Toward Consensus Epitopes B and T of Tropomyosin Involved in Cross-Reactivity across Diverse Allergens: An In Silico Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
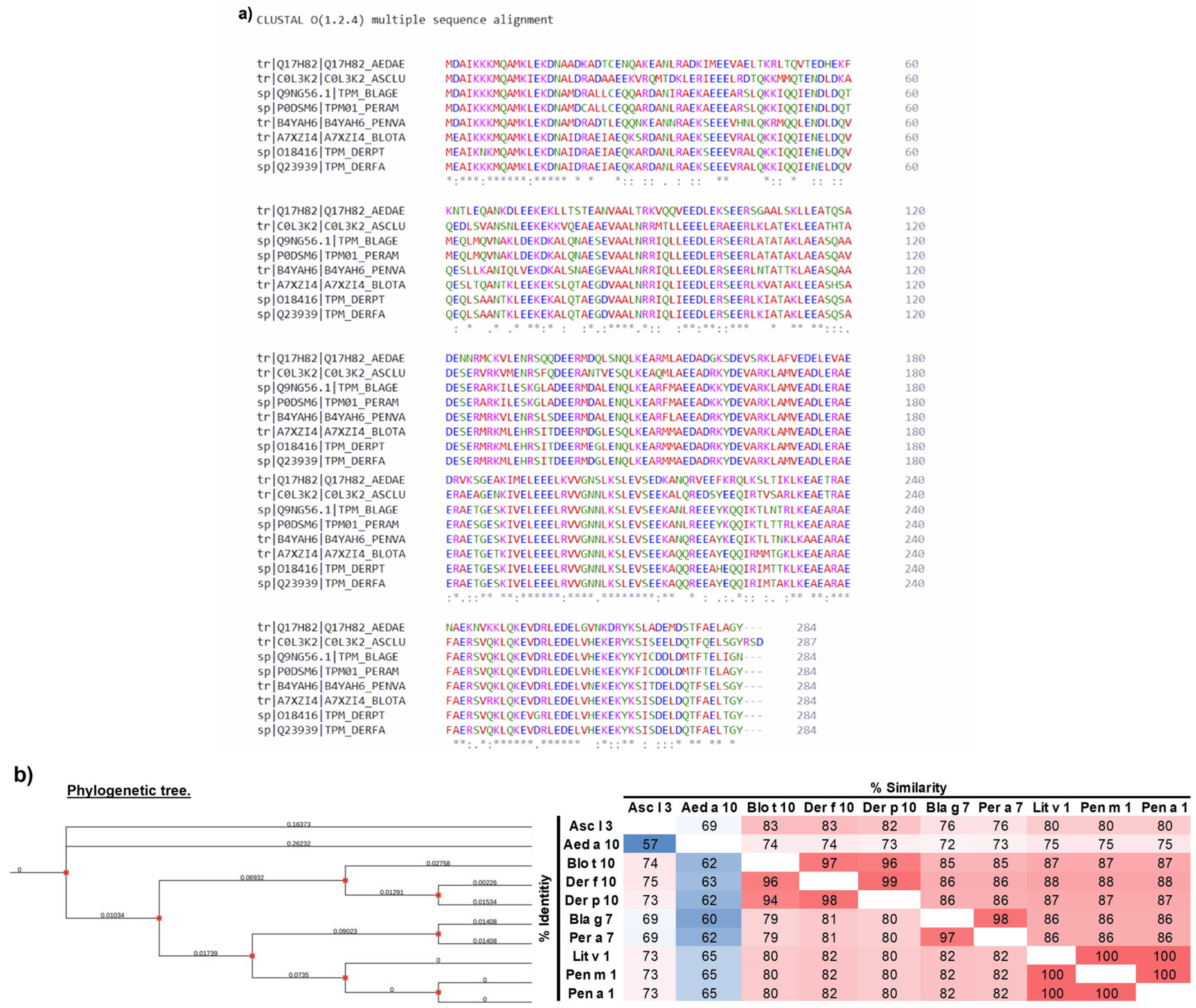
2.1. Phylogenetic and Multi-Alignment Analyses
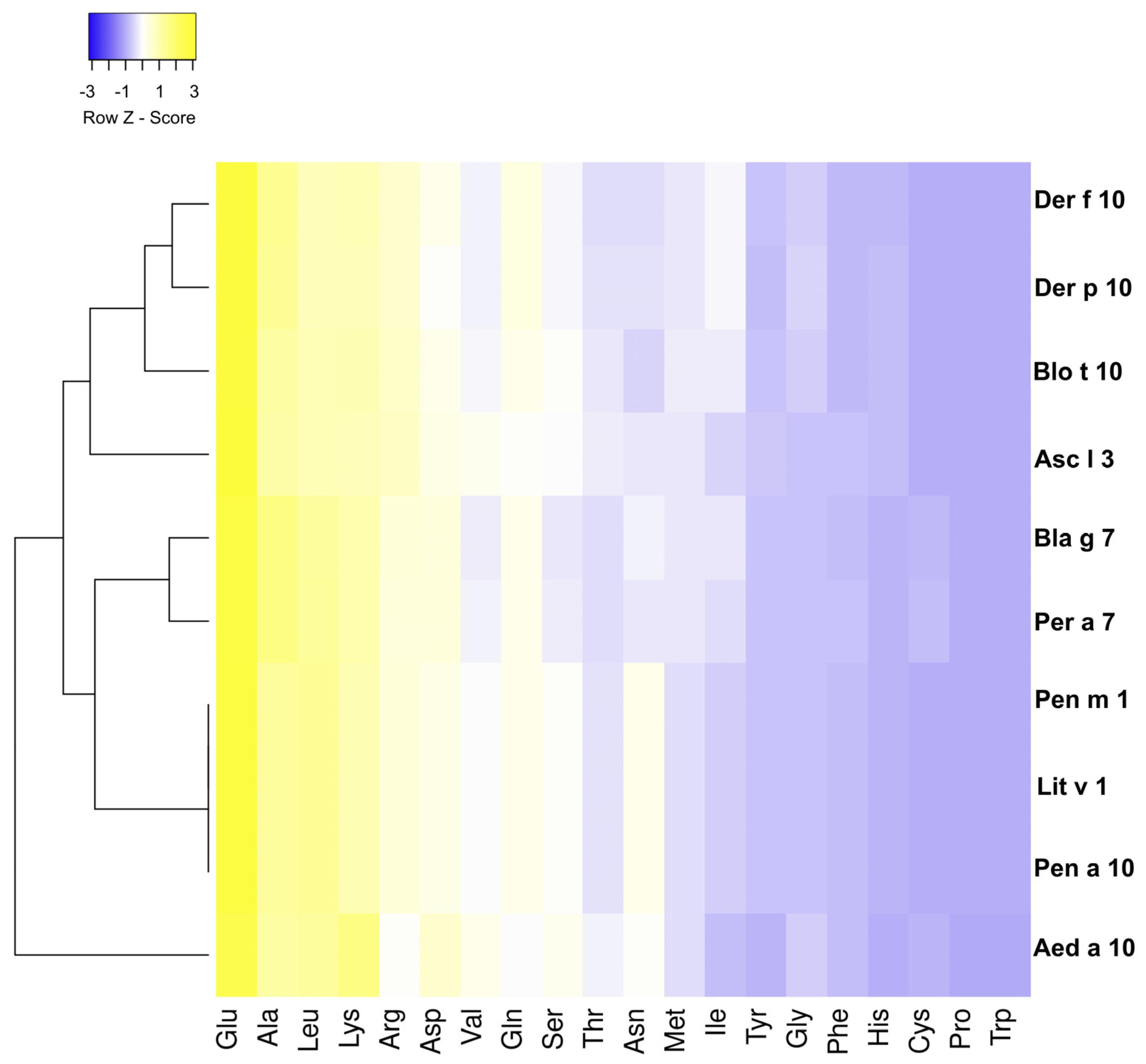
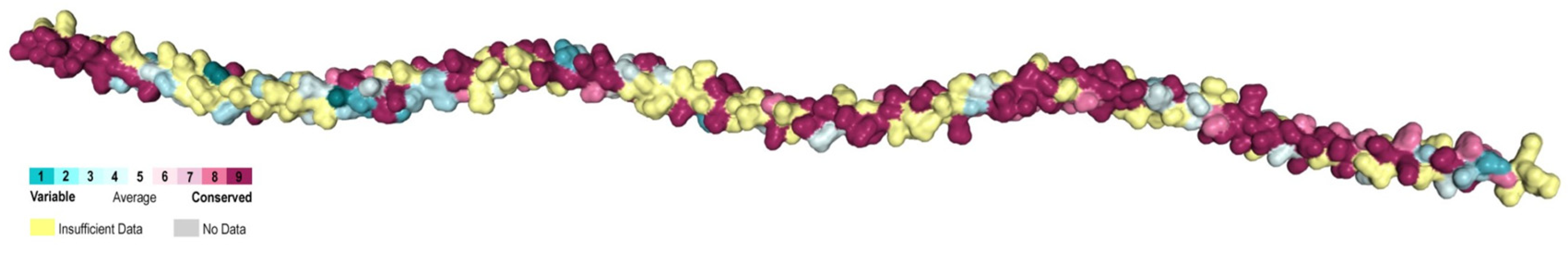
2.2. Conservation Analysis of Tropomyosins
2.3. Prediction of Linear B-Cell Epitopes and IgE Epitopes
2.4. Prediction of T-Cell Epitope/MHC-II Binding
2.5. B-Cell and T-Cell Epitope Consensus
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Amino Acid Sequence of Tropomyosin from Different Species
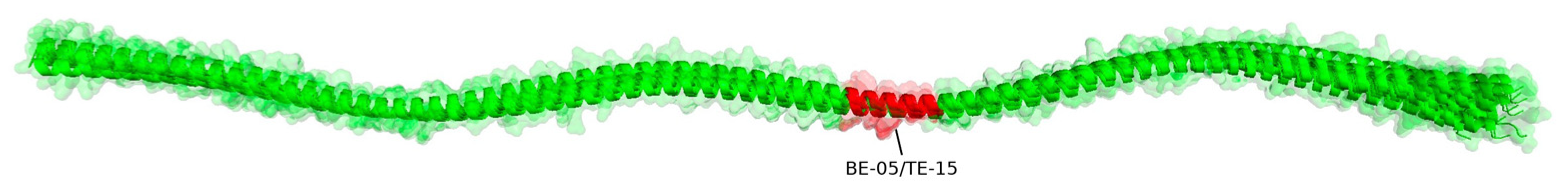
3.2. Highly Conserved B Epitopes in Invertebrate Species
3.3. In Silico Prediction of CD4 T-Cell Epitopes and Their MHC-Binding HLA Alleles
3.4. B/T Epitopes Consensus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddanakoppalu, N.P. Immunological Basis for the Development of Allergic Diseases-Prevalence, Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies. In Cell Interaction; Bhawana, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; Chart 5. [Google Scholar]
- Caraballo, L.; Zakzuk, J.; Lee, B.W.; Acevedo, N.; Soh, J.Y.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Hossny, E.; Garcia, E.; Rosario, N.; Ansotegui, I.; et al. Particularities of allergy in the Tropics. World Allergy Organ. J. 2016, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantillo, J.F.; Puerta, L. Mosquitoes: Important Sources of Allergens in the Tropics. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 690406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, G.; Ayuso, R.; Lehrer, S.B. Tropomyosin: An invertebrate pan-allergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 119, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuso, R.; Reese, G.; Leong-Kee, S.; Plante, M.; Lehrer, S.B. Molecular basis of arthropod cross-reactivity: IgE-binding cross-reactive epitopes of shrimp, house dust mite and cockroach tropomyosins. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 129, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papia, F.; Bellia, C.; Uasuf, C.G. Tropomyosin: A panallergen that causes a worldwide allergic problem. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, e145–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanti, K.N.; Martin, B.M.; Nagpal, S.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Rao, P.V. Identification of tropomyosin as the major shrimp allergen and characterization of its IgE-binding epitopes. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 5354–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Ayuso, R.; Lehrer, S.B.; Reese, G. Identification of continuous, allergenic regions of the major shrimp allergen Pen a 1 (tropomyosin). Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 127, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, S.; Puerta, L.; Martinez, D.; Munoz, M.; Hernandez, K.; Sanchez, J. Clinical Relevance of Shrimp Sensitization in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis: Anti-Der p 10 IgE as Predictor. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asturias, J.A.; Gómez-Bayón, N.; Arilla, M.C.; Martínez, A.; Palacios, R.; Sánchez-Gascón, F.; Martínez, J. Molecular characterization of American cockroach tropomyosin (Periplaneta americana allergen 7), a cross-reactive allergen. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4342–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo, J.F.; Puerta, L.; Lafosse-Marin, S.; Subiza, J.L.; Caraballo, L.; Fernández-Caldas, E. Identification and Characterization of IgE-Binding Tropomyosins in Aedes aegypti. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 170, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, V.; Garcia, E.; Dennis, R.; Rojas, M.X.; Rondon, M.A.; Perez, A.; Penaranda, A.; Barragan, A.M.; Jimenez, S.; Kennedy, M.W.; et al. IgE responses to Ascaris and mite tropomyosins are risk factors for asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Erler, A.; Briza, P.; Puccio, F.; Ferreira, F.; Caraballo, L. Allergenicity of Ascaris lumbricoides tropomyosin and IgE sensitization among asthmatic patients in a tropical environment. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 154, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghofer, M.; Thomas, W.R.; Kronqvist, M.; Mari, A.; Purohit, A.; Pauli, G.; Horak, F.; Grönlund, H.; van Hage, M.; Valenta, R.; et al. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 38, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo, J.F.; Puerta, L.; Lafosse-Marin, S.; Subiza, J.L.; Caraballo, L.; Fernandez-Caldas, E. Allergens involved in the cross-reactivity of Aedes aegypti with other arthropods. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 118, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klueber, J.; Costa, J.; Randow, S.; Codreanu-Morel, F.; Verhoeckx, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Ollert, M.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Morisset, M.; Holzhauser, T.; et al. Homologous tropomyosins from vertebrate and invertebrate: Recombinant calibrator proteins in functional biological assays for tropomyosin allergenicity assessment of novel animal foods. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Caraballo, L. IgE cross-reactivity between Ascaris lumbricoides and mite allergens: Possible influences on allergic sensitization and asthma. Parasite Immunol. 2011, 33, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.B.; Rocha, G.M.; Oliver, C.; Ferriani, V.P.; Lima, R.C.; Palma, M.S.; Sales, V.S.; Aalberse, R.C.; Chapman, M.D.; Arruda, L.K. Cross-reactive IgE antibody responses to tropomyosins from Ascaris lumbricoides and cockroach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1040–1046.e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bublin, M.; Breiteneder, H. Cross-reactivities of non-homologous allergens. Allergy 2020, 75, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C. Assessment of allergen cross-reactivity. Clin. Mol. Allergy CMA 2007, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Crameri, R. IgE-binding epitopes: A reappraisal. Allergy 2011, 66, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westernberg, L.; Schulten, V.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Natali, S.; Tripple, V.; McKinney, D.M.; Frazier, A.; Hofer, H.; Wallner, M.; Sallusto, F.; et al. T-cell epitope conservation across allergen species is a major determinant of immunogenicity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 571–578.e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A.; Arkwright, P.D.; Brüggen, M.C.; Busse, W. Type 2 immunity in the skin and lungs. Allergy 2020, 75, 1582–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. A Public Protein Soc. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, B.; Yariv, E.; Kessel, A. Using evolutionary data to make sense of macromolecules with a “face-lifted” ConSurf. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. AlgPred: Prediction of allergenic proteins and mapping of IgE epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W202–W209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, J.N.; Høie, M.H.; Deleuran, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-3.0: Improved B-cell epitope prediction using protein language models. Protein Sci. A Public Protein Soc. 2022, 31, e4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.-H.; Sidney, J.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Sette, A. Development of an epitope conservancy analysis tool to facilitate the design of epitope-based diagnostics and vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, B.; Alvarez, B.; Paul, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.1 and NetMHCIIpan-4.0: Improved predictions of MHC antigen presentation by concurrent motif deconvolution and integration of MS MHC eluted ligand data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Marquez, M.L.; Yunis, J.J.; Layrisse, Z.; Ortega, F.; Carvallo-Gil, E.; Montagnani, S.; Makhatadze, N.J.; Pocino, M.; Granja, C.; Yunis, E. Immunogenetics of atopic asthma: Association of DRB1*1101 DQA1*0501 DQB1*0301 haplotype with Dermatophagoides spp.-sensitive asthma in a sample of the Venezuelan population. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 29, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Ezequiel, O.; Gazeta, G.S.; Amorim, M.; Serra-Freire, N.M. Evaluation of the acarofauna of the domiciliary ecosystem in Juiz de Fora, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2001, 96, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.R.; Hernandez, M. HLA haplotype segregation in families with allergic asthma. Tissue Antigens 1990, 35, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa Lima Caniatti, M.C.; Borelli, S.D.; Guilherme, A.L.; Tsuneto, L.T. Association between HLA genes and dust mite sensitivity in a Brazilian population. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.; He, L. Association of HLA-DRB1 Gene Polymorphism with Risk of Asthma: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2016, 22, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Karosiene, E.; Edwards, L.; Grifoni, A.; Paul, S.; Andreatta, M.; Weiskopf, D.; Sidney, J.; Nielsen, M.; Peters, B.; et al. Predicting HLA CD4 Immunogenicity in Human Populations. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, H.H.; Sidney, J.; Dinh, K.; Southwood, S.; Newman, M.J.; Sette, A. Predicting population coverage of T-cell epitope-based diagnostics and vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, N.; Woetzel, N.; Meiler, J. bcl::Cluster: A method for clustering biological molecules coupled with visualization in the Pymol Molecular Graphics System. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Adv. Bio Med. Sci. 2011, 2011, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Muñoz, A.; Rodríguez-Canul, R. In Silico Analysis of the Cross-Reactivity of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Allergens with Other Arthropod Species. Open J. Immunol. 2022, 12, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetang, J.; Tipmanee, V. In Silico Prediction of Cross-Reactive Epitopes of Tropomyosin from Shrimp and Other Arthropods Involved in Allergy. Molecules 2022, 27, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Khuri, N.; Dong, G.Q.; Winter, M.B.; Shifrut, E.; Friedman, N.; Craik, C.S.; Pratt, K.P.; Paz, P.; Aswad, F. Predicting CD4 T-cell epitopes based on antigen cleavage, MHCII presentation, and TCR recognition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, G.; Ferrante, A.; Gorski, J. Cross-reactivity of T cells and its role in the immune system. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangorsch, A.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Rösch, P.; Holzhauser, T.; Vieths, S. Mutational epitope analysis and cross-reactivity of two isoforms of Api g 1, the major celery allergen. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Wang, J.; Ni, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Identification of Allergenic Epitopes and Critical Amino Acids of Major Allergens in Chinese Shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) by Immunoinformatics Coupled with Competitive-Binding Strategy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oezguen, N.; Zhou, B.; Negi, S.S.; Ivanciuc, O.; Schein, C.H.; Labesse, G.; Braun, W. Comprehensive 3D-modeling of allergenic proteins and amino acid composition of potential conformational IgE epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravkov, E.V.; Pavlov, I.Y.; Martins, T.B.; Gleich, G.J.; Wagner, L.A.; Hill, H.R.; Delgado, J.C. Identification and validation of shrimp-tropomyosin specific CD4 T cell epitopes. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |

| Allergen | Organism | Uniprot N° | Allergome | Aa | kDa | 3D Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Der p 10 | Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus | O18416 | Der p 10.0101 | 284 | 32.9 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/O18416 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/O18416?csm=278AAF663E585DB9 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Der f 10 | Dermatophagoides farinae | Q23939 | Der f 10.0101 | 284 | 32.9 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q23939 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q23939?csm=E665D29BAAF33507 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Blo t 10 | Blomia tropicalis | A7XZI4 * | Blo t 10.0102 | 284 | 33 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/A7XZI4 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/A7XZI4?csm=C80E361A65A996F4 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Asc l 3 | Ascaris lumbricoides | C0L3K2 * | Asc l 3.0101 | 287 | 33.5 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/C0L3K2 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/C0L3K2?csm=911B0C202DE1EB3F accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Bla g 7 | Blattella germanica | Q9NG56 | Bla g 7.0101 | 284 | 32.8 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q9NG56 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q9NG56?csm=71DB260E3F594500 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Per a 7 | Periplaneta americana | P0DSM6 | Per a 7.0101 | 284 | 32.7 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/P0DSM6 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/P0DSM6?csm=1B91486A94446CF1 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Aed a 10 | Aedes aegypti | Q17H82 * | Aed a 10.0101 | 284 | 32.3 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q17H82 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Lit v 1 | Litopenaeus vannamei | B4YAH6 * | Lit v 1.0101 | 284 | 32.9 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/B4YAH6 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/B4YAH6?csm=BE53B602C37E85E2 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Pen m 1 | Penaeus monodon | A1KYZ2 | Pen m 1.0101 | 284 | 32.8 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/A1KYZ2 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/A1KYZ2?csm=BE53B602C37E85E2 accession on 21 July 2023 | ||||||
| Pen a 1 | Penaeus aztecus | Q3Y8M6 | Pen a 1.0102 | 284 | 32.8 | AlphaFold DB: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q3Y8M6 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Swiss-Model Repository: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q3Y8M6?csm=BE53B602C37E85E2 accession on 21 July 2023 |
| Residue | Identity % | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-Epitope ID | Start | End | Length | Consensus Sequences | Asc l 3 | Aed a 10 | Der p 10 | Der f 10 | Blo t 10 | Lit v 1 | Pen m 1 | Pen a 1 | Per a 7 | Bla g 7 |
| BE-01 | 48 | 55 | 8 | KRMQQLEN | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 63 | 63 |
| BE-02a | 85 | 104 | 20 | VAALNRRIQLLEEDLERSEE | 80 | 70 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| BE-02b | 85 | 104 | 20 | VAALNRRIQLIEEDLERSEE | 75 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 |
| BE-03 | 128 | 141 | 14 | KVLENRSQQDEERM | 79 | 100 | 71 | 71 | 71 | 86 | 86 | 86 | 57 | 57 |
| BE-04 | 132 | 153 | 22 | NRSLSDEERMDALENQLKEARF | 59 | 77 | 73 | 77 | 73 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 82 | 82 |
| BE-05 | 160 | 174 | 15 | RKYDEVARKLAMVEA | 100 | 67 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 93 | 93 |
| BE-06 | 192 | 223 | 32 | ELEEELRVVGNNLKSLEVSEEKANQREEAYKE | 88 | 78 | 88 | 91 | 91 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 91 | 91 |
| BE-07 | 251 | 261 | 11 | KEVDRLEDELV | 100 | 91 | 91 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Identity % | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Epitope ID | MHC-II Alleles | Consensus Sequence | Start | End | Asc l 3 | Aed a 10 | Der p 10 | Der f 10 | Blo t 10 | Lit v 1 | Pen m 1 | Pen a 1 | Bla g 7 | Per a 7 |
| TE-01 | HLA-DRB1*04:01 HLA-DRB1*04:04 | KMQAMKLEKDNAADKAD-- | 7 | 23 | 82 | 100 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 82 | 82 |
| TE-02 | HLA-DRB1*03:01 | -MQAMKIEKDNALDRADAA | 8 | 25 | 100 | 72 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 72 | 67 |
| TE-03 | HLA-DRB1*03:01 | --QAMKLEKDNAIDRAEI- | 9 | 24 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 75 |
| TE-04 | HLA-DRB1*03:01 | --QAMKLEKDNAMDRADT- | 9 | 24 | 81 | 88 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 88 | 81 |
| TE-05 | HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01 | ARDANIRAEKAEEEARS | 29 | 45 | 41 | 47 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 53 | 53 | 53 | 100 | 94 |
| TE-06 | HLA-DRB1*11:01 HLA-DRB1*11:04 HLA-DRB1*04:04 HLA-DRB1*04:05 | KSEEEVRALQKKIQQIENELDQVQE | 38 | 62 | 56 | 40 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 76 |
| TE-07 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 | -------SLQKKIQQIENDLDQTM- | 45 | 61 | 53 | 41 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 65 | 65 | 65 | 100 | 100 |
| TE-08 | HLA-DRB1*11:04 | SEEEVHNLQKRMQQLE | 39 | 54 | 50 | 44 | 69 | 69 | 69 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 56 | 56 |
| TE-09 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 | AQEDLSVANSNLEEKE | 60 | 75 | 100 | 50 | 69 | 69 | 63 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 38 | 38 |
| TE-10 | HLA-DRB1*14:01 HLA-DRB1*11:04 | LKANIQLVEKDKALSNAE | 65 | 82 | 44 | 44 | 56 | 56 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 61 | 61 |
| TE-11 | HLA-DRB1*11:01 HLA-DRB1*11:04 | STEANVAALTRKVQQVEE | 80 | 97 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| TE-12 | HLA-DRB1*11:04 HLA-DRB1*11:01 | TAEGDVAALNRRIQLIE | 80 | 96 | 65 | 47 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 76 | 76 |
| TE-13 | HLA-DRB1*11:04 | NAESEVAALNRRIQLLE | 80 | 96 | 76 | 47 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 100 | 100 |
| TE-14 | HLA-DRB1*11:04 HLA-DRB1*11:01 | NAEGEVAALNRRIQLLE | 80 | 96 | 76 | 47 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94 | 94 |
| TE-15 | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | ADRKYDEVARKLAMVE | 158 | 173 | 100 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94 | 94 |
| TE-16 | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | ADKKYDEVARKLAMVE | 158 | 173 | 94 | 75 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 100 | 100 |
| TE-17 | HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 | VARKLAMVEADLERAE | 165 | 180 | 100 | 69 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| TE-18 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 HLA-DRB1*03:01 | VGNSLKSLEVSEDKANQRVEE | 200 | 220 | 71 | 100 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 |
| TE-19 | HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 | VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAL----- | 200 | 215 | 100 | 81 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 |
| TE-20 | HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 HLA-DRB1*04:05 | VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAQ----- | 200 | 215 | 94 | 81 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 94 |
| TE-21 | HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 HLA-DRB1*04:05 | VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAN----- | 200 | 215 | 94 | 88 | 94 | 94 | 94 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| TE-22 | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | REDSYEEQIRTVSAR | 217 | 231 | 100 | 27 | 40 | 53 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 |
| TE-23 | HLA-DRB1*11:04 | ERSVQKLQKEVGRLE | 243 | 257 | 93 | 73 | 100 | 93 | 87 | 93 | 93 | 93 | 93 | 93 |
| TE-24 | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01 HLA-DRB1*04:01 HLA-DRB1*04:05 HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 | VHEKEKYKSISDELDQTFA | 261 | 279 | 84 | 53 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 74 | 74 |
| TE-25 | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01 HLA-DRB1*04:01 HLA-DRB1*04:05 HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 | VNEKEKYKSITDELDQTFS | 261 | 279 | 74 | 47 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 68 | 68 |
| TE-26 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01 | -HEKERYKSISEELDQTF- | 262 | 278 | 100 | 53 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 65 | 65 |
| TE-27 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 | --EKEKYKYICDDLDMTF- | 263 | 278 | 63 | 44 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 94 |
| TE-28 | HLA-DRB1*04:05 HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02 | VNKDRYKSLADEMDSTFA | 261 | 279 | 50 | 100 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 39 | 39 |
| Cluster Number | Epitope Number | B-Cell and T-Cell Consensus Epitope Sequence | Peptide |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Consensus | ELEEELRVVGNNLKSLEVSEEKANQRXEXYKE | - |
| 1.1 | 1 | ELEEELRVVGNNLKSLEVSEEKANQREEAYKE | B06 |
| 1.1 | 2 | --------VGNSLKSLEVSEDKANQRVEE--- | TE-18 |
| 1.1 | 3 | --------VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAL-------- | TE-19 |
| 1.1 | 4 | --------VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAQ-------- | TE-20 |
| 1.1 | 5 | --------VGNNLKSLEVSEEKAN-------- | TE-21 |
| 2.1 | Consensus | NAEGEVAALNRRIQLLEEDLERSEE | - |
| 2.1 | 1 | TAEGDVAALNRRIQLIE-------- | TE-12 |
| 2.1 | 2 | NAESEVAALNRRIQLLE-------- | TE-13 |
| 2.1 | 3 | NAEGEVAALNRRIQLLE-------- | TE-14 |
| 2.1 | 4 | -----VAALNRRIQLLEEDLERSEE | B02a |
| 2.1 | 5 | -----VAALNRRIQLIEEDLERSEE | B02b |
| 3.1 | Consensus | KMQAMKLEKDNAXDRADXA | - |
| 3.1 | 1 | KMQAMKLEKDNAADKAD-- | TE-01 |
| 3.1 | 2 | -MQAMKIEKDNALDRADAA | TE-02 |
| 3.1 | 3 | --QAMKLEKDNAIDRAEI- | TE-03 |
| 3.1 | 4 | --QAMKLEKDNAMDRADT- | TE-04 |
| 4.1 | Consensus | VHEKEKYKSIXDELDQTFX | - |
| 4.1 | 1 | VNEKEKYKSITDELDQTFS | TE-25 |
| 4.1 | 2 | VHEKEKYKSISDELDQTFA | TE-24 |
| 4.1 | 3 | -HEKERYKSISEELDQTF- | TE-26 |
| 4.1 | 4 | --EKEKYKYICDDLDMTF- | TE-27 |
| 5.1 | Consensus | ADRKYDEVARKLAMVEA | - |
| 5.1 | 1 | ADRKYDEVARKLAMVE- | TE-15 |
| 5.1 | 2 | ADKKYDEVARKLAMVE- | TE-16 |
| 5.1 | 3 | --RKYDEVARKLAMVEA | B05 |
| 6.1 | Consensus | SEEEVHNLQKRMQQLEN | - |
| 6.1 | 1 | SEEEVHNLQKRMQQLE- | TE-08 |
| 6.1 | 2 | ---------KRMQQLEN | B01 |
| 7.1 | Consensus | KSEEEVRXLQKKIQQIENXLDQXXE | - |
| 7.1 | 1 | KSEEEVRALQKKIQQIENELDQVQE | TE-06 |
| 7.1 | 2 | -------SLQKKIQQIENDLDQTM- | TE-07 |
| 8.1 | Singleton | KVLENRSQQDEERM | B03 |
| 9.1 | Singleton | NRSLSDEERMDALENQLKEARF | B04 |
| 10.1 | Singleton | STEANVAALTRKVQQVEE | TE-11 |
| 11.1 | Singleton | ERSVQKLQKEVGRLE | TE-23 |
| 12.1 | Singleton | VNKDRYKSLADEMDSTFA | TE-28 |
| 13.1 | Singleton | KEVDRLEDELV | B07 |
| 14.1 | Singleton | ARDANIRAEKAEEEARS | TE-05 |
| 15.1 | Singleton | AQEDLSVANSNLEEKE | TE-09 |
| 16.1 | Singleton | LKANIQLVEKDKALSNAE | TE-10 |
| 17.1 | Singleton | REDSYEEQIRTVSAR | TE-22 |
| 18.1 | Singleton | VARKLAMVEADLERAE | TE-17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, D.; Fang, L.; Meza-Torres, C.; Garavito, G.; López-Lluch, G.; Egea, E. Toward Consensus Epitopes B and T of Tropomyosin Involved in Cross-Reactivity across Diverse Allergens: An In Silico Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040884
Martínez D, Fang L, Meza-Torres C, Garavito G, López-Lluch G, Egea E. Toward Consensus Epitopes B and T of Tropomyosin Involved in Cross-Reactivity across Diverse Allergens: An In Silico Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040884
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Dalgys, Luis Fang, Catherine Meza-Torres, Gloria Garavito, Guillermo López-Lluch, and Eduardo Egea. 2024. "Toward Consensus Epitopes B and T of Tropomyosin Involved in Cross-Reactivity across Diverse Allergens: An In Silico Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 4: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040884
APA StyleMartínez, D., Fang, L., Meza-Torres, C., Garavito, G., López-Lluch, G., & Egea, E. (2024). Toward Consensus Epitopes B and T of Tropomyosin Involved in Cross-Reactivity across Diverse Allergens: An In Silico Study. Biomedicines, 12(4), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040884





