Small Acetone Sensor with a Porous Colorimetric Chip for Breath Acetone Detection Using the Flow–Stop Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
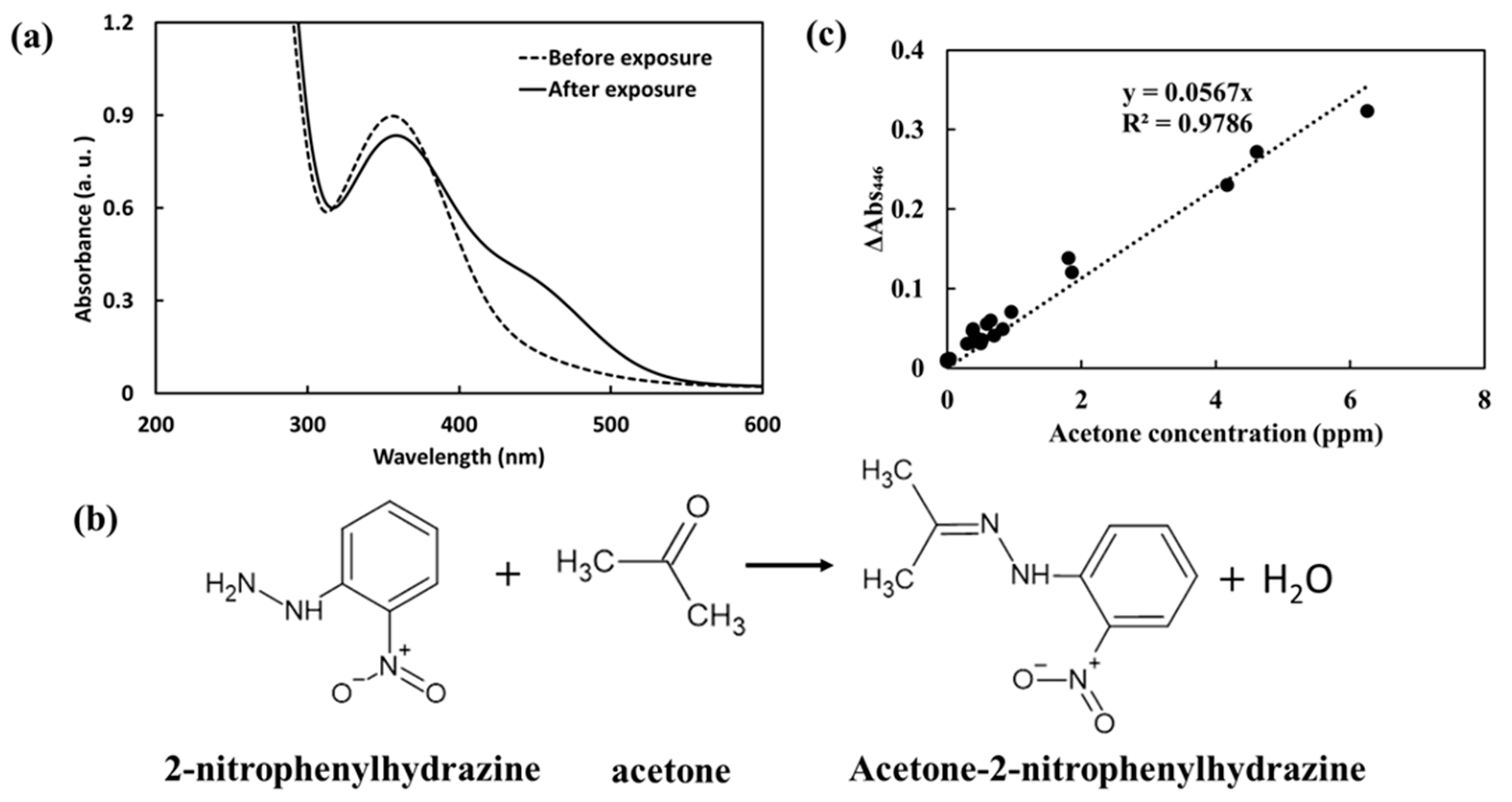
2.1. Analytical Chip
2.2. Preparation of an Acetone Atmosphere
2.3. Humidity Dependency Evaluation
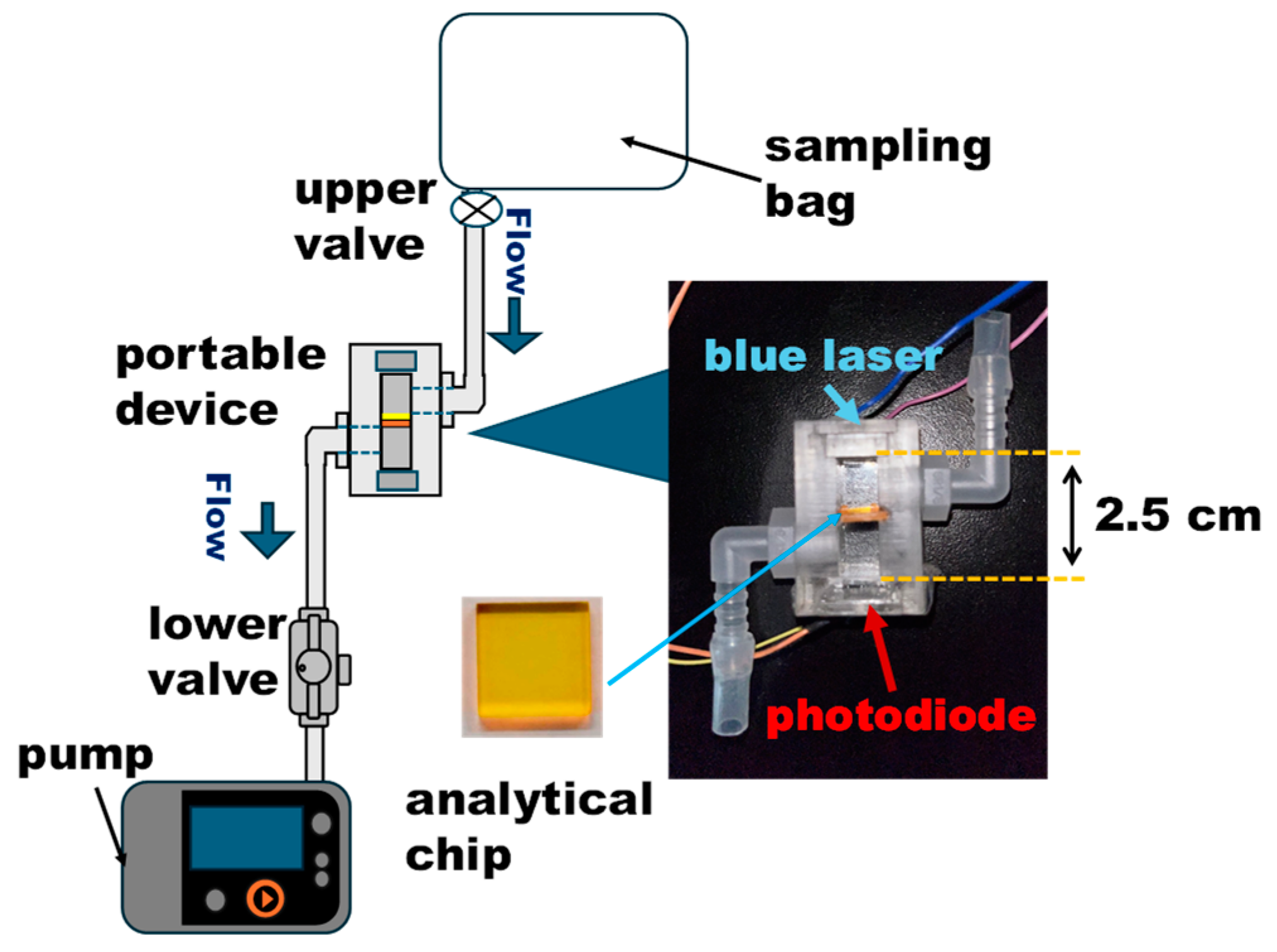
2.4. Portable Device and Measurement Method
2.4.1. Portable Device and Measurement Setup
2.4.2. Constant Flow Measurement
2.4.3. Flow–Stop Measurement
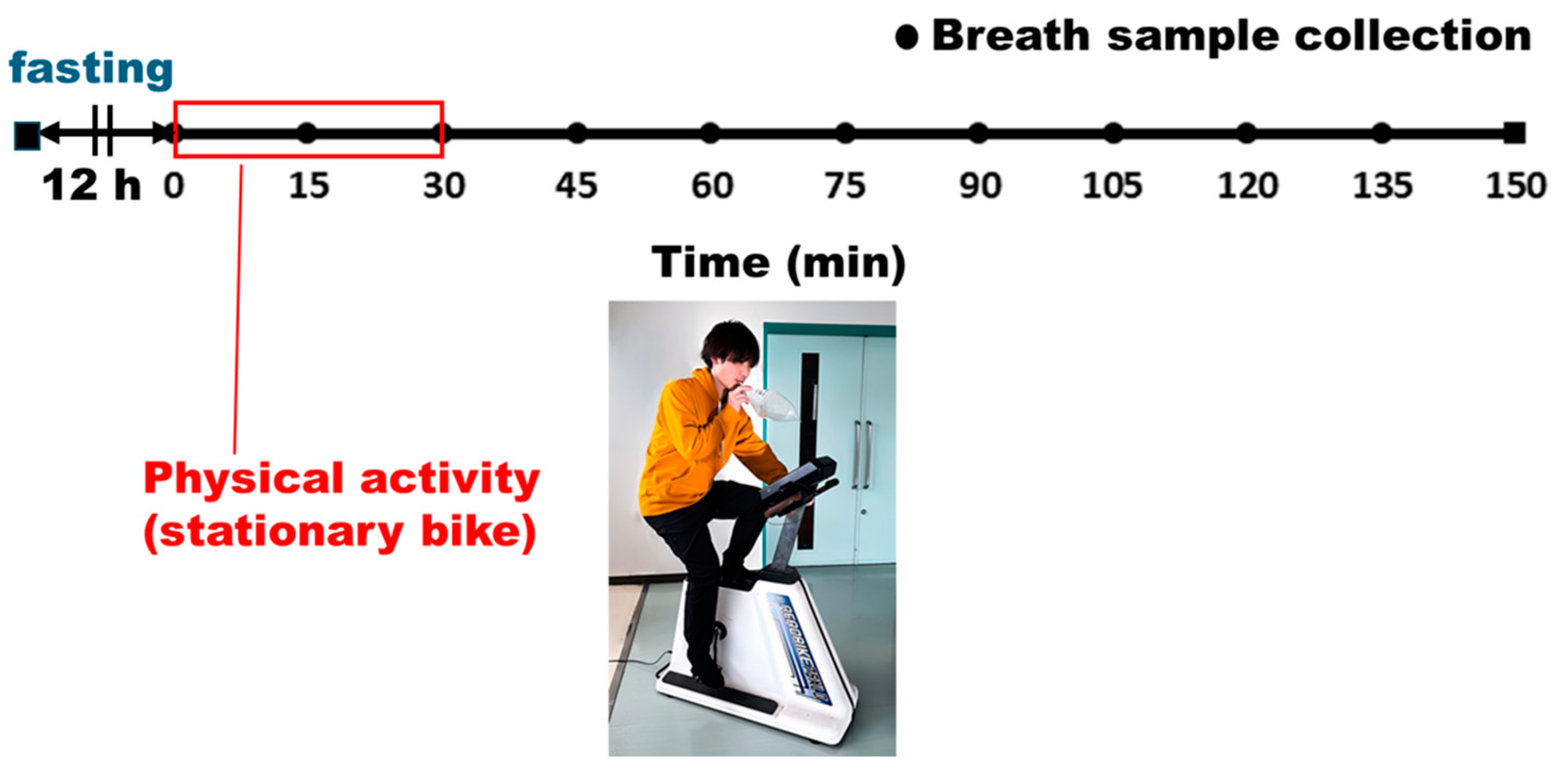
2.5. Exhaled Air Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Acetone Analysis Chip
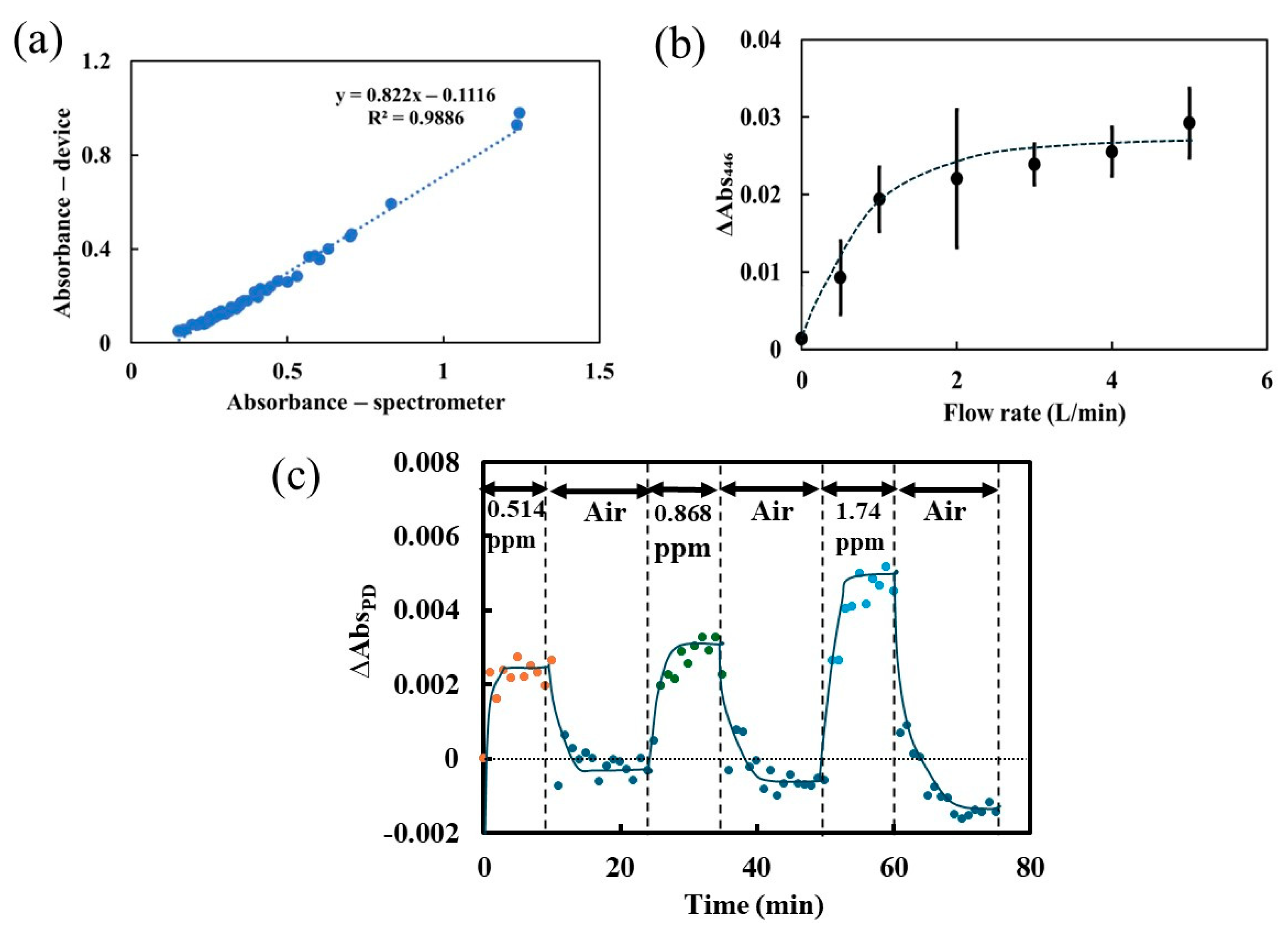
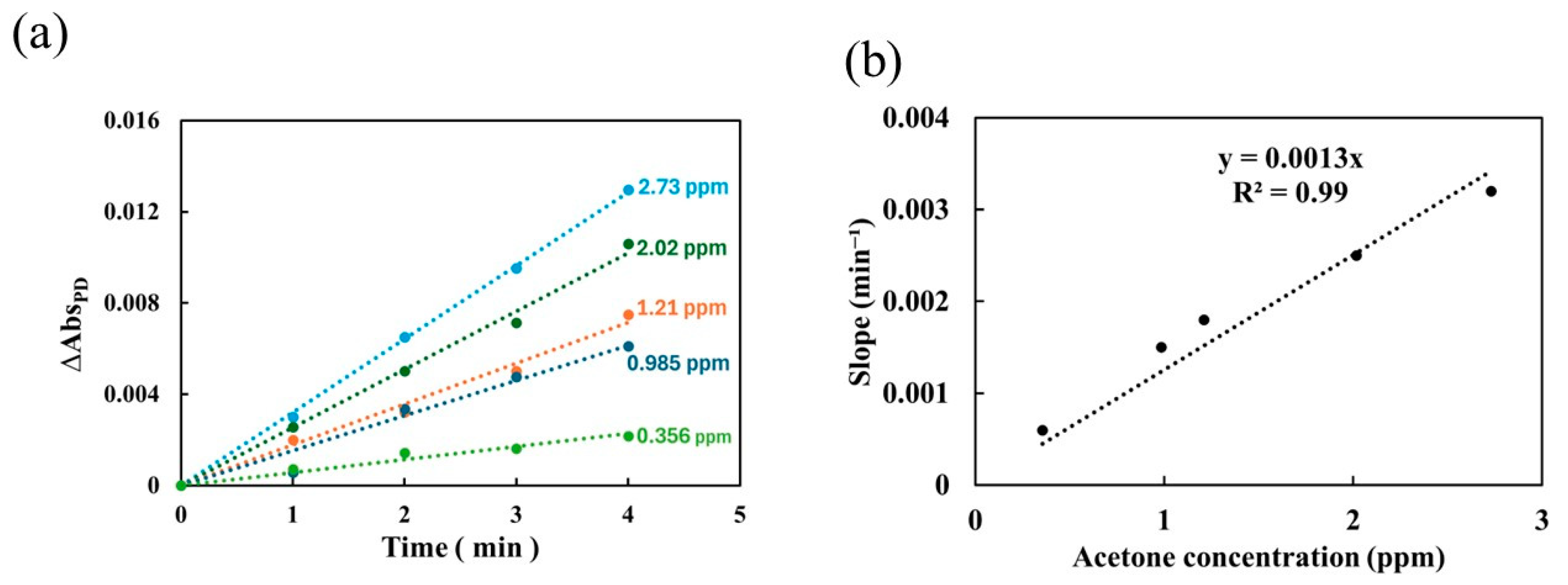
3.2. Performance of the Portable Device Using Constant Flow Method
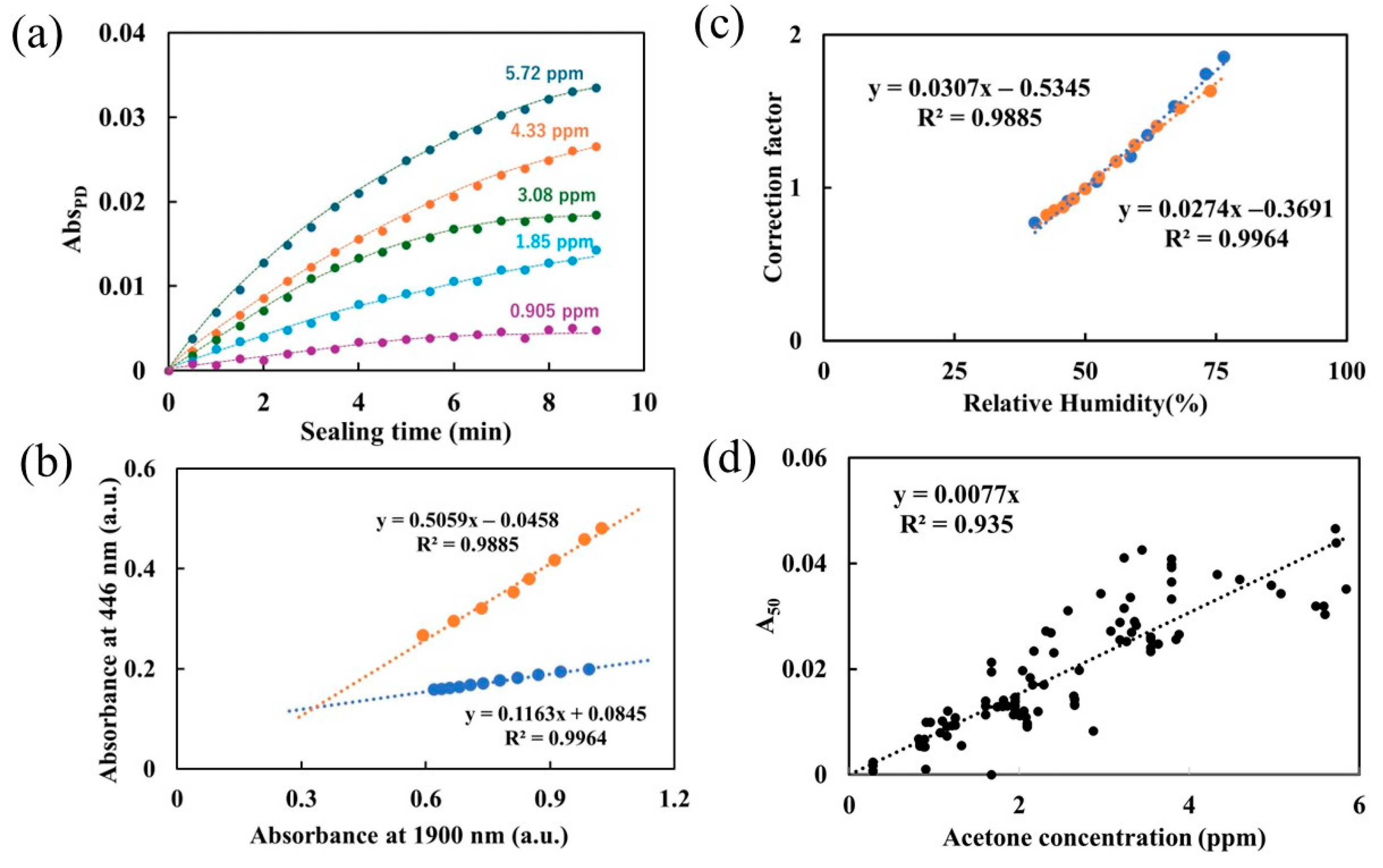
3.3. Performance of the Portable Device Using Flow–Stop Measurement
- (i)
- The A value was calculated by using the results of the flow–stop measurements and Equation (4).
- (ii)
- The A value is corrected using Equations (6) and (7).
- (iii)
- Acetone concentration is calculated using Equation (8) and the corrected A value.
3.4. Exhaled Breath Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VOC | Volatile organic compound |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| GO@CNC | Graphene oxide@cellulose nanocrystal |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| 4-NPH | 4-nitrophenylhydrazine |
| 2-NPH | 2-nitrophenylhydrazine |
| A-2-NPH | Acetone-2-NPH |
References
- Buszewski, B.; Kęsy, M.; Ligor, T.; Amann, A. Human exhaled air analytics: Biomarkers of diseases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajo-Fernández, M.; Souza-Silva, É.A.; Barbas, C.; Rey-Stolle, M.F.; García, A. GC-MS-based metabolomics of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath: Applications in health and disease. A review. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 10, 1295955. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.C.; Chou, H.H.; Wu, T.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Ho, K.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Ho, Y.P. The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2008, 43, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoman, H.; Rashid Habib, S.; Alghamdi, S.; Al-Juhani, H.; Daabash, R.; Al-Khalid, W.; Al-Askar, M.; Al-Johany, S. Relationship between fixed dental crowns and volatile sulphur compounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, P.; Loeseken, C.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W. Breath gas aldehydes as biomarkers of lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mochalski, P.; Leja, M.; Slefarska-Wolak, D.; Mezmale, L.; Patsko, V.; Ager, C.; Królicka, A.; Mayhew, C.A.; Shani, G.; Haick, H. Identification of key volatile organic compounds released by gastric tissues as potential non-invasive biomarkers for gastric cancer. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Is breath acetone a biomarker of diabetes? A historical review on breath acetone measurements. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 037109. [Google Scholar]
- Samudrala, D.; Geurts, B.; Brown, P.A.; Szymańska, E.; Mandon, J.; Jansen, J.; Buydens, L.; Harren, F.J.M.; Cristescu, S.M. Changes in urine headspace composition as an effect of strenuous walking. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasa, V.; Malwela, T.; Beukes, M.; Mokgotho, M.; Liu, C.-P.; Mwakikunga, B. Sensing technologies for detection of acetone in human breath for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.; Sharma, S.; Galpin, M.; Lunn, D.; Megson, C.; Peverall, R.; Richmond, G.; Ritchie, G.A.D.; Owen, K.R. The correlation between breath acetone and blood betahydroxybutyrate in individuals with type 1 diabetes. J. Breath Res. 2020, 15, 017101. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Diabetes. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Continuous monitoring of breath acetone, blood glucose and blood ketone in 20 type 1 diabetic outpatients over 30 days. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2017, 8, 1000386. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Sun, C.; Huang, W.; Cui, X. A review of non-invasive blood glucose monitoring through breath acetone and body surface. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2024, 374, 115500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukes, V.; Beukes, M.; Lemmer, Y.; Mwakikunga, B. Blood ketone bodies and breath acetone analysis and their correlations in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Demetrowitsch, T.; Schwarz, K.; Kunze, T. New perspectives on ‘Breathomics’: Metabolomic profiling of non-volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath using DI-FT-ICR-MS. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Filipiak, W.; Sponring, A.; Baur, M.M.; Ager, C.; Filipiak, A.; Wiesenhofer, H.; Nagl, M.; Troppmair, J.; Amann, A. Characterization of volatile metabolites taken up by or released from Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae by using GC-MS. Microbiology 2012, 158, 3044–3053. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.W.; Zhang, K.; Tech, K.; Hayward, D.G.; Krynitsky, A.J.; Cassias, I.; Schenck, F.J.; Banerjee, K.; Dasgupta, S.; Brown, D. Multiresidue pesticide analysis of ginseng powders using acetonitrile- or acetone-based extraction, solid-phase extraction cleanup, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/selective ion monitoring (GC-MS/SIM) or tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5884–5896. [Google Scholar]
- Mendel, J.; Frank, K.; Edlin, L.; Hall, K.; Webb, D.; Mills, J.; Holness, H.K.; Furton, K.G.; Mills, D. Preliminary accuracy of COVID-19 odor detection by canines and HS-SPME-GC-MS using exhaled breath samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Synergy 2021, 3, 100155. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, K.; Pizzini, A.; Arendacká, B.; Zerlauth, K.; Filipiak, W.; Schmid, A.; Dzien, A.; Neuner, S.; Lechleitner, M.; Scholl-Bürgi, S.; et al. Breath acetone-aspects of normal physiology related to age and gender as determined in a PTR-MS study. J. Breath Res. 2009, 3, 027003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Slingers, G.; Pedrotti, M.; Pugliese, G.; Malásková, M.; Bryant, L.; Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Moreno, S.; Cordell, R.; et al. The peppermint breath test benchmark for PTR-MS and SIFT-MS. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquencourt, C.; Grassin-Delyle, S.; Théevenot, E.A. ptairMS: Real-time processing and analysis of PTR-TOF-MS data for biomarker discovery in exhaled breath. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Španěl, P.; Dryahina, K.; Rejšková, A.; Chippendale, T.W.E.; Smith, D. Breath acetone concentration; biological variability and the influence of diet. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, N23–N31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Acevedo, C.M.; Carrillo Gómez, J.K.; Cuastumal Vasquez, C.A.; Ramos, J. Prostate cancer detection in Colombian patients through E-senses devices in exhaled breath and urine samples. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lv, S.; Tang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; et al. YSZ-based acetone sensor using a Cd2SnO4 sensing electrode for exhaled breath detection in medical diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 345, 130321. [Google Scholar]
- Orasugh, J.T.; Saasa, V.; Ray, S.S.; Mwakikunga, B. Supersensitive metal free in-situ synthesized graphene oxide@cellulose nanocrystals acetone sensitive bioderived sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124514. [Google Scholar]
- Jahromi, H.D.; Kazemi, M.; Sheikhi, M.H. Room temperature and highly sensitive acetone sensor based on lead sulfide nanosheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 267, 115082. [Google Scholar]
- Rabih, A.A.S.; Dennis, J.O.; Ahmed, A.Y.; Md Khir, M.H.; Ahmed, M.G.A.; Idris, A.; Mian, M.U. MEMS-Based acetone vapor sensor for non-invasive screening of diabetes. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9740–9747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, C.; Liang, T.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Qi, L.; Ghaffar, A.; Xiong, J. Acetone sensor based on FAIMS-MEMS. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, A. MEMS based tin oxide thin film gas sensor for diabetes mellitus applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Kawamura, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Maruo, Y.Y. Colorimetric detection of gaseous acetone based on a reaction between acetone and 4-nitrophenylhydrazine in porous glass. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105428. [Google Scholar]
- Mochalski, P.; Mochalski, J.; Mochalski, M.; Mochalski, K.; Hinterhuber, H.; Baumann, M.; Amann, A. Blood and breath levels of selected volatile organic compounds in healthy volunteers. Analyst 2013, 138, 2134–2145. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muramatsu, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Osada, M.; Tajima, K.; Karashima, A.; Maruo, Y.Y. Small Acetone Sensor with a Porous Colorimetric Chip for Breath Acetone Detection Using the Flow–Stop Method. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040136
Muramatsu Y, Watanabe S, Osada M, Tajima K, Karashima A, Maruo YY. Small Acetone Sensor with a Porous Colorimetric Chip for Breath Acetone Detection Using the Flow–Stop Method. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuramatsu, Yuto, Sota Watanabe, Mahiro Osada, Kohsuke Tajima, Akihiro Karashima, and Yasuko Yamada Maruo. 2025. "Small Acetone Sensor with a Porous Colorimetric Chip for Breath Acetone Detection Using the Flow–Stop Method" Chemosensors 13, no. 4: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040136
APA StyleMuramatsu, Y., Watanabe, S., Osada, M., Tajima, K., Karashima, A., & Maruo, Y. Y. (2025). Small Acetone Sensor with a Porous Colorimetric Chip for Breath Acetone Detection Using the Flow–Stop Method. Chemosensors, 13(4), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040136




