Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics: New Directions for Didactics in U.S. Mathematics Education
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Literature
2.1. Research on Mathematics Didactics in the U.S.
2.2. Critical Mathematics Didactics (Since the Term Didactics Is Not Commonly Used in the United States, We Simply Use the Words Teaching or Pedagogy in Its Place for the Remainder of the Paper)
2.3. Uncharted Territories in Critical Mathematics Pedagogies
2.3.1. Structural Requirements
2.3.2. Homogenous Student Populations
2.3.3. Ethical Dimensions of Mathematics Education
2.4. Ethics and Social Justice
3. Materials and Methods
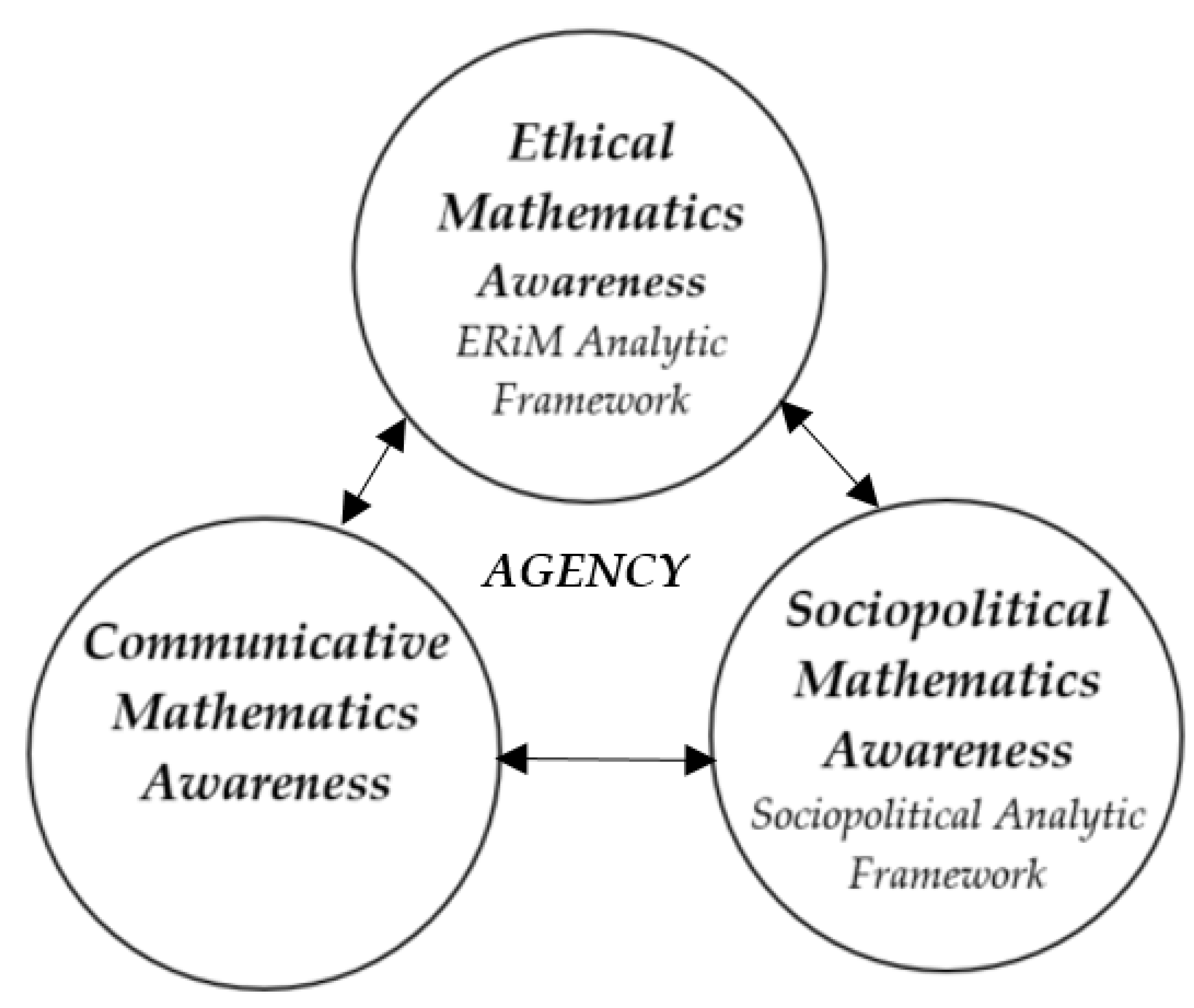
3.1. Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics (ERiM)
- The Ethical Mathematics Awareness that human beings do mathematics; thus, there are potential ethical dilemmas and implications in mathematical work.
- The Communicative Mathematics Awareness that mathematical communication has the power to educate and mis-educate society and encourage the masses to act in certain ways.
- The Sociopolitical Mathematics Awareness that mathematics is used to model and interpret the real world and can be used to make decisions both at the individual and systemic levels that may be oppressive or liberatory.
3.2. Ethical Reasoning in the Mathematics Analytic Framework
3.3. Participants
3.4. Data Collection
4. Results
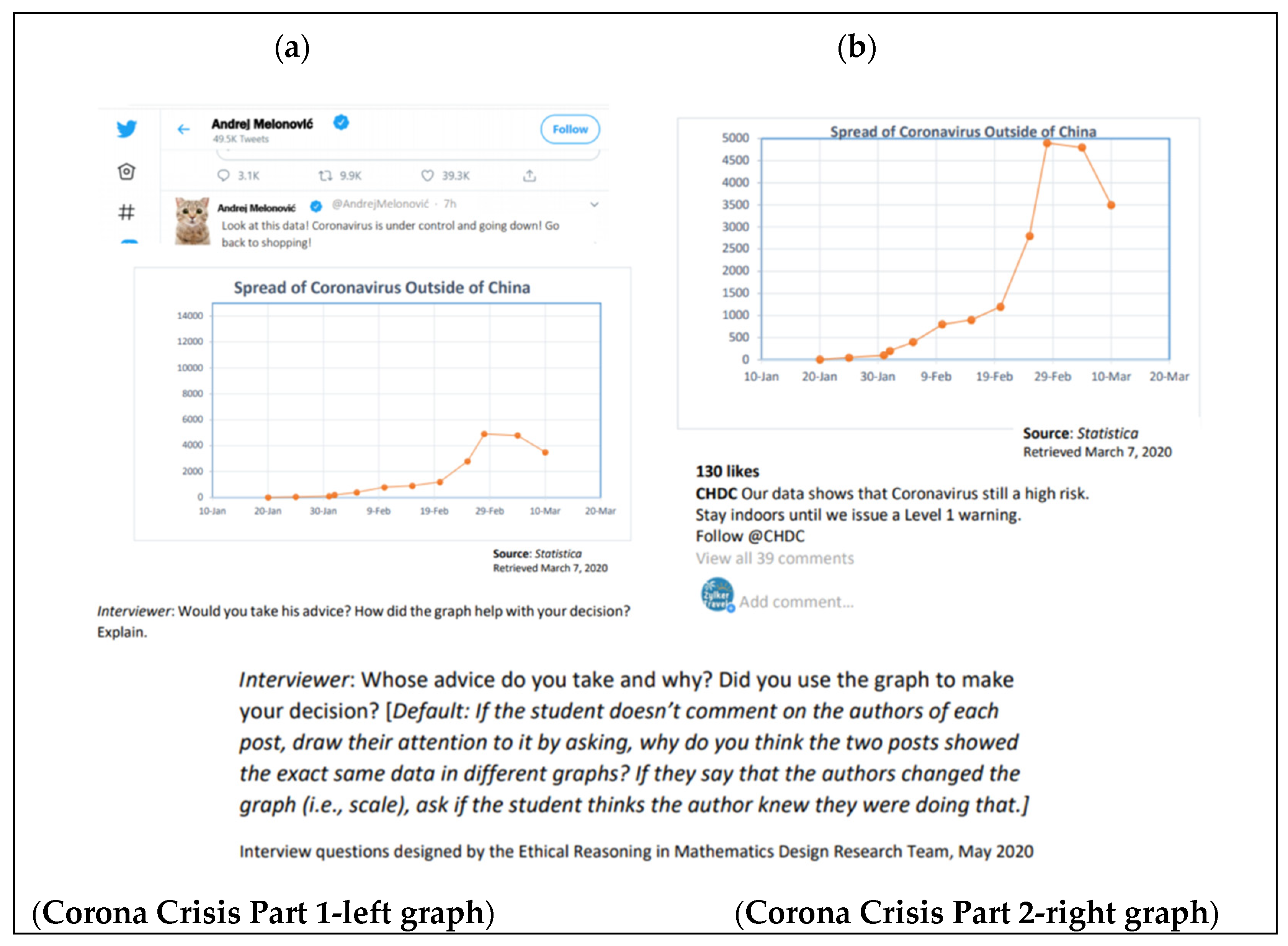
4.1. Corona Crisis
4.1.1. Reasoning with Dynamic Graphs
4.1.2. Questioning Accuracy and Accountability in Data Dissemination
4.1.3. Exhibiting Communicative Mathematical Awareness
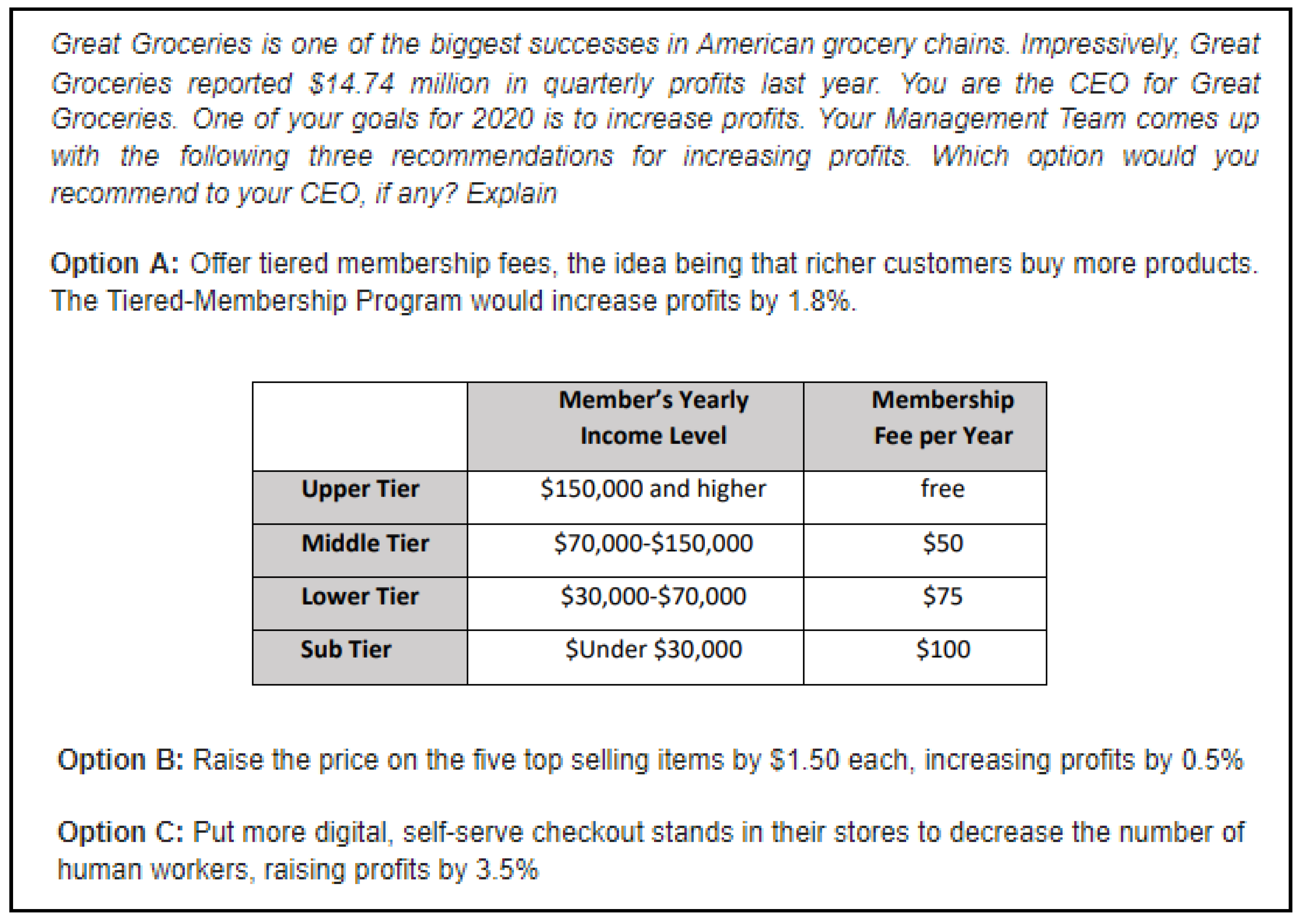
4.2. Great Groceries
4.2.1. Profit
4.2.2. Ethical Reasoning
4.2.3. Connecting to the Coronavirus Pandemic
4.2.4. Synthesis of Analyses
5. Discussion and Design Implications
5.1. Where to Start: Accessibility
5.2. Ethical Decision Making
5.3. Progression from Ethics to Social Justice
5.4. Moving Forward
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesh, R.; Chval, K.; Hollebrands, K.; Konold, C.; Stephan, M.; Walker, E.; Wanko, J. The NCTM research presession: A brief history and reflection. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2014, 45, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.; Herbel-Eisenmann, B.; Celédon-Pattichis, S.; Civil, M.; Sinclair, N.; Stephan, M.; Clements, D.; Pape, S.; Wilkerson, T. Equity within mathematics education research as a political act: Moving from choice to intentional collective professional responsibility. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2017, 48, 124–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutstein, E.; Fey, J.T.; Heid, M.K.; DeLoach-Johnson, I.; Middleton, J.A.; Larson, M.; Dougherty, B.; Tunis, H. Equity in school mathematics education: How can research contribute? J. Res. Math. Educ. 2005, 36, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, W.; Artigue, M.; Mariotti, M.; Sträßer, R.; Van den Heuvel-Panhuizen, M. European didactic traditions in mathematics: Introduction and overview. In European Traditions in Didactics of Mathematics; Blum, W., Artigue, M., Mariotti, M., Sträßer, R., Van den Heuvel-Panhuizen, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Margolinas, C.; Drijvers, P. Didactical engineering in France: An insider’s and an outsider’s view on its foundations, its practice and its impact. ZDM Math. Educ. 2015, 47, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brousseau, G. Research in mathematics education. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Mathematical Education, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–11 July 2008; pp. 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, P.; Confrey, J.; DiSessa, A.; Lehrer, R.; Schauble, L. Design experiments in education research. Educ. Res. 2003, 32, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, M.; Bowers, J.; Cobb, P. Supporting Students’ Development of Measuring Conceptions: Analyzing Students’ Learning in Social Context; Stephan, M., Bowers, J., Cobb, P., Gravemeijer, K.P.E., Eds.; NCTM: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gravemeijer, K.; van Eerde, D. Design research as a means for building a knowledge base for teachers and teaching in mathematics education. Elem. Sch. J. 2009, 109, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sträßer, R. Didactics of mathematics: More than mathematics and school! ZDM 2007, 39, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R. The sociopolitical turn in mathematics education. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2012, 44, 37–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Principles to Actions: Ensuring Mathematics Success for All; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenstein, M. Critical mathematics education: An application of Paulo Freire’s epistemology. J. Educ. 1983, 165, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutstein, E. Reading and Writing the World with Mathematics: Toward a Pedagogy for Social Justice; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gutstein, E. Our issues, our people—Math as our weapon: Critical mathematics in a Chicago neighborhood high school. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2016, 47, 454–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokka, K. Social justice pedagogy for whom? Developing privileged students’ Critical Mathematics Consciousness. Urban Rev. 2020, 51, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, L. Equity-directed instructional practices: Beyond the dominant perspective. J. Urban Math. Educ. 2017, 10, 66–105. [Google Scholar]
- DeMarrais, K.B.; LeCompte, M.D. The Way Schools Work: A Sociological Analysis of Education; Longman Publishing Group: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, D.A. Who’s afraid of critical race theory? U. Ill. L. Rev. 1995, 1995, 893–910. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, R.; Stefanic, J. Critical Race Theory: An Introduction; University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, P.H. Black Feminist Thought: Knowledge, Consciousness, and the Politics of Empowerment; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hooks, B. Teaching to Transgress; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw, K. Mapping the margins: Intersectionality, identity Politics, and violence against women of color. Stanf. Law Rev. 1991, 43, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorde, A. Sister Outsider: Essays and Speeches; Penguin Classics: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ladson-Billings, G. Toward a theory of culturally relevant pedagogy. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1995, 32, 465–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, G. Preparing for culturally responsive teaching. J. Teach. Educ. 2002, 53, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, D.; Alim, H.S. Culturally Sustaining Pedagogies: Teaching and Learning for Justice in a Changing World; Teachers College Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Skovsmose, O. Towards a Philosophy of Critical Mathematics Education; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, P. Pedagogy of the Oppressed; Penguin Books: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, R. Why (urban) mathematics teachers need political knowledge. J. Urban Math. Educ. 2013, 6, 7–19. Available online: http://ed-osprey.gsu.edu/ojs/index.php/JUME/article/view/223/148 (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Atweh, B.; Brady, K. Socially response-able mathematics education: Implications of an ethical approach. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2009, 5, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutstein, E. Teaching and learning mathematics for social justice in an urban, latino school. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2003, 34, 37–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, T. Learning to teach mathematics for social justice: Negotiating social justice and mathematical goals. J. Res. Math. Educ. 2013, 44, 129–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miescu, E.; Pedulla, J.; Cannady, M.; Cochrane-Smith, M.; Jong, C. Measuring practices of teaching for social justice in elementary mathematics classrooms. Educ. Res. Q. 2011, 34, 15–39. [Google Scholar]
- Brantlinger, A. Rethinking critical mathematics: A comparative analysis of critical, reform, and traditional geometry instructional texts. Educ. Stud. Math. 2011, 78, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutstein, E.; Peterson, B. Rethinking Mathematics: Teaching Social Justice by the Numbers, 2nd ed.; Rethinking Schools Ltd.: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.Q., III; Conway, B.M., IV; Lawler, B.R.; Staley, J.W. High School Mathematics Lessons to Explore, Understand, and Respond to Social Injustice; Corwin Press: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, W. Race, retrenchment, and the reform of school mathematics. In Rethinking Mathematics: Teaching Social Justice by the Numbers, 2nd ed.; Gutstein, E., Peterson, B., Eds.; Rethinking Schools Ltd.: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013; pp. 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Trexler, L. Adventures of a beginning teacher with social justice mathematics. In Rethinking Mathematics: Teaching Social Justice by the Numbers, 2nd ed.; Gutstein, E., Peterson, B., Eds.; Rethinking Schools Ltd.: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013; pp. 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Esmonde, I. Nobody’s rich and nobody’s poor… It sounds good, but it’s actually not: Affluent students learning mathematics and social justice. J. Learn. Sci. 2014, 23, 348–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemer, M.A.; McWhirter, E.H.; Ozer, E.J.; Rapa, L.J. Advances in the conceptualization and measurement of critical consciousness. Urban Rev. 2015, 47, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, M. Ethical dimensions of mathematics education. Educ. Stud. Math. 2016, 92, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ignazio, C.; Klein, L.F. Data Feminism; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Puka, B. Teaching ethical excellence: Artful response-ability, creative integrity, character opus. Lib. Educ. 2005, 91, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambrosio, U. Mathematics and peace: Our responsibilities. Zent. Didakt. Math. 1998, 30, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwell, R. The mathematical formatting of climate change: critical mathematics education and post-normal science. Res. Math. Educ. 2013, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, D. Teaching mathematics for social justice: An ethical and moral imperative? J. Urban Math. Educ. 2014, 7, 1–5. Available online: http://ed-osprey.gsu.edu/ojs/index.php/JUME/article/view/252/165 (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Atweh, B. Is the good a desire or an obligation? The possibility of ethics for mathematics education. Philos. Math. Educ. J. 2013, 27. Available online: https://espace.curtin.edu.au/bitstream/handle/20.500.11937/39302/197529_110138_Atweh_-_Is_the_good_a_desire.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Ernest, P. The ethics of mathematics: Is mathematics harmful? In The Philosophy of Mathematics Education Today; Ernest, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, I. Education is politics: Paulo Freire’s critical pedagogy. In Paulo Freire: A Critical Encounter; Leonard, P., McLaren, P., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, M.; Register, J.; Reinke, L.; Robinson, C.; Pugalenthi, P.; Pugalee, D. People use math as a weapon: Critical mathematics consciousness in the time of COVID-19. Educ. Stud. Math. in press.
- Resnik, D. The Ethics of Science: An Introduction; Routledge Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chessell, M. Ethics for Big Data and Analytics. 2014. Available online: http://www.informatica.uniroma2.it/upload/2017/IA2/IBM-%20Ethics%20for%20BD&A.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Aoyama, K. Investigating a hierarchy of students’ interpretations of graphs. Int. Electron. J. Math. Educ. 2007, 2, 298–318. [Google Scholar]
- David, E.J.; Roh, K.H.; Sellers, M.E. Value-thinking and location-thinking: Two ways students visualize points and think about graphs. J. Math. Behav. 2019, 54, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.C.; Thompson, P.W. Shape thinking and students’ graphing activity. In Proceedings of the 18th Meeting of the MAA Special Interest Group on Research in Undergraduate Mathematics Education, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 19–21 February 2015; pp. 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.M.G.; Bain, K.; Towns, M.H.; Elmgren, M.; Ho, F.M. Covariational reasoning and mathematical narratives: Investigating students’ understanding of graphs in chemical kinetics. Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 2019, 20, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrall, C.W.; Makar, K.; Nilsson, P.; Shaughnessy, J.M. Teaching and learning probability and statistics: An integrated perspective. In Compendium for Research in Mathematics Education. Reston: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics; Cai, J., Ed.; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 490–525. [Google Scholar]
- Lamon, S.J. Ratio and Proportion: Preinstructional Cognitions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chiodo, M.; Vyas, R. The Role of Ethics in a Mathematical Education: A White Paper; Cambridge University Ethics in Mathematics Project, 2019. Available online: https://www.ethics.maths.cam.ac.uk (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Madden, S.R. Statistically, technologically, and contextually provocative tasks: Supporting teachers’ informal inferential reasoning. Math. Think. Learn. 2011, 13, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ethical Principles | Considerations | Professional Domains Addressing the Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | How does respect for freedom or personal autonomy apply? Is confidentiality required? Is consent needed or obtained? Is privacy violated? | NSPE 1, JMU, ASA, ACM/AI |
| Fairness (equality) | What is the fair or just thing to do? Is there fair access to systems that are created? | ACM, AIB, Data Analytics, JMU |
| Accuracy | Is data reliable and accurate? | NSPE, AIB, ACM/AI, Science, Data Sciences |
| Accountability | Who is accountable? Have they communicated the data in a misleading manner? Is the source reliable?) | NSPE, AIB, ACM/AI, Science, Data Sciences |
| Property | Whose data is it to sell? Who owns the data? | Data Sciences |
| Loyalty | Is the decision/activity loyal to the organization (e.g., makes profit, keeps ideas within organization, does not use organization’s ideas to make money elsewhere) | AIB, JMU |
| Accessibility | What information does an organization have the right to access about people? Who has access to this data? User? Buyer? | Data Sciences |
| Algorithm Bias | Are algorithms objective? Do algorithms (un)knowingly discriminate against individuals or groups? | AI |
| Transparency | Are the codes for algorithms readily available for inspection? | ACM/AI, Science, ASA |
| Ecological | Has the impact on humans and ecosystems been considered? | ACM/AI, NSPE |
| Employment | Will the decision/activity harm an individual’s or group’s employment status? | AI |
| Discrimination | Has the decision/activity avoided negative effects on oppressed societal groups? | Data Sciences, ACM/AI, AIB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Register, J.; Stephan, M.; Pugalee, D. Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics: New Directions for Didactics in U.S. Mathematics Education. Mathematics 2021, 9, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080799
Register J, Stephan M, Pugalee D. Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics: New Directions for Didactics in U.S. Mathematics Education. Mathematics. 2021; 9(8):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080799
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegister, Jordan, Michelle Stephan, and David Pugalee. 2021. "Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics: New Directions for Didactics in U.S. Mathematics Education" Mathematics 9, no. 8: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080799
APA StyleRegister, J., Stephan, M., & Pugalee, D. (2021). Ethical Reasoning in Mathematics: New Directions for Didactics in U.S. Mathematics Education. Mathematics, 9(8), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080799







