Academic Stress in University Students: The Role of Physical Exercise and Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instrument and Procedure
2.3. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Stress Level, and Sports Practice of University Students
3.2. Relationship between the Practice of Physical Exercise, Adherence to the MD, and Academic Stress
3.3. Academic Stress and Food Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babilonia, L.H.; Nuñez, W.N.; Santamaría, Á. Occupational Stress As A Conditioning Factor Of Occupational Risks. Webology 2022, 19, 409–428. [Google Scholar]
- Högberg, B.; Horn, D. National high-stakes testing, gender, and school stress in Europe: A difference-in-differences analysis. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2022, 38, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrio, N.; Mazo, R. Estrés académico. Rev. Psico. UAN 2012, 3, 55–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.M.; Lin, T.L.; Yang, K.S.; Mui, W.C.; Lu, T.H. The effect of learning stress on leisure benefits: Leisure coping strategies variables as moderators. Int. J. Organ. Innov. 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lefevor, G.T. Contemporary college student anxiety: The role of academic distress, financial stress, and support. J. Coll. Couns. 2018, 21, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate, N.E.; Soto, M.G.; Castro, M.L.; Quintero, J.R. Estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios: Medidas preventivas. Rev. Alta Tecnol. Soc. 2017, 9, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ángel, J.L.; Muentes, A.D.; Choez, J.; Valero, N.J. Estrés académico y salud mental en estudiantes universitarios en el área de salud. Polo Conoc. 2020, 5, 750–761. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, F.; Barbachan, E.; Pacovilca, G.; Leguia, J. Estrés académico y formación profesional. Conrado 2020, 16, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Ramos, M.F.; López-Cocotle, J.J.; Meza-Zamora, M.E.C. Estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios. Investig. Cienc. 2020, 28, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Botina, L.; Montero-Bolaños, C.; Carlosama-Rodríguez, D.; Tabares-Díaz, Y. Estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios de Iberoamérica: Una revisión sistemática. Cuad. Hispanoam. Psicol. 2021, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.E.; Sánchez, O.A.; Castañeda-Quirama, T. Estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios. Psicoespacios 2020, 14, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casuso, M.J. Estudio del Estrés, Engagement y Rendimiento Académico en Estudiantes Universitarios. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Málaga, Facultad de Enfermería, Fisioterapia, Podología y Terapia Ocupacional, Málaga, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Casuso, M.J.; Moreno, N.; Labajos, M.T.; Montero, F.J. The association between perceived health symptoms and academic stress in Spanish higher education students. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 12, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanach, R.G.; Souto-Gestal, A.; Franco, V. Escala de Estresores Académicos para la evaluación de los estresores académicos en estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Iberoam. Psicol. Salud 2016, 7, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, I.X.T.; Pacori, C.E.Z.; Cuevas, S.C.C.; Machaca, J.E.C. Impacto de la COVID-19 en el estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios. Dominio Cienc. 2021, 7, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Flores, E.; Sánchez-Trujillo, M.D.L.Á. Estrés académico en estudiantes de Ciencias de la Salud en la modalidad de educación a distancia en tiempos de COVID-19. Rev. Estud. Exp. Educ. 2022, 21, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Montero, E.M.; Naranjo-Hidalgo, T.; Poveda-Ríos, S.; Izurieta-Brito, D. Estrés académico en universitarios durante la pandemia de COVID-19. Rev. Med. Electron. 2022, 44, 468–482. [Google Scholar]
- Colten, M. Adolescent Stress: Causes and Consequences, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, D.G.; Reinhart, M.I. Psychological determinants of adolescent smoking behaviour: A prospective study. Aust. J. Psychol. 1998, 50, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persike, M.; Seiffge, I. Stress with parents and peers: How adolescents from 18 nations cope. Anxiety Stress 2016, 29, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, M.; Backes, S.; Brandstätter, V.; Nussbeck, F.W.; Bradbury, T.N.; Sutter, D.; Bodenmann, G. Approach-avoidance goals and relationship problems, communication of stress, and dyadic coping in couples. Motiv. Emot. 2017, 41, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciairano, S.; Menna, P.; Molinar, R.; Sestito, L.A. The relationships between perceived stress for the future and coping strategies in times of social uncertainty: A study of Italian adolescents. J. Psychol. Couns. 2009, 1, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Moksnes, K.; Espnes, G.; Haugan, G. Stress, sense of coherence and emotional symptoms in adolescents. Psychol. Health 2014, 29, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, M.; Puukko, L.R.; Lindberg, N.; Siimes, M.A.; Aalberg, V. Body dissatisfaction and body mass in girls and boys transitioning from early to mid-adolescence: Additional role of self-esteem and eating habits. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, R.; Viciana, M.; Palomares, J. Adherencia a la dieta mediterránea, la actividad física y su relación con el IMC, en estudiantes universitarios del grado de primaria, mención de educación física, de Granada. ESHPA 2018, 2, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, R.; Bibiloni, M.M.; Tur Marí, J.A. Patrones de consumo de alimentos en estudiantes universitarios de Zamora. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Baratucci, Y. Estrés y Alimentación. Trabajo Final de Grado. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Fasta, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra Mora, J. Assessment of physical activity, eating habits and their relationship with academic performance in adolescent schoolchildren from the COMEDUC Foundation (Chile). J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2019, 19, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar]
- Tárraga-Marcos, A.; Panisello-Royo, J.M.; Carbayo-Herencia, J.A.; López Gil, J.F.; García-Cantó, E.; Tárraga-López, P.J. Evaluation of adherence to the Mediterranean diet in university students of Health Sciences and its relationship with the level of physical activity. Hosp. Nutr. 2021, 38, 814–820. [Google Scholar]
- Canivell, B. Efecto del Confinamiento Durante la COVID-19 en los Hábitos Alimentarios en Estudiantes Universitarios. Ph.D.Thesis, Universidad de Sevilla, Andalucía, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Medrano, B. Consumo de Comida Chatarra Según el Estar en Época de Exámenes en Estudiantes Universitarios de Cinco Países en Latinoamérica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Continental, Huancayo, Peru, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Seiffge-Krenke, I.; Persike, M.; Karaman, N.G.; Cok, F.; Herrera, D.; Rohail, I.; Hyeyoun, H. Stress with parents and peers: How adolescents from six nations cope with relationship stress. J. Res. Adolesc. 2013, 23, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.; Ramírez, H. El estrés percibido en la vida de los estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Invest. Cient. Tecno. 2017, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, J.; Sovio, U. Stress-related eating and drinking behaviour and body mass index and predictors of this behaviour. Prev. Med. 2002, 34, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimore, P.; Caswell, N. Differential effects of active and passive stress on food intake in restrained and unrestrained eaters. Appetite 2004, 42, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo, L.; Henning, M.; García, S.; Pellon, M. Validación de un cuestionario de frecuencia alimentaria para estimar la ingesta de azúcares libres y alimentos ultraprocesados en población argentina. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Diet. 2022, 26, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarubbi, E.; Castaldo, R. Factores causales del estrés en los estudiantes universitarios. In Proceedings of the V Congreso Internacional de Investigación y Práctica Profesional en Psicología XX Jornadas de Investigación Noveno Encuentro de Investigadores en Psicología del MERCOSUR, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 27–30 November 2013; Facultad de Psicología, Universidad de Buenos Aires: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2013; p. 000-054. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, M.; Martínez, P.; Miró, E.; Sánchez, A. Bienestar psicológico y hábitos saludables: ¿están asociados a la práctica de ejercicio físico? Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2008, 8, 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- González, S.N.; Arias, A.; Elizondo, B.; Monge-Ortega, O.P. Psychoneuroimmunoendocrinology: Clinical implications. World Allergy Organ. J. 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Martínez, J.; De Irala, J.; Martínez, M.A. Determinants of the adherence to an «a priori» defined mediterranean dietary pattern. Eur. J. Nutr. 2002, 41, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, D.; Bot, M.; Brouwer, I.A.; Visser, M.; Giltay, E.J.; Penninx, B. Association of food groups with depression and anxiety disorders. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, I.; Morales, S.; Orellana, P.; Lorenzo, A. Efecto de las actividades físicas en la disminución del estrés laboral. Rev. Cuba. Med. Gen. Integral 2017, 33, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Norwitz, N.; Naidoo, U. Nutrition as Metabolic Treatment for Anxiety. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, M. Actividad Física y Salud en Estudiantes Universitarios Desde una Perspectiva Salutogénica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de les Illes Balears, Palma, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Norte, A.I.; Ortiz, R. Calidad de la dieta española según el índice de alimentación saludable. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Blampied, N.; Mulder, R.; Afzali, M.; Bhattacharya, O.; Blampied, M.; Rucklidge, J. Desastres, políticas y micronutrientes: La intersección entre ética, evidencia y acción efectiva. N. Zealand Med. J. 2020, 133, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, C.; González, X.; Herrera, G.; Hernández, Ó. Efectos del consumo de ácidos grasos omega-3 sobre la salud cardiovascular, cerebral y diversas enfermedades del sistema nervioso central. Rev. Venez. Ciencia. Tecno. Alim. 2016, 7, 28–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.F. Evaluación del Estrés Cotidiano en la Adolescencia. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Málaga, Andalucía, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Porras, D.; Bonilla-Cruz, N.J.; Carrillo-Sierra, S.M.; Forgiony-Santos, J.; Silva-Monsalve, G. Educación para la salud laboral: Perspectivas teóricas desde la intervención. Arch. Venez. Farmacol. Ter. 2019, 38, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadehç, M.; Vafa, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Feizi, A.; Majdzadeh, R.; Afshar, H.; Keshteli, A.H.; Adibi, P. Empirically derived dietary patterns in relation to psychological disorders. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, O.; Serrano, M.J.; Garcia, J.; Roca, M.; Garcia, M.; Pareja, A.; Gomez, R. The Mediterranean diet and micronutrient levels in depressive patients. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Sole, E.; Rucklidge, J.; Blampied, N. Anxiety and stress in children following an earthquake: Clinically beneficial effects of treatment with micronutrients. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2017, 26, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A short screener is valid for assessing Mediterranean diet adherence among older Spanish men and women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S. Bajos Niveles de Omega-3 y Vitamina-d Relacionados con la Gravedad de la COVID-19. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Cantabria, España, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arip, M.M.; Kamaruzaman, D.N.; Roslan, A.; Ahmad, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Malim, T. Development, validity and reliability of student stress inventory (SSI). Soc. Sci. 2015, 10, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Gómez, J.; Martínez-Costa, M.; Martínez-Lorente, A.R. A critical evaluation of the EFQM model. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2011, 28, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Serrano, M.Á.; Vaquero-Solís, M.; López-Gajardo, M.Á.; Sánchez-Miguel, P.A. Adherencia a la dieta mediterránea e importancia de la actividad física y el tiempo de pantalla en los adolescentes extremeños de enseñanza secundaria. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, J.; Hurtado, M.; Pons, R.; Fandos, E.; García, E.; Vinuesa, J.; Díaz, L.D. Informe del Comité Científico de la Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AESAN) de revisión y actualización de las Recomendaciones Dietéticas para la población española. Rev. Comité. Cient. AESAN 2020, 32, 11–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, V.; Bray, J.; Fernandes, A.C.; Luci Bernardo, G.; Hartwell, H.; Secchi, S.; Proença, R. Vegetable consumption and factors associated with increased intake among college students: A scoping review of the last 10 years. Nutrients 2019, 11, 16–34. [Google Scholar]
- Solera, A.; Gamero, A. Hábitos saludables en universitarios de ciencias de la salud y de otras ramas de conocimiento: Un estudio comparativo. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Diet. 2019, 23, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willet, W.; Sacks, F.; Trichopoulou, A.; Drescher, G.; Ferro, A.; Helsing, E. Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, M.P.; Montes, R.M.; Luque, R.M. Influencia del género en las relaciones entre inteligencia emocional, estrés académico y satisfacción de los estudiantes. Know Share Psychol. 2020, 1, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.E.; Sánchez, O.; Vallejo, G.; Quirama, T.C.; Sánchez, Y.; Cardona, P. Depresión y su relación con el consumo de sustancias psicoactivas, el estrés académico y la ideación suicida en estudiantes universitarios colombianos. Health Addict. 2018, 18, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.; Valle, J.; Angulo, J. Estrés percibido en estudiantes universitarios: Influencia del burnout y del engagement académico. IJERI 2018, 9, 220–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, L.; Pérez, C.L. Imagen corporal, IMC, afrontamiento, depresión y riesgo de TCA en jóvenes universitarios. Ann. Psychol. 2013, 29, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andreo, P.; García, N.; Sánchez, E.P. La microbiota intestinal y su relación con las enfermedades mentales a través del eje microbiota-intestino-cerebro. Disc. Clín. Neur. 2018, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, M.; Navarro, E.; Clemente, V.J. Patrones de comportamiento de pacientes con depresión y población control. Rev. Int. Inv. Amb. Salud Púb. 2022, 19, 9506. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, A.; Muñoz, M.J.; Planells, E.M.; López, I. La etapa universitaria no favorece el estilo de vida saludable en las estudiantes granadinas. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 975–979. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, R.; Puig, A.; García, O. Perceived Barriers to Physical Activity and Related Factors in Spanish University Students. Open J. Prev. Med. 2014, 4, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 24 | 2.12 | 18–30 |
| Hours per week dedicated to sports practice * | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0–3 |
| Level of Adherence to the MD ** | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0–2 |
| Stress level *** | 1.3 | 1.35 | 0–5 |
| Female | Male | I prefer not to say | |
| No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | |
| Hours of sports practice per week | |||
| Less than 2 h | 134 (22.7) | 22 (14.8) | 3 (75) |
| Between 2 and 4 h | 252 (42.8) | 52 (34.9) | 1 (25) |
| More than 4 h | 203 (34.4) | 75 (50.3) | 0 (0) |
| MD Adherence Level | |||
| Low | 402 (68.2) | 109 (73) | 4 (100) |
| Medium | 171 (29.0) | 36 (24) | 0 |
| High | 16 (2.7) | 4 (2.6) | 0 |
| Academic stress level | |||
| No stress | 234 (39.7) | 69 (46.3) | 1 (25.0) |
| Very low stress | 109 (18.5) | 32 (21.5) | 0 (0) |
| Low stress | 111 (18.8) | 22 (14.7) | 1 (25.0) |
| Medium stress | 86 (14.6) | 18 (12) | 2 (50.0) |
| High stress | 43 (7.3) | 6 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Very high stress | 6 (1.0) | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) |
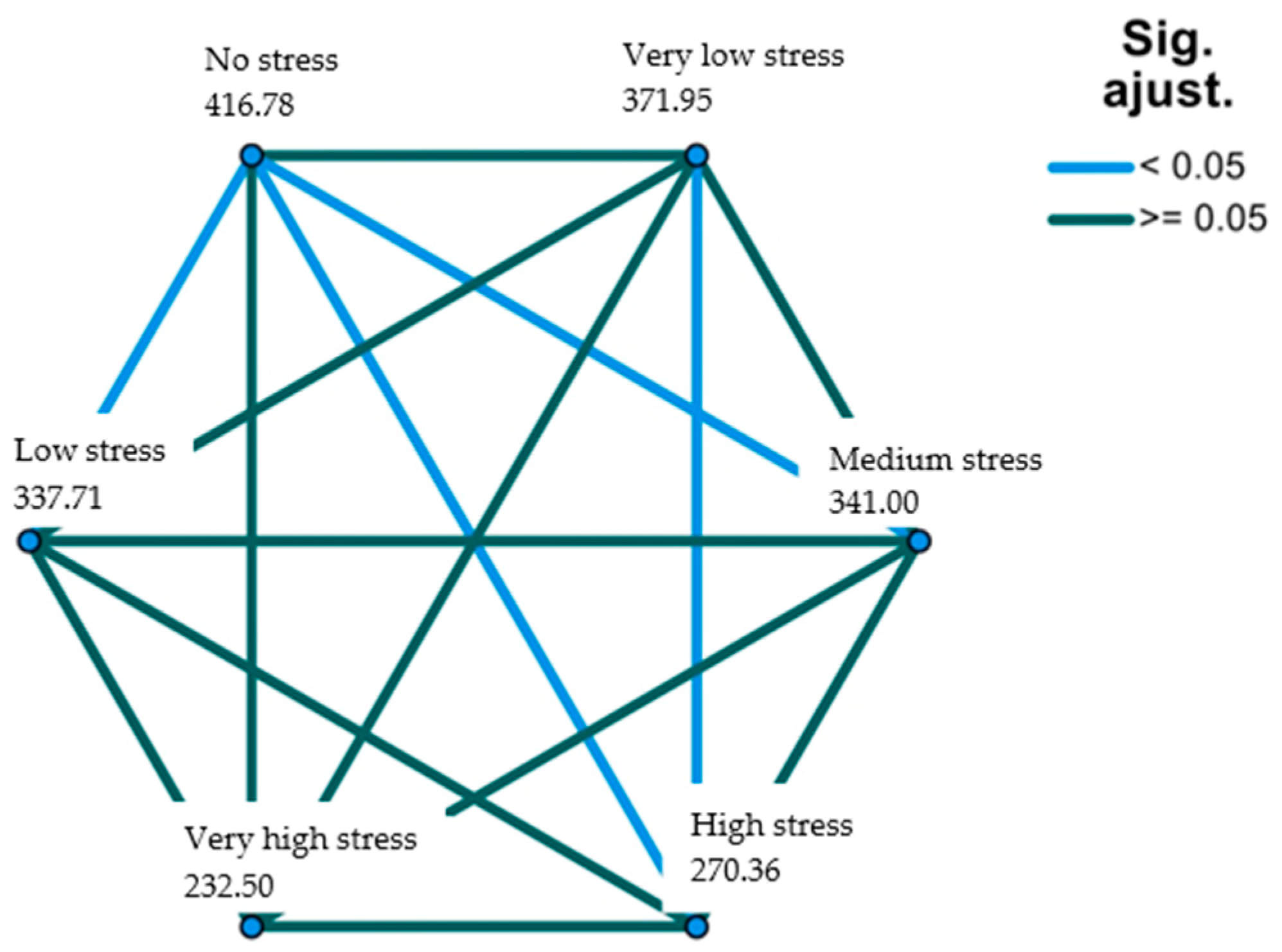
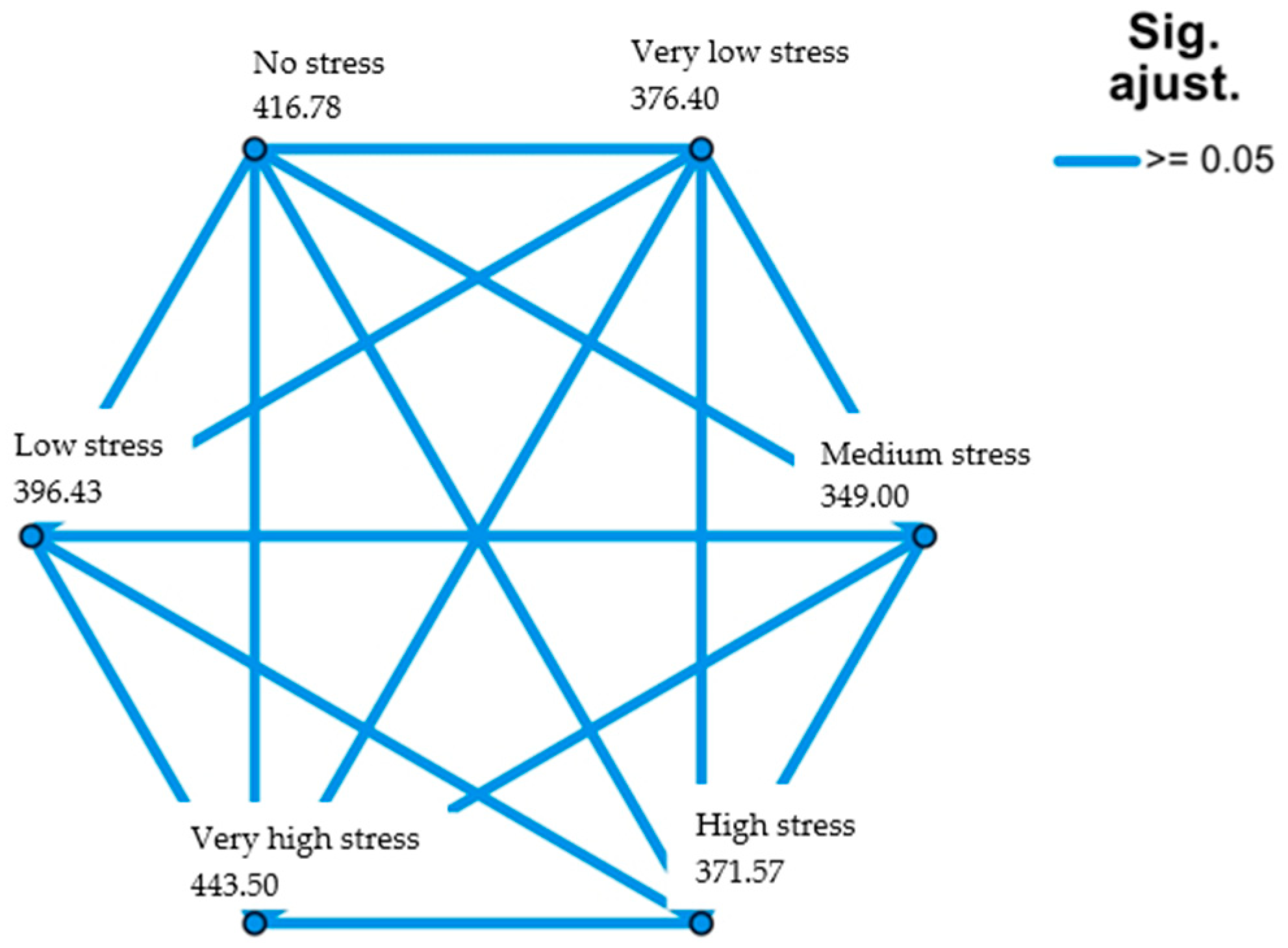
| Couples | Test Statistic | Standard Error | Standard Test Statistic | p | Adjusted Significance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very high stress–Low stress | 105.209 | 65.402 | 1.609 | 0.061 | 0.910 |
| Very high stress–Very low stress | 139.454 | 65.310 | 2.135 | 0.033 | 0.491 |
| Very high stress–No stress | 184.280 | 64.364 | 2.863 | 0.004 | 0.063 |
| High stress–Very low stress | 101.597 | 29.800 | 3.409 | <0.001 | 0.010 |
| High stress–No stress | 146.422 | 27.663 | 5.293 | <0.001 | 0.000 |
| Medium stress–No stress | 75.780 | 20.270 | 3.739 | <0.001 | 0.000 |
| Very low stress–No stress | 44.826 | 18.310 | 2.448 | 0.014 | 0.215 |
| Media | Standard Deviation | Hedges’ g | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No stress | 0.496 | 0.500 | 0.796 * |
| Very low stress | 0.319 | 0.532 | 0.754 * |
| Low stress | 0.283 | 0.452 | 0.455 |
| Medium stress | 0.292 | 0.457 | 0.475 |
| High stress | 0.102 | 0.102 | 0.285 |
| Very High stress | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.289 |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Fruit consumption | −962 | 0.007 |
| Olive oil consumption | −0.022 | 0.99 |
| Consumption of highly processed snacks | 0.962 | −0.007 |
| Consumption of sugary drinks | 0.902 | −0.038 |
| Consumption of processed baked goods | 0.955 | −0.030 |
| I consume natural and/or roasted nuts | −0.022 | 0.99 |
| Oily fish consumption | −0.022 | 0.98 |
| Factor 1 (Unhealthy Eating) | Factor 2 (Healthy Eating) | Academic Stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman’s Rho | Factor 1 (unhealthy eating) | 1.00 | −0.019 | 0.700 ** |
| Factor 2 (healthy eating) | −0.019 | 1.00 | 0.076 * | |
| Academic stress | 0.700 ** | 0.076 * | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monserrat-Hernández, M.; Checa-Olmos, J.C.; Arjona-Garrido, Á.; López-Liria, R.; Rocamora-Pérez, P. Academic Stress in University Students: The Role of Physical Exercise and Nutrition. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11172401
Monserrat-Hernández M, Checa-Olmos JC, Arjona-Garrido Á, López-Liria R, Rocamora-Pérez P. Academic Stress in University Students: The Role of Physical Exercise and Nutrition. Healthcare. 2023; 11(17):2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11172401
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonserrat-Hernández, Montserrat, Juan Carlos Checa-Olmos, Ángeles Arjona-Garrido, Remedios López-Liria, and Patricia Rocamora-Pérez. 2023. "Academic Stress in University Students: The Role of Physical Exercise and Nutrition" Healthcare 11, no. 17: 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11172401
APA StyleMonserrat-Hernández, M., Checa-Olmos, J. C., Arjona-Garrido, Á., López-Liria, R., & Rocamora-Pérez, P. (2023). Academic Stress in University Students: The Role of Physical Exercise and Nutrition. Healthcare, 11(17), 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11172401






