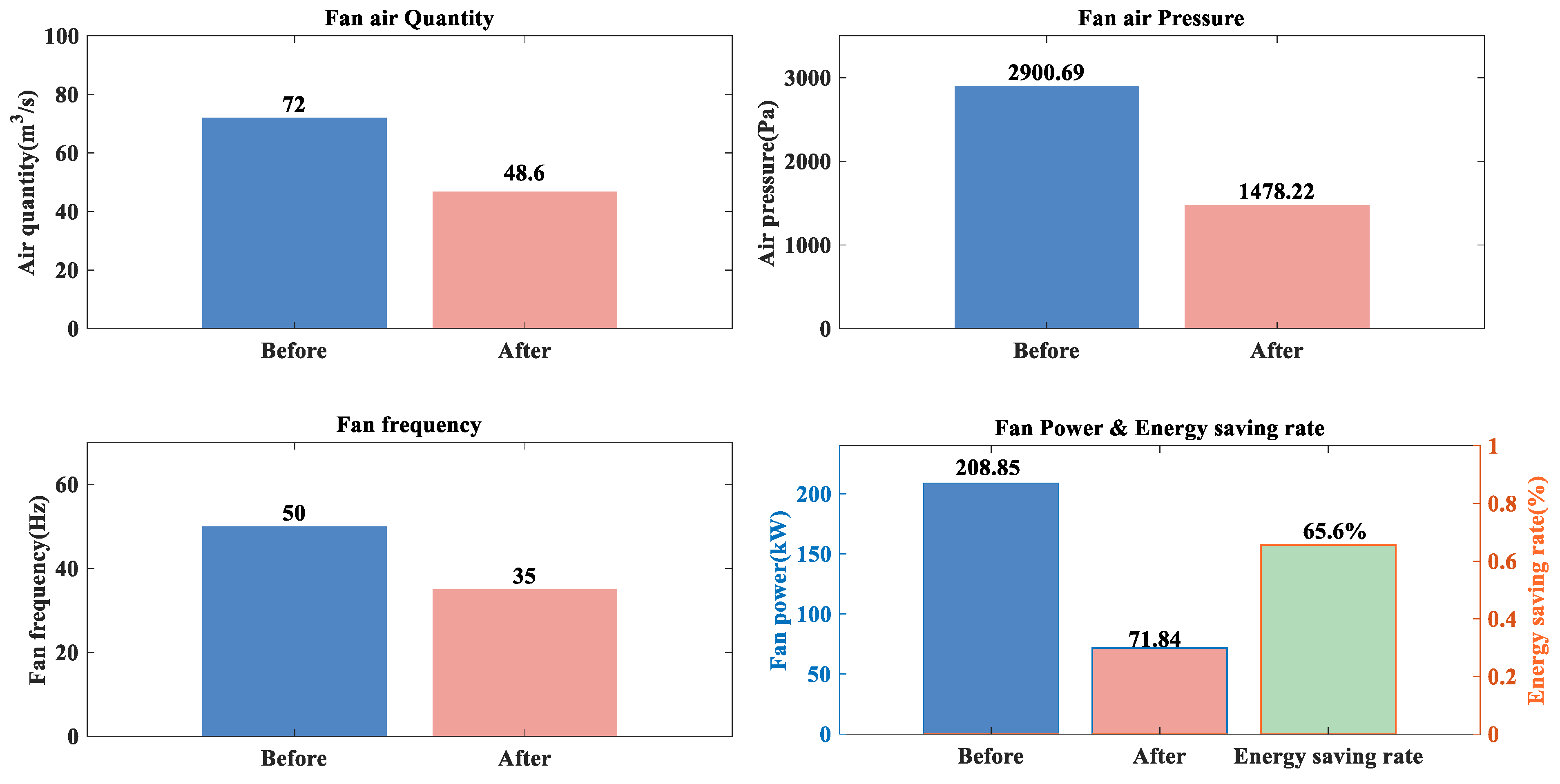
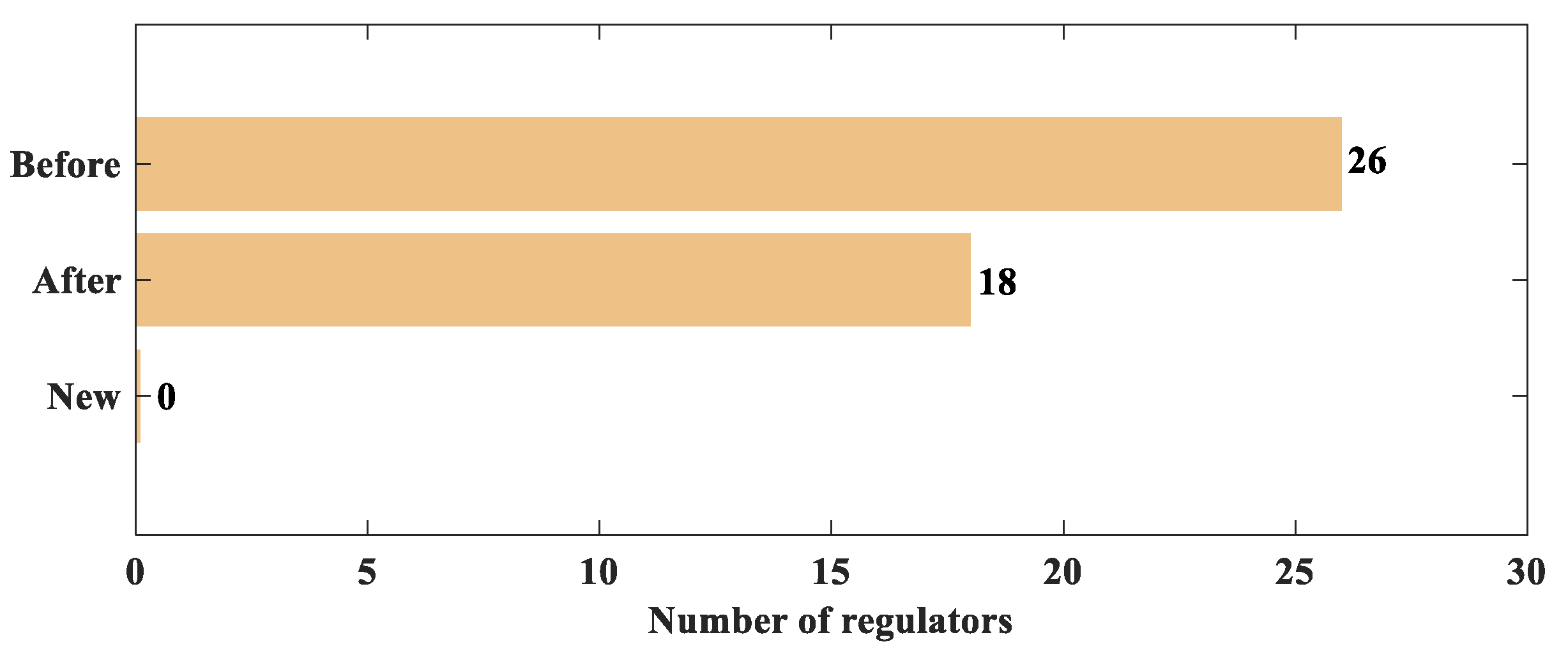
Since the mine is a coal mine and increasing energy regulation is generally avoided in coal mines, only increasing resistance regulation is considered in this regulation optimization process. The regulation levels for all branches are set to be non-positive, with the regulation level of regulator roadways set to 0. Based on the MIQCP mathematical optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation proposed in this paper, a Python program was developed to call the GUROBI 10.0.1 solver for the computation. The comparison of the main mine fan’s parameters before and after optimization is shown in Table 5 and Figure 4. The optimal ventilation network regulation scheme is shown in Table 6 and Figure 5.

Table 5.
Comparison of main fan parameters before and after optimization.
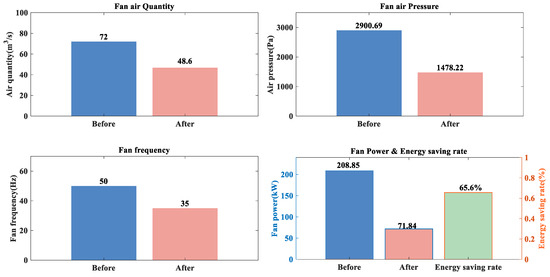
Figure 4.
Comparison of main fan parameters before and after optimization.

Table 6.
Ventilation network regulation scheme.
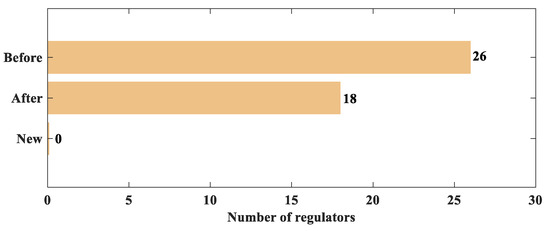
Figure 5.
Comparison of the number of regulators before and after optimization.
The power of the main fan in the current mine ventilation system is 208.85 kW, operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. By applying the method proposed in this paper, the optimized power of the main fan is reduced to 71.84 kW, with a frequency of 35 Hz, resulting in a 65.60% energy saving. As can be seen from Figure 5, in the final ventilation network regulation scheme, all regulation locations are located in the original regulation roadways. This means that there is no need to add new regulators to ensure underground safety, and the regulators in the existing 18 regulation roadways are sufficient for complete network optimization. This approach not only reduces the number of regulators requiring maintenance and upkeep by eight, but also significantly lowers the energy consumption and costs associated with regulating the ventilation network.
In summary, the optimization method of mine ventilation network regulation based on mixed-integer nonlinear programming can effectively reduce energy consumption, lower management and maintenance costs, and enhance the operational efficiency of the mine ventilation system, thereby providing robust decision support for the optimization of coal mine ventilation systems.
5. Conclusions and Future Works
In this paper, the optimization method of mine ventilation network regulation based on mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) is investigated. By introducing 0-1 binary variables and variable discretization strategy, the problem of not being able to optimize the regulation location, regulation mode, and the number of regulators at the same time in the traditional method is solved. The main conclusions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- An optimization model for mine ventilation network regulation was constructed, targeting the optimization of ventilation energy consumption, regulation location, regulation mode, and the number of regulators. The model construction methods were thoroughly analyzed for ventilation networks with and without fans.
- (2)
- To address the difficulty in solving the mixed-integer nonlinear programming model for mine ventilation networks with fans, a variable discretization strategy was proposed. By introducing 0-1 binary variables to discretize fan air quantity and frequency regulation ratio variables, the cubic terms in the objective function of minimum ventilation energy consumption were transformed into quadratic terms and linear terms, converting the model into a mixed-integer quadratic programming (MIQP) model. This approach provides a new solution to the optimization problem of mine ventilation network regulation.
- (3)
- The proposed optimization method was applied to a coal mine ventilation network, significantly reducing ventilation energy consumption with an energy saving rate of 65.60%. The optimization required no new regulators; instead, it is only necessary to deactivate the regulators in eight branches to achieve complete regulation of the entire ventilation network. This not only reduced the regulation costs but also lowered the management and maintenance costs of the ventilation network, providing technical support for intelligent ventilation systems.
Based on the findings of this study, future work will focus on developing dynamic regulation models capable of real-time adaptation to changing mine production conditions. This includes designing advanced control systems that continuously monitor and adjust the ventilation network using real-time data, thereby ensuring optimal performance across various operating scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W. (Lixue Wen) and D.Z.; methodology, L.W. (Lixue Wen) and D.Z.; software, L.W. (Lixue Wen); validation, L.W. (Lixue Wen), D.Z. and L.B.; formal analysis, L.W. (Lixue Wen) and D.Z.; investigation, L.W. (Lixue Wen), D.Z., L.B., L.W. (Liguan Wang), and Y.L.; resources, L.W. (Liguan Wang); data curation, L.W. (Lixue Wen); writing—original draft preparation, L.W. (Lixue Wen) and D.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.W. (Lixue Wen), D.Z., L.B., L.W. (Liguan Wang), and Y.L.; visualization, L.W. (Lixue Wen) and Y.L.; supervision, L.B.; project administration, L.W. (Lixue Wen); funding acquisition, L.B. and L.W. (Liguan Wang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2023YFC2907305, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2022YFC2904105, and the State Key Laboratory for Fine Exploration and Intelligent Development of Coal Resources, CUMT, grant number SKLCRSM24KF003.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We also thank the reviewers for their comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Deyun Zhong, Lin Bi and Liguan Wang were employed by the company Changsha DIMINE Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Hartman, H.L.; Mutmansky, J.M.; Ramani, R.V.; Wang, Y.J. Mine Ventilation and Air Conditioning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brodny, J.; Tutak, M. Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics in Research on Ventilation Safety during Underground Hard Coal Mining: A Systematic Literature Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 373–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shi, D. Diffusion Characteristics of Airflow and CO in the Dead-End Tunnel with Different Ventilation Parameters after Tunneling Blasting. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36269–36283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H. Optimization and Control of Mine Ventilation System Based on PSO Algorithm. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Han, Z.; Wei, L.; Zuo, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, A. Intelligent On-Demand Adjustment Algorithm and Key Technology of Mine Air Flow. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2021, 50, 725–734. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Research on Technology of Key Steps of Intelligent Ventilation in Mines. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 178–195. [Google Scholar]
- Acuña, E.I.; Lowndes, I.S. A Review of Primary Mine Ventilation System Optimization. Interfaces 2014, 44, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Topuz, E. Comparison of Methods for Determination of Booster Fan Locations in Underground Mines. In Proceedings of the 4th Mine Ventilation Symposium, Berkeley, CA, USA, 5–7 June 1989; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J. A Procedure for Solving a More Generalized System of Mine Ventilation Network Equations. In Proceedings of the 4th US. Mine Ventilation Symposium, Berkeley, CA, USA, 5–7 June 1989; SME: Littleton, CO, USA, 1989; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.S.; Topuz, E. Analysis of Mine Ventilation Systems Using Operations Research Methods. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 1998, 5, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaaba, W.; Frimpong, S.; El-Nagdy, K.A. Optimisation of Mine Ventilation Networks Using the Lagrangian Algorithm for Equality Constraints. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2015, 29, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueng, T.H.; Wang, Y.J. Analysis of Mine Ventilation Networks Using Nonlinear Programming Techniques. Int. J. Min. Eng. 1984, 2, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J. A Non-Linear Programming Formulation for Mine Ventilation Networks with Natural Splitting. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1984, 21, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Longson, I. The Optimization of Airflow Distribution in Ventilation Networks Using a Nonlinear Programming Method. Min. Sci. Technol. 1990, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowndes, I.S.; Yang, Z.Y. The Application of GA Optimisation Methods to the Design of Practical Ventilation Systems for Multi-Level Metal Mine Operations. Min. Technol. 2004, 113, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowndes, I.S.; Fogarty, T.; Yang, Z.Y. The Application of Genetic Algorithms to Optimise the Performance of a Mine Ventilation Network: The Influence of Coding Method and Population Size. Soft Comput. 2005, 9, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, V.R.; Maity, T.; Burman, S. Energy Saving Possibilities of Mine Ventilation Fan Using Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), Chennai, India, 3–5 March 2016; pp. 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, W.-L.; Qi, J.-J. Research on Control Optimization Method of Mine Ventilation System Based on Intelligent Optimization Algorithm. J. Compurters 2023, 34, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shao, L. A Mine Ventilation System Energy Saving Technique Based on an Improved Equilibrium Optimizer. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 913817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Xue, Y.; Wen, L.; Shi, D. Optimization of Airflow Distribution in Mine Ventilation Networks Using the Modified Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 41, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Si, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, R.; Shao, H.; Zhao, H. Optimization of Air Quantity Regulation in Mine Ventilation Networks Using the Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm and Critical Path Method. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y. Multi-Objective Intelligent Decision and Linkage Control Algorithm for Mine Ventilation. Energies 2022, 15, 7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shao, L. An Optimization Method of Mine Ventilation System Based on R2 Index Hybrid Multi-Objective Equilibrium Optimization Algorithm. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11003–11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, K.; Prosser, B.; Stinnette, J.D. The Practice of Mine Ventilation Engineering. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, V.R.; Maity, T.; Prasad, H. Energy Saving Techniques for Ventilation Fans Used in Underground Coal Mines—A Survey. J. Min. Sci. 2015, 51, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, S.; Kegenhoff, J.; Papesch, M. Ventilation on Demand-Controllable Mine Fans, Applications and Limitations. Min. Rep. 2017, 153, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.-S. Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms: Challenges and Open Problems. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 46, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.M. Evolutionary Algorithms for Large-Scale Global Optimisation: A Snapshot, Trends and Challenges. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2016, 5, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhang, W.; Pei, X.; Cui, C. Intelligent Safety Adjustment of Branch Airflow Volume during Ventilation-on-Demand Changes in Coal Mines. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. Optimization Theory and Application of Mine Ventilation Systems; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2003; ISBN 978-7-81070-756-5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.-S. Solution of Problems Relevant to Optimal Control of Mine Ventilation Network by Non-Linear Programming Technique. J. China Coal Soc. 1995, 20, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).