Disinhibition-Like Behavior Correlates with Frontal Cortex Damage in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
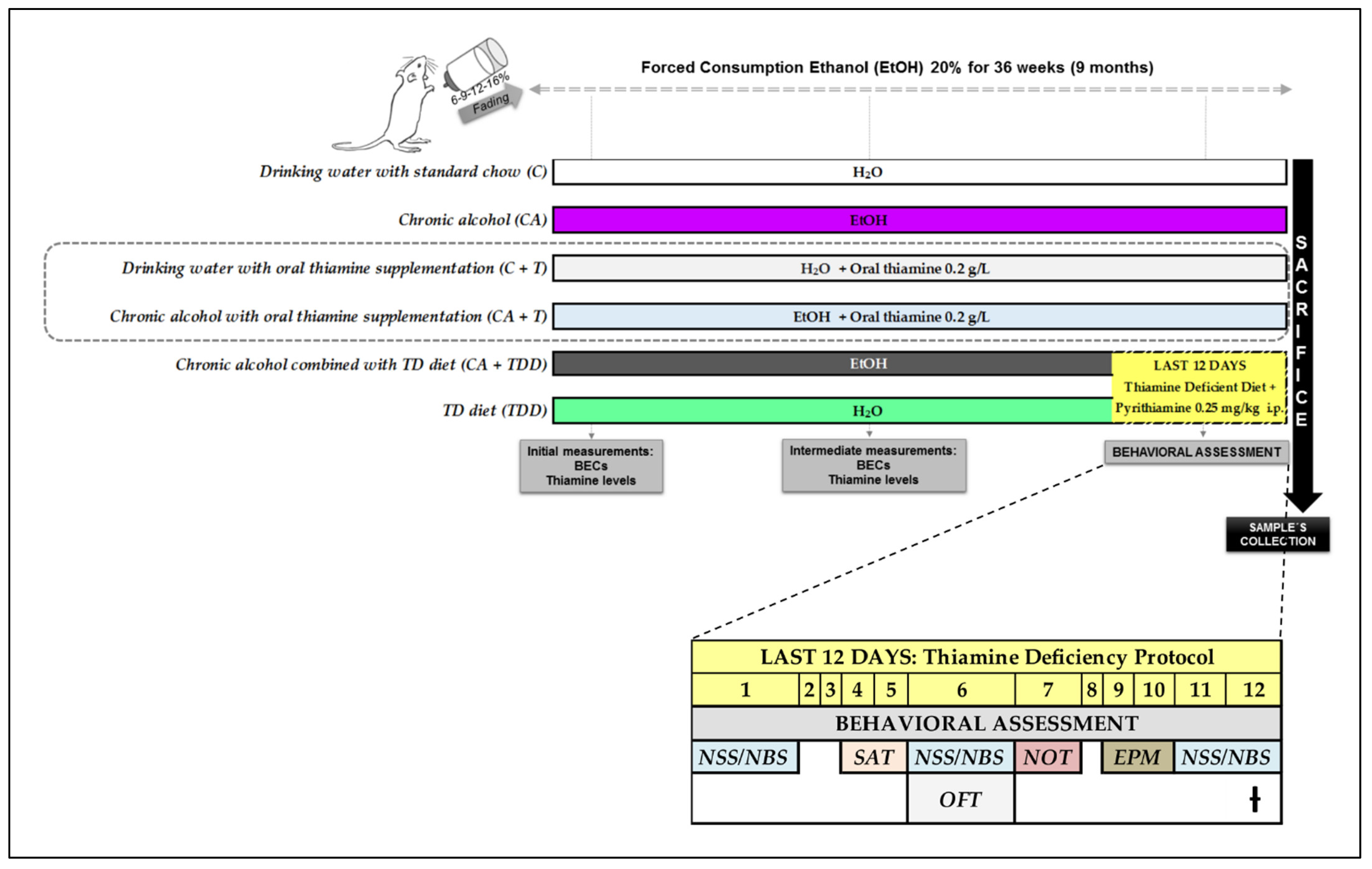
2.2. Experimental Groups
- Chronic alcohol (CA)
- TD diet (TDD)
- Chronic alcohol combined with TD diet in the last days of treatment (CA+TDD)
- Chronic alcohol with oral thiamine supplementation (CA+T)
- Drinking water with oral thiamine supplementation (C+T)
- Drinking water with standard chow (C)
Experimental Procedures
2.3. Blood Ethanol Concentrations (BECs) and Thiamine Measurements
2.4. Behavioral Assessment
- Neurological assessment
- Motor function: locomotion
- Cognitive domain: disinhibition-like behavior and memory
2.5. Blood and Tissue Sample Collection
2.6. Protein Assay
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Plasma Nitrites (NO2−) Levels
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weight and Consumptions
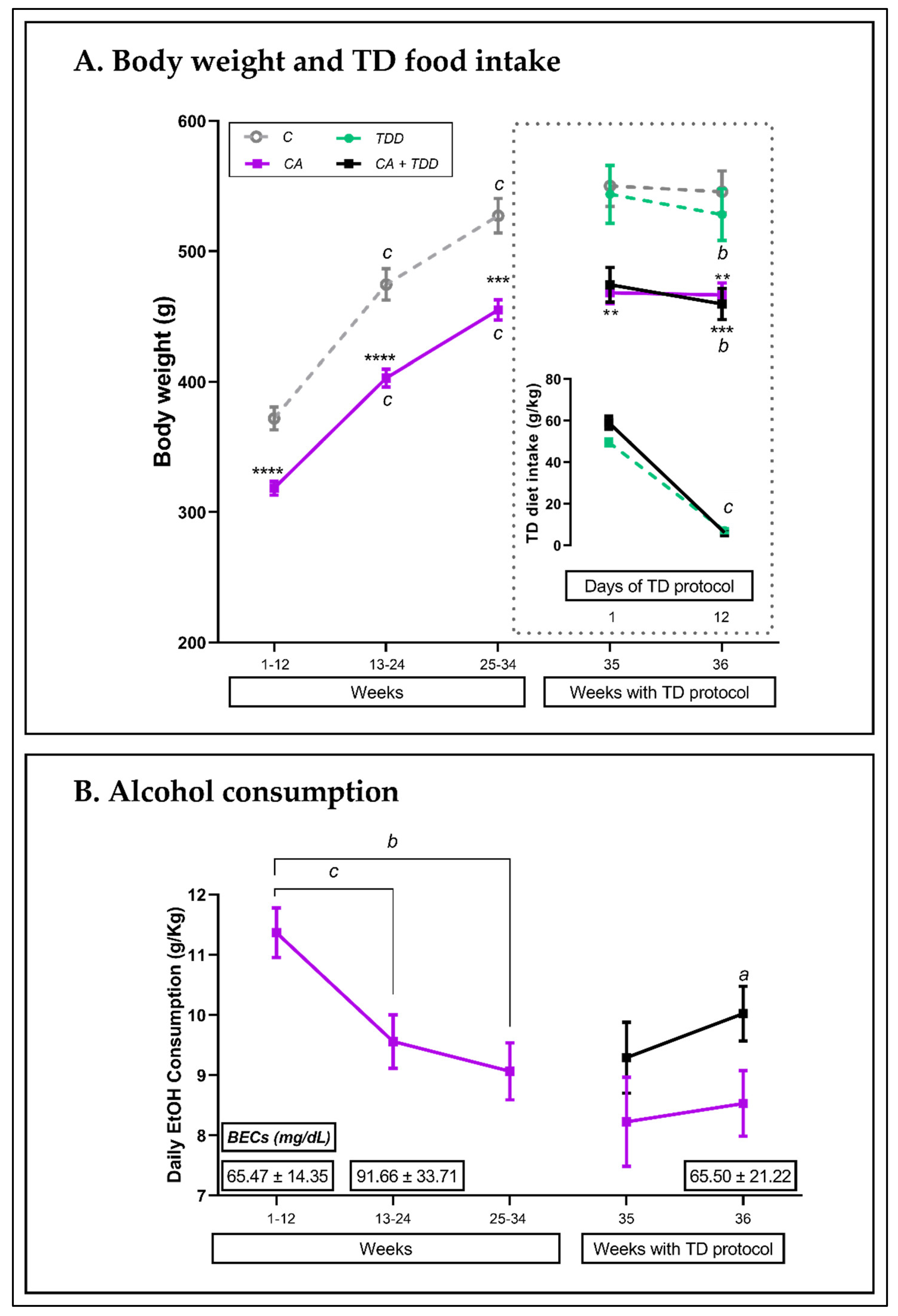
3.1.1. Body Weight throughout the 36 Weeks of the Experiment and TD Diet Intake
3.1.2. Alcohol Intake and BECs
3.2. Neurological Examination
3.3. Behavioral Outcomes
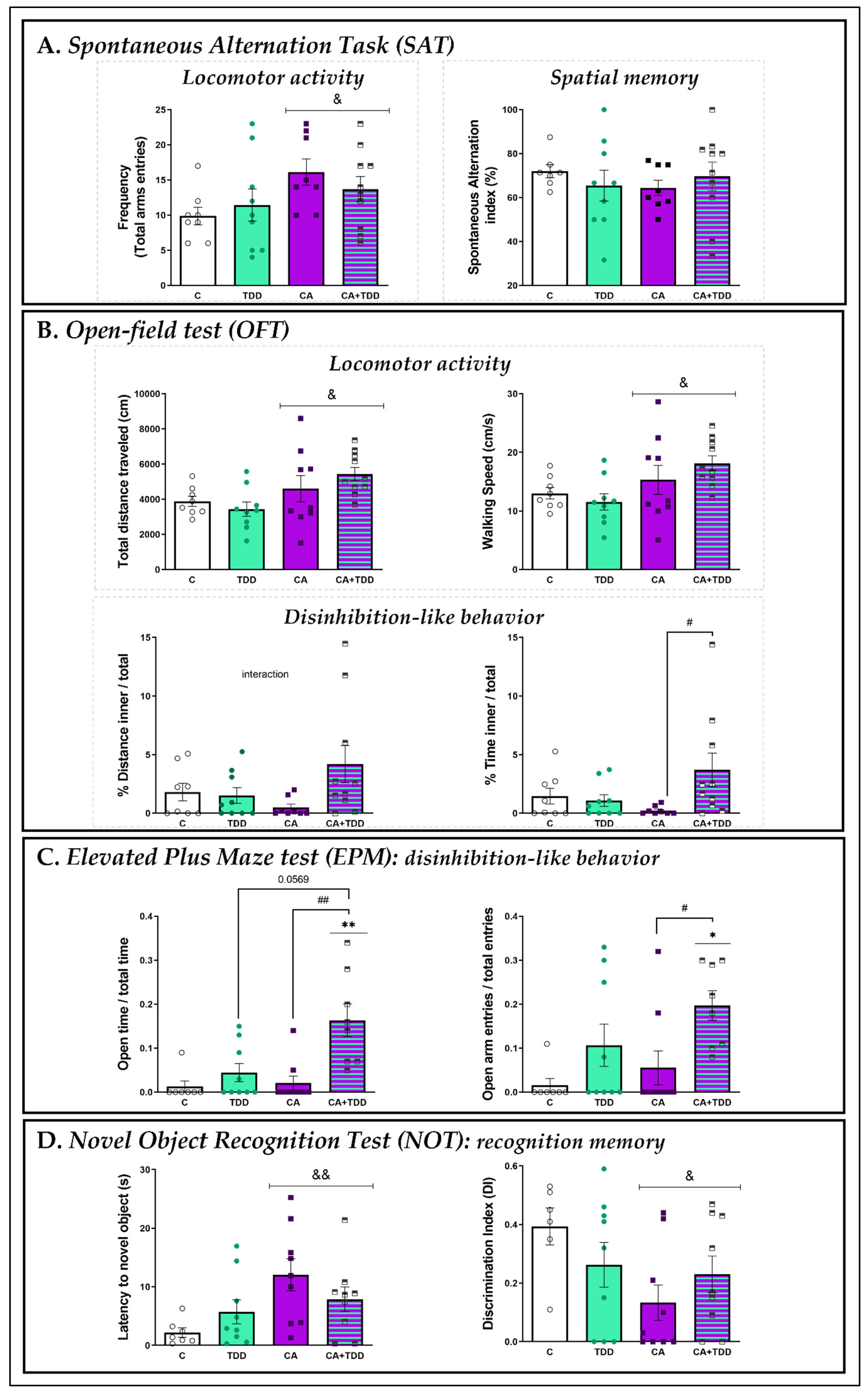
3.3.1. Effects on Locomotor Activity and Spatial Memory: SAT
3.3.2. Effects on Locomotor Activity and Disinhibition-Like Behavior: OFT
3.3.3. Effects on Disinhibition-Like Behavior: EPM
3.3.4. Effects on Recognition Memory: NOT
3.4. Alterations Found in the Frontal Cortex and Plasma
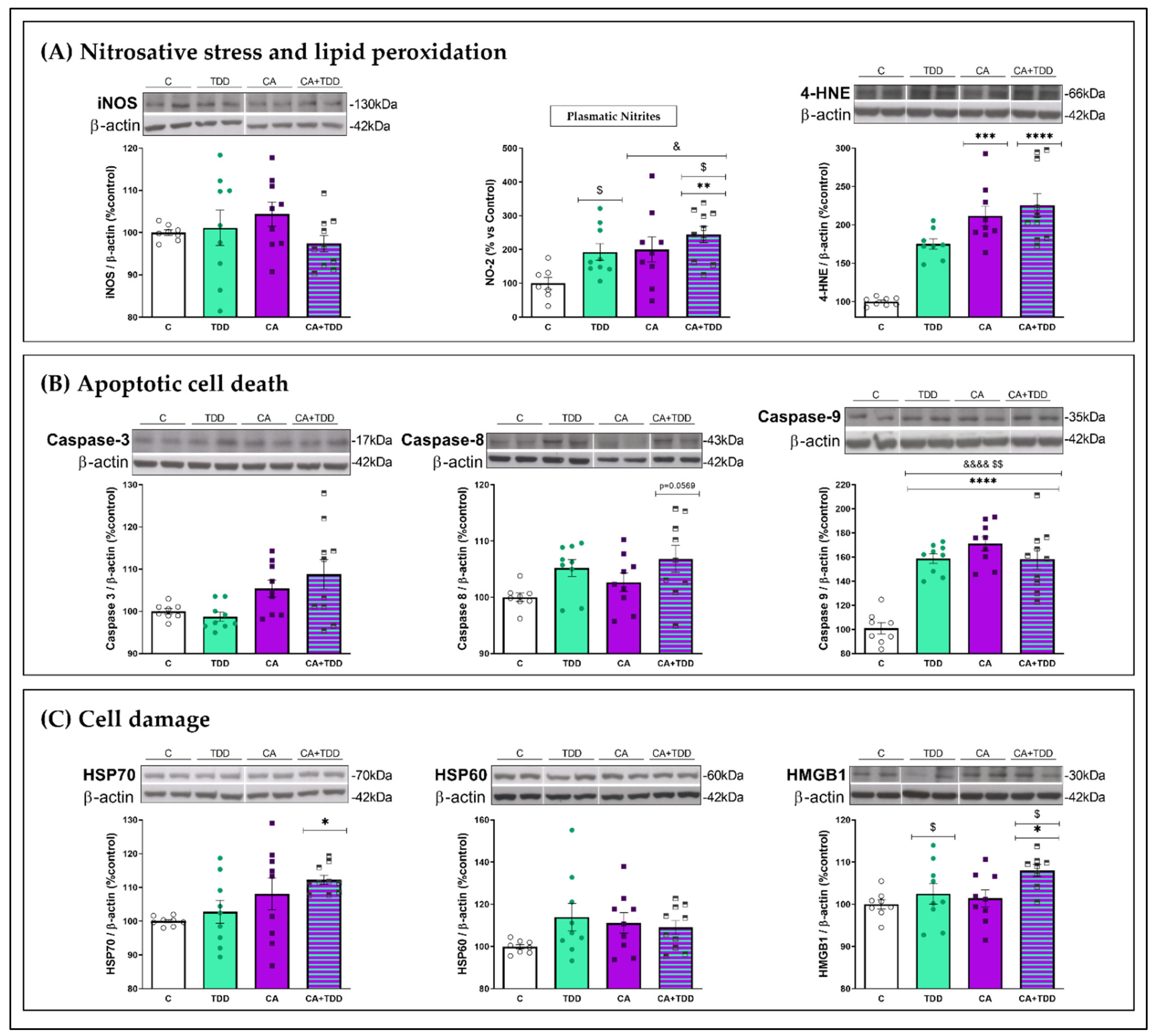
3.4.1. Effects on Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation Markers
3.4.2. Effects on Apoptotic Markers
3.4.3. Effects on Cell Damage Markers
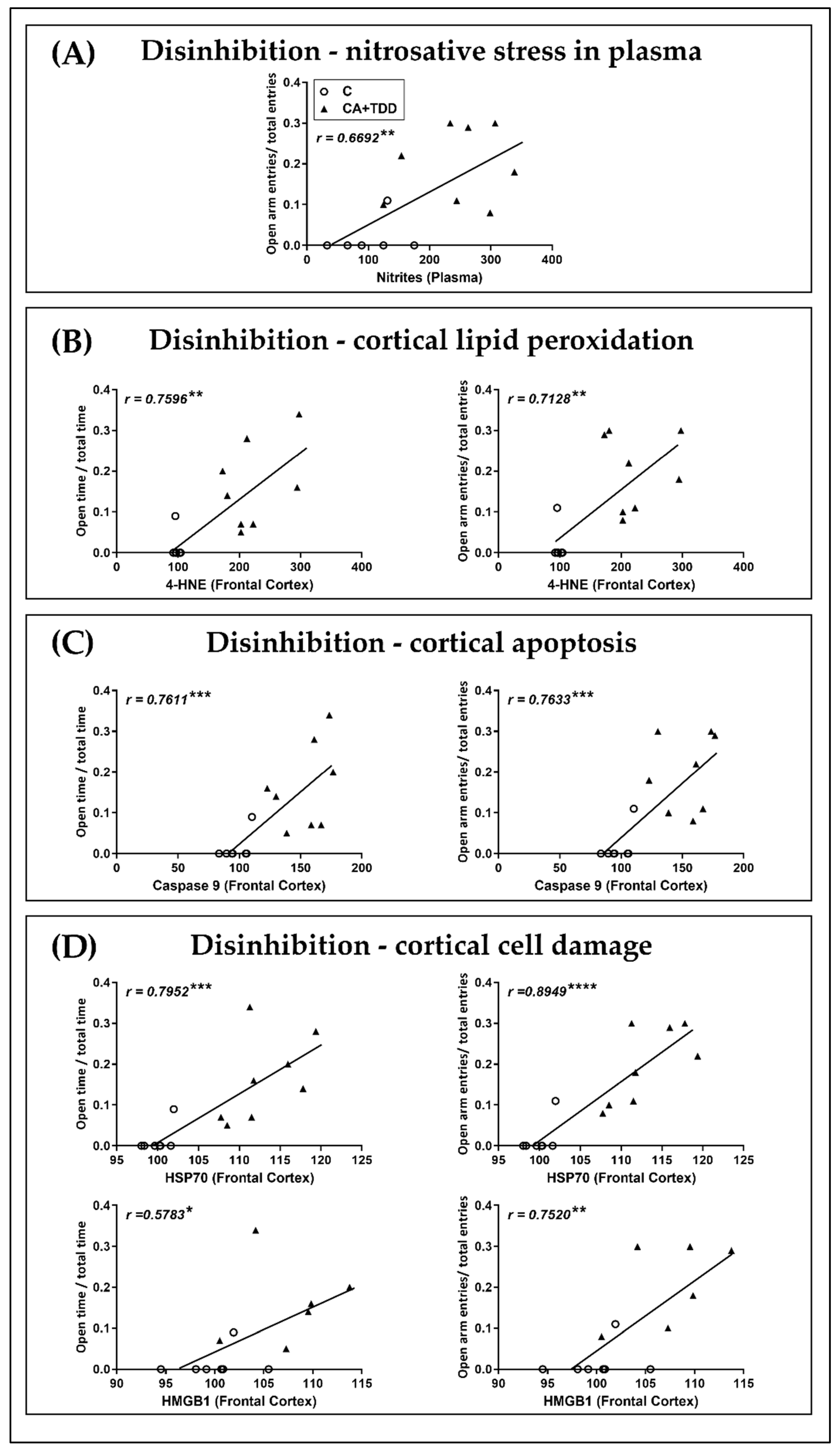
3.5. Correlations and Linear Regression Analyses between Biochemical and Behavioral Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Supplemental Discussion of the Physiological Results: Body Weight, Alcohol Intake and Neurological State
Appendix B. Thiamine: Plasma Levels and Oral Supplementation Treatment. Results and Conclusions



References
- Orio, L.; Alen, F.; Pavón, F.J.; Serrano, A.; García-Bueno, B. Oleoylethanolamide, Neuroinflammation, and Alcohol Abuse. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, N.J.; Walvoort, S.J.; Kessels, R.P. Korsakoff’s Syndrome: A Critical Review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 2875–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zahr, N.M.; Kaufman, K.L.; Harper, C.G. Clinical and Pathological Features of Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, M.D. The Korsakoff Syndrome. Br. J. Psychiatry 1995, 166, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, S.; Law-Min, R.; Fearnley, D. Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome Following Small Bowel Obstruction. Behav. Neurol. 2001, 13, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhala, S.S.; Hazell, A.S. Modeling Neurodegenerative Disease Pathophysiology in Thiamine Deficiency: Consequences of Impaired Oxidative Metabolism. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.C.; Houts, R. Parental Drinking, Parent-Child Communication, and Social Skills in Young Adults. J. Stud. Alcohol. 1992, 53, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, J.; Bates, M.E. Effects of Executive Function Impairment on Change Processes and Substance Use Outcomes in 12-Step Treatment. J. Stud. Alcohol. 1999, 60, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerridzen, I.J.; Hertogh, C.M.P.M.; Depla, M.F.; Veenhuizen, R.B.; Verschuur, E.M.L.; Joling, K.J. Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in People With Korsakoff Syndrome and Other Alcohol-Related Cognitive Disorders Living in Specialized Long-Term Care Facilities: Prevalence, Severity, and Associated Caregiver Distress. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, K.M.; Dal Monte, O.; Schintu, S.; Wassermann, E.M.; Raymont, V.; Grafman, J.; Krueger, F. Areas of Brain Damage Underlying Increased Reports of Behavioral Disinhibition. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 27, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, R.R.; Lishman, W.A. Cortical and Diencephalic Lesions in Korsakoff’s Syndrome: A Clinical and CT Scan Study. Psychol. Med. 1990, 20, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernigan, T.L.; Schafer, K.; Butters, N.; Cermak, L.S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Alcoholic Korsakoff Patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 1991, 4, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Paller, K.A.; Acharya, A.; Richardson, B.C.; Plaisant, O.; Shimamura, A.P.; Reed, B.R.; Jagust, W.J. Functional Neuroimaging of Cortical Dysfunction in Alcoholic Korsakoff’s Syndrome. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aupée, A.M.; Desgranges, B.; Eustache, F.; Lalevée, C.; de la Sayette, V.; Viader, F.; Baron, J.C. Voxel-Based Mapping of Brain Hypometabolism in Permanent Amnesia with PET. Neuroimage 2001, 13, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.G.; Longmore, B.E. The Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome. In Clinical Neuropsychology of Alcoholism, 1st ed.; Psychology Press: London, UK, 1994; pp. 267–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, P.T.; Kipp, B.T.; Reitz, N.L.; Savage, L.M. Aging with Alcohol-Related Brain Damage: Critical Brain Circuits Associated with Cognitive Dysfunction. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 148, 101–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón, M.; Alén, F.; Gómez de Heras, R.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.J.; Leza, J.C.; García-Bueno, B.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Orio, L. Oleoylethanolamide Prevents Neuroimmune HMGB1/TLR4/NF-KB Danger Signaling in Rat Frontal Cortex and Depressive-like Behavior Induced by Ethanol Binge Administration: OEA Blocks Ethanol TLR4 Signaling. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, M.; San Felipe, D.; Ballesta, A.; Alén, F.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; García-Bueno, B.; Marco, E.M.; Orio, L. Cerebellar and Cortical TLR4 Activation and Behavioral Impairments in Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome: Pharmacological Effects of Oleoylethanolamide. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 108, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, F.; Rossetti, Z.L. Chronic Ethanol Consumption: From Neuroadaptation to Neurodegeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 385–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Matsumoto, I. Ethanol and Brain Damage. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V.; Mathalon, D.H.; Lim, K.O. Frontal Lobe Volume Loss Observed with Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Older Chronic Alcoholics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, W.-C.; Ro, L.-S.; Chen, C.-M.; Chang, H.-S.; Kuo, H.-C. Non-Alcoholic Wernicke’s Encephalopathy with Cortical Involvement and Polyneuropathy Following Gastrectomy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.M.; Stewart, W.N.; Savage, L.M. Chronic Drinking During Adolescence Predisposes the Adult Rat for Continued Heavy Drinking: Neurotrophin and Behavioral Adaptation after Long-Term, Continuous Ethanol Exposure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bâ, A.; Seri, B.V.; Han, S.H. Thiamine Administration during Chronic Alcohol Intake in Pregnant and Lactating Rats: Effects on the Offspring Neurobehavioural Development. Alcohol. Alcohol. 1996, 31, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bâ, A.; Seri, B.V.; Aka, K.J.; Glin, L.; Tako, A. Comparative Effects of Developmental Thiamine Deficiencies and Ethanol Exposure on the Morphometry of the CA3 Pyramidal Cells. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1999, 21, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bâ, A. Alcohol and B1 Vitamin Deficiency-Related Stillbirths. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2009, 22, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bâ, A. Comparative Effects of Alcohol and Thiamine Deficiency on the Developing Central Nervous System. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bâ, A. Paradoxical Effects of Alcohol and Thiamine Deficiency on the Eye Opening in Rat Pups. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2012, 25, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantzie, L.L.; Oppong, A.Y.; Conteh, F.S.; Yellowhair, T.R.; Kim, J.; Fink, G.; Wolin, A.R.; Northington, F.J.; Robinson, S. Repetitive Neonatal Erythropoietin and Melatonin Combinatorial Treatment Provides Sustained Repair of Functional Deficits in a Rat Model of Cerebral Palsy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwknecht, J.A.; Spiga, F.; Staub, D.R.; Hale, M.W.; Shekhar, A.; Lowry, C.A. Differential Effects of Exposure to Low-Light or High-Light Open-Field on Anxiety-Related Behaviors; Relationship to c-Fos Expression in Serotonergic and Non-Serotonergic Neurons in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 72, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosquer, B.; Galani, R.; Kuster, N.; Cassel, J.-C. Whole-Body Exposure to 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Fields Does Not Alter Anxiety Responses in Rats: A plus-Maze Study Including Test Validation. Behav. Brain. Res. 2005, 156, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.F.; Krause, E.G.; Melhorn, S.J.; Sakai, R.R.; Benoit, S.C. Dominant Rats Are Natural Risk Takers and Display Increased Motivation for Food Reward. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, U.; Evans, J.E.; Joseph, R.; Emmerich, T.; Saltiel, N.; Lungmus, C.; Oberlin, S.; Langlois, H.; Ojo, J.; Mouzon, B.; et al. Oleoylethanolamide Treatment Reduces Neurobehavioral Deficits and Brain Pathology in a Mouse Model of Gulf War Illness. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dember, W.N.; Fowler, H. Spontaneous Alternation Behavior. Psychol. Bull. 1958, 55, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, E.M.; Valero, M.; de la Serna, O.; Aisa, B.; Borcel, E.; Ramirez, M.J.; Viveros, M.-P. Maternal Deprivation Effects on Brain Plasticity and Recognition Memory in Adolescent Male and Female Rats. Neuropharmacology 2013, 68, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of Nitrate, Nitrite, and [15N]Nitrate in Biological Fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnia, J.W.; Oudman, E. Biomarkers of Delirium as a Clue to Diagnosis and Pathogenesis of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legastelois, R. Sensitization to the Stimulant Motor Effects of Ethanol Is Not Dependent On Tolerance to Ataxic or Sedative Properties of Ethanol in Female Mice. J. Alcohol. Drug Depend. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, K.R.; Knapp, D.J.; Saiff, E.I.; Pohorecky, L.; Benjamin, D. Sensitization to Ethanol Demonstrated in Place-Preference and Locomotor Activation. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 1992, 18, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshaw, B.A.; Lewis, M.J. Behavioral Sensitization to Ethanol in Rats: Evidence from the Sprague-Dawley Strain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 68, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kang, U.G. Characteristics of Ethanol-Induced Behavioral Sensitization in Rats: Molecular Mediators and Cross-Sensitization between Ethanol and Cocaine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 160, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, A.; Cabé, N.; Viader, F.; Pitel, A.-L. Neuropsychological Deficits in Alcohol Use Disorder. In Cognition and Addiction: A Researcher’s Guide from Mechanisms Towards Interventions; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Chapter 8; pp. 103–128. ISBN 978-0-12-815298-0. [Google Scholar]
- García-Moreno, L.M.; Conejo, N.M.; Capilla, A.; García-Sánchez, O.; Senderek, K.; Arias, J.L. Chronic Ethanol Intake and Object Recognition in Young and Adult Rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 26, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedder, L.C.; Hall, J.M.; Jabrouin, K.R.; Savage, L.M. Interactions between Chronic Ethanol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency on Neural Plasticity, Spatial Memory, and Cognitive Flexibility. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; Antonelli, L.; Biondini, M.; Perfumi, M.; Pompei, P.; Massi, M. Memory Impairment Following Combined Exposure to Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol and Ethanol in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 449, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, N.J.; Squire, L.R.; Clark, R.E. Spatial Memory, Recognition Memory, and the Hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14515–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morici, J.F.; Bekinschtein, P.; Weisstaub, N.V. Medial Prefrontal Cortex Role in Recognition Memory in Rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.-K.; Thompson, J.; Chen, L.; Dagda, M.; Dertien, J.; Dossou, K.S.S.; Moaddel, R.; Bergeson, S.E.; Kruman, I.I. Differential Sensitivity of Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus to Alcohol-Induced Toxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, E.K.; Collado-Rodriguez, A.; MacPherson, L.; Lejuez, C. Chapter 21—Impulsivity, Disinhibition, and Risk Taking in Addiction. In Principles of Addiction; Miller, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 203–212. ISBN 978-0-12-398336-7. [Google Scholar]
- Robinet, P.M.; Rowlett, J.K.; Bardo, M.T. Individual Differences in Novelty-Induced Activity and the Rewarding Effects of Novelty and Amphetamine in Rats. Behav. Processes 1998, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Boettiger, C.A. Impulsivity, Frontal Lobes and Risk for Addiction. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 93, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toledo Nunes, P.; Vedder, L.C.; Deak, T.; Savage, L.M. A Pivotal Role for Thiamine Deficiency in the Expression of Neuroinflammation Markers in Models of Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.-S.; Hu, K.; Yang, L.-Q.; Guo, J.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Song, F.-L.; Hou, F.-L.; Liang, C.-Y. Comparative Effects of EtOH Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency on Cognitive Impairment, Oxidative Damage, and β-Amyloid Peptide Overproduction in the Brain. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ke, Z.-J.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z.; Luo, J. Ethanol Promotes Thiamine Deficiency-Induced Neuronal Death: Involvement of Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bâ, A. Alcohol and Thiamine Deficiency Trigger Differential Mitochondrial Transition Pore Opening Mediating Cellular Death. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołota, A.; Głąbska, D.; Oczkowski, M.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J. Influence of Alcohol Consumption on Body Mass Gain and Liver Antioxidant Defense in Adolescent Growing Male Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larue-Achagiotis, C.; Poussard, A.M.; Louis-Sylvestre, J. Alcohol Drinking, Food and Fluid Intakes and Body Weight Gain in Rats. Physiol. Behav. 1990, 47, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Alimov, A.P.; Wang, H.; Frank, J.A.; Katz, W.; Xu, M.; Ke, Z.-J.; Luo, J. Thiamine Deficiency Induces Anorexia by Inhibiting Hypothalamic AMPK. Neuroscience 2014, 267, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeWit, D.J.; Adlaf, E.M.; Offord, D.R.; Ogborne, A.C. Age at First Alcohol Use: A Risk Factor for the Development of Alcohol Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, S.; Vetreno, R.P.; Ramos, R.L.; Savage, L.M. Cortical Cholinergic Abnormalities Contribute to the Amnesic State Induced by Pyrithiamine-Induced Thiamine Deficiency in the Rat: Cortical Cholinergic Abnormalities. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, B.; Desjardins, P.; Butterworth, R.F. Selective Increase of Neuronal Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Expression in Vulnerable Brain Regions of Rats with Experimental Wernicke’s Encephalopathy: Effect of Nimesulide. Metab. Brain Dis. 2008, 23, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Ramos, R.L.; Anzalone, S.; Savage, L.M. Brain and Behavioral Pathology in an Animal Model of Wernicke’s Encephalopathy and Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome. Brain Res. 2012, 1436, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, C. The Neuropathology of Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2009, 44, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Neurocircuitry in Alcoholism: A Substrate of Disruption and Repair. Psychopharmacology 2005, 180, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohorecky, L.A.; Cagan, M.; Brick, J.; Jaffe, S.L. The Startle Response in Rats: Effect of Ethanol. Pharmacol.Biochem. Behav. 1976, 4, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahr, N.M.; Alt, C.; Mayer, D.; Rohlfing, T.; Manning-Bog, A.; Luong, R.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Associations between in Vivo Neuroimaging and Postmortem Brain Cytokine Markers in a Rodent Model of Wernicke’s Encephalopathy. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 261, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latt, N.; Dore, G. Thiamine in the Treatment of Wernicke Encephalopathy in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorders. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portari, G.V.; Vannucchi, H.; Jordao, A.A. Liver, Plasma and Erythrocyte Levels of Thiamine and Its Phosphate Esters in Rats with Acute Ethanol Intoxication: A Comparison of Thiamine and Benfotiamine Administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein | Primary Antibody 1 | Secondary Antibody |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid peroxidation marker | 1:1000 BSA 3% | Mouse (1:2000) |
| 4-HNE | MAB3249 R&D Systems | |
| Cell damage markers | ||
| HSP70 | 1:1000 sc-1060 | Goat (1:4000) |
| HSP60 | 1:1000 sc-13,966 | Rabbit (1:2000) |
| HMGB1 | 1:1000 sc-56,698 | Mouse (1:2000) |
| Apoptosis markers | ||
| Caspase 3 | 1:500 sc-56,053 | Mouse (1:2000) |
| Caspase 8 | 1:400 sc-81,656 | Mouse (1:2000) |
| Caspase and pro-9 | 1:500 BSA 1% sc-56,076 | Mouse (1:2000) |
| Nitrosative stress marker | ||
| iNOS | 1:500 BSA 2% sc-650 | Rabbit (1:2000) |
| Housekeeping β-actin | 1:10,000 A5441 Sigma | Mouse (1:10,000) |
| Percentages in Open Arms in the Elevated Plus Maze 1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Entries | |||||||||
| Protein Marker 2 | r | Slope | Constant | p-Value | q-Value | r | Slope | Constant | p-Value | q-Value |
| Plasma NO−2 | 0.5044 | 0.0005792 | −0.00688 | 0.0659 | 0.0659 | 0.6692 | 0.0008195 | −0.03051 | 0.0089 | 0.0111 |
| 4-HNE | 0.7596 | 0.001149 | −0.09649 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.7128 | 0.001158 | −0.07876 | 0.0029 | 0.0043 |
| Caspase-9 | 0.7611 | 0.002541 | −0.2306 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.7633 | 0.002739 | −0.2364 | 0.0009 | 0.002 |
| HSP70 | 0.7952 | 0.0118 | −1.169 | 0.0004 | 0.002 | 0.8949 | 0.01427 | −1.413 | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| HMGB1 | 0.5783 | 0.01111 | −1.07 | 0.0384 | 0.0427 | 0.752 | 0.01704 | −1.659 | 0.003 | 0.0043 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moya, M.; López-Valencia, L.; García-Bueno, B.; Orio, L. Disinhibition-Like Behavior Correlates with Frontal Cortex Damage in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020260
Moya M, López-Valencia L, García-Bueno B, Orio L. Disinhibition-Like Behavior Correlates with Frontal Cortex Damage in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020260
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoya, Marta, Leticia López-Valencia, Borja García-Bueno, and Laura Orio. 2022. "Disinhibition-Like Behavior Correlates with Frontal Cortex Damage in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020260
APA StyleMoya, M., López-Valencia, L., García-Bueno, B., & Orio, L. (2022). Disinhibition-Like Behavior Correlates with Frontal Cortex Damage in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Thiamine Deficiency. Biomedicines, 10(2), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020260








