Abstract
Background/Objectives: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI), characterized by irreversible heart muscle damage and impaired cardiac function caused by myocardial ischemia, is a leading cause of global mortality. The damage associated with reperfusion, particularly mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, has emerged as a crucial factor in the pathogenesis of cardiac diseases, leading to the recognition of mitochondrial proteins as potential markers for myocardial damage. This study aimed to identify differentially expressed proteins based on the type of cardiac injury, in particular those with and without reperfusion. Methods: Male C57Bl/6J mice were either left untreated, sham-operated, received non-reperfused AMI, or reperfused AMI. Twenty-four hours after the procedures, left ventricular (LV) function and morphological changes including infarct size were determined using echocardiography and triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, respectively. In addition, plasma was isolated and subjected to untargeted mass spectrometry and, further on, the ELISA-based validation of candidate proteins. Results: We identified mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 (Ckmt2) as a differentially regulated protein in plasma of mice with reperfused but not non-reperfused AMI. Elevated levels of Ckmt2 were significantly associated with infarct size and impaired LV function following reperfused AMI, suggesting a specific involvement in reperfusion damage. Conclusions: Our study highlights the potential of plasma Ckmt2 as a biomarker for assessing reperfusion injury and its impact on cardiac function and morphology in the acute phase of MI.
1. Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is one of the most common clinical manifestations of cardiovascular disease, representing a primary cause of mortality and affecting more than 3 million people worldwide each year [1]. Myocardial ischemia is caused by a reduction in coronary blood flow and a lack of oxygen supply, resulting in irreversible damage to the heart muscle and impairment of systolic and diastolic function [2,3]. The timely restoration of blood flow to enable reperfusion is widely accepted as the most effective measure to salvage vital myocardium. However, the reperfusion of ischemic tissue itself can induce mitochondrial enlargement and the release of mitochondrial pro-apoptotic components, particularly cytochrome c, into the cytosol, where they may initiate the apoptotic cascade [4,5,6,7]. Mitochondrial reprogramming, dysfunction and damage to its ultrastructure are established hallmarks of a pathologically affected heart [8].
Current technology allows for profiling the plasma proteome and utilizing it in biomarker discovery [9]. A higher abundance of mitochondrial proteins indicates multiple cell death-associated conditions, like ischemic stroke [10], prostate cancer [11], intensive interval exercises [12] and MI [13]. This underscores its indispensable contribution to ATP synthesis and respiratory chain performance [14,15]. Mitochondrial stress and dysfunction are strongly implicated in the progression of cardiac diseases, making it an attractive target for therapeutic strategies [16].
This study aimed to identify plasma proteins associated with mitochondrial damage following cardiac ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) damage. We identified candidate proteins and tested differential expression in reperfused and non-reperfused AMI. We further evaluated mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 (Ckmt2) as a reliable and specific marker in the plasma of mice subjected to reperfused versus non-reperfused AMI, as well as in sham-operated controls. Additionally, we investigated the correlations between plasma levels of Ckmt2 and cardiac functions, such as ejection fraction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
Male C57BL/6J wild-type mice were purchased from Janvier Labs (Saint-Berthevin, France). All mice were 10–12 weeks of age at the beginning of the experiments and received standard chow and drinking water ad libitum. Mice were kept in climate-controlled rooms with a 12 h light/dark cycle. All animal experiments were performed according to ARRIVE (Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments) II guidelines and approved by LANUV (North Rhine-Westphalia State Agency for Nature, Environment and Consumer Protection) in accordance with the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and other Scientific Purposes (License Approval Numbers: 81-02.04.2020.A225).
2.2. Induction of Reperfused AMI
After general anesthesia under ventilation at a respiratory volume of 0.2–0.25 mL and a respiratory rate of 140 breaths per minute with isoflurane (3%) and oxygenated air (30%), mice underwent either sham surgery or a 45 min occlusion of the LAD to induce AMI, as previously described [17]. Following 45 min of ischemia controlled by visual inspections and changes in the electrocardiogram with the regular monitoring of body temperature (37 °C), the occlusion was resolved and the myocardium reperfused at various time points. Animals received buprenorphine (0.1 mg/kg body weight) subcutaneously.
2.3. Induction of Non-Reperfused AMI
After general anesthesia with ketamine and xylazine and ventilation at a respiratory volume of 0.2–0.25 mL and a respiratory rate of 140 breaths per minute with isoflurane (3%) and oxygenated air with 30% oxygen, mice underwent permanent occlusion of the LAD to induce AMI, as previously described [18]. Successful ligation was controlled by the occurrence of a characteristic ST-elevation in the electrocardiogram. Animals received buprenorphine (0.1 mg/kg body weight) subcutaneously and were controlled for further experiments until sacrifice. Another difference to the reperfused AMI model was the immediate closure of the chest after the control of the successful ligation of the LAD.
2.4. Plasma Protein Analysis via ELISA
CKMT2 measurements were conducted using murine plasma samples collected one day after the ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) operation. Plasma specimens were isolated by centrifuging EDTA blood for 15 min at 1000× g and promptly frozen and stored at −80 °C until analysis, with a maximum storage duration of six months before analysis. CKMT2 quantification was carried out following the manufacturer’s instructions using a CKMT2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Abbexa, Cambridge, UK, abx529771).
2.5. Echocardiography
A Fujifilm Visualsonics Vevo 3100 Ultra-High-Frequency Imaging Platform (18–38 MHz linear array micro scan transducer; Visual Sonics, Toronto, ON, Canada) was used to acquire cardiac images and perform all functional analyses. Mice were anesthetized with 1.5–2% isoflurane and placed on a heated, bench-mounted adjustable rail system with constant monitoring of their electrocardiogram, respiratory rate, heart rate and body temperature. A chemical hair remover was used to scrape off the fur from the chest of mice to improve cardiac image quality. Imaging was performed along the parasternal long axis. Cardiac parameters such as the LV chamber volume in EDV and ESV were measured in B-Mode using the Vevo LV-Trace function and strain. SV, EF and cardiac output (CO) were calculated with EDV and ESV. Imaging was performed on untreated mice prior to surgery and at 24 h post-surgery.
2.6. Determination of Infarct and Scar Size with TTC
Hearts were removed quickly and transferred to cold, isotonic 0.9% saline solution (Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg, Germany) supplemented with 1 mL heparin (5000 I.E.) (B. Braun, Melsungen, Germany). Subsequently, Evans blue dye solution (1% in PBS; Merck, Taufkirchen, Germany) was injected into the aorta through to the myocardium to delineate the ischemic AAR from the non-ischemic area. Stained hearts were stored at −20 °C for 1 h. Hearts were sliced (1 mm) in series along the long axis, weighed and incubated in TTC solution (1%) for 5–7 min at 37 °C to allow for the identification of viable and dead myocardium within the AAR. The infarct and viable area, as well as the AAR, were assessed by independent evaluators blinded to the experimental protocol using computer-assisted planimetry, taking the slice weights into account. The infarct area is expressed as a ratio of the dead area (TTC-negative) of AAR.
2.7. Mass Spectrometry
A pooled master mix of the respective lysates was used to generate a spectral library for the following experiments by data independent acquisition. Therefore, peptides dissolved in 10 mM ammonium acetate/0.4 mM formiate (pH 8.0) were separated on a C18 RP chromatography column. Peptides were fractionated at a flow rate of 12.5 μL/min with the following gradient with solvent B (84% (v/v) acetonitrile in 10 mM ammonium acetate, 0.4 mM formiate, pH 8.0): 3–10% for 10 min, 10–25% for 35 min, 25–40% for 20 min, 40–95% for 10 min, 95% for 5 min and 20 min equilibration at 3%. Fractionation was accomplished in 60 s intervals, concatenating each sample into 6 fractions.
For the generation of a spectral library, all lyophilized pH 8 derived fractions were dissolved in 0.1% (v/v) TFA with an appropriate amount of Biognosys Indexed Retention Time (iRT) kit (Bruker Daltonics; Part No:1816351) peptides and analyzed by nano LC-MS/MS using 1 μg, respectively. Samples were loaded on an Ultimate 3000 Rapid Separation Liquid chromatography (RSLC) nano system with a ProFlow flow control device coupled to a Q Exactive HF orbitrap mass spectrometer (both from Thermo Scientific, Darmstadt, Germany). Loaded peptides were concentrated on a trapping column (Acclaim C18 PepMap100, 100 μm, 2 cm) using 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 10 μL/min. For sample separation, a reversed phase column (Acclaim C18 PepMap100, 75 μm 50 cm) using a binary gradient was used (3% solvent B (84% ACN with 0.1% TFA) for 10 min, a linear increase in solvent B to 35% for 90 min, a linear increase in solvent B to 95% for 10 min, followed by a linear decrease in solvent B to 3% for 5 min). MS survey scans were acquired using the following settings: a mass spectrometer was operated in data-dependent acquisition mode (DDA) with full MS scans from 300 to 1500 m/z at a resolution of 60,000. The automatic gain control (AGC) was set to 3 × 106 with a maximum injection time of 120 ms. Most intense ions above a threshold ion count of 1.5 × 104 were selected for fragmentation at a normalized collision energy (nCE) of 27%, following each survey scan. Dynamic exclusion was set to 15 s. Fragment ions were acquired at a resolution of 15,000 with an AGC of 5 × 104 with a maximum injection time of 200 ms. Acquired data were imported into the software Spectronaut (Biognosys, version 14.9.201124.47784), and identification was accomplished using a mouse FASTA database selected from UniProt (www.uniprot.org). Processing settings were set as follows: the enzyme was trypsin; the minimum and maximum peptide lengths were set to 7 and 52, respectively; and missed cleavages were set to 2. Carbamidomethyl for cysteine was set as a fixed modification, and acetyl (Protein N-term) and the oxidation of methionine were set as variable modifications. All settings regarding the library generation including tolerances, identification, filters, iRT calibration and workflow were set to factory defaults.
For the data-independent acquisition (DIA) approach, the same nano LC-MS/MS setup as for the DDA acquisition was used. Full MS scans were acquired from 300 to 900 m/z at a resolution of 60,000. The automatic gain control (AGC) was set to 3 × 106, and the maximum injection time was set to 20 ms. Full MS scans were followed by 15 DIA windows acquired at a resolution 30,000 with an AGC set to 3 × 106 and nCE of 27%. For the analysis of the samples acquired with nano-LC-MS/MS in DIA mode, the data were introduced to the Spectronaut software and analyzed with a library-based search using the above-created spectral library. Search and extraction settings were kept as standard (BGS Factory settings).
2.8. Statistics
Statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software, Version 10, Boston, MA, USA) and R (Version 4.1.2). Mass spectrometry data were presented as mean ± SD. Multiple comparisons were analyzed by paired one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, to identify group differences, or if they were not normal, a distributed Kruskal–Wallis test was performed. The correlation was calculated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Results with p-values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
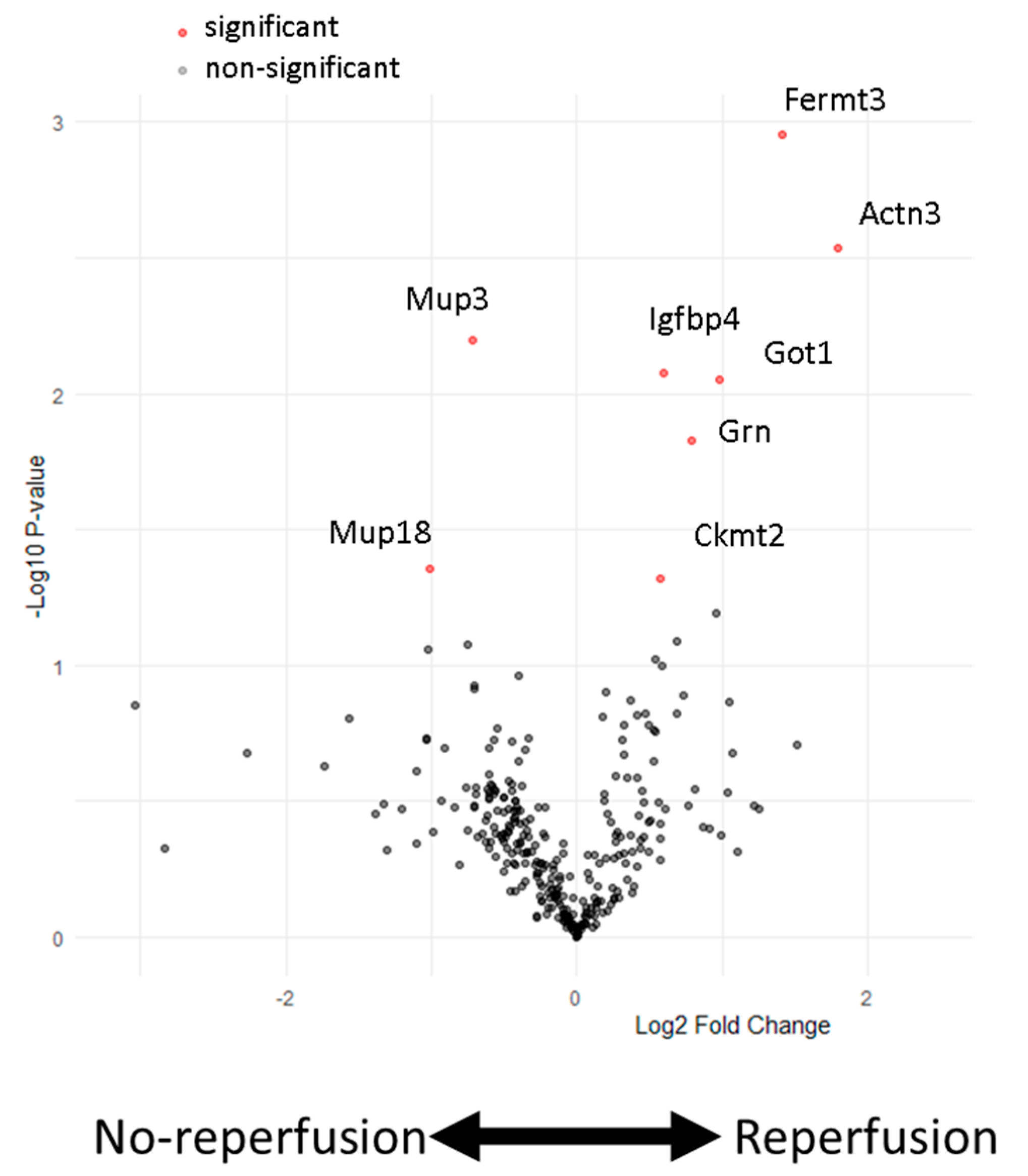
We examined the plasma protein abundance in two different murine models of AMI and their respective controls by untargeted mass spectrometry. The experimental groups included mice that were either untreated or sham-operated (open-chest surgery without coronary ligation) or received non-reperfused AMI (permanent ligation of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery) or reperfused AMI (45 min transient LAD ligation followed by reperfusion). When comparing non-reperfused and reperfused AMI 24 h post induction, we identified eight differentially abundant proteins (Figure 1).
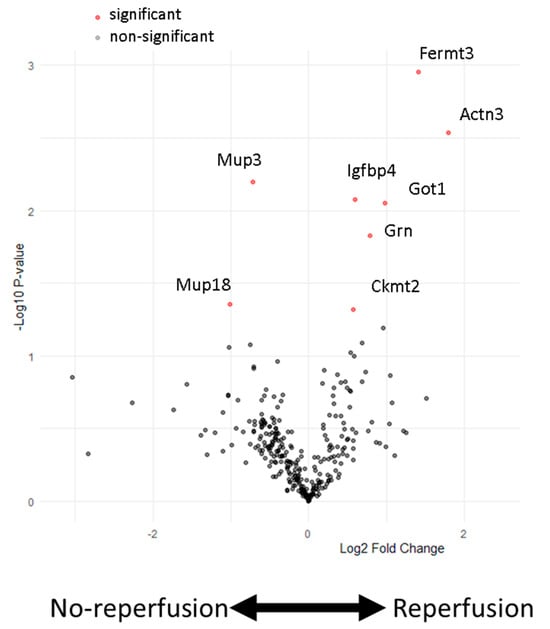
Figure 1.
Protein abundance in the plasma of mice subjected to experimental AMI with and without reperfusion. A volcano plot illustrating the relative abundance (log2 fold changes) versus probability (−log10 p-values) in the plasma of mice that received either non-reperfused or reperfused AMI. Multiple t-test analyses with False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction were used to determine significance (indicated by red dots). Significant proteins are defined as those with a fold change > | ±1.5| and a p-value < 0.05. Two proteins are significantly upregulated in the non-reperfusion group (Mup3, Mup18), while six proteins are significantly upregulated in the reperfusion-operated mice (Ckmt2, Grn, Got1, Igfbp4, Got1, Actn3, Fermt3). n = 5 samples per group.
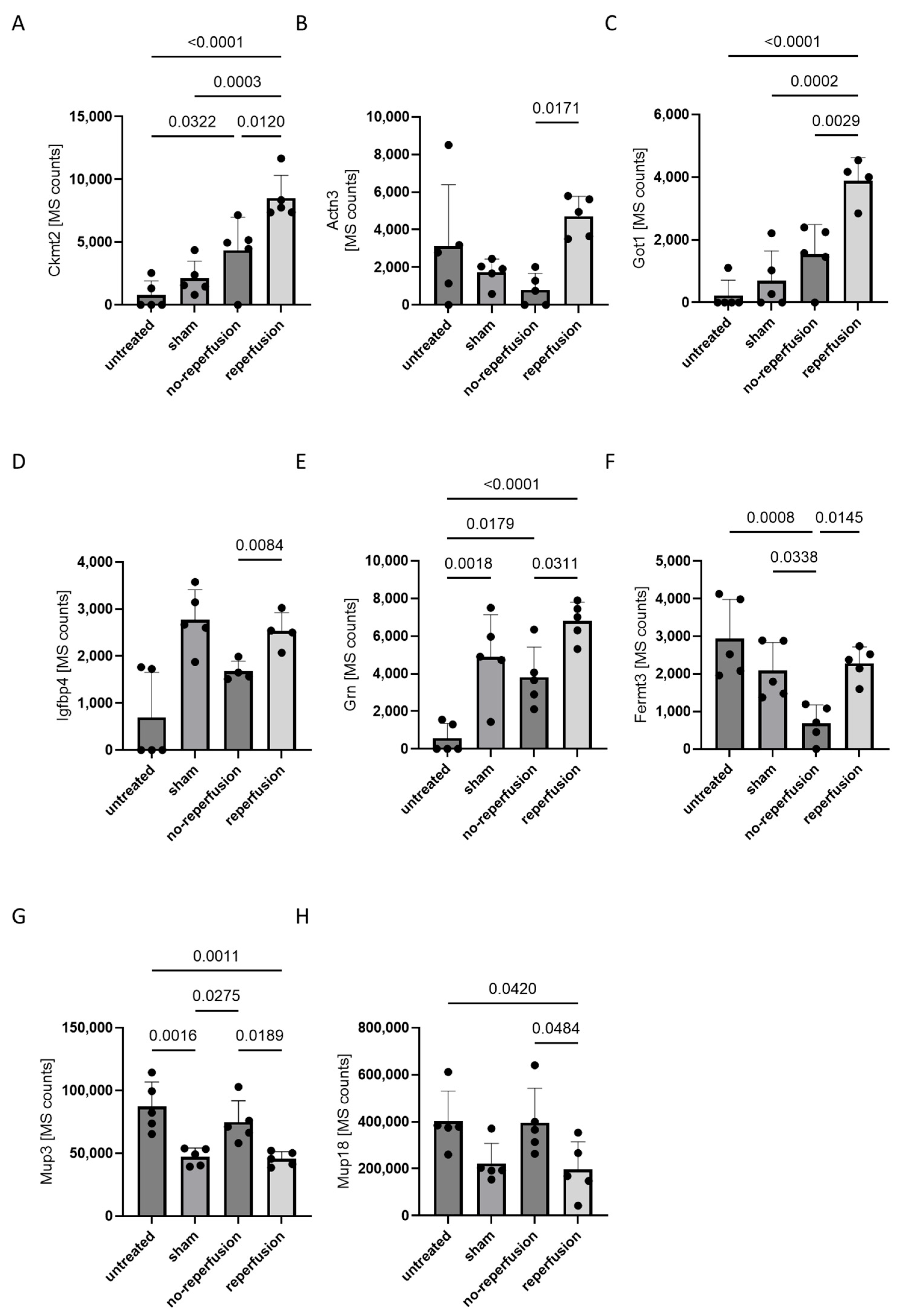
Upregulated in the reperfused AMI group were fermitin family homolog 3 (Fermt3), alpha-actinin-3 (Actn3), insulin-like growth hactor binding protein 4 (Ifgbp4), glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1 (Got1), granulin precursor (Grn) and mitochondrial creatinin kinese 2 (Ckmt2), while those elevated following non-reperfused AMI were Mup3 and Mup18. Although these proteins exhibited changes between non-reperfused AMI and reperfused AMI, only Ckmt2, Actn3 and Got1 were significantly upregulated compared to untreated, sham-operated and non-reperfused AMI animals (Figure 2A–C). Got1 was not detectable in all measured samples of the non-reperfusion and reperfusion groups compered to Ckmt2 and Tctn3, indicating its limitations in reproducibility. The other five proteins exhibited similar changes between the non-reperfused and reperfused AMI groups; however, they did not show significant changes compared to sham-operated animals (Figure 2D–H).
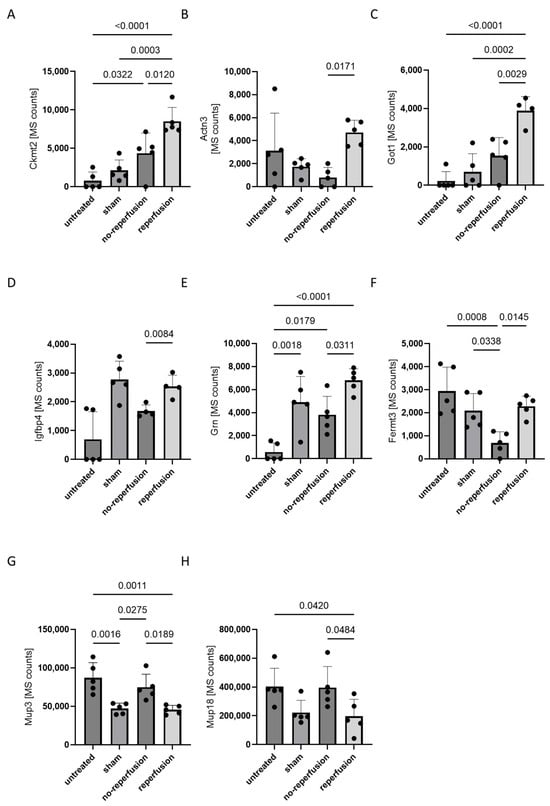
Figure 2.
The mass spectrometric quantification of eight proteins significantly altered in plasma between non-reperfusion- and reperfusion-operated mice and their abundance in the respective controls. Plasma was isolated 24 h after the induction of sham-operated, non-reperfused AMI, and reperfused AMI and in untreated animals and was analyzed by untargeted mass spectrometry. Each bar plot represents the mean value with standard deviation (SD), with individual data points overlaid to show the distribution of measurements. Statistical significance between groups was determined using paired one-way ANOVA for normally distributed data or Kruskal–Wallis test for non-normally distributed data, with a p-value < 0.05 considered significant. Figure panels correspond to specific proteins: (A) Ckmt2, (B) Actn3, (C) Got1, (D) Igfbp4, (E) Grn, (F) Fermt3, (G) Mup3 and (H) Mup18. (A–F) show proteins that are upregulated in reperfusion-operated mice compared to non-reperfusion-operated mice, while (G,H) show proteins that are downregulated. Protein levels that were not detected are valued as 0. n = 5 per group.
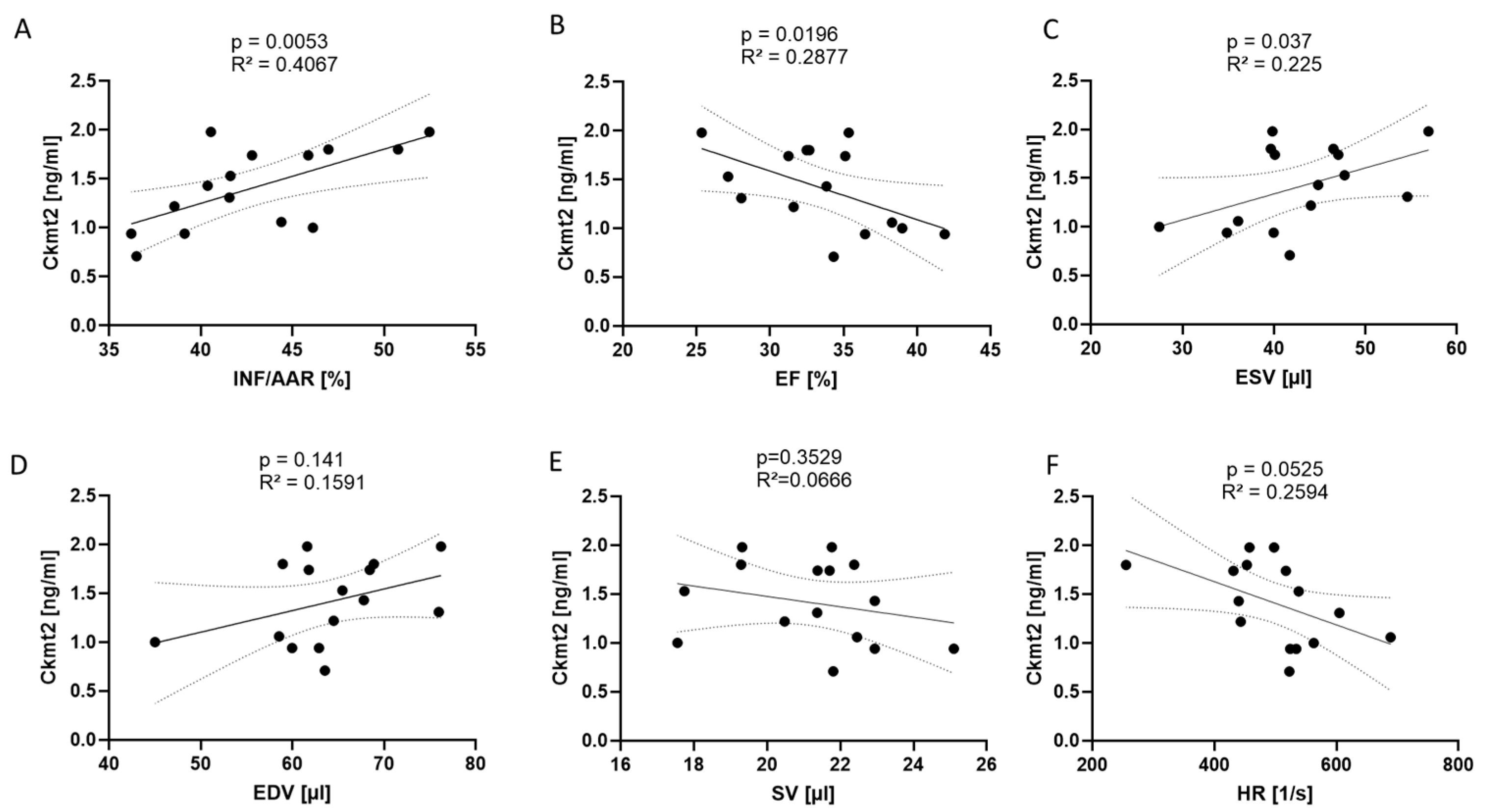
To clarify whether rising levels of Ckmt2 were causally related to the specific effects of reperfusion damage (following 45 min of reperfusion after ischemia), we examined the relationship between these factors, infarct size and parameters of left ventricular (LV) function in a larger group of operated animals. We employed TTC staining to measure the extent of the infarct (INF) compared to the area at risk (AAR) 24 h after performing reperfused AMI. Concurrently, we evaluated LV function by echocardiography in the same animals. The analysis revealed significant associations between Ckmt2 levels in mouse plasma, as evaluated by ELISA, and infarct size determined by TTC staining (Figure 3A). Accordingly, Ckmt2 levels were negatively associated with ejection fraction (EF) 24 h post AMI induction while showing positive correlation with end-systolic volume (ESV) (Figure 3B,C), highlighting impaired systolic LV function in conjunction with larger infarct size. There was no significant correlation observed between end-diastolic volume (EDV), stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR) (Figure 3D–F). The simultaneous increase in Ckmt2 levels and higher ESV and a decline in EF indicates noticeable alterations in systolic heart function corresponding to the extent of tissue injury following an AMI.
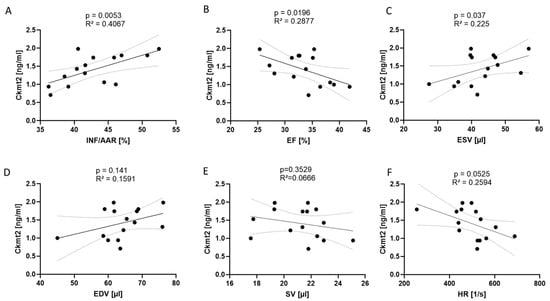
Figure 3.
Ckmt2 correlates to infarct size and left ventricular dysfunction 24 h following reperfused myocardial infarction. (A) Ckmt2 plasma levels detected by ELISA show a significant positive correlation with infarct size (INF) relative to the area at risk (AAR), a negative relationship with (B) ejection fraction (EF) and a positive relationship with (C) end-systolic volume (ESV). (D) No significant correlation is observed between Ckmt2 levels and end-diastolic volume (EDV), (E) stroke volume (SV) or (F) heart rate (HR). Correlations are performed using Pearson’s correlation. Each dot represents an individual measurement from one mouse. Significance is defined as p < 0.05, and correlations are displayed with R2 values. n = 15.
4. Discussion
Despite significant progress in cardiovascular medicine, the mortality rate associated with AMI remains high. While reperfusion of the occluded area is essential to limit myocardial damage, it also introduces its own adverse effects [19,20]. Current pharmacological interventions, like ROS scavengers, have limited success in preventing reperfusion injury, emphasizing the need for a deeper understanding of its pathogenesis to develop more effective treatments [21,22]. The identification of reliable biomarkers for myocardial reperfusion injury is crucial for advancing treatment strategies. Over the past decades, multiple markers for AMI have been identified, including troponin, creatine kinase MB type (CK-MB), and Heart-Type Fatty Acid Binding Protein (hFABP) [23]. However, markers that are specific for myocardial reperfusion injury are limited [24,25]. Potential drivers of myocardial cell death during and after reperfusion include ferroptosis and mitochondrial membrane permeability [26]. While some markers are associated with ROS, new therapeutic targets for cardiac protection (e.g., SLC4A1) are under investigation [27,28]. To better understand the pathophysiology of cardiac reperfusion injury, it is crucial to identify and quantify suitable markers for this phenomenon.
Here, we aimed to identify plasma protein markers in murine experimental models of non-reperfusion and reperfusion, comparing their abundancy with those in untreated and sham-operated mice. Among the eight proteins that were significantly regulated 24 h post AMI (both models), only three showed significant upregulation in the plasma of mice with reperfused AMI compared to non-reperfused AMI, sham-operated, and untreated animals. This overlap indicates that these three proteins may serve as functional biomarkers for distinguishing reperfusion damage, with a reduced likelihood of being false positives.
Cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase (Got1) is associated with heart failure [29] and has been described as a potential marker for cancer [30]. Although Got1 shows significant upregulation in plasma of mice with reperfused AMI compared to non-reperfused AMI and sham-operated mice, its lower detection levels and inconsistent presence across samples suggest its limited reliability as a marker.
Alpha-actinin-3 (Actn3) is essential for the formation of actin and myosin filaments and sarcomeric structures. Specific mutations in this protein lead to decreased long-term survival in patients with chronic heart failure [31]. It is also described as a rapidly altering protein in the early response to myocardial infarction in pigs [32].
Mitochondrial proteins play a critical role in cellular energy production and are intricately linked to heart function [33]. Mitochondria undergo dynamic changes, such as increased calcium influx and oxidative stress, which contribute to the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. This leads to mitochondrial enlargement and the release of pro-apoptotic components into the cytoplasm, initiating the apoptotic cascade [6,7]. Ckmt2 is a pivotal enzyme within the mitochondrial creatine kinase system, which is essential for maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. In the heart, Ckmt2 is responsible for the rapid regeneration of ATP through the phosphocreatine shuttle, which is crucial during periods of high energy demand, such as during or after hypoxia [34]. The disruption of Ckmt2 activity can lead to impaired ATP production, exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction and contributing to cell death during reperfusion injury [35]. Enhancing Ckmt2 expression or activity can protect against myocardial injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury [36]. In experimental models, the overexpression of mitochondrial creatine kinase has been shown to delay the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), a key event in reperfusion-induced cell death. This delay reduces the extent of mitochondrial damage and, consequently, the overall infarct size [35,36]. The correlations observed between Ckmt2 levels and critical clinical outcomes, such as infarct size and left ventricular function, observed in our study underscore its possible value as an indicator of myocardial damage severity [35,36]. Unlike traditional biomarkers, which primarily reflect necrosis, Ckmt2 offers insights into the metabolic and mitochondrial health of cardiac cells, providing a more comprehensive assessment of myocardial injury.
Our study identified plasma protein markers in murine models of non-reperfusion and reperfusion, with Ckmt2 emerging as a particularly promising candidate. To advance Ckmt2 towards clinical application, further validation in clinical cohorts is necessary to establish its efficacy as a biomarker for acute myocardial infarction. Additionally, exploring its potential in guiding targeted therapies aimed at improving patient outcomes could significantly enhance its clinical utility. Beyond cardiovascular disease, investigating Ckmt2’s role in other mitochondria-related conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and certain cancers, may further broaden its relevance and inform future therapeutic strategies.
5. Conclusions
We identified Ckmt2 as a novel marker of reperfused but not non-reperfused AMI, correlating with infarct size and impaired cardiac function, highlighting its potential as a biomarker for reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L., N.G., C.J., D.O., S.P., M.G. and M.K. (Madlen Kaldirim); methodology, Y.R. and A.S.; software, Y.R. and A.L.; validation, A.L., K.S., M.B. (Marcel Benkhoff) and M.B. (Maike Barcik); formal analysis, Y.R.; investigation, A.L., K.S. and M.B. (Marcel Benkhoff); resources, A.L., N.G., M.K. (Malte Kelm), C.J. and A.S.; data curation, A.L., M.B. (Marcel Benkhoff), M.B. (Maike Barcik), L.D. and K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L., N.G., M.B. (Marcel Benkhoff) and K.S.; writing—review and editing, A.L., Y.R., S.P., M.B. (Marcel Benkhoff) and K.S.; visualization, A.L.; supervision, A.L., S.P. and N.G.; project administration, N.G.; funding acquisition, A.L., N.G., A.P., M.K. (Malte Kelm), M.G., A.S. and C.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the following grants: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—Grant No. 236177352-CRC1116; projects B06, B09, B12, S01 to M.K. (Malte Kelm), C.J., N.G., A.P., A.S. and Grant No. 397484323-CRC/TRR259; project A05 to N.G.; the Research Commission of the Medical Faculty of Heinrich-Heine University to A.L (No. 2021-10). M.K. (Madlen Kaldirim) was supported by a GEROK stipend of CRC1116. This work was also supported by the MODS project funded by the program “Profilbildung 2020” (grant no. PROFILNRW-2020-107-A), an initiative of the Ministry of Culture and Science of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia. We acknowledge the support of the Susanne-Bunnenberg-Stiftung at the Düsseldorf Heart Center.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were performed according to ARRIVE (Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments) II guidelines and approved by LANUV (North Rhine-Westphalia State Agency for Nature, Environment and Consumer Protection) in accordance with the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes (License Approval Number: 81-02.04.2020.A225).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD055738.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Murray, C.J.L.; Roth, G.A. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks, 1990–2022. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2350–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, G.W.; Rossi, J.E.; Cannon, C.P. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2017, 389, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechanic, O.J.; Gavin, M.; Grossman, S.A.; Ziegler, K. Acute Myocardial Infarction (Nursing); StatPearls: Saint Petersburg, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lisa, F.; Bernardi, P. Mitochondria and ischemia-reperfusion injury of the heart: Fixing a hole. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 70, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lisa, F.; Canton, M.; Carpi, A.; Kaludercic, N.; Menabo, R.; Menazza, S.; Semenzato, M. Mitochondrial injury and protection in ischemic pre- and postconditioning. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 14, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, D.; Rong, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Z. Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Mechanisms of injury and implications for management (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, L.; Lei, S.; Shi, S.; Chen, C.; Xia, Z. Maslinic Acid Inhibits Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury-Induced Apoptosis and Necroptosis via Promoting Autophagic Flux. DNA Cell Biol. 2022, 41, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, A.; Wu, Y.; Jia, J.; Sun, A.; Zou, Y.; Qian, J.; Ge, J. Cardiac Proteome Profiling in Ischemic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy Mouse Models. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, P.E.; Holdt, L.M.; Teupser, D.; Mann, M. Revisiting biomarker discovery by plasma proteomics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagging, C.; Klasson, S.; Pedersen, A.; Nilsson, S.; Jood, K.; Stanne, T.M.; Jern, C. Investigation of 91 proteins implicated in neurobiological processes identifies multiple candidate plasma biomarkers of stroke outcome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Howard, L.; Wan, J.; Wiggins, E.; Vidal, A.; Cohen, P.; Freedland, S.J. Low circulating levels of the mitochondrial-peptide hormone SHLP2: Novel biomarker for prostate cancer risk. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94900–94909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, J.S.T.; D’Souza, R.F.; Hedges, C.P.; Wan, J.; Berridge, M.V.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Cohen, P.; Hickey, A.J.R.; Mitchell, C.J.; Merry, T.L. High-intensity interval exercise increases humanin, a mitochondrial encoded peptide, in the plasma and muscle of men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenzi, G.; Cosentino, N.; Boeddinghaus, J.; Trinei, M.; Giorgio, M.; Milazzo, V.; Moltrasio, M.; Cardinale, D.; Sandri, M.T.; Veglia, F.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of Circulating Cytochrome c in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolder, M.; Wendt, S.; Wallimann, T. Mitochondrial creatine kinase in contact sites: Interaction with porin and adenine nucleotide translocase, role in permeability transition and sensitivity to oxidative damage. Biol. Signals Recept. 2001, 10, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.G.; Kane, D.A.; Herbst, E.A.; Mukai, K.; Lark, D.S.; Wright, D.C.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Neufer, P.D.; Spriet, L.L.; Holloway, G.P. Mitochondrial creatine kinase activity and phosphate shuttling are acutely regulated by exercise in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 5475–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoples, J.N.; Saraf, A.; Ghazal, N.; Pham, T.T.; Kwong, J.Q. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmann, P.; Kuhn, V.; Suvorava, T.; Muessig, J.M.; Fischer, J.W.; Isakson, B.E.; Haberkorn, S.M.; Flögel, U.; Schrader, J.; Jung, C.; et al. Anaemia is associated with severe RBC dysfunction and a reduced circulating NO pool: Vascular and cardiac eNOS are crucial for the adaptation to anaemia. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2020, 115, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzin, A.; Dannenberg, L.; Benkhoff, M.; Barcik, M.; Keul, P.; Ayhan, A.; Weske, S.; Ahlbrecht, S.; Trojovsky, K.; Helten, C.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate improves outcome of no-reflow acute myocardial infarction via sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, L.N.; Popov, S.V.; Mukhomedzyanov, A.V.; Naryzhnaya, N.V.; Voronkov, N.S.; Ryabov, V.V.; Boshchenko, A.A.; Khaliulin, I.; Prasad, N.R.; Fu, F.; et al. Reperfusion Cardiac Injury: Receptors and the Signaling Mechanisms. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 18, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.B.; Samangouei, P.; Kalkhoran, S.B.; Hausenloy, D.J. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its role in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 78, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, T.; Tian, K.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: From mechanism to therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zuurbier, C.J.; Huhn, R.; Torregroza, C.; Hollmann, M.W.; Preckel, B.; van den Brom, C.E.; Weber, N.C. Pharmacological Cardioprotection against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury-The Search for a Clinical Effective Therapy. Cells 2023, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Ugur, K.; Aydin, S.; Sahin, İ.; Yardim, M. Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction: Current perspectives. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellon, D.M.; Hausenloy, D.J. Myocardial Reperfusion Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halladin, N.L. Oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries. Dan. Med. J. 2015, 62, B5054. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.K.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T.T.; Wu, Q. Ferroptosis: Opportunities and Challenges in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9929687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Andreadou, I.; Oelze, M.; Davidson, S.M.; Hausenloy, D.J. Discovery of new therapeutic redox targets for cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart failure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 163, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, D.J.; Harata, M.; Murphy, E.; Karch, J. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore-dependent necrosis. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2023, 174, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cen, T.; Wei, B.; Wei, L.; Wu, H.; Su, L.; Sooranna, S.R.; et al. A plasma proteomic approach in patients with heart failure after acute myocardial infarction: Insights into the pathogenesis and progression of the disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1153625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase 1 as a potential target in human cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardez-Pereira, S.; Santos, P.C.; Krieger, J.E.; Mansur, A.J.; Pereira, A.C. ACTN3 R577X polymorphism and long-term survival in patients with chronic heart failure. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.A.; Alwi, I.; Soetisna, T.W.; Gunanti; Sandora, N.; Busro, P.W.; Supomo; Fitria, N.A.; Kusuma, T.R. Remodeling in early myocardial infarction: Alteration of extracellular matrix; Collagen-1, Collagen-3, α-SMA, and α-Actinin in Porcine heart model. Bali Med. J. 2023, 12, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.Y.; Ruiz-Velasco, A.; Bui, T.; Collins, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. Mitochondrial function in the heart: The insight into mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 4302–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lyu, P.; Andreev, D.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Bozec, A. Hypoxia-immune-related microenvironment prognostic signature for osteosarcoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 974851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, H.J.; Ostrowski, P.J.; McAndrew, D.J.; Cao, F.; Shaw, A.; Eykyn, T.R.; Lake, H.A.; Tyler, J.; Schneider, J.E.; Neubauer, S.; et al. Over-expression of mitochondrial creatine kinase in the murine heart improves functional recovery and protects against injury following ischaemia–reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervou, S.; Whittington, H.J.; Ostrowski, P.J.; Cao, F.; Tyler, J.; Lake, H.A.; Neubauer, S.; Lygate, C.A. Increasing creatine kinase activity protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury but not against anthracycline toxicity in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).