Advances in Musculoskeletal Imaging in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Update in Ultrasound
3. Update in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASAS | Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society |
| CDUS | Color Doppler Ultrasound |
| CT | Computer Tomography |
| CRMO | Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis |
| DCE-MRI | Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI |
| DIR | Double Inversion Recovery |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted Imaging |
| EFSUMB | European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology |
| ERA | Enthesitis Related Arthritis |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| GRE | Gradient Echo |
| HeC | Health-e-Child |
| JAMRIS | Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis MRI Score |
| JIA | Juvenile Idiopathies Arthritis |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MSK | Musculoskeletal |
| mSMI | monochromatic Superb Microvascular Imaging |
| OMERACT | Outcome Measures in Rheumatology |
| PDUS | Power Doppler Ultrasound |
| PRES | Pediatric Rheumatology European Society |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| RAMRIS | Rheumatoid Arthritis MRI Scoring |
| SI | Signal Intensity |
| SMI | Superb Microvascular Imaging |
| SpA | Spondyloarthritis |
| STIR | Short Tau Inversion Recovery |
| SWE | Shear Wave Elastography |
| TMJ | Temporomandibular joint |
| TSE | Time Spin Echo |
| US | Ultrasound |
| VI | Vascularity Index |
| VIBE | Volume-Interpolated Breath-hold Examination |
| WBMRI | Whole- Body MRI |
References
- Ostrowska, M.; Gietka, P.; Mańczak, M.; Michalski, E.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. MRI Findings in Hip in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, D.J. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Clinical features. In Primer on the Rheumatic Diseases; Klippel, J.H., Stone, J.H., Crofford, L.J., White, P.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- El-Azeem, M.I.A.; Taha, H.A.; El-Sherif, A.M. Role of MRI in evaluation of hip joint involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2012, 34, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulou, M.; Fanis, S.L.; Xenakis, T.; Efremidis, S.C.; Siamopoulou, A. The role of MRI in the evaluation of hip joint disease in clinical subtypes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Br. J. Radiol. 2002, 75, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.G.; Ridley, N.T.; Mitchell, N.; Rooney, M. Juvenile chronic arthritis of the hip: Value of contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Clin. Radiol. 1996, 51, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Jans, L.; Jurik, A.G.; Hemke, R.; Eshed, I.; Boutry, N. Imaging Features of the Juvenile Inflammatory Arthropathies. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2018, 22, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.A.; Narváez, J.; de Lama, E.; de Albert, M. MR imaging of early rheumatoid arthritis. Radiographics 2010, 30, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malattia, C.; Damasio, M.B.; Basso, C.; Verri, A.; Magnaguagno, F.; Viola, S.; Gattorno, M.; Ravelli, A.; Toma, P.; Martini, A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of disease activity in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2009, 49, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onel, K.B.; Horton, D.B.; Lovell, D.J.; Shenoi, S.; Cuello, C.A.; Angeles-Han, S.T.; Becker, M.L.; Cron, R.Q.; Feldmann, B.M.; Ferguson, P.J.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Recommendations for nonpharmacologic therapies, medication monitoring, immunizations, and imaging. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pracoń, G.; Simoni, O.P.; Gietka, P.; Aparisi, P.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. Conventional Radiography and Ultrasound Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Affecting the Pediatric Population. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2021, 25, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, D.; Rodriguez-Garcia, S.C.; Cantisani, V.; Hammer, H.B.; Hartung, W.; Klauser, A.; Martinolli, C.; Terslev, L.; Alfageme, F.; Bong, D.; et al. The EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations for musculoskeletal ultrasound. Part I: Extra-articular pathologies. Ultraschall Med. 2022, 43, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naredo, E.; Rodriguez-Garcia, S.C.; Terslev, L.; Martinoli, C.; Klauser, A.; Hartung, W.; Hammer, H.B.; Cantisani, V.; Zaottini, F.; Vlad, V.; et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for Musculoskeletal Ultrasound—Part II: Joint Pathologies, Pediatric Applications, and Guided Procedures. Ultraschall Med. 2022, 43, 252–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plagou, A.; Teh, J.; Grainger, A.J.; Schueller-Weidekamm, C.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Rennie, W.; Aström, G.; Feydy, A.; Girardo, C.; Guerini, H.; et al. Recommendations of the ESSR Arthritis Subcommittee on Ultrasonography in Inflammatory Joint Disease. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2016, 20, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosskopf, A.B.; Martinoli, C.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Gitto, S.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Andrea, B. Sonography of tendon pathology in the hand and wrist. J. Ultrason. 2021, 21, e306–e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamzam, M.M. The role of ultrasound in differentiating septic arthritis from transient synovitis of the hip in children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2006, 15, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, J.C.; Denning, J.R.; Riccio, A.I.; Jo, C.H.; Joglar, J.M.; Wimberly, R.L. The use of ultrasound in the management of septic arthritis of the hip. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2015, 24, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, K.; Samora, J.B.; Klingele, K.E. Septic arthritis in infants younger than 3 months: A retrospective review. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e787–e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.W.Y.; Tse, K.S. Clinical and Radiological Differentiation of Septic Arthritis and Transient Synovitis of the Hip. Hong Kong J. Radiol. 2017, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessar, M.A.; Hassan, H.A.; Mokhtar, W.A. Role of high resolution ultrasonography in diagnosing septic hip arthritis in premature neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2017, 48, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Banna, H.S.; Nada, D.W.; Hussein, M.S.; Hablas, S.A.; Darwish, N.F.; Abu-Zaid, M.H.; Gadou, S.E. Role of musculoskeletal ultrasonography in the detection of subclinical synovitis in oligo and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis children. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; El Ganzouri, A.M.I.; Ahmed, S.F.; Sayed, S.M. High frequency power doppler ultrasonography in oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Correlation with disease severity. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2015, 37, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanni, S.; Marafon, D.P.; Civino, A.; Alongi, A.; Proverbio, E.; Agostoni, C.; Ravelli, A.; Fiilocamo, G. Comparison between clinical and ultrasound assessment of the ankle region in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2021, 73, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terslev, L.; Naredo, E.; Iagnocco, A.; Balint, P.V.; Wakefield, R.J.; Aegerter, P.; Aydin, S.Z.; Bachta, A.; Hammer, H.B.; Bruyn, G.A.W.; et al. Defining enthesitis in spondyloarthritis by ultrasound: Results of a Delphi process and of a reliability reading exercise. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, J.; Collado, P.; Janta, I.; Carmona, L.; Malattia, C.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Susic, G.; Tzaribachev, N.; Ravagnani, V.; Rossi-Semerano, L.; et al. THU 0548 Standardised procedures for ultrasound imaging in paediatric rheumatology: Progress of eular/pres task force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyn, G.A.; Iagnocco, A.; Naredo, E.; Balint, B.V.; Gutierrez, M.; Hammer, H.B.; Collado, P.; Filippou, G.; Schmidt, W.A.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; et al. OMERACT Definitions for Ultrasonographic Pathologies and Elementary Lesions of Rheumatic Disorders 15 Years On. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sande, N.K.; Boyesen, P.; Aga, A.-B.; Hammer, H.B.; Flato, B.; Roth, J.; Lilleby, V. Development and reliability of a novel ultrasonographic joint-specific scoring system for synovitis with reference atlas for patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauser, A.S.; Sailer-Hoeck, M.; Abdellah, M.M.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Siedentopf, C.; Auer, T.; Brunner, J.; Jaschke, W.R. Feasibility of Ultrasound-Guided Sacroiliac Joint Injections in Children Presenting with Sacroiliitis. Ultraschall Med. 2016, 37, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alis, D.; Erol, B.C.; Akbas, S.; Barut, K.; Kasapcopur, O.; Adaletli, I. Superb microvascular imaging compared with power doppler ultrasound in assessing synovitis of the knee in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A preliminary study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.T.; Song, J.S. The superb microvascular imaging is more sensitive than conventional power Doppler imaging in detection of active synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O.F.; Bayramoglu, Z.; Adaletli, I. Evaluation of Periarticular Soft Tissues in Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis by Superb Microvascular Imaging and Shear Wave Elastography. Arch. Rheumatol. 2020, 35, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeral, K.; Hojreh, A.; Kasprian, G.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Weber, M.; Mitter, C.; Berger, A.; Prayer, D.; Brugger, P.C.; Vergesslich-Rothschild, K.; et al. Microvessel ultrasound of neonatal brain parenchyma: Feasibility, reproducibility, and normal imaging features by superb microvascular imaging (SMI). Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto-González, J.C.; Rodríguez, A.; Gámir-Gámir, M.L.; Boteanu, A.; López-Robledillo, J.C.; Garulo, D.C.; Collado, P.; Calvo, C.; Garrido, J.; Saez, I.M.; et al. Can ultrasound-detected subclinical synovitis be an indicator of flare recurrence in juvenile idiopathic arthritis remission patients on tapered TNFi. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Spârchez, M.; Fodor, D. What’s new in musculoskeletal ultrasound in pediatric rheumatology. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torp-Pedersen, S.; Christensen, R.; Szkudlarek, M.; Ellegaard, K.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Iagnocco, A.; Naredo, E.; Balint, P.; Wakefield, R.J.; Torp-Pedersen, A.; et al. Power and color Doppler ultrasound settings for inflammatory flow: Impact on scoring of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Velez, N.F.; Lam, C.; Famia, A.; Granter, S.S.; Townsend, H.B.; Vleugels, R.A. Dermatomyositis induced by anti-tumour necrosis factor in a patient with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietka, P.; Rutkowska-Sak, L.; Lisowska, M. Myositis in the course of the systemic form juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Reumatologia 2014, 52, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindehammar, H.; Lindvall, B. Muscle involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindehammar, H.; Backman, E. Muscle function in juvenile chronic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, C.D.; Fleckenstein, J.L.; Witt, T.N.; Müller-Felber, W.; Pongratz, D.E. Muscular ultrasound in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies of adults. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 16, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, N.L.; Hobson-Webb, L.D. Neuromuscular ultrasound in clinical practice: A review. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2019, 4, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljanovic, M.S.; Gimber, L.H.; Becker, G.W.; Latt, L.D.; Klauser, A.S.; Melville, D.M.; Gao, L.; Witte, R.S. Shear-wave elastography: Basic physics and musculoskeletal applications. Radiographics 2017, 37, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachannsson, D.; Dubois, G.J.R.; Allenbach, Y.; Benveniste, O.; Hogrel, J.Y. Muscle shear wave elastography in inclusion body myositis: Feasibility, reliability and relationship with muscle impairments. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, A.; Tufan, A.; Mercan, R.; Teber, M.A.; Tezcan, M.E.; Bitik, B.; Goker, B.; Haznedaroglu, S. Real-time sonoelastography of Achilles tendon in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschke, V.; Jones, J.G.; Lemmey, A.B.; Maddison, P.J.; Thom, J.M. Patellar tendon properties and lower limb function in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis versus healthy controls: A cross-sectional study. Sci. World J. 2013, 514743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemke, R.; Herregods, N.; Jaremko, J.L.; Aström, G.; Avenarius, D.; Becce, F.; Bielecki, D.K.; Boesen, M.; Dalili, D.; Giraudo, C.; et al. Imaging assessment of children presenting with suspected or known juvenile idiopathic arthritis: ESSR-ESPR points to consider. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5237–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Giraudo, C.; Oei, E.H.G.; Jans, L. Imaging update in inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 20, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramalingam, I.M.S.; Conaghan, P.G.; Keen, H.I. An update on imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Treat. Options Rheum. 2020, 6, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Teh, J.; Cotton, A. Rheumatoid Hand and Other Hand-deforming Rheumatic Conditions. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2021, 25, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemke, R.; Van Rossum, M.A.J.; van Veenendaal, M.; Terra, M.P.; Deurloo, E.E.; de Jonge, M.C.; van den Berg, J.M.; Doman, K.M.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Maas, M. Reliability and responsiveness of the Juvenile Arthritis MRI Scoring (JAMRIS) system for the knee. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemke, R.; Tzaribachev, N.; Nusman, C.M.; Van Rossum, M.A.J.; Maas, M.; Doria, A.S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the knee as an outcome measure in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: An OMERACT reliability study on MRI scales. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemke, R.; Nusman, C.M.; van der Heijde, D.M.F.M.; Doria, A.S.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Maas, M.; van Rossum, M.A.J. Frequency of joint involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis during a 5-year follow-up of newly diagnosed patients: Implications for MR imaging as outcome measure. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenarius, D.F.M.; Nusman, C.; Malattia, C.; de Horatio, L.T.; Rosendahl, K.; Maas, M.; Müller, L.-.S.O. Current status of wrist imaging in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, M.; Peterfy, C.; Conaghan, P.; McQueen, F.; Bird, P.; Ejbjerg, B.; Shnier, R.; O’Connor, P.; Klarlund, M.; Emery, P.; et al. OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1385–1386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malattia, C.; Tzaribachev, N.; van den Berg, J.M.; Magni-Manzoni, S. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis—The role of imaging from a rheumatologist’s perspective. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska, M.; Michalski, E.; Gietka, P.; Mańczak, M.; Posadzy, M.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. Ankle MRI in JIA versus in non-JIA juveniles with arthralgia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, M.L.; Kau, C.H.; Waite, P.D.; Cron, R.Q. Temporomandibular joint arthritis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, now what? Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2018, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angenete, O.W.; Augdal, T.A.; Rygg, M.; Rosendahl, K. MRI in the Assessment of TMJ-Arthritis in Children with JIA; Repeatability of a Newly Devised Scoring System. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 29, 1362–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolend, M.A.; Twilt, M.; Cron, R.Q.; Tzaribachev, N.; Guleria, S.; von Kalle, T.; Koos, B.; Miller, E.; Stimec, J.; Vaid, Y.; et al. Toward Establishing a Standardized Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System for Temporomandibular Joints in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolend, M.; Doria, A.S.; Meyers, A.B.; Larheim, T.A.; Abramowicz, S.; Aguet, J.; Appenzeller, S.; Arvidsson, L.Z.; Averill, L.W.; Feldman, B.M.; et al. Assessing the Reliability of the OMERACT Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Scoring System for Temporomandibular Joints (JAMRIS-TMJ). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkhus, E.; Gunderson, R.B.; Smith, H.J.; Flato, B.; Hetlevik, S.O.; Larheim, T.; Arvidsson, L. Temporomandibular joint involvement in childhood arthritis: Comparison of ultrasonography-assessed capsular width and MRI-assessed synovitis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016, 45, 20160195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechler, B.L.; Phero, J.A.; van Mater, H.; Matthews, N.S. Ultrasound versus magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, E.J.I.; Tolend, M.; Junhasavasdikul, T.; Stimec, J.; Tzaribachev, N.; Koos, B.; Spiegel, L.; Moineddin, R.; Doria, A.S. Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of temporomandibular joint MRI protocols for juvenile idiopathic arthritis at 1.5 and 3.0T. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 98, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiho, K.; Savolainen, A.; Kautiainen, H.; Kekki, P.; Kauppi, M. The cervical spine in juvenile chronic arthritis. Spine J. 2002, 2, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospach, T.; Maier, J.; Müller-Abt, P.; Patel, A.; Horneff, G.; von Kalle, T. Cervical spine involvement in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis—MRI follow-up study. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2014, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ključevšek, D.; Emeršič, N.; Toplak, N.; Avčin, T. Clinical and MRI outcome of cervical spine lesions in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis treated with anti-TNFα drugs early in disease course. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2017, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Patil, K.; Miller, E.; Uleryk, E.; Twilt, M.; Spiegel, L. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis of the axial joints: A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy and predictive value of conventional MRI. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecki, M.; Gietka, P.; Posadzy, M.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. Radiographs and MRI of the Cervical Spine in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. J. Clin Med. 2021, 10, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregods., N.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Jans, L.; Otobo, T.M.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Meyers, A.B.; van Rossum, M.A.J.; Kirkhus, E.; Panwar, J.; Appenzeller, S.; et al. Atlas of MRI findings of sacroiliitis in pediatric sacroiliac joints to accompany the updated preliminary OMERACT pediatric JAMRIS (Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis MRI Score) scoring system: Part I: Active lesions and part II: Structural damage lesions. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymowych, W.P.; Lambert, R.G.W.; Østergaard, M.; Pedersen, S.J.; Machado, P.M.; Weber, U.; Bennett, A.; Braun, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; de Hooge, M.; et al. MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joints of patients with spondyloarthritis: An update of definitions and validation by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.G.; Bakker, P.A.; van der Heijde, D.; Weber, U.; Rudwaleit, M.; Hermann, K.G.; Sieper, J.; Baraliakos, X.; Bennett, A.; Braun, J.; et al. Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: Update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudwaleit, M.; Jurik, A.G.; Hermann, K.G.; Landewe, R.; van der Heijde, D.; Baraliakos, X.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Ostergaard, M.; Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: A consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregods, N.; Jans, L.B.O.; Chen, M.; Paschke, J.; de Buyser, S.L.; Renson, T.; Dhoorne, J.; Joos, R.; Lamberg, R.G.W.; Jaremko, J.L. Normal subchondral high T2 signal on MRI mimicking sacroiliitis in children: Frequency, age distribution, and relationship to skeletal maturity. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 29, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, N.A.; Xiao, R.; Brandon, T.G.; Biko, D.M.; Francavilla, M.; Khrichenko, D.; Weiss, P. MRI of the sacroiliac joint in healthy children. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 11, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, P.F.; Brandon, T.G.; Bohnsack, J.; Heshin-Bekenstein, M.; Francavilla, M.L.; Jaremko, J.L.; Liaou, L.; McHugh, A.; Oberle, E.J.; Rumsey, D.; et al. Variability in magnetic resonance imaging interpretation of the pediatric sacroiliac joint. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herregods, N.; Lambert, R.G.W.; Schiettecatte, E.; Dehoorne, J.; Renson, T.; Laloo, F.; van den Berghe, T.; Jans, L.B.O.; Jaremko, J.L. Blurring and irregularity of the subchondral cortex in pediatric sacroiliac joints on T1 images: Incidence of normal findings that can mimic erosions. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otobo, T.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Maksymowych, W.P.; van der Heijde, D.; Weiss, P.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Herregods, N.; Jaremko, J.L.; Meyers, A.B.; Rumsey, D.; et al. Preliminary Definitions for Sacroiliac Joint Pathologies in the OMERACT Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis MRI Score (OMERACT JAMRIS-SIJ). J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otobo, T.M.; Herregods, N.; Jaremko, J.L.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Meyers, A.B.; Weiss, P.; Tse, S.; Paschke, J.; Moineddin, R.; et al. Reliability of the Preliminary OMERACT Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis MRI Score (OMERACT JAMRIS-SIJ). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemke, R.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Berg, J.V.D.; Van Veenendaal, M.; Dolman, K.M.; Van Rossum, M.A.J.; Maas, M. The diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced MRI in the assessment of joint abnormalities in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesen, M.; Kubassova, O.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Maas, M.; Hansen, P.; Nybing, J.D.; Oei, E.H.G.; Hemke, R.; Guermazi, A. MR Imaging of Joint Infection and Inflammation with Emphasis on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging. PET Clinics 2018, 13, 523–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusman, C.M.; Hemke, R.; Lavini, C.; Schonenberg-Neinema, D.; van Rossum, M.A.J.; Doman, K.M.; van den Berg, J.M.; Maas, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging can play a role in predicting flare in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 88, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulani, V.; Calamante, F.; Shellock, F.G.; Kanal, E.; Reeder, S.B. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Gadolinium deposition in the brain: Summary of evidence and recommendations. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, A.; Agarwal, Y.; Garg, K.J. Gadolinium based contrast agents in current practice: Risks of accumulation and toxicity in patients with normal renal function. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2017, 27, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusman, C.M.; Hemke, R.; Benninga, M.A.; Schonenberg-Meinema, D.; Kindermann, A.; van Rossum, M.A.J.; van den Berg, J.M.; Maas, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Contrast-enhanced MRI of the knee in children unaffected by clinical arthritis compared to clinically active juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barendregt, A.M.; van Gulik, E.C.; Lavini, C.; Nusman, C.M.; van den Berg, J.M.; Schonenberg-Meinema, D. Diffusion-weighted imaging for assessment of synovial inflammation in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A promising imaging biomarker as an alternative to gadolinium-based contrast agents. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4889–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbert, F.; Holl-Wieden, A.; Sauer, A.; Köstler, H.; Neubauer, H. Intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging of the knee joint in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, J.; Tolend, M.; Redd, B.; Srinivasalu, H.; Coblert, R.A.; Akikusa, J.; Appenzeller, S.; Carrino, J.A.; Herregods, N.; Jans, L.; et al. Consensus-driven conceptual development of a standardized whole body-MRI scoring system for assessment of disease activity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: MRI in JIA OMERACT working group. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, C.; Lecouvet, F.E.; Cotton, A.; Eshed, I.; Jans, L.; Jurik, A.G.; Maas, M.; Weber, M.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging in inflammatory diseases: Where are we now? Results of an International Survey by the European Society of Musculoskeletal Radiology. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 136, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraliakos, X.; Hoffmann, F.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, F.; Braun, J. Detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints of patients with axial spondyloarthritis using the magnetic resonance imaging VIBE technique. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekhoff, T.; Greese, J.; Sieper, J.; Poddubnyy, D.; Hamm, B.; Hermann, K.G.A. Improved detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints on MRI with volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (VIBE): Results from the SIMACT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, L.B.O.; Chen, M.; Elewaut, D.; van den Bosch, F.; Carron, P.; Jachques, P.; Wittoek, R.; Jaremko, J.L.; Herregods, N. MRI-based synthetic CT in the detection of structural lesions in patients with suspected sacroiliitis: Comparison with MRI. Radiology 2021, 289, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


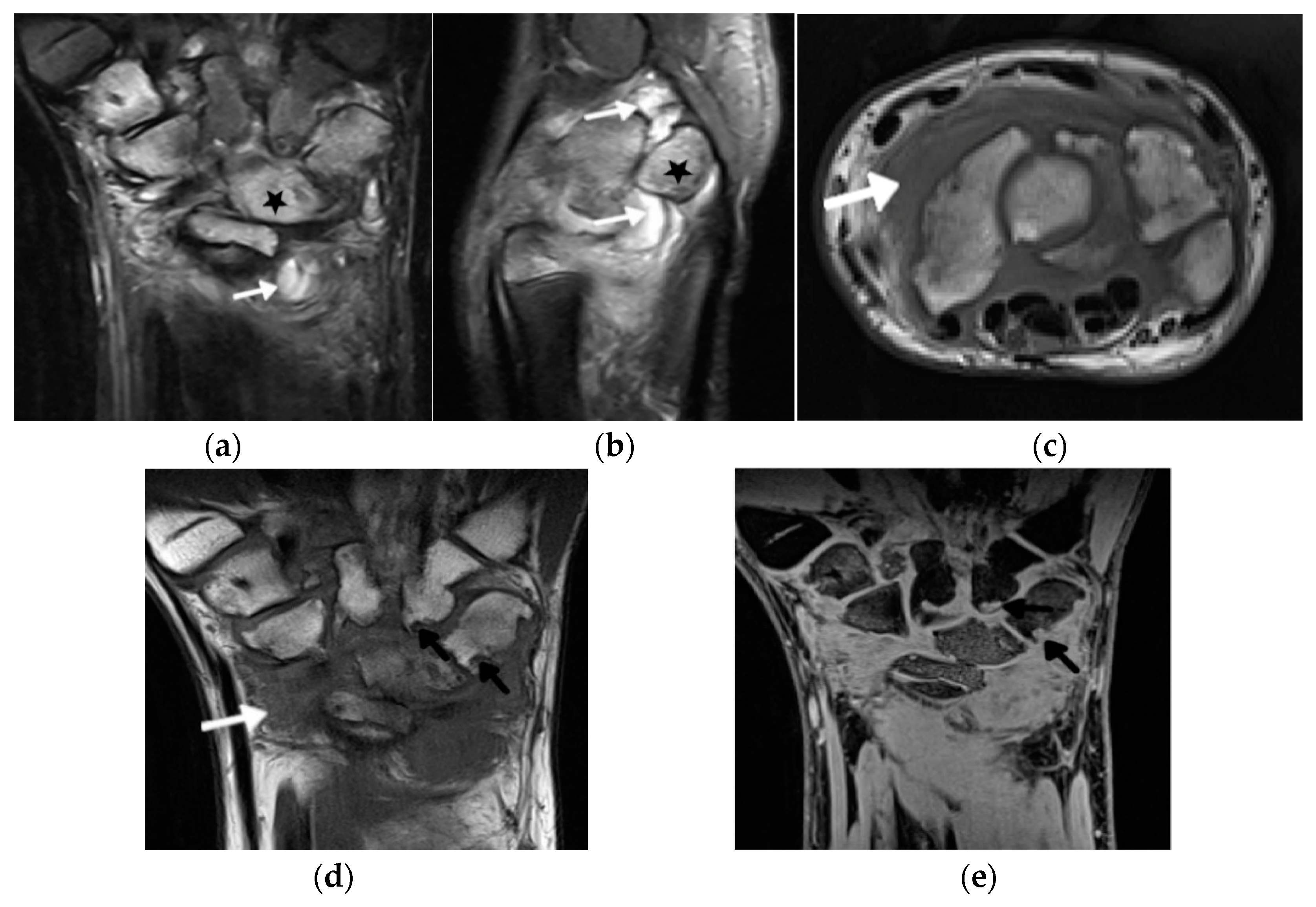
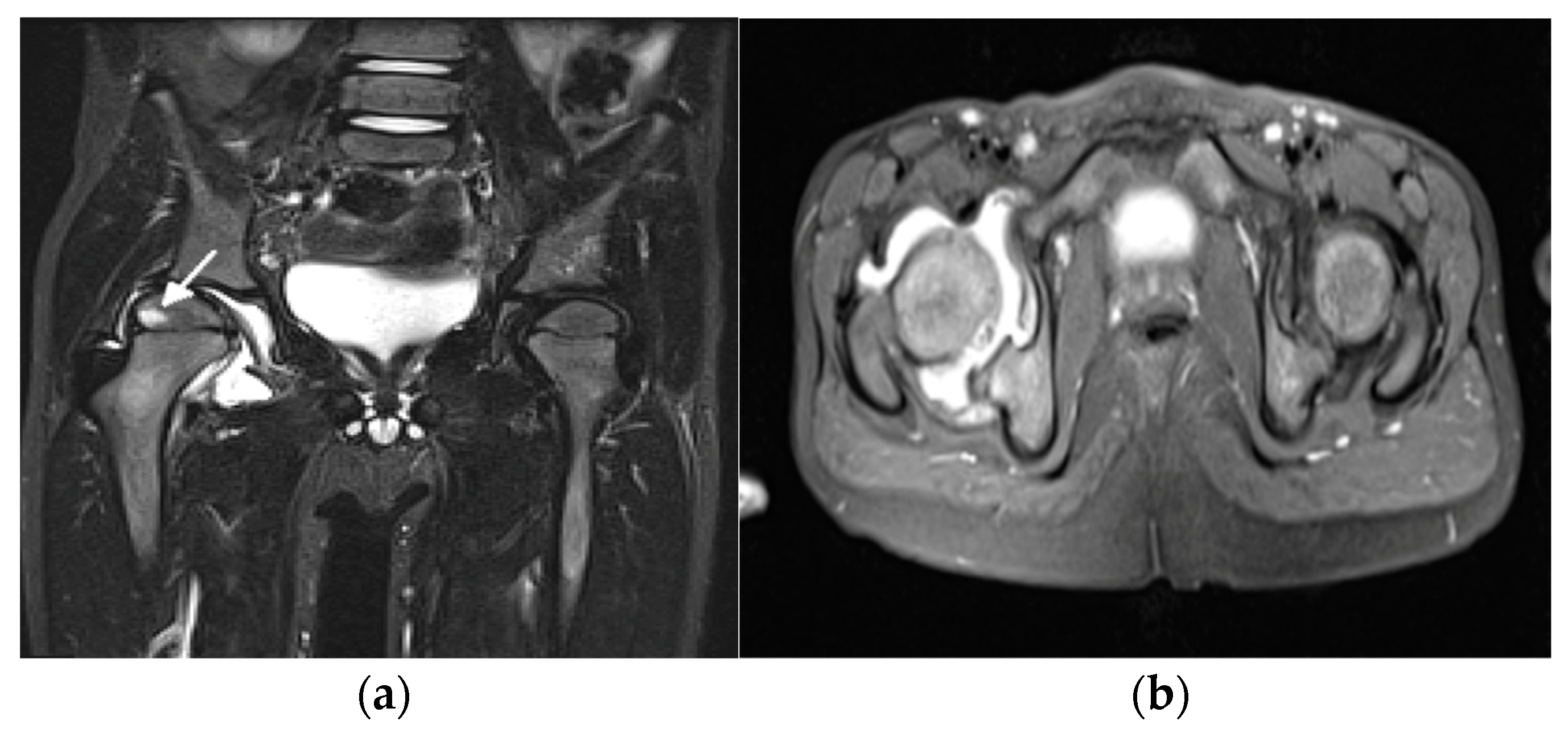

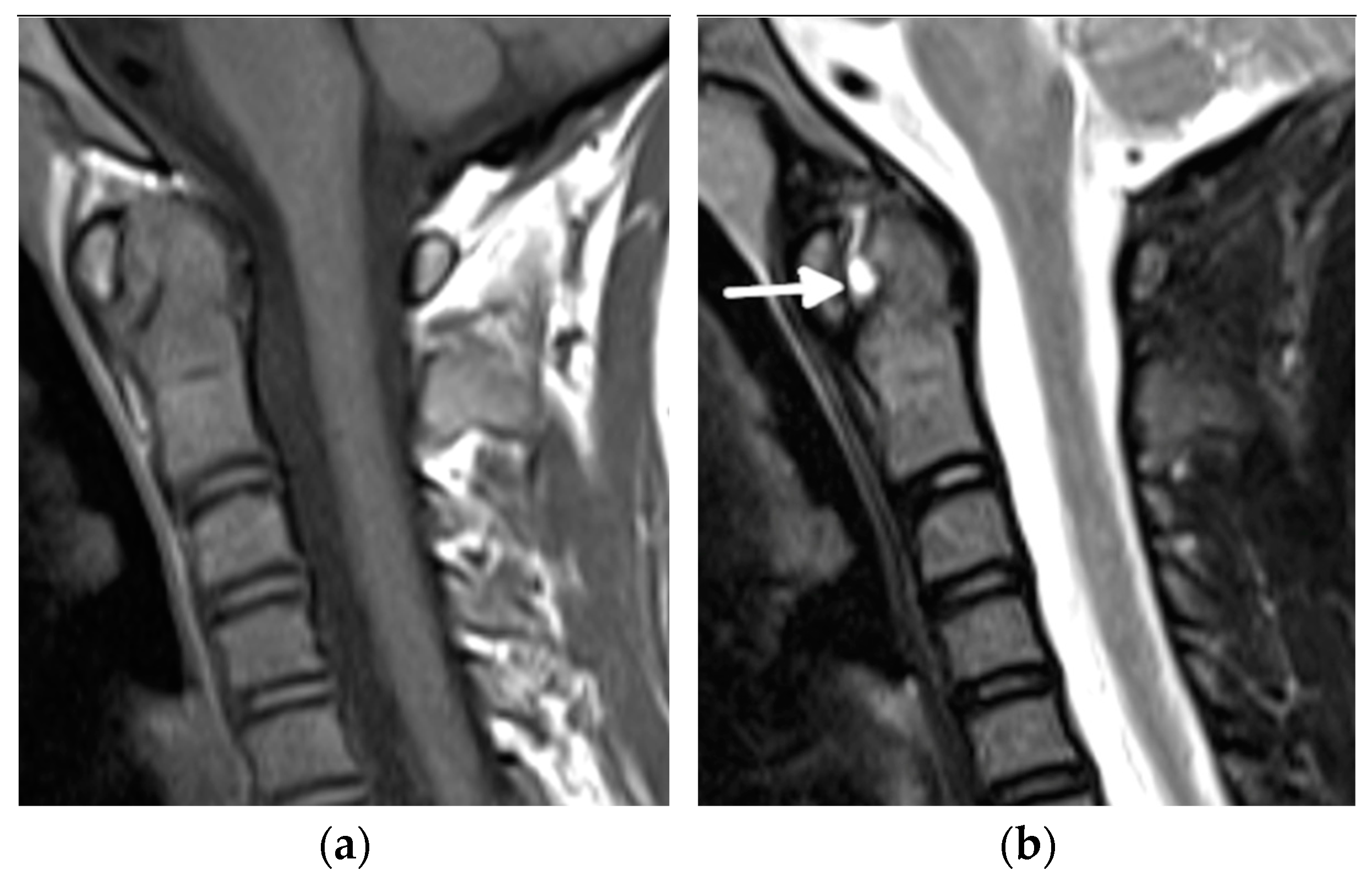

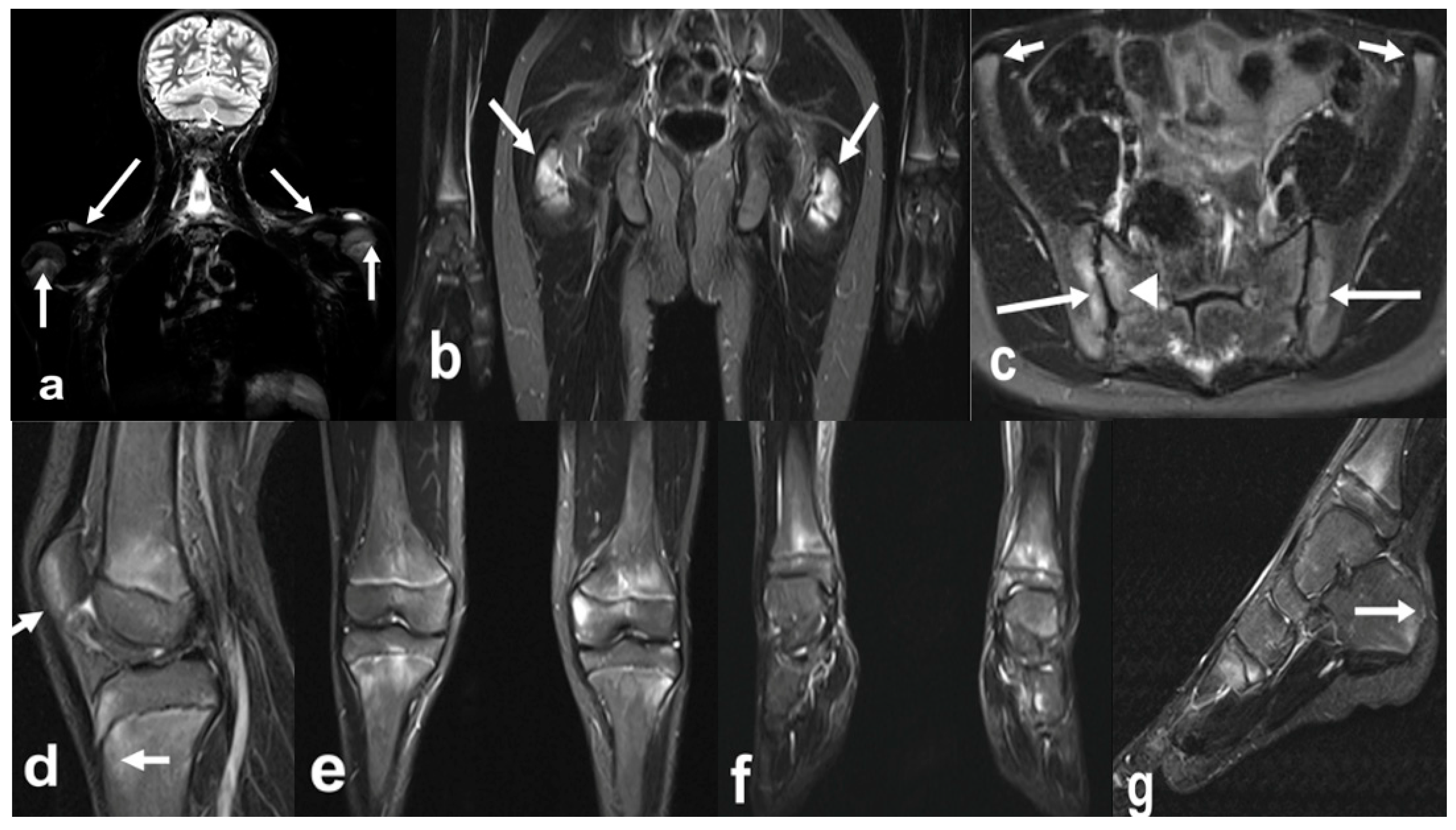


| Grade | B Mode | Doppler |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No signs of synovial effusion or synovial hypertrophy (i.e., no joint recess enlargement/capsular distension). | Absence of color/power Doppler signal within synovial hypertrophy with or without detection of normal physiological Doppler signals. |
| 1 (mild) | Synovial effusion and/or synovial hypertrophy that leads to a mild change of joint recess appearance (i.e., mild joint recess enlargement/capsular distension). | Detection of up to 3 single Doppler signals within the area of synovial hypertrophy with or without normal physiological Doppler signals. |
| 2 (moderate) | Synovial effusion and/or synovial hypertrophy that leads to a moderate change of joint recess appearance (i.e., moderate joint recess enlargement/capsular distension). | Detection of more than 3 single Doppler signals but less than 30% of the area of synovial hypertrophy with or without normal physiological Doppler signals. |
| 3 (severe) | Synovial effusion and/or synovial hypertrophy that leads to a severe change of joint recess appearance (i.e., severe joint recess enlargement/capsular distension). | Detection of Doppler signals at more than 30% of area of synovial hypertrophy with or without normal physiological Doppler signals. |
| Item | Definition | Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmentation/Slice | Range/Slice | ||
| BME | An ill-defined area of high bone marrow signal intensity within the subchondral bone in the ilium or sacrum on fluid-sensitive images | 4 quadrants/SIJ | 0–8 |
| BME Intensity | Presence of hyperintensity of the marrow on fluid-sensitive images using the signal of the presacral veins or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) as reference | 1 score/SIJ | 0–2 |
| BME depth | Continuing increased signal on fluid-sensitive images at depths ≥5 mm/≥1 cm from the articular surface | 1 score/SIJ | 0–2 |
| Osteitis | An ill-defined area of high bone marrow signal intensity within the subchondral bone in the ilium or sacrum on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences | 4 quadrants/SIJ | 0–8 |
| Joint space fluid | High signal intensity equivalent to the CSF on fluid-sensitive sequences within the joint space of the cartilaginous portion of SIJ | halves/SIJ | 0–4 |
| Joint space enhancement | Increased signal intensity on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences within the joint space of the cartilaginous portion of SIJ | halves/SIJ | 0–4 |
| Inflammation in erosion cavity | Increased signal intensity on fluid-sensitive or contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences in an erosion cavity of cartilaginous portion of SIJ | halves/SIJ | 0–4 |
| Enthesitis | Increased signal intensity in bone marrow and/or adjacent soft tissue on fluid-sensitive or contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences at sites where ligaments and tendons attach to a bone, excluding retroarticular enthesitis | score per case | 0–1 |
| Capsulitis | Increased signal on fluid-sensitive or contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences involving superior portion of SIJ capsule | superior halves/SIJ | 0–2 |
| Item | Definition | Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmentation/Slice | Range/Slice | ||
| Sclerosis | A substantially wider than normal area of very low bone marrow signal intensity within the subchondral bone in the ilium or sacrum on a nonfat suppressed sequence, preferably a nonfat suppressed T1-weighted sequence; this feature must also be present on all other sequences, as available | 4 quadrants/SIJ | 0–8 |
| Erosions | A focal loss of low signal of cortical bone at osteochondral interface and adjacent marrow matrix on T1-weighted images | 4 quadrants/SIJ | 0–8 |
| Fat lesion/Fat metaplasia | Homogeneous increased signal intensity within subchondral bone marrow on T1-weighted images | 4 quadrants/SIJ | 0–8 |
| Backfill | A high signal on non-contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences in a typical location for erosion, with signal intensity greater than normal bone marrow, clearly demarcated from adjacent bone marrow by an irregular band of low signal, reflecting sclerosis at border of original erosion | halves/SIJ | 0–4 |
| Ankylosis | Presence of signal equivalent to regional bone marrow continuously bridging a portion of the joint space between iliac and sacral bones | halves/SIJ | 0–4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Herregods, N.; Doria, A.S.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Gietka, P.; Tzaribachev, N.; Klauser, A.S. Advances in Musculoskeletal Imaging in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102417
Sudoł-Szopińska I, Herregods N, Doria AS, Taljanovic MS, Gietka P, Tzaribachev N, Klauser AS. Advances in Musculoskeletal Imaging in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102417
Chicago/Turabian StyleSudoł-Szopińska, Iwona, Nele Herregods, Andrea S. Doria, Mihra S. Taljanovic, Piotr Gietka, Nikolay Tzaribachev, and Andrea Sabine Klauser. 2022. "Advances in Musculoskeletal Imaging in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102417
APA StyleSudoł-Szopińska, I., Herregods, N., Doria, A. S., Taljanovic, M. S., Gietka, P., Tzaribachev, N., & Klauser, A. S. (2022). Advances in Musculoskeletal Imaging in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102417







