Abstract
The clinical response to classical immunosuppressant drugs (cIMDs) is highly variable among individuals. We performed a systematic review of published evidence supporting the hypothesis that gut microorganisms may contribute to this variability by affecting cIMD pharmacokinetics, efficacy or tolerability. The evidence that these drugs affect the composition of intestinal microbiota was also reviewed. The PubMed and Scopus databases were searched using specific keywords without limits of species (human or animal) or time from publication. One thousand and fifty five published papers were retrieved in the initial database search. After screening, 50 papers were selected to be reviewed. Potential effects on cIMD pharmacokinetics, efficacy or tolerability were observed in 17/20 papers evaluating this issue, in particular with tacrolimus, cyclosporine, mycophenolic acid and corticosteroids, whereas evidence was missing for everolimus and sirolimus. Only one of the papers investigating the effect of cIMDs on the gut microbiota reported negative results while all the others showed significant changes in the relative abundance of specific intestinal bacteria. However, no unique pattern of microbiota modification was observed across the different studies. In conclusion, the available evidence supports the hypothesis that intestinal microbiota could contribute to the variability in the response to some cIMDs, whereas data are still missing for others.
1. Introduction
Classical immunosuppressant drugs (cIMD), which include glucocorticoids (GCs), cyclosporine (CyA), tacrolimus (TAC), the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors sirolimus (SIR) and everolimus (EVERO), and the Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitor mycophenolic acid (MPA) and its prodrug mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), still have a central role in transplant medicine since they represent the cornerstone of the pharmacological treatment to prevent and treat organ rejection [1]. In addition, these drugs are also used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases in selected circumstances in which biological immunosuppressant drugs are not indicated. The use of cIMDs in clinical practice is complicated by their narrow therapeutic window, which makes it difficult to achieve good immunosuppression without toxicity [2]. A further element complicating the use of many cIMDs is their unpredictable pharmacokinetics with large variations in the plasma concentrations that are attained when similar doses are given to different patients [3,4,5]. This problem has traditionally been addressed by performing therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), assessing the concentration of cIMDs in the blood and then adjusting their doses according to the results obtained [6]. Whilst this approach improves safety and efficacy of the treatment, it is far from optimal due to the empirical “fail and correct” approach, which implies that drug plasma concentrations could be dangerously higher (or lower) than optimal for a while before being corrected. As a matter of fact, organ rejection and cIMD toxicity also occur in patients undergoing accurate TDM [7]. It would be, therefore, highly desirable to identify difficult patients early to design their therapeutic plan on a personalized basis. Even though it has not yet been routinely implemented yet in transplant medicine, pharmacogenotyping might help achieve this goal by identifying patients with polymorphisms in genes encoding key enzymes involved in immunosuppressant drug metabolism [8]. A new factor, only recently identified, that could be responsible for the interindividual variability in drug response is the patient’s microbiota, i.e., the whole population of microorganisms living in a commensal status in humans (or animals) [9]. These microorganisms are metabolically active and able to affect host health in different ways, such as processing of nutrient molecules, modulating immune response in the gut and liver, and the generating small molecule mediators acting systemically, after being absorbed into the general circulation [10]. Importantly, human microbiota may also affect patient response to pharmacological therapy [11]. The term Pharmacomicrobiomics has been coined, in consonance with the already existing term Pharmacogenomics, to design the whole array of interactions by which microbiota may modify host response to pharmacologically active substances [12,13]. Some evidence that bacteria of the intestinal microflora could metabolize specific drugs and, therefore, affect their efficacy was already obtained long time ago, and probably the first documented case of such an interaction is the conversion of the inactive dye prontosil red into the potent antibacterial compound sulphanilamide, reported in 1937 [14]. Thereafter, several other drugs such as digoxin have been demonstrated to be victims of bacterial metabolism in the gut. In addition, pharmacological strategies have been developed to exploit the metabolizing capacities of intestinal bacteria in the design of new drugs. More specifically, the ability of bacteria selectively located in the colon to perform azoreduction reactions has been used to design drugs intended to be specifically active in the colon such as sulphasalazine and its congeners, which still have an important pharmacological role in the treatment of ulcerative colitis [12]. Whilst what has just been mentioned represents well acquainted issues in the pharmacology of selected medicines, much more recently the interest in microbial metabolism of drugs has reemerged strongly since it has been realized that it may contribute to the interindividual variability in the response to a wider group of drugs than originally suspected [15] either by exerting a pre-systemic metabolism or by accumulating some of these drugs (e.g., duloxetine, montelukast, rosiglitazone and roflumilast) in their cytoplasm and, therefore, preventing their absorption and reducing their bioavailability and, possibly, clinical efficacy [16]. Therefore, it has been suggested that microbiota composition should be included among the factors to be evaluated in precision medicine [17] also considering that the composition of human microbiota varies interindividually in healthy subjects, and it may be severely modified in specific diseases [18]. These considerations suggest that part of the interindividual variability in the clinical response to cIMDS could be dependent on patient microbiota. Therefore, in the present paper we performed a systematic review of the published studies on the impact of intestinal microbiota on orally given cIMDs with the aim of evaluating the strength of evidence in support of this hypothesis.
2. Materials and Methods
The protocol of this systematic review has been registered in the International Platform of Registered Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (INPLASY, Middletown, DE, USA) with registration number is INPLASY202380129 and is freely available at the address: https://inplasy.com/?s=INPLASY202380129 (accessed on 31 August 2023).
2.1. Purpose
The present systematic review addressed the following two research questions:
- Does the intestinal microbiota affect cIMD pharmacology (pharmacokinetics, efficacy or tolerability)?
- Do cIMDs modify the composition of intestinal microbiota?
The following Section 2.2, Section 2.3, Section 2.4 and Section 2.5 report the PICO (Population–Intervention–Comparison–Outcome) framework of our systematic review.
2.2. Population
Preclinical studies performed in healthy animals or in animals with experimental organ transplantation or with autoimmune diseases receiving cIMDs, and clinical studies conducted in humans treated with these drugs because recipients of organ transplantation or because affected with autoimmune diseases were considered for the review. Studies with one or more of the following features were evaluated for being included in the revision:
- Metagenomic characterization of fecal or ileal microbiota,
- Pharmacokinetics analysis of the administered immunosuppressant drugs,
- Analysis of cIMD efficacy and/or toxicity, and
- Analysis of the effect of wide-spectrum antibiotics on points from 1 to 3.
We also considered studies using reconstituted systems in vitro that examined the effect of fecal extracts/bacterial cultures/bacterial enzymes on cIMDs.
2.3. Intervention
The present systematic review only included studies in which the following cIMDs were given orally in various combinations: CyA, EVERO, GCs, MMF, MPA, SIR or TAC.
2.4. Comparison
We considered for inclusion in the review both studies in which a control group (vehicle treated animals in preclinical experimentations or age-matched healthy controls in clinical studies) was compared with a group receiving cIMDs, and pre-, post-studies in which the same animals/individuals were compared before and after the treatment with these drugs.
2.5. Outcome
The outcomes of the studies considered in the present review were changes in the efficacy/tolerability of cIMDs and/or in their pharmacokinetic parameters.
2.6. Information Sources and Search Strategy
A systematic literature search was performed through 3 December 2022 using the PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and Scopus (https://www.scopus.com/) databases and the following keywords in various combinations: cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus, everolimus, mycophenolic acid, mycophenolate mofetil, prednisone, methylprednisone, pharmacomicrobiomics, gastrointestinal microbiome, metabolism, microbes, and bioaccumulation. No specific limit was posed on the year of publication. Only original English language studies were considered for review; narrative reviews, systematic reviews, metanalyses, guidelines, consensus papers, case reports, editorials and commentaries were all excluded.
2.7. Data Extraction
The database search was performed independently by A.M. and L.D. A first screening of the papers retrieved was performed by A.M. and M.C. after reading and examining their titles and abstracts. Selected papers underwent further selection by A.M. and M.C. upon reading and examining the full text of the articles.
2.8. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
The risk of bias of animal studies was evaluated using the SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies, which is and adaption to animal studies of the RoB2 tool [19].
The risk of bias of observational studies in humans was evaluated using the Grade Criteria which consider five different categories of bias: (1) Inappropriate eligibility criteria; (2) Inappropriate methods for exposure and outcome variables; (3) Not controlled for confounding; (4) Incomplete or inadequate follow-up; (5) Other limitations [20]. For all the observational human studies the risk related to the aforementioned risk categories was conjunctly rated by A.M. and M.C. as either “no risk”, “unclear risk” or “high risk” and the results obtained were reported in a tabular format both as average percentage for the whole group of papers and as individual data for the single studies.
The risk of bias of randomized trials was assessed using the five categories of the Grade Criteria (lack of allocation concealment, lack of blinding, incomplete accounting of patients and outcome events, selective outcome reporting, and other limitations). As for observational studies, the risk for each of these categories was conjunctly rated by A.M. and M.C. as either “no risk”, “unclear risk” or “high risk”.
2.9. Data Synthesis
The main findings of the selected studies were summarized in a narrative form in the text of the article and in two tables, the first (Table 1) concerning the papers on the effect of the intestinal microbiota on cIMDs [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], and the second (Table 2) concerning the papers on effect of cIMDs on intestinal microbiota [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. The following variables were extracted and included in Table 1: 1—lead author and year of publication, 2—the experimental model used, 3—the drugs tested, 4—the presence/absence of changes in the pharmacokinetic properties of the tested drugs, and 5—a detailed description of the effect of intestinal microbiota on cIMD pharmacokinetics. The variables extracted to prepare Table 2 were: 1—lead author and year of publication, 2—the species (human, mice, rats) object of the experimentation, 3—the condition/disease either spontaneous or experimental that was treated with cIMDs, 4—the specific cIMDs that were used with doses, administration modalities and duration of treatment, 5—the presence or absence of intestinal microbiota modifications upon treatment with cIMDs, and 6—a detailed description of the changes occurring in intestinal microbiota including, when available, data on α- and β-diversity and taxonomic information at the level of phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. No metanalysis of the data was considered feasible considering the heterogeneity in the research questions addressed, in the species and in the experimental models used in the experimentations and in the drugs administered.

Table 1.
Studies investigating the effect of intestinal microbiota on cIMD pharmacokinetics, efficacy and tolerability.

Table 2.
Studies investigating the effect of cIMDs on the intestinal microbiota.
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
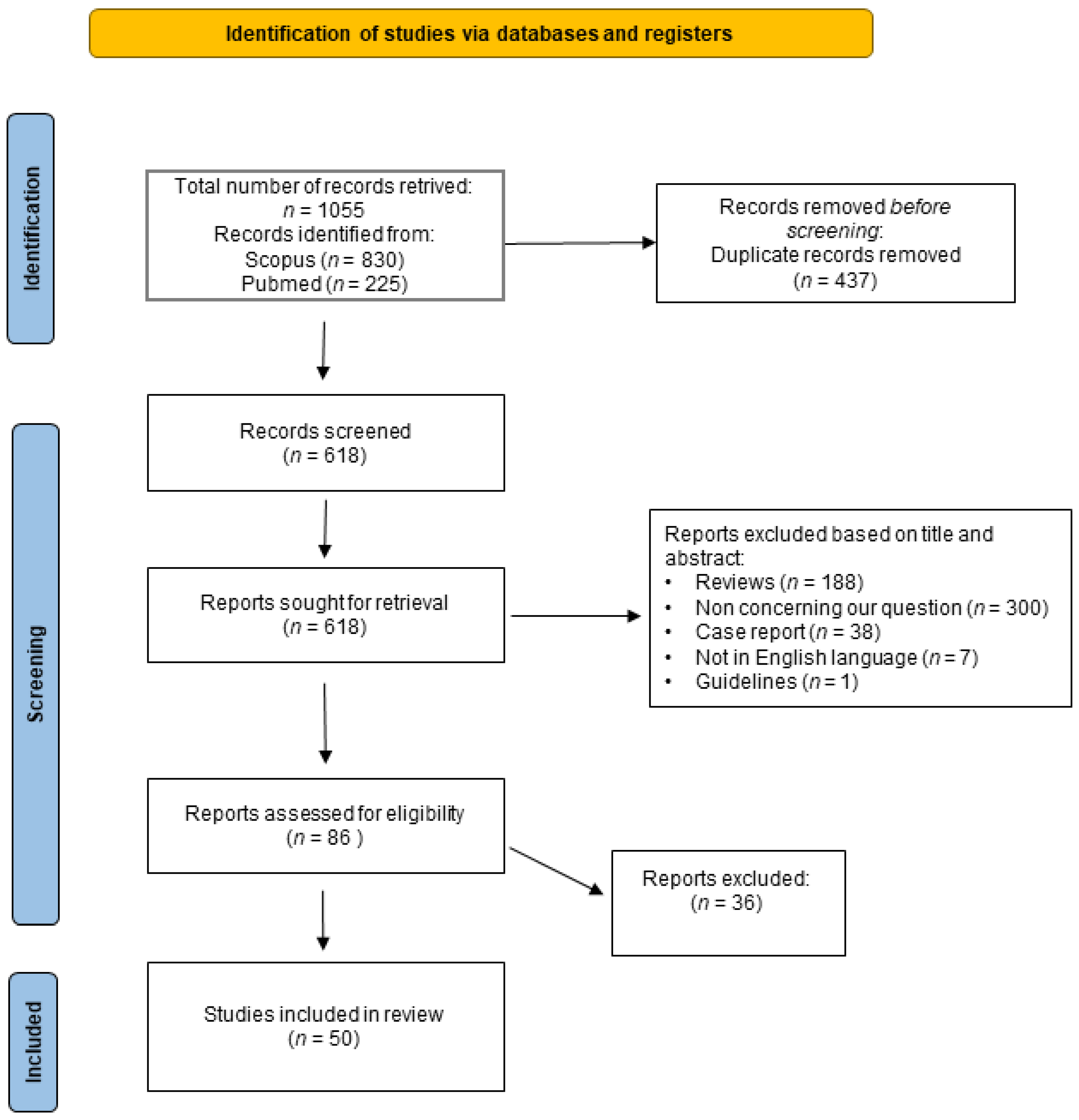
The results of the literature search that we performed are summarized in Figure 1 which shows the PRISMA flowchart of this study. A total of 1055 published papers were retrieved at the initial database search: 225 were obtained by searching PubMed and 830 searching Scopus. Four hundred thirty-seven records were duplicated in the two databases and, therefore, after correcting for duplication, the total number of papers that were considered for title and abstract analysis was 618. After excluding the publications not complying with inclusion criteria, 86 records were considered suitable for full-text analysis. After reading these papers and examining their content the two reviewers identified 50 papers [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] as suitable for inclusion in the systematic review, whereas the remaining 36 [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106] were excluded since they were not compliant with one or more of the inclusion or exclusion criteria.
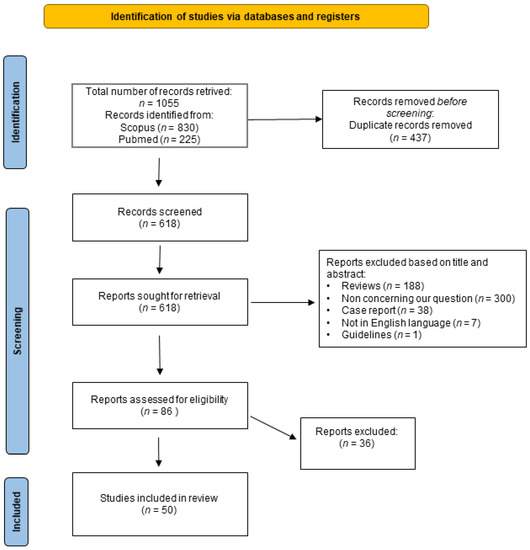
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the systematic review. The figure shows the flowchart of this study prepared according to Page et al., 2021 [107]. For more information, visit: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2023).
Seven of the reviewed studies were entirely performed in vitro [23,25,26,30,31,36,37], twenty-three reported the results of studies performed in vivo only in animal models, eight in rats [39,42,44,50,51,61,62,70] and fifteen in mice [43,45,46,47,48,49,52,53,57,58,63,66,67,68,69], whereas one paper included the results of experiments performed in both mice and humans [34]. Nineteen papers were investigations performed only in humans. Eighteen of them were observational studies [21,22,24,27,28,29,32,33,35,38,40,41,54,55,56,60,64,65] and only one was a randomized clinical trial [59].
3.2. Quality Assessment
None of the reviewed animal studies fully complied with the SYRCLE’s requirement for risk of bias assessment [19]. In particular, no information was reported on the methods of randomization and of allocation concealment (selection bias), random housing and blinding of caregivers/investigators (performance bias), random selection of the animals for assessment and blinding of the assessors (detection bias), and strategies used to handle incomplete data (attrition bias). Therefore, for all these categories, we assigned the score “uncertain risk of bias”. Conversely, no apparent risk of bias was found for group similarity of at baseline (selection bias) and for selective outcome reporting (reporting bias).
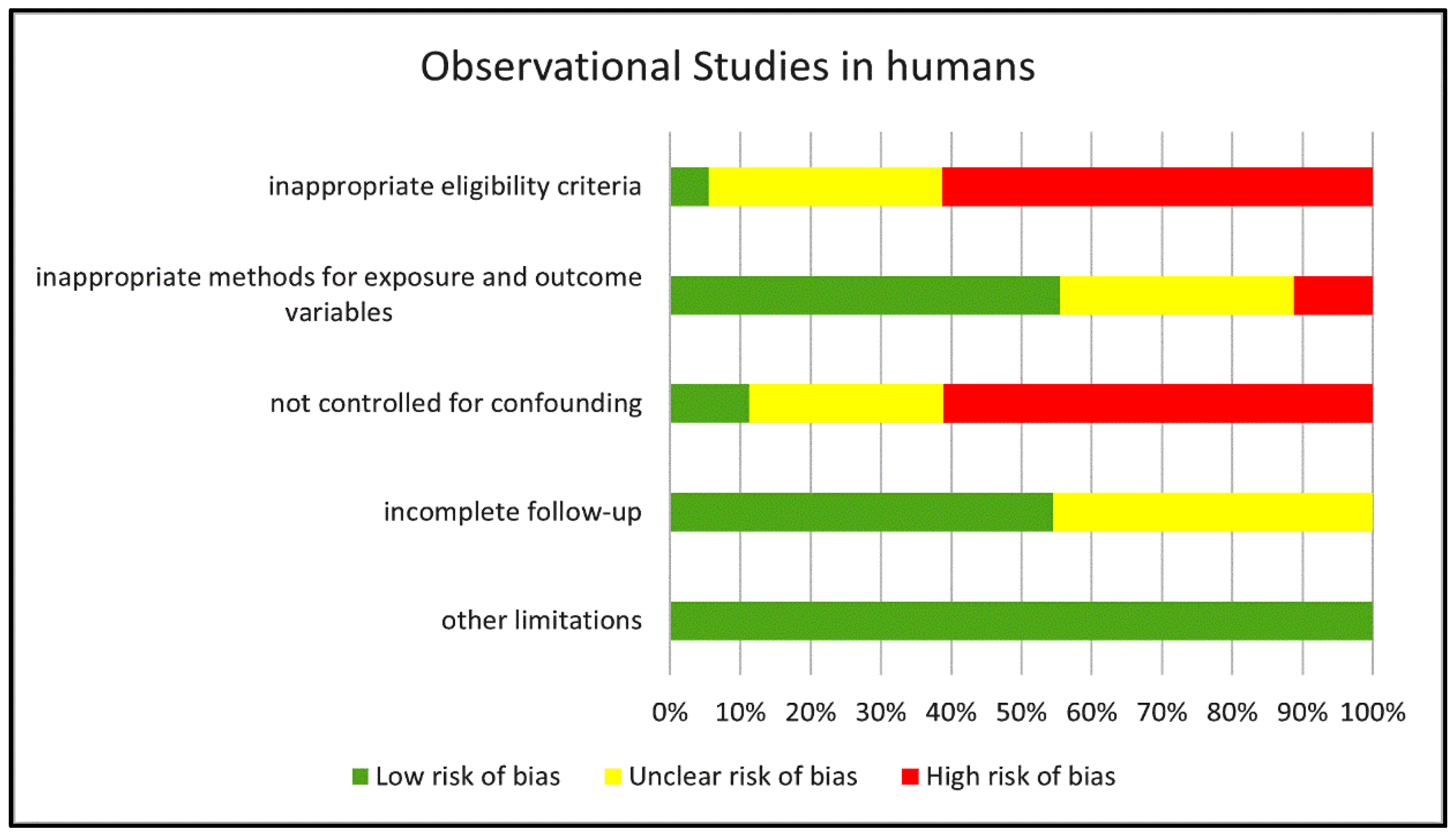
The risk of bias of the eighteen observational studies in humans was assessed according to the Grade Criteria for observational studies (see methods for more details). Figure 2 reports a summary of the results of our quality assessment shown as the percentage of studies rated as “low”, “unclear” and “high” risk of bias for each of the five categories of bias considered in the Grade Criteria.
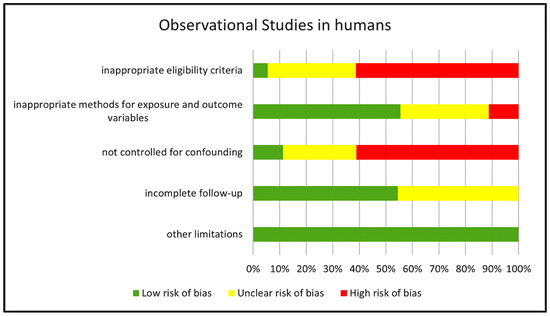
Figure 2.
Risk of bias in the human observational studies examined. The chart reports the risk of bias in the reviewed human observational studies estimated for each of the GRADE categories and expressed as percentage of studies with “low”, “unclear” or “high” risk score.
We identified a high risk of bias in more than 60% of the studies for two of these categories: Inappropriate eligibility criteria and Not controlled for confounding. In addition, we rated the risk of bias for eligibility criteria as “unclear” in approximately 30% of the studies (mostly retrospective investigations) since no clear inclusion and/or exclusion criteria were reported besides identifying the disease under evaluation. Only 11% of the studies included a correction for confounding factors and, therefore, were rated as “no risk of bias”; in approximately 28% of the studies, the risk originated by the lack of correction was unclear since no clear difference in covariates emerged from reported data, whereas in the remaining 61% of the studies, we rated the bias risk as high because of major disparities among groups in variables such as gender or pharmacological treatment with drugs other than cIMDs that were not corrected for. Seven studies had a cross-sectional design and, therefore, did not include any follow-up of the recruited patients. In six of the remaining eleven prospective studies the follow-up was complete with no risk of bias, whereas in five we identified some incompleteness in the follow-up with unclear consequences on the risk of bias. We identified critical points for the category Methods for exposure and outcome, whose implications for bias risk were major in two studies and unclear in six.
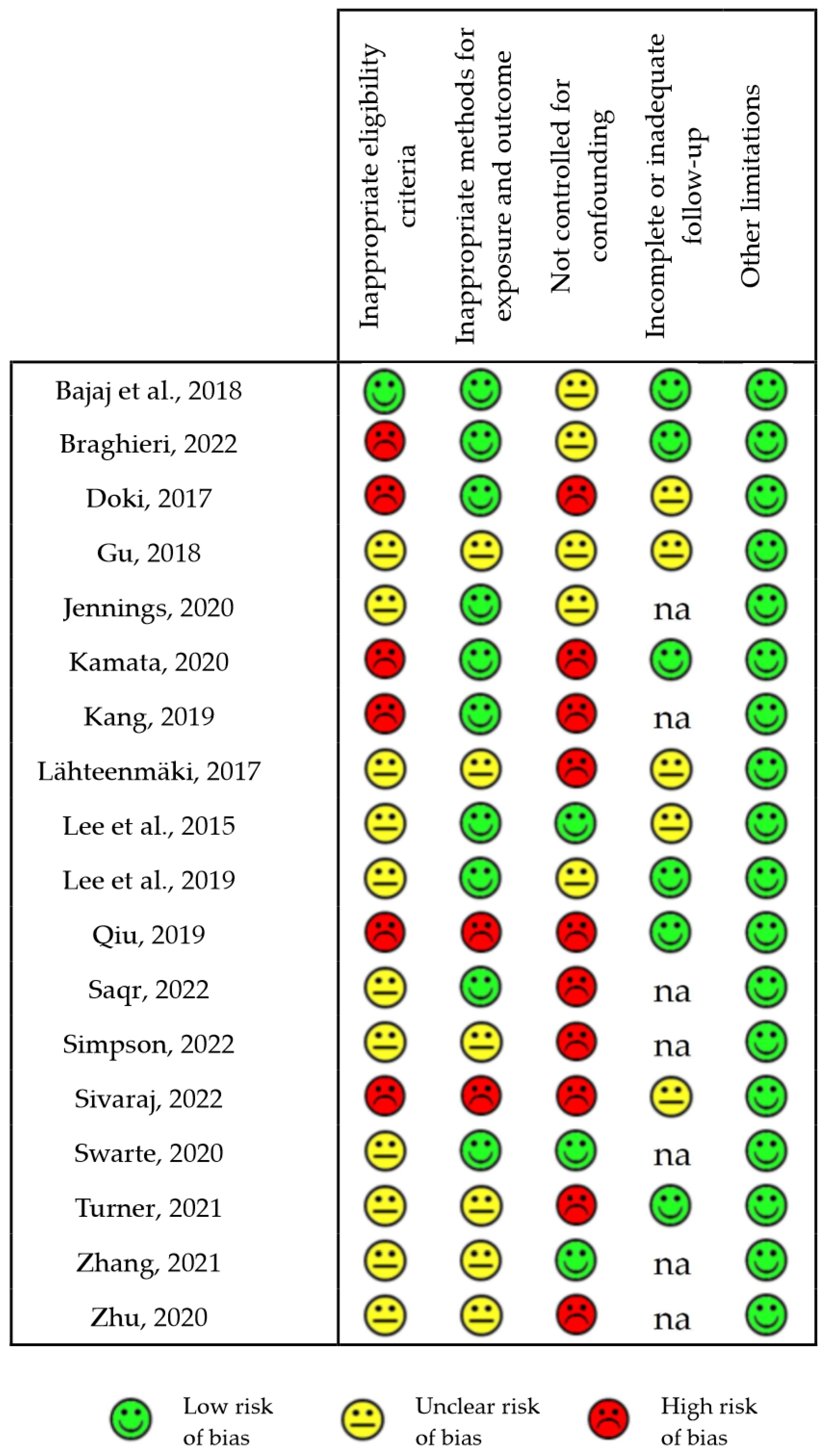
Figure 3 reports the detailed score for the various categories of risk of bias in each of the eighteen reviewed human observational studies examined.
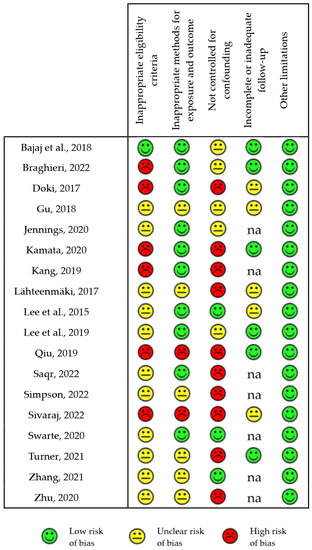
Figure 3.
Risk of bias of observational human studies [21,22,24,27,28,29,32,33,35,38,40,41,54,55,56,60,64,65]. The chart reports the risk of bias for each of the individually estimated GRADE categories in all the reviewed human observational studies and classified as “low”, “unclear” or “high”. na: not applicable.
The study by Pigneur et al. [59] was the only randomized clinical trial among the papers included in the present systematic review. At the bias risk assessment, we did not find information about allocation concealment, which, therefore, we scored as “unclear”. Blinding was reported for the assessors, whereas it was not declared but probably impossible (due to the type of intervention, exclusive enteral nutrition versus GCs) for patients. We did not find any evidence of incomplete accounting of patients and outcome events, of selective outcome reporting, or of other limitations and, therefore, we scored these three categories as free of risk.
3.3. Effect of Intestinal Microbiota on cIMDs
We reviewed 20 papers addressing our research question 1: Does the intestinal microbiota affect cIMD pharmacology (pharmacokinetics, efficacy or tolerability)? Table 1 summarizes the main findings of these studies. Eight studies were on MMF, ten on TAC, four on CyA, and ten on GCs. We found no studies on the effect of the intestinal microbiota on EVERO or SIR. Seventeen studies showed significant effect of fecal microbiota, or enzymes produced by intestinal bacteria on cIMDs [21,22,23,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,38,39,40], whereas no effect was observed in the remaining three studies [24,36,37].
Seven papers reported results of studies performed in vitro either by using living cells (cell lines or bacteria) or acellular systems with cell extracts or purified enzymes [23,25,26,30,31,36,37], twelve papers were on studies performed in vivo [21,22,24,27,28,29,32,34,35,38,39,40] and one included both in vitro ed in vivo experiments [33]. Seven of the in vitro studies evaluated cIMD metabolism either by cultured fecal bacteria from human stool (two papers [25,26]), or by human fecal material (three papers [33,36,37]) or by purified enzymes (two papers [30,31]). One paper investigated the effect of deoxycholic acid (DCA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), generated from bile salts by bacterial metabolism, on the activity of ABC-B1, a pump responsible for CyA efflux from intestinal epithelial cells [23]. The main findings of the in vitro studies were that: (1) GCs can be degraded by fecal bacteria through the action of desmolases (DesA and DesB) [26,30,31], (2) TAC is converted to the less active metabolites M1/M2 by the bacterial enzymes TacA and TacB [25]; (3) The main metabolite of MMF, mycophenolate glucuronide (MPAG) is deglucuronated by bacterial β-Glucuronidase (GUS) to MPA [26]; (4) MFA is not degraded by fecal microbiota [26]; (5) CyA is not significantly metabolized by intestinal bacteria [26,37] but DCA and CDCA, generated from bile salts by bacterial metabolism, increase its cytotoxicity impairing ABC-B1 activity [23]; (6) data are missing for EVERO and SIR.
Of the thirteen in vivo studies, eleven were performed in human patients who underwent kidney [24,28,29,33,38], heart [21,27,34] or hemopoietic stem cell transplantation [22,32] or were affected with ulcerative colitis (UC) [40], one study in rats and one in both mice and in humans [34]. Five of the ten studies performed in humans investigated the effect of the intestinal microbiota on cIMD toxicity (four on diarrhea [24,29,33,38] and one on neutropenia [21]). Of the remaining six studies, two were on cIMD pharmacokinetics (one on MPA, performed in humans [32] and the other on CyA, performed in rats [39]), and four on cIMD efficacy (two on the need for TAC dose escalation [27,28], one on GC responsiveness [40], and two on the occurrence of graft vs. host disease (GvHD), as a consequence of immunosuppressive therapy failure [22,35]). The main findings of these studies were: (1) The intestinal microbiota is different in patients developing or not neutropenia during the immunosuppressant therapy with MMF and TAC [21]; (2) the composition of the intestinal microbiota is different in patients who develop or not acute GvHD after allogenic hemopoietic stem cell transplantation [22] and in patients with acute GvHD responding or not to PRED; (3) the conversion of MPAG back to MPA, and, consequently, MPA enterohepatic recirculation, depend on the composition of the intestinal microbiota [32]; (4) the composition of the intestinal microbiota is different in patients who develop or not diarrhea during treatment with MMF-containing regimens [29,38] and bacterial GUS activity correlates with the risk of developing MMF-induced diarrhea [33,34,38]; (5) the composition of the intestinal microbiota is different in patients requiring low or high TAC doses [27,28]; (6) the composition of the intestinal microbiota affects CyA bioavailability in rats [39]. The previous points are just a list of the main findings of the studies detailed in Table 1. In fact, we could not produce a real synthesis of the data since, for each of the cIMDs, we retrieved only very few papers, that, moreover, used, heterogeneous experimental techniques therefore hindering any joint analysis.
3.4. Effect of cIMDs on Intestinal Microbiota
We reviewed 32 papers addressing our research question 2: Do cIMDs modify the composition of intestinal microbiota? Table 2 summarizes the main findings of these studies. Twenty-three papers reported the results of studies performed in experimental animals, seven in rats [42,44,50,51,61,62,70] and sixteen in mice [34,43,45,46,47,48,49,52,53,57,58,63,66,67,68,69]. The remaining nine studies were conducted in humans who received cIMDs either because they were recipients of organ transplantation (LT in two studies [41,64], KT in two [33,65] and HSCT in one [56], or because affected with autoimmune diseases (autoimmune pancreatitis [54], nephrotic syndrome [55], Crohn disease [59], or transverse myelitis [60]). In most of the studies performed in animals only one cIMD was used, even though in some of them different groups of animals each receiving a different cIMD were studied. In six of these studies TAC was investigated [42,46,51,52,66,69], in seven SIR [42,43,47,49,53,58,68], in six MMF [34,45,57,61,62,66], in six GC (in four PRED [48,66,67,70] and in two PREDN [44,63]), in one CyA [50] and in another one EVERO [66]. One study performed in normal mice evaluated not only the effect of PRED, TAC, EVERO and MMF given alone but also of the combined treatment with PRED, TAC, and MMF [66]. In four of the nine studies performed in humans only a cIMD was used, and more specifically it was a GC (PRED in three papers [55,59,60] and PREDN in one [54]). In the remaining five papers, patients were treated with multiple cIMDs as part of multidrug combination immunosuppressive regimens: TAC was given in four of these five studies [33,41,64,65], CyA in three [41,56,65], MMF in four [33,41,56,65], SIR in one [64] and PRED in two [64,65].
All the studies that we reviewed showed that the treatment with cIMD was associated with changes in the intestinal microbiota with the only exception of one study performed in mice treated with SIR [58]. The effect on α-diversity was variable among studies with nine papers reporting no effect [42,44,47,52,53,58,62,69,70], six an increase [46,50,51,57,67,68] and two a decrease [45,61]; data on α-diversity were not available in six studies [34,43,48,49,63,66]. A decrease in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (either as directly reported or as evident from data on the relative abundance of these two phyla) was observed in three of the animal studies [46,48,62] (but in [48] TAC was given together with antibiotics), an increase in four studies [45,57,66,68], whereas no change was evident in six studies [42,44,53,61,67,70]; no data were reported in the remaining ten papers [43,47,49,50,51,52,58,63,67,70].
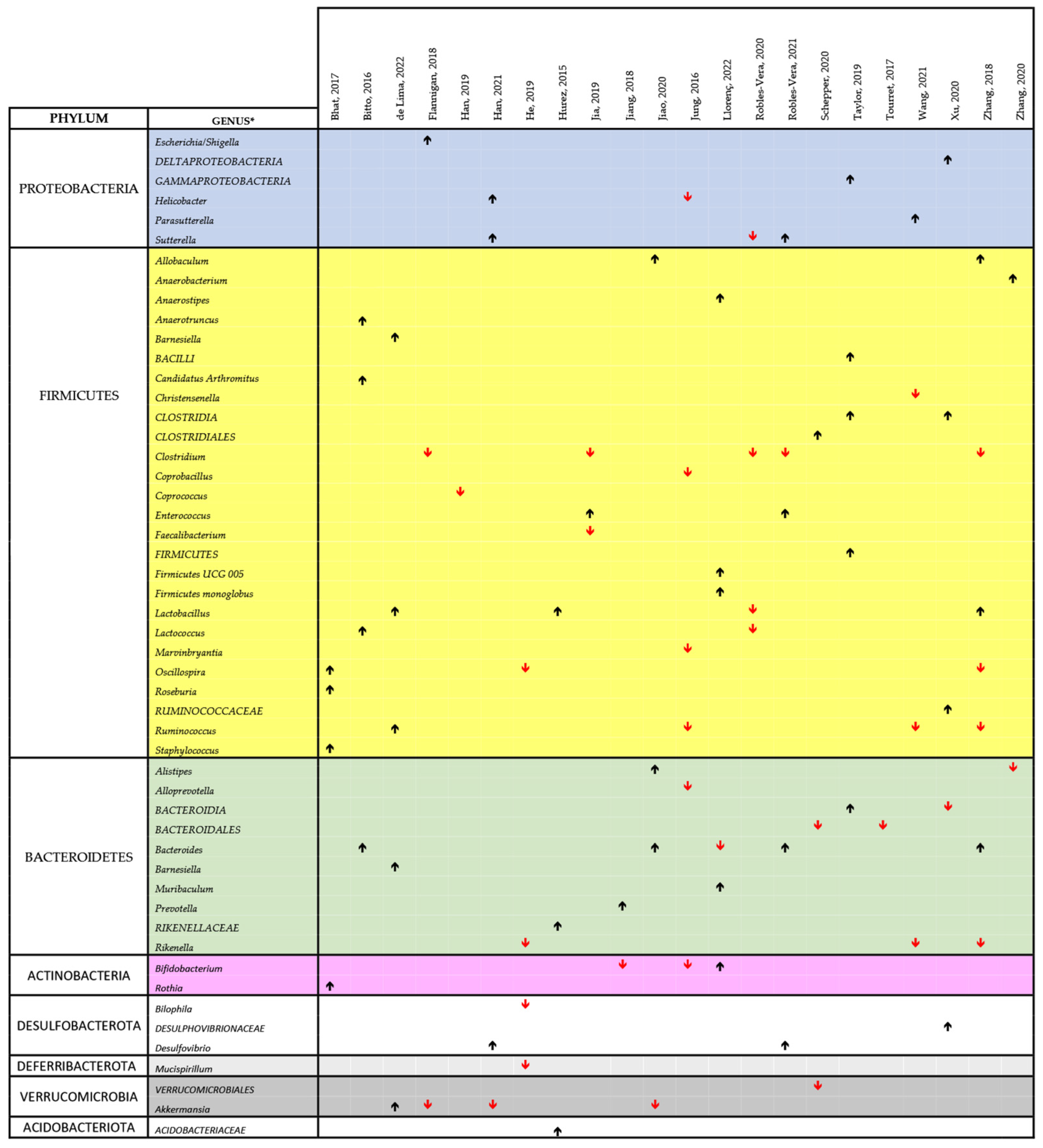
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show a synthesis of the findings of the papers listed in Table 2 on the changes in the microbiota, related to cIMDs administration, respectively, in animals and humans. In both figures, we reported the main changes at the genus level (or, when these data were missing, at the level of order or family) for each of the reviewed papers, and the genera involved were grouped according to their phyla. As evident from both these figures, not all the studies covered the whole repertoire of the main bacterial genera of gut microbiota. Therefore, in measuring the prevalence of the change in the abundance of a specific genus (or phylum) we only considered the number of papers reporting data on this specific genus or phylum. Using this approach and looking at the studies performed in animals (Figure 4), we observed that 7/9 (78%) of the reviewed studies reporting data on the respective phyla showed an increase in Proteobacteria, 25/42 (59.5%) an increase in Firmicutes, 10/19 (52.6%) a decrease in Bacteroidetes, 4/5 (80%) a decrease in Verrucomicrobia, and 2/4 (50%) a decrease in Actinobacteria. At the genus level, we could not identify any specific bacterial signature of cIMD-induced microbiota remodeling even though some changes were observed more frequently than others. Specifically, Lactobacillus was increased in 3 of 4 papers, and Bacteroides in 4 of 5, whereas Clostridium was decreased in 5 of 5, and Akkermansia in 3 of 4.
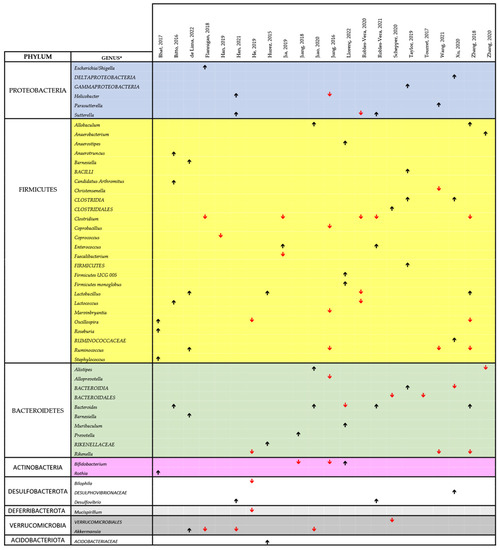
Figure 4.
Comprehensive view of the effect of cIMDs on bacterial composition of the intestinal microbiota in animal studies [34,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,57,61,62,63,66,67,68,69,70]. The chart shows the main alterations in the composition of the intestinal microbiota at the genus level as identified in the text and/or tables of the respective papers. The black upward and the red downward arrows indicate respectively an increase or a decrease in the relative abundance of the respective bacterial genus. For reasons of space and to make the chart readable, we could not include all the data reported in each paper or in their supplementary information, but we have focused on those on which the authors of each publication emphasized. The study by Lyons et al., 2018 [59] was not included since no change in the composition of the intestinal microbiota was observed upon treatment of mice with SIR. * Whenever available in the original publications, the data reported are related to changes observed at the genus level. When this information was not available, we reported the data at the closest classification level (order or family).
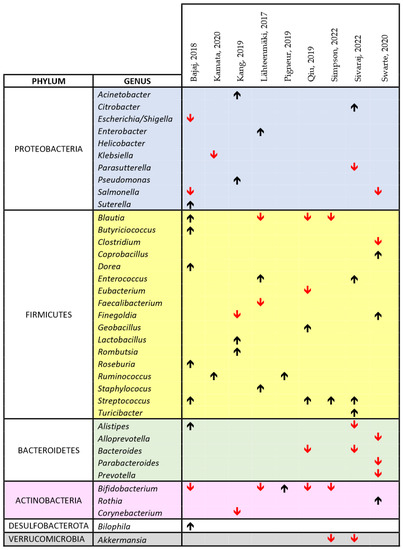
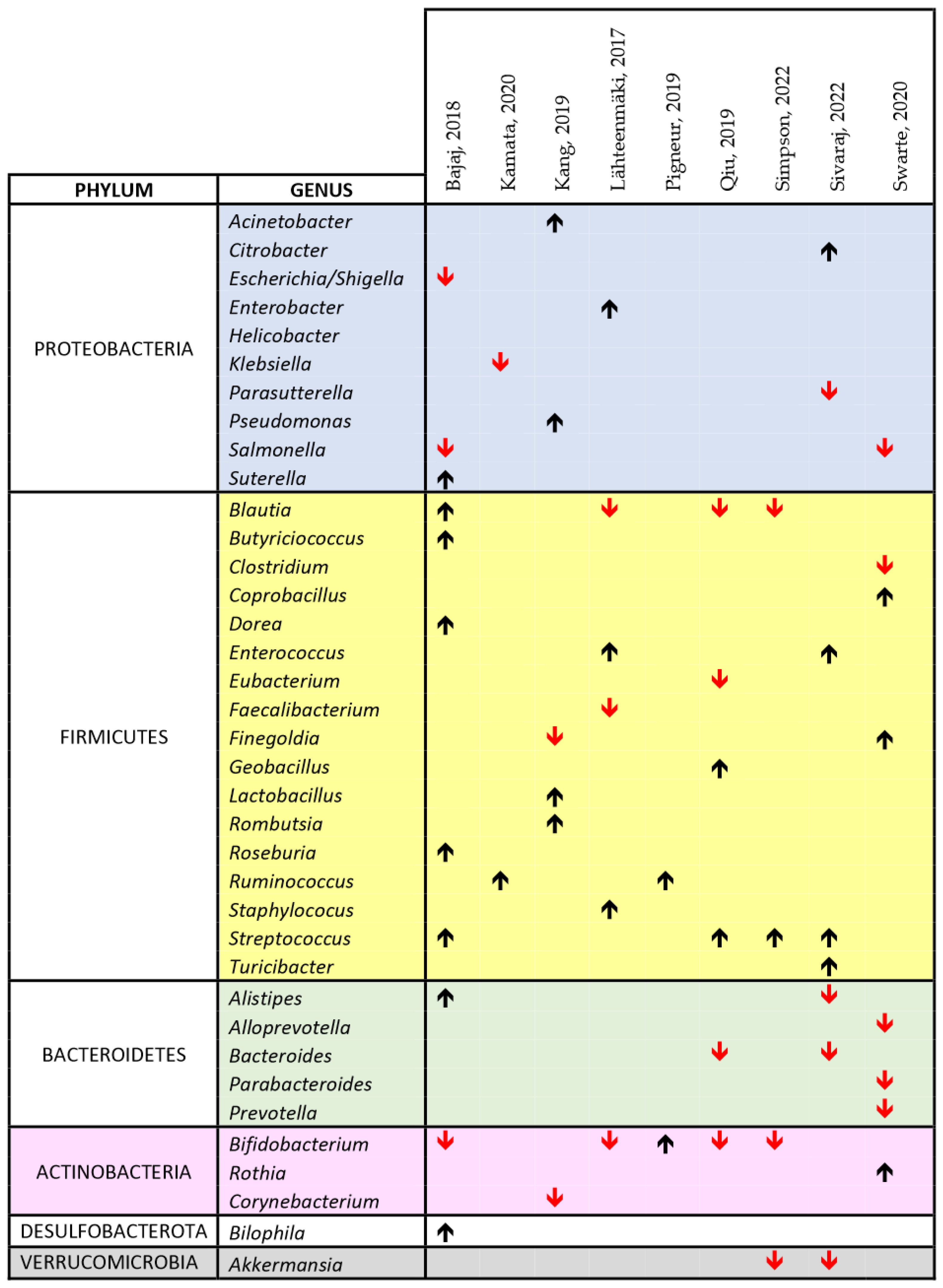
Figure 5.
Comprehensive view of the effect of cIMDs on bacterial composition of the intestinal microbiota in human studies [33,41,54,55,56,59,60,64,65]. The chart shows the main alterations in the composition of the intestinal microbiota at the genus level as identified in the text and/or tables of the respective papers. The black upward and the red downward arrows indicate respectively an increase or a decrease in the relative abundance of the respective bacterial genus. For reasons of space and to make the chart readable, we could not include all the data reported in each paper or in their supplementary information, but we have focused on those on which the authors of each publication emphasized.
In the human studies, we observed, at phylum level, an increase in Proteobacteria in 5/10 studies (50%), and in Firmicutes in 19/23 (73%) studies, a decrease in Bacteroidetes in 6/7 (85%) studies, in Verrucomicrobia in 2/2 (100%) studies, and in Actinobacteria in 5/7 (71%) studies (Figure 5). As for animal studies, also the papers performed in humans did not disclose at the genus level an unique bacterial signature of cIMD effect on the microbiota. Nonetheless, some genera were affected more often than others. Specifically, Streptococcus was increased in 4 of 4 papers whereas Blautia and Bifidobacterium were decreased in 3 of 4, and Akkermansia in 2 of 2 (Figure 5).
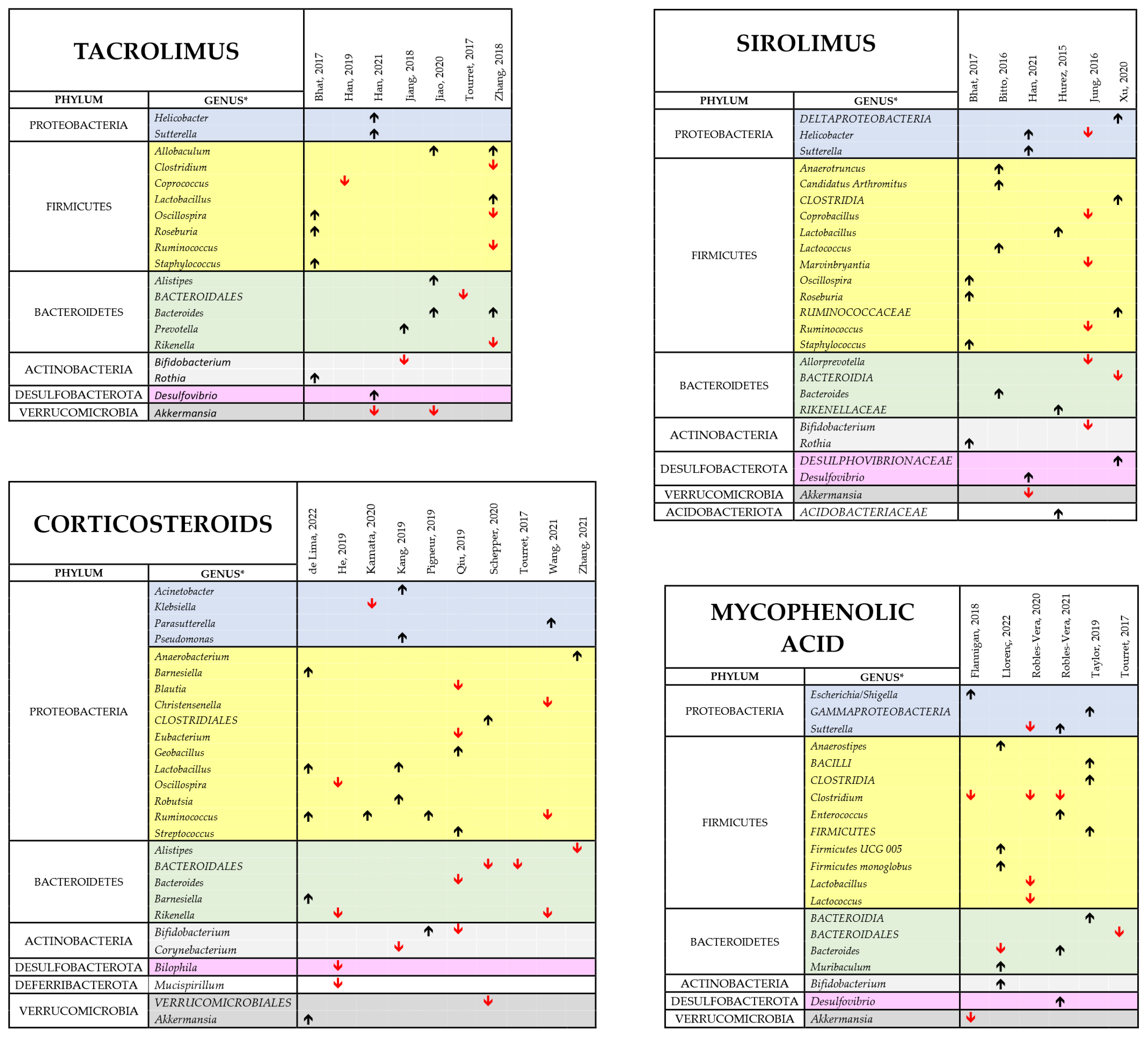
Several factors could account for the heterogeneity in these studies of the findings on cIMD effects on microbiota and for the lack of a bacterial signature of cIMD effects on gut microbiota. They include the different species used and/or the different spontaneous or experimental disease statuses investigated. It is also to be considered that, as mentioned before, not all the papers reviewed report comprehensive data on gut microbiota composition and that, in some cases, the only information directly available is on few bacterial species on which the authors put their emphasis because of their potentially important pathophysiological role. An additional factor that makes difficult to produce an effective synthesis of the reviewed papers is that these studies used different cIMDs, sometimes in different combinations. To pinpoint drug-dependent variability we performed a separated analysis of the changes in the gut microbiota occurring when the various cIMDs were given alone and not in combination. Figure 6 shows the results of this synthesis for GCs, MMF, SIR and TAC, whereas CyA and EVERO could not be analyzed since they were studied only in one single paper. Due to the limited number of papers on each of the single cIMDS, we grouped the studies performed in humans and animals. When evaluating the results at the phylum level, the changes induced by the different cIMDs were similar. In fact, an increase in Firmicutes was observed in 66% of the studies with TAC that reported changes in this phylum, in 73% with GCs, in 75% with SIR and in 58% with MMF. Likewise, 100% of the studies with TAC that showed changes in Proteobacteria observed an increase in this phylum, whereas the percentage was 75% for GCs, SIR and MMF. By contrast, a decrease in Bacteroidetes was described in 67%, 86%, 50% and 60% of the studies, respectively, with TAC, GCs, SIR and MMF which reported changes in this phylum. When the data were, instead, at the level of genus no obvious drug-specific signature of drug-induced change in the microbiota could be identified since there was a large variability across the different studies. Nonetheless, some changes were recurrent in different papers. Specifically, in the case of TAC the two papers reporting data on Allobaculum both showed an increase in its abundance. Likewise, Bacteroides were increased in both the papers that measured its abundance, whereas Akkermansia was decreased in both the papers examining this genus. The most recurrent finding with MMF was a decrease in the abundance of Clostridium (observed in three papers out of three), whereas, with GCs, an increased abundance of Ruminococcus (3 of 4 papers) and Lactobacillus (2 of 2 papers) was observed, whereas Bacteroidales decreased in all the three papers measuring their abundance.
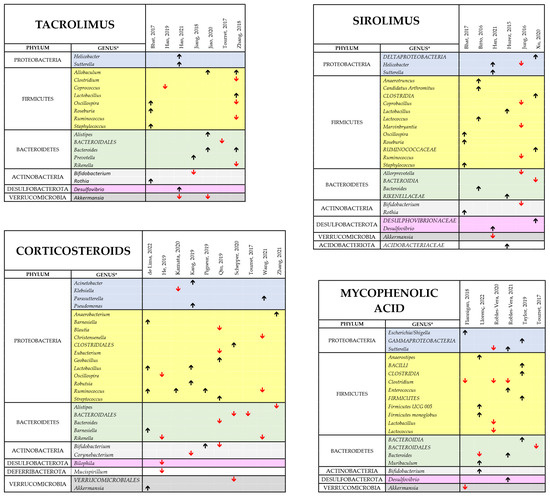
Figure 6.
Comprehensive view of the effect of TAC, SIR, GCs and MMF bacterial composition of the intestinal microbiota [34,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,51,52,53,54,55,57,59,60,61,62,63,66,67,68,69,70]. The different panel show the main findings of the studies performed with each of the indicated cIMDs given alone to either experiment animals or human patients. The black upward and the red downward arrows indicate respectively an increase or a decrease in the relative abundance of the respective bacterial genus. No data have been reported for the other two cIMDs, CyA and EVERO since only one study was available for each of them. * Whenever available in the original publications, the data reported are related to changes observed at the genus level. When this information was not available, we reported the data at the closest classification level (order or family).
4. Discussion
In the present manuscript we reported the results of our systematic review of the evidence supporting the hypothesis that the intestinal microbiota affects cIMD pharmacology, whereas cIMDs affect the composition of the intestinal microbiota. The main finding of our study was that most of the published papers on these two issues corroborate the two aforementioned hypotheses. While this is true for the general picture of the reciprocal interrelationship between cIMDs and intestinal microbiota, the evidence becomes weaker for the subtopics that it covers.
Concerning the first point, 17/20 papers showed some effect of the intestinal microbiota on cIMD pharmacology, but only two papers were pharmacokinetics studies (moreover on two different drugs), only five were on toxicity (four of which on diarrhea and one on GvHD) and only six on cIMD efficacy (of which three on TAC and three on GCs). This fragmentation of the available evidence implies that the conclusions that can be drawn have to be considered preliminary and need further data to be confirmed. Moreover, evidence is missing for some cIMDs, i.e., SIR and EVERO. The hypothesis that cIMD pharmacology is affected by gut microorganisms should be placed in a more general context that assumes that the composition of the intestinal microbiota represents one of the factors responsible for the interindividual variability in patient response to drug therapy [108,109], together with pharmacogenomics with which it possibly interacts in a clinically significant manner [110]. As a matter of fact, one of the papers included in our systematic review showed that 13% of the 438 drugs successfully tested with a new method for the high throughput screening of drug metabolism by intestinal bacteria from human stools, were metabolized by intestinal microorganisms [26]. These metabolized drugs belonged to different therapeutic categories, including antiepileptic (clonazepam), antihypertensive (nicardipine and spironolactone), antipsychotic (risperidone), anticancer (capecitabine) and antiviral drugs (famciclovir). Amongst the cIMDs, GCs and MMF were positive, whereas CyA and EVERO were apparently not metabolized by human microbiota. The ability of the gut microbiota to metabolize GCs has been observed also in others of the studies that we reviewed [30,31]. The microbial enzyme involved has been identified with 17,20 desmolase which catalyzes the conversion of cortisol and its derivatives into 21-deoxysteroids, for instance, by converting hydrocortisone and hydrocortisone acetate in 20β-dihydrocortisone [26,111,112,113,114]. The evidence linking intestinal bacteria and 17,20 desmolase to corticosteroid metabolism is limited to in vitro testing. Two old papers, which were not retrieved in our search, showed that the urinary concentrations of 17-ketosteroids sharply increased after the intrarectal infusion of hydrocortisone and that this effect was abrogated by the oral administration of neomycin, suggesting that intestinal bacteria were involved [115,116]. However, according to our search, no formal pharmacokinetic study has been performed so far to assess the impact of this bacterial enzyme on the exposure to GCs and, therefore, the relevance of this pharmacomicrobiomic factor on the efficacy or tolerability of these immunosuppressive drugs still remains to be proved. Nonetheless it is worth to mention that high levels of (endogenous) 21-deoxysteroids have been found in patients with Cushing’s disease [117] and hypertension [118] and in vitro studies showed that they act as weak agonist on glucocorticoid receptors (GR) [119] and may transactivate the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) although to a lesser extent than aldosterone and fludrocortisone [120]. These data suggest that microbial degradation of corticosteroids in the gut could generate metabolites that enhance their cardiovascular toxicity. The involvement of gut microflora in the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid and of MMF has long been hypothesized to explain the enterohepatic recirculation of MPA, which, after being glucuronated to MPAG in the liver and released in the bile, is deglucuronated in the gut to generate MPA which is reabsorbed in the portal circulation [121]. Two papers included in the present systematic review demonstrated that the intestinal metabolism of MPAG is mediated by GUS producing bacteria [33,34]. In addition, the in vitro screening study by Javadan et al. [26], that we mentioned before, showed that bacteria from human stools may convert MMF into MPA. Importantly, the impact of intestinal microbiota composition on MMF and MPA has been demonstrated also in a pharmacokinetic study in humans, included in our systematic review [32]. This paper by Saqr et al., clearly showed in vivo, in patients who underwent HSCT that MPA enterohepatic recirculation and, consequently, MPA exposure were affected by intestinal GUS-expressing bacteria. Importantly, Simpson et al. [33] showed that the most important predictive factor for MPAG reactivation in the gut was the presence of GUS producing bacteria. The effect of intestinal bacteria on MPA pharmacokinetics could be clinically relevant as suggested by a study published after we finished our literature search, which showed a substantial decrease in MPA exposure in a very small case series of patients with signs of immunosuppressive therapy failure after starting an antibiotic treatment [122]. A paper by Guo et al. (2019) [25] examined the ability of intestinal bacteria to metabolize TAC and showed that Faecalibacterium prausnitzii converts this cIMD into a C-9 keto-reduction product, the M1 metabolite, which is approximately 15-fold less potent than the parent drug. These experiments were performed in vitro by incubating TAC with bacterial cultures; no formal pharmacokinetic study was performed even though M1 was measured in stool samples from healthy individuals and kidney transplant recipients. Preliminary data confirming the presence of M1 in the blood of patients receiving TAC were published as a letter by Guo et al. (2020) [123] but no pharmacokinetic investigation was performed. As discussed below, Lee et al. (2019) [28] demonstrated a correlation between the abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the fecal microbiota and the dose of TAC required to attain therapeutic plasma concentration in the blood of patients with kidney transplantation, but, once again, no formal pharmacokinetic study was performed and M1 concentrations were not assessed neither in plasma or in stools. Recently, after we completed our literature search, a paper was published by Degraeve et al. (2023) [124] assessing the impact of the gut microbiota on TAC pharmacokinetics in vivo in mice. Whilst this study confirms that the gut microbiota profoundly affects TAC pharmacokinetics, the mechanism highlighted is completely different and consists in the decrease by bacterial released mediators in the activity of ABCB1 pumps, which extrude TAC form enterocytes and prevent their systemic absorption. In fact, upon antibiotic treatment, TAC exposure increased in a manner totally reversible with the ABC1B1 blocker zosuquidar. While the study by Guo et al. [25] seem to suggest that fecal microbiota reduces TAC bioavailability, the data reported by Degraeve et al. (2023) [124] seem to propend for the opposite scenario of intestinal bacteria enhancing TAC absorption. The inconsistent findings of these two studies (one performed in man and the other in mice) leave open the question of how the intestinal microbiota affects TAC pharmacokinetics and whether species-specific factors are involved. We retrieved only one paper by Zhou et al. that evaluated the effect of the intestinal microbiota on CyA pharmacokinetics [39]. The results of this investigation, which showed changes in CyA bioavailability depending on gut microbiota composition, contrast with the results of in vitro studies showing that this cIMD is not degraded in vitro by intestinal microorganisms [26,37]. A possible explanation for these apparently incongruent findings is that, in a similar way to what described by Degraeve et al. (2023) [124] for TAC, intestinal bacteria affect ABCB1. As a matter of fact, Zhou et al. [39] showed that intestinal microbiota disruption with antibiotic caused an increase in CyA bioavailability in rats that was accompanied by a decrease in protein levels of CYP3A1 and UGT1A1, which are involved in CyA metabolism in the liver and in the intestinal epithelium and ABCB1, the pump responsible for CyA efflux from hepatocytes and intestinal epithelial cells [39]. An additional factor (yet to be investigated) could be the ability (demonstrated in vitro in cultured intestinal cells [23]) of DCA and CDCA, generated by certain intestinal bacteria, to reduce the activity of ABCB1pumps, hence decreasing the efflux of CyA from the gut epithelium and, potentially, increasing its bioavailability.
Intestinal bacteria of the human microbiota may not only metabolize but also accumulate drugs such as duloxetine, montelukast, rosiglitazone and roflumilast that, after being internalized in their cytoplasm, become unavailable for systemic absorption with the final result of a reduced bioavailability and, possibly, clinical efficacy [16]. However, we did not find in our literature review any evidence that this also occurs with cIMDs.
Differences in the composition of intestinal microbiota were observed between GC-responsive and GC-unresponsive patients [40] and in patients requiring high or low TAC doses [28], suggesting that the efficacy of immunosuppressant therapy could depend on gut microbes. The most obvious explanation for such a correlation between intestinal microbiota and cIMD responsiveness could be that patients with different gut microorganisms had a different pre-systemic metabolism of these drugs. This hypothesis was not directly assessed for GCs in any of the papers that we reviewed. By contrast, a higher abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, the microorganism responsible for TAC metabolism, was observed in patients requiring TAC dose escalation [28].
Differences in the composition of gut microbiota were also observed between patients experiencing or not some cIMD toxicities, specifically diarrhea [24,29,33,38] and neutropenia [21]. The mechanism linking gut microbiota and diarrhea has been elucidated in the case of MMF and it is represented by the ability of certain bacterial species to produce GUS, deconjugate MPAG and, consequently, to increase the local concentrations of MPA which damages the intestinal mucosa [34,38]. Likewise, an increased abundance of the GUS-producing bacterium Bacteroides dorei has been observed, leading to a higher exposure to MPA in patients developing neutropenia when treated with MMF [21].
Concerning the second point under investigation, only one of the 32 papers investigating the effect of cIMDs on the intestinal microbiota had negative results. Therefore, as for the first point, i.e., the effect of the microbiota on cIMDs, the big picture of a bidirectional interrelationship between cIMDs and intestinal microbiota seems to be confirmed. At the phylum level, the most commonly observed finding, in both animal and in human studies, was a decrease in Bacteroidetes and Verrucomicrobia. The decrease in Firmicutes was more prevalent in human (85%) than in animal (53%) studies. At the genus level, however, we were unable to identify, an unique pattern of changes in the gut microbiota composition. Several factors may have contributed to the marked variability across studies including major differences in the species used, the disease conditions investigated and the administered cIMDs. The latter point would be of major relevance in the perspective of the present systematic review. However, based on our literature search, the evidence accumulated so far does not permit to identify drug-specific fingerprints of gut microbiota modifications. In fact, we identified only a limited number of papers investing the effects of single cIMDs. Most of them were animal studies, whereas, more cIMDs were generally used in humans, with the only exception of four studies in which a corticosteroid with no other drug was given to study participants without other cIMDs. Nonetheless, when we stratified the findings of reviewed studies without species constraints, we observed, for the different cIMDs, quite similar patterns at the phylum level, with an increase in the abundance of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria and a decrease in Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia, but major differences in the genera involved. As described in Section 3 no microbiological signature of cIMD-induced alterations in gut microbiota emerged from our analysis even though some findings were in line with previous analyses, such as the increase in Allobaculum with TAC, the decrease in Clostridium with MMF or the increase in Lactobacillus with GCs [125].
Mechanistically, different factors could account for the ability of cIMDs to modify the composition of intestinal microbiota (see Gabarre et al., 2022 [125] for review). First, a wealth of experimental data show that non-antibiotic drugs may exert antibacterial effects in vitro and in vivo as clearly demonstrated, for instance for calcium channel blockers or antipsychotic drugs [126,127]. Such a mechanism could be relevant in the case of MPA, which, as a matter of fact, was originally identified as an antibiotic and not as an immunosuppressive drug [128,129], but does not seem to be relevant for the other cIMDs considered in the present systematic review. In fact, whereas a decrease in the severity of experimental mycobacterial infection was observed with the mTOR inhibitors, SIR and EVERO, this effect was due to the promotion of autophagy by this two cIMDs with no direct antibacterial toxicity [130,131]. Likewise, CyA and TACRO do not seem to have direct antibacterial effects even though they may exert an antifungal and antiviral activity, possibly by interfering with intracellular signaling cascades [132]. However, additional mechanisms may account for cIMD-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota, independently from a direct antibacterial effect. Specifically, the immunosuppressive activity of these drugs may interfere with the immune surveillance mechanisms that limit the proliferation of potentially pathogenetic bacteria whilst maintaining a condition of immune tolerance for commensal bacteria [133]. For instance, TACRO, GCs and the mTOR inhibitors decrease synthesis and release of the lectins RegIIIb and RegIIIg, two lectins with antibacterial properties [66]. The integrity of the mucosal barrier is another crucial factor in maintaining the normal composition of the intestinal microbiota, which may be altered by cIMDs. In fact, GCs decrease the synthesis and secretion of mucin and IgA [134,135], whereas MPA may directly damage gut epithelium loosening its tight junctions [136].
Another major point still to be clarified, since we did not find any paper directly addressing it, is how cIMD effects on the gut microbiota could impact on cIMD pharmacology. In other words, it remains to be established whether and to what extent the remodelling of gut microbiota occurring upon treatment with a given cIMD could promote the overgrowth (or, conversely, reduce the abundance) of bacterial species that metabolize or accumulate this specific cIMD. Such a phenomenon could be relevant in explaining changes in the efficacy of the immunosuppressant therapy occurring during treatment. In addition, considering that, as mentioned before, drugs belonging to multiple therapeutic classes besides immunosuppressants, the response to other, concomitant therapies could be affected as well.
The present systematic review has several important limitations. First, we considered both studies performed in humans and in rodents. Whilst this was largely a forced choice due to the limited number of papers published on cIMD pharmacomicrobiomics, it also implies potential problems in the interpretation of the results obtained. In fact, important differences exist in the composition of human and mice microbiota despite a 90% similarity at the phylum level and a 89% similarity at the genus level [137,138]. Another major limitation is the high heterogeneity of the experimental models that were used in the reviewed study. If we start considering the studies on cIMD pharmacology, a large fraction of them were just “pharmaceutical” investigations totally performed in vitro and exploring moiety degradation, only a few papers were performed in vivo and most of them were not specifically designed as “pharmacological studies” but, instead, they were clinical studies recording the occurrence of unwanted drug effect or therapy failure. Additionally, when we move to the studies aiming to investigate the effect of cIMDs on the intestinal microbiota, one of the major factor complicating and possibly biasing the interpretation of their results is the heterogeneity of the species and of the experimental models considered. As a matter of fact, only few studies, all performed in animals, tested the effect of selected cIMDs in healthy probands. On the contrary, in most of the animal studies and in all the studies performed in humans either diseases requiring cIMDS, such as organ transplantation or autoimmune diseases, or disease conditions induced by cIMDs such as obesity or diabetes were evaluated. Considering that the underlying disease may itself cause alterations in the intestinal microbiota as shown, for instance in chronic kidney disease (reviewed in [139,140] or in inflammatory bowel disease [141]), it is very hard to understand to what extent the modifications observed in its composition upon treatment with cIMDs are due to a direct effect of these drugs or to the improvement of the clinical condition requiring their use. Obviously, this conundrum is even harder to solve in the case of organ transplantation. For instance, in the case of liver transplantation, the important impact of the liver on the gut microbiota in the so-called gut–liver axis must be considered [142]. While animal studies adopted, in general, a controlled parallel group randomized design, most of the human studies were observational investigations and this raises further concerns about the reliability of the controls used in these studies.
5. Conclusions
The systematic literature review that we performed confirms and extends the findings of previous reviews and metanalyses showing that the gut microbiota is bidirectionally interrelated with cIMDs in a potentially clinically relevant manner [81,143,144,145]. The general conclusion emerging from all the evidence that we examined is that although pharmacomicrobiomics is a promising new tool to optimize the treatment with cIMDs, it is still in its infancy. Prospectively, one can imagine that, in the future, the dosage of cIMDs to be given to every single patient will be adjusted according to the composition of his/her intestinal microbiota and that further adjustment will be done during the treatment on the basis of changes occurring in gut microorganisms (even including those caused by the use of the same immunosuppressive drugs). However, a lot of experimental work remains to be done before this scenario can become clinical reality. In fact, most of the available evidence is limited to a small number of papers/patients and needs to be extended. In addition, data are still missing for some of the cIMDs considered such as SIR and EVERO. Even more importantly, the evidence that the composition microbiota has a causative role in determining the fate of transplanted organs or the prognosis of autoimmune disease is still limited and mostly related to animal models [146,147,148,149,150]. Likewise, it is still to be definitely demonstrated that interventions on the microbiota by the means either of probiotics supplementation or of genetic modification of resident gut bacteria may improve the prognosis in patients recipients of organ transplantation or affected with autoimmune diseases. With all these points still to be deeply explored we are hopefully at the beginning of a new exciting season of research advancement in the field of cIMD pharmacomicrobiomics. A final note concerning the data that have been reviewed in the present paper is that all the pharmacomicrobiomics interferences with cIMD pharmacology took place in the gut lumen and were strictly dependent on the oral administration of these drugs. This implies that, potentially, part of the pharmacomicrobiomic-related variability could be abated by using alternative administration routes and, in this perspective the use of new, emerging methods such as subcutaneous microneedles appears very intriguing [151,152].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C.; methodology, A.M. and M.C.; formal analysis, A.M. and M.C.; investigation, A.M., L.D., C.G., M.D.L., G.N., F.M. and E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; writing—review and editing, A.R., T.D.R., B.G., G.T. and M.C.; funding acquisition, M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministero della Salute, Piano Nazionale di Ripresa e Resilienza (PNRR) Missione 6—Componente 22.1 Valorizzazione e Potenziamento della Ricerca Biomedica del SSN, grant number PNRR-MAD-2022-12376812 “Presystemic metabolism of immunosuppressant drugs by gut microbiota as a risk factor for kidney transplant rejection: mitigation strategies” to M.C.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Karam, S.; Wali, R.K. Current State of Immunosuppression: Past, Present, and Future. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2015, 25, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, D.R.; Vanrenterghem, Y.C. Tailoring immunosuppressive therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2002, 17, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Albring, A.; Wendt, L.; Harz, N.; Engler, H.; Wilde, B.; Kribben, A.; Lindemann, M.; Schedlowski, M.; Witzke, O. Relationship between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplant patients. Clin. Transpl. 2015, 29, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCune, J.S.; Bemer, M.J. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacogenomics of Immunosuppressants in Allogeneic Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Part I. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 525–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCune, J.S.; Bemer, M.J.; Long-Boyle, J. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacogenomics of Immunosuppressants in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Part II. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 551–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Holt, D.W. Immunosuppressant drugs--the role of therapeutic drug monitoring. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 52 (Suppl. S1), 61S–73S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, H.; Naesens, M.; Kuypers, D.R. New insights into the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the calcineurin inhibitors and mycophenolic acid: Possible consequences for therapeutic drug monitoring in solid organ transplantation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobakht, E.; Jagadeesan, M.; Paul, R.; Bromberg, J.; Dadgar, S. Precision Medicine in Kidney Transplantation: Just Hype or a Realistic Hope? Transpl. Direct. 2021, 7, e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doestzada, M.; Vila, A.V.; Zhernakova, A.; Koonen, D.P.Y.; Weersma, R.K.; Touw, D.J.; Kuipers, F.; Wijmenga, C.; Fu, J. Pharmacomicrobiomics: A novel route towards personalized medicine? Protein Cell. 2018, 9, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, R.; Rizkallah, M.R.; Aziz, R.K. Gut Pharmacomicrobiomics: The tip of an iceberg of complex interactions between drugs and gut-associated microbes. Gut Pathog. 2012, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, A.T. Is p-aminobenzenesulphonamide the active agent in protonsil therapy? Lancet 1937, 229, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klünemann, M.; Andrejev, S.; Blasche, S.; Mateus, A.; Phapale, P.; Devendran, S.; Vappiani, J.; Simon, B.; Scott, T.A.; Kafkia, E.; et al. Bioaccumulation of therapeutic drugs by human gut bacteria. Nature 2021, 597, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Liu, J.; Ao, H.; Yue, S.; Peng, C. Targeting gut microbiota for precision medicine: Focusing on the efficacy and toxicity of drugs. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11278–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.; Brożek, J.; Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A. (Eds.) GRADE Handbook for Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations; Updated October 2013; Evidence Prime Inc.: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2013; Available online: https://www.rama.mahidol.ac.th/ceb/sites/default/files/public/pdf/journal_club/2017/GRADE%20handbook.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Braghieri, L.; Jennings, D.L.; Bohn, B.; Habal, M.; Pinsino, A.; Mondellini, G.M.; Ladanyi, A.; Latif, F.; Clerkin, K.; Restaino, S.; et al. Temporal shifts in safety and efficacy profile of mycophenolate mofetil 2 g versus 3 g daily early after heart transplantation. Pharmacotherapy 2022, 42, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, N.; Suyama, M.; Sasajima, S.; Ota, J.; Igarashi, A.; Mimura, I.; Morita, H.; Fujioka, Y.; Sugiyama, D.; Nishikawa, H.; et al. Clinical impact of pre-transplant gut microbial diversity on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, E.F.; Govindarajan, K.; Darrer, R.; MacSharry, J.; Joyce, S.A.; Gahan, C.G.M. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Bile Acid Transformations Alter the Cellular Response to Multidrug Resistant Transporter Substrates in Vitro: Focus on P-glycoprotein. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5711–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Bo, G.Z.; Ke, C. Exploration of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in the Treatment of Refractory Diarrhea After Renal Transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2018, 50, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Won, K.J.; Yang, X.; Lee, J.R.; Orjala, J.; Lee, H.; Jeong, H. Commensal Gut Bacteria Convert the Immunosuppressant Tacrolimus to Less Potent Metabolites. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javdan, B.; Lopez, J.G.; Chankhamjon, P.; Lee, Y.J.; Hull, R.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chatterjee, S.; Donia, M.S. Personalized Mapping of Drug Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell 2020, 181, 1661–1679.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, D.L.; Bohn, B.; Zuver, A.; Onat, D.; Gaine, M.; Royzman, E.; Hupf, J.; Brunjes, D.; Latif, F.; Restaino, S.; et al. Gut microbial diversity, inflammation, and oxidative stress are associated with tacrolimus dosing requirements early after heart transplantation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R.; Muthukumar, T.; Dadhania, D.; Taur, Y.; Jenq, R.R.; Toussaint, N.C.; Ling, L.; Pamer, E.; Suthanthiran, M. Gut microbiota and tacrolimus dosing in kidney transplantation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R.; Magruder, M.; Zhang, L.; Westblade, L.F.; Satlin, M.J.; Robertson, A.; Edusei, E.; Crawford, C.; Ling, L.; Taur, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and diarrhea in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2019, 19, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, L.K.; Rowles, J.L., 3rd; Paul, H.M.; Alves, J.M.P.; Yemm, C.; Wolf, P.M.; Devendran, S.; Hudson, M.E.; Morris, D.J.; Erdman, J.W., Jr.; et al. Bacterial steroid-17, 20-desmolase is a taxonomically rare enzymatic pathway that converts prednisone to 1, 4-androstanediene-3, 11, 17-trione, a metabolite that causes proliferation of prostate cancer cells. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 199, 105567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Ouyang, H.; Gordils-Valentin, L.; Hong, J.; Jayaraman, A.; Zhu, X. Identification of Gut Bacterial Enzymes for Keto-Reductive Metabolism of Xenobiotics. ACS. Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, A.; Carlson, B.; Staley, C.; Rashidi, A.; Al-Kofahi, M.; Kaiser, T.; Holtan, S.; MacMillan, M.; Young, J.A.; Jurdi, N.E.; et al. Reduced Enterohepatic Recirculation of Mycophenolate and Lower Blood Concentrations Are Associated with the Stool Bacterial Microbiome after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 372.e1–372.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.B.; Sekela, J.J.; Graboski, A.L.; Borlandelli, V.B.; Bivins, M.M.; Barker, N.K.; Sorgen, A.A.; Mordant, A.L.; Johnson, R.L.; Bhatt, A.P.; et al. Metagenomics combined with activity-based proteomics point to gut bacterial enzymes that reactivate mycophenolate. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.R.; Flannigan, K.L.; Rahim, H.; Mohamud, A.; Lewis, I.A.; Hirota, S.A.; Greenway, S.C. Vancomycin relieves mycophenolate mofetil-induced gastrointestinal toxicity by eliminating gut bacterial β-glucuronidase activity. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, G.; Smith, M.; Hoeschen, A.L.; Wilson, J.A.; Kennedy, J.; Abramson, M.; Cao, Q.; El Jurdi, N.; MacMillan, M.L.; Weisdorf, D.J.; et al. Shotgun sequencing of the faecal microbiome to predict response to steroids in patients with lower gastrointestinal acute graft-versus-host disease: An exploratory analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, e69–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertzoni, M.; Kersten, E.; van der Mey, D.; Muenster, U.; Reppas, C. Evaluating the clinical importance of bacterial degradation of therapeutic agents in the lower intestine of adults using adult fecal material. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 125, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yadav, V.; Smart, A.L.; Tajiri, S.; Basit, A.W. Stability of peptide drugs in the colon. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 78, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T.; Westblade, L.F.; Iqbal, F.; Taylor, M.R.; Chung, A.; Satlin, M.J.; Magruder, M.; Edusei, E.; Albakry, S.; Botticelli, B.; et al. Gut microbiota profiles and fecal beta-glucuronidase activity in kidney transplant recipients with and without post-transplant diarrhea. Clin. Transpl. 2021, 35, e14260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, R.; Guo, P.; Li, P.; Huang, X.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effects of intestinal microbiota on pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine a in rats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1032290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, J.; Yang, Z.; Miao, Y. High-throughput sequencing analysis of differences in intestinal microflora between ulcerative colitis patients with different glucocorticoid response types. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Cox, I.J.; Nittono, H.; Takei, H.; White, M.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Heuman, D.M.; Gilles, H.C.; et al. Alterations in gut microbial function following liver transplant. Liver Transpl. 2018, 24, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.; Pasini, E.; Copeland, J.; Angeli, M.; Husain, S.; Kumar, D.; Renner, E.; Teterina, A.; Allard, J.; Guttman, D.S.; et al. Impact of Immunosuppression on the Metagenomic Composition of the Intestinal Microbiome: A Systems Biology Approach to Post-Transplant Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitto, A.; Ito, T.K.; Pineda, V.V.; LeTexier, N.J.; Huang, H.Z.; Sutlief, E.; Tung, H.; Vizzini, N.; Chen, B.; Smith, K.; et al. Transient rapamycin treatment can increase lifespan and healthspan in middle-aged mice. Elife 2016, 5, e16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, A.M.D.L.; de Lima Rosa, G.; Müller Guzzo, E.F.; Padilha, R.B.; Costa da Silva, R.; Silveira, A.K.; de Lima Morales, D.; Conci de Araujo, M.; Fonseca Moreira, J.C.; Barth, A.L.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation by prednisolone in a rat kindling model of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-induced seizure. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 163, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannigan, K.L.; Taylor, M.R.; Pereira, S.K.; Rodriguez-Arguello, J.; Moffat, A.W.; Alston, L.; Wang, X.; Poon, K.K.; Beck, P.L.; Rioux, K.P.; et al. An intact microbiota is required for the gastrointestinal toxicity of the immunosuppressant mycophenolate mofetil. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2018, 37, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ling, Q.; Wu, L.; Wu, P.; Tang, R.; Xu, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; et al. Antibiotics-mediated intestinal microbiome perturbation aggravates tacrolimus-induced glucose disorders in mice. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wu, L.; Ling, Q.; Wu, P.; Zhang, C.; Jia, L.; Weng, H.; Wang, B. Intestinal Dysbiosis Correlates with Sirolimus-induced Metabolic Disorders in Mice. Transplantation 2021, 105, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Kong, X.; Shao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, C. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota Associated with Promoting Efficacy of Prednisone by Bromofuranone in MRL/lpr Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurez, V.; Dao, V.; Liu, A.; Pandeswara, S.; Gelfond, J.; Sun, L.; Bergman, M.; Orihuela, C.J.; Galvan, V.; Padrón, Á.; et al. Chronic mTOR inhibition in mice with rapamycin alters T, B, myeloid, and innate lymphoid cells and gut flora and prolongs life of immune-deficient mice. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Ren, Z.; Lu, H.; He, N.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Structural shifts in the intestinal microbiota of rats treated with cyclosporine A after orthotropic liver transplantation. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.W.; Ren, Z.G.; Lu, H.F.; Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Cui, G.Y.; Jia, J.J.; Xie, H.Y.; Chen, X.H.; He, Y.; et al. Optimal immunosuppressor induces stable gut microbiota after liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gong, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Butyric acid normalizes hyperglycemia caused by the tacrolimus-induced gut microbiota. Am. J. Transpl. 2020, 20, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.J.; Lee, J.; Shin, N.R.; Kim, M.S.; Hyun, D.W.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, P.S.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, K.; Watanabe, T.; Minaga, K.; Hara, A.; Sekai, I.; Otsuka, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Park, A.M.; Kudo, M. Gut microbiome alterations in type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis after induction of remission by prednisolone. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 202, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Feng, D.; Law, H.K.; Qu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, G.H.; Huang, W.Y. Compositional alterations of gut microbiota in children with primary nephrotic syndrome after initial therapy. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lähteenmäki, K.; Wacklin, P.; Taskinen, M.; Tuovinen, E.; Lohi, O.; Partanen, J.; Mättö, J.; Vettenranta, K. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation induces severe dysbiosis in intestinal microbiota of paediatric ALL patients. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017, 52, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Llorenç, V.; Nakamura, Y.; Metea, C.; Karstens, L.; Molins, B.; Lin, P. Antimetabolite Drugs Exhibit Distinctive Immunomodulatory Mechanisms and Effects on the Intestinal Microbiota in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Ghazi, P.C.; Starchenko, A.; Tovaglieri, A.; Baldwin, K.R.; Poulin, E.J.; Gierut, J.J.; Genetti, C.; Yajnik, V.; Breault, D.T.; et al. The colonic epithelium plays an active role in promoting colitis by shaping the tissue cytokine profile. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2002417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigneur, B.; Lepage, P.; Mondot, S.; Schmitz, J.; Goulet, O.; Doré, J.; Ruemmele, F.M. Mucosal Healing and Bacterial Composition in Response to Enteral Nutrition Vs Steroid-based Induction Therapy-A Randomised Prospective Clinical Trial in Children with Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Xia, Z.; Deng, J.; Jiao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J. Glucorticoid-induced obesity individuals have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Biofactors 2019, 45, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Jiménez, R.; Moleón, J.; González-Correa, C.; Romero, M.; Yang, T.; Raizada, M.K.; et al. Mycophenolate Improves Brain-Gut Axis Inducing Remodeling of Gut Microbiota in DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitación, N.; Toral, M.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Jiménez, R.; Romero, M.; Duarte, J. Mycophenolate mediated remodeling of gut microbiota and improvement of gut-brain axis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepper, J.D.; Collins, F.; Rios-Arce, N.D.; Kang, H.J.; Schaefer, L.; Gardinier, J.D.; Raghuvanshi, R.; Quinn, R.A.; Britton, R.; Parameswaran, N.; et al. Involvement of the gut microbiota and barrier function in Glucocorticoid-Induced osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraj, S.; Copeland, J.K.; Malik, A.; Pasini, E.; Angeli, M.; Azhie, A.; Husain, S.; Kumar, D.; Allard, J.; Guttman, D.S.; et al. Characterization and predictive functional profiles on metagenomic 16S rRNA data of liver transplant recipients: A longitudinal study. Clin. Transpl. 2022, 36, e14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarte, J.C.; Douwes, R.M.; Hu, S.; Vich Vila, A.; Eisenga, M.F.; van Londen, M.; Gomes-Neto, A.W.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Bakker, S.J.L. Characteristics and Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiome in Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourret, J.; Willing, B.P.; Dion, S.; MacPherson, J.; Denamur, E.; Finlay, B.B. Immunosuppressive Treatment Alters Secretion of Ileal Antimicrobial Peptides and Gut Microbiota, and Favors Subsequent Colonization by Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Transplantation 2017, 101, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; Bao, J.; He, Z. Gut microbiota mediated the therapeutic efficacies and the side effects of prednisone in the treatment of MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, C.; He, D.; Jiang, N.; Bai, Y.; Xin, Y. Rapamycin and MCC950 modified gut microbiota in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse by brain gut axis. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Tang, H.; Jiao, W.; Zeng, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Mukherjee, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Immunosuppressive effect of the gut microbiome altered by high-dose tacrolimus in mice. Am. J. Transpl. 2018, 18, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, D.; Law, H.K.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, G.H.; Huang, W.Y.; Kang, Y. Integrative Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites in Rats after Prednisone Treatment. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0065021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Park, H.; Taborda, C.C.; Gordillo, C.; Mapara, M.Y.; Assal, A.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Reshef, R. Antibiotic Exposure, Not Alloreactivity, Is the Major Driver of Microbiome Changes in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.S.; Hittle, L.; Xiong, Y.; Saxena, V.; Smyth, E.M.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wagner, C.; Fricke, W.F.; Simon, T.; et al. Gut microbiota-dependent modulation of innate immunity and lymph node remodeling affects cardiac allograft outcomes. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, B.J.; Johnson, C.P.; Edmiston, C.E.; Hlava, M.A.; Moore, G.H.; Roza, A.M.; Telford, G.L.; Adams, M.B. Small bowel transplantation promotes bacterial overgrowth and translocation. J. Surg. Res. 1991, 51, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Ding, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhou, J.Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, D.; Xu, M.; Shi, G.; et al. Total flavone of Abelmoschus Manihot improves colitis by promoting the growth of Akkermansia in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Maghzi, A.H.; Liu, S.; Tankou, S.K.; Dhang, F.H.; Willocq, V.; Song, A.; Wasén, C.; Tauhid, S.; Chu, R.; et al. Gut Microbiome in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Li, P.; Xu, L.; Peng, Z.; Xiang, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ji, G.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Step-up fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) strategy. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizman, N.; Hsu, J.; Bergerot, P.G.; Gillece, J.D.; Folkerts, M.; Reining, L.; Trent, J.; Highlander, S.K.; Pal, S.K. Randomized trial assessing impact of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiome and clinical outcome from targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, C.S.; Kwak, M.J.; Han, D.S.; Lee, A.R.; Park, D.I.; Yang, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.F. Does the intestinal microbial community of Korean Crohn’s disease patients differ from that of western patients? BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geunes-Boyer, S.; Heitman, J.; Wright, J.R.; Steinbach, W.J. Surfactant protein D binding to Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae is calcineurin-sensitive. Med. Mycol. 2010, 48, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gianotti, L.; Alexander, J.W.; Fukushima, R.; Pyles, T. Steroid therapy can modulate gut barrier function, host defense, and survival in thermally injured mice. J. Surg. Res. 1996, 62, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, C.M.; Childs-Kean, L.M.; Naziruddin, Z.; Howell, C.K. The alteration of the gut microbiome by immunosuppressive agents used in solid organ transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ai, F.; Ji, C.; Tu, P.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, F.; Yu, T. A Rapid Screening Method of Candidate Probiotics for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and the Anti-inflammatory Effect of the Selected Strain Bacillus smithii XY1. Front Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardou, M.; Provost, Q.; Brossier, C.; Pinault, É.; Sauvage, F.L.; Lawson, R. Alteration of the gut microbiome in mycophenolate-induced enteropathy: Impacts on the profile of short-chain fatty acids in a mouse model. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenq, R.R.; Ubeda, C.; Taur, Y.; Menezes, C.C.; Khanin, R.; Dudakov, J.A.; Liu, C.; West, M.L.; Singer, N.V.; Equinda, M.J.; et al. Regulation of intestinal inflammation by microbiota following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaysen, A.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Muller, E.E.L.; Narayanasamy, S.; Wampach, L.; Laczny, C.C.; Graf, N.; Simon, A.; Franke, K.; Bittenbring, J.; et al. Integrated meta-omic analyses of the gastrointestinal tract microbiome in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transl. Res. 2017, 186, 79–94.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H.; Onyeaghala, G.C.; Rashidi, A.; Holtan, S.G.; Khoruts, A.; Israni, A.; Jacobson, P.A.; Staley, C. Fecal β-glucuronidase activity differs between hematopoietic cell and kidney transplantation and a possible mechanism for disparate dose requirements. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L.; Kwok, S.K. Lactobacillus acidophilus Supplementation Exerts a Synergistic Effect on Tacrolimus Efficacy by Modulating Th17/Treg Balance in Lupus-Prone Mice via the SIGNR3 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Liang, X.; Wei, X.H.; Chen, F.L.; Tang, Q.F.; Tan, X.M. Comparative metabolism of the eight main bioactive ingredients of gegen qinlian decoction by the intestinal flora of diarrhoeal and healthy piglets. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; et al. Characteristics in gut microbiome is associated with chemotherapy-induced pneumonia in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, J. Lactobacillus improves the effects of prednisone on autoimmune hepatitis via gut microbiota-mediated follicular helper T cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddaus, M.A.; Wells, C.L.; Platt, J.L.; Condie, R.M.; Simmons, R.L. Effect of T cell modulation on the translocation of bacteria from the gut and mesenteric lymph node. Ann. Surg. 1988, 207, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraki, S.; Bafaloukos, D.; Chatzinikolaou, I.; Datseris, G.; Samonis, G. Gut colonization of mice by yeast: Effects of methylprednisolone and antibiotics. Hepatogastroenterology 1998, 45, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marazzato, M.; Iannuccelli, C.; Guzzo, M.P.; Nencioni, L.; Lucchino, B.; Radocchia, G.; Gioia, C.; Bonfiglio, G.; Neroni, B.; Guerrieri, F.; et al. Gut Microbiota Structure and Metabolites, Before and After Treatment in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Pilot Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 921675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modena, B.D.; Milam, R.; Harrison, F.; Cheeseman, J.A.; Abecassis, M.M.; Friedewald, J.J.; Kirk, A.D.; Salomon, D.R. Changes in Urinary Microbiome Populations Correlate in Kidney Transplants with Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy Documented in Early Surveillance Biopsies. Am. J. Transpl. 2017, 17, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Guerrero-Araya, E.; Cortés-Tapia, C.; Plaza-Garrido, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Paredes-Sabja, D. Comprehensive genome analyses of Sellimonas intestinalis, a potential biomarker of homeostasis gut recovery. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, C.; O’Sullivan, Ó.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Connor, P.M.; Shanahan, F.; Cullen, A.; Rea, M.C.; Hill, C.; Coulter, I.; Ross, R.P. Encapsulated cyclosporine does not change the composition of the human microbiota when assessed ex vivo and in vivo. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raineri, S.; Sherriff, J.A.; Thompson, K.S.J.; Jones, H.; Pfluger, P.T.; Ilott, N.E.; Mellor, J. Pharmacologically induced weight loss is associated with distinct gut microbiome changes in obese rats. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvig, D.; Piceno, Y.; Terdiman, J.; Zydek, M.; Umetsu, S.E.; Balitzer, D.; Fadrosh, D.; Lynch, K.; Lamere, B.; Leith, T.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Pouchitis: Clinical; Endoscopic; Histologic; and Microbiota Results from a Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.B.; Allegretti, A.S.; Nigwekar, S.U.; Kalim, S.; Zhao, S.; Lelouvier, B.; Servant, F.; Serena, G.; Thadhani, R.I.; Raj, D.S.; et al. Blood Microbiome Profile in CKD: A Pilot Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Lin, H.C. Autophagy counters LPS-mediated suppression of lysozyme. Innate Immun. 2017, 23, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Babak, S.D.; Shekhar, T.; Smith, A.M.; Giaever, G.; Nislow, C.; Cowen, L.E. A novel calcineurin-independent activity of cyclosporin A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, A.Y.; Karau, M.J.; Clark, C.R.; Patel, R.; Rajagopalan, G. The impact of tacrolimus on the immunopathogenesis of staphylococcal enterotoxin-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome and pneumonia. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossen, J.M.; Guiot, H.F.; Lankester, A.C.; Vossen, A.C.; Bredius, R.G.; Wolterbeek, R.; Bakker, H.D.; Heidt, P.J. Complete suppression of the gut microbiome prevents acute graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, D.; Liang, S. Identification and metabolomic analysis of chemical elicitors for tacrolimus accumulation in Streptomyces tsukubaensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7541–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaza, G.; Dalla Gassa, A.; Felis, G.; Granata, S.; Torriani, S.; Lupo, A. Impact of maintenance immunosuppressive therapy on the fecal microbiome of renal transplant recipients: Comparison between an everolimus- and a standard tacrolimus-based regimen. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Nardini, C. A method for automated pathogenic content estimation with application to rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, S.M.; Gonzales, C.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Momper, J.D.; Ma, J.D. Contribution of the Gut Microbiome to Drug Disposition, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Variability. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Huang, W.; Jin, M.; Gao, Z. The influence of the gut microbiota on the bioavailability of oral drugs. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1789–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsila, T.; Balasopoulou, A.; Tsagaraki, I.; Patrinos, G.P. Pharmacomicrobiomics informs clinical pharmacogenomics. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Siddiqui, Z.A.; Musharraf, S.G.; Nawaz, S.A.; Atta-Ur-Rahman. Microbial transformation of prednisone. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.S.; El-Hadi, A.A.; Abo-Zied, K.M. Biotransformation of prednisolone to hydroxy derivatives by Penicillium aurantiacum. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2017, 35, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Wu, M.; Zhang, R.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. Transformation of prednisolone to a 20β-hydroxy prednisolone compound by Streptomyces roseochromogenes TS79. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, L.K.; Doden, H.L.; Ridlon, J.M. Gut feelings about bacterial steroid-17, 20-desmolase. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 525, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabarro, J.D.; Moxham, A.; Walker, G.; Slater, J.D. Rectal hydrocortisone. Br. Med. J. 1957, 2, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, A.P.; Slater, J.D.; Kellie, A.E.; Holliday, M.E. Urinary excretion of 17-ketosteroids following rectal infusion of cortisol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1959, 19, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöneshöfer, M.; Weber, B.; Nigam, S. Increased urinary excretion of free 20 alpha- and 20 beta-dihydrocortisol in a hypercortisolemic but hypocortisoluric patient with Cushing’s disease. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornel, L.; Miyabo, S.; Saito, Z.; Cha, R.-W.; Wu, F.-T. Corticosteroids in human blood. VIII. Cortisol metabolites in plasma of normotensive subjects and patients with essential hypertension. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1975, 40, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.A.; Beck, K.R.; Nixon, M.; Homer, N.Z.M.; Crawford, A.A.; Melchers, D.; Houtman, R.; Meijer, O.C.; Stomby, A.; Anderson, A.J.; et al. Carbonyl reductase 1 catalyzes 20β-reduction of glucocorticoids, modulating receptor activation and metabolic complications of obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, S.; Bouvattier, C.; Fagart, J.; Martinerie, L.; Viengchareun, S.; Pussard, E.; Lombès, M. Interaction between accumulated 21-deoxysteroids and mineralocorticoid signaling in 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E102–E110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullingham, R.E.; Nicholls, A.J.; Kamm, B.R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoons, M.; Naipal, K.A.T.; de Jong, H.; den Hoed, C.M.; de Winter, B.C.M.; Mulder, M.B. Oral antibiotics lower mycophenolate mofetil drug exposure, possibly by interfering with the enterohepatic recirculation: A case series. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2023, 11, e01103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Lee, H.; Edusei, E.; Albakry, S.; Jeong, H.; Lee, J.R. Blood Profiles of Gut Bacterial Tacrolimus Metabolite in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Direct. 2020, 6, e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraeve, A.L.; Haufroid, V.; Loriot, A.; Gatto, L.; Andries, V.; Vereecke, L.; Elens, L.; Bindels, L.B. Gut microbiome modulates tacrolimus pharmacokinetics through the transcriptional regulation of ABCB1. Microbiome 2023, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarre, P.; Loens, C.; Tamzali, Y.; Barrou, B.; Jaisser, F.; Tourret, J. Immunosuppressive therapy after solid organ transplantation and the gut microbiota: Bidirectional interactions with clinical consequences. Am. J. Transpl. 2022, 22, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalhoff, A. Are antibacterial effects of non-antibiotic drugs random or purposeful because of a common evolutionary origin of bacterial and mammalian targets? Infection 2021, 49, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R. Mycophenolic Acid: A one hundred year odyssey from antibiotic to immunosuppressant. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3801–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosio, B. Sperimentate su culture pure di bacilli del carbonchio demonstrarano notevole potere antisettica. CR Acad. Med. Torino 1893, 61, 484. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, D.; Hernandez, J.; Cao, R.; To, K.; Yegiazaryan, A.; Abrahem, R.; Nguyen, T.; Owens, J.; Lambros, M.; Subbian, S.; et al. Antimycobacterial Effects of Everolimus in a Human Granuloma Model. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, D.M.; De Maio, F.; Santarelli, G.; Palucci, I.; Salustri, A.; Bianchetti, G.; Maulucci, G.; Citterio, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Tamburrini, E.; et al. Evaluation of Everolimus Activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using In Vitro Models of Infection. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.P. The antimicrobial activities of cyclosporine, FK506, and rapamycin. Transplantation 1994, 57, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamer, E.G. Immune responses to commensal and environmental microbes. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafuji, H.; Iida, N.; Kitamura, K.; Seishima, J.; Wang, Z.; Yutani, M.; Yoshio, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Honda, M.; et al. Oral Corticosteroids Impair Mucin Production and Alter the Posttransplantation Microbiota in the Gut. Digestion 2022, 103, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena-Garitaonaindia, M.; Arredondo-Amador, M.; Mascaraque, C.; Asensio, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Sánchez de Medina, F. Modulation of intestinal barrier function by glucocorticoids: Lessons from preclinical models. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Rahman, H.; Ahmed, R.; Oellerich, M.; Asif, A.R. Mycophenolic acid mediated disruption of the intestinal epithelial tight junctions. Exp. Cell. Res. 2014, 322, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krych, L.; Hansen, C.H.F.; Hansen, A.K.; van den Berg, F.W.J.; Nielsen, D.S. Quantitatively different, yet qualitatively alike: A meta-analysis of the mouse core gut microbiome with a view towards the human gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis. Model Mech. 2015, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallu, A.; Sharma, S.; Ramezani, A.; Muralidharan, J.; Raj, D. Gut microbiome in chronic kidney disease: Challenges and opportunities. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina Mikusic, N.L.; Kouyoumdzian, N.M.; Choi, M.R. Gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: Evidences and mechanisms that mediate a new communication in the gastrointestinal-renal axis. Pflugers Arch. 2020, 472, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Ishimoto, T.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. The Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 733992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.; Ruff, W.E.; Longbrake, E.E. Influence of immunomodulatory drugs on the gut microbiota. Transl. Res. 2021, 233, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghai Arassi, M.; Zeller, G.; Karcher, N.; Zimmermann, M.; Toenshoff, B. The gut microbiome in solid organ transplantation. Pediatr. Transpl. 2020, 24, e13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Sze, C.; Barbar, T.; Lee, J.R. New insights into the microbiome in kidney transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transpl. 2021, 26, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Stefka, A.T.; Molinero, L.L.; Theriault, B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Sivan, A.S.; Nagler, C.R.; Gajewski, T.F.; et al. The composition of the microbiota modulates allograft rejection. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 126, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, P.L.; Martínez, I.; Sun, Y.; Walter, J.; Peterson, D.A.; Mercer, D.F. Characterization of the Ileal Microbiota in Rejecting and Nonrejecting Recipients of Small Bowel Transplants. Am. J. Transpl. 2012, 12, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, H.; Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, L. Intestinal microbial variation may predict early acute rejection after liver transplantation in rats. Transplantation 2014, 98, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, K.; Manku, S.; Enns, W.; Van Rossum, T.; Bushell, K.; Morin, R.D.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; Choy, J.C. Disruption of the Gut Microbiota with Antibiotics Exacerbates Acute Vascular Rejection. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, C.; Gao, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Dai, C.; Zhang, K.; Shi, B.; Liu, M.; et al. Intestinal microbiota links to allograft stability after lung transplantation: A prospective cohort study. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.S. Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles. Polymers 2023, 15, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.N.; Park, J.H. Local dermal delivery of cyclosporin A, a hydrophobic and high molecular weight drug, using dissolving microneedles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).