Angiopoietin-like 2 Protein and Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A New Biomarker for Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Protocol
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
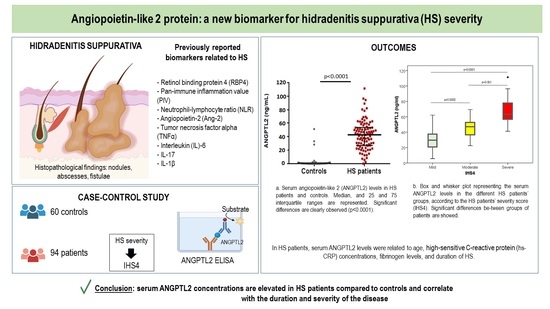
3.1. Baseline Features and Serum ANGPTL2
3.2. ANGPTL2 and HS Severity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Desai, N.; Emtestam, L.; Hunger, R.E.; Ioannides, D.; Juhász, I.; Lapins, J.; Matusiak, L.; Prens, E.P.; Revuz, J.; et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 619–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, A.R.J.V.; Van Der Zee, H.H.; Prens, E.P. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review Integrating Inflammatory Pathways Into a Cohesive Pathogenic Model. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, G.S.; Ergun, T.; Eyüboğlu, I.P.; Akkiprik, M. Serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-17A and IL-23 levels in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.M.; Naik, H.B.; Clancy, S.; Pauli, M.; Smith, K.M.; Bi, Y.; Dunstan, R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Paul, M.; Harris, H.; et al. Immunopathogenesis of hidradenitis suppurativa and response to anti–TNF-α therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7, e139932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-López, M.A.; Ocejo-Viñals, J.G.; Mata, C.; Vilanova, I.; Guiral, S.; Portilla, V.; Blanco, R.; Hernández, J.L. Association of retinol binding protein4 (RBP4) and ghrelin plasma levels with insulin resistance and disease severity in non-diabetic patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.A.; Ocejo-Viñals, J.G.; López-Sundh, A.E.; Guiral, S.; Ruiz-Solana, M.; Mata, C.; Portilla, V.; Corrales, A.; Blanco, R.; Hernández, J.L. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriano, T.M.; Benesh, G.; Babbush, K.M.; Hosgood, H.D.; Lin, J.; Cohen, S.R. Serum inflammatory markers and leukocyte profiles accurately describe hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Hessam, S.; Cramer, P.; Abu Rached, N.; Bechara, F. Complete blood collection-based systemic inflammation biomarkers for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; Merz, V.; Simionato, F.; Santoro, R.; Zecchetto, C.; Tortora, G.; Melisi, D. Angiopoietin-Like Proteins in Angiogenesis, Inflammation and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, J.; Mukai, N.; Nagata, M.; Ohara, T.; Yoshida, D.; Kishimoto, H.; Shibata, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Endo, M.; Ago, T.; et al. Serum Angiopoietin-Like Protein 2 Is a Novel Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease in the Community: The Hisayama Study. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Tsukano, H.; Endo, M.; Tabata, M.; Miyata, K.; Kadomatsu, T.; Miyashita, K.; Semba, K.; Nakamura, E.; Tsukano, M.; et al. Synoviocyte-Derived Angiopoietin-Like Protein 2 Contributes to Synovial Chronic Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, A.; Endo, M.; Aoi, J.; Takahashi, O.; Kadomatsu, T.; Miyata, K.; Tian, Z.; Jinnin, M.; Fukushima, S.; Ihn, H.; et al. The role of angiopoietin-like protein 2 in pathogenesis of dermatomyositis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oike, Y.; Tabata, M. Angiopoietin-Like Proteins Potential Therapeutic Targets for Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, M.; Kadomatsu, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyata, K.; Ito, Y.; Endo, M.; Urano, T.; Zhu, H.J.; Tsukano, H.; Tazume, H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like Protein 2 Promotes Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Obesity-Related Systemic Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Takahashi, O.; Mukai, N.; Hata, J.; Iwase, M.; Kitazono, T.; Oike, Y.; Kiyohara, Y. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 and risk of type 2 diabetes in a general Japanese population: The Hisayama study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorin-Trescases, N.; Thorin, E. High Circulating Levels of ANGPTL2: Beyond a Clinical Marker of Systemic Inflammation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1096385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Noma, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Kihara, Y. Endothelial function and oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2009, 73, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Biomarkers of endothelial activation and dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Tuo, S.; Li, Y. Correlation between angiopoietin-like proteins in inflammatory mediators in peripheral blood and severity of coronary arterial lesion in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussen, A.M.; Ricci, F.; Paris, L.P.; Korn, C.; Quezada-Ruiz, C.; Zarbin, M. Angiopoietin/Tie2 signalling and its role in retinal and choroidal vascular diseases: A review of preclinical data. Eye 2021, 35, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorin-Trescases, N.; Thorin, E. Angiopoietin-like-2: A multifaceted protein with physiological and pathophysiological properties. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2014, 16, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wan, X.; Chen, X.; Hirayasu, K.; Sun, H.; Lam, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. A motif in LILRB2 critical for Angptl2 binding and activation. Blood 2014, 124, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, W.; He, X.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Endothelial cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 supports hematopoietic stem cell activities in bone marrow niches. Blood 2022, 139, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revuz, J.E.; Jemec, G.B. Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Dermatol. Clin. 2016, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Tzellos, T.; Kyrgidis, A.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Bechara, F.G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Ingram, J.R.; Kanni, T.; Karagiannidis, I.; Martorell, A.; et al. Development and validation of the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS 4), a novel dynamic scoring system to assess HS severity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horio, E.; Kadomatsu, T.; Miyata, K.; Arai, Y.; Hosokawa, K.; Doi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Horiguchi, H.; Endo, M.; Tabata, M.; et al. Role of Endothelial Cell–Derived Angptl2 in Vascular Inflammation Leading to Endothelial Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Progression. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, A.; Plate, K.H.; Reiss, Y. Angiopoietin-2: A multifaceted cytokine that functions in both angiogenesis and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1347, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Pang, J. The effects and mechanisms of ghrelin upon angiogenesis in human coronary artery endothelial cells under hypoxia. Peptides 2023, 160, 170921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwii, R.G.; Sajib, M.S.; Zahra, F.T.; Mikelis, C.M. Role of Angiopoietin-2 in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cells 2019, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, H.H.; de Ruiter, L.; van den Broecke, D.G.; Dik, W.A.; Laman, J.D.; Prens, E.P. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: A rationale for targeting TNF-α and IL-1β. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.A.; Ocejo-Viñals, J.G.; Mata, C.; Díaz, D.; Guiral, S.; Portilla, V.; Corrales, A.; González-Vela, M.C.; González-Gay, M.A.; Blanco, R.; et al. Evaluation of serum omentin-1 and apelin concentrations in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2021, 38, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.-Y.; Zou, J.-J.; Wang, W.-Z.; Feng, X.-Y.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, G.; Liu, Z.-M. Tumor necrosis factor-α increases angiopoietin-like protein 2 gene expression by activating Foxo1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 339, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, S.; Hirose, N.; Yanoshita, M.; Takano, M.; Kubo, N.; Yamauchi, Y.; Onishi, A.; Ito, S.; Sakata, S.; Kita, D.; et al. ANGPTL2 Induces Synovial Inflammation via LILRB2. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, M.Z.; Sabry, J.H.; Akl, E.; Emam, N.A.H. Angiopoietin-Like Protein 2 in Psoriasis: A New Linkage with Metabolic Syndrome. 260 Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variable | HS Patients (N = 94) | Controls (N = 60) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs | 42.1 ± 11.4 | 45.6 ± 12.9 | 0.07 |
| Sex (female), % | 50.0 | 50.0 | 1.00 |
| Current smokers, % | 70.2 | 18.3 | <0.0001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.2 ± 5.3 | 26.5 ± 4.5 | 0.001 |
| Waist perimeter, cm | 99.7 ± 14.4 | 91.2 ± 13.8 | 0.001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 130.2 ± 16.3 | 124.1 ± 15.9 | 0.025 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 80.4 ± 14.1 | 77.0 ± 8.4 | 0.09 |
| Metabolic syndrome, % | 37.2 | 11.7 | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension, % | 16.0 | 15.0 | 0.87 |
| Dyslipidemia, % | 11.8 | 16.7 | 0.39 |
| hs-CRP, mg/dL | 0.40 (0.22–0.87) | 0.10 (0.10–0.20) | <0.0001 |
| ESR, mm/h | 8.0 (3.0–16.5) | 13.5 (6.3–24.8) | 0.006 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 0.92 |
| LDL-c, mg/dL | 117.0 ± 31.4 | 122.2 ± 29.4 | 0.31 |
| HDL-c, mg/dL | 46.0 (39.0–55.3) | 52.5 (46.3–70.5) | 0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 101.9 ± 51.8 | 97.6 ± 67.0 | 0.65 |
| Fasting plasma glucose, mg/dL | 94.8 ± 13.6 | 89.1 ± 8.1 | 0.001 |
| Fasting plasma insulin, µIU/mL | 9.8 (5.3–16.8) | 7.2 (4.8–10.7) | 0.01 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.20 (1.10–3.75) | 1.47 (0.88–2.27) | 0.003 |
| IR, % | 43.9 | 20.0 | 0.003 |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 310.0 (268.0–369.0) | 266.5 (236.8–298.0) | <0.001 |
| ANGPTL2, ng/mL | 45.10 (30.24–57.97) | 0.37 (0.09–0.92) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández, J.L.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; Renuncio-García, M.; González-López, E.; Blanco, R.; González-López, M.A. Angiopoietin-like 2 Protein and Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A New Biomarker for Disease Severity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041204
Hernández JL, Ocejo-Vinyals JG, Renuncio-García M, González-López E, Blanco R, González-López MA. Angiopoietin-like 2 Protein and Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A New Biomarker for Disease Severity. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(4):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041204
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández, José L., J. Gonzalo Ocejo-Vinyals, Mónica Renuncio-García, Elena González-López, Ricardo Blanco, and Marcos A. González-López. 2023. "Angiopoietin-like 2 Protein and Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A New Biomarker for Disease Severity" Biomedicines 11, no. 4: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041204
APA StyleHernández, J. L., Ocejo-Vinyals, J. G., Renuncio-García, M., González-López, E., Blanco, R., & González-López, M. A. (2023). Angiopoietin-like 2 Protein and Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A New Biomarker for Disease Severity. Biomedicines, 11(4), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041204