Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Collection and Risk of Bias within Individual Studies
2.3. Statistical Analysis
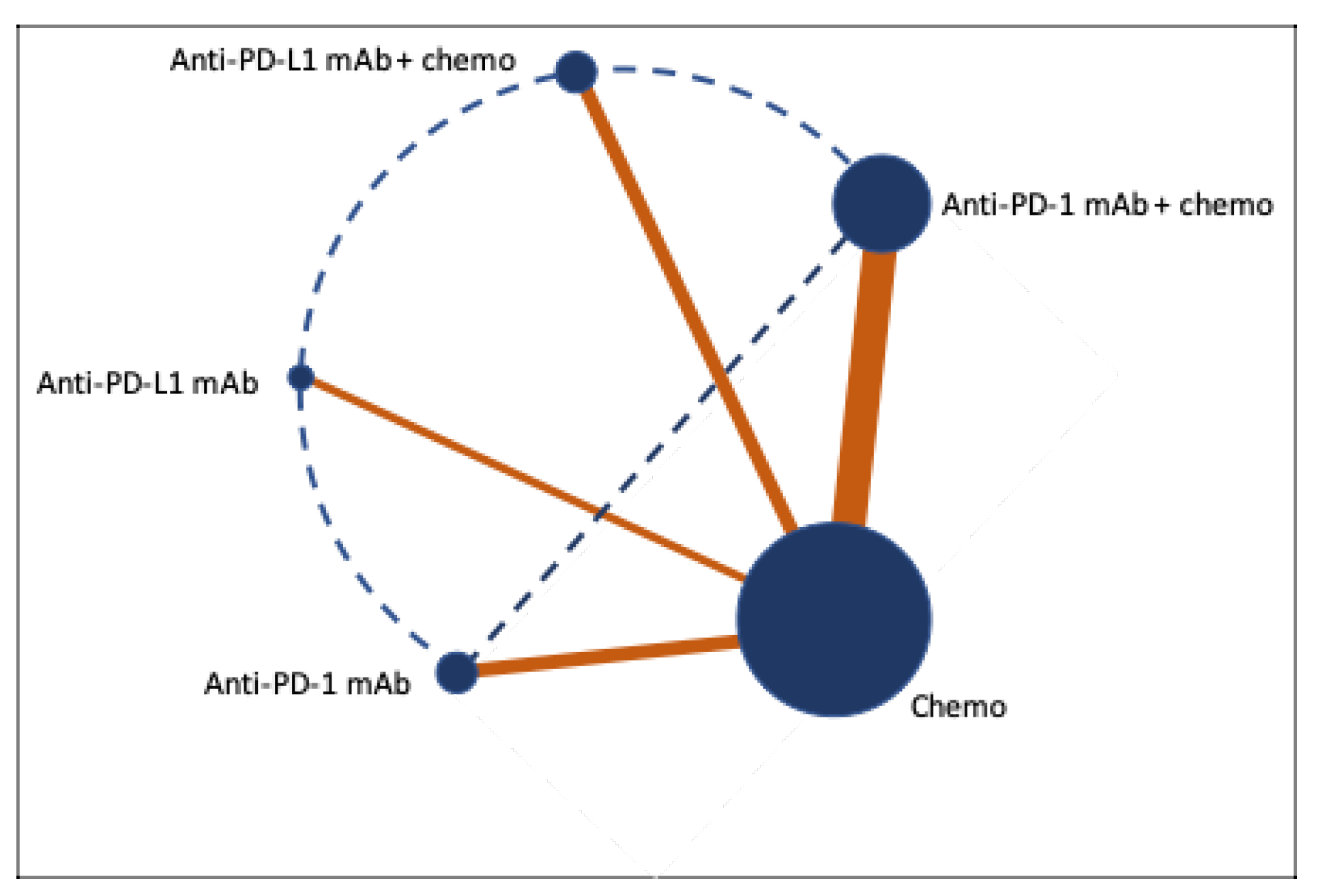
3. Results
3.1. This Systematic Review and Study Characteristics
3.2. Pairwise Meta-Analyses for Survival and Tumor Response
3.2.1. Overall Survival
3.2.2. Progression-Free Survival
3.2.3. Objective Tumor Radiological Response Rate and Grade 3 and Higher Toxcities
3.3. Pairwise Meta-Analyses for Overall Survival According to Histology Type and PD-L1 TPS
3.4. Heterogeneity and Transitivity Assessments
3.5. Network Meta-Analyses for Survival and Tumor Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications
4.2. Limitations and Future Directions
- Is chemotherapy still necessary in the PD-L1 TPS > 90% population? According to 3-year update from correlative analysis presented at the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in 2022, the ORR for pembrolizumab in PD-L1 TPS > 90% is 47.9% [66]. Interestingly, KEYNOTE 189 showed chemoimmunotherapy could achieve an ORR of 61.4% in the PD-L1 TPS > 50% population [8]. These results indicate that chemotherapy may still be beneficial regardless of PD-L1 status;
- Are anti-PD-1 mAbs better than anti-PD-L1 mAbs in mNSCLC with sensitizing driver mutations or in subsequent line therapies?
- Are anti-PD-1 mAbs superior to anti-PD-L1 in combination with bevacizumab, TKIs, or other ICIs?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A







References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, J.A.; Daniel, B.; Satpathy, A.T. Epigenetic regulation of T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Speranza, G.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; Dómine, M.; Hui, R.; Hochmair, M.J.; Clingan, P.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Updated Analysis from KEYNOTE-189: Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Pemetrexed and Platinum for Previously Untreated Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; et al. IMpower150 Final Overall Survival Analyses for Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.G.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Cobo-Dols, M.; Bennouna, J.; Cheng, Y.; Mizutani, H.; Lingua, A.; Reyes, F.; Reinmuth, N.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. First-line (1L) nivolumab (NIVO) + ipilimumab (IPI) + 2 cycles of chemotherapy (chemo) versus chemo alone (4 cycles) in patients (pts) with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): 3-year update from CheckMate 9LA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S17), LBA9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Song, Y.; Tian, W. How to select IgG subclasses in developing anti-tumor therapeutic antibodies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Chung, J.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.S.; Suh, K.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, J.-O.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-W.; et al. Effect of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy on PD-L1 Expression on Tumor Cells in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2019, 51, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Song, P.; Xue, X.; Guo, C.; Han, L.; Fang, Q.; Ying, J.; Gao, S.; Li, W. Variation of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression after Platinum-based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Lung Cancer. J. Immunother. 2019, 42, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá-López, F.; Tobías, A.; Cameron, C.; Moher, D.; Hutton, B. Network meta-analysis for comparing treatment effects of multiple interventions: An introduction. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addeo, A.; Banna, G.L.; Metro, G.; Di Maio, M. Chemotherapy in Combination with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the First-Line Treatment of Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Literature-Based Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bai, H.; Wang, C.; Seery, S.; Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; Li, S.; Xue, P.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Immunotherapy Combinations for Advanced NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 1099–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, A.B.C.; Camandaroba, M.P.G.; de Lima, V.C.C. Anti-PD1 versus anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.; Çiçin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. LBA52 EMPOWER-Lung 1: Phase III first-line (1L) cemiplimab monotherapy vs platinum-doublet chemotherapy (chemo) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) ≥50%. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1182–S1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogishvili, M.; Mobashery, N.; Makharadze, T.; Navarro, M.; Snodgrass, P.; Chen, H.; Lowy, I.; Rietschel, P.; Lee, S. P2.01-26 EMPOWER-Lung 3: Phase 3 Study of Combinations of Cemiplimab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment of Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ai, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Tislelizumab Plus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Locally Advanced or Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC (RATIONALE 304): A Randomized Phase 3 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Lu, S.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, K.; et al. Phase III study of tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone as first-line (1L) treatment for advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer (sq NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S15), 9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Cho, B.C.; Reinmuth, N.; Lee, K.H.; Luft, A.; Ahn, M.-J.; Van Den Heuvel, M.M.; Cobo, M.; Vicente, D.; Smolin, A.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab vs Standard Chemotherapy in First-line Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The MYSTIC Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.L.; Cho, B.C.; Luft, A.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Geater, S.L.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Ursol, G.; Hussein, M.; Lim, F.L.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase III POSEIDON Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 41, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Jian, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sun, M.; Han, L.; et al. Sintilimab plus bevacizumab biosimilar IBI305 and chemotherapy for patients with EGFR-mutated non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor therapy (ORIENT-31): First interim results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J.; Yu, Q.; Han, B.; Cang, S.; Chen, G.; Mei, X.; Yang, Z.; Stefaniak, V.; et al. Final overall survival data of sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum as First-Line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC in the Phase 3 ORIENT-11 study. Lung Cancer 2022, 171, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Huang, D.; Cang, S.; Yang, Z.; et al. Sintilimab Plus Platinum and Gemcitabine as First-Line Treatment for Advanced or Metastatic Squamous NSCLC: Results From a Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial (ORIENT-12). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Li, B.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Wu, X.; Fan, Y.; et al. Final progression-free survival, interim overall survival, and biomarker analyses of CHOICE-01: A phase 3 study of toripalimab versus placebo in combination with first-line chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC without EGFR/ALK mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cao, L.; Ma, Z.; Wu, R.; Yu, Y.; Yao, W.; Chang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Sugemalimab versus placebo, in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, as first-line treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (GEMSTONE-302): Interim and final analyses of a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Borghaei, H.; Patnaik, A.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Powell, S.F.; Gentzler, R.D.; Martins, R.G.; Stevenson, J.P.; Altan, M.; et al. Long-Term Overall Survival From KEYNOTE-021 Cohort G: Pemetrexed and Carboplatin with or without Pembrolizumab as First-Line Therapy for Advanced Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Updated Analysis of KEYNOTE-024: Pembrolizumab Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score of 50% or Greater. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Robinson, A.; Parra, H.S.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Cicin, I.; Medgyasszay, B.; Rodríguez-Cid, J.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Squamous NSCLC: Protocol-Specified Final Analysis of KEYNOTE-407. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Jiang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, G.; Pan, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Camrelizumab Plus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Squamous NSCLC (CameL-Sq): A Phase 3 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lin, L.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Shu, Y.; Shi, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Reck, M.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Bhagavatheeswaran, P.; Nathan, F.E.; Brahmer, J.R. Nivolumab (Nivo) + platinum-doublet chemotherapy (Chemo) vs chemo as first-line (1L) treatment (Tx) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with <1% tumor PD-L1 expression: Results from CheckMate 227. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. S15). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.M.; Cicin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: A multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogishvili, M.; Melkadze, T.; Makharadze, T.; Giorgadze, D.; Dvorkin, M.; Penkov, K.; Laktionov, K.; Nemsadze, G.; Nechaeva, M.; Rozhkova, I.; et al. Cemiplimab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized, controlled, double-blind phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G., Jr.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.; McCleod, M.; Hussein, M.; Morabito, A.; Rittmeyer, A.; Conter, H.J.; Kopp, H.G.; Daniel, D.; McCune, S.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotte, R.; Cappuzzo, F.; Vynnychenko, I.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Hussein, M.; Soo, R.; Conter, H.J.; Kozuki, T.; Huang, K.-C.; et al. Atezolizumab in Combination with Carboplatin and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Squamous NSCLC (IMpower131): Results from a Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M.; Barlesi, F.; West, H.; Ball, S.; Bordoni, R.; Cobo, M.; Longeras, P.D.; Goldschmidt, J.; Novello, S.; Orlandi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab Plus Chemotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Nonsquamous NSCLC: Results from the Randomized Phase 3 IMpower132 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.P.; Reck, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Creelan, B.; Horn, L.; Steins, M.; Felip, E.; van den Heuvel, M.M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Badin, F.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab in Stage IV or Recurrent Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Barlesi, F.; Yang, J.-H.; Westeel, V.; Felip, E.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Dols, M.C.; Sullivan, R.; Kowalski, D.; Andric, Z.; et al. OA15.03 Avelumab vs Chemotherapy for First-line Treatment of Advanced PD-L1+ NSCLC: Primary Analysis from JAVELIN Lung 100. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Inui, N.; Hida, T.; Lee, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, H.; Yang, C.-T.; et al. Nivolumab with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Lopes, G.D.L.; Yu, H.; Aryal, M.R.; Ji, W.; Frumento, K.S.; Wallis, C.J.D.; Klaassen, Z.; Park, H.S.; Goldberg, S.B. Comparative efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy versus immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Cancer 2021, 127, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieswasser, T.; Van Loenhout, J.; Boullosa, L.F.; Eynde, A.V.D.; De Waele, J.; Van Audenaerde, J.; Lardon, F.; Smits, E.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, J. Clinically Relevant Chemotherapeutics Have the Ability to Induce Immunogenic Cell Death in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Adjemian, S.; Mattarollo, S.R.; Yamazaki, T.; Aymeric, L.; Yang, H.; Portela Catani, J.P.; Hannani, D.; Duret, H.; Steegh, K.; et al. Anticancer chemotherapy-induced intratumoral recruitment and differentiation of antigen-presenting cells. Immunity 2013, 38, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, D.; Larmonier, N. Chemotherapeutic targeting of cancer-induced immunosuppressive cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2663–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojkó, L.; Reiniger, L.; Téglási, V.; Fábián, K.; Pipek, O.; Vágvölgyi, A.; Agócs, L.; Fillinger, J.; Kajdácsi, Z.; Tímár, J.; et al. Chemotherapy treatment is associated with altered PD-L1 expression in lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zens, P.; Bello, C.; Scherz, A.; von Gunten, M.; Ochsenbein, A.; Schmid, R.A.; Berezowska, S. The effect of neoadjuvant therapy on PD-L1 expression and CD8+lymphocyte density in non-small cell lung cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamochi, K.; Hara, K.; Hayashi, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Takahashi, F.; Suehara, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Suzuki, K. Clinical relevance of PD-L2 expression in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2022, 168, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Mori, K.; Kurabe, N.; Kahyo, T.; Mori, H.; Kawase, A.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Inui, N.; et al. Clinical significance of PD-L1 and PD-L2 copy number gains in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32113–32128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, R.; Huang, C.L.; Fujita, M.; Cho, H.; Date, H. Differential expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 is associated with the tumor microenvironment of TILs and M2 TAMs and tumor differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okadome, K.; Baba, Y.; Yasuda-Yoshihara, N.; Nomoto, D.; Yagi, T.; Toihata, T.; Ogawa, K.; Sawayama, H.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression status in relation to chemotherapy in primary and metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghatchian, M.; Fizazi, K.; Borel, C.; Ducreux, M.; Ruffié, P.; Le Chevalier, T.; Théodore, C. Carcinoma of an unknown primary site: A chemotherapy strategy based on histological differentiation—Results of a prospective study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2001, 12, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, N.; Niitani, H.; Tominaga, K.; Eguchi, K.; Koketsu, H.; Fujino, T.; Ishikawa, S. Comparison of survival in nonresected well differentiated and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1980, 97, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.N.; de Langen, A.J.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.; Menon, H.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Tang, C.; Altan, M.; Hess, K.; de Groot, P.; Nguyen, Q.-N.; Varghese, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without radiation therapy for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized phase I/II trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Hobbs, B.P.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; Chang, J.Y.; de Groot, P.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Dong, S.; Liao, R.-Q.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, J.-T.; Lin, J.-T.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Nie, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. LBA2 Phase II study of PD-L1 expression guidance on neoadjuvant (NA) nivolumab (Nivo) monotherapy with or without platinum-doublet chemotherapy in resectable NSCLC. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2022, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, S.K.; Lee, K.H.; Frost, N.; Breder, V.; Kowalski, D.M.; Pollock, T.; Levchenko, E.; Reguart, N.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Houghton, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab Plus Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy in Patients with Unresectable, Locally Advanced, Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase 2 KEYNOTE-799 Nonrandomized Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Elkrief, A.; Alessi, J.V.M.; Wang, X.; Barrichello, A.P.D.C.; Pecci, F.; Lamberti, G.; Lindsay, J.; Sharma, B.; Felt, K.; et al. Three-year outcomes and correlative analyses in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and a very high PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥ 90% treated with first-line pembrolizumab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study No. | Study Name | Number of Patients | Study Arms | Lung Cancer Histology Type | PD-L1 Status | Antibody Used to Determine PD-L1 Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KEYNOTE 021 cohort G | ChemoIO: 60 Chemo: 63 | Arm A: Pembrolizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 2 | KEYNOTE 189 | ChemoIO: 410 Chemo: 206 | Arm A: Pembrolizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 3 | KEYNOTE 407 | ChemoIO: 278 Chemo: 281 | Arm A: Pembrolizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 4 | CheckMate 227 | ChemoIO: 177 IO alone: 396 Chemo: 397 | Arm A: Nivolumab + ipilimumab + Platinum doublet Arm B (PD-L1 < 1%): nivolumab + Platinum doublet Arm C (PD-L1 > 1%): nivolumab alone Arm D: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 28-8 pharmDX |
| 5 | CHOICE 01 | ChemoIO: 309 Chemo: 156 | Arm A: Toripalimab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | JS311 MEDx |
| 6 | CameL | ChemoIO: 205 Chemo: 207 | Arm A: Camrelizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 7 | CameL-Sq | ChemoIO: 193 Chemo: 196 | Arm A: Camrelizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | E1L3N AmoyDx |
| 8 | EMPOWER-Lung 3 | ChemoIO: 312 Chemo: 154 | Arm A: Cemiplimab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | SP263 |
| 9 | ORIENT 11 | ChemoIO: 266 Chemo: 131 | Arm A: Sintilimab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 10 | ORIENT 12 | ChemoIO: 179 Chemo: 178 | Arm A: Sintilimab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 11 | RATIONALE 304 | ChemoIO: 223 Chemo: 111 | Arm A: Tislelizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | SP263 |
| 12 | RATIONALE 307 | ChemoIO Arm A: 120 ChemoIO Arm B: 119 Chemo: 121 | Arm A: Tislelizumab + Platinum + Paclitaxel Arm B: Tislelizumab + Platinum + Nab-paclitaxel Arm C: Platinum + Paclitaxel | Squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | SP263 |
| 13 | IMpower 130 | ChemoIO: 451 Chemo: 228 | Arm A: Atezolizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% (TC) PD-L1 < 1%, 1–9%, >10% (IC) | SP142 |
| 14 | IMpower 131 | ChemoIO Arm A: 338 ChemoIO Arm B: 343 Chemo: 340 | Arm A: Atezolizumab + Platinum + Paclitaxel Arm B: Atezolizumab + Platinum + Nab-paclitaxel Arm C: Platinum + Nab-paclitxel | Squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% (TC) PD-L1 < 1%, 1–9%, >10% (IC) | SP142 |
| 15 | IMpower 132 | ChemoIO: 292 Chemo: 286 | Arm A: Atezolizumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-squamous | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% (TC) PD-L1 < 1%, 1–9%, >10% (IC) | SP142 |
| 16 | GEMSTONE 302 | ChemoIO: 320 Chemo: 159 | Arm A: Sugemalimab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | SP263 |
| 17 | POSEIDON | ChemoIO: 338 Chemo: 337 | Arm A: Durvalumab + Platinum doublet Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 < 1%, 1–49%, >50% | SP263 |
| 18 | Checkmate 026 | ChemoIO: 271 Chemo: 270 | Arm A: Nivolumab Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 > 5%, >50% | 28-8 pharmDX |
| 19 | Keynote 024 | ChemoIO: 154 Chemo: 151 | Arm A: Pembrolizumab Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 > 50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 20 | Keynote 042 | ChemoIO: 637 Chemo: 636 | Arm A: Pembrolizumab Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 1–49%, >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 21 | EMPOWER-Lung 1 | ChemoIO: 356 Chemo: 354 | Arm A: Cemiplimab Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 >50% | 22C3 pharmDX |
| 22 | IMpower 110 | ChemoIO: 227 Chemo: 227 | Arm A: Atezolizumab Arm B: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 > 1%, >5%, >50% | SP142 |
| 23 | JAVELIN Lung 100 | ChemoIO Arm A: 366 ChemoIO Arm B: 322 Chemo: 526 | Arm A: Avelumab Q2W Arm B: Avelumab QW Arm C: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 > 1%, >50%, >80% | 73-10 pharmDx |
| 24 | MYSTIC | ChemoIO Arm A: 374 ChemoIO Arm B: 372 Chemo: 372 | Arm A: Durvalumab Arm B: Durvalumab + Tremelimumab Arm C: Platinum doublet | Non-small cell | PD-L1 > 25% | SP263 |
| Treatment | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-PD-1 mAbs + chemotherapy > chemotherapy | All patients | 0.67 (0.62–0.73) |
| PD-L1 TPS < 1% | 0.76 (0.66–0.87) | |
| PD-L1 TPS 1–49% | 0.61 (0.52–0.71) | |
| PD-L1 TPS > 50% | 0.66 (0.54–0.81) | |
| Squamous | 0.69 (0.58–0.83) | |
| Non-squamous | 0.67 (0.58–0.76) | |
| Anti-PD-L1 + chemotherapy > chemotherapy | All patients | 0.83 (0.76–0.91) |
| PD-L1 TPS < 1% | 0.85 (0.74–0.99) | |
| PD-L1 TPS > 50% | 0.64 (0.51–0.81) | |
| Non-Squamous | 0.83 (0.73–0.93) | |
| Anti-PD-L1 + chemotherapy = chemotherapy | PD-L1 TPS 1–49% | 0.97 (0.82–1.15) |
| Squamous | 0.87 (0.74–1.01) | |
| Anti-PD-1 > chemotherapy | PD-L1 TPS > 1% | 0.83 (0.70–0.97) |
| PD-L1 TPS > 50% | 0.71 (0.61–0.84) | |
| Anti-PD-L1 > chemotherapy | PD-L1 TPS > 1% | 0.88 (0.79–0.99) |
| PD-L1 TPS > 50% | 0.78 (0.68–0.90) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.Q.; Yuile, A.; Itchins, M.; Kong, B.Y.; Li, B.T.; Pavlakis, N.; Chan, D.L.; Clarke, S.J. Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071827
Wei JQ, Yuile A, Itchins M, Kong BY, Li BT, Pavlakis N, Chan DL, Clarke SJ. Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071827
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Joe Q., Alexander Yuile, Malinda Itchins, Benjamin Y. Kong, Bob T. Li, Nick Pavlakis, David L. Chan, and Stephen J. Clarke. 2023. "Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071827
APA StyleWei, J. Q., Yuile, A., Itchins, M., Kong, B. Y., Li, B. T., Pavlakis, N., Chan, D. L., & Clarke, S. J. (2023). Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071827







