Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
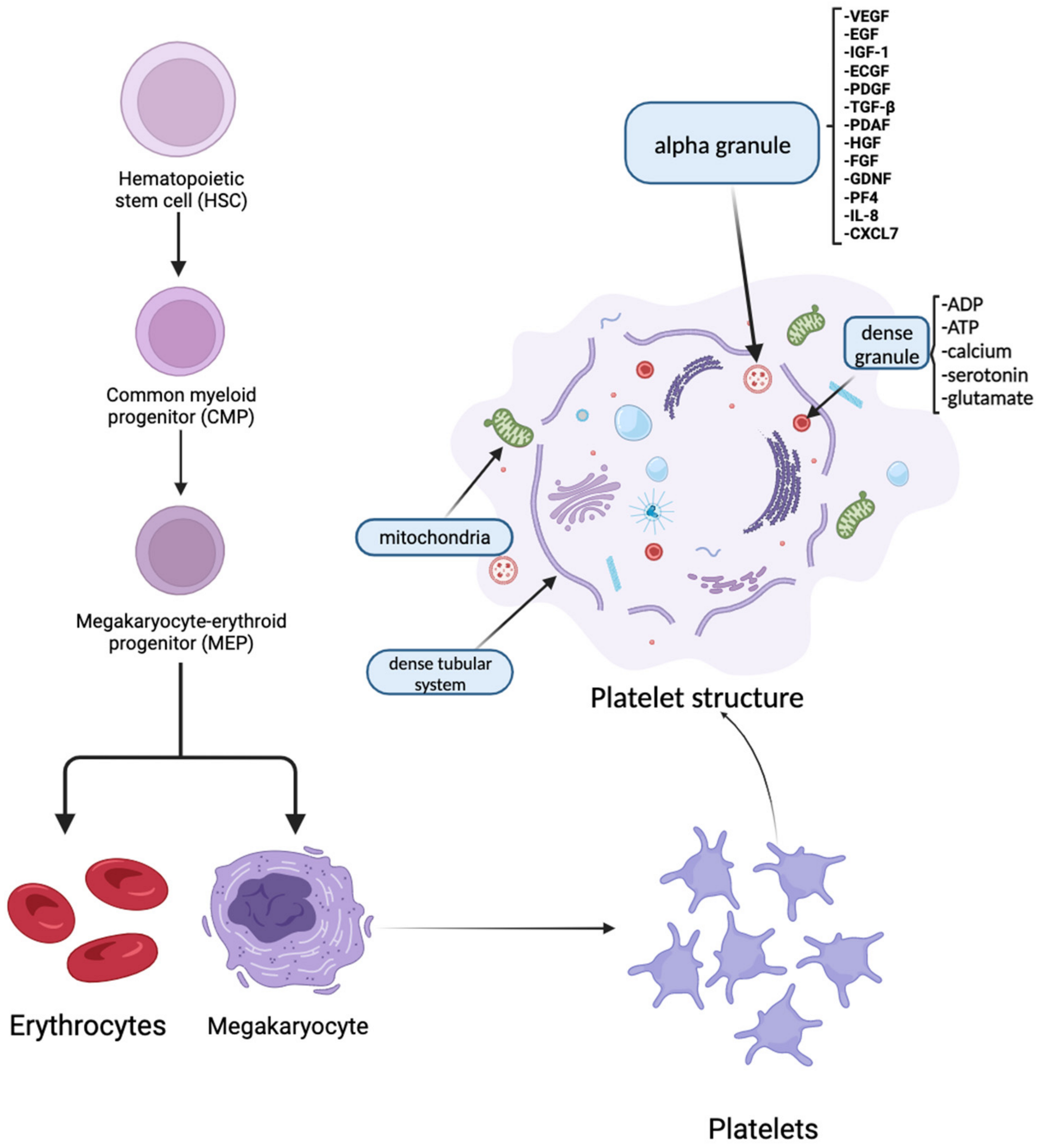
:1. Introduction
2. Wound Healing
3. PRP in the Treatment of Hair Disorders: Androgenetic Alopecia and Alopecia Areata
4. Pigmentary Disorders
4.1. Melasma
4.2. Vitiligo
5. Rejuvenation and Scars
6. Lichen Sclerosus and Other Inflammatory Disorders
6.1. Lichen Sclerosus
6.2. Psoriasis
6.3. Behçet Disease
6.4. Morphea
6.5. Inflammatory Nail Disorders
6.6. Oral Lichen Planus
7. Discussion and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thon, J.N.; Italiano, J.E. Platelets: Production, morphology and ultrastructure. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 210, pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.; van der Sluijs, P. Platelet secretory behaviour: As diverse as the granules… or not? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubkowska, A.; Dolegowska, B.; Banfi, G. Growth factor content in PRP and their applicability in medicine. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26 (Suppl. S1), 3S–22S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Renaud, H.J.; Rapaport, J.A. Platelet-rich Plasma and Cell Therapy: The New Horizon in Hair Loss Treatment. Dermatol. Clin. 2021, 39, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashore, S.; Chouhan, K.; Nanda, S.; Sharma, A. Preparation of platelet-rich plasma: National IADVL PRP taskforce recommendations. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 12 (Suppl. S1), 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-rich plasma: Evidence to support its use. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andia, I.; Abate, M. Platelet-rich plasma: Underlying biology and clinical correlates. Regen. Med. 2013, 8, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesseler, M.J.; Shyam, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Utilities in Alopecia: A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Paliczak, A.; Delgado, D. Evidence-based indications of platelet-rich plasma therapy. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gou, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Qiu, S. Platelet-rich plasma and regenerative dentistry. Aust. Dent. J. 2020, 65, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeling, C.; Heyneman, A.; Hoeksema, H.; Verbelen, J.; Stillaert, F.; Monstrey, S. The use of platelet-rich plasma in plastic surgery: A systematic review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Peng, J.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy in the Treatment of Diseases Associated with Orthopedic Injuries. Tissue Eng. Rev. 2020, 26, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit-Ciećkiewicz, D.; Kołodyńska, A.; Futyma-Gąbka, K.; Grzybowska, M.E.; Gołacki, J.; Futyma, K. Platelet Rich Plasma in Gynecology—Discovering Undiscovered—Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.; Brahs, A.; Dorton, D.; Witfill, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Applications in Medical and Aesthetic Dermatology. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maddheshiya, N.; Srivastava, A.; Rastogi, V.; Shekhar, A.; Sah, N.; Kumar, A. Platelet-rich plasma protein as a therapeutic regimen for oral lichen planus: An evidence-based systematic review. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 14, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria-Angeliki, G.; Konstantinos, K.; Alexandros-Efstratios, K.; Dimitris, R. Platelet-rich plasma as a potential treatment for noncicatricial alopecias. Int. J. Trichology 2015, 7, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A.; Paichitrojjana, A. Platelet Rich Plasma and Its Use in Hair Regrowth: A Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Saita, Y.; Nishio, H.; Ikeda, H.; Takazawa, Y.; Nagao, M.; Takaku, T.; Komatsu, N.; Kaneko, K. Leukocyte concentration and composition in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) influences the growth factor and protease concentrations. J. Orthop. Sci. 2016, 21, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnek, M.; Moreira, H.; Płaczkowska, S.; Barg, E.; Reichert, P.; Królikowska, A. Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Effective Source of Molecules That Modulate Local Immune and Inflammatory Cell Responses. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8059622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayan, S.; Sarvajnamurthy, S.S.; Hurkudli, S.D.; Budamakuntla, L. Autologous platelet rich plasma in pyoderma gangrenosum—Two case reports. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J. Platelets in wound healing and regenerative medicine. Platelets 2018, 29, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Hwang, S.R.; Yoon, I.-S. Advanced Growth Factor Delivery Systems in Wound Management and Skin Regeneration. Molecules 2017, 22, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkini, M.-A.; Kouskoukis, A.-E.; Tripsianis, G.; Rigopoulos, D.; Kouskoukis, K. Study of platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia through an one-year period. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 7, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicharro-Alcántara, D.; Rubio-Zaragoza, M.; Damiá-Giménez, E.; Carrillo-Poveda, J.M.; Cuervo-Serrato, B.; Peláez-Gorrea, P.; Sopena-Juncosa, J.J. Platelet Rich Plasma: New Insights for Cutaneous Wound Healing Management. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devereaux, J.; Nurgali, K.; Kiatos, D.; Sakkal, S.; Apostolopoulos, V. Effects of platelet-rich plasma and platelet-poor plasma on human dermal fibroblasts. Maturitas 2018, 117, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Kumar, S.; Garg, P.; Verma, Y.K. Platelet-rich plasma: A comparative and economical therapy for wound healing and tissue regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023, 24, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-H.; Xiang, L.-J.; Shi, H.-X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.-P.; Cai, P.-T.; Lin, Z.-L.; Lin, B.-B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factors Stimulate Hair Growth through β-Catenin and Shh Expression in C57BL/6 Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 730139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miricescu, D.; Badoiu, S.C.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.-I.; Totan, A.R.; Stefani, C.; Greabu, M. Growth Factors, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Metformin—Promoters of the Wound Healing Process in Burns? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovska, B.; Miladinova, D.; Pejkova, S.; Trajkova, A.; Georgieva, G.; Jovanoski, T.; Jovanovska, K. Platlet-Rich Plasma—Review of Literature. Prilozi 2021, 42, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, N.; Bao, Z.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. A Treatment Combination of IGF and EGF Promotes Hair Growth in the Angora Rabbit. Genes 2020, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bortolin, M.; Taschieri, S.; Ceci, C.; Weinstein, R.L. Antimicrobial properties of platelet-rich preparations. A systematic review of the current pre-clinical evidence. Platelets 2016, 27, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Damien, P.; Chabert, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Cognasse, F.; Garraud, O. Platelets and Infections—Complex Interactions with Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Platelets in inflammation and infection. Platelets 2015, 26, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scurtu, L.G.; Simionescu, O. Soluble Factors and Receptors Involved in Skin Innate Immunity—What Do We Know So Far? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganor, Y.; Besser, M.; Ben-Zakay, N.; Unger, T.; Levite, M. Human T Cells Express a Functional Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor GluR3, and Glutamate by Itself Triggers Integrin-Mediated Adhesion to Laminin and Fibronectin and Chemotactic Migration. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Nouri, M.; Zarrabi, M.; Fatemi, M.J.; Shpichka, A.; Timashev, P.; Hassan, M.; Vosough, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicine: Possible Applications in Management of Burns and Post-Burn Scars: A Review. Cell J. 2023, 25, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-Q.; Du, B.; Dong, H.-J.; Duan, G.-H.; Du, A.-C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.-X.; Shao, W. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Repairs Burn Wound and Reduces Burn Pain in Rats. J. Burn. Care Res. 2022, 43, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, M.; Kaushik, A. Platelet-rich plasma: The journey so far! Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Garcovich, S. Systematic Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma Use in Androgenetic Alopecia Compared with Minoxidil®, Finasteride®, and Adult Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jimenez, J.J. Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia Using PRP to Target Dysregulated Mechanisms and Pathways. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 843127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, M.P.; Kealey, T. Effects of EGF on the Morphology and Patterns of DNA Synthesis in Isolated Human Hair Follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, N.; Shin, S.; Song, S.U.; Sung, J.-H. Minoxidil Promotes Hair Growth through Stimulation of Growth Factor Release from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Choi, H.-I.; Choi, D.-K.; Sohn, K.-C.; Im, M.; Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Potential Therapeutic Tool for Promoting Hair Growth. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38 Pt 1, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Cole, J.P.; Cole, M.A.; Garcovich, S.; Bielli, A.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Insalaco, C.; Cervelli, V.; Piva, T. Evaluation of Not-Activated and Activated PRP in Hair Loss Treatment: Role of Growth Factor and Cytokine Concentrations Obtained by Different Collection Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almohanna, H.M.; Ahmed, A.A.; Griggs, J.W.; Tosti, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Alopecia Areata: A Review. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2020, 20, S45–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pixley, J.N.; Cook, M.K.; Singh, R.; Larrondo, J.; McMichael, A.J. A comprehensive review of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of dermatologic disorders. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2023, 34, 2142035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofny, E.R.M.; Abdel-Motaleb, A.A.; Ghazally, A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hussein, M.R.A. Platelet-rich plasma is a useful therapeutic option in melasma. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuknayat, A.; Thami, G.P.; Bhalla, M.; Sandhu, J.K. Autologous intralesional platelet rich plasma improves melasma. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Nishimura, E.K.; Xin, H.; Zhou, A.; Guo, Y.; Dong, L.; Denning, M.F.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Cui, R. Inhibition of PAX3 by TGF-β Modulates Melanocyte Viability. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Park, K.-C. Transforming growth factor-β1 decreases melanin synthesis via delayed extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamea, M.M.; Kamal, D.A.; Donia, A.A.; Hegab, D.S. Comparative study between topical tranexamic acid alone versus its combination with autologous platelet rich plasma for treatment of melasma. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, W.J.; Bang, S.H.; Min, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.W.; Chang, S.E. Epidermal Growth Factor and Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Attenuate Laser-Induced Melanogenesis. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, R.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Li, L. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Melasma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Arámbula, A.; Torres-Álvarez, B.; Cortés-García, D.; Fuentes-Ahumada, C.; Castanedo-Cázares, J.P. CD4, IL-17, and COX-2 Are Associated with Subclinical Inflammation in Malar Melasma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2015, 37, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Liu, S.-X. Progress in the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Treat Vitiligo and Melasma. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 4, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Z.A.; A El-Ashmawy, A.; A El-Tatawy, R.; A Sallam, F. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the outcome of short-term narrowband–ultraviolet B phototherapy in the treatment of vitiligo: A pilot study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Lin, C.-S.; Hu, S.; Chung, W.-H. Progress in the Use of Platelet-rich Plasma in Aesthetic and Medical Dermatology. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, H. Current art of combination therapy with autologous platelet-rich plasma for stable vitiligo: A meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, R.; Ahmed, N.A.; Darwish, H.M. Combined treatment with fractional carbon dioxide laser, autologous platelet-rich plasma, and narrow band ultraviolet B for vitiligo in different body sites: A prospective, randomized comparative trial. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.A.; Li, M.O. TGF-β: Guardian of T Cell Function. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, E.; Hattier, G.; Wang, J.V.; Saedi, N. Platelet-rich plasma for facial rejuvenation: An early examination. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 38, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, Z.; Alimohamadi, Y.; Janani, M.; Hejazi, P.; Kamali, M.; Goodarzi, A. Platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of scars, to suggest or not to suggest? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 16, 875–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabi, S.; Sundaram, H. The Potential of Topical and Injectable Growth Factors and Cytokines for Skin Rejuvenation. Facial Plast. Surg. 2014, 30, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Lu, Y.; Bi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, N.; Liu, T. Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates senescence-like phenotypes in a cellular photoaging model. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Je, Y.J.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. Can Platelet-rich Plasma Be Used for Skin Rejuvenation? Evaluation of Effects of Platelet-rich Plasma on Human Dermal Fibroblast. Ann. Dermatol. 2011, 23, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Stojanovic, P. Platelet Rich Plasma: A short overview of certain bioactive components. Open Med. 2016, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Cho, J.-W.; Kim, S.-A. Platelet-rich plasma induces increased expression of G1 cell cycle regulators, type I collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Levy, F.M. Autologous platelet concentrates for facial rejuvenation. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2022, 30, e20220020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.L. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Skin Rejuvenation: Facts, Fiction, and Pearls for Practice. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2019, 27, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayzullin, A.; Ignatieva, N.; Zakharkina, O.; Tokarev, M.; Mudryak, D.; Khristidis, Y.; Balyasin, M.; Kurkov, A.; Churbanov, S.; Dyuzheva, T.; et al. Modeling of Old Scars: Histopathological, Biochemical and Thermal Analysis of the Scar Tissue Maturation. Biology 2021, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, R.C.; Ibrahim, O. Utility of platelet-rich plasma in aesthetics. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 40, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalpando, B.K.; Wyles, S.P.; Schaefer, L.A.; Bodiford, K.J.; Bruce, A.J. Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of lichen sclerosus. Plast. Aesthet. Res. 2021, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, C.M.; García, A.C.; Cea, L.d.l.C.; Cuesta, A.B.O. Mid-term symptomatic relief after platelet-rich plasma infiltration in vulvar lichen sclerosus. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, N.; Chan, I.; Neill, S.M.; Hamada, T.; South, A.P.; Wessagowit, V.; Wojnarowska, F.; D’Cruz, D.; Hughes, G.J.; Black, M.M.; et al. Autoantibodies to extracellular matrix protein 1 in lichen sclerosus. Lancet 2003, 362, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krapf, J.M.; Mitchell, L.; A Holton, M.; Goldstein, A.T. Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus: Current Perspectives. Int. J. Womens Health 2020, 12, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.A.; Tan, X.; Macri, C.J.; Goldstein, A.T.; Fu, S.W. Lichen Sclerosus: An autoimmunopathogenic and genomic enigma with emerging genetic and immune targets. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlou, A.; Santegoets, L.A.; van der Meijden, W.I.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Swagemakers, S.M.; van der Spek, P.J.; Ewing, P.C.; van Beurden, M.; Helmerhorst, T.J.; Blok, L.J. An Autoimmune Phenotype in Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus: A Th1 Response and High Levels of MicroRNA-155. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132 Pt 1, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.B.; Park, G.S.; Park, S.S.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, K.J.; Park, E.J. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on proliferation and migration in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Kushida, S.; Ogawa, T.; Kusumoto, K. Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Med Mol. Morphol. 2014, 47, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufir, N.; Queille, S.; Liboutet, M.; Thibaudeau, O.; Bachelier, F.; Delestaing, G.; Balloy, B.; Breuer, J.; Janin, A.; Dubertret, L.; et al. Inactivation of the CDKN2A and the p53 tumour suppressor genes in external genital carcinomas and their precursors. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spekreijse, J.J.; Streng, B.M.; Vermeulen, R.F.; Voss, F.O.; Vermaat, H.; van Beurden, M. The risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma in patients with anogenital lichen sclerosis: A systematic review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 157, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravdhanula, U.; Anbarasu, K.; Verma, V.K.; Beevi, S.S. Clinical efficacy of platelet rich plasma in combination with methotrexate in chronic plaque psoriatic patients. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 29, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldminz, A.; Au, S.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.; Lizzul, P. NF-κB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendinelli, P.; Matteucci, E.; Dogliotti, G.; Corsi, M.M.; Banfi, G.; Maroni, P.; Desiderio, M.A. Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: Mechanisms of NF-κB inhibition via HGF. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.C.; Montalvão, S.A.d.L.; Sachetto, Z.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Characterization of autologous platelet rich plasma (PRP) and its biological effects in patients with Behçet’s Disease. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, S.R.; Di Nicola, M.R.; Bianchi, V.G.; Paolino, G. Adult-Onset Linear Morphea (en coupe de sabre) of the Face Successfully Treated with Photoactivated Low-Temperature Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Valid Therapeutic Option. Medicina 2023, 59, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Khashaba, S.; Elhanfi, A. Morphea patients treated with platelet rich plasma:a pilot study. Zagazig Univ. Med J. 2022, 28, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.; Jakhar, D. Intramatricial platelet-rich plasma therapy: A novel treatment modality in refractory nail disorders. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Krishan, K.; Latif, I.; Sudan, E.; Sultan, J.; Hassan, I. Intra-individual Right-Left Comparative Study of Combined Therapy of Intramatricial Triamcinolone and Platelet-Rich Plasma vs. Intramatricial Triamcinolone Only in Lichen Planus-Associated Nail Dystrophy. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2021, 14, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, U.S.; Puri, N.; More, C.B.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, D. Comparative evaluation of effectiveness of autologous platelet rich plasma and intralesional corticosteroids in the management of erosive oral Lichen planus- a clinical study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, A.; Ahmed, W.; Gaafar, S. Efficacy of intralesional injections of platelet-rich plasma in patients with oral lichen planus: A pilot randomized clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohidnezhad, M.; Wruck, C.-J.; Slowik, A.; Kweider, N.; Beckmann, R.; Bayer, A.; Houben, A.; Brandenburg, L.-O.; Varoga, D.; Sönmez, T.-T.; et al. Role of platelet-released growth factors in detoxification of reactive oxygen species in osteoblasts. Bone 2014, 65, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, S.; Hasan, S.; Alqarni, A.; Alam, T.; Kaleem, S.M.; Aziz, S.; Durrani, H.K.; Ajmal, M.; Dawasaz, A.A.; Saeed, S. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy in Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Tuan, R.S. Biology of platelet-rich plasma and its clinical application in cartilage repair. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopoulou, M.; Dai, C.; Tan, X.; Wen, X.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Liu, Y. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Action by Disrupting Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallis, P.; Michalopoulos, E.; Panagouli, E.; Dimou, Z.; Sarri, E.F.; Georgiou, E.; Gkioka, V.; Stavropoulos-Giokas, C. Selection Criteria of Cord Blood Units for Platelet Gel Production: Proposed Directions from Hellenic Cord Blood Bank. Comment on Mallis et al. Short Term Results of Fibrin Gel Obtained from Cord Blood Units: A Preliminary in Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 66. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallis, P.; Gontika, I.; Dimou, Z.; Panagouli, E.; Zoidakis, J.; Makridakis, M.; Vlahou, A.; Georgiou, E.; Gkioka, V.; Stavropoulos-Giokas, C.; et al. Short Term Results of Fibrin Gel Obtained from Cord Blood Units: A Preliminary in Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarkanova, D.; Codinach, M.; Montemurro, T.; Mykhailova, L.; Tancredi, G.; Gallerano, P.; Mallis, P.; Michalopoulos, E.; Wynn, L.; Calvo, J.; et al. Multi-component cord blood banking: A proof-of-concept international exercise. Blood Transfus. 2023, 21, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarkanova, D.; Cox, S.; Hernandez, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Madrigal, A.; Querol, S. Cord Blood Platelet Rich Plasma Derivatives for Clinical Applications in Non-transfusion Medicine. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Rosmarin, D.; Schön, M.P.; Ständer, S.; Boch, K.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M.; Thaci, D.; Schmidt, E.; Cole, C.; et al. Unmet Medical Needs in Chronic, Non-communicable Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 875492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel-Campbell, A.L.; Ismail, A.; Reynolds, K.A.; Poon, E.; Serrano, L.; Grushchak, S.; Farid, C.; West, D.P.; Alam, M. A systematic review of the safety and effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hunt, C.; Morrow, A.S.; Urtecho, M.; Amin, M.; Shah, S.; Hasan, B.; Abd-Rabu, R.; Ashmore, Z.; et al. The Effectiveness and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognia, J.L. (Ed.) Dermatology: Expert Consult, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pakhomova, E.E.; Smirnova, I.O. Comparative Evaluation of the Clinical Efficacy of PRP-Therapy, Minoxidil, and Their Combination with Immunohistochemical Study of the Dynamics of Cell Proliferation in the Treatment of Men with Androgenetic Alopecia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, M.S.; Kumar, A.S.; Kirit, R.; Konathan, R.; Sivamani, R.K. Systematic review of the use of platelet-rich plasma in aesthetic dermatology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoz, M.T.; Mohamed, D.A.; Ibrahim, Z.A.; Hassan, G.F.R. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of platelet rich plasma injection in treatment of rosacea. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijaya, M.; Lee, G.; Fischer, G. Quality of life of women with untreated vulval lichen sclerosus assessed with vulval quality of life index (VQLI). Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabona, F.; Gambelli, I.; Casabona, F.; Santi, P.; Santori, G.; Baldelli, I. Autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in chronic penile lichen sclerosus: The impact on tissue repair and patient quality of life. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, S.; Elsensohn, A.N.; Mauskar, M.M.; Kraus, C.N. Plasma cell vulvitis: A systematic review. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2021, 7, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.J.; Conde, L.V.; Robles, R.C.; Gomez, J.G.; Díaz, V.M.; Rodriguez, O.P.; Pérez-González, Y.C. Zoon Vulvitis Treated Successfully with Platelet-Rich Plasma: First Case Reported. J. Low. Genit. Tract Dis. 2017, 21, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oli, P.; Adhikari, H.; Thapa, D.P. Plasma Cell Vulvitis Treated with Platelet-rich Plasma: A Case Report. J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2022, 60, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranum, A.B.; Pearson, D.R.M. The impact of genital lichen sclerosus and lichen planus on quality of life: A review. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2022, 8, e042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vladulescu, D.; Scurtu, L.G.; Simionescu, A.A.; Scurtu, F.; Popescu, M.I.; Simionescu, O. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010007
Vladulescu D, Scurtu LG, Simionescu AA, Scurtu F, Popescu MI, Simionescu O. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleVladulescu, Denisa, Lucian G. Scurtu, Anca Angela Simionescu, Francesca Scurtu, Marco I. Popescu, and Olga Simionescu. 2024. "Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010007
APA StyleVladulescu, D., Scurtu, L. G., Simionescu, A. A., Scurtu, F., Popescu, M. I., & Simionescu, O. (2024). Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines, 12(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010007




