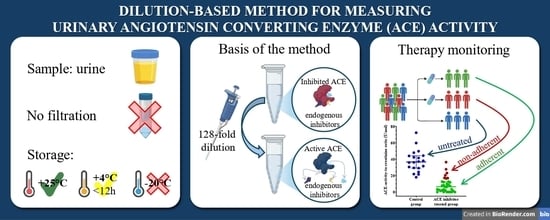
Interference-Free Measurement of Urinary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Monitoring Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Ethical Approval
2.2. Urine Samples
2.3. ACE Activity Measurement with the Fluorescent Kinetic Assay
2.4. Sensitivity Testing of uACE Activity Assay
2.5. Measurement of Creatinine Concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Role of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
3. Results
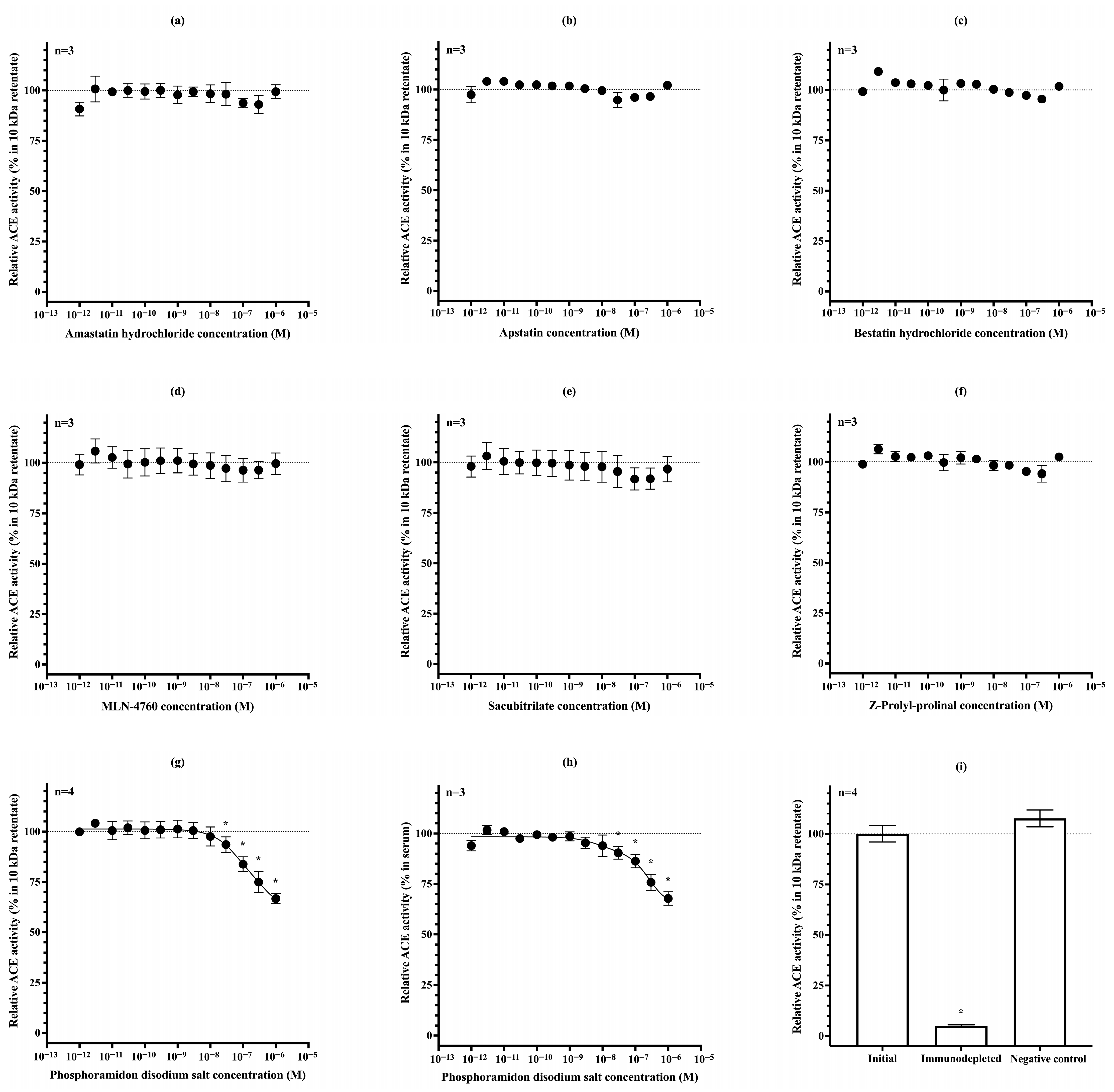
3.1. Only Low-Molecular-Weight (<5 kDa) Endogenous ACE Inhibitors Are Present in Urine
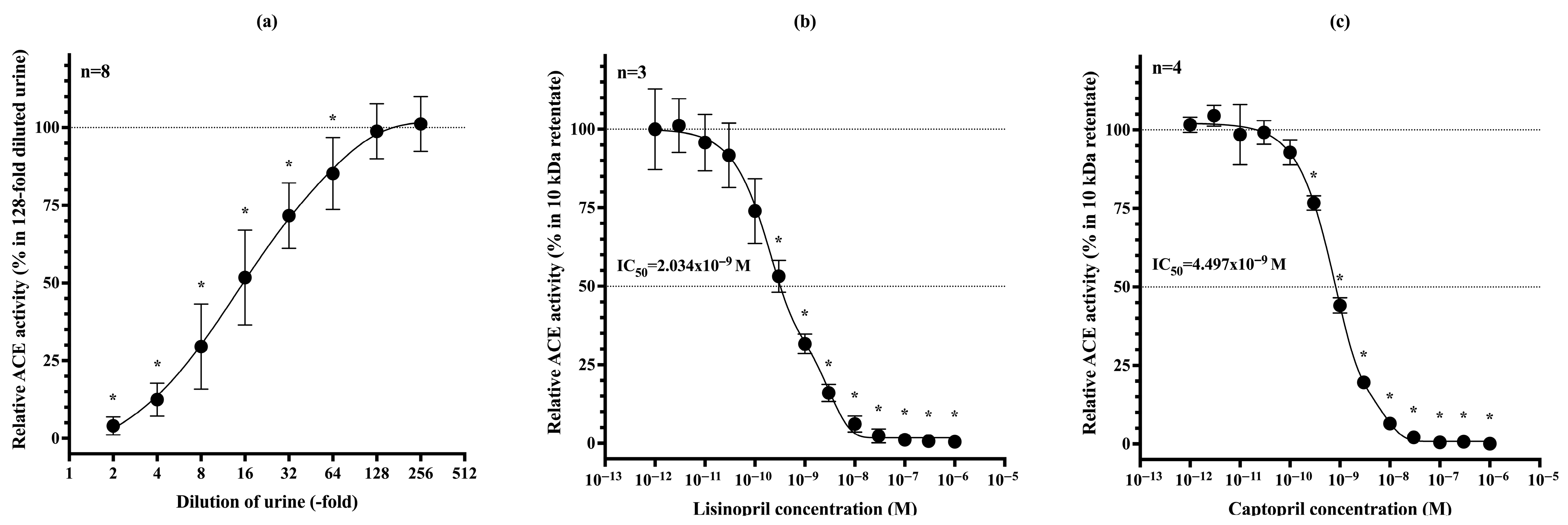
3.2. Dilutional Reversibility and Pharmacological Inhibition of uACE Activity
3.3. Sensitivity Testing of uACE Activity Assay
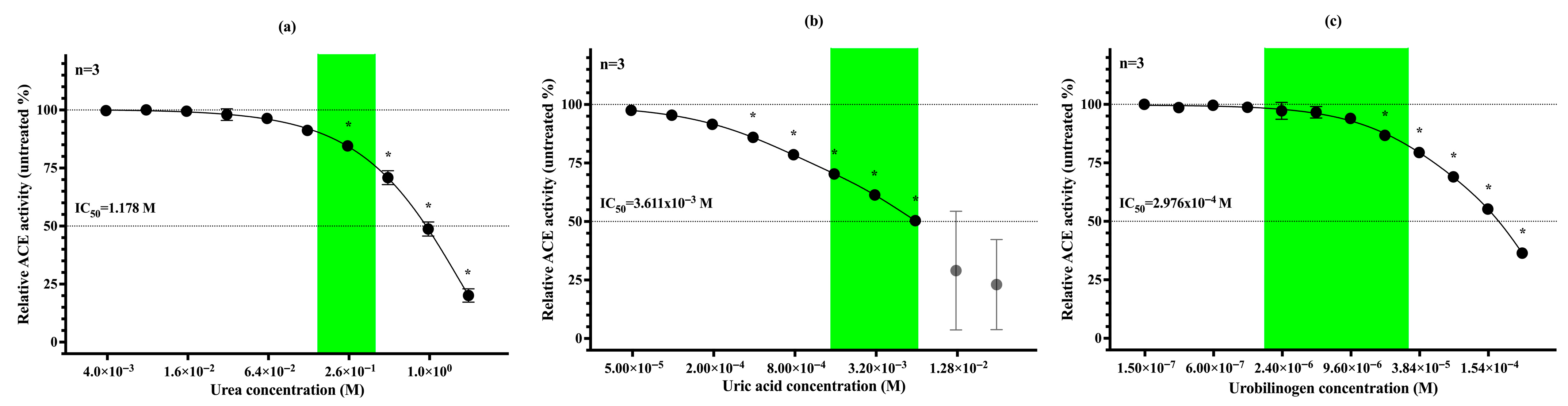
3.4. Urea, Uric Acid and Urobilinogen Act as Physiological Inhibitors of uACE
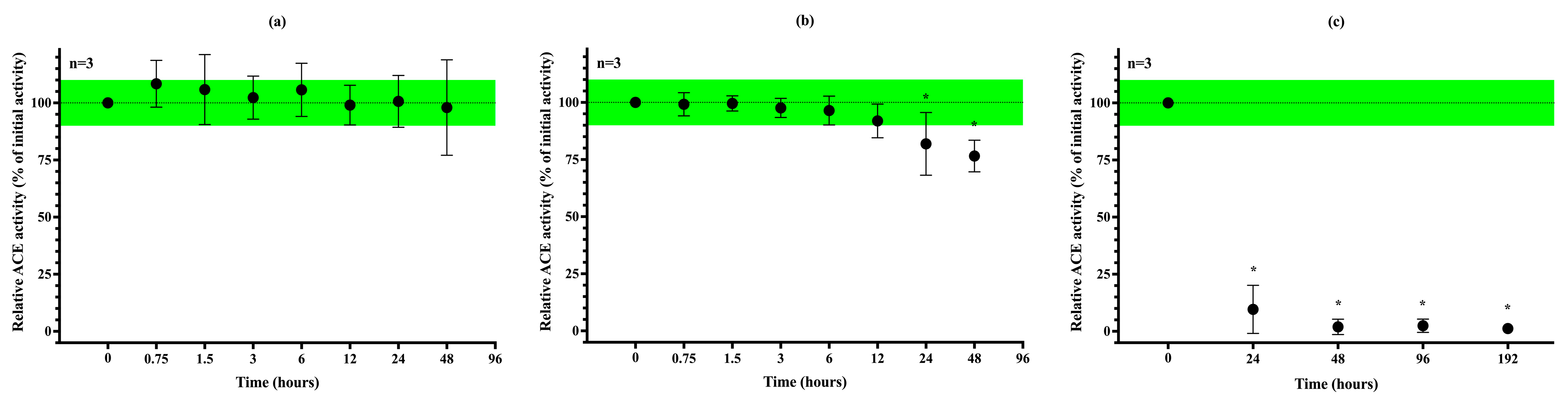
3.5. Stability of uACE Activity Under Different Storage Conditions
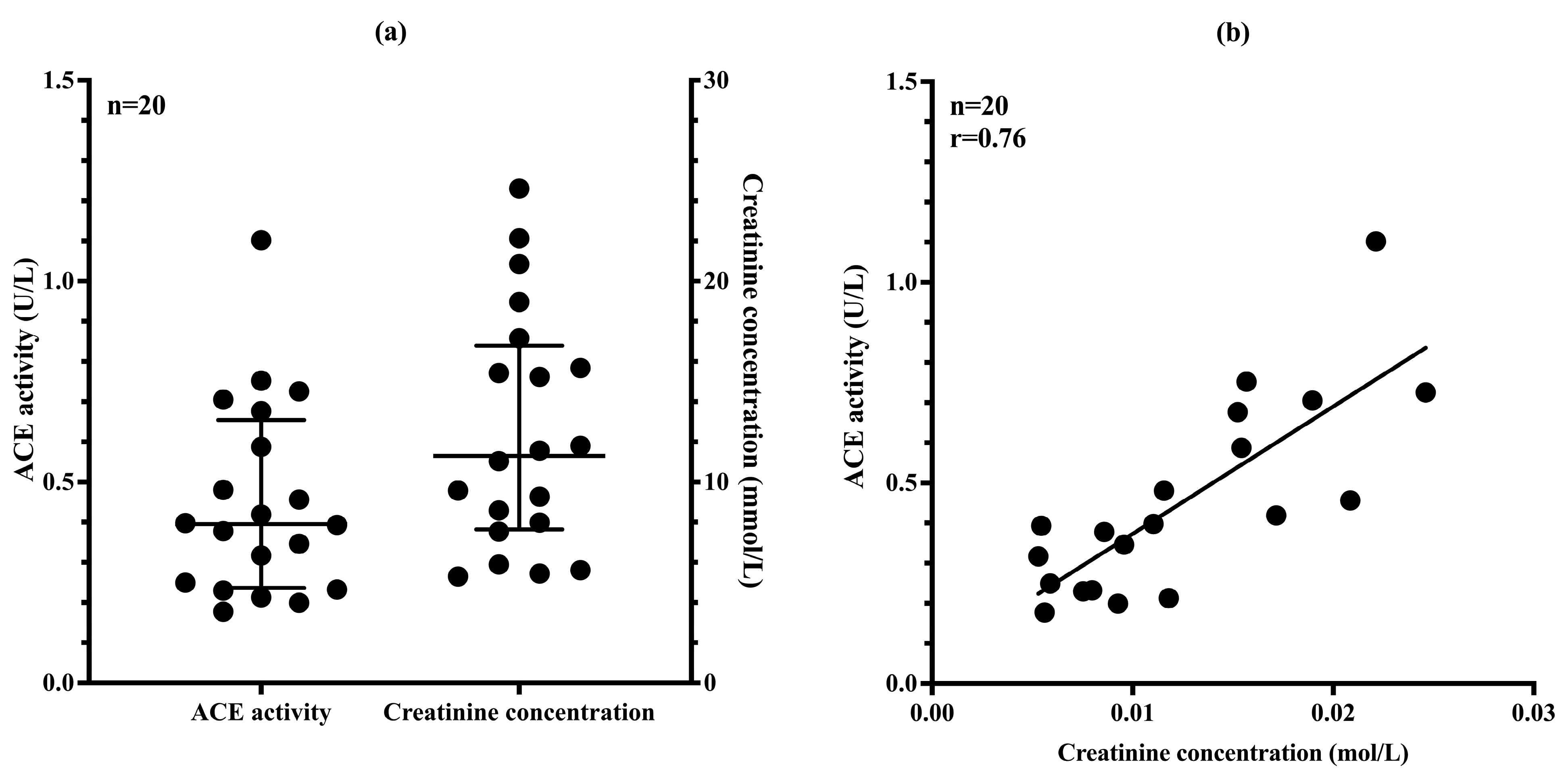
3.6. uACE Activity Correlates Well with Urinary Creatinine Concentration
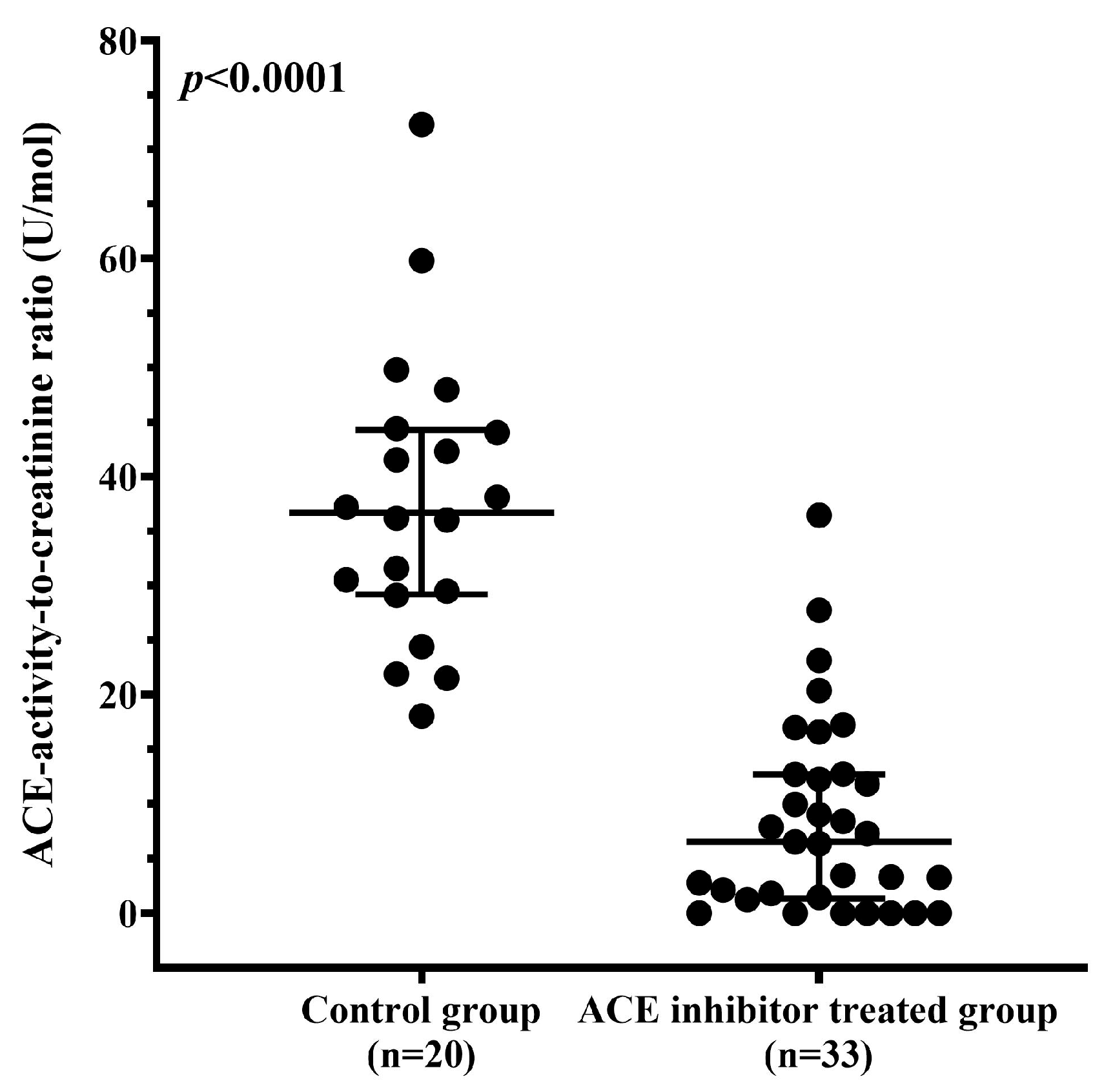
3.7. ACE Inhibitor Treatment Reduces uACE Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ACEi | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ACE I/D | Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| TRIS | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride |
| uACE | Urinary angiotensin-converting enzyme |
References
- Skeggs, L.T.; Kahn, J.R.; Shumway, N.P. The Preparation and Function of the Hypertensin-Converting Enzyme. J. Exp. Med. 1956, 103, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Braunwald, E.; Moyé, L.A.; Basta, L.; Brown, E.J.; Cuddy, T.E.; Davis, B.R.; Geltman, E.M.; Goldman, S.; Flaker, G.C.; et al. Effect of Captopril on Mortality and Morbidity in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.D.; Gurley, S.B.; Oliverio, M.I.; Pazmino, A.K.; Griffiths, R.; Flannery, P.J.; Spurney, R.F.; Kim, H.-S.; Smithies, O.; Le, T.H.; et al. Distinct Roles for the Kidney and Systemic Tissues in Blood Pressure Regulation by the Renin-Angiotensin System. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, R.; Franke, F.E.; Bohle, R.M.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Danilov, S.M. Heterogeneous Distribution of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (CD143) in the Human and Rat Vascular Systems: Vessel, Organ and Species Specificity. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 81, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, P.R.B.; Seegal, B.C.; Hsu, K.C.; Das, M.; Soffer, R.L. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: Vascular Endothelial Localization. Science 1976, 191, 1050–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, D. The Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuch, A.J.; Petukhov, P.A.; Fagyas, M.; Popova, I.A.; Lindeblad, M.O.; Bobkov, A.P.; Kamalov, A.A.; Toth, A.; Dudek, S.M.; Danilov, S.M. Urinary ACE Phenotyping as a Research and Diagnostic Tool: Identification of Sex-Dependent ACE Immunoreactivity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneval, P.; Hinglais, N.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Tricottet, V.; Corvol, P.; Menard, J.; Camilleri, J.P.; Bariety, J. Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme in Human Intestine and Kidney. Histochemistry 1986, 85, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defending, R.; Zimmerman, E.A.; Weare, J.A.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Erdös, E.G. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Epithelial and Neuroepithelial Cells. Neuroendocrinology 1983, 37, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, J.V. The Significance of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme in Granulomatous Inflammation. Functions of ACE in granulomas. Sarcoidosis 1986, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Abu-Izneid, T. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone (RAAS): The Ubiquitous System for Homeostasis and Pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, G.; Bhat, G. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Heart Failure. Cardiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudeva, K.; Balyan, R.; Munshi, A. ACE-Triggered Hypertension Incites Stroke: Genetic, Molecular, and Therapeutic Aspects. Neuromolecular Med. 2020, 22, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, Á.; Guillén-Grima, F.; Morales, G.; Muñoz, S.; Aguinaga-Ontoso, I. Trends in Mortality from Stroke in the European Union, 1996–2015. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Guan, J.; Xin, A.; Zhang, F.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Global Trends in Heart Failure from 1990 to 2019: An Age-period-cohort Analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 3264–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabito Colafella, K.M.; Bovée, D.M.; Danser, A.H.J. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Its Therapeutic Targets. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 186, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D.; Riordan, J.F.; Ehlers, M.R.W. Ace Revisited: A New Target for Structure-Based Drug Design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.J.; Gaggin, H.K.; Zhou, M.; Bash, L.D.; Lautsch, D.; Djatche, L.; Song, Y.; Signorovitch, J.; Stevenson, A.S.; Blaustein, R.O.; et al. Treatment Patterns of Patients with Worsening Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 1932–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudpour, S.H.; Baranova, E.V.; Souverein, P.C.; Asselbergs, F.W.; de Boer, A.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. Determinants of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitor (ACEI) Intolerance and Angioedema in the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrell, S.; Alhomoud, I.S.; Mehta, A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Van Tassell, B.; Dixon, D.L. ACE-Inhibitors in Hypertension: A Historical Perspective and Current Insights. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostis, W.J.; Shetty, M.; Chowdhury, Y.S.; Kostis, J.B. ACE Inhibitor-Induced Angioedema: A Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepho, R.W. Overview of the Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibitors. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2000, 57, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobbee, D.E.; Filippatos, G.; Desai, N.R.; Coats, A.J.S.; Pinto, F.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Kammerer, J.; de Arellano, A.R. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Hyperkalaemia in Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 1821–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Cravedi, P.; Remuzzi, G. The RAAS in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, Z.; Mohan, A.; Johnson, M.L.; Essien, E.J.; Barner, J.C.; Serna, O.; Gallardo, E.; Fleming, M.L.; Ordonez, N.; Holstad, M.M.; et al. Patient-Reported Barriers to Adherence Among ACEI/ARB Users from a Motivational Interviewing Telephonic Intervention. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2022, 16, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawruch, M.; Petrova, M.; Tesar, T.; Murin, J.; Schnorrerova, P.; Paduchova, M.; Celovska, D.; Havelkova, B.; Trnka, M.; Alfian, S.D.; et al. Factors Associated with Non-Adherence to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Older Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1199669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosthuizen, D.; Sturrock, E.D. Exploring the Impact of ACE Inhibition in Immunity and Disease. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2022, 2022, 9028969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyedi, E.E.; Petukhov, P.A.; Kozuch, A.J.; Dudek, S.M.; Toth, A.; Fagyas, M.; Danilov, S.M. ACE Phenotyping in Human Blood and Tissues: Revelation of ACE Outliers and Sex Differences in ACE Sialylation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubu, T.; Kato, I.; Nishimura, K.; Hiwada, K.; Ueda, E. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme in Human Urine. Clin. Chim. Acta 1978, 89, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, W.W.; Hagler, H.K.; Buja, L.M.; Erdös, E.G. Ultrastructural Localization of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (EC 3.4.15.1) and Neutral Metalloendopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) in the Proximal Tubule of the Human Kidney. Lab. Investig. 1988, 59, 789–797. [Google Scholar]
- Erdös, E.G. Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme and the Changes in Our Concepts through the Years. Lewis K. Dahl Memorial Lecture. Hypertens. 1990, 16, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, R.; Bohle, R.M.; Pauls, K.; Eichner, G.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Danilov, S.M.; Franke, F.E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Non-Neoplastic Kidney Diseases. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Baussant, T.; Hubert, C.; Soubrier, F.; Corvol, P. The Angiotensin Converting Enzyme in the Kidney. J. Hypertens. 1989, 7, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, I.; Takada, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Hiwada, K.; Kokubu, T. Increased Urinary Excretion of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme in Patients with Renal Diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1982, 20, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosojima, H.; Miyauchi, E.; Morimoto, S. Urinary Excretion of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme in NIDDM Patients With Nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1989, 12, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.W.; Martin, L.C.; Chung, A.; Pena, G.A. Mammalian Inhibitors of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (Kininase II). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1979, 120B, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baudin, B.; Bénéteau-Burnat, B.; Baumann, F.C.; Giboudeau, J. A Reliable Radiometric Assay for the Determination of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Activity in Urine. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1990, 28, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csongrádi, A.; Enyedi, A.; Takács, I.; Végh, T.; Mányiné, I.S.; Pólik, Z.; Altorjay, I.T.; Balla, J.; Balla, G.; Édes, I.; et al. Optimized Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity Assay for the Accurate Diagnosis of Sarcoidosis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.G.; O’Malley, K. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of the Newer ACE Inhibitors: A Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 19, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, H.; Yang, B. Elevated Urinary Urea by High-Protein Diet Could Be One of the Inducements of Bladder Disorders. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezioso, D.; Strazzullo, P.; Lotti, T.; Bianchi, G.; Borghi, L.; Caione, P.; Carini, M.; Caudarella, R.; Gambaro, G.; Gelosa, M.; et al. Dietary Treatment of Urinary Risk Factors for Renal Stone Formation. A Review of CLU Working Group. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2015, 87, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, E.; Milne, M.D.; Stokes, G.S. Mechanisms of Renal Excretion of Urobilinogen. BMJ 1965, 2, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klauser, R.J.; Robinson, C.J.; Marinkovic, D.V.; Erdös, E.G. Inhibition of Human Peptidyl Dipeptidase (Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme: Kininase II) by Human Serum Albumin and Its Fragments. Hypertension 1979, 1, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagyas, M.; Úri, K.; Siket, I.M.; Daragó, A.; Boczán, J.; Bányai, E.; Édes, I.; Papp, Z.; Tóth, A. New Perspectives in the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) I: Endogenous Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibition. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cheng, A.; Sun, J.; Fan, C.; Meng, R. The Role of Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio as a Biomarker to Predict Stroke. Brain Circ. 2021, 7, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tynkevich, E.; Flamant, M.; Haymann, J.-P.; Metzger, M.; Thervet, E.; Boffa, J.-J.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Houillier, P.; Froissart, M.; Stengel, B.; et al. Decrease in Urinary Creatinine Excretion in Early Stage Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waikar, S.S.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Bonventre, J.V. Normalization of Urinary Biomarkers to Creatinine during Changes in Glomerular Filtration Rate. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuiri, S.; Hemmi, H.; Kumanomidou, H.; Iwamoto, M.; Miyagi, M.; Sakai, K.; Aikawa, A.; Ohara, T.; Yamada, K.; Shimatake, H.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) I/D Genotype and Renal ACE Gene Expression. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, P.O.M.; Helland, A.; Spigset, O.; Hegstad, S. Quantification of 21 Antihypertensive Drugs in Serum Using UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1089, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, E.M.P.; Gerber, C.; Song, Y.; Leggett, C.; Ritchie, U.; Turner, S.; Garg, S. A New LC-MS/MS Bioanalytical Method for Perindopril and Perindoprilat in Human Plasma and Milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6141–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control Group | Study Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | Men | Women | Men | ||
| n | 11 | 9 | 11 | 22 | |
| Age (years) | 49.42 ± 17.32 | 48.04 ± 18.42 | 67.60 ± 7.93 | 70.57 ± 10.39 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.64 (23.53–28.04) | 28.15 ± 6.14 | 29.51 ± 5.61 | 29.80 ± 5.31 | |
| eGFR epi (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 90.00 (85.00–90.00) | 90.00 (86.50–90.00) | 74.82 ± 19.70 | 81.00 (70.50–90.00) | |
| Cardiovascular disease (n, (%)) | 5 (45%) | 4 (44%) | 11 (100%) | 21 (95%) | |
| Hypertension (n, (%)) | 3 (27%) | 2 (22%) | 9 (82%) | 19 (86%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus (n, (%)) | 3 (27%) | 1 (11%) | 5 (45%) | 12 (55%) | |
| Renal failure (n, (%)) | 1 (9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Smoking (n, (%)) | 3 (27%) | 4 (44%) | 3 (27%) | 4 (18%) | |
| ACEI drug type (n, (%)) | perindopril | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (91%) | 17 (77%) |
| ramipril | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (23%) | |
| lisinopril | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) | 0 (0%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, A.Á.; Enyedi, E.E.; Pintér, T.B.; Mányiné, I.S.; Váradi, C.; Bányai, E.; Tóth, A.; Papp, Z.; Fagyas, M. Interference-Free Measurement of Urinary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Monitoring Implications. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102528
Szabó AÁ, Enyedi EE, Pintér TB, Mányiné IS, Váradi C, Bányai E, Tóth A, Papp Z, Fagyas M. Interference-Free Measurement of Urinary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Monitoring Implications. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102528
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Attila Ádám, Enikő Edit Enyedi, Tamás Bence Pintér, Ivetta Siket Mányiné, Csongor Váradi, Emese Bányai, Attila Tóth, Zoltán Papp, and Miklós Fagyas. 2025. "Interference-Free Measurement of Urinary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Monitoring Implications" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102528
APA StyleSzabó, A. Á., Enyedi, E. E., Pintér, T. B., Mányiné, I. S., Váradi, C., Bányai, E., Tóth, A., Papp, Z., & Fagyas, M. (2025). Interference-Free Measurement of Urinary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Monitoring Implications. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102528