Sodium Tungstate (NaW) Decreases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Cells: New Cellular Antioxidant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
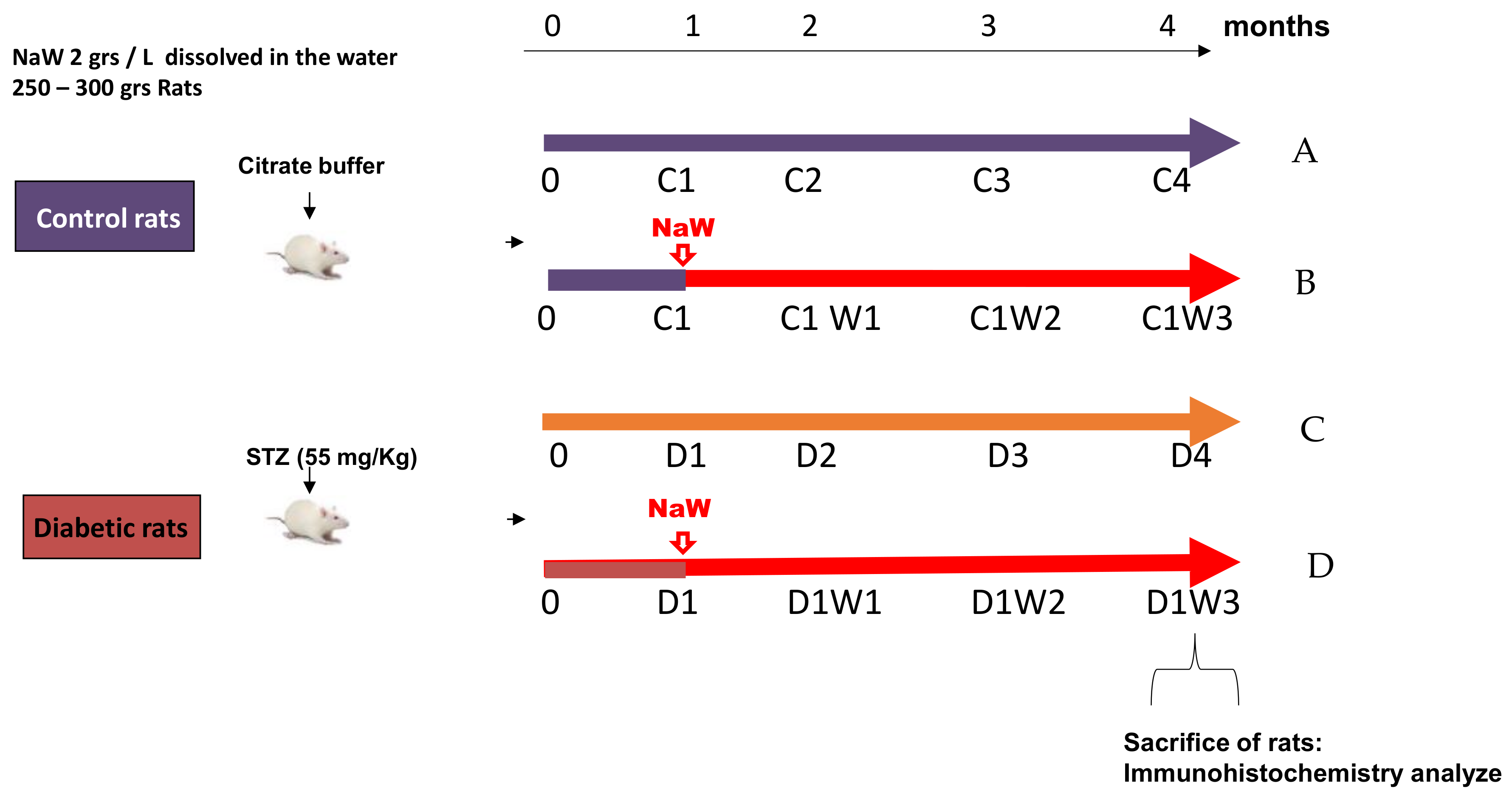
2.1. Diabetic Rat Model and Sodium Tungstate Treatment
2.2. Isolation of Bovine Neutrophils
2.3. Estimation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Bovine Neutrophils Using Luminol
2.4. HK-2 Cell Culture and Treatments
2.5. Estimation of ROS Production in HK-2 Cells by Flow Cytometry
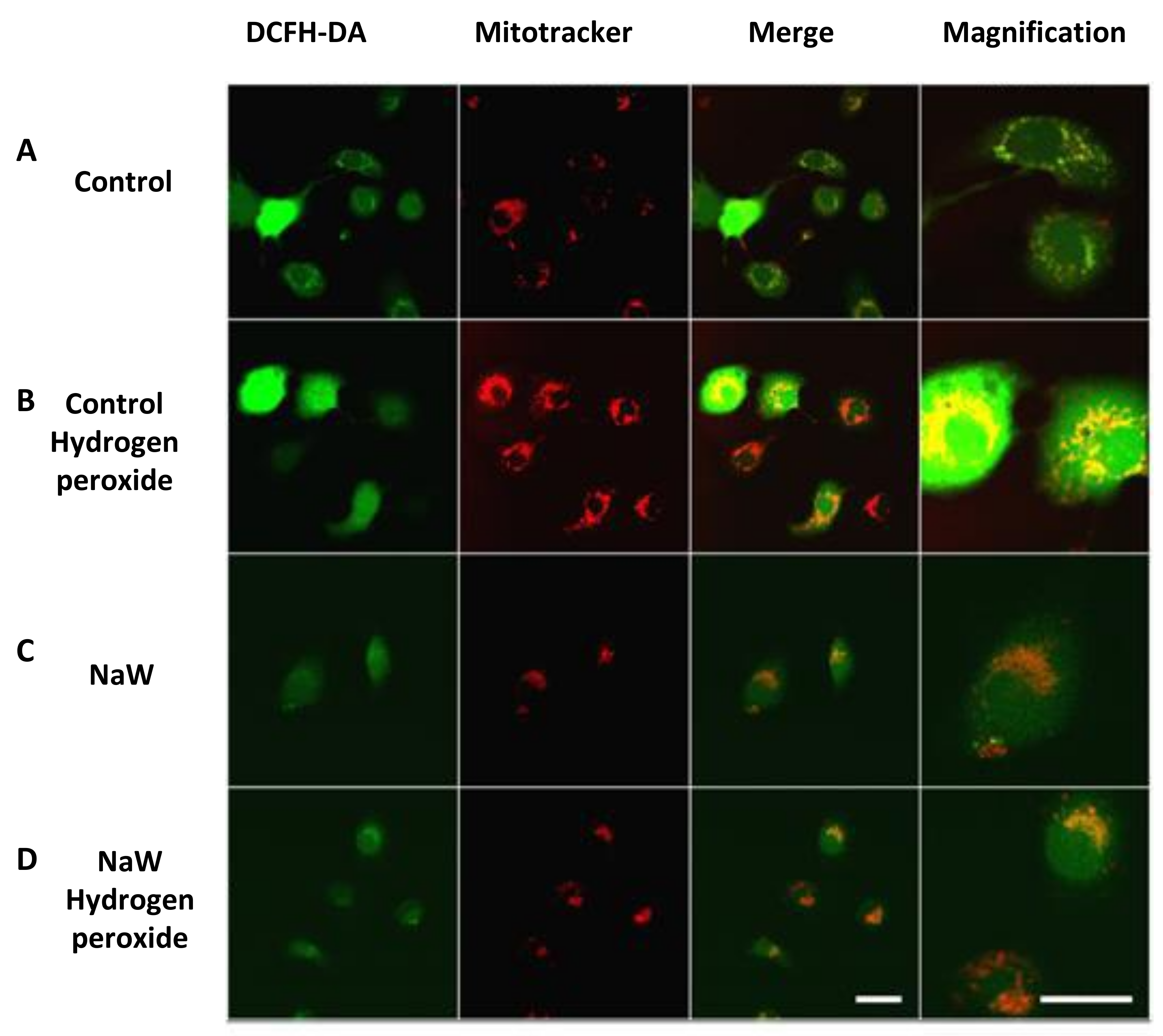
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Immunohistochemistry in Tissue
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
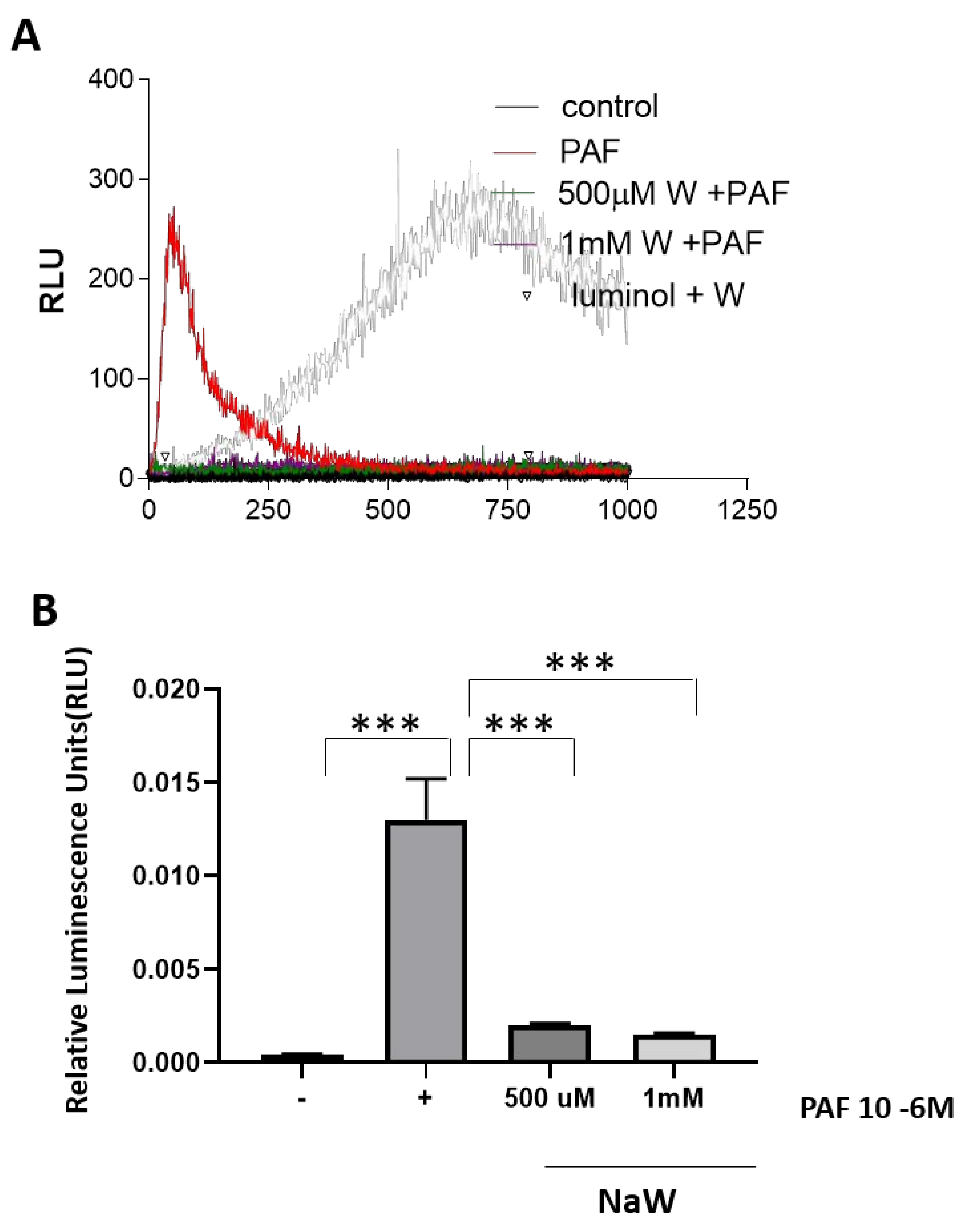
3.1. The Effect of Sodium Tungstate on ROS Production in Bovine Neutrophils Stimulated with PAF
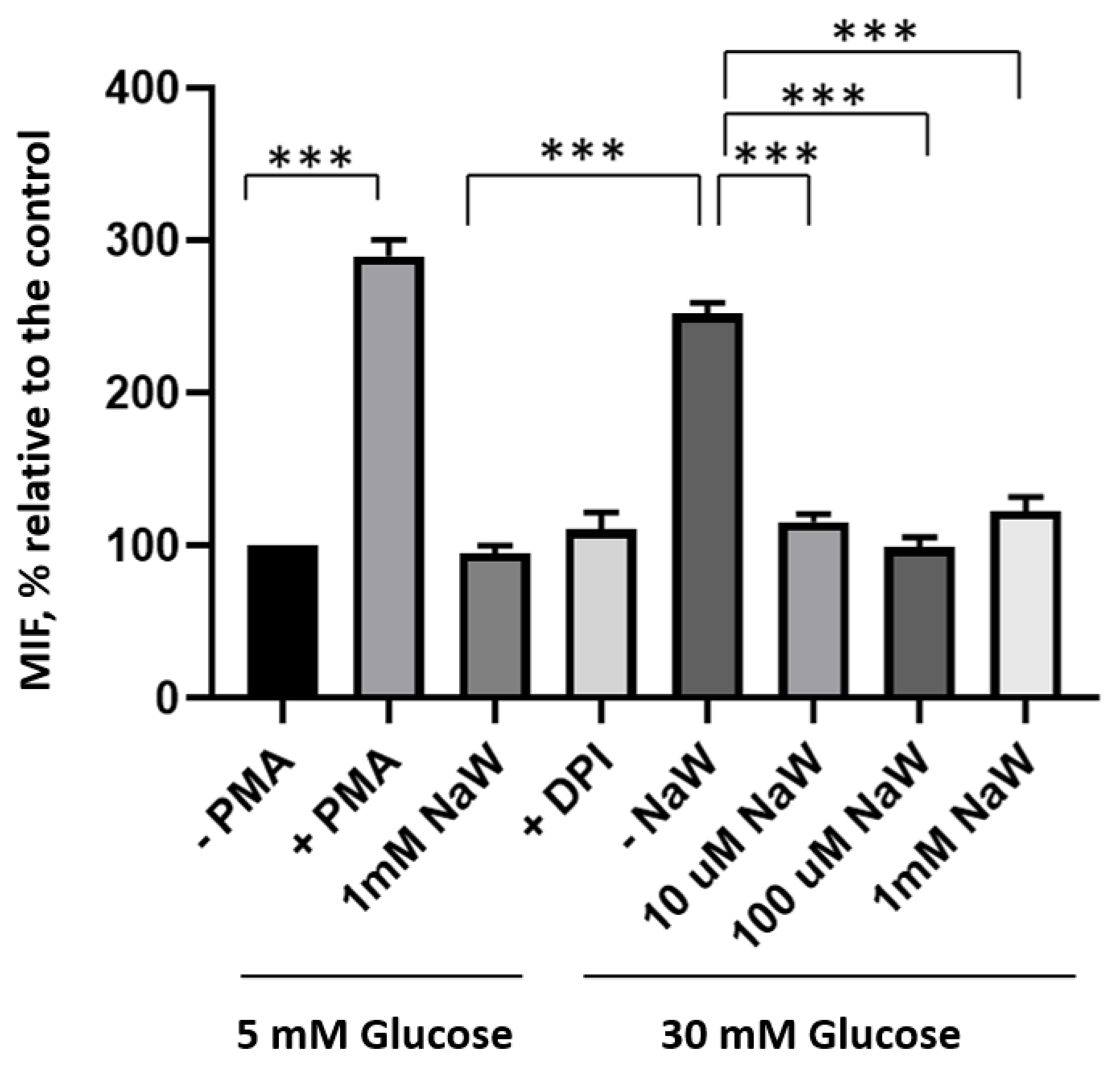
3.2. The Effect of Sodium Tungstate on ROS Production in HK-2 Cells Incubated with High Glucose
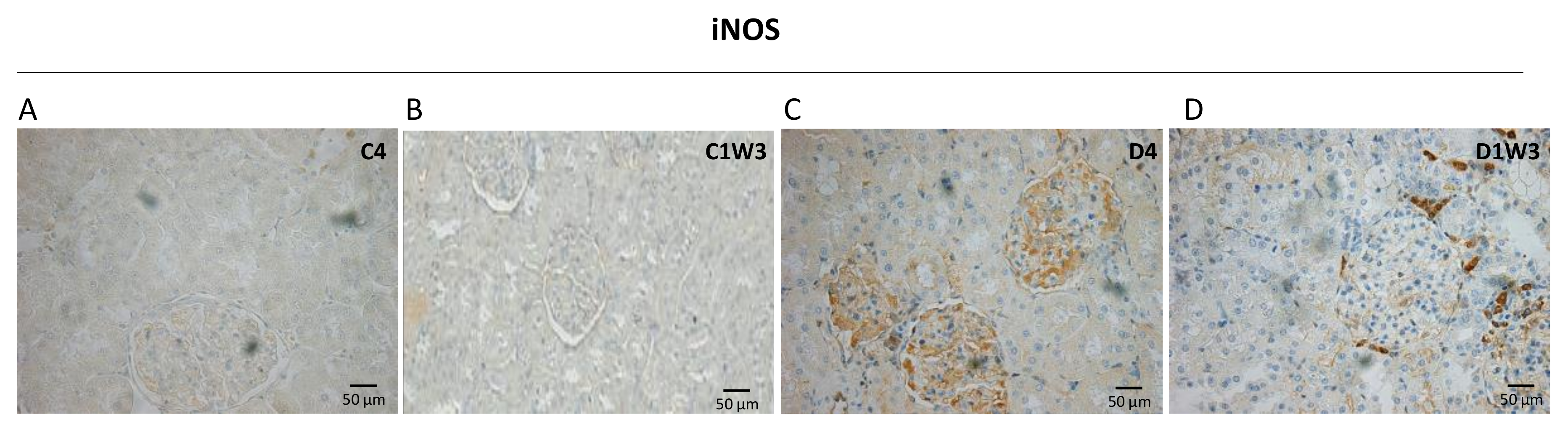
3.3. Effect of Sodium Tungstate on Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression in Diabetic Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, C.; Wu, W.; Tang, A.; Luo, N.; Tan, Y. lncRNA GAS5/miR-452-5p Reduces Oxidative Stress and Pyroptosis of High-Glucose-Stimulated Renal Tubular Cells. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocevar, B.A.; Brown, T.L.; Howe, P.H. TGF-beta induces fibronectin synthesis through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent, Smad4-independent pathway. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, K.; Miyata, T.; Maeda, K.; Miyata, S.; Sugiyama, S.; Sakai, H.; van Ypersole de Strihou, C.; Monnier, V.M.; Witztum, J.L.; Kurokawa, K. Immunohistochemical colocalization of glycoxidation products and lipid peroxidation products in diabetic renal glomerular lesions. Implication for glycoxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2995–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; Goto, A.; Fujita, T.; Wilcox, C.S. Oxidative stress and nitric oxide synthase in rat diabetic nephropathy: Effects of ACEI and ARB. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etoh, T.; Inoguchi, T.; Kakimoto, M.; Sonoda, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Kuroda, J.; Sumimoto, H.; Nawata, H. Increased expression of NAD(P)H oxidase subunits, NOX4 and p22phox, in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and its reversibity by interventive insulin treatment. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, Y.S.; Wada, J.; Sun, L.; Xie, P.; Wallner, E.I.; Chen, S.; Chugh, S.; Danesh, F.R. Diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Nguyen-Khoa, T. Oxidative stress and chronic renal failure: Markers and management. J. Nephrol. 2002, 15, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Koya, D.; Hayashi, K.; Kitada, M.; Kashiwagi, A.; Kikkawa, R.; Haneda, M. Effects of antioxidants in diabetes-induced oxidative stress in the glomeruli of diabetic rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14 (Suppl. S3), S250–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Canaud, B.; Eckardt, K.U.; Stenvinkel, P.; Wanner, C.; Zoccali, C. Oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease: An emerging threat to patient outcome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezniceanu, M.L.; Liu, F.; Wei, C.C.; Tran, S.; Sachetelli, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Guo, D.F.; Filep, J.G.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Chan, J.S. Catalase overexpression attenuates angiotensinogen expression and apoptosis in diabetic mice. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Opazo-Ríos, L.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; García-Caballero, C.; Vázquez-Carballo, C.; Mas, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Herencia, C.; Mezzano, S.; et al. Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rubertis, F.R.; Craven, P.A.; Melhem, M.F.; Salah, E.M. Attenuation of renal injury in db/db mice overexpressing superoxide dismutase: Evidence for reduced superoxide-nitric oxide interaction. Diabetes 2004, 53, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaba, K.; Tojo, A.; Onozato, M.L.; Goto, A.; Quinn, M.T.; Fujita, T.; Wilcox, C.S. Effects of NADPH oxidase inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thallas-Bonke, V.; Thorpe, S.R.; Coughlan, M.T.; Fukami, K.; Yap, F.Y.; Sourris, K.C.; Penfold, S.A.; Bach, L.A.; Cooper, M.E.; Forbes, J.M. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase prevents advanced glycation end product-mediated damage in diabetic nephropathy through a protein kinase C-alpha-dependent pathway. Diabetes 2008, 57, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashihara, N.; Haruna, Y.; Kondeti, V.K.; Kanwar, Y.S. Oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4256–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L. Vanadium and tungsten derivatives as antidiabetic agents: A review of their toxic effects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002, 88, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberà, A.; Fernàndez-Alvarez, J.; Truc, A.; Gomis, R.; Guinovart, J.J. Effects of tungstate in neonatally streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Mechanism leading to normalization of glycaemia. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberà, A.; Gomis, R.R.; Prats, N.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Domingo, M.; Gomis, R.; Guinovart, J.J. Tungstate is an effective antidiabetic agent in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: A long-term study. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.C.; Barberà, A.; Domínguez, J.; Fernàndez-Alvarez, J.; Gomis, R.; Guinovart, J.J. Effects of tungstate, a new potential oral antidiabetic agent, in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, M.D.; Caballero, J.J.; Vargas, A.M.; Suárez, M.D.; Guinovart, J.J.; Salto, R. Modulation of glucose transporters in rat diaphragm by sodium tungstate. FEBS Lett. 2003, 542, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Alvarez, J.; Barberà, A.; Nadal, B.; Barceló-Batllori, S.; Piquer, S.; Claret, M.; Guinovart, J.J.; Gomis, R. Stable and functional regeneration of pancreatic beta-cell population in nSTZ-rats treated with tungstate. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertinat, R.; Westermeier, F.; Gatica, R.; Nualart, F. Sodium tungstate: Is it a safe option for a chronic disease setting, such as diabetes? J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Q.; Lin, J.G.; Hu, M.S.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, R. The role of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cultured human renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Koide, H. Production of hydrogen peroxide by neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes in patients with diabetic nephropathy. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1993, 7, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, M.; Koya, D.; Sugimoto, T.; Isono, M.; Araki, S.; Kashiwagi, A.; Haneda, M. Translocation of glomerular p47phox and p67phox by protein kinase C-beta activation is required for oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, Y.S.; Sun, L.; Xie, P.; Liu, F.Y.; Chen, S. A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 395–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.K.; Zheng, G.; Hsu, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Lee, V.W.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Harris, D.C. Macrophage matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro in murine renal tubular cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Yu, M.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Kitamura, M.; Lee, H.B. Role of high glucose-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogyorósi, A.; Ziyadeh, F.N. GLUT1 and TGF-beta: The link between hyperglycaemia and diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 2827–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Ma, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, K.; Ye, C.; Zhu, S. VX-765 ameliorates inflammation and extracellular matrix accumulation by inhibiting the NOX1/ROS/NF-κB pathway in diabetic nephropathy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ni, H.; Ma, K.; Zou, J. ANGPTL2 regulates autophagy through the MEK/ERK/Nrf-1 pathway and affects the progression of renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5472–5486. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, S.; Shan, J.; Varma, D.R.; Mulay, S. Augmentation of diabetes-associated renal hyperfiltration and nitric oxide production by pregnancy in rats. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 161, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yañez, A.J.; Jaramillo, K.; Blaña, C.; Burgos, R.A.; Isla, A.; Silva, P.; Aguilar, M. Sodium Tungstate (NaW) Decreases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Cells: New Cellular Antioxidant. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020417
Yañez AJ, Jaramillo K, Blaña C, Burgos RA, Isla A, Silva P, Aguilar M. Sodium Tungstate (NaW) Decreases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Cells: New Cellular Antioxidant. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020417
Chicago/Turabian StyleYañez, Alejandro J., Karen Jaramillo, Camila Blaña, Rafael A. Burgos, Adolfo Isla, Pamela Silva, and Marcelo Aguilar. 2023. "Sodium Tungstate (NaW) Decreases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Cells: New Cellular Antioxidant" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020417
APA StyleYañez, A. J., Jaramillo, K., Blaña, C., Burgos, R. A., Isla, A., Silva, P., & Aguilar, M. (2023). Sodium Tungstate (NaW) Decreases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Cells: New Cellular Antioxidant. Biomedicines, 11(2), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020417





