The Endothelial Glycocalyx in Pig-to-Baboon Cardiac Xenotransplantation—First Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Study Groups
2.2. Anesthesia, Surgical Procedure and Heart Preservation
2.3. Immunosuppression, Anti-Inflammatory and Additive Therapy
2.4. Blood Sampling and Lactate Measurements
2.5. Measurement of Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Values of the Circulating Plasma Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
3.2. Perioperative Changes of the Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
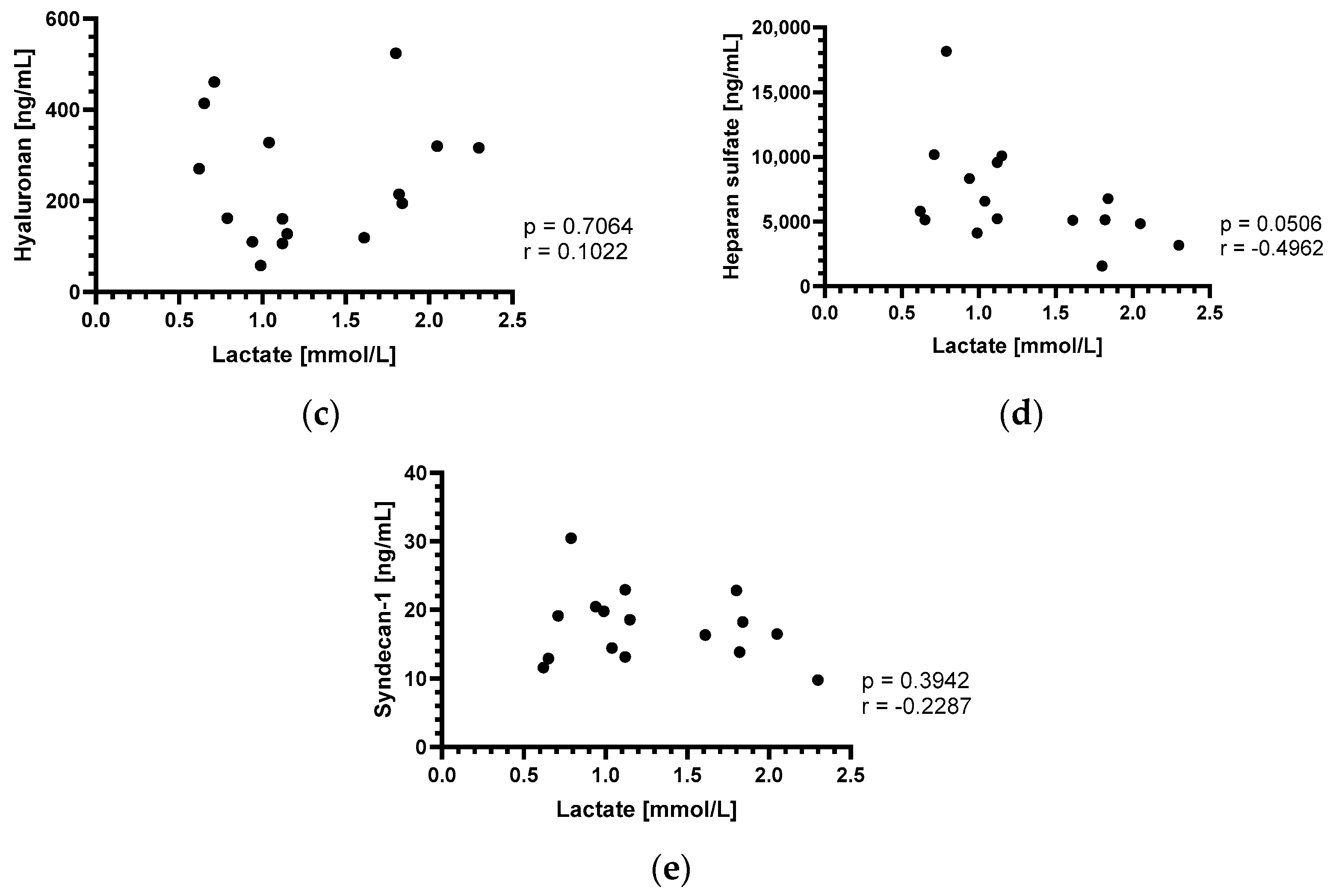
3.3. Perioperative Lactate Changes and Correlation with Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
3.4. Postoperative Changes of the Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
4. Discussion
4.1. Baseline Values of the Circulating Plasma Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
4.2. Perioperative Changes of the Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
4.3. Perioperative Lactate Changes and Correlation with Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
4.4. Postoperative Changes of the Endothelial Glycocalyx Components
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichart, B.; Cooper, D.K.C.; Langin, M.; Tonjes, R.R.; Pierson, R.N.; Wolf, E. Cardiac xenotransplantation: From concept to clinic. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3499–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.M.; Reichart, B.; Byrne, G.W.; McGregor, C.G.A. Current status of pig heart xenotransplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23 Pt B, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmoeckel, D.M.; Längin, M.; Reichart, B.; Abicht, J.-M.; Bender, M.; Michel, S.; Kamla, C.-E.; Denner, J.; Tönjes, R.R.; Schwinzer, R.; et al. Current status of cardiac xenotransplantation. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 72, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Längin, M.; Mayr, T.; Reichart, B.; Michel, S.; Buchholz, S.; Guethoff, S.; Dashkevich, A.; Baehr, A.; Egerer, S.; Bauer, A.; et al. Consistent success in life-supporting porcine cardiac xenotransplantation. Nature 2018, 564, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichart, B.; Längin, M.; Radan, J.; Mokelke, M.; Buttgereit, I.; Ying, J.; Fresch, A.K.; Mayr, T.; Issl, L.; Buchholz, S.; et al. Pig-to-non-human primate heart transplantation: The final step toward clinical xenotransplantation? J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2020, 39, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.M.; Goerlich, C.E.; Singh, A.K.; Zhang, T.; Tatarov, I.; Lewis, B.; Sentz, F.; Hershfeld, A.; Braileanu, G.; Odonkor, P.; et al. Progressive genetic modifications of porcine cardiac xenografts extend survival to 9 months. Xenotransplantation 2022, 29, e12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuensch, A.; Baehr, A.; Bongoni, A.K.; Kemter, E.; Blutke, A.; Baars, W.; Haertle, S.; Zakhartchenko, V.; Kurome, M.; Kessler, B.; et al. Regulatory sequences of the porcine THBD gene facilitate endothelial-specific expression of bioactive human thrombomodulin in single- and multitransgenic pigs. Transplantation 2014, 97, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Corcoran, P.C.; Thomas Iii, M.L.; Clark, T.; Lewis, B.G.; Hoyt, R.F.; Eckhaus, M.; Pierson Iii, R.N.; Belli, A.J.; et al. Chimeric 2C10R4 anti-CD40 antibody therapy is critical for long-term survival of GTKO.hCD46.hTBM pig-to-primate cardiac xenograft. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, S.; Paskevicius, A.; Liao, Q.; Sjöberg, T. Safe orthotopic transplantation of hearts harvested 24 hours after brain death and preserved for 24 hours. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2016, 50, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Längin, M.; Reichart, B.; Steen, S.; Sjöberg, T.; Paskevicius, A.; Liao, Q.; Qin, G.; Mokelke, M.; Mayr, T.; Radan, J.; et al. Cold non-ischemic heart preservation with continuous perfusion prevents early graft failure in orthotopic pig-to-baboon xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 2021, 28, e12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Längin, M.; Buttgereit, I.; Reichart, B.; Panelli, A.; Radan, J.; Mokelke, M.; Neumann, E.; Bender, M.; Michel, S.; Ellgass, R.; et al. Xenografts Show Signs of Concentric Hypertrophy and Dynamic Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction After Orthotopic Pig-to-baboon Heart Transplantation. Transplantation 2023, 107, e328–e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerlich, C.E.; Griffith, B.; Hanna, P.; Hong, S.N.; Ayares, D.; Singh, A.K.; Mohiuddin, M.M. The growth of xenotransplanted hearts can be reduced with growth hormone receptor knockout pig donors. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 165, e69–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, M.; Panelli, A.; Reichart, B.; Radan, J.; Mokelke, M.; Neumann, E.; Buttgereit, I.; Michel, S.; Bauer, A.; Fresch, A.K.; et al. Hemodynamics in pig-to-baboon heterotopic thoracic cardiac xenotransplantation: Recovery from perioperative cardiac xenograft dysfunction and impairment by cardiac overgrowth. Xenotransplantation 2024, 31, e12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denner, J.; Längin, M.; Reichart, B.; Krüger, L.; Fiebig, U.; Mokelke, M.; Radan, J.; Mayr, T.; Milusev, A.; Luther, F.; et al. Impact of porcine cytomegalovirus on long-term orthotopic cardiac xenotransplant survival. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Gulich, B.; Keßler, B.; Längin, M.; Fishman, J.A.; Wolf, E.; Boller, K.; Tönjes, R.R.; Godehardt, A.W. PCR and peptide based PCMV detection in pig—Development and application of a combined testing procedure differentiating newly from latent infected pigs. Xenotransplantation 2023, 30, e12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, J.A. Risks of Infectious Disease in Xenotransplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2258–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hara, H.; Wang, Y.; Esmon, C.; Cooper, D.K.C.; Iwase, H. Evidence for the important role of inflammation in xenotransplantation. J Inflamm. 2019, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.P.; Jagdale, A.; Walcott, G.; Iwase, H.; Foote, J.B.; Cron, R.Q.; Hara, H.; Cleveland, D.C.; Cooper, D.K.C. A perspective on the potential detrimental role of inflammation in pig orthotopic heart xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 2021, 28, e12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Reichart, B.; Figueiredo, C.; Burgmann, J.M.; Leuschen, M.; Wall, F.; Radan, J.; Neumann, E.; Mokelke, M.; Buttgereit, I.; et al. Controlling inflammation and coagulation in pig-to-baboon cardiac xenotransplantation. 2024, 16, 214–221, Manuscript submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, M.; Längin, M.; Reichart, B.; Mokelke, M.; Radan, J.; Neumann, E.; Michel, S.; Ellgass, R.; Cowan, P.J.; Wolf, E.; et al. Overcoming perioperative inflammation as a hurdle for successful preclinical orthotopic cardiac xenogeneic transplantations—Particular in regard of the mandatory use of heart-lung machines. Xenotransplantation 2022, 29, e12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Scobie, L.; Goerlich, C.E.; Grazioli, A.; Saharia, K.; Crossan, C.; Burke, A.; Drachenberg, C.; Oguz, C.; et al. Graft dysfunction in compassionate use of genetically engineered pig-to-human cardiac xenotransplantation: A case report. Lancet 2023, 402, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, B.P.; Goerlich, C.E.; Singh, A.K.; Rothblatt, M.; Lau, C.L.; Shah, A.; Lorber, M.; Grazioli, A.; Saharia, K.K.; Hong, S.N.; et al. Genetically Modified Porcine-to-Human Cardiac Xenotransplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC). UM Medicine Faculty-Scientists and Clinicians Perform Second Historic Transplant of Pig Heart into Patient with End-Stage Cardiovascular Disease. 2023. Available online: https://www.medschool.umaryland.edu/news/2023/um-medicine-faculty-scientists-and-clinicians-perform-second-historic-transplant-of-pig-heart-into-patient-with-end-stage-cardiovascular-disease.html#:~:text=It%20is%20with%20great%20sadness,six%20weeks%20following%20the%20surgery (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Laumonier, T.; Mohacsi, P.J.; Matozan, K.M.; Banz, Y.; Haeberli, A.; Korchagina, E.Y.; Bovin, N.V.; Vanhove, B.; Rieben, R. Endothelial cell protection by dextran sulfate: A novel strategy to prevent acute vascular rejection in xenotransplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummer, L.; Zaradzki, M.; Vijayan, V.; Arif, R.; Weigand, M.A.; Immenschuh, S.; Wagner, A.H.; Larmann, J. Vascular Signaling in Allogenic Solid Organ Transplantation—The Role of Endothelial Cells. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.A.; oude Egbrink, M.G. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pflug. Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Song, J.W.; Zullo, J.; Lipphardt, M.; Coneh-Gould, L.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial cell dysfunction and glycocalyx—A vicious circle. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, A.R.; Kuebler, W.M. Normal endothelium. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2006, 176, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum, S.; Tarbell, J.M.; Damiano, E.R. The structure and function of the endothelial glycocalyx layer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 9, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siren, E.M.J.; Luo, H.D.; Tam, F.; Montgomery, A.; Enns, W.; Moon, H.; Sim, L.; Rey, K.; Guan, Q.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Prevention of vascular-allograft rejection by protecting the endothelial glycocalyx with immunosuppressive polymers. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passov, A.; Schramko, A.; Mäkisalo, H.; Nordin, A.; Andersson, S.; Pesonen, E.; Ilmakunnas, M. Graft glycocalyx degradation in human liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladden, T.M.; Yerkovich, S.; Grant, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Trotter, M.; Hopkins, P.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chambers, D.C. Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding Predicts Donor Organ Acceptability and Is Associated With Primary Graft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeijs, M.G.; Vink, H.; Voesten, N.; Christiaans, M.H.; Daemen, J.W.; Peppelenbosch, A.G.; Tordoir, J.H.; Peutz-Kootstra, C.J.; Buurman, W.A.; Schurink, G.W.; et al. Acute ischemic injury to the renal microvasculature in human kidney transplantation. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 299, F1134–F1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusev, A.; Ren, J.; Despont, A.; Shaw, J.; Längin, M.; Bender, M.; Abicht, J.M.; Mokelke, M.; Radan, J.; Neumann, E.; et al. Glycocalyx dynamics and the inflammatory response of genetically modified porcine endothelial cells. Xenotransplantation 2023, 30, e12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, J.L.; Lindman, B.J.; Geller, R.L.; Noreen, H.J.; Swanson, J.L.; Dalmasso, A.P.; Bach, F.H. The role of natural antibodies in the activation of xenogenic endothelial cells. Transplantation 1991, 52, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.L.; Dalmasso, A.P.; Lindman, B.J.; Ihrcke, N.S.; Bach, F.H. The role of C5a and antibody in the release of heparan sulfate from endothelial cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 2887–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, T.; Bauer, A.; Reichart, B.; Guethoff, S.; Schoenmann, U.; Längin, M.; Panelli, A.; Kind, A.; Brenner, P.; Abicht, J.M. Hemodynamic and perioperative management in two different preclinical pig-to-baboon cardiac xenotransplantation models. Xenotransplantation 2017, 24, e12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lower, R.R.; Shumway, N.E. Studies on orthotopic homotransplantation of the canine heart. Surg. Forum 1960, 11, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castonguay, A.C.; Lasanajak, Y.; Song, X.; Olson, L.J.; Cummings, R.D.; Smith, D.F.; Dahms, N.M. The glycan-binding properties of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor are evolutionary conserved in vertebrates. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bruegger, D.; Schwartz, L.; Chappell, D.; Jacob, M.; Rehm, M.; Vogeser, M.; Christ, F.; Reichart, B.; Becker, B.F. Release of atrial natriuretic peptide precedes shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx equally in patients undergoing on- and off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruegger, D.; Brettner, F.; Rossberg, I.; Nussbaum, C.; Kowalski, C.; Januszewska, K.; Becker, B.F.; Chappell, D. Acute degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in infants undergoing cardiac surgical procedures. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 99, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennevig, K.; Hoel, T.; Thiara, A.; Kolset, S.; Castelheim, A.; Mollnes, T.; Brosstad, F.; Fosse, E.; Svennevig, J. Syndecan-1 plasma levels during coronary artery bypass surgery with and without cardiopulmonary bypass. Perfusion 2008, 23, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, S.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Ishimaru, T.; Peña, O.M.; Montaño, A.M.; Maeda, H.; Velez-Castrillon, S.; Nishioka, T.; Fachel, A.A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Heparan sulfate levels in mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, M.; Bruegger, D.; Christ, F.; Conzen, P.; Thiel, M.; Jacob, M.; Chappell, D.; Stoeckelhuber, M.; Welsch, U.; Reichart, B.; et al. Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx in patients undergoing major vascular surgery with global and regional ischemia. Circulation 2007, 116, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.; Berkestedt, I.; Bodelsson, M. Circulating glycosaminoglycan species in septic shock. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warttinger, U.; Kramer, R. Instant determination of the potential biomarker heparan sulfate in human plasma by a mix-and-read fluorescence assay. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.05288. [Google Scholar]
- Bruegger, D.; Rehm, M.; Abicht, J.; Paul, J.O.; Stoeckelhuber, M.; Pfirrmann, M.; Reichart, B.; Becker, B.F.; Christ, F. Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx during cardiac surgery: On-pump versus off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 1445–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, W.; Zhou, J.; He, G.; Ye, J.; Fang, F.; Luo, J.; Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, W. Correlation between acute degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx and microcirculation dysfunction during cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. Microvasc. Res. 2019, 124, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesonen, E.; Passov, A.; Andersson, S.; Suojaranta, R.; Niemi, T.; Raivio, P.; Salmenperä, M.; Schramko, A. Glycocalyx Degradation and Inflammation in Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passov, A.; Schramko, A.; Salminen, U.S.; Aittomäki, J.; Andersson, S.; Pesonen, E. Endothelial glycocalyx during early reperfusion in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, A.A.; Vink, H.; Spaan, J.A. Endothelial cell glycocalyx modulates immobilization of leukocytes at the endothelial surface. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, S.A.; Cheng, M.J.; Homayoni, H.; Plouffe, B.D.; Coury, A.J.; Ebong, E.E. Regeneration of glycocalyx by heparan sulfate and sphingosine 1-phosphate restores inter-endothelial communication. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.B.; Duling, B.R.; McClatchey, P.M.; Schafer, M.; Hunter, K.S.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Filho, I.P.T.; Torres, L.N.; Salgado, C.; Dubick, M.A.; et al. Permeation of the luminal capillary glycocalyx is determined by hyaluronan. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, H508–H514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, A.; Groß, S.; Neumann, T.; Illerhaus, A.; Vink, H.; Klasen, G.; Gathof, B.; Annecke, T. Immediate effects of whole blood donation on the endothelial surface layer and glycocalyx shedding. Blood Transfus. 2021, 19, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, A.R.; Jennings, C.A. Neutralisation of heparan sulphate and low molecular weight heparin by protamine. Thromb. Haemost. 1985, 53, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrales, P.; Vázquez, B.Y.; Tsai, A.G.; Intaglietta, M. Microvascular and capillary perfusion following glycocalyx degradation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, J.; Simon, C.; Vara, E.; Sanchez, G.; Rancan, L.; Abubakra, S.; Calvo, A.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Garutti, I. Sevoflurane anesthetic preconditioning protects the lung endothelial glycocalyx from ischemia reperfusion injury in an experimental lung autotransplant model. J. Anesth. 2016, 30, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, L.; Simón, C.; Sánchez Pedrosa, G.; Aymonnier, K.; Shahani, P.M.; Casanova, J.; Muñoz, C.; Garutti, I.; Vara, E. Glycocalyx Degradation after Pulmonary Transplantation Surgery. Eur. Surg. Res. 2018, 59, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, J.; Garutti, I.; Simon, C.; Giraldez, A.; Martin, B.; Gonzalez, G.; Azcarate, L.; Garcia, C.; Vara, E. The effects of anesthetic preconditioning with sevoflurane in an experimental lung autotransplant model in pigs. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruegger, D.; Jacob, M.; Rehm, M.; Loetsch, M.; Welsch, U.; Conzen, P.; Becker, B.F. Atrial natriuretic peptide induces shedding of endothelial glycocalyx in coronary vascular bed of guinea pig hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1993–H1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, C.; Haberer, A.; Tiefenthaller, A.; Januszewska, K.; Chappell, D.; Brettner, F.; Mayer, P.; Dalla Pozza, R.; Genzel-Boroviczény, O. Perturbation of the microvascular glycocalyx and perfusion in infants after cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 1474–1481.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Paul, O.; Mehringer, L.; Chappell, D.; Rehm, M.; Welsch, U.; Kaczmarek, I.; Conzen, P.; Becker, B.F. Albumin augmentation improves condition of guinea pig hearts after 4 hr of cold ischemia. Transplantation 2009, 87, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annecke, T.; Chappell, D.; Chen, C.; Jacob, M.; Welsch, U.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Rehm, M.; Conzen, P.F.; Becker, B.F. Sevoflurane preserves the endothelial glycocalyx against ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, D.; Heindl, B.; Jacob, M.; Annecke, T.; Chen, C.; Rehm, M.; Conzen, P.; Becker, B.F. Sevoflurane reduces leukocyte and platelet adhesion after ischemia-reperfusion by protecting the endothelial glycocalyx. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chappell, D.; Annecke, T.; Conzen, P.; Jacob, M.; Welsch, U.; Zwissler, B.; Becker, B.F. Sevoflurane mitigates shedding of hyaluronan from the coronary endothelium, also during ischemia/reperfusion: An ex vivo animal study. Hypoxia 2016, 4, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marechal, X.; Favory, R.; Joulin, O.; Montaigne, D.; Hassoun, S.; Decoster, B.; Zerimech, F.; Neviere, R. Endothelial glycocalyx damage during endotoxemia coincides with microcirculatory dysfunction and vascular oxidative stress. Shock 2008, 29, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunden, M.S.; Bornscheuer, A.; Schuster, A.; Kiefmann, R.; Goetz, A.E.; Heckel, K. Glycocalyx degradation causes microvascular perfusion failure in the ex vivo perfused mouse lung: Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 pretreatment attenuates this response. Shock 2012, 38, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Pavlidis, G.; Katsimbri, P.; Lambadiari, V.; Parissis, J.; Andreadou, I.; Tsoumani, M.; Boumpas, D.; Kouretas, D.; Iliodromitis, E. Tocilizumab improves oxidative stress and endothelial glycocalyx: A mechanism that may explain the effects of biological treatment on COVID-19. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwdorp, M.; Meuwese, M.C.; Mooij, H.L.; van Lieshout, M.H.; Hayden, A.; Levi, M.; Meijers, J.C.; Ince, C.; Kastelein, J.J.; Vink, H.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition protects against endotoxin-induced endothelial glycocalyx perturbation. Atherosclerosis 2009, 202, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Koczera, P.; Zechendorf, E.; Schuerholz, T. The Endothelial Glycocalyx: New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches in Sepsis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3758278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka-Tojo, M. Endothelial glycocalyx damage as a systemic inflammatory microvascular endotheliopathy in COVID-19. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Abdullah, S.; Shaheen, F.; Mueller, L.; Gagen, B.; Duchesne, J.; Steele, C.; Pociask, D.; Kolls, J.; Jackson-Weaver, O. Glycocalyx degradation and the endotheliopathy of viral infection. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerta-Guardo, H.; Glasner, D.R.; Harris, E. Dengue Virus NS1 Disrupts the Endothelial Glycocalyx, Leading to Hyperpermeability. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, D.T.; Wills, B. Systemic vascular leakage associated with dengue infections—The clinical perspective. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 338, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly-Andersen, A.M.; Thunberg, T.; Ahlm, C. Endothelial activation and repair during hantavirus infection: Association with disease outcome. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2014, 1, ofu027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatti, M.N.; Fabro, A.T.; Miranda, C.H. Endothelial glycocalyx shedding in the acute respiratory distress syndrome after flu syndrome. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Lu, F.; Tian, H.; Hu, H.; Ning, F.; Shang, Q.; Hao, D.; Zhu, W.; Kong, G.; Ma, X.; et al. Association between plasma glycocalyx component levels and poor prognosis in severe influenza type A (H1N1). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, A.W.; Galbraith, D.; McEwan, P.; Onions, D. Evaluation of porcine cytomegalovirus as a potential zoonotic agent in xenotransplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1999, 31, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potje, S.R.; Costa, T.J.; Fraga-Silva, T.F.C.; Martins, R.B.; Benatti, M.N.; Almado, C.E.L.; de Sá, K.S.G.; Bonato, V.L.D.; Arruda, E.; Louzada-Junior, P.; et al. Heparin prevents in vitro glycocalyx shedding induced by plasma from COVID-19 patients. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.F.; Jacob, M.; Leipert, S.; Salmon, A.H.; Chappell, D. Degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in clinical settings: Searching for the sheddases. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Nijst, P.; Kiefer, K.; Tang, W.H. Endothelial Glycocalyx as Biomarker for Cardiovascular Diseases: Mechanistic and Clinical Implications. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2017, 14, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kitai, T.; Morales, R.; Kiefer, K.; Chaikijurajai, T.; Tang, W.H.W. Usefulness of Serum Biomarkers of Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage in Prognosis of Decompensated Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 176, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R.L. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Universities Federation For Animal Welfare (UFAW): Wheathampstead, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G.; Patel, V.; Dull, R.O. Human glycocalyx shedding: Systematic review and critical appraisal. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2021, 65, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Experiment | DPZ-ID | Donor | Recipient | Group | Survival | Growth Inhibition | Preservation | Causes for Euthanasia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Weight | Sex | Weight | |||||||
| 1 | #16755 | M | 15.8 kg | M | 16.0 kg | - | 30 days | No | Ischemic | Heart and liver failure [4] |
| 2 | #17186 | F | 19.3 kg | M | 21.5 kg | I | 90 days | Yes | Non-ischemic | Study endpoint [4,5] |
| 3 | #17290 | F | 12.7 kg | M | 13.7 kg | I | 90 days | Yes | Non-ischemic | Study endpoint [4,5] |
| 4 | #17494 | M | 11.6 kg | M | 16.0 kg | II | 15 days | Yes | Non-ischemic | Multiorgan failure (PCMV/PRV) [5,14] |
| 5 | #17492 | F | 24.0 kg | M | 26.0 kg | II | 27 days | Yes | Non-ischemic | Multiorgan failure (PCMV/PRV) [5,14] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bender, M.; Abicht, J.-M.; Reichart, B.; Leuschen, M.; Wall, F.; Radan, J.; Neumann, E.; Mokelke, M.; Buttgereit, I.; Michel, S.; et al. The Endothelial Glycocalyx in Pig-to-Baboon Cardiac Xenotransplantation—First Insights. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061336
Bender M, Abicht J-M, Reichart B, Leuschen M, Wall F, Radan J, Neumann E, Mokelke M, Buttgereit I, Michel S, et al. The Endothelial Glycocalyx in Pig-to-Baboon Cardiac Xenotransplantation—First Insights. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(6):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061336
Chicago/Turabian StyleBender, Martin, Jan-Michael Abicht, Bruno Reichart, Maria Leuschen, Felicia Wall, Julia Radan, Elisabeth Neumann, Maren Mokelke, Ines Buttgereit, Sebastian Michel, and et al. 2024. "The Endothelial Glycocalyx in Pig-to-Baboon Cardiac Xenotransplantation—First Insights" Biomedicines 12, no. 6: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061336
APA StyleBender, M., Abicht, J.-M., Reichart, B., Leuschen, M., Wall, F., Radan, J., Neumann, E., Mokelke, M., Buttgereit, I., Michel, S., Ellgass, R., Gieseke, K., Steen, S., Paskevicius, A., Denner, J., Godehardt, A. W., Tönjes, R. R., Hagl, C., Ayares, D., ... Längin, M. (2024). The Endothelial Glycocalyx in Pig-to-Baboon Cardiac Xenotransplantation—First Insights. Biomedicines, 12(6), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061336







