Banana Flour Adulteration Key Marker Unravelled by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry Assisted by Chemometric Tools
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Reagents and Standards
2.3. Samples
2.4. Microwave-Assisted Digestion
2.5. Chemometric Models with ICP-OES Data
3. Results and Discussion
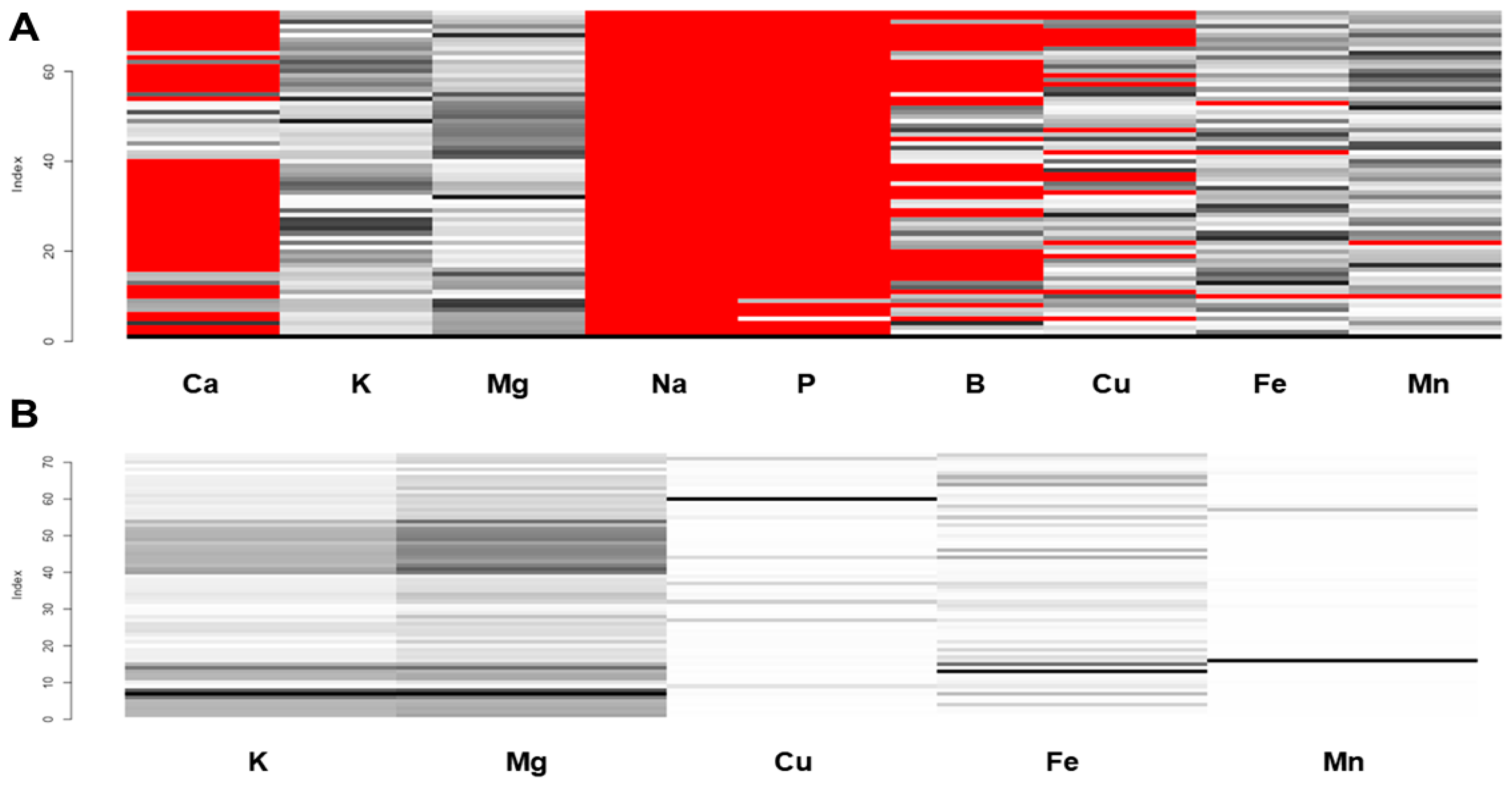
3.1. Missing Data Imputation
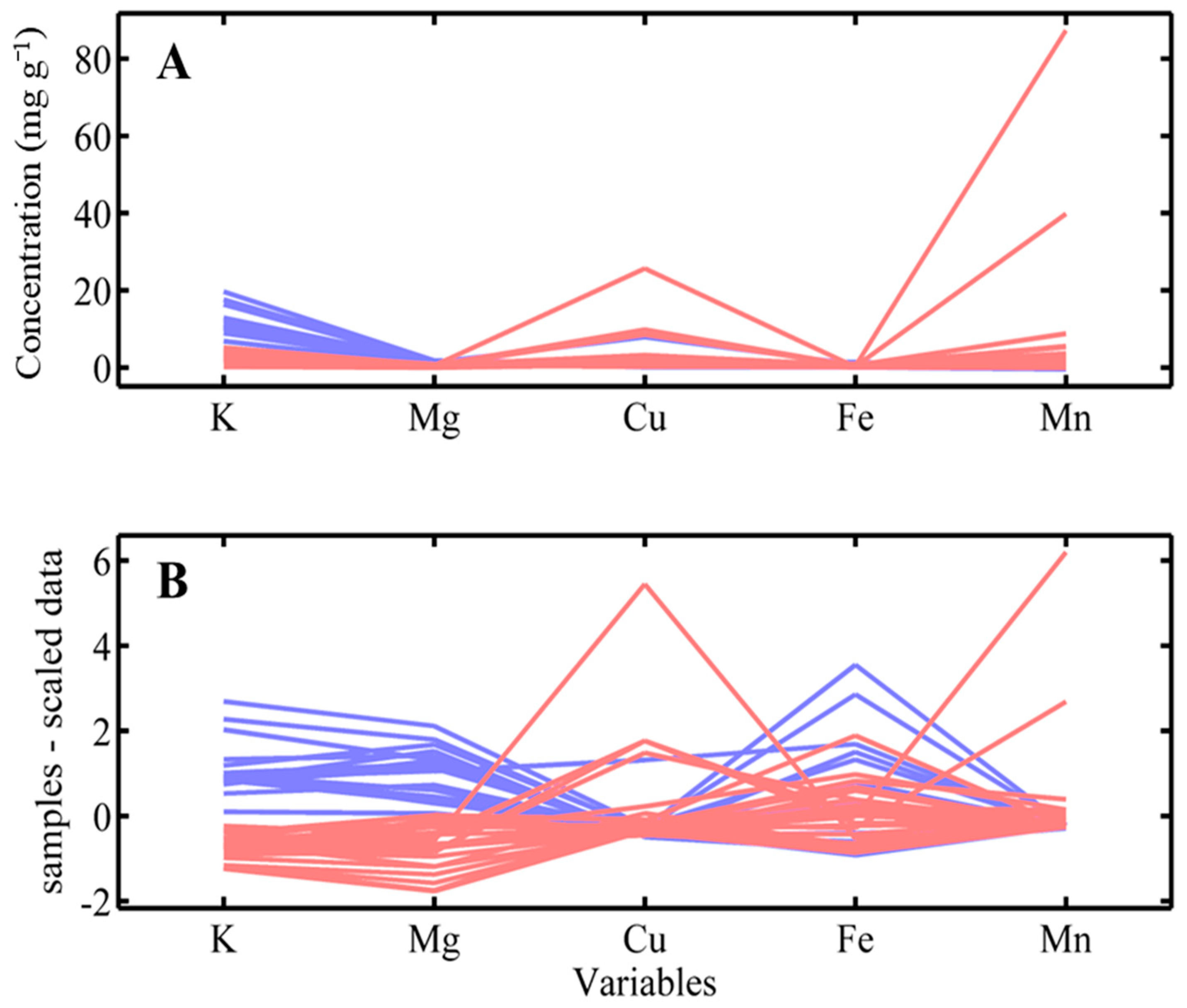
3.2. Data Preprocessing
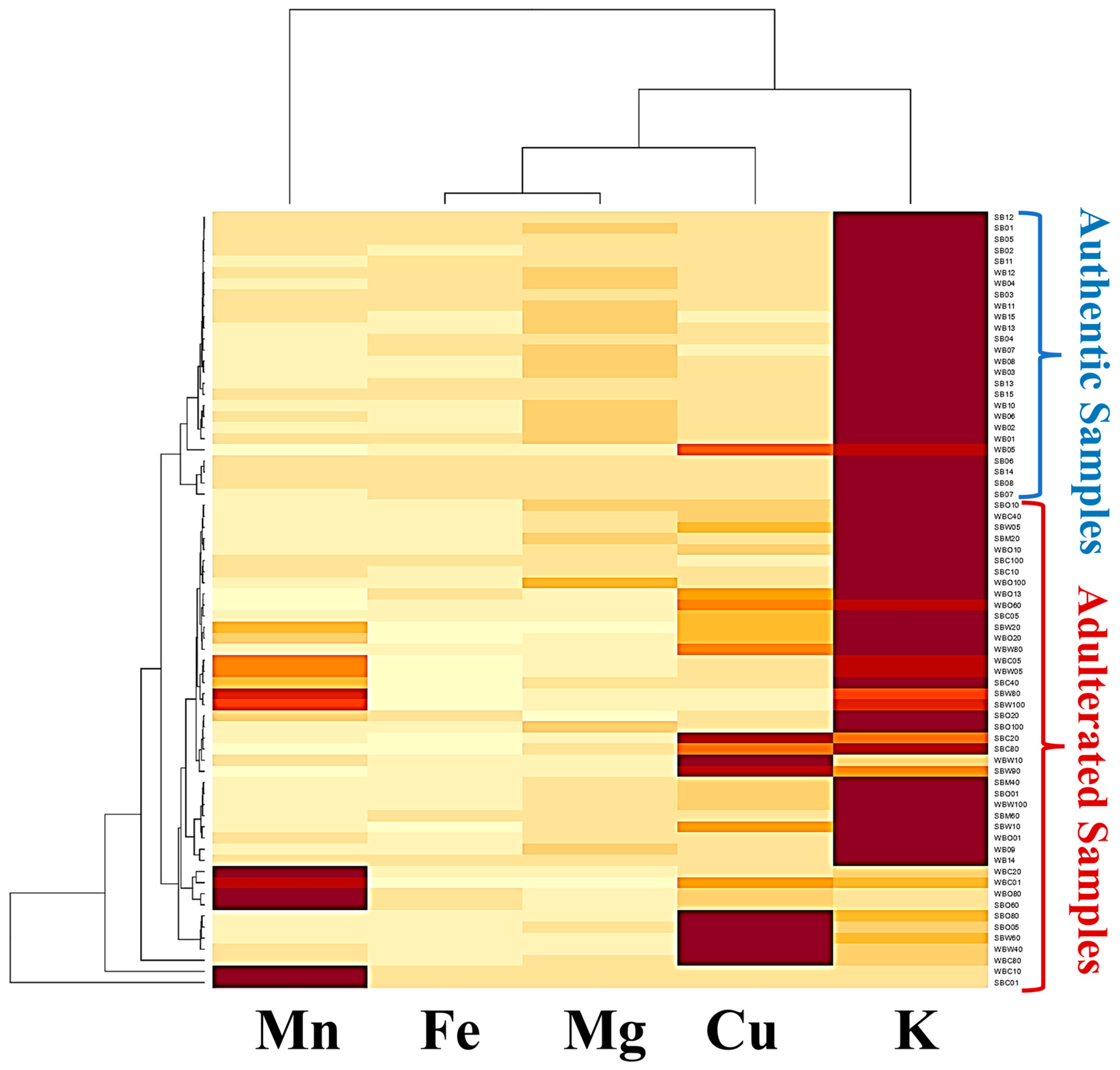
3.3. Heatmap
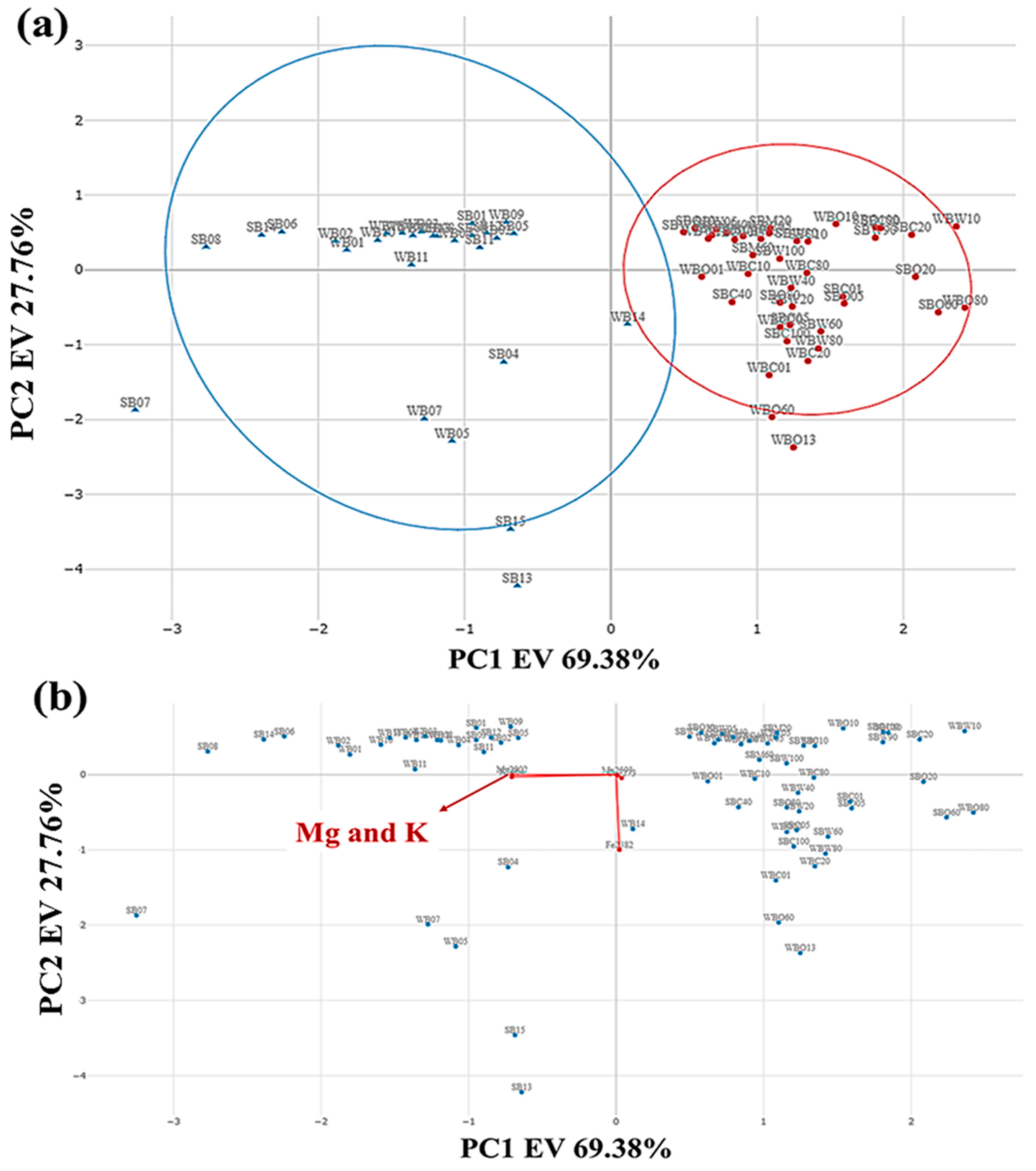
3.4. Detection of Anomalous Samples and Exploratory Analysis
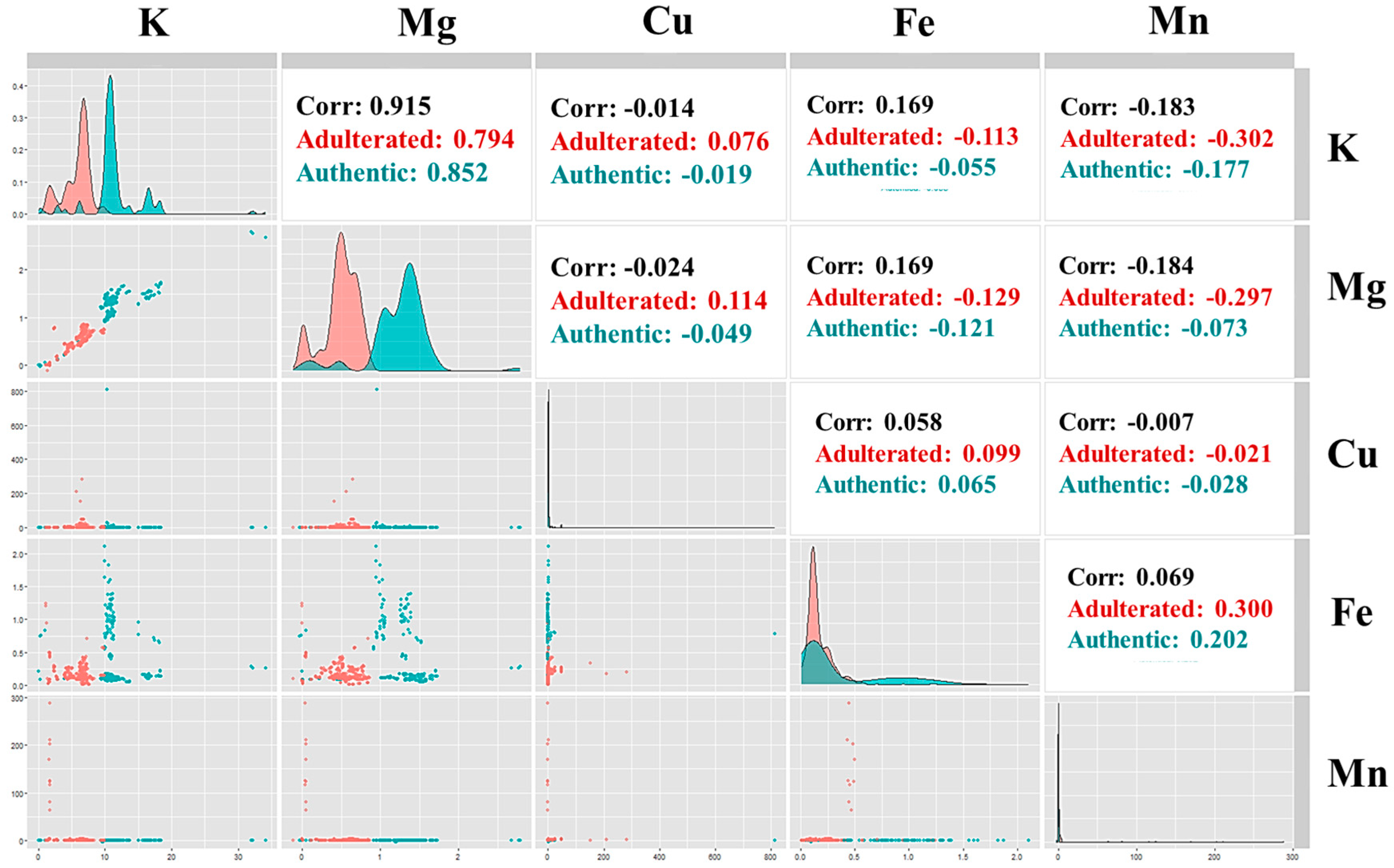
3.5. Correlation Map
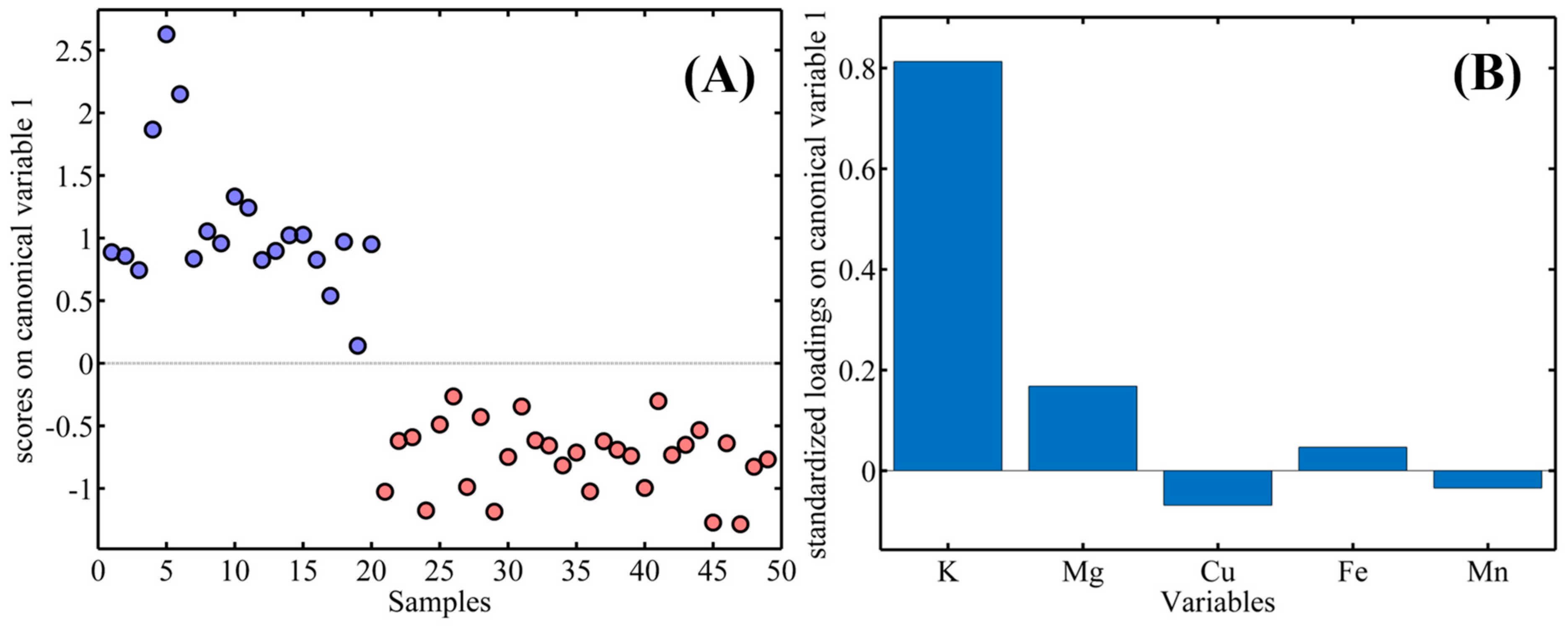
3.6. Data Analysis by LDA and PLS-DA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndlovu, P.F.; Magwaza, L.S.; Tesfay, S.Z.; Mphahlele, R.R. Vis-NIR Spectroscopic and Chemometric Models for Detecting Contamination of Premium Green Banana Flour with Wheat by Quantifying Resistant Starch Content. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, E.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Magwaza, L.S.; Nturambirwe, J.F.I.; Fawole, O.A.; Opara, U.L. Recent Advancements on Vibrational Spectroscopic Techniques for the Detection of Authenticity and Adulteration in Horticultural Products with a Specific Focus on Oils, Juices and Powders. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, T.; Brhane, G. Determination Of Quality And Adulteration Effects Of Honey From Adigrat And Its Surrounding Areas. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Emerg. Eng. Res. 2014, 2, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Başlar, M.; Ertugay, M.F. Determination of Protein and Gluten Quality-Related Parameters of Wheat Flour Using near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy (NIRS). Turk. J. Agric. For. 2011, 35, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidle Neto, A.J.; Lopes, D.d.C. Chemometrics Coupled with near Infrared Spectroscopy for Detecting Adulteration Levels in Herbal Teas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannor, R.K.; Arthur, K.K.; Oppong, D.; Oppong-Kyeremeh, H.A. Comprehensive systematic review and bibliometric analysis of food fraud from a global perspective. J. Agr. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100686. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Determination of the Mineral Composition of Foods by Infrared Spectroscopy: A Review of a Green Alternative. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 44, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Turco, V.; Nava, V.; Potortì, A.G.; Sgrò, B.; Arrigo, M.A.; Di Bella, G. Total Polyphenol Contents and Mineral Profiles in Commercial Wellness Herbal Infusions: Evaluation of the Differences between Two Preparation Methods. Foods 2024, 13, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, F.; Nava, V.; Giarratana, F.; Gervasi, T.; Cicero, N. Assessment of Heavy- and Semi-Metals Contamination in Edible Seaweed and Dried Fish Sold in Ethnic Food Stores on the Italian Market. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 104, 104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.; Jung, S.-C.; Seo, H.W.; Kim, J.-S. Prebiotic Potential of Green Banana Flour: Impact on Gut Microbiota Modulation and Microbial Metabolic Activity in a Murine Model. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1249358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.M.; Author, C.; Bhatt, H.G. Application of Mass Spectrometry in Detection of Food Adulteration: A Review. Pharma Innov. J. 2021, SP-10, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Azcarate, S.M.; Martinez, L.D.; Savio, M.; Camiña, J.M.; Gil, R.A. Classification of Monovarietal Argentinean White Wines by Their Elemental Profile. Food Control 2015, 57, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, M.; Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F. Chemometric Methods for Classification and Feature Selection. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 82, 265–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zaldarriaga Heredia, J.; Wagner, M.; Jofré, F.C.; Savio, M.; Azcarate, S.M.; Camiña, J.M. An Overview on Multi-Elemental Profile Integrated with Chemometrics for Food Quality Assessment: Toward New Challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8173–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darzé, B.C.; Lima, I.C.A.; Pinto, L.; Luna, A.S. Chemometrics Web App Part 1: Data Handling. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2022, 231, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzé, B.C.; Lima, I.C.A.; Luna, A.S.; Pinto, L. Chemometrics Web App’s Part 2: Dimensionality Reduction and Exploratory Analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 237, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, R.W.; Stone, L.A. Computer Aided Design of Experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, R.; Araujo, M.; Jose, G.; Pontes, M.; Silva, E.; Saldanha, T. A Method for Calibration and Validation Subset Partitioning. Talanta 2005, 67, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification Tools in Chemistry. Part 1: Linear Models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, G.G.F.; de Deus, J.A.L. Diagnosis of Soil Fertility and Banana Crop Nutrition in the State of Santa Catarina. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2021, 43, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares Campos, B.O. Evaluation of the Incidence of Banana Wilt and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. In Banana Production in Venezuela; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | R2 | LOD (µg g−1) | LOQ (µg g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 0.9965 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| K | 0.9899 | 0.007 | 0.021 |
| Mg | 0.9914 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Na | 0.9964 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| P | 0.9961 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| B | 0.9999 | 3 | 9 |
| Cu | 0.9999 | 1.4 | 4.2 |
| Fe | 0.9999 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| Mn | 0.9999 | 3 | 9 |
| Training—LDA | |||
| Real/Predicted Class | Class 1 | Class 2 | Not Assigned |
| Class 1 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 0 | 29 | 0 |
| Class | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
| Class 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Class 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| LDA Test Result | |||
| Real/Predicted Class | Class 1 | Class 2 | Not Assigned |
| Class 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Class | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
| Class 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Class 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Training—PLS-DA | |||
| Real/Predicted Class | Class 1 | Class 2 | Not Assigned |
| Class 1 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 0 | 29 | 0 |
| Class | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
| Class 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Class 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Resultado Teste PLS-DA | |||
| Real/Predicted Class | Class 1 | Class 2 | Not Assigned |
| Class 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Class | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
| Class 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Class 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes Júnior, S.L.; Gonçalves, P.M.; Batista, D.B.; Luna, A.S.; Ferreira, F.N.; Pinto, L.; de Gois, J.S. Banana Flour Adulteration Key Marker Unravelled by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry Assisted by Chemometric Tools. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040153
Fernandes Júnior SL, Gonçalves PM, Batista DB, Luna AS, Ferreira FN, Pinto L, de Gois JS. Banana Flour Adulteration Key Marker Unravelled by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry Assisted by Chemometric Tools. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(4):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040153
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes Júnior, Silvio Luiz, Paula Mothé Gonçalves, Diego Barros Batista, Aderval S. Luna, Fernanda Nunes Ferreira, Licarion Pinto, and Jefferson Santos de Gois. 2025. "Banana Flour Adulteration Key Marker Unravelled by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry Assisted by Chemometric Tools" Chemosensors 13, no. 4: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040153
APA StyleFernandes Júnior, S. L., Gonçalves, P. M., Batista, D. B., Luna, A. S., Ferreira, F. N., Pinto, L., & de Gois, J. S. (2025). Banana Flour Adulteration Key Marker Unravelled by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry Assisted by Chemometric Tools. Chemosensors, 13(4), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13040153







