Sensory Dysfunction in ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Relevance, Histopathology, Neurophysiology, and Insights from Neuroimaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Clinical Spectrum of Motor Neuron Disease
1.2. Disease Heterogeneity and Extra-Motor Manifestations
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Observations
3.1.1. Pain and Paraesthesia
3.1.2. Gait and Balance Impairment
3.1.3. Gustatory, Olfactory, Pharyngeal and Laryngeal Manifestations
3.1.4. Insights from Electrophysiology Studies
3.1.5. Histopathology and Animal Model Data
3.1.6. Neuroimaging
3.2. Other Motor Neuron Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
References
- Querin, G.; Bede, P.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Pradat, P.F. Biomarkers of Spinal and Bulbar Muscle Atrophy (SBMA): A Comprehensive Review. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudlo, J.; Bißbort, C.; Glass, A.; Grossmann, A.; Hauenstein, K.; Benecke, R.; Teipel, S.J. White matter pathology in ALS and lower motor neuron ALS variants: A diffusion tensor imaging study using tract-based spatial statistics. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, B.S.; Rustemeijer, L.M.M.; Bakker, L.A.; Schröder, C.D.; Veldink, J.H.; van den Berg, L.H.; Nijboer, T.C.W.; van Es, M.A. Cognitive and behavioural changes in PLS and PMA:challenging the concept of restricted phenotypes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebouteux, M.V.; Franques, J.; Guillevin, R.; Delmont, E.; Lenglet, T.; Bede, P.; Desnuelle, C.; Pouget, J.; Pascal-Mousselard, H.; Pradat, P.F. Revisiting the spectrum of lower motor neuron diseases with snake eyes appearance on magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradat, P.F.; Bernard, E.; Corcia, P.; Couratier, P.; Jublanc, C.; Querin, G.; Morelot Panzini, C.; Salachas, F.; Vial, C.; Wahbi, K.; et al. The French national protocol for Kennedy’s disease (SBMA): Consensus diagnostic and management recommendations. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Siah, W.F.; Chipika, R.H.; Chang, K.M.; McKenna, M.C.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Donaghy, C.; et al. Evolving diagnostic criteria in primary lateral sclerosis: The clinical and radiological basis of “probable PLS”. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 417, 117052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, O.; van den Berg, L.H.; Kiernan, M.C. Clinical diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, P.G.; Evans, J.; Knopp, M.; Forster, G.; Hamdalla, H.H.; Wharton, S.B.; Shaw, P.J. Corticospinal tract degeneration in the progressive muscular atrophy variant of ALS. Neurology 2003, 60, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.J.; Abrahams, S.; Goldstein, L.H.; Woolley, S.; McLaughlin, P.; Snowden, J.; Mioshi, E.; Roberts-South, A.; Benatar, M.; HortobaGyi, T.; et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—frontotemporal spectrum disorder (ALS-FTSD): Revised diagnostic criteria. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2017, 18, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Corcia, P.; Couratier, P.; Siah, W.F.; Pradat, P.F.; Bede, P. Frontotemporal Pathology in Motor Neuron Disease Phenotypes: Insights From Neuroimaging. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 723450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, T.J.; de Albuquerque, M.; Lamas, G.M.; Martinez, A.R.; Campos, B.M.; Casseb, R.F.; Silva, C.B.; Branco, L.M.; D’Abreu, A.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; et al. Multimodal MRI-based study in patients with SPG4 mutations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulkerrin, G.; França, M.C., Jr.; Lope, J.; Tan, E.L.; Bede, P. Neuroimaging in hereditary spastic paraplegias: From qualitative cues to precision biomarkers. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 22, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.K. The hereditary spastic paraplegias. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 196, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wen, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Jiang, K.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, M.; et al. Benign monomelic amyotrophy of lower limb in a cohort of chinese patients. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglia, C.; Calvo, A.; Brunetti, M.; Chiò, A.; Grassano, M. Broadening the clinical spectrum of FUS mutations: A case with monomelic amyotrophy with a late progression to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamala, J.M.; Geevasinga, N.; Huynh, W.; Dharmadasa, T.; Howells, J.; Simon, N.G.; Menon, P.; Vucic, S.; Kiernan, M.C. Cortical function and corticomotoneuronal adaptation in monomelic amyotrophy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Walsh, R.; Fagan, A.J.; Hardiman, O. “Sand-watch” spinal cord: A case of inferior cervical spinal cord atrophy. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Bokde, A.L.; Byrne, S.C.; Elamin, M.; Walsh, R.J.; Hardiman, O. Waterskier’s Hirayama syndrome. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, K.; Tomonaga, M.; Kitano, K.; Yamada, T.; Kojima, S.; Arai, K. Focal cervical poliopathy causing juvenile muscular atrophy of distal upper extremity: A pathological study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Hi Shing, S.; Chipika, R.H.; Finegan, E.; Murray, D.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Post-polio Syndrome: More Than Just a Lower Motor Neuron Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Hi Shing, S.; Lope, J.; McKenna, M.C.; Chipika, R.H.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Increased cerebral integrity metrics in poliomyelitis survivors: Putative adaptation to longstanding lower motor neuron degeneration. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.; Nunes, P.P.; Lima, E.T.I.; Assis, A.C.D.; Naylor, F.G.M.; Chieia, M.A.T.; Souza, P.V.S.; Oliveira, A.S.B. O’Sullivan-McLeod syndrome: Unmasking a rare atypical motor neuron disease. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadiri-Sani, M.; Huda, S.; Larner, A.J. O’Sullivan-McLeod syndrome: Clinical features, neuroradiology and nosology. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2014, 75, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walhout, R.; Schmidt, R.; Westeneng, H.J.; Verstraete, E.; Seelen, M.; van Rheenen, W.; de Reus, M.A.; van Es, M.A.; Hendrikse, J.; Veldink, J.H.; et al. Brain morphologic changes in asymptomatic C9orf72 repeat expansion carriers. Neurology 2015, 85, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Hi Shing, S.; McKenna, M.C.; Siah, W.F.; Chipika, R.H.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. The imaging signature of C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansions: Implications for clinical trials and therapy development. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021, 15, 2693–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulé, D.E.; Müller, H.P.; Finsel, J.; Weydt, P.; Knehr, A.; Winroth, I.; Andersen, P.; Weishaupt, J.; Uttner, I.; Kassubek, J.; et al. Deficits in verbal fluency in presymptomatic C9orf72 mutation gene carriers-a developmental disorder. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cistaro, A.; Pagani, M.; Montuschi, A.; Calvo, A.; Moglia, C.; Canosa, A.; Restagno, G.; Brunetti, M.; Traynor, B.J.; Nobili, F.; et al. The metabolic signature of C9ORF72-related ALS: FDG PET comparison with nonmutated patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Lulé, D.; Müller, H.P.; Tan, E.L.; Dorst, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J. Presymptomatic grey matter alterations in ALS kindreds: A computational neuroimaging study of asymptomatic C9orf72 and SOD1 mutation carriers. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 4235–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.R.; Hammers, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Shaw, C.E.; Andersen, P.M.; Brooks, D.J.; Leigh, P.N. Distinct cerebral lesions in sporadic and ’D90A’ SOD1 ALS: Studies with [11C]flumazenil PET. Brain 2005, 128, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sábado, J.; Casanovas, A.; Tarabal, O.; Hereu, M.; Piedrafita, L.; Calderó, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Accumulation of misfolded SOD1 in dorsal root ganglion degenerating proprioceptive sensory neurons of transgenic mice with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 852163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.Q.; Wei, Q.; Wu, Z.Y. Sensory nerve disturbance in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Omer, T.; Finegan, E.; Chipika, R.H.; Iyer, P.M.; Doherty, M.A.; Vajda, A.; Pender, N.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Hutchinson, S.; et al. Connectivity-based characterisation of subcortical grey matter pathology in frontotemporal dementia and ALS: A multimodal neuroimaging study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassone, J.; Taiana, M.; Lombardi, R.; Porretta-Serapiglia, C.; Freschi, M.; Bonanno, S.; Marcuzzo, S.; Caravello, F.; Bendotti, C.; Lauria, G. ALS mouse model SOD1G93A displays early pathology of sensory small fibers associated to accumulation of a neurotoxic splice variant of peripherin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W. The phenotypic variability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Iyer, P.M.; Schuster, C.; Elamin, M.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Kenna, K.; Hardiman, O. The selective anatomical vulnerability of ALS: ’disease-defining’ and ’disease-defying’ brain regions. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2016, 17, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, M.; Silva, A.; Glass, J.; Sladky, J.T.; Benatar, M. Clinical, electrophysiologic, and pathologic evidence for sensory abnormalities in ALS. Neurology 2007, 69, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbay, S.S.; Kahana, E.; Zilber, N.; Cooper, G.; Pintov, S.; Leibowitz, Y. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A study of its presentation and prognosis. J. Neurol. 1985, 232, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, J.D.; Dean, A.F.; Shaw, C.E.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Mills, K.R.; Leigh, P.N. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with sensory neuropathy: Part of a multisystem disorder? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.; Mills, K.; Donaghy, M. Progressive sensory nerve dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A prospective clinical and neurophysiological study. J. Neurol. 1993, 240, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, R.A.; Erwin, A.; Erwin, C.W. Abnormal sensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 1986, 36, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, C.; Sangari, S.; El Mendili, M.M.; Benali, H.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Pradat, P.F. Electrophysiological and spinal imaging evidences for sensory dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugdahl, K.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; de Carvalho, M.; Johnsen, B.; Fawcett, P.R.; Labarre-Vila, A.; Liguori, R.; Nix, W.A.; Schofield, I.S. Generalised sensory system abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A European multicentre study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugdahl, K.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Johnsen, B.; de Carvalho, M.; Fawcett, P.R.; Labarre-Vila, A.; Liguori, R.; Nix, W.A.; Schofield, I.S. A prospective multicentre study on sural nerve action potentials in ALS. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, X.; Hu, J.; Liang, M.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Altered Brain Network in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Resting Graph Theory-Based Network Study at Voxel-Wise Level. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, M.S.; Pannek, K.; Coulthard, A.; McCombe, P.A.; Rose, S.E.; Henderson, R.D. Exposing asymmetric gray matter vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lule, D.; Diekmann, V.; Muller, H.P.; Kassubek, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Birbaumer, N. Neuroimaging of multimodal sensory stimulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipika, R.H.; Mulkerrin, G.; Murad, A.; Lope, J.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Alterations in somatosensory, visual and auditory pathways in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An under-recognised facet of ALS. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Bella, E.; Lombardi, R.; Porretta-Serapiglia, C.; Ciano, C.; Gellera, C.; Pensato, V.; Cazzato, D.; Lauria, G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis causes small fiber pathology. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isak, B.; Pugdahl, K.; Karlsson, P.; Tankisi, H.; Finnerup, N.B.; Furtula, J.; Johnsen, B.; Sunde, N.; Jakobsen, J.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. Quantitative sensory testing and structural assessment of sensory nerve fibres in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 373, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolano, M.; Provitera, V.; Manganelli, F.; Iodice, R.; Caporaso, G.; Stancanelli, A.; Marinou, K.; Lanzillo, B.; Santoro, L.; Mora, G. Non-motor involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: New insight from nerve and vessel analysis in skin biopsy. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2017, 43, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.; Katona, I.; Muller-Newen, G.; Sommer, C.; Necula, G.; Hendrich, C.; Ludolph, A.C.; Sperfeld, A.D. Small-fiber neuropathy in patients with ALS. Neurology 2011, 76, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Brettschneider, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Del Tredici, K. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis--a model of corticofugal axonal spread. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Del Tredici, K.; Toledo, J.B.; Robinson, J.L.; Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Suh, E.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Wood, E.M.; Baek, Y.; et al. Stages of pTDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisset, X.; Cornut-Chauvinc, C.; Clavelou, P.; Pereira, B.; Dallel, R.; Guy, N. Is there pain with neuropathic characteristics in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? A cross-sectional study. Palliat. Med. 2016, 30, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camu, W.; Khoris, J.; Moulard, B.; Salachas, F.; Briolotti, V.; Rouleau, G.A.; Meininger, V. Genetics of familial ALS and consequences for diagnosis. French ALS Research Group. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 165 (Suppl. S1), S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Stevens, J.C.; Mulder, D.W.; Espinosa, R.E. Frequency of nerve fiber degeneration of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Morphometry of deep and superficial peroneal nerves. Neurology 1975, 25, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoris, J.; Moulard, B.; Briolotti, V.; Hayer, M.; Durieux, A.; Clavelou, P.; Malafosse, A.; Rouleau, G.A.; Camu, W. Coexistence of dominant and recessive familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with the D90A Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation within the same country. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elian, M. Olfactory impairment in motor neuron disease: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1991, 54, 927–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Shephard, B.C.; Geddes, J.F.; Body, G.D.; Martin, J.E. Olfactory disorder in motor neuron disease. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 150, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, R.; Schrempf, W.; Hahner, A.; Hummel, T.; Wolz, M.; Storch, A.; Hermann, A. Impairment in Respiratory Function Contributes to Olfactory Impairment in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, R.; Richter, N.; Sauerbier, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Storch, A.; Hermann, A. Non-Motor Symptoms in Patients Suffering from Motor Neuron Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlarini, C.; Greco, L.C.; Lizio, A.; Gerardi, F.; Sansone, V.A.; Lunetta, C. Taste changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and effects on quality of life. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmatis, L.; Atallah, G.; Scott, S.H.; Taylor, S. The feasibility of using robotic technology to quantify sensory, motor, and cognitive impairments associated with ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor-Gray, L.; Vasilopoulos, T.; Wheeler-Hegland, K.; Wymer, J.; Plowman, E.K. Reflexive Airway Sensorimotor Responses in Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoppolo, G.; Onesti, E.; Gori, M.C.; Schettino, I.; Frasca, V.; Biasiotta, A.; Giordano, C.; Ceccanti, M.; Cambieri, C.; Greco, A.; et al. Laryngeal Sensitivity in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.R.; Harris, D.; Cassel, S.G.; Grimes, E.; Heiman-Patterson, T. Sensory testing in the assessment of laryngeal sensation in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2006, 115, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Bento, M.; de Carvalho, M.; Evangelista, T.; Sales Luís, M.L. Sympathetic sudomotor function and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2001, 2, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, J.; Manvir, B.; Sumit, S.; Vinay, G.; Trilochan, S.; Garima, S.; Padma, M.V.; Madhuri, B. Quantitative thermal sensory testing in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using reaction time exclusive method of levels (MLE). Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 46, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhang, S.; Kang, D.X.; Fan, D.S. Fully intact contact heat evoked potentials in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Polychronopoulos, P.; Talelli, P.; Chroni, E. F wave study in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Assessment of balance between upper and lower motor neuron involvement. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouget, J. Electroneuromyographic criteria of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2006, 162, 4S34–4S42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Underwood, C.K.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Butler, T.J.; Cowin, G.J.; Wallace, R.H. Non-invasive diffusion tensor imaging detects white matter degeneration in the spinal cord of a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, B.A.; Griffin, J.W.; Crain, B.J.; Scavina, M.; Chance, P.F.; Cornblath, D.R. Autosomal dominant juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 1999, 122, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Canu, E.; Inuggi, A.; Chio, A.; Riva, N.; Silani, V.; Calvo, A.; Messina, S.; Falini, A.; Comi, G.; et al. Resting state functional connectivity alterations in primary lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, E.; Zachou, A.; Breza, M.; Kladi, A.; Karadima, G.; Koutsis, G. Disentangling balance impairments in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 705, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, H.; Guan, Y. Comparison of clinical and physiological characteristics between Kennedy disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2014, 34, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.M.; Alberman, E.; Swash, M. Comparison of sporadic and familial disease amongst 580 cases of motor neuron disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siniscalchi, A. Tolerability of riluzole: A review of the literature. Clin. Ter. 2004, 155, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.L.; Landis, B.E. Riluzole: A new agent for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 1997, 31, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, H.M.; Fulton, B.; Benfield, P. Riluzole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic potential in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Drugs 1996, 52, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, G.A.; Weir, A.I.; Hansen, S.; Ballantyne, J.P. Sensory involvement in motor neuron disease: Further evidence from automated thermal threshold determination. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1985, 48, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, M.; de Marco, G.; Grami, F.; Termoz, N.; Couillandre, A.; Querin, G.; Bede, P.; Pradat, P.F. Neural Correlates of Motor Imagery of Gait in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, M.; Pradat, P.F.; Termoz, N.; Couillandre, A.; Bede, P.; de Marco, G. Motor imagery in amyotrophic lateral Sclerosis: An fMRI study of postural control. NeuroImage Clinical 2022, 35, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, M.; Couillandre, A.; Mseddi, E.; Termoz, N.; Abidi, M.; Bardinet, E.; Delgadillo, D.; Lenglet, T.; Querin, G.; Welter, M.L.; et al. Extrapyramidal deficits in ALS: A combined biomechanical and neuroimaging study. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipika, R.H.; Mulkerrin, G.; Pradat, P.F.; Murad, A.; Ango, F.; Raoul, C.; Bede, P. Cerebellar pathology in motor neuron disease: Neuroplasticity and neurodegeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradat, P.F.; Bruneteau, G.; Munerati, E.; Salachas, F.; Le Forestier, N.; Lacomblez, L.; Lenglet, T.; Meininger, V. Extrapyramidal stiffness in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Chipika, R.H.; Christidi, F.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Karavasilis, E.; Argyropoulos, G.D.; Lope, J.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Velonakis, G.; Dupuis, L.; et al. Genotype-associated cerebellar profiles in ALS: Focal cerebellar pathology and cerebro-cerebellar connectivity alterations. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamagoe, K.; Yamada, S.; Kawakami, R.; Miyake, Z.; Tozaka, N.; Okune, S.; Takeda, H.; Koganezawa, T.; Tamaoka, A. Vestibular dysfunction as cortical damage with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 397, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahedl, M.; Tan, E.L.; Kleinerova, J.; Delaney, S.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Doherty, M.A.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Pradat, P.F.; Raoul, C.; Ango, F.; et al. Progressive Cerebrocerebellar Uncoupling in Sporadic and Genetic Forms of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurology 2024, 103, e209623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, I.; Dalin, D.; Heimbach, B.; Wiesmeier, I.K.; Maurer, C. Abnormal trunk control determines postural abnormalities in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 44, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, S.; Milicev, M.; Peric, S.; Basta, I.; Kostic, V.; Stevic, Z. Gait in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Is gait pattern differently affected in spinal and bulbar onset of the disease during dual task walking? Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2014, 15, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Wang, J.; He, P. Multi-resolution entropy analysis of gait symmetry in neurological degenerative diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjak, M.; Hirsch, M.A.; Bravver, E.K.; Bockenek, W.L.; Norton, H.J.; Brooks, B.R. Vestibular deficits leading to disequilibrium and falls in ambulatory amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukomski, M.; Klimek, A. Electronystagmographic examination in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 1993, 27, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, D. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and their clinical utility in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Elamin, M.; Byrne, S.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Kenna, K.; Vajda, A.; Fagan, A.; Bradley, D.G.; Hardiman, O. Patterns of cerebral and cerebellar white matter degeneration in ALS. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Abou-Zeid, E.; Bartoshuk, L.; Rudnicki, S. Is Taste Altered in Patients with ALS? Chemosens. Percept. 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.J.; Schwandner, K.; Hecht, M. Do patients with motor neuron disease suffer from disorders of taste or smell? Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2011, 12, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogyoros, I.; Kiernan, M.C.; Burke, D.; Bostock, H. Ischemic resistance of cutaneous afferents and motor axons in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1998, 21, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, P.; Massoulard, A.; Marin, B.; Nicol, M.; Laplagne, O.; Baptiste, A.; Gindre-Poulvelarie, L.; Couratier, P.; Fraysse, J.L.; Desport, J.C. First assessment at home of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients by a nutrition network in the French region of Limousin. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2012, 13, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoppolo, G.; Schettino, I.; Frasca, V.; Giacomelli, E.; Prosperini, L.; Cambieri, C.; Roma, R.; Greco, A.; Mancini, P.; De Vincentiis, M.; et al. Dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Prevalence and clinical findings. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 128, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.M.; Miller, A.J. Sensory input pathways and mechanisms in swallowing: A review. Dysphagia 2010, 25, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, L.F.; Kim, D.Y.; Paydarfar, D. Sensory dysphagia: A case series and proposed classification of an under recognized swallowing disorder. Head Neck 2019, 41, E71–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunusova, Y.; Plowman, E.K.; Green, J.R.; Barnett, C.; Bede, P. Clinical Measures of Bulbar Dysfunction in ALS. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kawata, A.; Kato, S.; Hayashi, M.; Takamoto, K.; Hayashi, H.; Hirai, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Komori, T.; Oda, M. Autonomic failure in ALS with a novel SOD1 gene mutation. Neurology 2000, 54, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, S.; Stevic, Z.; Milovanovic, B.; Milicic, B.; Rakocevic-Stojanovic, V.; Lavrnic, D.; Apostolski, S. Impairment of cardiac autonomic control in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemisa, K.; Kaelber, D.; Parikh, S.A.; Mackall, J.A. Autonomic etiology of heart block in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, A.; Kato, S.; Hayashi, H.; Hirai, S. Prominent sensory and autonomic disturbances in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with a Gly93Ser mutation in the SOD1 gene. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 153, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hineno, A.; Nakamura, A.; Shimojima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Oyanagai, K.; Ikeda, S. Distinctive clinicopathological features of 2 large families with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis having L106V mutation in SOD1 gene. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 319, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanović, I.V.; Selak-Djokić, B.; Perić, S.; Janković, M.; Arsenijević, V.; Basta, I.; Lavrnić, D.; Stefanova, E.; Stević, Z. Comparison of the clinical and cognitive features of genetically positive ALS patients from the largest tertiary center in Serbia. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Giess, R.; Magnus, T.; Puls, I.; Reiners, K.; Toyka, K.V.; Naumann, M. Progressive sudomotor dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Vecchia, L.; De Maria, B.; Marinou, K.; Sideri, R.; Lucini, A.; Porta, A.; Mora, G. Cardiovascular neural regulation is impaired in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. A study by spectral and complexity analysis of cardiovascular oscillations. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.C.G.; Galhardoni, R.; Silva, V.; Jorge, F.M.H.; Yeng, L.T.; Callegaro, D.; Chadi, G.; Teixeira, M.J.; Ciampi de Andrade, D. Beyond weakness: Characterization of pain, sensory profile and conditioned pain modulation in patients with motor neuron disease: A controlled study. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truini, A.; Biasiotta, A.; Onesti, E.; Di Stefano, G.; Ceccanti, M.; La Cesa, S.; Pepe, A.; Giordano, C.; Cruccu, G.; Inghilleri, M. Small-fibre neuropathy related to bulbar and spinal-onset in patients with ALS. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, G.; Grisan, E.; Scarpa, F.; Fazio, R.; Comola, M.; Quattrini, A.; Comi, G.; Rama, P.; Riva, N. Corneal confocal microscopy reveals trigeminal small sensory fiber neuropathy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.J.; Kuncl, R.W. Decreased glutamate transport by the brain and spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. New Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirguin, I.; Brenner, T.; Argov, Z.; Steiner, I. Multifocal motor nerve conduction abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1992, 112, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hamida, M.; Hentati, F. Charcot’s disease and juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 1984, 140, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jokelainen, M. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Finland. II: Clinical characteristics. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1977, 56, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, M.; Schaumann, B. Hereditary Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. A report of two families. Eur. Neurol. 1976, 14, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isak, B.; Tankisi, H.; Johnsen, B.; Pugdahl, K.; Torvin MØLler, A.; Finnerup, N.B.; Christensen, P.B.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. Involvement of distal sensory nerves in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkantrakorn, K.; Suksasunee, D. Clinical, electrodiagnostic, and outcome correlation in ALS patients in Thailand. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 43, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Song, M.; Sui, K. Analysis of clinical and electrophysiological characteristics of 150 patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in China. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.T.; Cui, F.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.H.; Ling, L.; Huang, X.S. An analysis of characteristics of nerve conduction in 154 cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2016, 55, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefner, J.M.; Tyler, H.R.; Krarup, C. Abnormalities in the sensory action potential in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theys, P.A.; Peeters, E.; Robberecht, W. Evolution of motor and sensory deficits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis estimated by neurophysiological techniques. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegat, A.; Bouhour, F.; Mouzat, K.; Vial, C.; Pegat, B.; Leblanc, P.; Broussolle, E.; Millecamps, S.; Lumbroso, S.; Bernard, E. Electrophysiological Characterization of C9ORF72-Associated Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 82, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnia, M.; Kelly, J.J. Role of electromyography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, E.; Nakamura, T.; Atsuta, N.; Nakatochi, M.; Suzuki, M.; Harada, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Hayashi, N.; Sobue, G.; Katsuno, M. A nerve conduction study predicts the prognosis of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2524–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasheiff, R.M.; Drake, M.E.; Brendle, A.; Erwin, C.W. Abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 60, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangari, S.; Giron, A.; Marrelec, G.; Pradat, P.F.; Marchand-Pauvert, V. Abnormal cortical brain integration of somatosensory afferents in ALS. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Bokuda, K.; Kimura, H.; Kamiyama, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Kawata, A.; Isozaki, E.; Ugawa, Y. Sensory cortex hyperexcitability predicts short survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2018, 90, e1578–e1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isak, B.; Tankisi, H.; Johnsen, B.; Pugdahl, K.; Finnerup, N.B.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. Laser and somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 3322–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, J.S.; Yiannikas, C. Multimodality evoked potentials in motor neuron disease. Arch. Neurol. 1990, 47, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgesco, M.; Salerno, A.; Carlander, B.; Léger, J.J.; Camu, W.; Billiard, M.; Cadilhac, J. Somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 1994, 150, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinovici, A. Abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rom. J. Neurol. Psychiatry 1993, 31, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mondelli, M.; Rossi, A.; Passero, S.; Guazzi, G.C. Involvement of peripheral sensory fibers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Electrophysiological study of 64 cases. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszewicz, M.; Bilińska, M.; Podemski, R. Electrophysiological estimation of the peripheral nerves conduction parameters and the autonomic nervous system function in the course of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2005, 39, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, M.; Swash, M. Nerve conduction studies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardelli, A.; Inghilleri, M.; Formisano, R.; Accornero, N.; Manfredi, M. Stimulation of motor tracts in motor neuron disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swash, M. Sensorimotor integration is problematic in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 849–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ueda, M.; Hirayama, M.; Katsuno, M. Impaired pain processing and its association with attention disturbance in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 3327–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norioka, R.; Shimizu, T.; Bokuda, K.; Morishima, R.; Kawazoe, T.; Kimura, H.; Asano, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Takahashi, K. Enlarged high frequency oscillations of the median nerve somatosensory evoked potential and survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, R.; Golaszewski, S.; Thomschewski, A.; Sebastianelli, L.; Versace, V.; Brigo, F.; Orioli, A.; Saltuari, L.; Höller, Y.; Trinka, E. Disinhibition of sensory cortex in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 722, 134860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höffken, O.; Schmelz, A.; Lenz, M.; Gruhn, K.; Grehl, T.; Tegenthoff, M.; Sczesny-Kaiser, M. Excitability in somatosensory cortex correlates with motoric impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, J.M.; Howells, J.; Dharmadasa, T.; Huynh, W.; Park, S.B.; Burke, D.; Kiernan, M.C. Excitability of sensory axons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, J.Y.; Lu, F.Z.; Xia, X.L.; Wang, L.X.; Zheng, C.J. Electrophysiological differences between Hirayama disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cervical spondylotic amyotrophy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, I.L.; Tortelli, R.; Samarelli, V.; D’Errico, E.; Sardaro, M.; Difruscolo, O.; Calabrese, R.; Francesco Vde, V.; Livrea, P.; de Tommaso, M. Laser evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 288, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, M.; Hanajima, R.; Terao, Y.; Sato, F.; Okano, T.; Yuasa, K.; Furubayashi, T.; Okabe, S.; Arai, N.; Ugawa, Y. Median nerve somatosensory evoked potentials and their high-frequency oscillations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, K.; Tobimatsu, S.; Furuya, H.; Kira, J. Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis showing abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials: A report of three cases. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi 2001, 92, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, A.; Kawashima, A.; Doi, S.; Moriwaka, F.; Tashiro, K. The spinal somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in relation to the spinal cord conduction velocities. No Shinkei 1999, 51, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Mattler, W.J.; Jakob, M.; Zierz, S. Focal sensory nerve abnormalities in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 162, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeryk-Szajewska, B.; Kostera-Pruszczyk, A.; Rowińska-Marcińska, K.; Karwańska, A. Median nerve electrophysiological assessment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 1998, 32, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mogyoros, I.; Kiernan, M.C.; Burke, D.; Bostock, H. Strength-duration properties of sensory and motor axons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 1998, 121, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgesco, M.; Salerno, A.; Camu, W. Somatosensory evoked potentials elicited by stimulation of lower-limb nerves in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 104, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, G.; Tinazzi, M.; Polo, A.; Rizzuto, N. Motor neuron disease with pyramidal tract dysfunction involves the cortical generators of the early somatosensory evoked potential to tibial nerve stimulation. Neurology 1996, 47, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Guadagnino, M.; Brescia Morra, V.; Nolfe, G. Multimodality evoked potentials in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A statistical approach. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1993, 33, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.X.; Tang, X. Relation between the clinical manifestations and electromyographic findings in motor neurone disease. Zhonghua Shen Jing Jing Shen Ke Za Zhi 1991, 24, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zanette, G.; Polo, A.; Gasperini, M.; Bertolasi, L.; De Grandis, D. Far-field and cortical somatosensory evoked potentials in motor neuron disease. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facco, E.; Micaglio, G.; Liviero, M.C.; Ceccato, M.B.; Toffoletto, F.; Martinuzzi, A.; Angelini, C. Sensory-motor conduction time in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Riv. Di Neurol. 1989, 59, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Cosi, V.; Poloni, M.; Mazzini, L.; Callieco, R. Somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, M.; Tan, R.; Halliday, G.M.; Kril, J.J. Spread of pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Assessment of phosphorylated TDP-43 along axonal pathways. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, F.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H.; Ludolph, A. The multisystem degeneration amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—neuropathological staging and clinical translation. Arch. Ital. De Biol. 2017, 155, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, F.; Brandmeir, N.J.; Kwong, L.K.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Elman, L.; McCluskey, L.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Evidence of multisystem disorder in whole-brain map of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, F.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Robinson, J.; Uryu, K.; Neumann, M.; Brandmeir, N.J.; Xie, S.X.; Kwong, L.K.; Elman, L.; McCluskey, L.; et al. Clinical and pathological continuum of multisystem TDP-43 proteinopathies. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behler, A.; Müller, H.P.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H.; Ludolph, A.C.; Lulé, D.; Kassubek, J. Multimodal in vivo staging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using artificial intelligence. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldaranov, D.; Khomenko, A.; Kobor, I.; Bogdahn, U.; Gorges, M.; Kassubek, J.; Muller, H.P. Longitudinal Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Based Assessment of Tract Alterations: An Application to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassubek, J.; Muller, H.P.; Del Tredici, K.; Brettschneider, J.; Pinkhardt, E.H.; Lule, D.; Bohm, S.; Braak, H.; Ludolph, A.C. Diffusion tensor imaging analysis of sequential spreading of disease in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis confirms patterns of TDP-43 pathology. Brain 2014, 137, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassubek, J.; Müller, H.P.; Del Tredici, K.; Lulé, D.; Gorges, M.; Braak, H.; Ludolph, A.C. Imaging the pathoanatomy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in vivo: Targeting a propagation-based biological marker. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.P.; Del Tredici, K.; Lulé, D.; Müller, K.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J. In vivo histopathological staging in C9orf72-associated ALS: A tract of interest DTI study. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Dyck, P.J.; Shimono, M.; Okazaki, H.; Tateishi, J.; Doi, H. Morphometric comparison of the vulnerability of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1981, 40, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.M.; South, P.W. The topographic distribution of brain atrophy in frontal lobe dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1993, 85, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.A.; Neumann, M.; Baborie, A.; Sampathu, D.M.; Du Plessis, D.; Jaros, E.; Perry, R.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Mann, D.M.A.; Lee, V.M.Y. A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Lope, J.; Bede, P.; Tan, E.L. Thalamic pathology in frontotemporal dementia: Predilection for specific nuclei, phenotype-specific signatures, clinical correlates, and practical relevance. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J.; Devos, D.; Moreau, C.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Deramecourt, V.; Pasquier, F.; Maurage, C.A.; Cordonnier, C.; Leys, D.; et al. Topographic distribution of brain iron deposition and small cerebrovascular lesions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: A post-mortem 7.0-tesla magnetic resonance imaging study with neuropathological correlates. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2017, 117, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, Y.; Robinson, A.C.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Troakes, C.; Rollinson, S.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Suzuki, G.; Nonaka, T.; Shi, J.; et al. Neurodegeneration in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neurone disease associated with expansions in C9orf72 is linked to TDP-43 pathology and not associated with aggregated forms of dipeptide repeat proteins. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troakes, C.; Maekawa, S.; Wijesekera, L.; Rogelj, B.; Siklos, L.; Bell, C.; Smith, B.; Newhouse, S.; Vance, C.; Johnson, L.; et al. An MND/ALS phenotype associated with C9orf72 repeat expansion: Abundant p62-positive, TDP-43-negative inclusions in cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum but without associated cognitive decline. Neuropathology 2012, 32, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyanagi, K.; Mochizuki, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Nagao, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Matsubara, S.; Komori, T. Marked preservation of the visual and olfactory pathways in ALS patients in a totally locked-in state. Clin. Neuropathol. 2015, 34, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; El Mendili, M.M.; Morizot-Koutlidis, R.; Lehericy, S.; Meininger, V.; Blancho, S.; Rossignol, S.; Benali, H.; Pradat, P.F. Involvement of spinal sensory pathway in ALS and specificity of cord atrophy to lower motor neuron degeneration. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2013, 14, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, W.G.; Good, P.; Rasool, C.G.; Adelman, L.S. Morphometric and biochemical studies of peripheral nerves in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 14, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heads, T.; Pollock, M.; Robertson, A.; Sutherland, W.H.; Allpress, S. Sensory nerve pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Conte, A.; Del Grande, A.; Bisogni, G.; Romano, A.; Sabatelli, M. Sural nerve pathology in ALS patients: A single-centre experience. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devigili, G.; Uçeyler, N.; Beck, M.; Reiners, K.; Stoll, G.; Toyka, K.V.; Sommer, C. Vasculitis-like neuropathy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis unresponsive to treatment. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, N.; Kataoka, H.; Sugie, K.; Kawahara, M.; Horikawa, H.; Kusunoki, S.; Ueno, S. Clinical analysis and outcomes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with demyelinating polyneuropathy. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2012, 13, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hamida, M.; Letaief, F.; Hentati, F.; Ben Hamida, C. Morphometric study of the sensory nerve in classical (or Charcot disease) and juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 78, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.K.; Sutherland, N.M.; Zhang, S.; Hatzipetros, T.; Vieira, F.; Valdez, G. The ALS-inducing factors, TDP43(A315T) and SOD1(G93A), directly affect and sensitize sensory neurons to stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, S.K.; Kemp, Z.; Hatzipetros, T.; Vieira, F.; Valdez, G. Degeneration of proprioceptive sensory nerve endings in mice harboring amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-causing mutations. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 2477–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcuzzo, S.; Bonanno, S.; Figini, M.; Scotti, A.; Zucca, I.; Minati, L.; Riva, N.; Domi, T.; Fossaghi, A.; Quattrini, A.; et al. A longitudinal DTI and histological study of the spinal cord reveals early pathological alterations in G93A-SOD1 mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 293, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filali, M.; Lalonde, R.; Rivest, S. Sensorimotor and cognitive functions in a SOD1(G37R) transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.; Murray, E.A. Functional interaction of medial mediodorsal thalamic nucleus but not nucleus accumbens with amygdala and orbital prefrontal cortex is essential for adaptive response selection after reinforcer devaluation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.R.; Culver, D.G.; Davis, A.A.; Tennant, P.; Wang, M.; Coleman, M.; Asress, S.; Adalbert, R.; Alexander, G.M.; Glass, J.D. The WldS gene modestly prolongs survival in the SOD1G93A fALS mouse. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.S.; Wu, D.X.; Wu, H.R.; Wu, S.Y.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Bu, H.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, C.Y. Sensory involvement in the SOD1-G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.A.; Herrando-Grabulosa, M.; Vilches, J.J.; Navarro, X. Involvement of sensory innervation in the skin of SOD1(G93A) ALS mice. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2016, 21, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Schuster, J.E.; Fu, R.; Siddique, T.; Heckman, C.J. Progressive changes in synaptic inputs to motoneurons in adult sacral spinal cord of a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15031–15038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowin, G.J.; Butler, T.J.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Watson, C.; Wallace, R.H. Magnetic resonance microimaging of the spinal cord in the SOD1 mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis detects motor nerve root degeneration. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard-Marissal, N.; Médard, J.J.; Azzedine, H.; Chrast, R. Dysfunction in endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria crosstalk underlies SIGMAR1 loss of function mediated motor neuron degeneration. Brain 2015, 138, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.R.; Gregory, J.M.; Dando, O.; Carter, R.N.; Burr, K.; Nanda, J.; Story, D.; McDade, K.; Smith, C.; Morton, N.M.; et al. Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficits in C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor neurons cause dysfunctional axonal homeostasis. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, L.; Shankar, S.K.; Santosh, V.; Taly, A.B.; Nagaraja, D.; Devi, G.; Satishchandra, P.; Swamy, H.S.; Das, S.; Nagraj, D.; et al. Light and ultrastructural pathology of spinal cords in sporadic forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from South Asia. Neurol. India 1995, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bączyk, M.; Alami, N.O.; Delestrée, N.; Martinot, C.; Tang, L.; Commisso, B.; Bayer, D.; Doisne, N.; Frankel, W.; Manuel, M.; et al. Synaptic restoration by cAMP/PKA drives activity-dependent neuroprotection to motoneurons in ALS. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, A.Y.T.; Agrawal, I.; Ho, W.Y.; Yen, Y.C.; Pinter, A.J.; Liu, J.; Phua, Q.X.C.; Koh, K.B.; Chang, J.C.; Sanford, E.; et al. Loss of TDP-43 in astrocytes leads to motor deficits by triggering A1-like reactive phenotype and triglial dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29101–29112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Soto, M.; Riancho, J.; Tapia, O.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M.T. Satellite Glial Cells of the Dorsal Root Ganglion: A New “Guest/Physiopathological Target” in ALS. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 595751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasekera, A.; Crabbé, M.; Tomé, S.O.; Gsell, W.; Sima, D.; Casteels, C.; Dresselaers, T.; Deroose, C.; Van Huffel, S.; Rudolf Thal, D.; et al. Non-invasive characterization of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a hTDP-43(A315T) mouse model: A PET-MR study. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 27, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Quinn, K.; Spigelman, I.; Pantazis, A.; Olcese, R.; Wiedau-Pazos, M.; Chandler, S.H.; Venugopal, S. Circuit-Specific Early Impairment of Proprioceptive Sensory Neurons in the SOD1(G93A) Mouse Model for ALS. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8798–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Bokde, A.L.; Byrne, S.; Elamin, M.; Fagan, A.J.; Hardiman, O. Spinal cord markers in ALS: Diagnostic and biomarker considerations. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2012, 13, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mendili, M.M.; Querin, G.; Bede, P.; Pradat, P.F. Spinal Cord Imaging in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Historical Concepts-Novel Techniques. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoanandrianina, H.; Grapperon, A.M.; Taso, M.; Girard, O.M.; Duhamel, G.; Guye, M.; Ranjeva, J.P.; Attarian, S.; Verschueren, A.; Callot, V. Region-specific impairment of the cervical spinal cord (SC) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A preliminary study using SC templates and quantitative MRI (diffusion tensor imaging/inhomogeneous magnetization transfer). NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipika, R.H.; Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; McKenna, M.C.; Christidi, F.; Chang, K.M.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Pender, N.; et al. “Switchboard” malfunction in motor neuron diseases: Selective pathology of thalamic nuclei in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipika, R.H.; Siah, W.F.; Shing, S.L.H.; Finegan, E.; McKenna, M.C.; Christidi, F.; Chang, K.M.; Karavasilis, E.; Vajda, A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; et al. MRI data confirm the selective involvement of thalamic and amygdalar nuclei in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machts, J.; Loewe, K.; Kaufmann, J.; Jakubiczka, S.; Abdulla, S.; Petri, S.; Dengler, R.; Heinze, H.J.; Vielhaber, S.; Schoenfeld, M.A.; et al. Basal ganglia pathology in ALS is associated with neuropsychological deficits. Neurology 2015, 85, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christidi, F.; Kleinerova, J.; Tan, E.L.; Delaney, S.; Tacheva, A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Doherty, M.A.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Hardiman, O.; Siah, W.F.; et al. Limbic Network and Papez Circuit Involvement in ALS: Imaging and Clinical Profiles in GGGGCC Hexanucleotide Carriers in C9orf72 and C9orf72-Negative Patients. Biology 2024, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocchetta, M.; Gordon, E.; Cardoso, M.J.; Modat, M.; Ourselin, S.; Warren, J.D.; Rohrer, J.D. Thalamic atrophy in frontotemporal dementia—Not just a C9orf72 problem. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.C.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Murad, A.; Lope, J.; Hardiman, O.; Hutchinson, S.; Bede, P. Focal thalamus pathology in frontotemporal dementia: Phenotype-associated thalamic profiles. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 436, 120221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetta, M.; Iglesias, J.E.; Neason, M.; Cash, D.M.; Warren, J.D.; Rohrer, J.D. Thalamic nuclei in frontotemporal dementia: Mediodorsal nucleus involvement is universal but pulvinar atrophy is unique to C9orf72. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Menke, R.A.L.; Talbot, K.; Kiernan, M.C.; Turner, M.R. Regional thalamic MRI as a marker of widespread cortical pathology and progressive frontotemporal involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, R.A.L.; Proudfoot, M.; Talbot, K.; Turner, M.R. The two-year progression of structural and functional cerebral MRI in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Yao, J.C.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Abnormal cortical-basal ganglia network in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A voxel-wise network efficiency analysis. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 333, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhour, M.S.; Doidy, F.; Mondou, A.; Pélerin, A.; Carluer, L.; Eustache, F.; Viader, F.; Desgranges, B. Voxel-based mapping of grey matter volume and glucose metabolism profiles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Ji, B.; Zhou, C.Y.; Li, L.C.; Li, Z.H.; Hu, X.P.; Hu, J. Differential Impairment of Thalamocortical Structural Connectivity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Senda, J.; Watanabe, H.; Epifanio, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Imai, K.; Riku, Y.; Li, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Ito, M.; et al. Involvement of the caudate nucleus head and its networks in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia continuum. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2016, 17, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laere, K.; Vanhee, A.; Verschueren, J.; De Coster, L.; Driesen, A.; Dupont, P.; Robberecht, W.; Van Damme, P. Value of 18fluorodeoxyglucose-positron-emission tomography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A prospective study. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, G.; Nicoletti, G.; Cherubini, A.; Trotta, M.; Tallarico, T.; Chiriaco, C.; Nistico, R.; Salvino, D.; Bono, F.; Valentino, P.; et al. Diffusion tensor MRI changes in gray structures of the frontal-subcortical circuits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Aoki, S.; Iwata, N.K.; Abe, O.; Mori, H.; Ohtomo, K. Magnetic resonance imaging in patients of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with and without dementia. Brain Nerve 2009, 61, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Yu, B.; Xue, K.; Luo, C.; Xu, Y.; Gong, Q.; He, C.; Zhou, D.; He, L.; et al. Structural and functional changes mapped in the brains of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients with/without dysphagia: A pilot study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivard, L.; Pradat, P.F.; Lehericy, S.; Lacomblez, L.; Dormont, D.; Chiras, J.; Benali, H.; Meininger, V. Diffusion tensor imaging and voxel based morphometry study in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Relationships with motor disability. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.R.; Cagnin, A.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Miller, C.C.; Shaw, C.E.; Brooks, D.J.; Leigh, P.N.; Banati, R.B. Evidence of widespread cerebral microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sach, M.; Winkler, G.; Glauche, V.; Liepert, J.; Heimbach, B.; Koch, M.A.; Buchel, C.; Weiller, C. Diffusion tensor MRI of early upper motor neuron involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2004, 127, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.R.; Sheriff, S.; Maudsley, A.; Govind, V. Diffusion tensor imaging of basal ganglia and thalamus in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuroimaging 2013, 23, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.L.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; Murphy, J.; Henry, R.G.; Kramer, J.H.; Miller, B.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. A voxel-based morphometry study of patterns of brain atrophy in ALS and ALS/FTLD. Neurology 2005, 65, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.M.; Bocchetta, M.; Todd, E.G.; Tse, N.Y.; Devenney, E.M.; Tu, S.; Caga, J.; Hodges, J.R.; Halliday, G.M.; Irish, M.; et al. Tackling clinical heterogeneity across the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia spectrum using a transdiagnostic approach. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosottini, M.; Pesaresi, I.; Piazza, S.; Diciotti, S.; Cecchi, P.; Fabbri, S.; Carlesi, C.; Mascalchi, M.; Siciliano, G. Structural and functional evaluation of cortical motor areas in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosskreutz, J.; Kaufmann, J.; Fradrich, J.; Dengler, R.; Heinze, H.J.; Peschel, T. Widespread sensorimotor and frontal cortical atrophy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.L.; Babu, S.; Anteraper, S.A.; Triantafyllou, C.; Keil, B.; Rowe, O.E.; Rangaprakash, D.; Paganoni, S.; Lawson, R.; Dheel, C.; et al. Ultra-high field (7T) functional magnetic resonance imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A pilot study. NeuroImage Clinical 2021, 30, 102648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Elamin, M.; Byrne, S.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Kenna, K.; Vajda, A.; Pender, N.; Bradley, D.G.; Hardiman, O. Basal ganglia involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2013, 81, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Tai, P.; Genge, A.; Arnold, D.L. Rapid improvement in cortical neuronal integrity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioro, E.P.; Antel, J.P.; Cashman, N.R.; Arnold, D.L. Detection of cortical neuron loss in motor neuron disease by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in vivo. Neurology 1994, 44, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, R.; Dowd, E.; Zang, Y.; Gong, H.; Wang, Z. Alterations in regional functional coherence within the sensory-motor network in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 558, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.; Pannek, K.; Bell, C.; Baumann, F.; Hutchinson, N.; Coulthard, A.; McCombe, P.; Henderson, R. Direct evidence of intra- and interhemispheric corticomotor network degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An automated MRI structural connectivity study. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2661–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Chen, Q.; Huang, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Huang, X.; Tang, H.; Gong, Q.; Shang, H.F. Patterns of spontaneous brain activity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A resting-state FMRI study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahams, S.; Goldstein, L.H.; Simmons, A.; Brammer, M.; Williams, S.C.; Giampietro, V.; Leigh, P.N. Word retrieval in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain 2004, 127, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, M.; Bede, P.; Turner, M.R. Imaging Cerebral Activity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Bokde, A.; Elamin, M.; Byrne, S.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Jordan, N.; Hampel, H.; Gallagher, L.; Lynch, C.; Fagan, A.J.; et al. Grey matter correlates of clinical variables in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A neuroimaging study of ALS motor phenotype heterogeneity and cortical focality. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell, T.; Hartung, V.; Tietz, F.; Penzlin, S.; Ilse, B.; Schweser, F.; Deistung, A.; Bokemeyer, M.; Reichenbach, J.R.; Witte, O.W.; et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging provides insight into white matter damage in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, G.; Woo, J.H.; Chawla, S.; Wang, S.; Sheriff, S.; Elman, L.B.; McCluskey, L.F.; Grossman, M.; Melhem, E.R.; Maudsley, A.A.; et al. Whole-Brain Analysis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis by Using Echo-Planar Spectroscopic Imaging. Radiology 2013, 267, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meoded, A.; Kwan, J.Y.; Peters, T.L.; Huey, E.D.; Danielian, L.E.; Wiggs, E.; Morrissette, A.; Wu, T.; Russell, J.W.; Bayat, E.; et al. Imaging findings associated with cognitive performance in primary lateral sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2013, 3, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, T. Disrupted effective connectivity of the sensorimotor network in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Huang, N.X.; Zou, T.X.; Chen, H.J. Brain Cortical Complexity Alteration in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Preliminary Fractal Dimensionality Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1521679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.P.A.; Pinaya, W.H.L.; Moura, L.M.; Bertoux, M.; Radakovic, R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Souza, L.C.; Hornberger, M.; Sato, J.R. Structural and functional papez circuit integrity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, M.Q.; Ma, L. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Voxel-based Morphometry Study. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2018, 33, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; de Leon, M.; Wang, X.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.H. Relationship between Clinical Parameters and Brain Structure in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients According to Onset Type: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Albuquerque, M.; Anjos, L.G.; Maia Tavares de Andrade, H.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Castellano, G.; Junqueira Ribeiro de Rezende, T.; Nucci, A.; Franca Junior, M.C. MRI Texture Analysis Reveals Deep Gray Nuclei Damage in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.J.; McMillan, C.T.; Brettschneider, J.; Libon, D.J.; Powers, J.; Rascovsky, K.; Toledo, J.B.; Boller, A.; Bekisz, J.; Chandrasekaran, K.; et al. Cognitive decline and reduced survival in C9orf72 expansion frontotemporal degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mioshi, E.; Lillo, P.; Yew, B.; Hsieh, S.; Savage, S.; Hodges, J.R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Hornberger, M. Cortical atrophy in ALS is critically associated with neuropsychiatric and cognitive changes. Neurology 2013, 80, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorns, J.; Jansma, H.; Peschel, T.; Grosskreutz, J.; Mohammadi, B.; Dengler, R.; Münte, T.F. Extent of cortical involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis--an analysis based on cortical thickness. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Kollewe, K.; Samii, A.; Krampfl, K.; Dengler, R.; Munte, T.F. Decreased brain activation to tongue movements in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with bulbar involvement but not Kennedy syndrome. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Hayashi, H.; Yagishita, A. Involvement of the frontotemporal lobe and limbic system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: As assessed by serial computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 116, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, V.; Pioro, E.P. Corticospinal Tract and Related Grey Matter Morphometric Shape Analysis in ALS Phenotypes: A Fractal Dimension Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, V.; Pioro, E.P. Differential involvement of corticospinal tract (CST) fibers in UMN-predominant ALS patients with or without CST hyperintensity: A diffusion tensor tractography study. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 14, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheelakumari, R.; Madhusoodanan, M.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Ranjith, G.; Thomas, B. A Potential Biomarker in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Can Assessment of Brain Iron Deposition with SWI and Corticospinal Tract Degeneration with DTI Help? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojsi, F.; Caiazzo, G.; Corbo, D.; Piccirillo, G.; Cristillo, V.; Femiano, C.; Ferrantino, T.; Cirillo, M.; Monsurro, M.R.; Esposito, F.; et al. Microstructural changes across different clinical milestones of disease in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Oh, J.S.; Sung, J.J.; Lee, K.W.; Song, I.C.; Hong, Y.H. Diffusion tensor tractography analysis of the corpus callosum fibers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 10, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Valsasina, P.; Absinta, M.; Riva, N.; Sala, S.; Prelle, A.; Copetti, M.; Comola, M.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Sensorimotor functional connectivity changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Lin, J.H.; Cai, L.M.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Zou, Z.Y.; Chen, H.J. Abnormal Stability of Dynamic Functional Architecture in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Preliminary Resting-State fMRI Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 744688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J. Precentral degeneration and cerebellar compensation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A multimodal MRI analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, B.; Hu, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, X. Aberrant interhemispheric homotopic functional and structural connectivity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poujois, A.; Schneider, F.C.; Faillenot, I.; Camdessanche, J.P.; Vandenberghe, N.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Antoine, J.C. Brain plasticity in the motor network is correlated with disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Kollewe, K.; Samii, A.; Dengler, R.; Munte, T.F. Functional neuroimaging at different disease stages reveals distinct phases of neuroplastic changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisharady, P.K.; Eberly, L.E.; Cheong, I.; Manousakis, G.; Guliani, G.; Clark, H.B.; Bathe, M.; Walk, D.; Lenglet, C. Tract-specific analysis improves sensitivity of spinal cord diffusion MRI to cross-sectional and longitudinal changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olney, N.T.; Bischof, A.; Rosen, H.; Caverzasi, E.; Stern, W.A.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; Miller, B.L.; Henry, R.G.; Papinutto, N. Measurement of spinal cord atrophy using phase sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) imaging in motor neuron disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, J.; Lin, H.; Sun, G. Detecting neuronal dysfunction of hand motor cortex in ALS: A MRSI study. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2017, 34, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, L.; Huang, X.; Lou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, N.; Liu, T.; Guo, X. Preliminary study on cervical spinal cord in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using MR diffusion tensor imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finegan, E.; Chipika, R.H.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Donaghy, C.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Pender, N.; Hardiman, O.; et al. The clinical and radiological profile of primary lateral sclerosis: A population-based study. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2718–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Chipika, R.H.; Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Hutchinson, S.; Donaghy, C.; McLaughlin, R.L.; et al. Brainstem pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis: A longitudinal neuroimaging study. NeuroImage Clinical 2019, 24, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioro, E.P.; Turner, M.R.; Bede, P. Neuroimaging in primary lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2020, 21, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Chipika, R.H.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Donaghy, C.; Pender, N.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Hardiman, O.; et al. Widespread subcortical grey matter degeneration in primary lateral sclerosis: A multimodal imaging study with genetic profiling. NeuroImage Clinical 2019, 24, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegan, E.; Shing, S.L.H.; Chipika, R.H.; Chang, K.M.; McKenna, M.C.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Pender, N.; Donaghy, C.; et al. Extra-motor cerebral changes and manifestations in primary lateral sclerosis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021, 15, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegan, E.; Hi Shing, S.L.; Chipika, R.H.; McKenna, M.C.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Donaghy, C.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Hutchinson, S.; et al. Thalamic, hippocampal and basal ganglia pathology in primary lateral sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Evidence from quantitative imaging data. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, M.C.; Laluz, V.; Rowe, A.; Findlater, K.; Lee, D.H.; Kennedy, K.; Kramer, J.H.; Strong, M.J. Brain atrophy in primary lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2009, 72, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butman, J.A.; Floeter, M.K. Decreased thickness of primary motor cortex in primary lateral sclerosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kassubek, J.; Juengling, F.D.; Sperfeld, A.D. Widespread white matter changes in Kennedy disease: A voxel based morphometry study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.H.; Liu, R.S.; Yang, B.H.; Wang, P.S.; Lin, K.P.; Lee, Y.C.; Soong, B.W. Cerebral involvement in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy’s disease): A pilot study of PET. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 335, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unrath, A.; Muller, H.P.; Riecker, A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Sperfeld, A.D.; Kassubek, J. Whole brain-based analysis of regional white matter tract alterations in rare motor neuron diseases by diffusion tensor imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, C.C.; Konrad, C.; Sommer, J.; Teismann, I.; Schiffbauer, H. Structural changes of central white matter tracts in Kennedy’s disease—a diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Chen, S.; Qiao, K.; Wang, N.; Wu, Z.Y. Genotype-phenotype correlation in Chinese patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.E.; Freeman, B.K.; Auh, S.; Kokkinis, A.D.; La Pean, A.; Chen, C.; Lehky, T.J.; Shrader, J.A.; Levy, E.W.; Harris-Love, M.; et al. Clinical features of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Brain 2009, 132, 3242–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Hirayama, M.; Hara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Atsuta, N.; Banno, H.; Suzuki, K.; Katsuno, M.; Tanaka, F.; Sobue, G. Discrimination of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using sensory nerve action potentials. Muscle Nerve 2012, 45, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, D. Upper motor neuron involvement in Kennedy disease evaluated by triple stimulation technique. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015, 95, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, M.A.; Wilbourn, A.J. The characteristic electrodiagnostic features of Kennedy’s disease. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhang, S.; Kang, D.X.; Fan, D.S. Test of sensory nerve in patients with Kennedy disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008, 88, 2771–2774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chu, C.C.; Wu, Y.R.; Ro, L.S.; Liu, C.S.; Huang, C.C. Long-term follow-up of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Sugeno, N.; Tateyama, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Kato, M.; Aoki, M. Postural leg tremor in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, E.J.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, K.K. Correlation between the CAG repeat size and electrophysiological findings in patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W. Pathological features of muscles and peripheral nerves of Kennedy’s disease: A report of 12 cases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015, 95, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, T.H.; Soong, B.W.; Chen, J.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lai, K.L.; Wu, Z.A.; Liao, K.K. Multimodal evoked potentials of Kennedy’s disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 34, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntrup, S.; Kristina Teismann, I.; Steinstraeter, O.; Bernd Ringelstein, E.; Pantev, C.; Dziewas, R. Decreased cortical somatosensory finger representation in X-linked recessive bulbospinal neuronopathy (Kennedy disease): A magnetoencephalographic study. J. Neuroimaging 2010, 20, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Hi Shing, S.; Lope, J.; Chipika, R.H.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Extra-motor manifestations in post-polio syndrome (PPS): Fatigue, cognitive symptoms and radiological features. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4569–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, R.L.; Cohen, J.M.; Galski, T.; Frick, N.M. The neuroanatomy of post-polio fatigue. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1994, 75, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodian, D. Histopathologic basis of clinical findings in poliomyelitis. Am. J. Med. 1949, 6, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, M.; Rhines, R.; McCarter, J.C.; Magoun, H.W. Distribution of lesions of the brain stem in poliomyelitis. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1948, 59, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzke, H.A.; Baker, A.B. Poliomyelitis. IV. A study of the midbrain. AMA Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1951, 65, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhan, J.A. Epidemic poliomyelitis; some pathologic observations on human material. Arch. Pathol. 1946, 42, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.C. Post-polio syndrome spinal cord pathology. Case report with immunopathology. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 1995, 753, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokhorenko, O.A.; Vasconcelos, O.M.; Lupu, V.D.; Campbell, W.W.; Jabbari, B. Sensory physiology assessed by evoked potentials in survivors of poliomyelitis. Muscle Nerve 2008, 38, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Hi Shing, S.; Lope, J.; Chipika, R.H.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Imaging data indicate cerebral reorganisation in poliomyelitis survivors: Possible compensation for longstanding lower motor neuron pathology. Data Brief 2021, 38, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Z.; Zheng, H.H.; Ma, Q.L.; Wang, C.; Fan, L.P.; Wu, H.M.; Wang, D.N.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhan, Y.H. Cortical Damage Associated With Cognitive and Motor Impairment in Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: Evidence of a Novel SPAST Mutation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servelhere, K.R.; Rezende, T.J.R.; de Lima, F.D.; de Brito, M.R.; de França Nunes, R.F.; Casseb, R.F.; Pedroso, J.L.; Barsottini, O.G.P.; Cendes, F.; França, M.C., Jr. Brain Damage and Gene Expression Across Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Subtypes. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanaro, D.; Vavla, M.; Frijia, F.; Aghakhanyan, G.; Baratto, A.; Coi, A.; Stefan, C.; Girardi, G.; Paparella, G.; De Cori, S.; et al. Multimodal MRI Longitudinal Assessment of White and Gray Matter in Different SPG Types of Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, I.; Martinez, A.R.M.; de Rezende, T.J.R.; Martins, C.R., Jr.; Martins, M.P.; Lourenço, C.M.; Marques, W., Jr.; Montecchiani, C.; Orlacchio, A.; Pedroso, J.L.; et al. SPG11 mutations cause widespread white matter and basal ganglia abnormalities, but restricted cortical damage. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 19, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Sánchez, F.J.; Fernández-Pena, A.; Martín de Blas, D.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Marcos-Vidal, L.; Guzmán-de-Villoria, J.A.; Fernández-García, P.; Romero, J.; Catalina, I.; Lillo, L.; et al. Thalamic atrophy in patients with pure hereditary spastic paraplegia type 4. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindig, T.; Bender, B.; Hauser, T.K.; Mang, S.; Schweikardt, D.; Klose, U.; Karle, K.N.; Schüle, R.; Schöls, L.; Rattay, T.W. Gray and white matter alterations in hereditary spastic paraplegia type SPG4 and clinical correlations. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaranch, L.; Riverol, M.; Masdeu, J.C.; Lorenzo, E.; Vidal-Taboada, J.M.; Irigoyen, J.; Pastor, M.A.; de Castro, P.; Pastor, P. SPG11 compound mutations in spastic paraparesis with thin corpus callosum. Neurology 2008, 71, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehr, U.; Bauer, P.; Winner, B.; Schule, R.; Olmez, A.; Koehler, W.; Uyanik, G.; Engel, A.; Lenz, D.; Seibel, A.; et al. Long-term course and mutational spectrum of spatacsin-linked spastic paraplegia. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlén, H.; Melberg, A.; Raininko, R.; Kumlien, E.; Entesarian, M.; Söderberg, P.; Påhlman, M.; Darin, N.; Kyllerman, M.; Holmberg, E.; et al. SPG11 mutations cause Kjellin syndrome, a hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum and central retinal degeneration. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150b, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, S.; Ueda, M.; Kamiya, T.; Mizumura, S.; Terashi, A.; Katayama, Y. Neurological and neuroradiological progression in hereditary spastic paraplegia with a thin corpus callosum. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2000, 102, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurs-Hoeijmakers, J.H.; Geraghty, M.T.; Kamsteeg, E.J.; Ben-Salem, S.; de Bot, S.T.; Nijhof, B.; van de, V., II; van der Graaf, M.; Nobau, A.C.; Otte-Höller, I.; et al. Mutations in DDHD2, encoding an intracellular phospholipase A(1), cause a recessive form of complex hereditary spastic paraplegia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakhanyan, G.; Martinuzzi, A.; Frijia, F.; Vavla, M.; Hlavata, H.; Baratto, A.; Martino, N.; Paparella, G.; Montanaro, D. Brain white matter involvement in hereditary spastic paraplegias: Analysis with multiple diffusion tensor indices. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czell, D.; Neuwirth, C.; Weber, M.; Sartoretti-Schefer, S.; Gutzeit, A.; Reischauer, C. Nine Hole Peg Test and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: Useful to Evaluate Dexterity of the Hand and Disease Progression in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurol. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7397491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, J.; Hübner, I.; Kroczka, S. Correlation of electrophysiological parameters of peripheral nerves and manual dexterity in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Wiad. Lek. 2018, 71, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, I.; Yamada, A.; Sonoda, Y.; Wakita, K.; Nishioka, T.; Harada, Y.; Ogawa, N.; Kitamura, A.; Sanada, M.; Tani, T.; et al. Occupational therapy using a robotic-assisted glove ameliorates finger dexterity and modulates functional connectivity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 107, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, A.C.; McLinden, S.L.; Sparkman, J.; Oskarsson, B. Evaluating surface EMG control of motorized wheelchairs for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, M.J.; Barlow, S.M. Laryngeal somatosensory deficits in Parkinson’s disease: Implications for speech respiratory and phonatory control. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 201, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viguera, C.; Wang, J.; Mosmiller, E.; Cerezo, A.; Maragakis, N.J. Olfactory dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipika, R.H.; Christidi, F.; Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; McKenna, M.C.; Chang, K.M.; Karavasilis, E.; Doherty, M.A.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; et al. Amygdala pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 417, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, H.; Alexander, D.C.; Durrleman, S.; Routier, A.; Rinaldi, D.; Houot, M.; Couratier, P.; Hannequin, D.; Pasquier, F.; et al. Neurite density is reduced in the presymptomatic phase of C9orf72 disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westeneng, H.J.; Walhout, R.; Straathof, M.; Schmidt, R.; Hendrikse, J.; Veldink, J.H.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; van den Berg, L.H. Widespread structural brain involvement in ALS is not limited to the C9orf72 repeat expansion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, A.; Logroscino, G.; Traynor, B.J.; Collins, J.; Simeone, J.C.; Goldstein, L.A.; White, L.A. Global epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review of the published literature. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Murad, A.; Hardiman, O. Pathological neural networks and artificial neural networks in ALS: Diagnostic classification based on pathognomonic neuroimaging features. J. Neurol. 2021, 269, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bede, P.; Murad, A.; Lope, J.; Hardiman, O.; Chang, K.M. Clusters of anatomical disease-burden patterns in ALS: A data-driven approach confirms radiological subtypes. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4404–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Murad, A.; Lope, J.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Finegan, E.; Chipika, R.H.; Hardiman, O.; Chang, K.M. Phenotypic categorisation of individual subjects with motor neuron disease based on radiological disease burden patterns: A machine-learning approach. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 432, 120079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukic, S.; McMackin, R.; Costello, E.; Metzger, M.; Buxo, T.; Fasano, A.; Chipika, R.; Pinto-Grau, M.; Schuster, C.; Hammond, M.; et al. Resting-state EEG reveals four subphenotypes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2022, 145, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querin, G.; Bede, P.; El Mendili, M.M.; Li, M.; Pelegrini-Issac, M.; Rinaldi, D.; Catala, M.; Saracino, D.; Salachas, F.; Camuzat, A.; et al. Presymptomatic spinal cord pathology in c9orf72 mutation carriers: A longitudinal neuroimaging study. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querin, G.; El Mendili, M.M.; Bede, P.; Delphine, S.; Lenglet, T.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Pradat, P.F. Multimodal spinal cord MRI offers accurate diagnostic classification in ALS. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.A.; Karas, M.; Burke, K.M.; Straczkiewicz, M.; Scheier, Z.A.; Clark, A.P.; Iwasaki, S.; Lahav, A.; Iyer, A.S.; Onnela, J.P.; et al. Wearable device and smartphone data quantify ALS progression and may provide novel outcome measures. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Warita, H.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, N.; Nishiyama, S.; Tano, O.; Akiyama, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kuroda, H.; et al. Prominent sensory involvement in a case of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis carrying the L8V SOD1 mutation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 150, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipika, R.H.; Siah, W.F.; McKenna, M.C.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. The presymptomatic phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Are we merely scratching the surface? J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4607–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahedl, M.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Finegan, E.; Chipika, R.H.; Lope, J.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Propagation patterns in motor neuron diseases: Individual and phenotype-associated disease-burden trajectories across the UMN-LMN spectrum of MNDs. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 109, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahedl, M.; Tan, E.L.; Chipika, R.H.; Hengeveld, J.C.; Vajda, A.; Doherty, M.A.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Siah, W.F.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Brainstem-cortex disconnection in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Bulbar impairment, genotype associations, asymptomatic changes and biomarker opportunities. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 3511–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahedl, M.; Chipika, R.H.; Lope, J.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Cortical progression patterns in individual ALS patients across multiple timepoints: A mosaic-based approach for clinical use. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipika, R.H.; Finegan, E.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Tracking a Fast-Moving Disease: Longitudinal Markers, Monitoring, and Clinical Trial Endpoints in ALS. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münte, T.F.; Tröger, M.C.; Nusser, I.; Wieringa, B.M.; Johannes, S.; Matzke, M.; Dengler, R. Alteration of early components of the visual evoked potential in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 1998, 245, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, J.K.; Harrington, H.J.; Hallett, M. Abnormalities of multimodality evoked potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 1986, 43, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, P.; de Hoz, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; Ferreras, A.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.L.; Urcelay-Segura, J.L.; Salazar, J.J.; Ramírez, J.M. Changes in Retinal OCT and Their Correlations with Neurological Disability in Early ALS Patients, a Follow-Up Study. Brain sciences 2019, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübers, A.; Müller, H.P.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Böhm, K.; Lauda, F.; Tumani, H.; Kassubek, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Pinkhardt, E.H. Retinal involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A study with optical coherence tomography and diffusion tensor imaging. J. Neural. Transm. 2016, 123, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, T.; Elamin, M.; Bede, P.; Pinto-Grau, M.; Lonergan, K.; Hardiman, O.; Pender, N. Discordant performance on the ’Reading the Mind in the Eyes’ Test, based on disease onset in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2016, 17, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, F.; Karavasilis, E.; Velonakis, G.; Ferentinos, P.; Rentzos, M.; Kelekis, N.; Evdokimidis, I.; Bede, P. The Clinical and Radiological Spectrum of Hippocampal Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegan, E.; Chipika, R.H.; Li Hi Shing, S.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. Pathological Crying and Laughing in Motor Neuron Disease: Pathobiology, Screening, Intervention. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, S.; Newton, J.; Niven, E.; Foley, J.; Bak, T.H. Screening for cognition and behaviour changes in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2014, 15, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Cudkowicz, M.; Shaw, P.J.; Andersen, P.M.; Atassi, N.; Bucelli, R.C.; Genge, A.; Glass, J.; Ladha, S.; Ludolph, A.L.; et al. Phase 1-2 Trial of Antisense Oligonucleotide Tofersen for SOD1 ALS. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, C.J.; Zhang, P.W.; Pham, J.T.; Haeusler, A.R.; Mistry, N.A.; Vidensky, S.; Daley, E.L.; Poth, E.M.; Hoover, B.; Fines, D.M.; et al. RNA toxicity from the ALS/FTD C9ORF72 expansion is mitigated by antisense intervention. Neuron 2013, 80, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, C.V.; Miller, T.M. Emerging antisense oligonucleotide and viral therapies for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
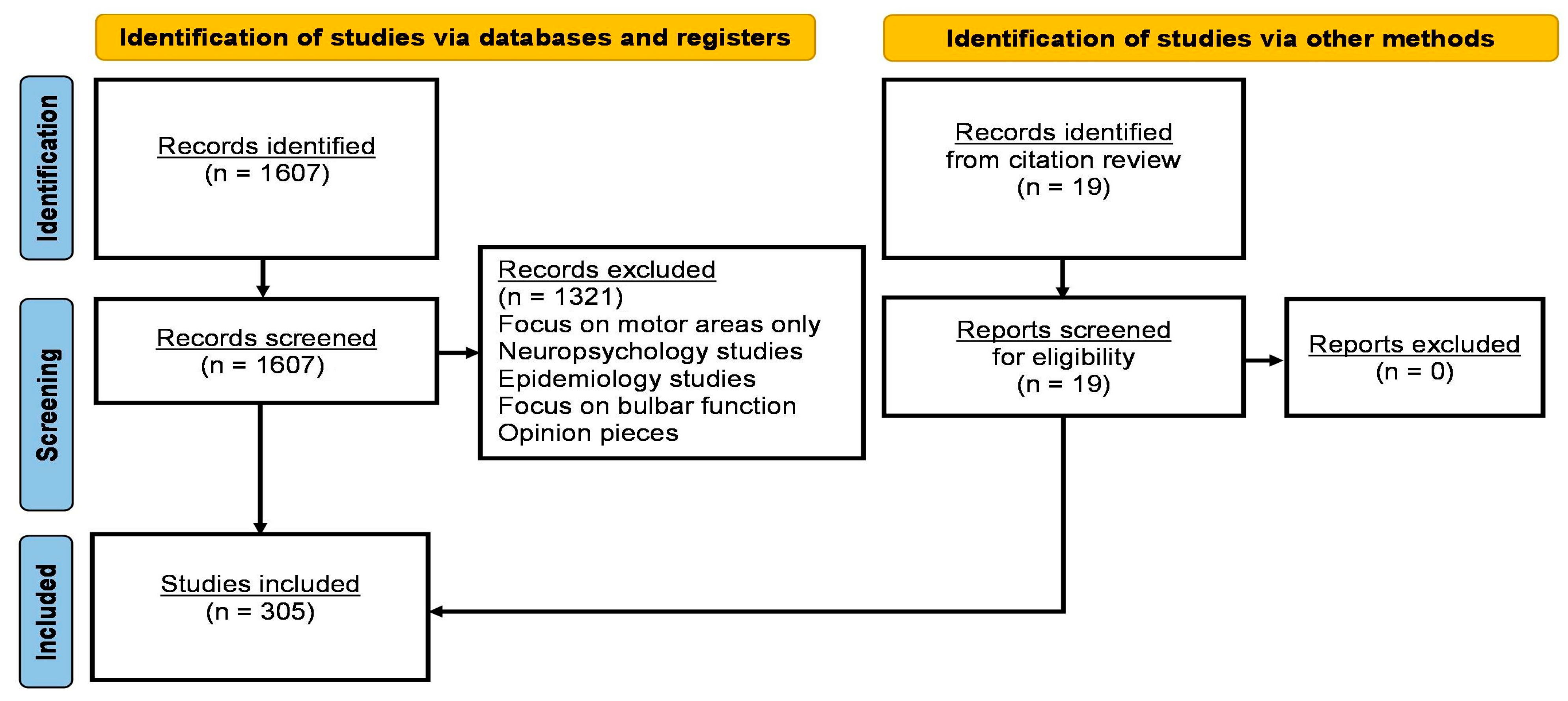

| Author and Year of Publication | Study Participants | Method of Assessment | Significant Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tabor-Gray et al., 2021 [64] | 32 with ALS, 34 healthy controls | Sensory patients rated urge to cough (UtC), cough spirometry metrics |
|
| Krieg et al., 2019 [90] | 12 with ALS, 12 healthy controls | Spontaneous sway measures, measures of postural reactions |
|
| Simmatis et al., 2019 [63] | 17 with ALS | Robot-based sensorimotor, cognitive and proprioceptive performance |
|
| Tarlarini et al., 2019 [62] | 32 with ALS | Taste observations |
|
| Gunther et al., 2018 [60] | 94 with ALS, 81 healthy controls | Olfactory performance-Sniffin Sticks |
|
| Lopes et al., 2018 [113] | 80 with MND, 32 healthy controls | QST, CPM, clinical |
|
| Isak et al., 2017 [49] | 32 with ALS, 32 healthy controls | QST and IENFD skin biopsy |
|
| Marjanovic et al., 2017 [110] | 241 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Gunther et al., 2016 [61] | 90 with MND, 96 healthy controls | NMS questionnaire |
|
| Moisset et al., 2016 [54] | 96 with ALS | Pain assessment |
|
| Ruoppolo et al., 2016 [65] | 114 with ALS | evaluation of swallowing, including a fibre-optic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing and biopsy |
|
| Truini et al., 2015 [114] | 24 with ALS | SNAP, NCV, QST |
|
| Ferrari et al., 2014 [115] | 8 with ALS, 7 healthy controls | Corneal confocal microscopy |
|
| Radovanovic et al., 2014 [91] | 27 with ALS, 29 healthy controls | Simple walking test, dual-motor task, dual-mental task, combined motor and mental tasks |
|
| Sanjak et al., 2014 [93] | 19 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | Clinical |
|
| Hineno et al., 2012 [109] | 24 with ALS | Clinical, neurophysiology, neuropathology |
|
| Jesus et al., 2012 [100] | 40 ALS | Clinical |
|
| Lang et al., 2011 [98] | 26 with ALS, 26 healthy controls | Olfactory performance- Sniffin Sticks |
|
| Pradat et al., 2009 [86] | 39 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Liao et al., 2008 [92] | 13 with ALS, 51 healthy controls | Gait assymetry |
|
| Hammad et al., 2007 [36] | 103 with ALS | SNAP, biopsy |
|
| Amin et al., 2006 [66] | 22 with ALS | Laryngeal sensation |
|
| Deepika et al., 2006 [68] | 20 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | QST |
|
| Khoris et al., 2000 [57] | NA | Genetics |
|
| Camu et al., 1999 [55] | 109 with ALS | Clinical observations |
|
| Hawkes et al., 1998 [59] | 58 with MND, 135 healthy controls | UPSIT, OEP |
|
| Mogyoros et al., 1998 [99] | 21 with ALS, 14 healthy controls | Paraesthesia due to ischemic compression |
|
| Rothstein et al., 1992 [116] | 13 with ALS, 15 with Alzheimer’s disease, 12 with Huntington’s, 17 healthy controls | Glutamate transport |
|
| Wirguin et al., 1992 [117] | 31 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Elian et al., 1991 [58] | 15 with MND, 10 healthy controls | UPSIT |
|
| Li et al., 1988 [77] | NA | Clinical |
|
| Gubbay et al., 1985 [37] | 318 with ALS | Clinical observations |
|
| Jamal et al., 1985 [81] | 40 with MND, 40 healthy controls | Heat threshold and cold threshold |
|
| Hamida et al., 1984 [118] | 102 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Jokelainen et al., 1977 [119] | 255 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Alter et al., 1976 [120] | 14 with ALS | Clinical |
|
| Author and Year of Publication | Study Participants | Methodology | Significant Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harada et al., 2021 [142] | 23 with ALS, 14 healthy controls | SEP |
|
| Norioka et al., 2021 [143] | 145 with ALS, 57 healthy controls | SEP |
|
| Imai et al., 2020 [129] | 190 with ALS | SNAP |
|
| Nardone et al., 2020 [144] | 10 with ALS, 10 healthy controls | SEP |
|
| Hoffken et al., 2019 [145] | 15 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | SEP |
|
| Liu et al., 2019 [123] | 150 with ALS | EMG |
|
| Pegat et al., 2019 [127] | 53 with ALS | Clinical and electrodiagnostic data |
|
| Matamala et al., 2018 [146] | 28 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | MUNE, SNAP |
|
| Sangari et al., 2018 [131] | 21 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | SEPs |
|
| Shimizu et al., 2018 [132] | 145 with ALS, 73 healthy controls | SEP (N13, N20, P25) |
|
| Kulkantrakorn et al., 2017 [122] | 25 with ALS, 11 with PMA, 1 with PLS, 1 with Kennedy disease | NCS |
|
| Dalla Bella et al., 2016 [48] | 57 with ALS | Sural nerve conduction study |
|
| Isak et al., 2016 [133] | 18 with ALS, 31 healthy controls | LEPs, SSEPs |
|
| Ren et al., 2016 [124] | 154 with ALS | SCV, SNAP |
|
| Iglesias et al., 2015 [41] | 21 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | SEPs |
|
| Jin et al., 2014 [147] | 97 with ALS, 100 with Hirayama disease, 32 with cervical spondylotic amyotrophy | SNAP, conduction velocity |
|
| Hineno et al., 2012 [109] | 24 with ALS | Neurophysiology, clinical |
|
| Simone et al., 2010 [148] | 24 with ALS, 23 healthy controls | LEPs |
|
| Xu et al., 2009 [69] | 60 with ALS, 60 healthy controls | Contact heat-evoked potentials |
|
| Pugdahl et al., 2008 [43] | 35 with ALS, 35 healthy controls | SNAP |
|
| Hamada et al., 2007 [149] | 26 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | SEPs, CMAP |
|
| Hammad et al., 2007 [36] | 103 with ALS | SNAP, biopsy |
|
| Pugdahl et al., 2007 [42] | 88 with ALS | SCNV, SNAP |
|
| Argyriou et al., 2006 [70] | 23 with ALS, 23 healthy controls | Sensory conduction study |
|
| Koszewicz et al., 2005 [138] | 19 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Sensory conduction study |
|
| Ogata et al., 2001 [150] | 12 with ALS | SEP |
|
| de Carvalho et al., 2000 [139] | 70 with ALS, 35 healthy controls | CMAP, CV, sensory potentials |
|
| Matsumoto et al., 1999 [151] | 14 with ALS | SSCV, SSEP |
|
| Rabin et al., 1999 [73] | 49 with ALS | Electrodiagnostic |
|
| Schulte-Mattler et al., 1999 [152] | 23 with ALS, 23 healthy controls | SNCV, SNAPA |
|
| Theys et al., 1999 [126] | 50 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Motor and sensory assessment |
|
| Theys et al., 1999 [126] | 50 with ALS | SEP, Thermal thresholds |
|
| Emeryk-Szajewska et al.,1998 [153] | 94 with ALS, 2 with PLS, 3 with primary bulbar palsy, 6 with primary motor spinal atrophy | Nerve conduction |
|
| Mogyoros et al., 1998 [154] | 23 with ALS, 32 healthy controls | CMAP, CSAP |
|
| Georgesco et al., 1997 [155] | 24 with ALS, 17 healthy controls | SEP |
|
| Zanette et al., 1996 [156] | 29 with ALS, 10 with PMA | SEP |
|
| Georgesco et al., 1994 [135] | 21 with ALS, 7 with PLS | SEPs |
|
| Constantinovici et al., 1993 [136] | 10 with ALS | SEPs |
|
| Gregory et al., 1993 [39] | 19 with ALS, 12 healthy controls | SNAP, SNCV |
|
| Lukomski et al., 1993 [94] | 18 with ALS | ENG exam |
|
| Mondelli et al., 1993 [137] | 64 with ALS, 60 healthy controls | MCV, SCV, SAPa |
|
| Palma et al., 1993 [157] | NA | BAEP, VEP, SEP |
|
| Behnia et al., 1991 [128] | 133 with ALS | SNAP |
|
| Gao et al., 1991 [158] | 343 with MND | Sensory nerve conduction velocities |
|
| Shefner et al., 1991 [125] | 18 with ALS | Compound sensory action potentials |
|
| Subramaniam et al., 1990 [134] | 27 with MND | SEP, PSVEP, BAEP |
|
| Zanette et al., 1990 [159] | 26 with MND, 20 healthy controls | SEPs |
|
| Facco et al., 1989 [160] | 19 with ALS | SEP |
|
| Berardelli et al., 1987 [140] | 11 with MND, 20 healthy controls | SEP, MCV |
|
| Radtke et al., 1986 [40] | 17 with ALS | Sensory evoked potential |
|
| Cosi et al., 1984 [161] | 45 with ALS | SEPs |
|
| Post Mortem | |||
| Author and Year of Publication | Study Participants | Significant Findings | |
| Mehta et al., 2021 [197] | 3 with C9orf72-positive ALS/FTD, 2 healthy controls |
| |
| De Reuck et al., 2017 [175] | 12 with ALS, 38 with FTLD, 28 healthy controls |
| |
| Fatima et al., 2015 [162] | 35 with ALS, 4 healthy controls |
| |
| Oyanagi et al., 2015 [178] | 7 with ALS |
| |
| Rabin et al., 1999 [73] | 49 with ALS |
| |
| Shankar et al., 1995 [198] | 3 with ALS |
| |
| Biopsy | |||
| Author and year of publication | Study participants | Region biopsied | Significant findings |
| Dalla Bella et al., 2016 [48] | 57 with ALS | Skin |
|
| Ruoppolo et al., 2016 [65] | 114 with ALS | Larynx |
|
| Truini et al., 2015 [114] | 24 with ALS | Skin |
|
| Luigetti et al., 2012 [182] | 17 with ALS | Sural nerve |
|
| Sawa et al., 2012 [184] | 3 with ALS | Sural nerve |
|
| Devigili et al., 2011 [183] | 18 with ALS | Sural nerve |
|
| Weis et al., 2011 [51] | 28 with ALS | Skin |
|
| Hammad et al., 2007 [36] | 103 with ALS | Sural nerve |
|
| Isaacs et al., 2007 [38] | 5 with ALS | Sensory nerve |
|
| Rabin et al., 1999 [73] | 49 with ALS | Skin |
|
| Hawkes et al., 1998 [59] | 58 with MND, 135 healthy controls | Olfactory bulbs |
|
| Heads et al., 1991 [181] | NA | Sural nerve |
|
| Hamida et al., 1987 [185] | 16 with ALS, 8 healthy controls | Superficial peroneal nerve |
|
| Dyck et al., 1975 [56] | 10 with ALS | Peroneal nerve |
|
| Animal models | |||
| Author and year of publication | Disease model | Significant findings | |
| Baczyk et al., 2020 [199] | presymptomatic mutSOD1 mice |
| |
| Peng et al., 2020 [200] | Mice with astroglial TDP-43 deletion |
| |
| Ruiz-Soto et al., 2020 [201] | SOD1(G93A) mouse model |
| |
| Weerasekera et al., 2020 [202] | TDP-43(A315T) mouse model |
| |
| Seki et al., 2019 [203] | SOD1G93A mouse |
| |
| Vaughan et al., 2018 [186] | TDP43A315T on sensory neurons in culture and in vivo, SOD1G93A sensory neurons |
| |
| Marcuzzo et al., 2017 [188] | G93A-SOD1 mouse model |
| |
| Bernard-Marissal et al., 2015 [196] | SIGMAR1 mice |
| |
| Vaughan et al., 2015 [187] | SOD1(G93A) and TDP43(A315T) |
| |
| Sabado et al., 2014 [30] | SOD1(G93A) mouse model |
| |
| Cowin et al., 2011 [195] | SOD1 mouse model |
| |
| Filali et al., 2011 [189] | SOD1(G37R) transgenic mouse model |
| |
| Underwood et al., 2011 [72] | SOD1 mice |
| |
| Izquierdo et al., 2010 [190] | nonhuman primates |
| |
| Guo et al., 2009 [192] | hSOD1-G93A mice |
| |
| Fischer et al., 2005 [191] | SOD/Wld(S) mice |
| |
| Author and Year of Publication | Study Participants | Methodology | Significant Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural imaging | |||
| Ahmed et al., 2021 [229] | 52 with ALS, 41 with ALS-FTD, 58 with bvFTD, 58 healthy controls | Structural (volumetry) |
|
| Barry et al., 2021 [232] | 12 with ALS, 9 healthy controls | Structural, MRS, rsfMRI |
|
| Chen et al., 2020 [246] | 22 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Chipika et al., 2020 [207] | 100 with ALS, 33 with PLS, 117 healthy controls | Structural (volumetry, shape analysis, ROI morphometry) |
|
| Bede et al., 2018 [32] | 36 with ALS, 26 with ALS-FTD, 10 with bvFTD, 11 with nfvPPA, 5 with svPPA, 50 healthy controls | Structural (volumetry, cortical thickness), diffusion |
|
| Bueno et al. 2018 [247] | 20 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | Structural, diffusion, rsfMRI |
|
| Chen et al., 2018 [248] | 65 with ALS, 65 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Buhour et al., 2017 [217] | 37 with ALS, 37 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Kim et al., 2017 [249] | 62 with ALS, 57 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| de Albuquerque et al., 2016 [250] | 32 ALS, 32 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Masuda et al., 2016 [219] | 44 with ALS, 7 with ALS-FTD, 24 healthy controls | Structural (VBM), diffusion |
|
| Devine et al., 2015 [45] | 30 with ALS, 17 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Machts et al., 2015 [209] | 42 with ALS-nci, 7 with ALS-FTD, 18 with ALS-plus, 39 healthy controls | Structural (volumetry, shape, density) |
|
| Irwin et al., 2013 [251] | 143 ALS | structural |
|
| Mioshi et al., 2013 [252] | 22 with ALS, 17 with ALS-FTD, 18 healthy controls | Structural (VBM) |
|
| Thorns et al., 2013 [253] | 14 with ALS, 14 healthy controls | Structural (cortical thickness) |
|
| Cosottini et al., 2012 [230] | 20 with ALS, 16 healthy controls | Structural (VBM), fMRI |
|
| Mohammadi et al., 2009 [254] | 20 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Structural, fMRI |
|
| Grosskreutz et al., 2006 [231] | 17 with ALS, 17 healthy controls | Structural |
|
| Chang et al., 2005 [228] | 10 with ALS, 10 with ALS-FTD, 22 healthy controls | Structural (VBM) |
|
| Kato et al., 1993 [255] | 22 with ALS | Structural |
|
| Diffusion imaging | |||
| Rajagopalan et al., 2021 [256] | 75 with ALS, 14 disease controls | diffusion |
|
| Rajagopalan et al., 2017 [257] | 45 with ALS, 14 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Zhang et al., 2017 [218] | 38 with ALS, 35 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Sheelakumari et al., 2016 [258] | 17 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | Diffusion, SWI |
|
| Trojsi et al., 2015 [259] | 54 with ALS, 18 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Barbagallo et al., 2014 [221] | 24 with ALS, 22 healthy controls | Diffusion, structural |
|
| Kim et al., 2014 [260] | 14 with ALS, 16 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Sharma et al., 2013 [227] | 14 with ALS, 12 healthy controls | Diffusion, structural |
|
| Rose et al., 2012 [237] | 15 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Diffusion, structural |
|
| Agosta et al., 2011 [261] | 26 with ALS, 15 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Thivard et al., 2007 [224] | 15 with ALS, 25 healthy controls | Diffusion, structural |
|
| Sach et al., 2004 [226] | 15 with ALS, 12 healthy controls | Diffusion, structural, |
|
| Functional imaging | |||
| Wei et al., 2021 [262] | 20 with ALS, 22 healthy controls | fMRI |
|
| Qiu et al., 2019 [263] | 60 with ALS, 60 healthy controls | rsfMRI, structural, diffusion |
|
| Menke et al., 2017 [215] | 13 with ALS, 3 with PLS | rsfMRI, structural (volumetry, shape analysis), diffusion |
|
| Xu et al., 2017 [216] | 20 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | rsfMRI |
|
| Zhang et al., 2017 [264] | 38 with ALS, 35 healthy controls | rsfMRI, diffusion |
|
| Fang et al., 2016 [245] | 20 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | rsfMRI |
|
| Zhou et al., 2016 [44] | 43 with ALS, 44 healthy controls | rsfMRI |
|
| Zhou et al., 2014 [236] | 12 with ALS, 12 healthy controls | rsfMRI |
|
| Poujois et al., 2013 [265] | 19 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | fMRI, diffusion |
|
| Luo et al., 2012 [238] | 20 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | fMRI, structural (VBM) |
|
| Mohammadi et al., 2011 [266] | 22 with ALS, 22 healthy controls | fMRI |
|
| Lule et al., 2010 [46] | 14 with ALS, 18 healthy controls | fMRI |
|
| Li et al., 2009 [223] | 10 with ALS, 10 healthy controls | fMRI, diffusion, structural |
|
| Other | |||
| De Reuck et al., 2017 [175] | 12 with ALS, 38 with FTLD, 28 healthy controls | Iron deposition |
|
| Pioro et al., 1994 [235] | 12 with MND, 6 healthy controls | 1H-MRSI |
|
| Spinal imaging | |||
| Pisharady et al., 2020 [267] | 20 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Olney et al., 2018 [268] | 3 with ALS, 2 with ALS-FTD, 1 with PLS, 2 with PMA, 2 with FOSMN, 10 healthy controls | Structural-axial 2D PSIR images and diffusion |
|
| Rasoanandrianina et al., 2017 [206] | 10 with ALS, 20 healthy controls | Diffusion, ihMT |
|
| Wang et al., 2017 [269] | 14 with ALS, 14 healthy controls | MRS |
|
| Iglesias et al., 2015 [41] | 21 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | Diffusion |
|
| Wang et al., 2014 [270] | 24 with ALS, 16 healthy controls | Structural, diffusion |
|
| Cohen-Adad et al., 2013 [179] | 29 with ALS, 21 healthy controls | Structural, diffusion, magnetization transfer |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kleinerova, J.; Chipika, R.H.; Tan, E.L.; Yunusova, Y.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Kassubek, J.; Pradat, P.-F.; Bede, P. Sensory Dysfunction in ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Relevance, Histopathology, Neurophysiology, and Insights from Neuroimaging. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030559
Kleinerova J, Chipika RH, Tan EL, Yunusova Y, Marchand-Pauvert V, Kassubek J, Pradat P-F, Bede P. Sensory Dysfunction in ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Relevance, Histopathology, Neurophysiology, and Insights from Neuroimaging. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030559
Chicago/Turabian StyleKleinerova, Jana, Rangariroyashe H. Chipika, Ee Ling Tan, Yana Yunusova, Véronique Marchand-Pauvert, Jan Kassubek, Pierre-Francois Pradat, and Peter Bede. 2025. "Sensory Dysfunction in ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Relevance, Histopathology, Neurophysiology, and Insights from Neuroimaging" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030559
APA StyleKleinerova, J., Chipika, R. H., Tan, E. L., Yunusova, Y., Marchand-Pauvert, V., Kassubek, J., Pradat, P.-F., & Bede, P. (2025). Sensory Dysfunction in ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Relevance, Histopathology, Neurophysiology, and Insights from Neuroimaging. Biomedicines, 13(3), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030559






