Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Baijiu Samples
2.2. E-Nose and Experimental Procedure
2.3. E-Tongue and Experimental Procedure
2.4. QDA
2.4.1. Panel and Training
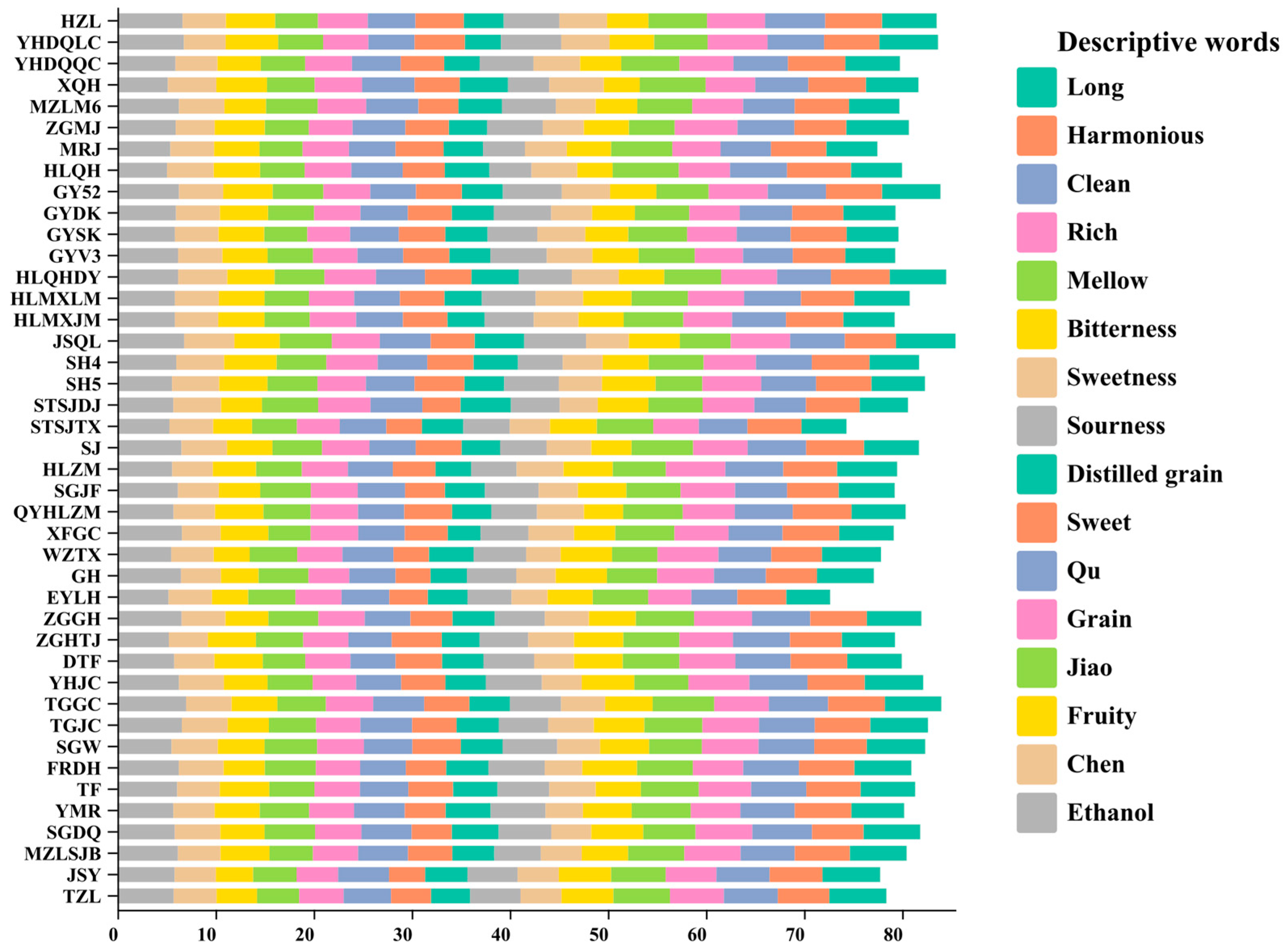
2.4.2. Development of Descriptive Words
2.4.3. Sample Evaluation
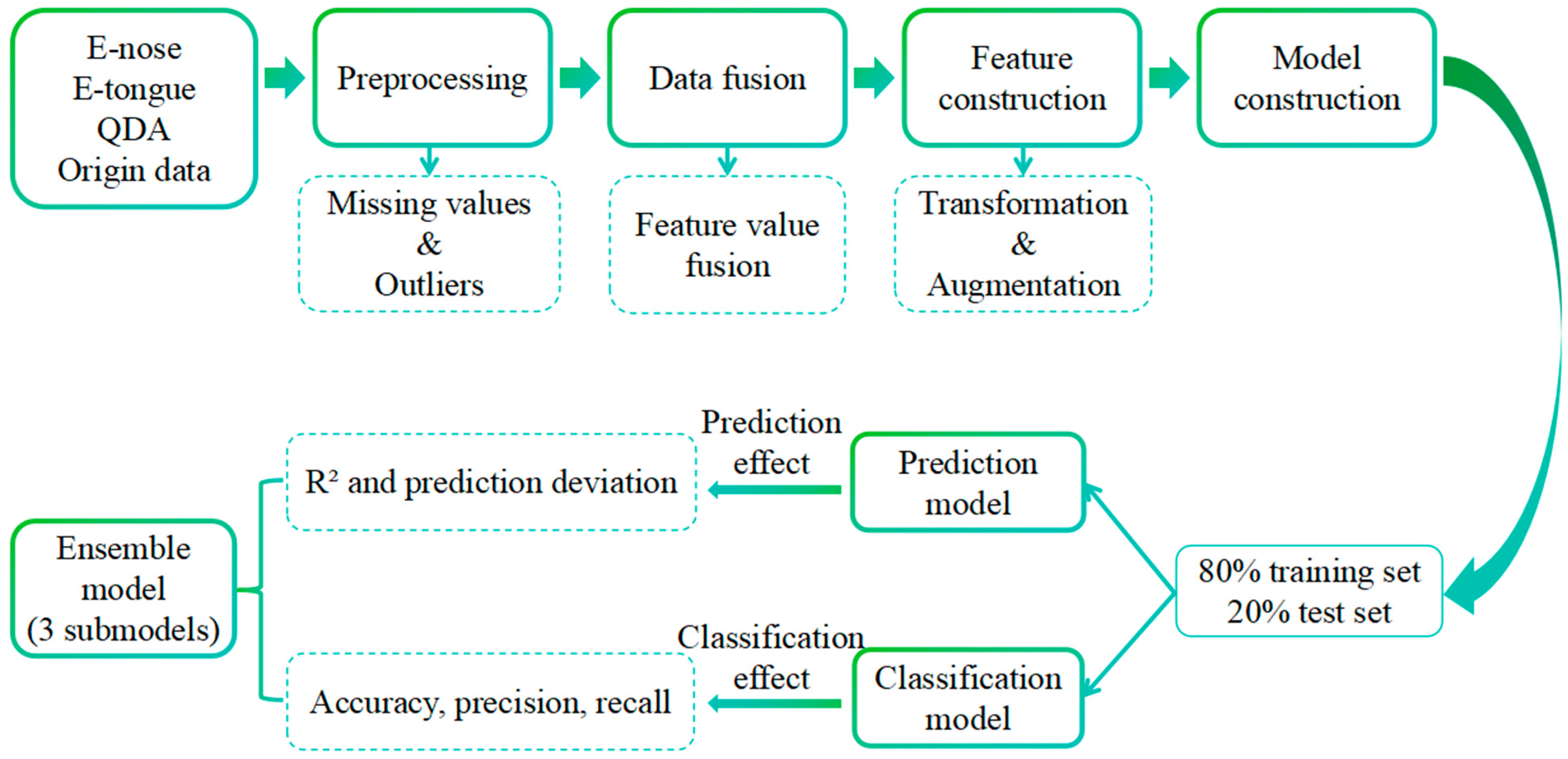
2.5. Machine Learning
2.5.1. Data Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
2.5.2. Model Construction
2.5.3. Model Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
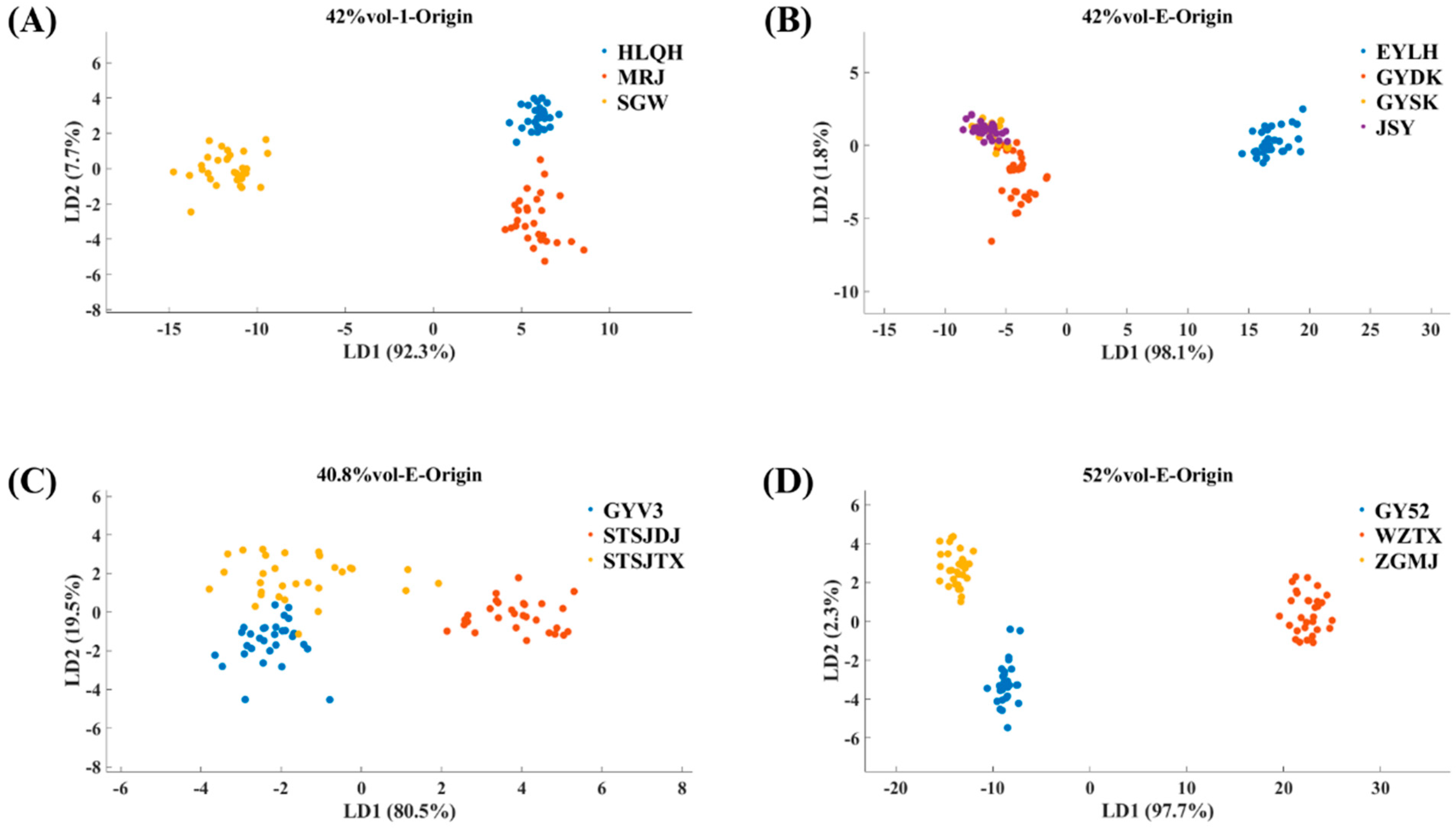
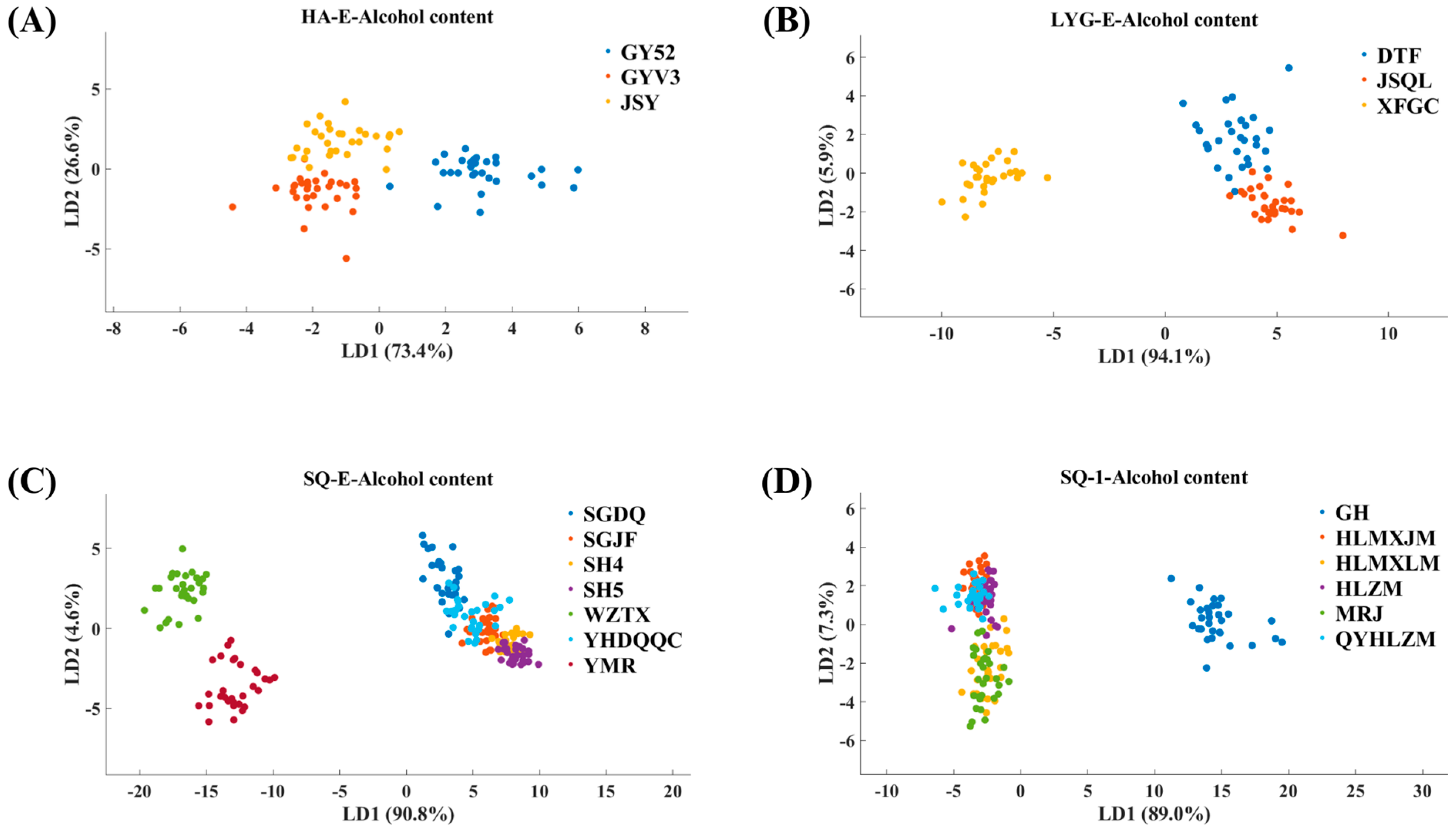
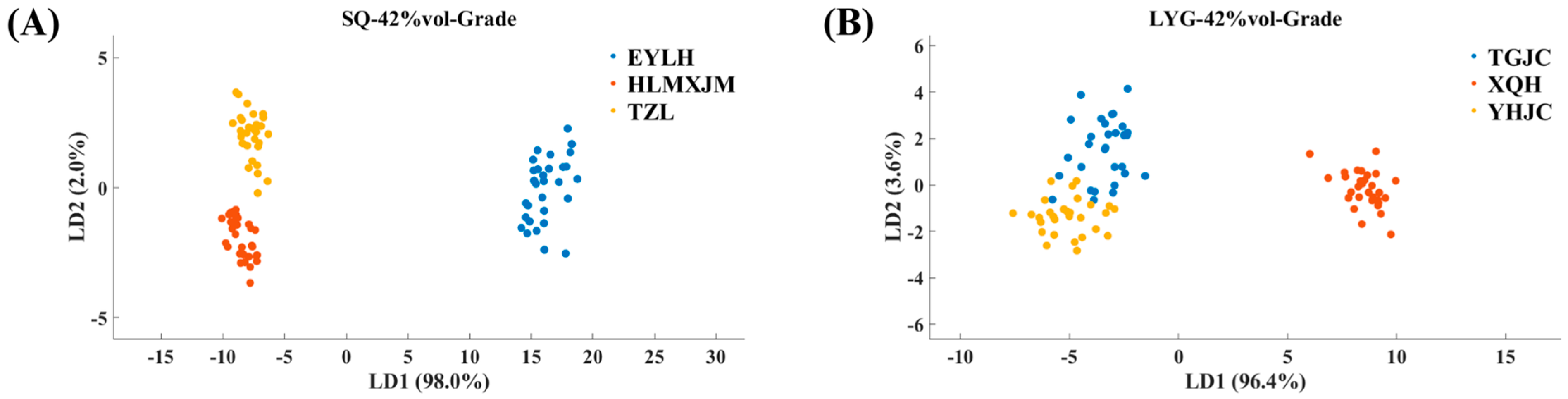
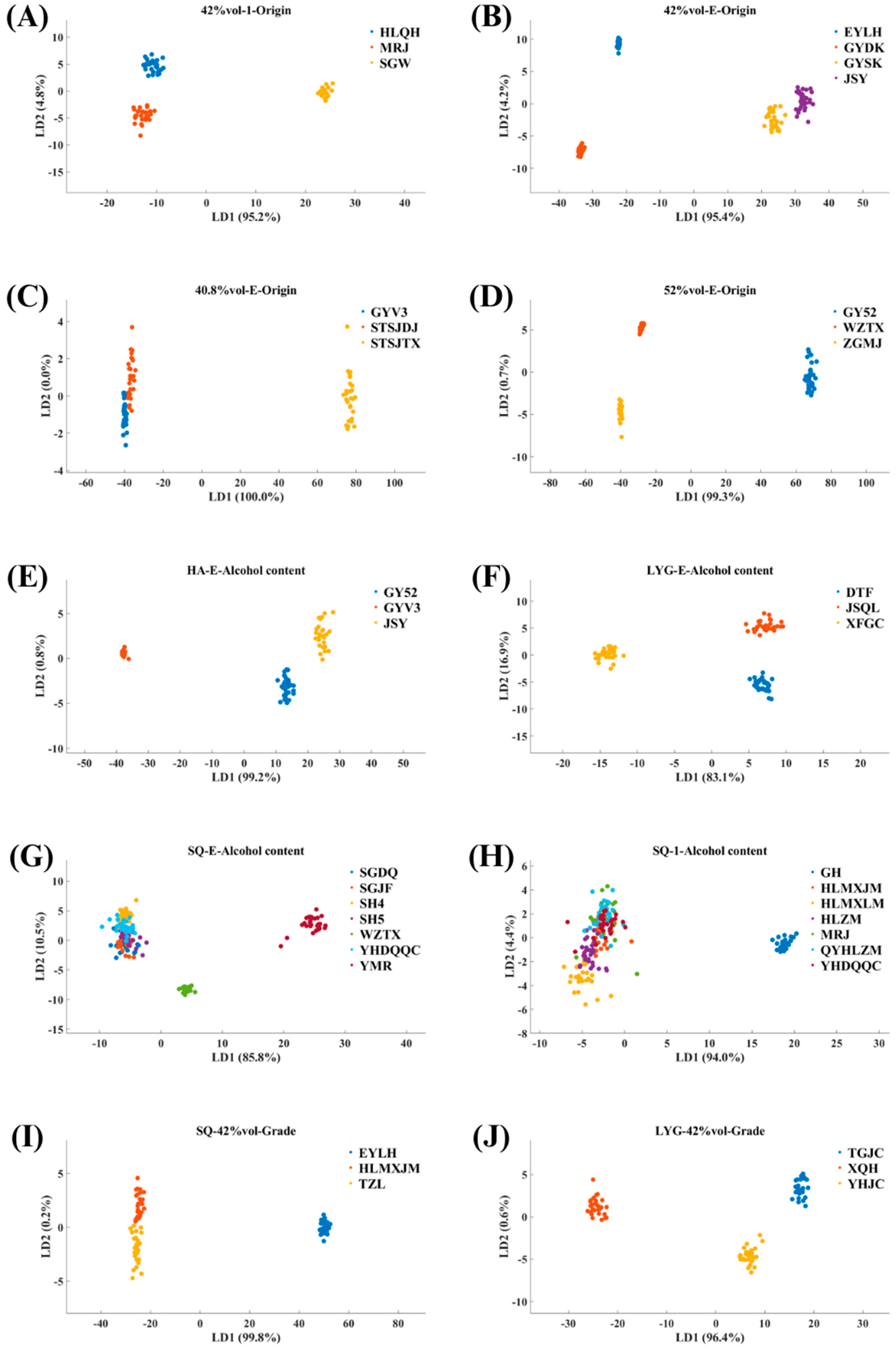
3.1. Results of LDA Analysis of E-Nose Data
3.2. Results of LDA Analysis of E-Tongue Data
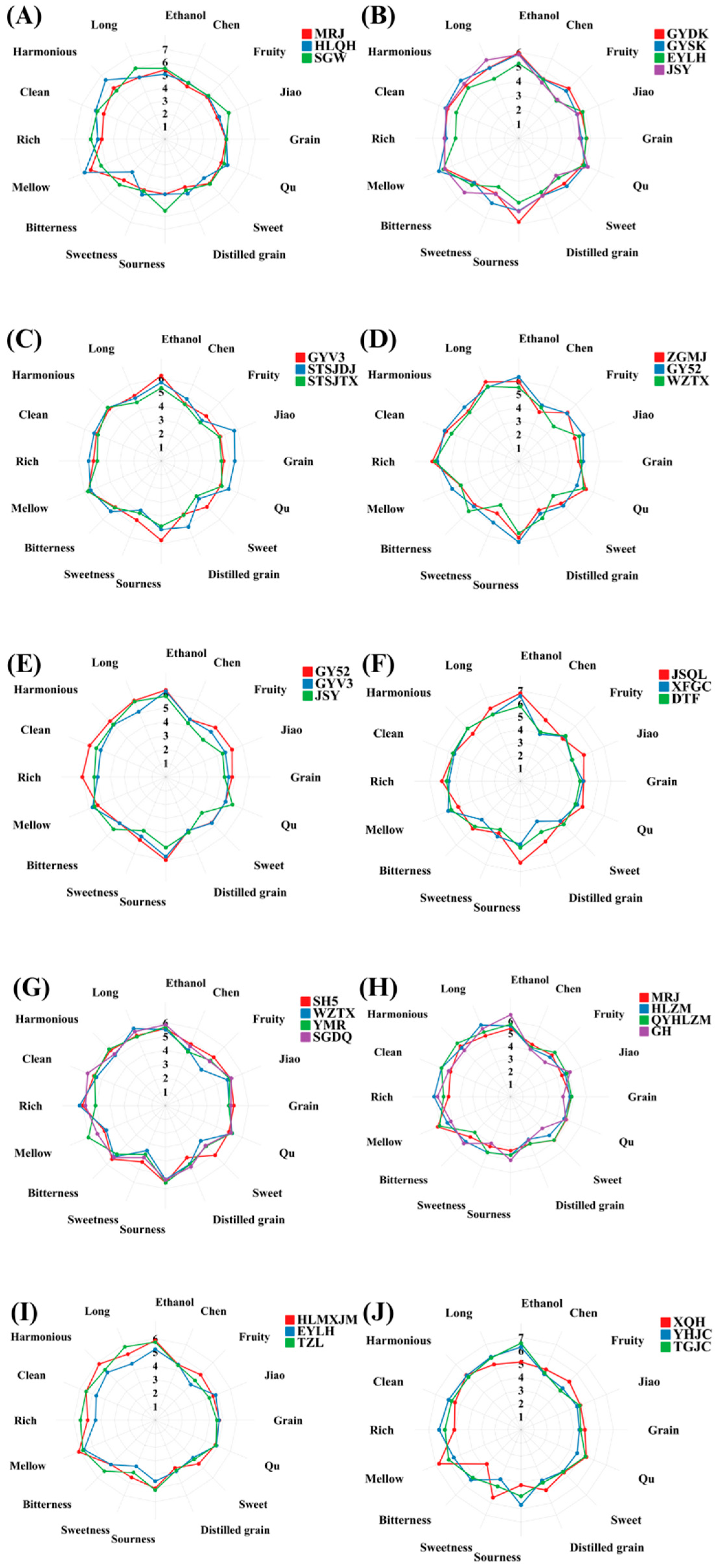
3.3. QDA Results
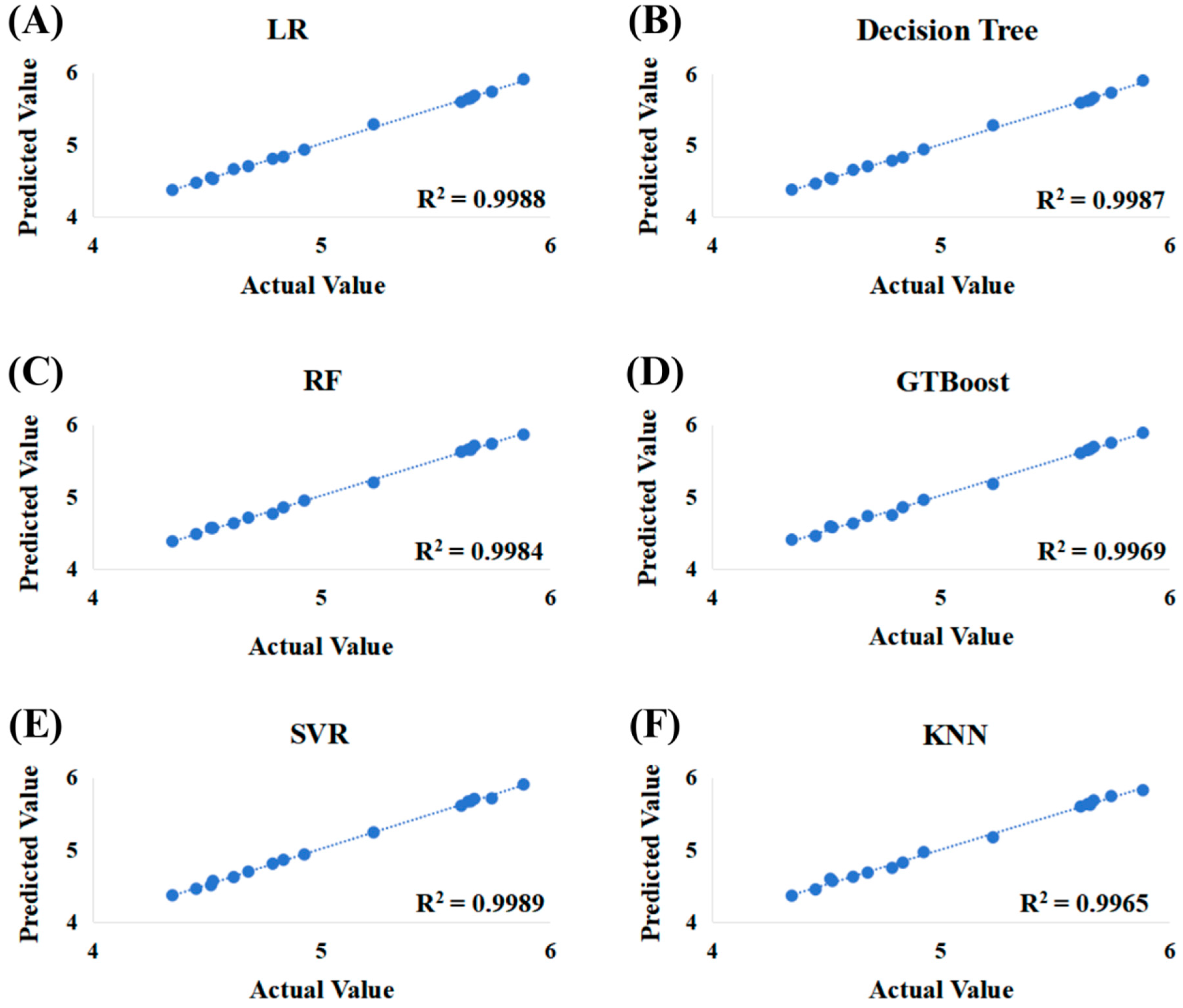
3.4. Baijiu Prediction and Classification Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, Z.G.; Li, X.T.; Sun, B.G. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.N.; Jing, S.; Wang, X.L.; Zheng, F.P.; Li, H.H.; Sun, B.G.; Li, Z.X. Evaluation of the Perceptual Interaction among Ester Odorants and Nonvolatile Organic Acids in Baijiu by GC-MS, GC-O, Odor Threshold, and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13987–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.S.; Zhao, D.R. Uncover the flavor code of strong-aroma baijiu: Research progress on the revelation of aroma compounds in strong-aroma baijiu by means of modern separation technology and molecular sensory evaluation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Chen, S.; Tang, K.; Qian, M.; Yu, X.W.; Xu, Y. Sensory characterization of Baijiu pungency by combined time-intensity (TI) and temporal dominance of sensations (TDS). Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Duan, J.W.; Li, H.H.; Zheng, F.P.; Cheng, H.; Ye, X.Q.; Sun, B.G. Characterization and comparison of the aroma-active compounds on different grades of sesame-flavor Baijiu by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-olfactometry-mass spectrometry. Food Sci. Hum. Well 2023, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.J.; Shi, X.X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, K. Comparison of the Aroma-Active Compounds and Sensory Characteristics of Different Grades of Light-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2023, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fan, S.H.; He, G.L.; Liang, S.Y.; Xu, Y.; Tang, K. Comparison of Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics between Two Different Types of Rice-Based Baijiu. Foods 2024, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hong, J.X.; Liu, X.X.; Wei, H.Y.; Tian, W.J.; Zhao, D.R.; et al. Integration of Chemometrics and Sensory Metabolomics to Validate Quality Factors of Aged Baijiu (Nianfen Baijiu) with Emphasis on Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters. Foods 2023, 12, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.L.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zou, L.; Zhu, H.; Cao, R.G.; Zhao, G. Combination of machine learning and intelligent sensors in real-time quality control of alcoholic beverages. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 42, e54622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Stancik, C.M.; Yin, Y.; Wu, J.; Duncan, S.E. Performance of cost-effective PET packaging with light protective additives to limit photo-oxidation in UHT milk under refrigerated LED-lighted storage condition. Food Packag. Shelf 2022, 31, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, S.; Lotesoriere, B.J.; Dellacà, R.L.; Capelli, L. Physical Confounding Factors Affecting Gas Sensors Response: A Review on Effects and Compensation Strategies for Electronic Nose Applications. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.C.; Wang, Y.R.; Qu, D.W.; Zhao, H.J.; Tian, L.X.; Zhou, J.P.; Liu, J.Z.; Guo, Z. Microbial communities, functional, and flavor differences among three different-colored high-temperature Daqu: A comprehensive metagenomic, physicochemical, and electronic sensory analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, J.K.; Durán, C.M.; Cáceres, J.M.; Cuastumal, C.A.; Ferreira, J.; Ramos, J.; Bahder, B.; Oates M and Ruiz, A. Assessment of E-Senses Performance through Machine Learning Models for Colombian Herbal Teas Classification. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, D.H.; He, J.F.; Wong, A.K.Y.; Hung, K. Channel Attention Convolutional Neural Network for Chinese Baijiu Detection With E-Nose. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16170–16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castells, R.; Modesti, M.; Moreno-García, J.; Rodríguez-Moreno, M.; Catini, A.; Capuano, R.; Di Natale, C.; Bellincontro, A.; Moreno, J. Differentiation through E-nose and GC-FID data modeling of rosé sparkling wines elaborated via traditional and Charmat methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 1, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celdran, A.C.; Oates, M.J.; Cabrera, C.M.; Pangua, C.; Tardaguila, J.; Ruiz-Canales, A. Low-Cost Electronic Nose for Wine Variety Identification through Machine Learning Algorithms. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunsa-Ard, W.; Kerdcharoen, T. Electronic Nose for Analysis of Coffee Beans Obtained from Different Altitudes and Origin. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chon buri, Thailand, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.H.; Yea, J.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.N.; Jekal, J.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.; Oh, S.; Song, S.; Son, J.; et al. Taste Bud-Inspired Single-Drop Multitaste Sensing for Comprehensive Flavor Analysis with Deep Learning Algorithms. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2023, 15, 46041–46053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.B.; Shi, Y.; Xia, X.X.; Ying, Y.X.; Men, H. A data processing method for electronic tongue based on computational model of taste pathways and convolutional neural network. Measurement 2022, 205, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.H.; Huang, G.B.; Liu, T.; Tan, X.H. Taste Recognition in E-Tongue Using Local Discriminant Preservation Projection. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Huang, Y.M.; Górska-Horczyczak, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Jelen, H.H. Rapid analysis of Baijiu volatile compounds fingerprint for their aroma and regional origin authenticity assessment. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Chen, R.Y.; Li, X.B.; Fu, Z.Y.; Xian, C.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X.Y. Comprehensive identification of key compounds in different quality grades of soy sauce-aroma type baijiu by HS-SPME-GC-MS coupled with electronic nose. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1132527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Rizk, H.; Bouveresse, D.J.R.; Chamberland, J.; Cordella, C.B.Y. Recent developments of e-sensing devices coupled to data processing techniques in food quality evaluation: A critical review. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 5410–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.J.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.R.; Li, M.S.; Wei, Z.B. Combination of an E-Nose and an E-Tongue for Adulteration Detection of Minced Mutton Mixed with Pork. J. Food Qual. 2019, 1, 4342509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.Z.; Pu, D.D.; Yan, W.J.; Zhang, Q.C.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. Recent advances and application of machine learning in food flavor prediction and regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hooti, H.S.; Al-Bulushi, I.M.; Al-Attabi, Z.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Subhi, L.K.; Al-Habsi, N.A. Efficiency of Electronic Nose in Detecting the Microbial Spoilage of Fresh Sardines. Foods 2024, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.Z.; Sun, H.B.; Liu, H.Q.; Wang, D.Q.; Shen, Y.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, J.L.; Huang, M.Q.; et al. Comparative analysis of the differences among Langya flavor Baijiu and strong and soy sauce flavor Baijiu by targeted flavor analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 122, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Cen, H.Y.; Xie, Y.Q. Study on grading of Xiaoqu Baijiu based on untargeted detection of electrochemical measurements. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.B.; Zhu, L.; Jing, S.; Li, Q.; Ji, J.; Zheng, F.P.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Sun, J.Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, M.M.; et al. Insights into the Role of 2-Methyl-3-furanthiol and 2-Furfurylthiol as Markers for the Differentiation of Chinese Light, Strong, and Soy Sauce Aroma Types of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7946–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.R.; Zhang, C.N.; Lang, Y.; Li, X.T.; Hu, S.L.; Xu, Y.Q.; Li, W.W.; Sun, B.G. Changes in Microbial Communities and Volatile Compounds during the Seventh Round of Sauce-Flavor baijiu Fermentation in Beijing Region. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2023, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ming, Y.Z.; Li, Y.M.; Huang, M.Q.; Luo, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Li, H.H.; Wu, J.H.; Sun, X.T.; Luo, X.L. Characterization and comparative study of the key odorants in Caoyuanwang mild-flavor style Baijiu using gas chromatography-olfactometry and sensory approaches. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Zhu, S.M.; Yu, Y. Quality assessment of Chinese liquor with different ages and prediction analysis based on gas chromatography and electronic nose. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Gu Y and Jia, J. Classification of Multiple Chinese Liquors by Means of a QCM-based E-Nose and MDS-SVM Classifier. Sensors 2017, 17, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geana, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Apetrei, C. Electrochemical Sensors Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis as Screening Tools for Wine Authentication Issues: A Review. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.X.; Wang, J.S.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, Z.G.; Tian, W.J.; Wu, Y.S.; Chen, H.; Zhao, D.R.; Sun, J.Y. Unraveling variation on the profile aroma compounds of strong aroma type of Baijiu in different regions by molecular matrix analysis and olfactory analysis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, K. Exploring the Mystery of the Sweetness of Baijiu by Sensory Evaluation, Compositional Analysis and Multivariate Data Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Name | Alcohol Content (%vol) | Grade | Origin | No. | Name | Alcohol Content (%vol) | Grade | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | QYHLZM | 42 | 1 a | Yanghe, Suqian | 22 | GYV3 | 40.8 | E | Lianshui, Huaian |
| 2 | MRJ | 42 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian | 23 | SGJF | 40.8 | E | Sihong, Suqian |
| 3 | HLMXJM | 42 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian | 24 | STSJTX | 40.8 | E | Sihong, Suqian |
| 4 | HLQH | 42 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian | 25 | STSJDJ | 40.8 | E | Sihong, Suqian |
| 5 | YHJC | 42 | 1 | Guannan, Lianyungang | 26 | MZLSJB | 40.8 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 6 | SGW | 42 | 1 | Guannan, Lianyungang | 27 | MZLM6 | 40.8 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 7 | GYDK | 42 | E b | Lianshui, Huaian | 28 | GH | 52 | 1 | Sucheng, Suqian |
| 8 | GYSK | 42 | E | Lianshui, Huaian | 29 | HLQHDY | 52 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 9 | JSY | 42 | E | Lianshui, Huaian | 30 | HLZM | 52 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 10 | FRDH | 42 | E | Donghai, Lianyungang | 31 | HLMXLM | 52 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 11 | ZGHTJ | 42 | E | Guannan, Lianyungang | 32 | GY52 | 52 | E | Lianshui, Huaian |
| 12 | DTF | 42 | E | Guannan, Lianyungang | 33 | WZTX | 52 | E | Sucheng, Suqian |
| 13 | TGGC | 42 | E | Guannan, Lianyungang | 34 | ZGMJ | 52 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 14 | TGJC | 42 | E | Guannan, Lianyungang | 35 | XQH | 42 | 1 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 15 | SJ | 42 | E | Sihong, Suqian | 36 | SH4 | 40.8 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 16 | EYLH | 42 | E | Sucheng, Suqian | 37 | SH5 | 50.8 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 17 | ZGGH | 42 | E | Sucheng, Suqian | 38 | YMR | 35.8 | E | Muyang, Suqian |
| 18 | YHDQLC | 42 | E | Yanghe, Suqian | 39 | SGDQ | 46 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 19 | YHDQQC | 42 | E | Yanghe, Suqian | 40 | XFGC | 53 | E | Ganyu, Lianyungang |
| 20 | HZL | 42 | E | Yanghe, Suqian | 41 | JSQL | 53 | E | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 21 | TZL | 42 | E | Yanghe, Suqian | 42 | TF | 40.8 | 1 | Guannan, Lianyungang |
| Descriptive Word | Definition | Reference Sample | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aroma | Ethanol | Aroma of alcohol and ester substances | 40–50% food-grade ethanol |
| Chen | A woody and honey aroma produced by long-term aging | 20–30% honey | |
| Fruity | A fruit-like aroma | 10–20% apple or pear juice | |
| Jiao | An earthy and musty aroma | 10–20 g/L Pu’er tea leaves | |
| Grain | Aroma of cooked sorghum or corn | 100 g/L sorghum | |
| Qu | Aroma of Aspergillus oryzae fermentation | 100 g/L Aspergillus oryzae fermentation | |
| Sweet | Aroma of vanilla extract | 0.1–0.2% vanilla extract | |
| Distilled grain | Aroma of distillers’ grains produced during fermentation | 100 g/L distillers’ grains | |
| Taste | Sourness | Sour taste similar to acetic acid | 0.1–0.2% acetic acid |
| Sweetness | Sweet taste similar to sucrose solution | 10–20 g/L sucrose | |
| Bitterness | Bitter taste similar to quinine sulfate solution | 0.002% quinine sulfate solution | |
| Mouthfeel | Mellow | A comfortable and smooth feeling in the mouth, without significant irritation | 50–100 mL/L soybean milk |
| Rich | Aroma and taste linger in the mouth for a long time | 10–20 g/L peanut butter | |
| Clean | A refreshing and non-greasy mouthfeel | 5–10 leaves/L fresh mint leaves | |
| Harmonious | Uniform distribution of various aromas and tastes | Equally proportioned mixed fruit juice | |
| Long | Aroma and taste linger in the mouth for a long time | 1–2 g/L black tea leaves | |
| Model | 32 Different Origins | 24 Different Grades | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | |
| Logistic Regression | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Support Vector Machine | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Naive Bayes | 98.57% | 0.99 | 1.00 | 93.75% | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| k-Nearest Neighbors | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Decision Tree | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliya; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070125
Aliya, Liu S, Zhang D, Cao Y, Sun J, Jiang S, Liu Y. Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(7):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070125
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliya, Shi Liu, Danni Zhang, Yufa Cao, Jinyuan Sun, Shui Jiang, and Yuan Liu. 2024. "Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning" Chemosensors 12, no. 7: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070125
APA StyleAliya, Liu, S., Zhang, D., Cao, Y., Sun, J., Jiang, S., & Liu, Y. (2024). Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning. Chemosensors, 12(7), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070125







