Abstract
Few studies have reported on polonium-210, a decay breakdown product of radon-222 and lead-210, in human lungs and there has been no study in patients with suspected lung cancer. The main aim of this “Polonium in vivo” study was to evaluate polonium-210 radioactivity in bronchopulmonary systems of smoker, ex-smoker and never smoker patients with suspected lung cancer. Alpha-spectrometric analyses were performed on bronchial lavage (BL) fluids from two Italian hospitals in 2013–2016. Socio-demographic, smoking, occupational and spirometric characteristics, lung cancer confirmation and histologic type and radon-222 concentration in patients’ homes were collected. Seventy BL samples from never (n = 13), former (n = 35) and current smokers (n = 22) were analyzed; polonium-210 was detected in all samples from current and former smokers and in 54% of samples from never smokers (p < 0.001; median values: 1.20, 1.43 and 0.40 mBq, respectively). Polonium-210 levels were significantly higher in COPD versus no COPD patients (median value: 3.60 vs. 0.97 mBq; p = 0.007); former and current smokers, without and with COPD, had significantly increased polonium-210 levels (p = 0.012); 96% of confirmed versus 69% of non-confirmed lung cancer patients recorded detectable polonium-210 levels (p = 0.018). A polonium-210 detectable activity was measured in BL samples from all current and former smokers. Polonium-210 in the lungs could be the result of lead-210 entrapment, which, with its half-life of 22 years, could provide a continuous emission of alpha radioactivity, even many years after quitting, thus proposing a possible explanation for the onset of lung cancer, particularly in former smokers.
1. Introduction
Tobacco smoke contains human carcinogens, including heavy metals like radioactive lead (210Pb; half-life: 22 years), and its daughter isotope polonium (210Po; half-life: 138 days); 210Pb is a beta-particle emitter, 210Po is an alpha-particle emitter (210Po), which has been reported to be associated with lung cancer, and in particular it has been hypothesized that it could be implicated in the histotype shift of lung cancer from a squamous cell type to adenocarcinoma [1].
Knowledge about tobacco radioactivity goes back to the sixties, when tobacco companies discovered that polonium was part of tobacco and tobacco smoke [2,3]. Two sources of tobacco radioactivity have been identified: Aitken particles, which are dust particles which contain radioactive radon (222Rn) absorbed from the atmosphere, and the uptake from the soil. The Aitken particles deposit and accumulate in the trichome of tobacco leaves where their decay products, 210Pb and 210Po, form insoluble complexes with resin and are resistant to rain and to tobacco curing. The soil, especially if fertilized with polyphosphates which boost the growth of tobacco plants, contain radium and its decay products. Thus, 210Pb and 210Po are highly concentrated in tobacco leaves. 210Po can be detected both in tobacco smoke gaseous and corpuscular phases, while 210Pb only in corpuscular phase [2,3,4].
It has been estimated that a burning cigarette emits into the air about 50% of its radioactive materials and its smoke, inhaled by the smoker, delivers about 32% of the 210Po to the lungs. Furthermore, radioactive materials can be inhaled by non-smokers, and are retained in cigarette butts and ashes [5].
In 2011, in the 10 best-selling cigarette brands in Italy, 210Pb and 210Po average levels were, respectively, 14.6 mBq and 15.8 mBq per cigarette and the annual dose assessment has been estimated to be equal to that from 27–28 chest radiographs (smoking 20 cigarettes/day) [6].
Since the discovery that the presence of radioactivity in tobacco leaves was higher than background levels, tobacco industries tried to remove 210Pb and 210Po in tobacco through washing tobacco leaves with acid treatments, measuring the radioactivity prior to manufacturing, filtering mainstream smoke, and employing genetic engineering techniques in order to reduce radioactivity in the leaves. As the results were not satisfactory or could compromise the optimal absorption of nicotine into the brain, they decided to stop research in this area and eliminate any evidence that might put their companies at risk for smoking and health litigation [5,7].
Indeed, since high concentrations of polonium have been found in bronchial epithelium of smokers, it was hypothesized that polonium may be implicated in the initiation of lung cancer [5,8]. Actually, 210Pb and 210Po might be implicated also in the initiation of other tumors, since the radioactive particles from the bronchopulmonary system might spread throughout the body and reach various organs and tissues. In smokers compared to non-smokers, 210Po levels are significantly higher in the blood, urine, liver, kidney, heart and skeletal muscles [3,9,10].
Although research indicating polonium as one of the major tobacco carcinogens is encouraging, a recent systematic review of this issue has shown that the study of radioactivity of tobacco smoke has been scientifically stagnant for 40 years. On the other hand, the extent to which the tobacco industry has understood the risks of polonium and has discussed its implications is impressive [11,12].
To our knowledge, few studies have reported measurements of 210Po in human lungs, and this is the first study to report levels of 210Po in smoker, ex-smoker and non-smoker patients with lung cancer.
The main aim of this paper was to show results of the “Polonium in vivo” study, aimed at evaluating 210Po radioactivity in bronchopulmonary systems among patients with suspected and confirmed lung cancer.
2. Materials and Methods
All consecutive patients undergoing a bronchoscopy for suspected lung cancer in the pneumology divisions of two major hospitals in Northern (Ospedale Maggiore in Bologna) and Southern Italy (Ospedale Cardarelli, Naples) were admitted if they were aged 35–85 years.
Patients were enrolled into three groups according to their smoking status: “never smokers”, if they had smoked < 100 cigarettes in their lifetime and were not exposed to second-hand smoke in the past 15 years; “former smokers”, if they had quit at least 5 years ago, with at least 20 years of smoking duration; “current smokers”, if they had smoked in the last 20 years.
The study was conducted between January 2013 and September 2014 and it was reopened in the first half of 2016 to increase the enrolment in the first group of “never smokers” patients; thus, 6 additional never smoking patients with suspected lung cancer were added to the study. Assuming a 50% difference in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) prevalence between ever and never smokers with lung cancer [13], a sample size of 18 patients per each smoking status group was necessary to conduct the study, with a significant level α = 0.05 and a 0.8 power.
The study protocol was approved by the Bologna Local Health Unit Ethical Committee on December 2012 (Prot. N. 1539/CE).
An information letter and the related consent form were provided to patients. An information letter was also sent to their general practitioner.
Alpha spectrometric analyses were carried on bronchial lavage (BL) fluids collected from recruited patients during bronchoscopy procedures; 15 mL of normal saline solution was used during the procedure. Fluids were collected into sterilized test tubes from the bronchoscopy and were sent to the laboratory.
Sociodemographic variables (gender, age), smoking history (pack-year of smoking, years since quitting), past occupational exposure to lung carcinogens and two spirometry measures were collected: forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), and the FEV1/FVC ratio (Tiffeneau index), i.e., the proportion of FEV1 to the full forced vital capacity (FVC). According to the GOLD classification, patients were classified as having or not COPD, and, among COPD patients, COPD severity level [14]. Results of cytological examinations of BL cells were collected: non-confirmed lung cancer or lung cancer histologic types (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, other non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and small cell lung cancer (SCLC)).
Since 210Po is a decay product of radon 222 (222Rn), 222Rn concentration at the patients’ homes was also measured.
In summary, BL fluids from 70 patients were collected and analyzed (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials); for 34 and 11 patients, respectively, radon and spirometric measures were not available and, for 10 patients only gender and smoking status were available.
Sample preparation and 210Po analyses were carried out according to standard procedures [15]. Samples were spiked with radioactive tracer 209Po at known concentrations. Sample decomposition was performed using conventional digestion techniques with acids. Then, samples were loaded in an extraction chromatographic resin (Sr Resin, Triskem International) to separate lead and polonium and to obtain a solution containing polonium that was recovered in low-molarity hydrochloric acid and then injected in a cell with a silver disc for 210Po deposition. The silver disc with deposited 210Po was then measured using alpha spectrometry with silicon detectors in a vacuum chamber and a multichannel analyzer. 210Po results referred to the date of laboratory analysis; correction to the sampling date was not needed because it is assumed that in tobacco smoke the 210Po/210Pb activity ratio is 1 [6]. If 210Po activity was below the detection limit, it was assumed to be zero.
Radon (222Rn) measurements were carried out by CR-39 nuclear track detectors. These passive detectors were installed in the patients’ homes for about three months. Radon particles in air damage the sensor, producing tracks that were analyzed in U-Series laboratory according to ISO 11665-4:2012 [16,17].
In order to test differences in categorical and continuous variables by smoking status, Chi-square test and Student’s t-test were used, respectively. The Kruskal–Wallis and the Mann–Whitney two-sample statistics were used for testing differences in 210Po levels by smoking status, and by having or not COPD or lung cancer.
3. Results
A total of 70 patients with suspected lung cancer were recruited and for 47 of them lung cancer confirmation was obtained during the collection of data. Table 1 reports the main characteristics of patients participating in the “Polonium in vivo” study.

Table 1.
Characteristics of patients participating in the “Polonium in vivo” study by smoking status (n = 70).
Among 60 patients with complete data, except for spirometric and radon measures, 75% were men and the average age was 62 years among current smokers and 71 years in never and former smokers (p = 0.017). The cumulative exposure to tobacco smoke was significantly lower in former compared to current smokers (43 vs. 64 pack-years on average, respectively; p = 0.012), and former smokers had stopped a mean of 17 years ago. Past occupational exposure to lung carcinogens was recorded in 27% of patients, with no significant differences by smoking status. Lung cancer was diagnosed in 50% of never, 82% of former, and 88% of current smokers; adenocarcinoma was the most frequent histopathological type among never and former smokers (60%), whereas among current smokers it was squamous cell carcinoma (53%). Among 49 patients who also had complete data for spirometric measures, FEV1 was significantly higher in never compared to former and current smokers (103, 87 and 69 on average, respectively; p = 0.004). COPD was detected in 8 former smokers (2 mild and 6 moderate COPD), and in 4 current smokers (2 moderate and 2 severe COPD). A total of 11 out of 12 COPD patients (92%) had confirmed lung cancer.
Table 2 reports levels of 210Po in patients with suspected lung cancer. Considering all 70 patients with 210Po measurements, 210Po was detected in 100% of BL fluids from current or former smokers and in 54% from never smokers (i.e., 210P > 0 mBq) (p < 0.001; Table 2).

Table 2.
Levels of 210Po in 70 patients with suspected lung cancer from the “Polonium in vivo” study by smoking status and by having or not COPD or lung cancer (if 210Po activity was below the detection limit it was assumed to be zero).
We did not observe any statistically significant difference in 210Po levels between current and former smokers (Table 2). For two never smokers, 210Po levels were very high: 16.35 mBq and 16.66 mBq. These two subjects lived in houses with the highest 222Rn concentration values recorded in this study: 330 Bq/m3 and 1100 Bq/m3, respectively. Excluding these two never smokers, the 210Po median value among never smokers was 0.00 mBq (interquartile range: 0.00–1.50 mBq) and the differences among ever versus never smokers significantly increased (Kruskal–Wallis test p-value = 0.013).
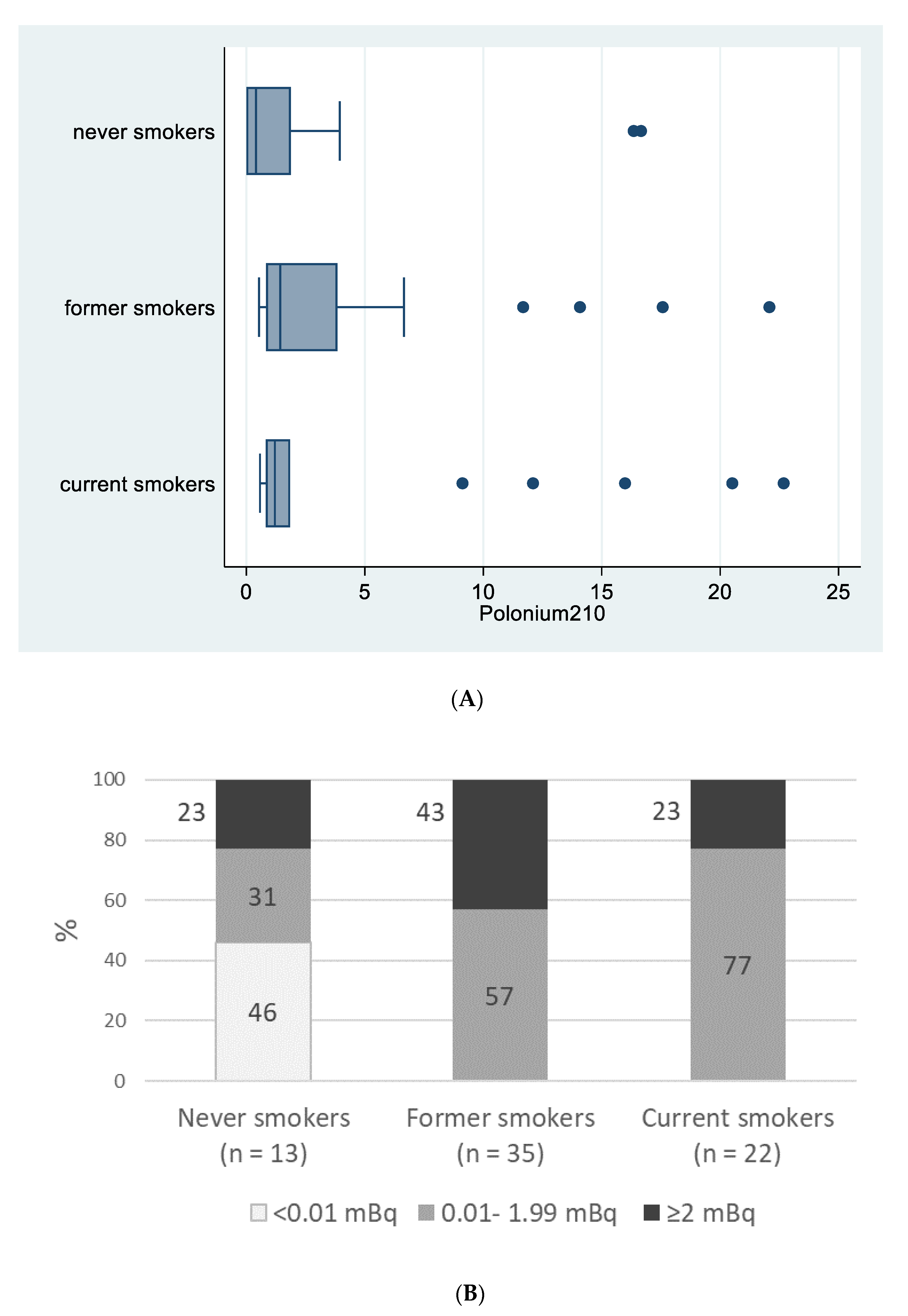
Figure 1A reports 210Po median values for never, former and current smokers (0.41, 1.43, 1.20, mBq, respectively; p = 0.149) and Figure 1B reports percentages of patients in the three 210Po categories (0, <2 and ≥2 mBq) according to their smoking status (p < 0.001).
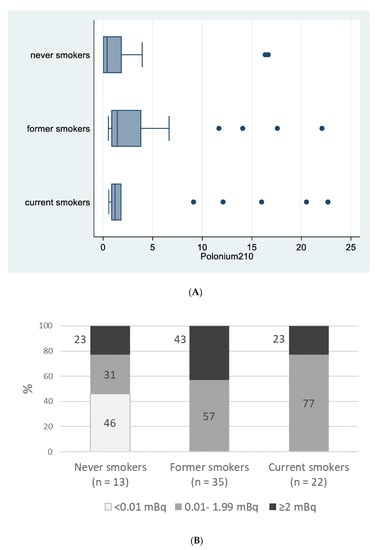
Figure 1.
Polonium-210 (in mBq) by smoking status, “Polonium in vivo” study (n = 70). (A) Box plot of polonium-210 (in mBq) by smoking status. The left and right borders of the box are the lower and upper quartiles; the solid line in the box is the median. The “whiskers”, that is, the lower and upper adjacent values, are used for identifying extreme values in the tails of the distribution. Dots greater than the upper adjacent value, represent outliers. (B) Polonium-210 levels (<0.01 mBq; 0.01–1.99 mBq; >=2 mBq) by smoking status.
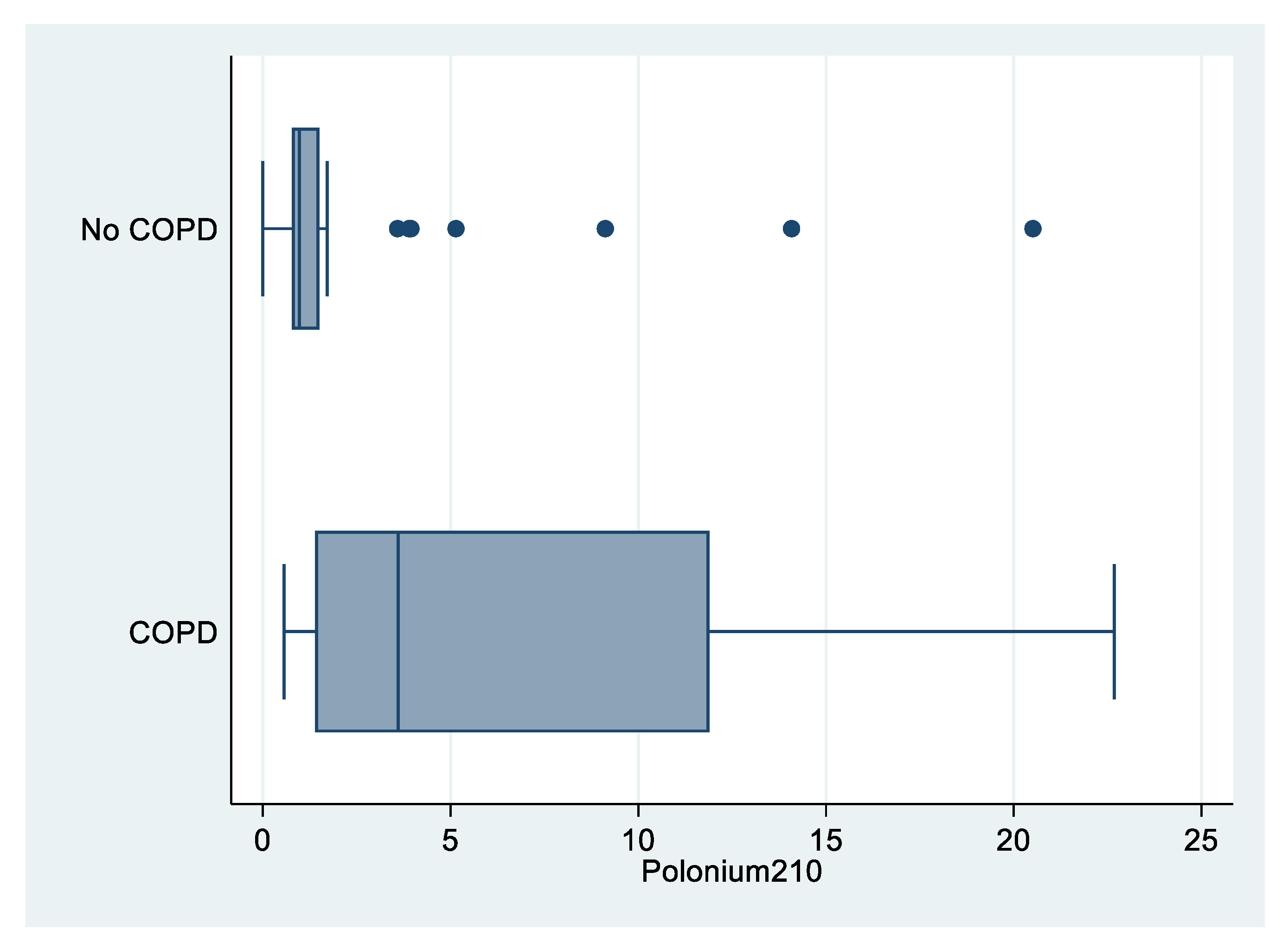
As shown in Figure 2, levels of 210Po were higher among COPD patients compared to patients with no COPD (median value: 3.60 vs. 0.97 mBq; p = 0.007; Table 2).
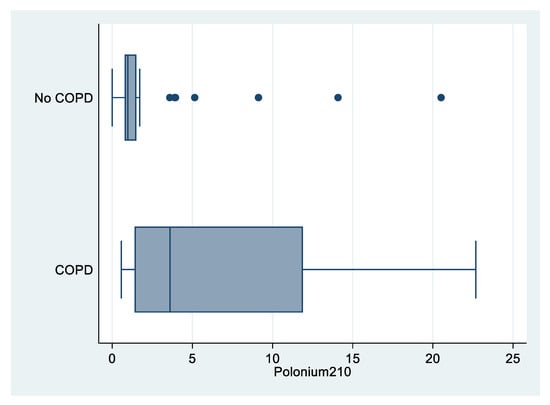
Figure 2.
Box plot of polonium-210 (in mBq) by COPD status, “Polonium in vivo” study (n = 49; 21 missing; COPD n = 12; no COPD n = 37). The left and right borders of the box are the lower and upper quartiles; the solid line in the box is the median. The “whiskers”, that is, the lower and upper adjacent values are used for identifying extreme values in the tails of the distribution. Dots greater than the upper adjacent value, represent outliers.
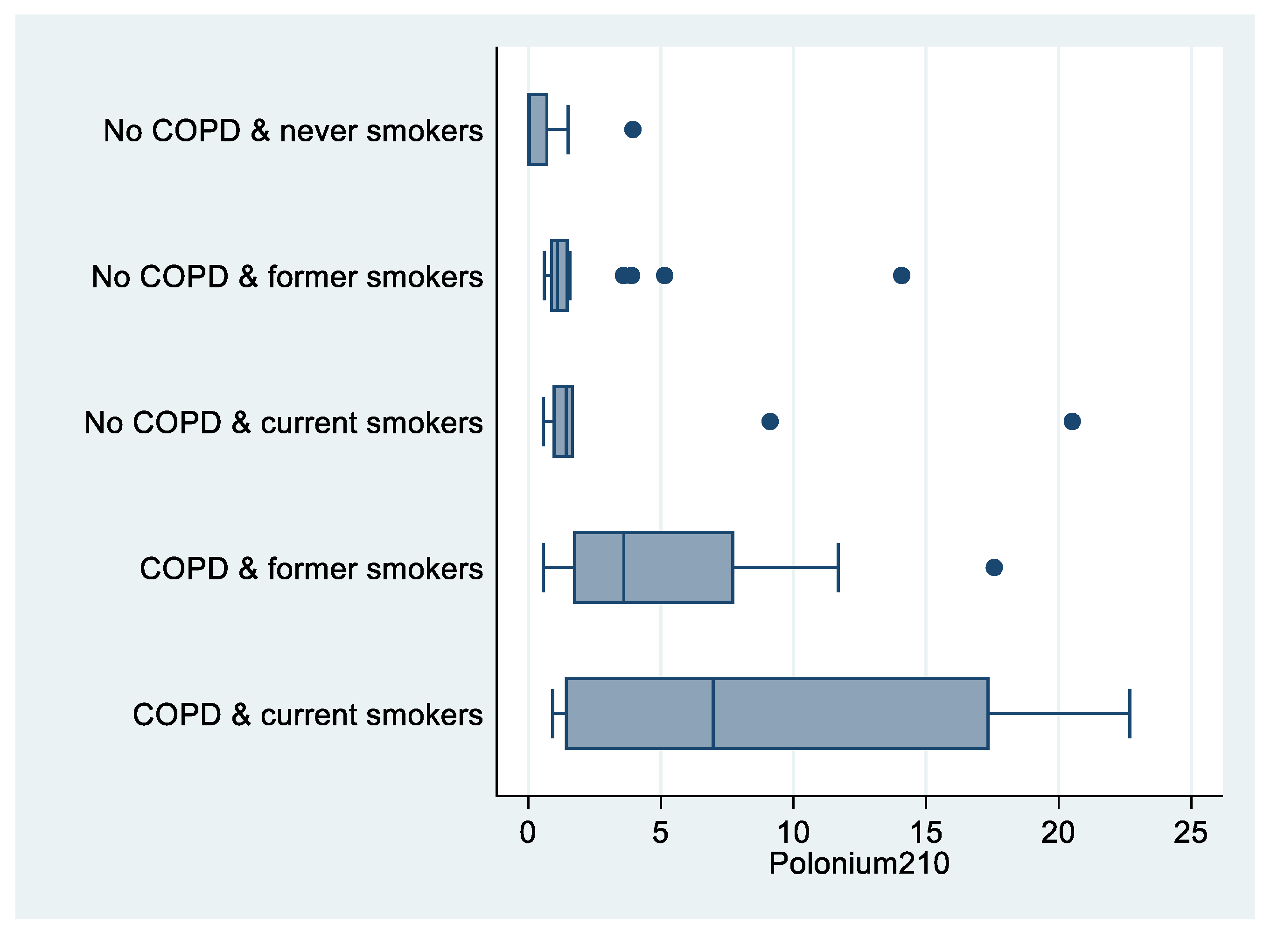
There were significant differences in 210Po levels among never smokers with no COPD (6 out of 8 210Po measures below the detection limit), compared to current smokers with COPD (median value: 6.97 mBq; p = 0.012; Table 2, Figure 3).
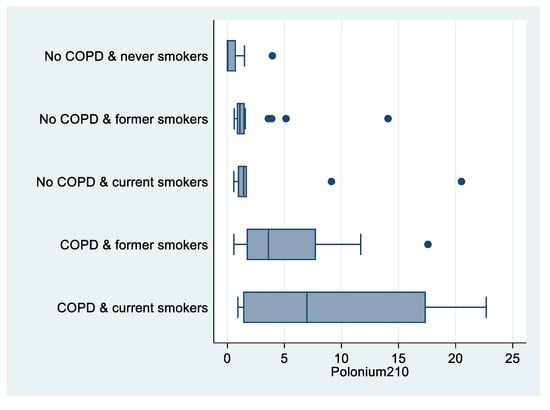
Figure 3.
Box plot of polonium-210 (in mBq) by COPD and smoking status, “Polonium in vivo” study (n = 49; 21 missing). The left and right borders of the box are the lower and upper quartiles; the solid line in the box is the median. The “whiskers”, that is, the lower and upper adjacent values, are used for identifying extreme values in the tails of the distribution. Dots greater than the upper adjacent value represent outliers.
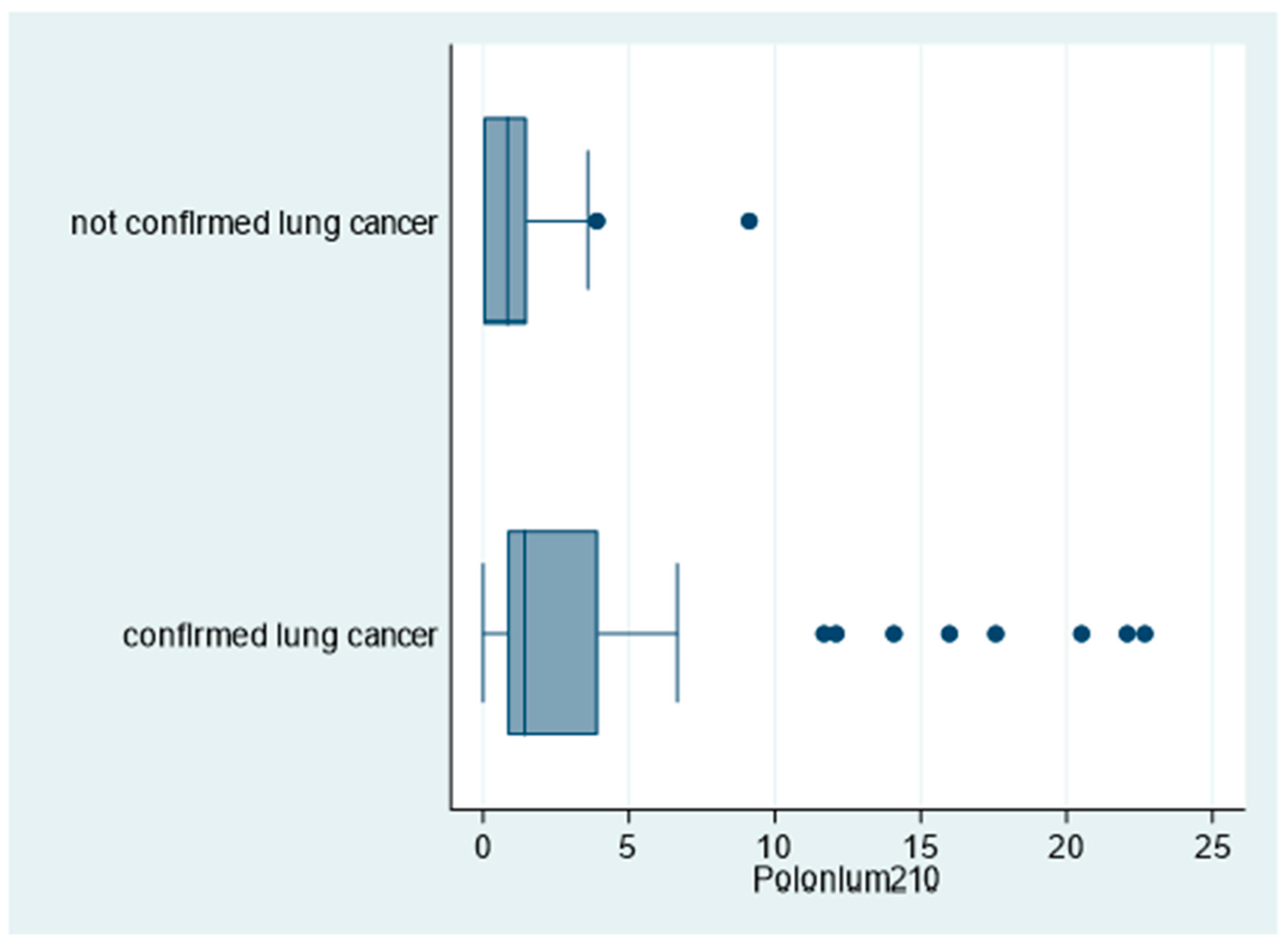
Moreover, as shown in Figure 4, 210Po levels were significantly higher among patients with confirmed lung cancer compared to patients with no lung cancer confirmation (96% and 69%, respectively for 210P > 0 mBq; p = 0.018; Table 2).
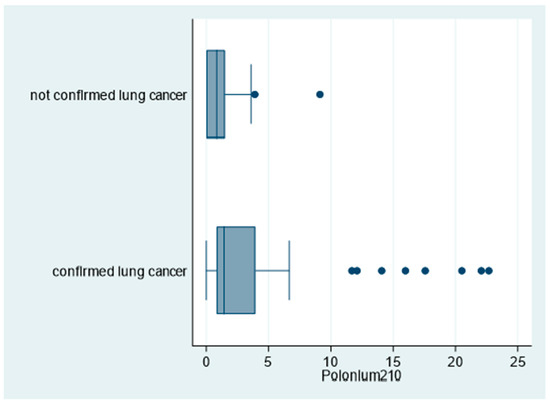
Figure 4.
Box plot of polonium-210 (in mBq) by lung cancer status, “Polonium in vivo” study (n = 60; 10 missing; not confirmed lung cancer n = 13; confirmed lung cancer n = 47). The left and right borders of the box are the lower and upper quartiles; the solid line in the box is the median. The “whiskers”, that is, the lower and upper adjacent values, are used for identifying extreme values in the tails of the distribution. Dots greater than the upper adjacent value, represent outliers.
No differences in 210Po levels were observed according to past occupational exposure to lung carcinogens or by histopathological type of lung cancer (data not shown).
A total of 34 out of 36 patients with radon measurements recorded radon levels ≤300 Bq/m3, with 210Po median value = 1.20 mBq. Only two patients recorded radon concentrations >300 Bq/m3, with higher 210Po levels (median value = 16.50 mBq; p = 0.027; Table 2). There were no differences in radon concentration by smoking status, excluding the two never smokers with very high radon concentration at home.
Considering only 47 patients with confirmed lung cancer, differences in 210Po levels by smoking status did not change significantly (Table 2).
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study measuring 210Po levels from BL fluids in patients with suspected or confirmed lung cancer, overall and by smoking status. Former and current smokers had significantly higher levels of 210Po compared to never smokers. Moreover, there were significant differences in 210Po levels among never smokers with no COPD compared to current smokers with COPD, and patients with confirmed lung cancer, compared to those with non-confirmed lung cancer, recorded significantly higher 210Po levels.
The finding of polonium in BL provides hints for etiological hypotheses. Polonium is an alpha decay breakdown product of radon and a beta decay breakdown product of radioactive lead isotopes, all of which can be associated with lung cancer development. Inhaled tobacco smoke compounds are readily dispersed and cleaned through the bronchial mucociliary clearance (MCC) [2,3]. High 210Po levels in smokers’ lungs could be due to the accumulation of insoluble 210Pb particles, the father of 210Po, due to an increasingly progressive MCC impairment in smokers, reaching a minimum in COPD patients. In all heavy smokers with COPD there are metaplastic lesions of the ciliated epithelium [18]. Radionuclides thus can better penetrate in de-epithelialized or poorly ciliated areas where mucus stagnates more [3,19]. Due to the relatively long half-life of 210Pb (22 years) and the progressive MCC impairment, particularly in COPD patients, the entrapment of 210Pb and 210Po can lead to replenishment of alpha radioactivity with persistent lung cancer risk even after many years. Thus, this study provides an etiological hypothesis for those studies which had identified COPD as an independent risk factor for lung cancer [20,21,22].
Practical consequences of this hypothesis are: (i) identifying COPD patients as early as possible; (ii) administering pharmacological treatments to improve MCC and to remove 210Pb particles.
The World Health Organization recommends a reference level of 100 Bq/m3 for 222Rn concentration in homes and the International Commission for Radiological Protection has also recommended a level not exceeding 300 Bq/m3 [23,24]; 222Rn concentration in homes >300 Bq/m3 may be the cause of 210Po detection in never smokers, which happened in this study. Further studies are needed to confirm this finding.
Adenocarcinoma was the most common histological type of cancer among former smokers in this study; part of these cancer cases could be induced by 210Pb. Animal studies confirm this hypothesis [25,26].
This study has some limitations and some strengths. One limitation is that the number of never smoker patients was lower than that estimated in the sample size calculation (18 patients), since never smokers with suspected lung cancer were very few. Moreover, for some patients not all data were available, since it was not possible for all recruited patients to collect radon measurements at their homes and to administer spirometry tests. The cross-sectional nature of the study does not allow us to evaluate a cause–effect relationship, but this is, to our knowledge, the first study that has found an association between radioactivity (210Po) in the bronchopulmonary systems of patients and lung cancer. We could not compare 210Po measurements between patients and healthy controls for ethical reasons due to the invasive procedure of BL. Further studies could consider evaluating 210Po measurements in all patients with indication of BL (not only for suspected lung cancer).
The strength of this study is that results showed 210Po levels in the lungs of patients with lung cancer. Moreover, 210Po was detected in 100% of BL fluids from current and former smokers (who had quit smoking for at least 5 years) and in 54% of never smokers (p < 0.001). Lastly, former smokers had levels of 210Po similar to those of current smokers and significantly higher levels than never smokers.
5. Conclusions
In former smokers, the presence of detectable 210Po may be supported by its “father” 210Pb, due to reduced MCC. This mechanism could partially explain the onset of lung cancer in former smokers even many years after quitting. If confirmed by large longitudinal studies, our study may have important implications from a public health perspective. Pharmacological treatments improving MCC might in fact reduce 210Pb and 210Po levels in the lungs, thus substantially decreasing the risk of lung cancer in current smokers and particularly in former smokers.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/9/1/4/s1, Table S1: Summary data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.Z. and P.B.; methodology, V.Z., M.S.C., P.B., M.E, V.F. and G.G.; software, G.G.; validation, V.Z., P.B., M.E., V.F., and G.G.; formal analysis, S.G. and G.G.; investigation, P.M., R.T., R.G., M.P., D.P.; resources, R.P.; data curation, V.Z., P.B., M.E., V.F., G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, V.Z., G.G.; writing—review and editing, V.Z., M.S.C., S.G. and G.G.; visualization, V.Z., M.S.C., P.M., R.P., R.T., P.B., R.G., M.P., D.P., M.E., V.F., S.G., G.G.; supervision, V.Z., M.S.C., S.G. and G.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was funded by the National Observatory on Smoking, Alcohol and Drugs, National Institute of Health (Istituto Superiore di Sanità), Rome, Italy (funding number: CIG Z3405E7D6F).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Bologna Local Health Unit Ethical Committee (Prot. N. 1539/CE, December 2012).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Table S1 in Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
Authors want to thank the late Piergiorgio Zuccaro, the former Director of the National Observatory on Smoking, Alcohol and Drugs of the National Institute of Health, Rome, for his support in this project; and the late Enrico Gattavecchia for his technical and scientifical support; and the Italian League against Cancer (LILT, Milan) for its support of the work of SG.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. R.P. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zagà, V.; Lygidakis, C.; Chaouachi, K.; Gattavecchia, E. Polonium and Lung Cancer. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 860103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, E.P., Jr.; Hunt, V.R. Polonium-210, a volatile radioelement in cigarettes. Science 1964, 143, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzman, R.B.; Ilcewicz, F.H. Lead-210 and Polonium-210 in tissues of cigarette smokers. Science 1966, 153, 1259–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, E.A. Radioactivity of tobacco trichomes and insoluble cigarette smoke particles. Nature 1974, 249, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagueuzian, H.S.; White, C.; Sayre, J.; Norman, A. Cigarette smoke radioactivity and lung cancer risk. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2012, 14, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taroni, M.; Zagà, V.; Bartolomei, P.; Gattavecchia, E.; Pacifici, R.; Zuccaro, P.; Esposito, M. 210Pb and 210Po concentrations in Italian cigarettes and effective dose evaluation. Health Phys. 2014, 107, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggli, M.E.; Ebbert, J.O.; Robertson, C.; Hurt, R.D. Waking a sleeping giant: The tobacco industry’s response to the polonium-210 issue. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.B.; Radford, E.P., Jr.; McCombs, H.L.; Hunt, V.R. Distribution of polonium-210 in pulmonary tissues of cigarette smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1965, 273, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, E.I.; Abd Elaziz, M.A.; Al-Arifi, M.N.; Al-Dhawailie, A.A.; Al-Bokari, M.M. Evaluation of the contribution of smoking to total blood polonium-210 in Saudi population. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2000, 52, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, E.S.; Baratta, E.J. Polonium 210 in Tobacco, Cigarette Smoke, and Selected Human Organs. Public Health Rep. 1966, 81, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laking, G.R. Human Exposure to Radioactivity from Tobacco Smoke: Systematic Review. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2019, 21, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, B. The Polonium brief: A hidden history of cancer, radiation, and the tobacco industry. Isis 2009, 100, 453–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, R.S.; Stover, D.E.; Shi, W.; Venkatraman, E. Prevalence of COPD in women compared to men around the time of diagnosis of primary lung cancer. Chest 2006, 129, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Pocket Guide to COPD Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention. A guide for Health Professionals. 2017. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/wms-GOLD-2017-Pocket-Guide.pdf (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Erickson, M.D. Lead-210 in Bone, Food, Urine, Feces, Blood, Air, and Water. DOE EML Procedures Manual HASL-300, Volume 1, 28th Ed. 1997. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/30/000/30000468.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- ISO 11665-4:2012—Measurement of Radioactivity in the Environment—Air: Radon-222—Integrated Measurement Method for Determining Average Activity Concentration Using Passive Sampling and Delayed Analysis; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Rossetti, M.; Esposito, M. Radon levels in underground workplaces: A map of the Italian regions. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 164, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, R.V.; Klimec, M.F.; Borowski, C.J. Deposition of 2 μ particles in the tracheobronchial tree of normal subjects—Smokers and nonsmokers. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.S.; Harley, N.H.; Tso, T.C. Clearance of polonium-210-enriched cigarette smoke from the rat trachea and lung. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1985, 79, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Casoni, G.; Caramori, G.; Guzzinati, I.; Boschetto, P.; Ravenna, F.; Calia, N.; Petruzzelli, S.; Corbetta, L.; Cavallesco, G.; et al. COPD increases the risk of squamous histological subtype in smokers who develop non-small cell lung carcinoma. Thorax 2004, 59, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.P.; Hopkins, R.J.; Christmas, T.; Black, P.N.; Metcalf, P.; Gamble, G.D. COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.P.; Hopkins, R.J. Link between COPD and lung cancer. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 758–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, H.; Shannoun, F. WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44149/9789241547673_eng.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; ICRP Publication 103; Ann ICRP 37. [Google Scholar]
- Yuile, C.L.; Berke, H.L.; Hull, T. Lung Cancer Following Polonium-210 Inhalation in Rats. Radiat. Res. 1967, 31, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R.; McGandy, R.B.; Little, J.B. Histochemical, light and electron microscopic study of polonium-210 induced peripheral tumors in hamster lungs: Evidence implicating the Clara cell as the cell of origin. Eur. J. Cancer 1977, 13, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).