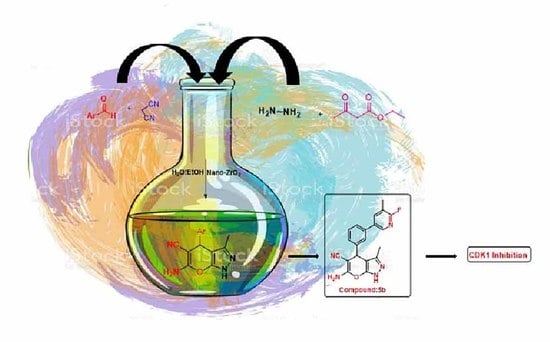
Nano-Zirconium Dioxide Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis of Bioactive Pyranopyrazoles That Target Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Nano-Zirconium Dioxide
2.2. Chemistry
2.2.1. General Procedure for Preparation of Newer Pyranopyrazole Derivatives 5(a–o)
2.2.2. Characterization of 6-Amino-3-methyl-4-(4-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydropy-rano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5a)
2.2.3. Characterization of 6-Amino-4-(3-(6-fluoro-5-methylpyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-3-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5b)
2.2.4. Characterization of 6-Amino-3-methyl-4-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5c)
2.2.5. Characterization of 6-Amino-4-(3-(6-chloro-5-methylpyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-3-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5d)
2.2.6. Characterization of 6-Amino-3-methyl-4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydropyra-no [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5e)
2.2.7. Characterization of 6-Amino-4-(4-(6-fluoro-5-methylpyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-3-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5f)
2.2.8. Characterization of 6-Amino-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-4-(3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazole-5-carbonitrile (5g)
2.3. Gibbs Free Energy Calculation
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. In Silico Mode-of-Action Analysis
2.6. Kinase Assay
2.7. In Silico Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano-Zirconium Dioxide
3.2. Synthesis of Pyranopyrazoles
3.3. In Silico Mechanistic Studies of Pyranopyrazole Products
3.4. Effect of Pyranopyrazoles on MCF-7 Cell Viability
3.5. In Silico Mode-of-Action Analysis of Compound 5b
3.6. In Vitro Inhibition of Lead Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 by Pyranopyrazoles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Asghar, U.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Turner, N.C.; Knudsen, E.S. The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Cao, J.; Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Xiong, X.; Ao, H.; Yu, M.; Lin, J.; Cui, Q. The Roles of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in Cell-Cycle Progression and Therapeutic Strategies in Human Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.L. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases and CTD Phosphatases in Cell Cycle Transcriptional Control: Conservation across Eukaryotic Kingdoms and Uniqueness to Plants. Cells 2022, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, S.R.; Mallinger, A.; Workman, P.; Clarke, P.A. Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases as cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 173, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, T.A.; Qayyum, A.; Rehman, K.; Tariq, M.; Akash, M.S.H. An insight into the emerging role of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of advanced cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Hei, R.; Li, X.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Cai, C. CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy, an overview of recent development. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 15, 1913–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Łukasik, P.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Kulczycka, K.; Gutowska, I. Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: Types and Their Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 10, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, P.M.; Schlessinger, A. DFGmodel: Predicting protein kinase structures in inactive states for structure-based discovery of type-II inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 16, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Tovar, C.; Chen, S.; Knezevic, D.; Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Heimbrook, D.C.; Chen, L. Selective small-molecule inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10660–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Shimanuki, M.; Shikami, M.; Andreeff, M.; Nakakuma, H. Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 inhibitor RO-3306 enhances p53-mediated Bax activation and mitochondrial apoptosis in AML. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.R.; Korolchuk, S.; Martin, M.P.; Stanley, W.A.; Moukhametzianov, R.; Noble, M.E.M.; Endicott, J.A. CDK1 structures reveal conserved and unique features of the essential cell cycle CDK. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; Lin, L.; Yao, S. A CIEF-LIF method for simultaneous analysis of multiple protein kinases and screening of inhibitors. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravec, J.; Krystof, V.; Hanus, J.; Havlícek, L.; Moravcová, D.; Fuksová, K.; Kuzma, M.; Lenobel, R.; Otyepka, M.; Strnad, M. 2,6,8,9-Tetrasubstituted purines as new CDK1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popowycz, F.; Fournet, G.; Schneider, C.; Bettayeb, K.; Ferandin, Y.; Lamigeon, C.; Tirado, O.M.; Mateo-Lozano, S.; Notario, V.; Colas, P.; et al. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]-1,3,5-triazine as a Purine Bioisostere: Access to Potent Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor (R)-Roscovitine Analogue. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Hobbie, E.K.; Kilin, D.S. First-Principles Molecular Dynamics of Monomethylhydrazine and Nitrogen Dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, A.; Hratchian, H.P., II; Dennington, R.D.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.; Nielsen, B.; Holder, A.J.; Hiscocks, J. GaussView Version 5.0.8; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, I.; Wu, J.; Xu, X. Extending the reliability and applicability of B3LYP. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3057–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Wang, B.; Mohan, C.D.; Raquib, A.R.; Rangappa, S.; Srinivasa, V.; Fuchs, J.E.; Girish, K.S.; Zhu, T.; Bender, A.; et al. Discovery of a small-molecule inhibitor of specific serine residue BAD phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 30, E10505–E10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Basappa, B.; Zhu, T.; Lobie, P.E.; Pandey, V. Inhibition of BAD-Ser99 phosphorylation synergizes with PARP inhibition to ablate PTEN-deficient endometrial carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 20, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveshegowda, S.N.; Metri, P.K.; Shivakumar, R.; Yang, J.R.; Rangappa, S.; Swamynayaka, A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Nagaraja, O.; Madegowda, M.; Babu Shubha, P.; et al. Development of 1-(4-(Substituted)piperazin-1-yl)-2-((2-((4-methoxybenzyl)thio)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)ethanones That Target Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basappa, B.; Chumadathil Pookunoth, B.; Shinduvalli Kempasiddegowda, M.; Knchugarakoppal Subbegowda, R.; Lobie, P.E.; Pandey, V. Novel Biphenyl Amines Inhibit Oestrogen Receptor (ER)-α in ER-Positive Mammary Carcinoma Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Kavitha, C.V.; Purushothaman, A.; Nevin, K.G.; Sugahara, K.; Rangappa, K.S. A small Oxazine compound as an anti-tumor agent:A novel pyranoside mimetic that bind to VEGF, HB-EGF and TNF-α. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Bharathkumar, H.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Kang, T.; Keerthy, H.K.; Fuchs, J.E.; Kwon, N.H.; Bender, A.; Kim, S.; Rangappa, K.S. Screening of quinoline, 1,3-benzoxazine, and 1,3-oxazine-based small molecules against iso-lated methionyl-tRNA synthetase and A549 and HCT116 cancer cells including an in silico binding mode analysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9381–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathkumar, H.; Sundaram, M.S.; Jagadish, S.; Paricharak, S.; Hemshekhar, M.; Mason, D.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S.; Bender, A.; Rangappa, K.S. Novel benzoxazines, Novel Benzoxazine-Based Aglycones Block Glucose Uptake In Vivo by Inhibiting Glycosidases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhorukov, A.Y.; Nirvanappa, A.C.; Swamy, J.; Ioffe, S.L.; Swamy, S.N.; Basappa; Rangappa, K.S. Synthesis and characterization of novel 1,2-oxazine-based small molecules that targets acetylcholinesterase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3618–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirvanappa, A.C.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Ananda, H.; Sukhorukov, A.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Sundaram, M.S.; Nayaka, S.C.; Girish, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; et al. Novel Synthetic Oxazines Target NF-κB in Colon Cancer In Vitro and Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G.; Rajeev, C.P.B.; Mohan, C.D.; Sinha, A.; Chu, T.T.; Anusha, S.; Ximei, H.; Fuchs, J.E.; Bender, A.; Rangappa, K.S.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of hydrazinyl phthalazines against malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3300–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongmoon, D.; Shetty, A.K.; Basappa; Yamada, S.; Sugiura, M.; Kongtawelert, P.; Sugahara, K. Chondroitinase-mediated Degradation of Rare 3-O-Sulfated Glucuronic Acid in Functional Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate K and E. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36895–36904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baburajeev, C.P.; Mohan, C.D.; Ananda, H.; Rangappa, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Jagadish, S.; Siveen, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Zayed, M.E.; et al. Development of Novel Triazolo-Thiadiazoles from Heterogeneous “Green” Catalysis as Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangappa, K.S.; Basappa. New cholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of 1,2-benzisoxazole series and novel imidazolyl-d2-isoxazolines. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2005, 18, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basappa; Kavitha, C.; Rangappa, K. Simple and an efficient method for the synthesis of 1-[2-dimethylamino-1-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-cyclohexanol hydrochloride: (±) venlafaxine racemic mixtures. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 3279–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadashiva, M.P.; Basappa, B.; NanjundaSwamy, S.; Li, F.; Manu, K.A.; Sengottuvelan, M.; Prasanna, D.S.; Anilkumar, N.C.; Sethi, G.; Sugahara, K.; et al. Anti-cancer activity of novel dibenzo[b,f]azepine tethered isoxazoline derivatives. BMC Chem. Biol. 2012, 12, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA. Dassault Systèmes, Discovery Studio Visualizer, 21.1.0.20298; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger, L.; DeLano, W. PyMOL. 2020. Available online: http://www.pymol.org/pymol (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Bharathkumar, H.; Mohan, C.D.; Ananda, H.; Fuchs, J.E.; Li, F.; Rangappa, S.; Surender, M.; Bulusu, K.C.; Girish, K.S.; Sethi, G.; et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic studies of novel estrogen receptor α ligands towards human breast cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1804–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.D.; Srinivasa, V.; Rangappa, S.; Mervin, L.; Mohan, S.; Paricharak, S.; Baday, S.; Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chinnathambi, A.; et al. Trisubstituted-Imidazoles Induce Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting the Oncogenic PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, K.S.; Jagadish, S.; Vinayaka, A.C.; Hemshekhar, M.; Paul, M.; Thushara, R.M.; Sundaram, M.S.; Swaroop, T.R.; Mohan, C.D.; Basappa; et al. A New Ibuprofen Derivative Inhibits Platelet Aggregation and ROS Mediated Platelet Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107182, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Hsu, A.; Woo, C.C.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, K.H.B.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Koh, A.P.F.; et al. Thymoquinone Inhibits Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells Through Abrogation of the CXCR4 Signaling Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ahn, K.S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Chang, Y.; Sethi, G.; et al. Oleuropein induces apoptosis via abrogating NF-κB activation cascade in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 4504–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Bian, J.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Formononetin-induced oxidative stress abrogates the activation of STAT3/5 signaling axis and suppresses the tumor growth in multiple myeloma preclinical model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Potential role of targeted therapies in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2016, 27, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhao, G.; Cheng, B.; Yan, B. Identification of potential matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibitors from natural products through advanced machine learning-based cheminformatics approaches. Mol. Divers. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldahdooh, J.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Tang, J.; Tanoli, Z. Using BERT to identify drug-target interactions from whole PubMed. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, R.; Sharpley, M.S.; Chi, F.; Braas, D.; Zhou, Y.; Kim, R.; Clark, A.T.; Banerjee, U. Nuclear Localization of Mitochondrial TCA Cycle Enzymes as a Critical Step in Mammalian Zygotic Genome Activation. Cell 2017, 168, 210–223.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Yang, W.; Fu, Z.; Xie, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, D.; Ge, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Selected using bioinformatics and molecular docking analyses, PHA-793887 is effective against osteosarcoma. Aging 2021, 13, 16425–16444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Entry | Solvent | Amount of Catalyst (mol%) | Time (min) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2O | 10 | 30 | 38 |
| 2 | EtOH | 10 | 30 | 45 |
| 3 | H2O:EtOH (1:1) | 10 | 30 | 53 |
| 4 | H2O:EtOH (1:1) | 10 | 50 | 62 |
| 5 | H2O:EtOH (1:1) | 20 | 30 | 68 |
| 6 | H2O:EtOH (1:1) | 20 | 50 | 75 |
| Entry | Aldehyde | Product | Time (min) | Melting Point (°C) | MCF-7 IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  1a |  5a | 60 | 196–198 b | 55 |
| 2 |  1b |  5b | 50 | 214–215 b | 17 |
| 3 |  1c |  5c | 30 | 245–247 b | ND |
| 4 |  1d |  5d | 50 | 212–214 b | 38.89 |
| 5 |  1e |  5e | 45 | 232–234 b | >100 |
| 6 |  1f |  5f | 60 | 268–269 b | 23.79 |
| 7 |  1g |  5g | 50 | 242–243 | ND |
| 8 |  1h |  5h | 40 | 232–234 | ND |
| 9 |  1i |  5i | 35 | 249–250 | ND |
| 10 |  1j |  5j | 60 | 196–198 a | ND |
| 11 |  1k |  5k | 45 | 211–213 | ND |
| 12 |  1l |  5l | 35 | 224–226 a | ND |
| 13 |  1m |  5m | 50 | 241–242 | ND |
| 14 |  1n |  5n | 40 | 233–234 | ND |
| 15 |  1o |  5o | 50 | 246–248 | ND |
| Olaparib | 3.28 | ||||
| Compound Name | IC50 (μM) (Alamar Blue) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T47D | BT-474 | SKBR3 | MDA-MB-231 | MCF-10A | |
| 5b | 27.48 | 23.66 | >100 | 13.47 | 90.52 |
| 5c | 33.71 | 21.28 | 69.38 | 14.95 | 88.25 |
| 5e | >100 | 50.17 | >100 | 22.07 | >100 |
| 5f | 45.79 | 15.23 | >100 | 19.1 | >100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basappa, B.; Poonacha, L.K.; Xi, Z.; Vishwanath, D.; Yang, J.-R.; Nagaraja, O.; Swamynayaka, A.; Madegowda, M.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; et al. Nano-Zirconium Dioxide Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis of Bioactive Pyranopyrazoles That Target Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010172
Basappa B, Poonacha LK, Xi Z, Vishwanath D, Yang J-R, Nagaraja O, Swamynayaka A, Madegowda M, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, et al. Nano-Zirconium Dioxide Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis of Bioactive Pyranopyrazoles That Target Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010172
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasappa, Basappa, Lisha K. Poonacha, Zhang Xi, Divakar Vishwanath, Ji-Rui Yang, Omantheswara Nagaraja, Ananda Swamynayaka, Mahendra Madegowda, Arunachalam Chinnathambi, Sulaiman Ali Alharbi, and et al. 2023. "Nano-Zirconium Dioxide Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis of Bioactive Pyranopyrazoles That Target Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010172
APA StyleBasappa, B., Poonacha, L. K., Xi, Z., Vishwanath, D., Yang, J.-R., Nagaraja, O., Swamynayaka, A., Madegowda, M., Chinnathambi, A., Alharbi, S. A., Gurudatt, D. M., Pandey, V., Shivananju, N., Ahn, K. S., Sethi, G., Lobie, P. E., & Shubha, P. B. (2023). Nano-Zirconium Dioxide Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis of Bioactive Pyranopyrazoles That Target Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines, 11(1), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010172