A Rotational Speed Sensor Based on Flux-Switching Principle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Machine Topology and Working Principle
2.1. Machine Topology
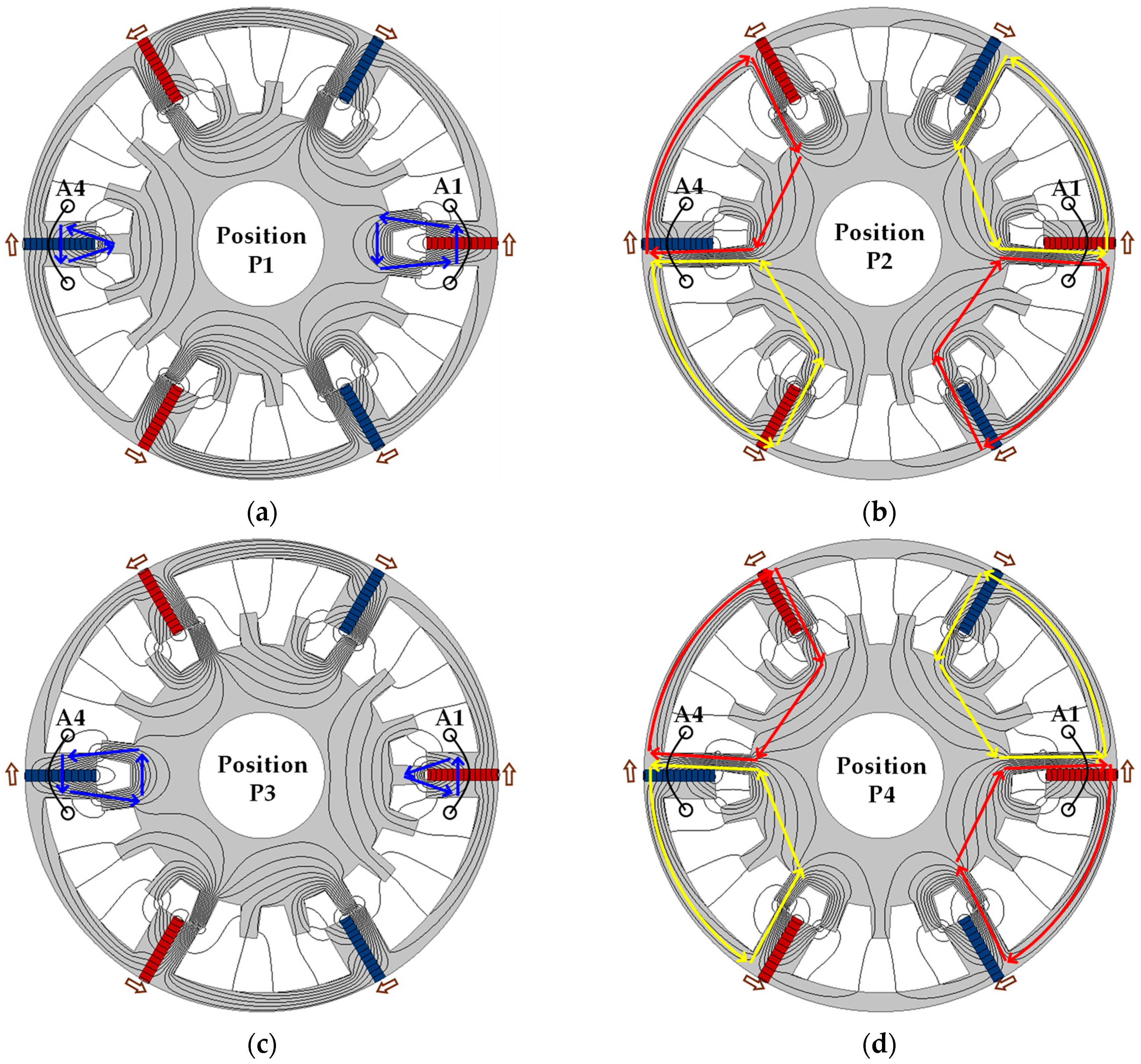
2.2. Working Principle
3. Analytical Modeling of Proposed Machine
3.1. Linear Analytical Model
3.1.1. Simplification and Layer Division
3.1.2. Rotor Slot (I), Airgap (II) and External Regions (VI)
3.1.3. Stator Slot and Stator Yoke Regions (III), (IV)
3.1.4. Boundary Conditions (BCs)
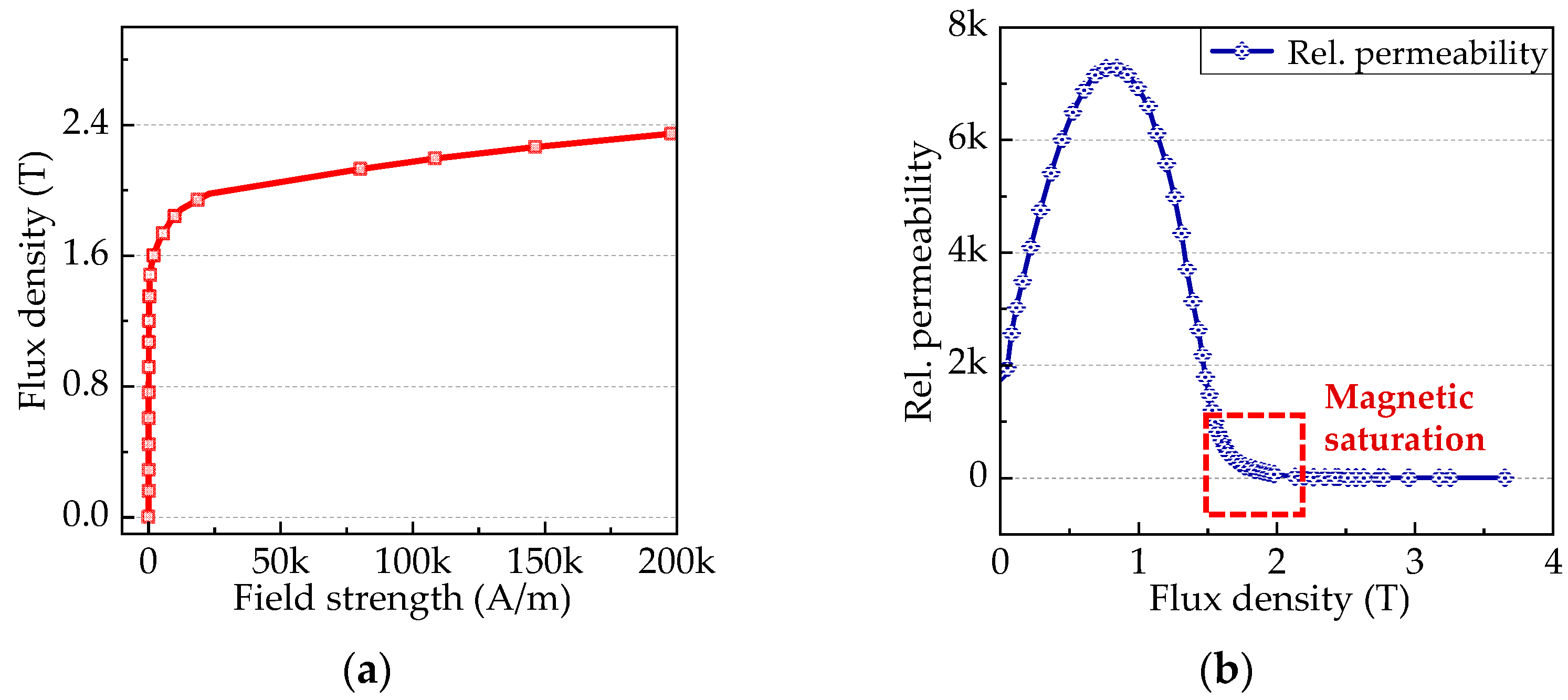
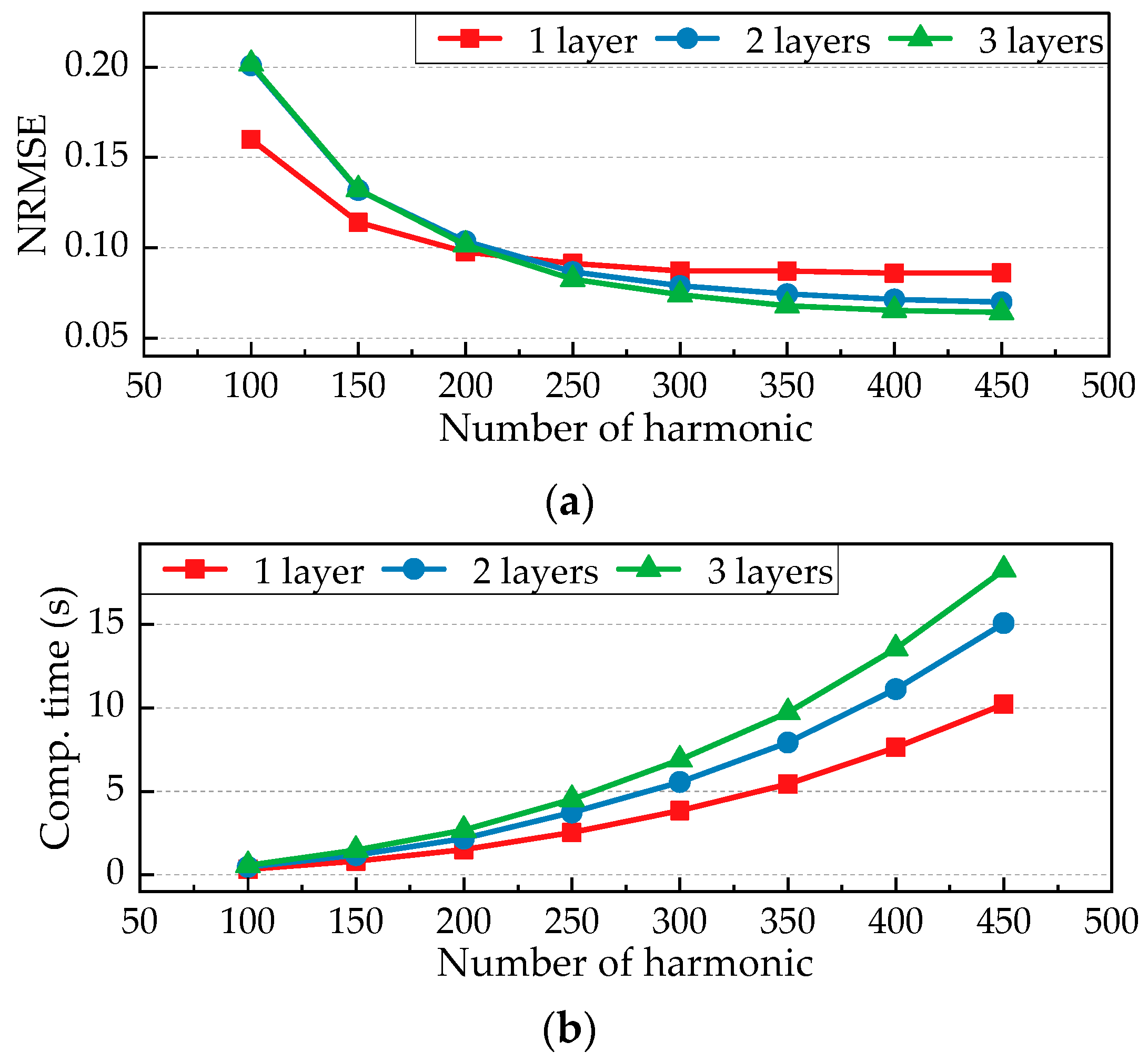
3.1.5. Nonlinear Solution Derivation
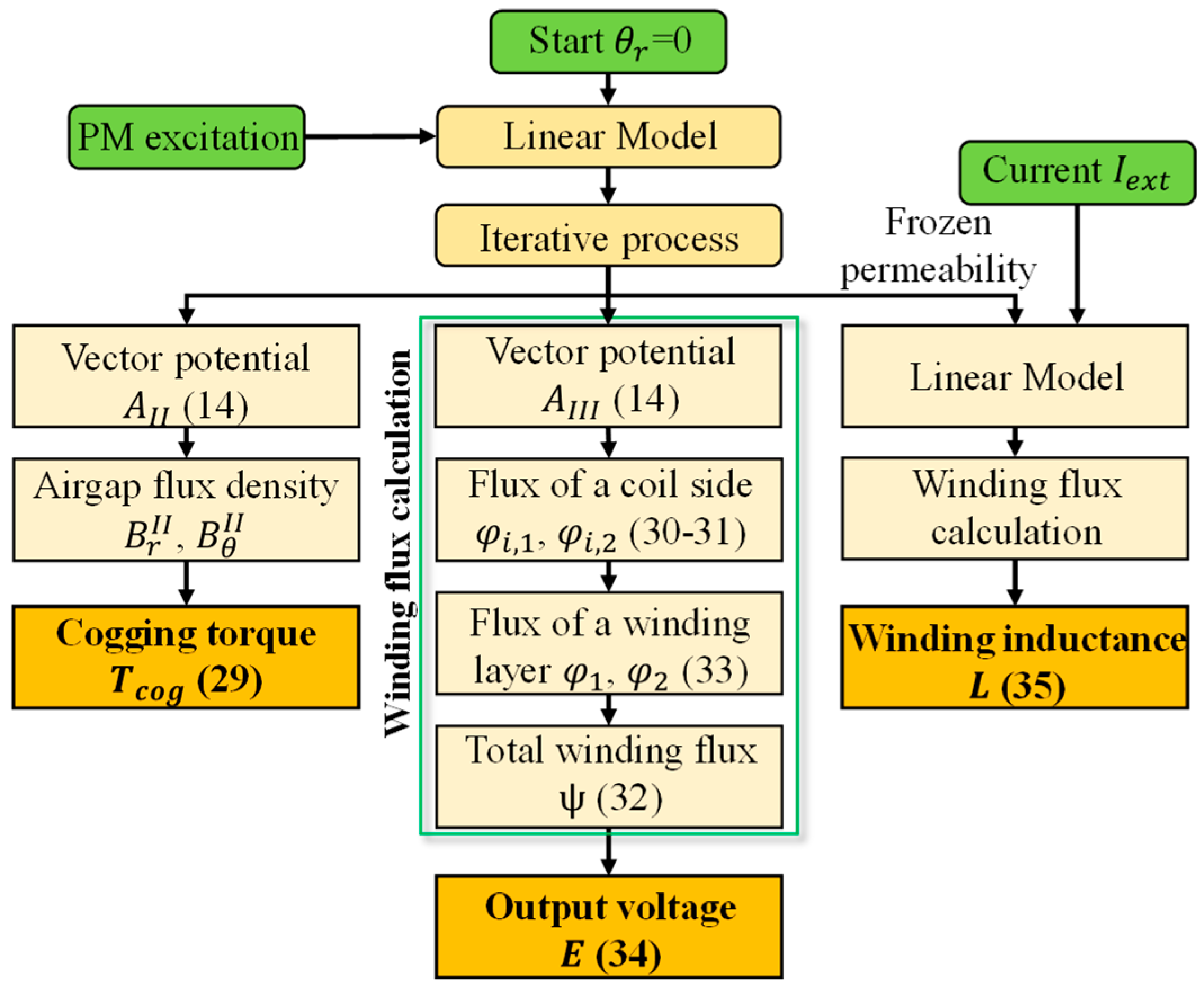
3.2. Performance Derivation
4. FEA Verification
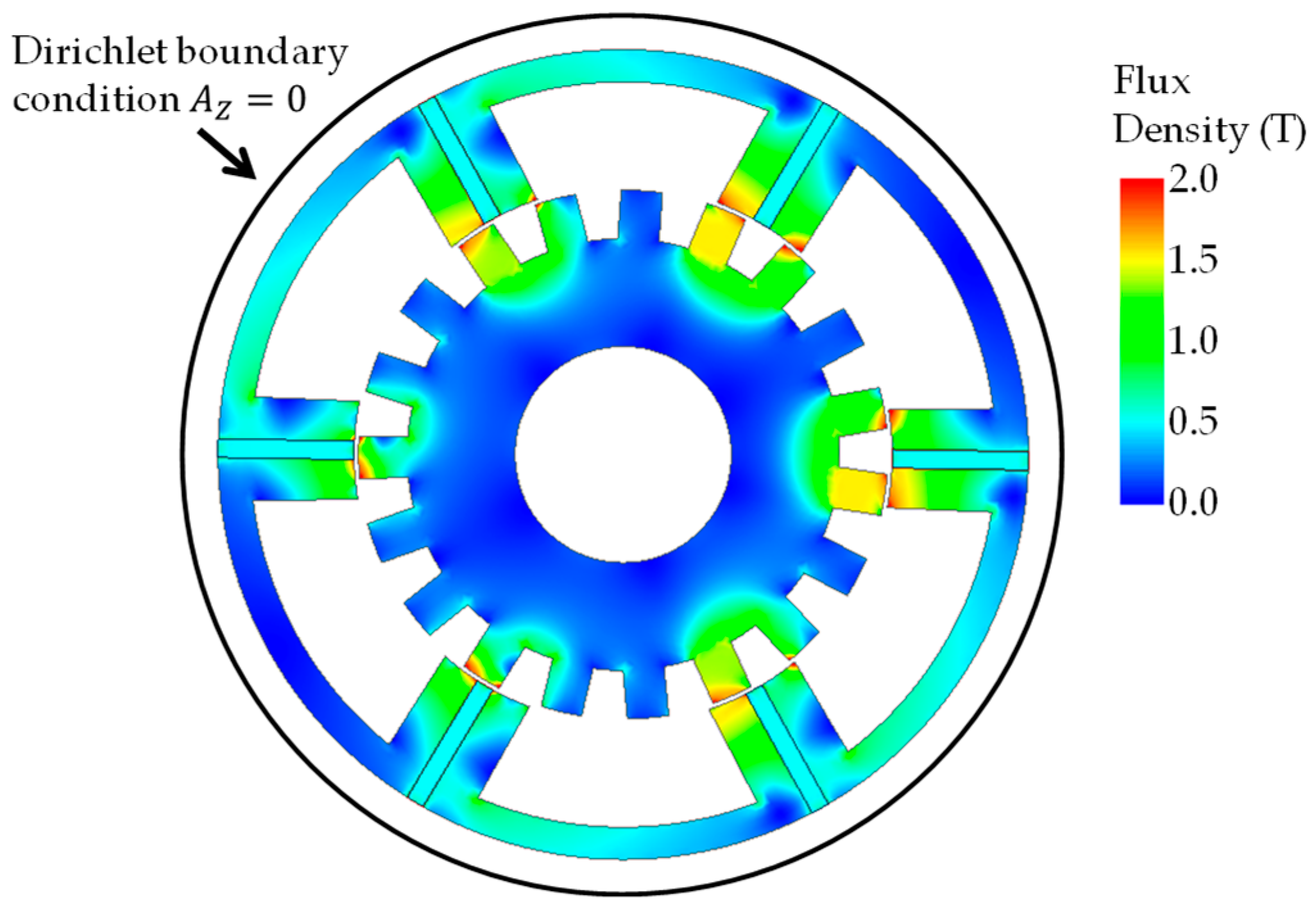
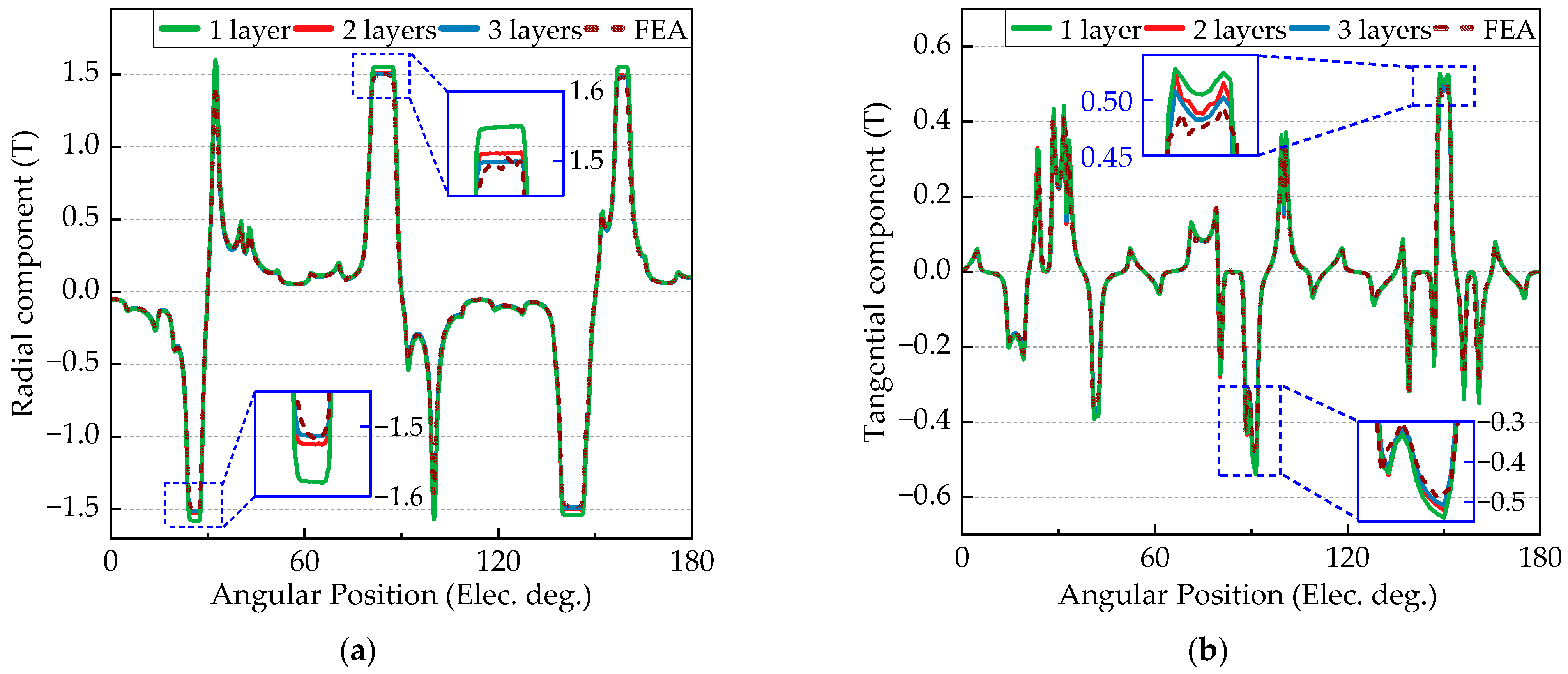
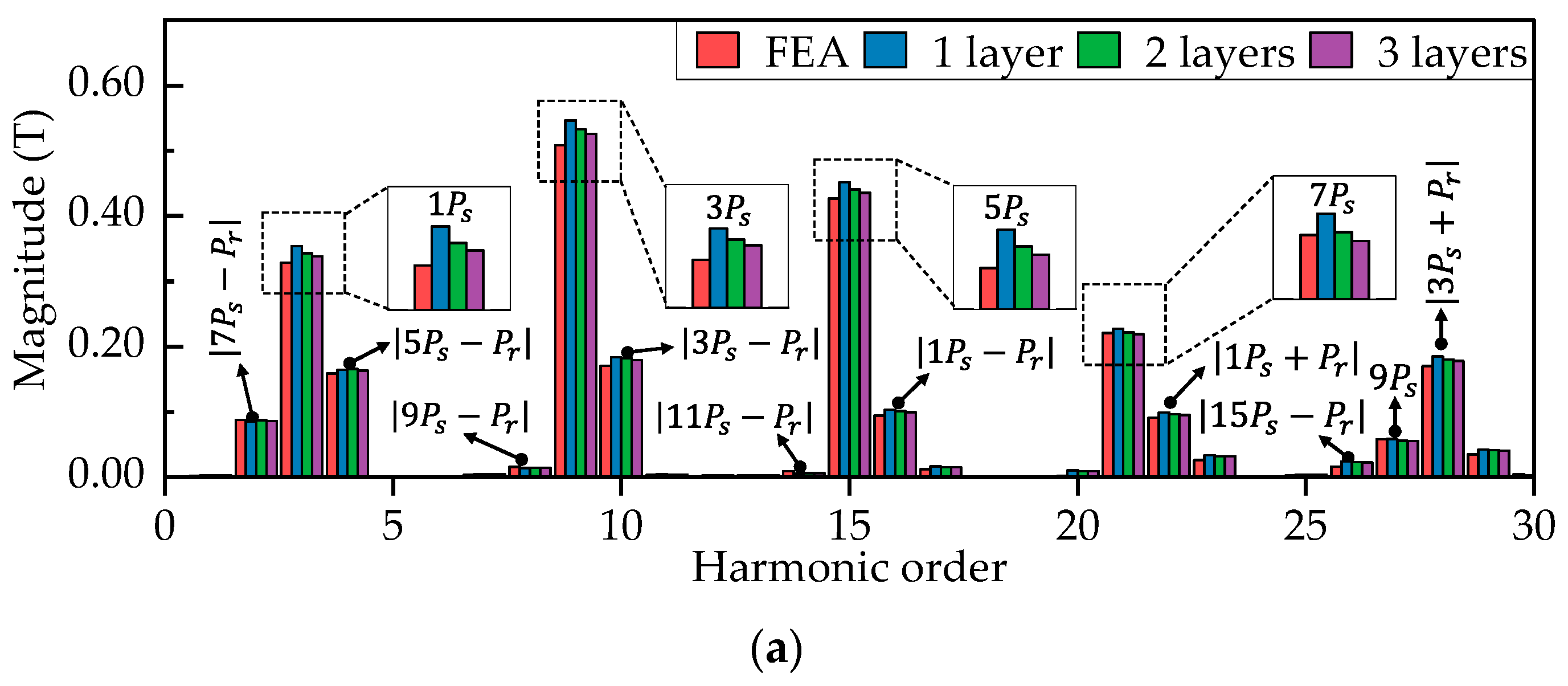
4.1. Magnetic Field Analysis
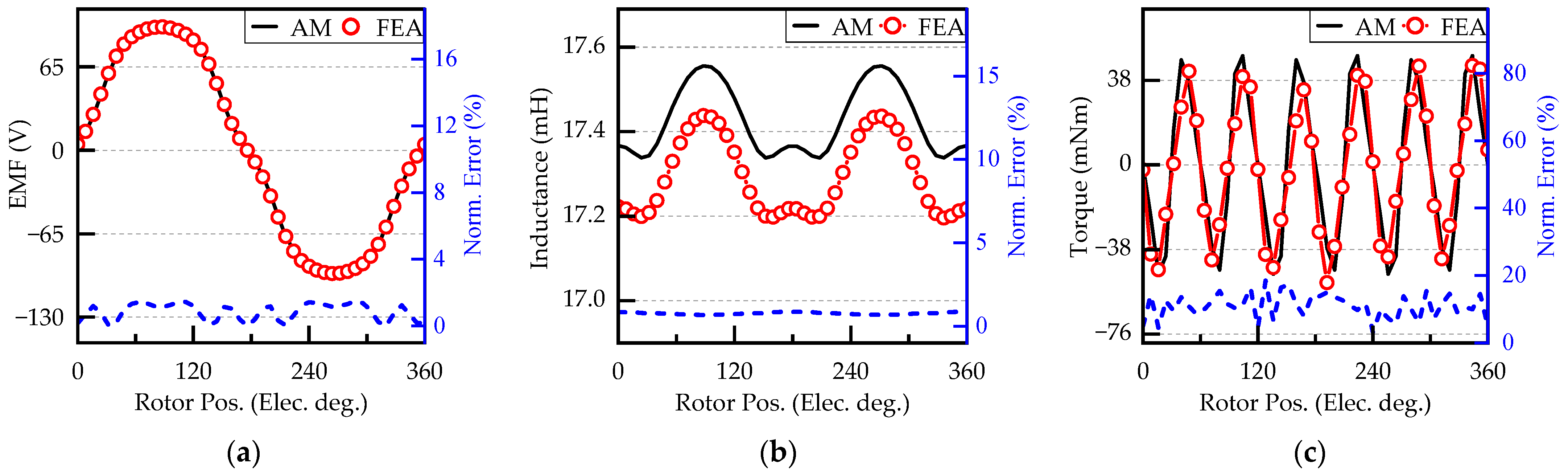
4.2. Performance Comparison
5. Parametric Optimization
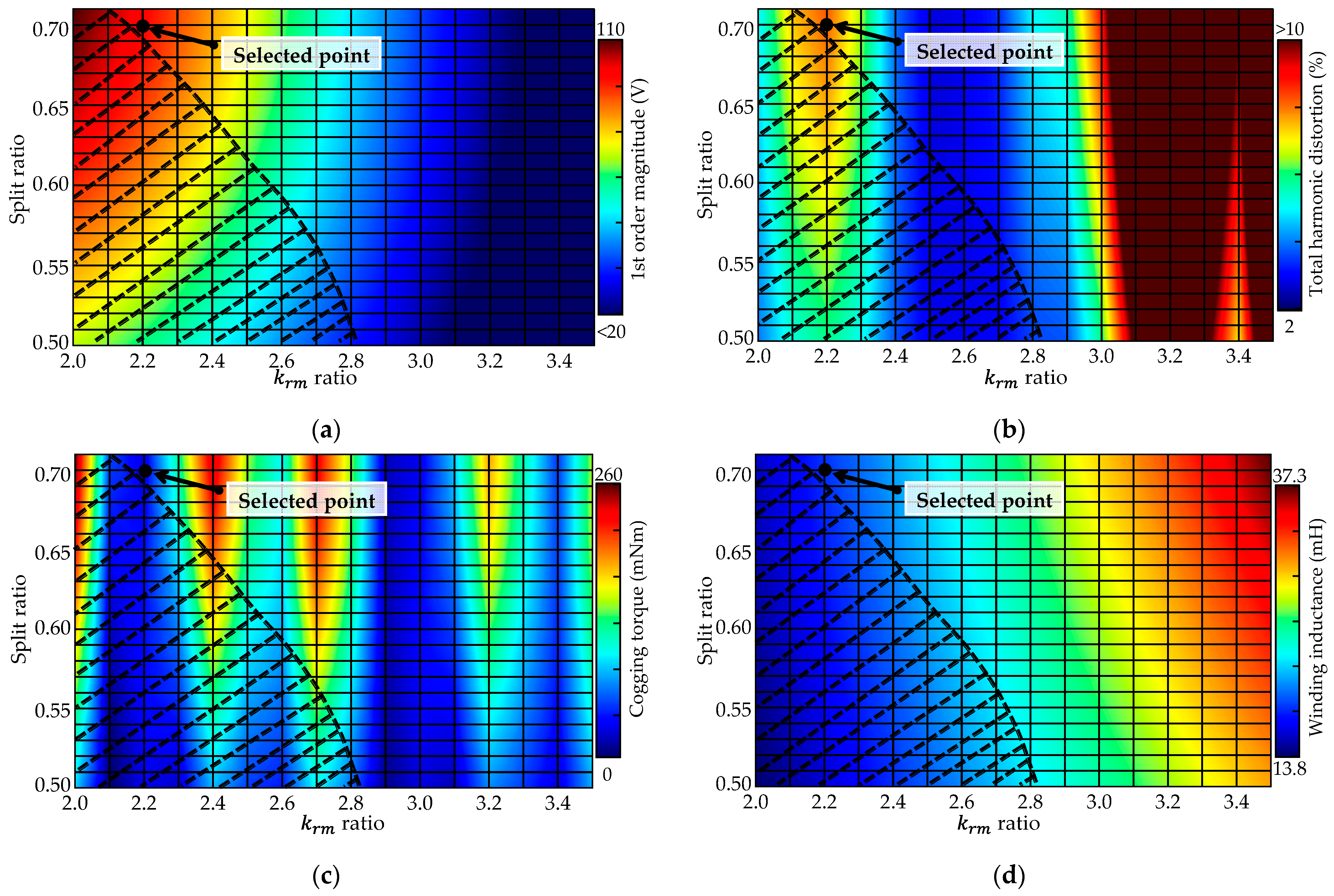
5.1. Split Ratio and Rotor Teeth Ratio
5.2. Stator and Rotor Teeth Width
6. Performance of Optimal Design
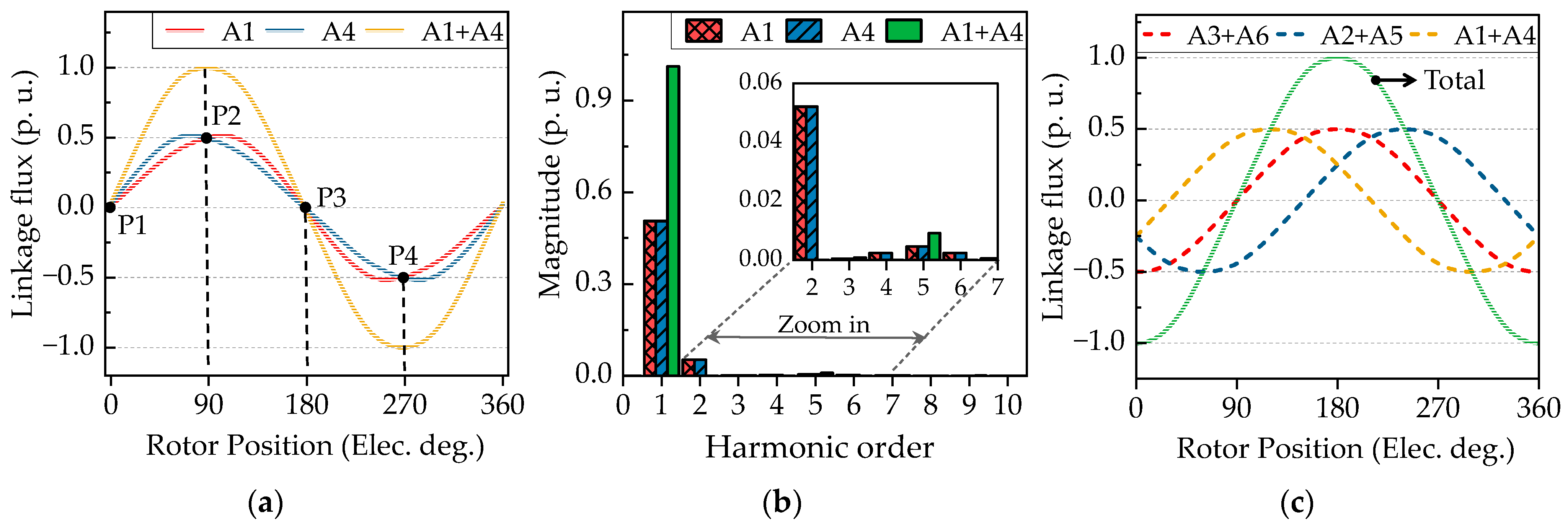
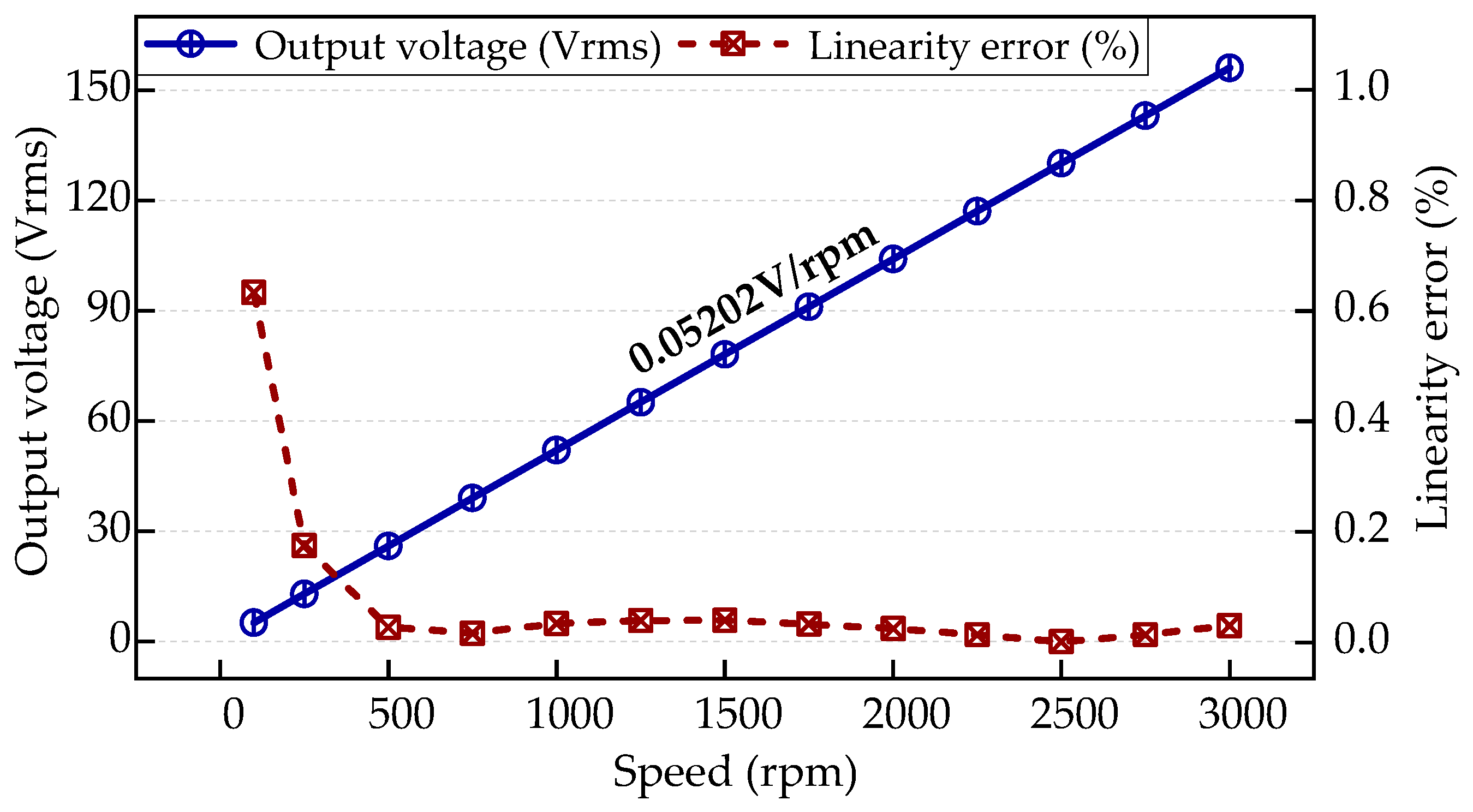
6.1. Voltage Characteristics (Constant Load Characteristics)
6.2. Varying Load Characteristics
7. Conclusions
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, B.; Deng, K.; Xie, L.; Xie, S.; Kang, Y. Speed Measurement Method for Moving Conductors Based on Motion-Induced Eddy Current. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 6005608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addabbo, T.; Di Marco, M.; Fort, A.; Landi, E.; Mugnaini, M.; Vignoli, V.; Ferretti, G. Instantaneous Rotation Speed Measurement System Based on Variable Reluctance Sensors for Torsional Vibration Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H. AC Motor Control and Electrical Vehicle Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L. Analysis and improvement on the structure of variable reluctance resolvers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, C.; Ge, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Woldegiorgis, A.; Chen, D.; Li, S. A Delay-Based Frequency Estimation Scheme for Speed-Sensorless Control of Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 2107–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Ripka, P.; Grim, V. A Novel Structure of an Eddy Current Sensor for Speed Measurement of Rotating Shafts. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüysüz, A.; Flankl, M.; Kolar, J.W.; Mütze, A. Eddy-current-based contactless speed sensing of conductive surfaces. In Proceedings of the SPEC, Auckland, New Zealand, 5–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, D.-T.; Nguyen, M.-D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Phung, A.-T.; Shin, K.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Improved Design of an Eddy-Current Speed Sensor Based on Harmonic Modeling Technique. Mathematics 2025, 13, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, J.J.; Pickard, A.C. A Novel Speed Measurement System for Turbomachinery. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 2, 2501204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Du, L. Modeling and Characteristic Analysis of Variable Reluctance Signal Variation of Rolling Bearing Outer Ring Fault. IEEE Access. 2022, 10, 49542–49550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamal, M. Ramli Development of sensors based on giant magnetoresistance material. Procedia Eng. 2012, 32, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsalis, V.C. Advances in Magnetic Field Sensors. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 939, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.A.; George, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Technologies and Applications of Angle Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, Y.; Hoang, E.; Gabsi, M.; Lécrivain, M.; Allano, S. Design and comparison of different flux-switch synchronous machines for an aircraft oil breather application. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2005, 15, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Winding configurations and optimal stator and rotor pole combination of flux-switching PM brushless AC machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Design of flux-switching permanent magnet machine considering the limitation of inverter and flux-weakening capability. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE IAS, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Taras, P.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q. Comparative Study of Fault-Tolerant Switched-Flux Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Iwasaki, S.; Deodhar, R.P. Influence of slot opening on optimal stator and rotor pole combination and electromagnetic performance of switched-flux PM brushless AC machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Nguyen, M.D.; Woo, J.H.; Shin, H.S.; Shin, K.H.; Phung, A.T.; Choi, J.Y. Volume optimization of high-speed surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor based on sequential quadratic programming technique and analytical solution. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 025319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Nguyen, M.D.; Kim, S.M.; Jung, W.S.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y. Nonlinear Analytical Solution for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using Harmonic Modeling. In Proceedings of the ICEM, Torino, Italy, 1–4 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, D.-T.; Nguyen, M.-D.; Kim, S.-M.; Bang, T.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, K.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Irreversible Demagnetization Prediction Due to Overload and High-Temperature Conditions in PMSM Based on Nonlinear Analytical Model. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, in press.
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Iwasaki, S.; Deodhar, R.P. A novel E-core switched-flux PM brushless AC machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Comparison of all and alternate poles wound flux-switching PM machines having different stator and rotor pole numbers. In Proceeding of the ECCE 2009, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Tong, M. Design Consideration for E-Core Outer-Rotor Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machines From the Perspective of the Stator-Poles and Rotor-Teeth Combinations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 61, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Stator and rotor pole combinations for multi-tooth flux-switching permanent-magnet brushless AC machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 4659–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djelloul-Khedda, Z.; Boughrara, K.; Dubas, F.; Kechroud, A.; Souleyman, B. Semi-Analytical Magnetic Field Predicting in Many Structures of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines Considering the Iron Permeability. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Luk, P.C.K.; Shen, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. A novel permanent-magnet flux switching machine with an outer-rotor configuration for in-wheel light traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W. An Outer-Rotor Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet-Machine With Light Traction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GE1214–Mechanically Connected Tachogenerator with Alternating Voltage Output Signal. Available online: https://www.noris-group.com/products-and-systems/sensors/encoders-and-tachogenerators/ge1214 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Li, J. Topologies and analysis of flux-modulation machines. In Proceeding of the ECCE 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Han, P.; Hua, W. General Airgap Field Modulation Theory for Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6063–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jian, L.; Wei, J.; Shao, Z.; Li, W.; Chan, C.C. A New Perspective on the Operating Principle of Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, B.; Djelloul-Khedda, Z.; Peng, F.; Yao, Y.; Dong, J. Magnetic Field Prediction in Cubic Spoke-Type Permanent-Magnet Machine Considering Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 2208–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Analysis and optimization of back EMF waveform of a flux-switching permanent magnet motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Symbol | Explanation | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radius/tangential and axial directions | th rotor tooth | ||
| Imaginary unit | Initial rotor position | ||
| Magnetic vector potential | Matrix form of magnetic vector potential | ||
| Magnetic flux density | Matrix form of magnetic flux density | ||
| Magnetic field strength | Matrix form of magnetic field strength | ||
| Current density vector | Matrix form of radial component of magnetization | ||
| Permeability | Matrix form of tangential component of magnetization | ||
| CFS coefficient of nth harmonic | |||
| Inverse coefficient of nth harmonic | Permeability convolution matrix in radial direction | ||
| Vacuum permeability | Permeability convolution matrix in tangential direction | ||
| Span angle of stator teeth | |||
| Span angle rotor teeth | Particular solution of Poisson’s equation | ||
| Span angle of PM | |||
| Number of subregions | |||
| Highest harmonic order | Region index | ||
| Radius at the middle of airgap | Stack length of the sensor | ||
| Cogging torque | th layer | ||
| Flux linkage and EMF of the winding | th layer | ||
| Winding inductance | th layer |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Stack length (mm) | 43.0 | |
| Outer/inner stator radius (mm) | 37.5/24.9 | |
| Outer/inner rotor radius (mm) | 24.4/20.0 | |
| Stator/Rotor teeth width (mm) | 3.70/3.85 | |
| PM width (mm) | 1.75 | |
| Stator yoke thickness (mm) | 3.0 | |
| PM remanence (T) | 1.28 | |
| Number of turns per coil | 63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoang, D.-T.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeong, K.-I.; Shin, K.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. A Rotational Speed Sensor Based on Flux-Switching Principle. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081341
Hoang D-T, Lee J-K, Jeong K-I, Shin K-H, Choi J-Y. A Rotational Speed Sensor Based on Flux-Switching Principle. Mathematics. 2025; 13(8):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081341
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoang, Duy-Tinh, Joon-Ku Lee, Kwang-Il Jeong, Kyung-Hun Shin, and Jang-Young Choi. 2025. "A Rotational Speed Sensor Based on Flux-Switching Principle" Mathematics 13, no. 8: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081341
APA StyleHoang, D.-T., Lee, J.-K., Jeong, K.-I., Shin, K.-H., & Choi, J.-Y. (2025). A Rotational Speed Sensor Based on Flux-Switching Principle. Mathematics, 13(8), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081341









