Reconstructive Surgery of Pressure Injuries in Spinal Cord Injury/Disorder Patients: Retrospective Observational Study and Proposal of an Algorithm for the Flap Choice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statistical Analysis
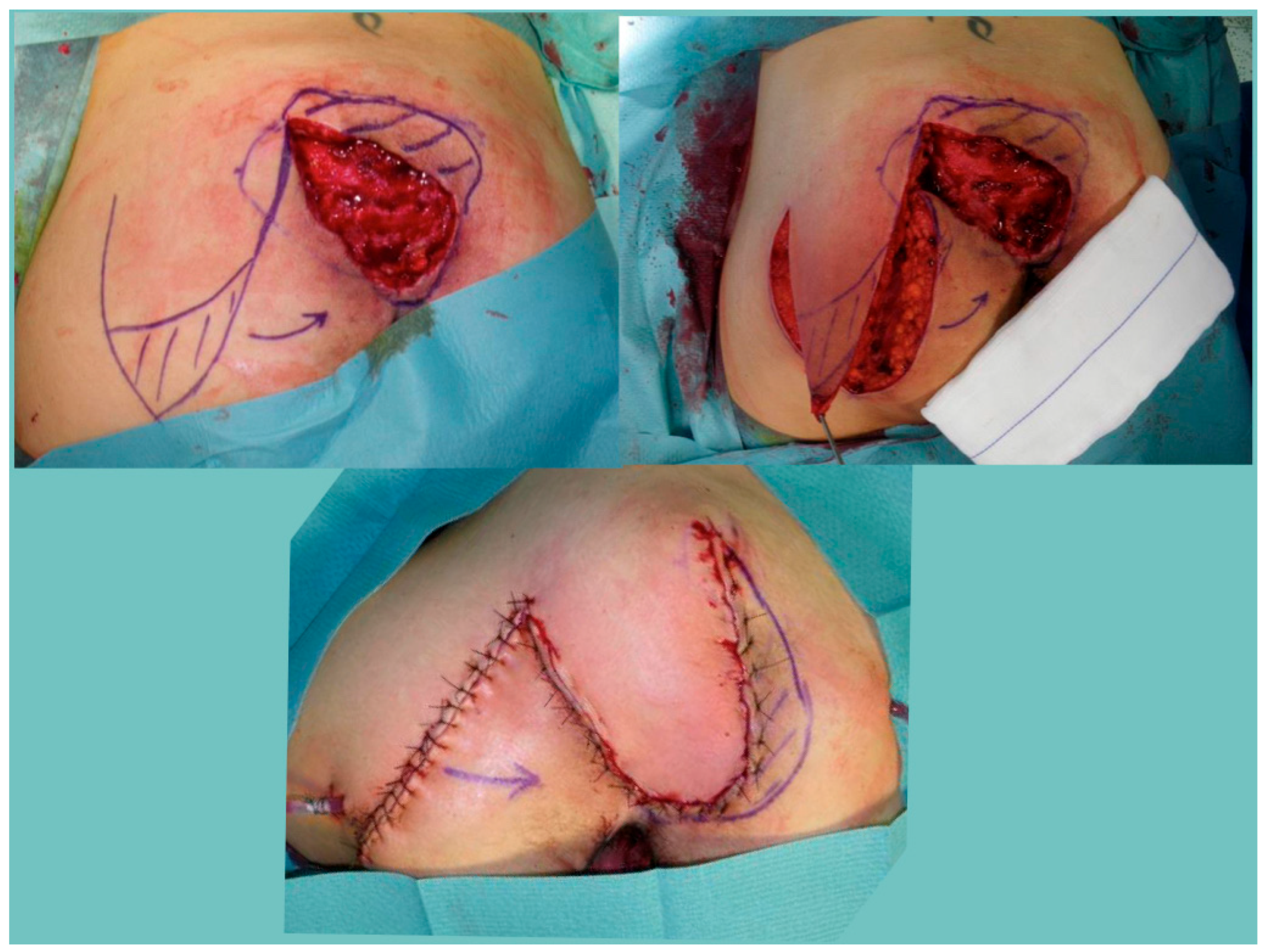
2.2. Surgical Treatment and Reconstructive Flap Choice Algorithm
3. Results
Patients’ Characteristics and Association with Minor and Major Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kreutzträger, M.; Voss, H.; Scheel-Sailer, A.; Liebscher, T. Outcome analyses of a multimodal treatment approach for deep pressure ulcers in spinal cord injuries: A retrospective cohort study. Spinal Cord. 2018, 56, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumiya, T.; Kawamura, K.; Tokuhiro, A.; Takechi, H.; Ogata, H. A survey of wheelchair use by paraplegic individuals in Japan. Part 2: Prevalence of pressure sores. Spinal Cord. 1997, 35, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, J.S.; Carlson, A.R.; Bonneau, L.A.; Kempton, S.J.; King, T.W.; Bentz, M.L.; Afifi, A.M. Reconstructive surgery and patients with spinal cord injury: Perioperative considerations for the plastic surgeon. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2016, 50, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, A.C.; Stenius, M.C.; Bjelak, S.; Lagergren, J.F. Surgery for pressure ulcers in spinal cord-injured patients following a structured treatment programme: A 10-year follow-up. Int. Wound J. 2016, 14, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglari, B.; Büchler, A.; Reitzel, T.; Swing, T.; Gerner, H.J.; Ferbert, T.; Moghaddam, A. A retrospective study on flap complications after pressure ulcer surgery in spinal cord-injured patients. Spinal Cord. 2014, 52, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braafhart, M.; de Laat, H.E.W.; Wagner, T.; van de Burgt, E.W.T.; Hummelink, S.; Ulrich, D.J.O. Surgical reconstruction of pressure ulcers in spinal cord injury individuals: A single- or two-stage approach? J. Tissue Viability 2020, 29, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarzani, R.; Tedeschi, S.; Trapani, F.F.; Capirossi, R.; Battilana, M.; Gaiani, L.; Palmonari, M.; Negosanti, L. Osteomyelitis of the pelvic bones in patients with spinal cord injury: Is magnetic resonance useful for preoperative diagnosis? Integr. Mol. Med. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, M.A.; Yan, M.; Hanna, T.P. Systematic Review of Modern Case Series of Squamous Cell Cancer Arising in a Chronic Ulcer (Marjolin’s Ulcer) of the Skin. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, S.; Negosanti, L.; Sgarzani, R.; Trapani, F.; Pignanelli, S.; Battilana, M.; Capirossi, R.; Brillanti Ventura, D.; Giannella, M.; Bartoletti, M.; et al. Superficial swab versus deep-tissue biopsy for the microbiological diagnosis of local infection in advanced-stage pressure ulcers of spinal-cord-injury patients: A prospective study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summo, V.; Sgarzani, R.; Negosanti, L.; Fabbri, E.; Vietti Michelina, V.; Villani, R.; D’Angelo, G.; Antoniazzi, E.; Cipriani, R.; Morselli, P.G. Pressure Ulcers in Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries: Concordance Between Swab and Intraoperative Culture. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2016, 4, e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarzani, R.; Maietti, E.; Tedeschi, S.; Trapani, F.F.; Battilana, M.; Landi, S.; Kiekens, C.; Negosanti, L. Multidisciplinary treatment protocol for ischiatic, sacral, trochanteric or other pressure injuries in people with spinal cord injury: A retrospective cohort study. Spinal Cord. 2023, 61, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edsberg, L.E.; Black, J.M.; Goldberg, M.; McNichol, L.; Moore, L.; Sieggreen, M. Revised National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel Pressure Injury Staging System: Revised Pressure Injury Staging System. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 2016, 43, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadiparthi, S.; Hartley, A.; Alzweri, L.; Mecci, M.; Siddiqui, H. Improving outcomes following reconstruction of pressure sores in spinal injury patients: A multidisciplinary approach. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 69, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce de Leon, M. Teamwork approach to prevention and treatment of skin breakdown in spinal cord patients. Continuum 2015, 21, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunn, G. Spinal cord injury pressure ulcer treatment: An experience-based approach. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, E.A.; Pires, M.; Ngann, Y.; Sterling, M.; Rubayi, S. Comprehensive management of pressure ulcers in spinal cord injury: Current concepts and future trends. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2013, 36, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.C.; Cadarette, S.M.; Wodchis, W.P.; Krahn, M.D.; Mittmann, N. The lifetime cost of spinal cord injury in Ontario, Canada: A population-based study from the perspective of the public health care payer. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, C.A.; Phillips, L.G. Evidence-based medicine: Pressure sores. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disa, J.J.; Carlton, J.M.; Goldberg, N.H. Efficacy of operative cure in pressure sore patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 89, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekas, A.D.; Mastorakos, D.P. The management of decubitus ulcers by musculocutaneous flaps: A five-year experience. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1992, 28, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, K.; Rutkowski, S.; Cope, C.; Hassall, M.; Barnett, R.; Richards, M.; Vandervord, J. Recurrance rates of ischial sores in para- and tetraplegics treated with hamstring flaps: An 8-year study. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1999, 52, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiessen, F.E.; Andrades, P.; Blondeel, P.N.; Hamdi, M.; Roche, N.; Stillaert, F.; Van Landuyt, K.; Monstrey, S. Flap surgery for pressure sores: Should the underlying muscle be transferred or not? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2011, 64, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ohura, T.; Shintomi, Y.; Sugihara, T.; Nohira, K.; Igawa, H. Superiority of the fasciocutaneous flap in reconstruction of sacral pressure sores. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1993, 30, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pufe, T.; Paulsen, F.; Peterson, W.; Mentlein, R.; Tsokos, M. The angiogenic peptide vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is expressed in chronic sacral pressure ulcers. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelahmetoglu, O.; Van Landuyt, K.; Yagmur, C.; Sommeling, C.E.; Keles, M.K.; Tayfur, V.; Simsek, T.; Demirtas, Y.; Guneren, E. A simple concept for covering pressure sores: Wound edge-based propeller perforator flap. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, T.M.; Mariappan, B.K.; Jaganmohan, J. Retrospective Cohort Observational Study on the Single Best Perforator-Based Pacman Flap in the Reconstruction of Stage IV Sacral Region Pressure Ulcers. Indian. J. Plast. Surg. 2020, 53, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameem, M.; Au, M.; Wood, T.; Farrokhyar, F.; Mahoney, J. A systematic review of complication and recurrence rates of musculocutaneous, fasciocutaneous, and perforator-based flaps for treatment of pressure sores. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 67e–77e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vathulya, M.; Praveen, A.J.; Barik, S.; Jagtap, M.P.; Kandwal, P. A Systematic Review Comparing Outcomes of Local Flap Options for Reconstruction of Pressure Sores. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, R.; Martin, D.; Mahoney, J.L. The operative treatment of pressure wounds: A 10-year experience in flap selection. Int. Wound J. 2009, 6, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, F.; Edstrom, L.; Szymanski, K.; Schmidt, S.; Bevivino, J.; Zienowicz, R.; Stark, J.; Taylor, H.O.; Podda, S.; Liu, P. Improving Pressure Ulcer Reconstruction: Our Protocol and the COP (Cone of Pressure) Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2017, 5, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauer, C.; Sonsino, G. The need for skin and muscle saving techniques in the repair of decubitus ulcers. A consecutive series of 72 patients and 100 ulcers over 5 years (1979/1984). Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 20, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfeehan, M.J.; Aljodah, M.A.; Al-Zajrawee, M.Z.; Marzook, A.A. Random pattern hatchet flap as a reconstructive tool in the treatment of pressure sores: Clinical experience with 36 patients. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2021, 103, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshgaran, G.; Cooper, M.N.; Park, J.; Pimentel, C.G.; Wong, A.K. Trochanteric pressure ulcers: Preoperative management and reconstructive considerations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negosanti, L.; Landi, S.; Gaiani, L.; Capirossi, R.; Battilana, M.; Sgarzani, R. Reconstructive procedure for treatment of trochanteric pressure ulcers in spinal-cord-injured patients. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2023, 46, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, R.; Madden, J.J.; Hoffman, A.N.; Kim, J.S.; Thayer, W.P.; Nanney, L.B.; Spear, M.E. Flap Reconstruction for Pressure Ulcers: An Outcomes Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2017, 5, e1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pre-Surgical Characteristics | Total (n = 375) | Without Complications (n = 314) | With Minor Complications (n = 46) | With Major Complications (n = 15) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 49.8 ± 13.9 | 49.6 ± 14.1 | 50.9 ± 12.9 | 50.1 ± 13.3 | 0.821 |
| Gender M, n (%) | 328 (87.5) | 274 (87.3) | 39 (84.8) | 15 (100) | 0.292 |
| Aetiology, n (%) | 0.034 * | ||||
| Trauma | 326 (86.9) | 277 (84.9) | 40 (12.3) | 9 (2.8) | |
| Vascular | 30 (8.0) | 22 (73.4) | 4 (13.3) | 4 (13.3) | |
| Other | 19 (5.1) | 15 (78.9) | 2 (10.5) | 2 (10.5) | |
| Tetraplegic, n (%) | 103 (27.5) | 90 (28.7) | 10 (21.7) | 3 (20.0) | 0.496 |
| Complete lesion (AIS A), n (%) | 317 (85.7) | 264 (84.1) | 39 (84.8) | 14 (93.3) | 0.625 |
| At least one comorbidity, n (%) | 214 (57.1) | 176 (56.1) | 31 (67.4) | 7 (46.7) | 0.247 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 42 (11.2) | 35 (11.1) | 4 (8.7) | 3 (20.0) | 0.482 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 103 (27.5) | 86 (27.4) | 14 (30.4) | 3 (20.0) | 0.732 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 114 (30.4) | 92 (29.3) | 18 (39.1) | 4 (26.7) | 0.380 |
| CKD, n (%) | 13 (3.5) | 12 (3.8) | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0) | 0.642 |
| CHD, n (%) | 8 (2.1) | 7 (2.2) | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0) | 0.843 |
| OSAS, n (%) | 6 (1.6) | 5 (1.6) | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | 0.203 |
| PI and Surgical Characteristics | Total (n = 434) | Without Complications (n = 358) | With Minor Complications (n = 59) | With Major Complications (n = 17) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More than 1 PI treated in one stage | 71 (16.4) | 59 (16.5) | 10 (16.9) | 2 (11.8) | 0.869 |
| Sacral, n (%) | 141 (32.5) | 105 (74.5) | 31 (22.0) | 5 (3.5) | 0.002 |
| Ischiatic, n (%) | 244 (56.2) | 210 (86.1) | 24 (9.8) | 10 (4.1) | 0.035 |
| Trochanter, n (%) | 68 (15.7) | 54 (79.4) | 11 (16.2) | 3 (4.4) | 0.764 |
| Other site, n (%) | 25 (5.8) | 24 (96.0) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0) | 0.181 |
| More than 1 PI treated (different sites) | 44 (10.1) | 35 (9.8) | 8 (13.6) | 1 (5.9) | 0.563 |
| Reconstructive flap, n (%) | 0.280 * | ||||
| Fasciocutaneous | 347 (80.0) | 288 (80.4) | 45 (76.3) | 14 (82.4) | |
| Muscular or musculocutaneous | 73 (16.8) | 56 (15.6) | 14 (23.7) | 3 (17.6) | |
| Fasciocutaneous Island perforator flap | 14 (3.2) | 14 (3.9) | 0 | 0 | |
| Osteomyelitis, n (%) | 239 (55.1) | 202 (56.4) | 29 (49.2) | 8 (47.1) | 0.463 |
| Fluidized bed, n (%) | 60 (13.8) | 49 (13.7) | 11 (18.6) | 0 (0) | 0.143 |
| Full Model RR (95% CI) | p-Value | Simplified Model RR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor complications | ||||
| Sacral PI | 2.27 (1.24–4.13) | 0.007 | 2.69 (1.55–4.67) | <0.001 |
| Ischiatic PI | 0.70 (0.36–1.33) | 0.277 | - | - |
| Vascular aetiology of the SCI/D vs. traumatic | 1.21 (0.38–3.80) | 0.743 | 1.25 (0.40–3.89) | 0.705 |
| Other aetiology vs. traumatic | 0.86 (0.18–4.20) | 0.852 | 0.88 (0.18–4.28) | 0.875 |
| Major complications | ||||
| Sacral PI | 1.29 (0.37–4.46) | 0.686 | 1.23 (0.41–3.68) | 0.704 |
| Ischiatic PI | 1.08 (0.35–3.37) | 0.891 | - | |
| Vascular aetiology of the SCI/D vs. traumatic | 5.05 (1.47–17.32) | 0.01 | 5.01 (1.47–17.05) | 0.01 |
| Other aetiology vs. traumatic | 3.74 (0.73–19.18) | 0.114 | 3.72 (0.73–18.99) | 0.114 |
| Pre-Surgical Characteristics | With Recurrence (n = 6) | Without Recurrence (n = 369) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 45.7 ± 20.1 | 49.8 ± 13.8 | 0.234 |
| Gender M, n (%) | 6 (100) | 322 (87.3) | 0.350 |
| Aetiology, n (%) | 0.347 * | ||
| Trauma | 5 (83.3) | 321 (87.0) | |
| Vascular | 0 (0) | 30 (8.1) | |
| Other | 1 (16.7) | 18 (4.9) | |
| Tetraplegic, n (%) | 1 (16.7) | 102 (27.6) | 0.550 |
| Complete lesion (AIS A), n (%) | 4 (66.7) | 313 (84.8) | 0.222 |
| At least one comorbidity, n (%) | 6 (100) | 209 (56.6) | 0.033 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 1 (16.7) | 41 (11.1) | 0.669 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 2 (33.3) | 101 (27.4) | 0.746 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 4 (66.7) | 111 (30.1) | 0.054 |
| CKD, n (%) | 2 (33.3) | 12 (3.3) | 0.018 |
| CHD, n (%) | 1 (16.7) | 8 (2.2) | 0.136 |
| OSAS, n (%) | 0 (0) | 6 (1.6) | 0.753 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sgarzani, R.; Rucci, P.; Landi, S.; Battilana, M.; Capirossi, R.; Aramini, B.; Negosanti, L. Reconstructive Surgery of Pressure Injuries in Spinal Cord Injury/Disorder Patients: Retrospective Observational Study and Proposal of an Algorithm for the Flap Choice. Healthcare 2024, 12, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010034
Sgarzani R, Rucci P, Landi S, Battilana M, Capirossi R, Aramini B, Negosanti L. Reconstructive Surgery of Pressure Injuries in Spinal Cord Injury/Disorder Patients: Retrospective Observational Study and Proposal of an Algorithm for the Flap Choice. Healthcare. 2024; 12(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleSgarzani, Rossella, Paola Rucci, Siriana Landi, Micaela Battilana, Rita Capirossi, Beatrice Aramini, and Luca Negosanti. 2024. "Reconstructive Surgery of Pressure Injuries in Spinal Cord Injury/Disorder Patients: Retrospective Observational Study and Proposal of an Algorithm for the Flap Choice" Healthcare 12, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010034
APA StyleSgarzani, R., Rucci, P., Landi, S., Battilana, M., Capirossi, R., Aramini, B., & Negosanti, L. (2024). Reconstructive Surgery of Pressure Injuries in Spinal Cord Injury/Disorder Patients: Retrospective Observational Study and Proposal of an Algorithm for the Flap Choice. Healthcare, 12(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12010034







