3D Printing of PLA/Magnetic Ferrite Composites: Effect of Filler Particles on Magnetic Properties of Filament
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Filler Particles
- (1)
- Cobalt ferrite CoFe2O4 (CFO);
- (2)
- Mixture (1:1) of CoFe2O4 and zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite Zn0.3Co0.7Fe2O4 (CFO/ZCFO);
- (3)
- Barium hexaferrite BaFe12O19 (BaFO).
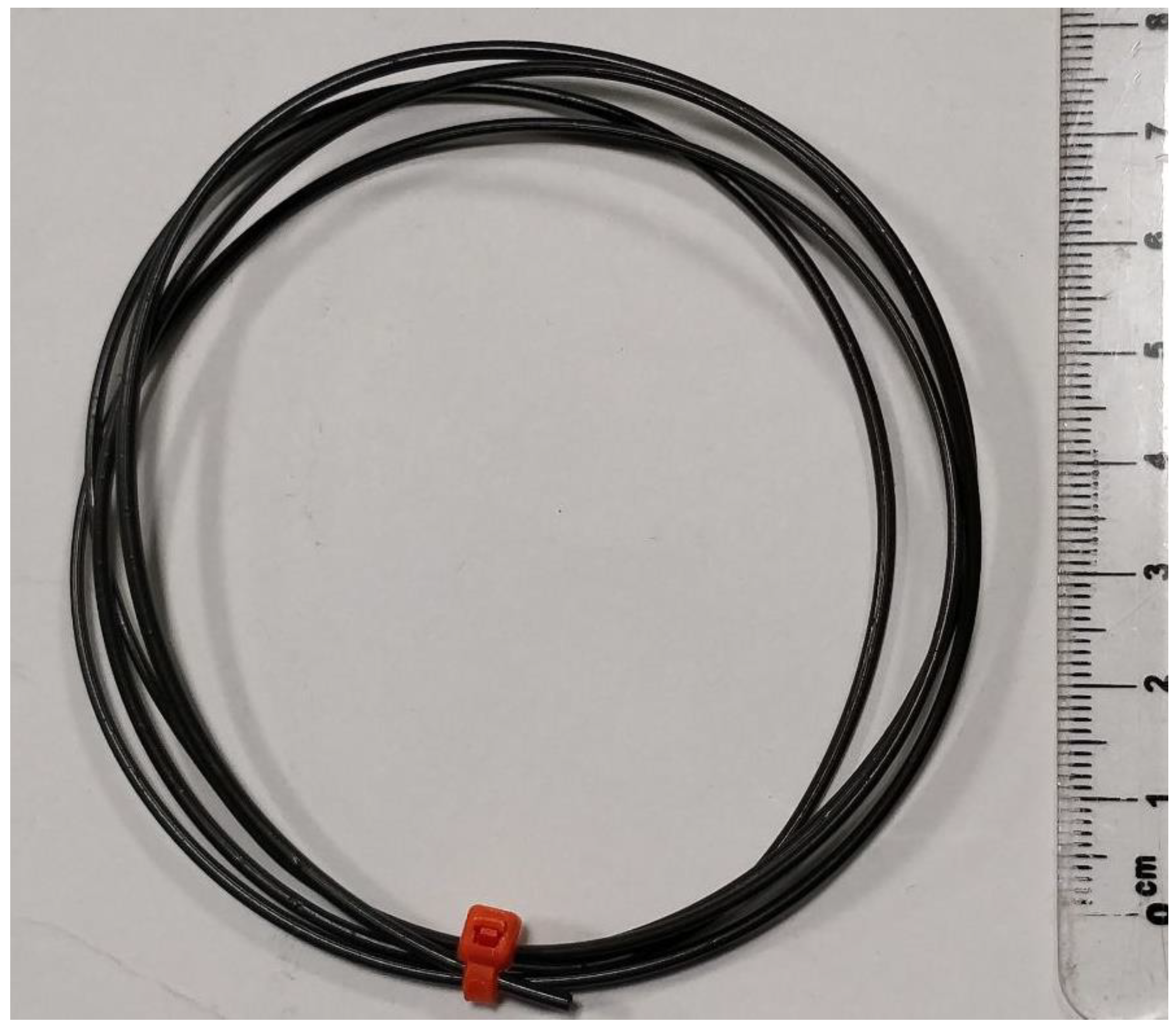
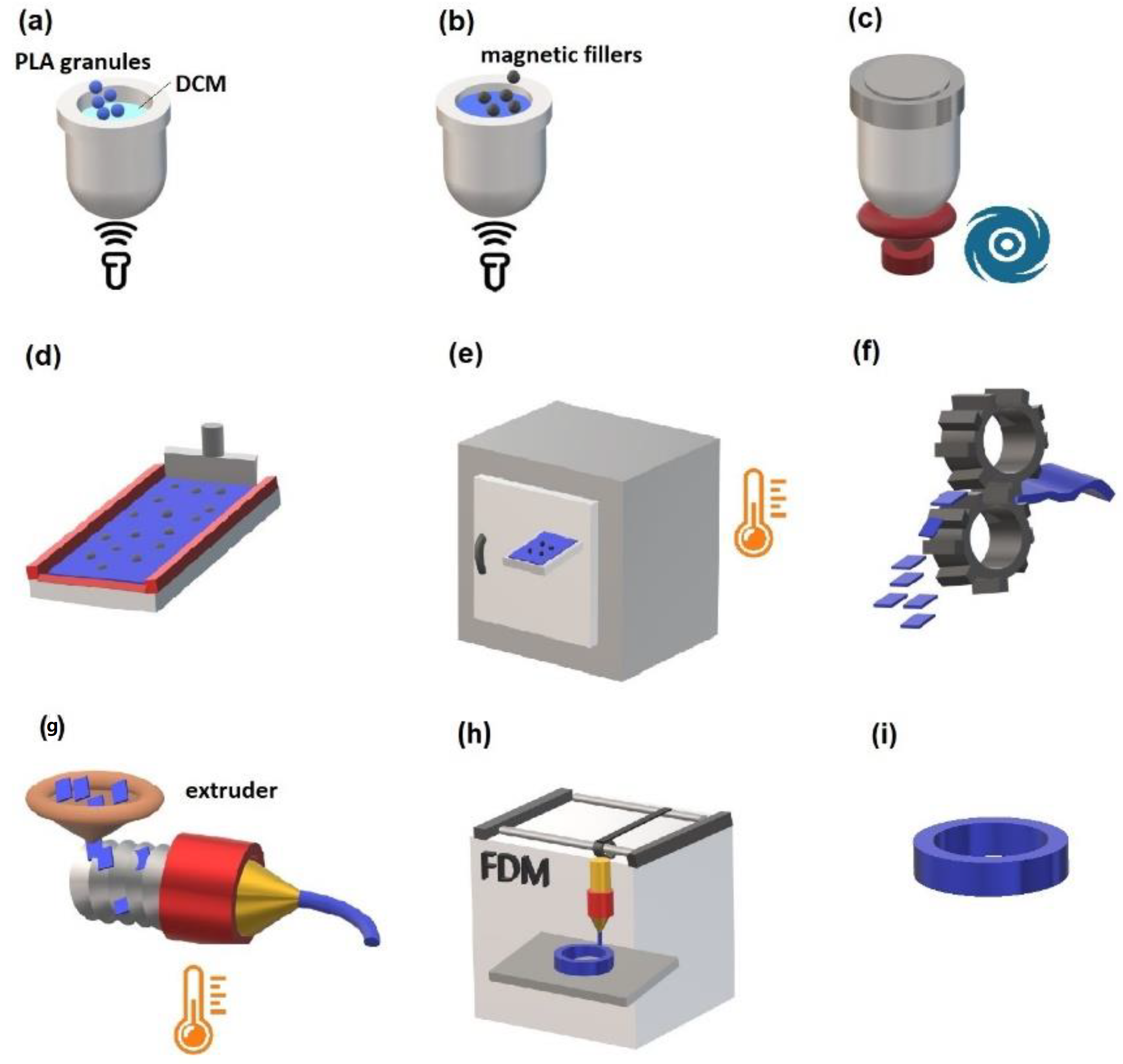
2.2. Fabrication of Filaments
- 1.
- Preparation of the PLA solution (Figure 1a)
- 2.
- Adding the filler (Figure 1b)
- 3.
- Homogenization (Figure 1c)
- 4.
- Composite film preparation (Figure 1d)
- 5.
- Drying (Figure 1e)
- 6.
- Pelletizing (Figure 1f)
- 7.
- Extrusion (Figure 1g)
- 8.
- FDM printing of the objects (Figure 1h)
2.3. Characterization of Structural and Magnetic Properties of Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Filaments
3.2. Magnetic Properties
3.3. 3D Printing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y. Overview of additive manufacturing technology and materials. In Materials for Additive Manufacturing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamood, R.M.; Jen, T.C.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Hassan, S.; Abdulrahman, K.O.; Akinlabi, E.T. Role of additive manufacturing in the era of Industry 4.0. In Additive Manufacturing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, K.; Tripathy, P.K. Preparation of Smart Materials by Additive Manufacturing Technologies: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiawan, R.B.; Imaduddin, F.; Ariawan, D.; Ubaidillah; Arifin, Z. A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, P.M.; Samouhos, M.; Taxiarchou, M. Functional fillers in composite filaments for fused filament fabrication; A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 4031–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammona, G.; Craparo, E. Biomedical Applications of Polylactide (PLA) and Its Copolymers. Molecules 2018, 23, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iron-Filled Metal Composite PLA, (n.d.). Available online: www.proto-pasta.com/products/magnetic-iron-pla (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Patton, M.V.; Ryan, P.; Calascione, T.; Fischer, N.; Morgenstern, A.; Stenger, N.; Nelson-Cheeseman, B.B. Manipulating magnetic anisotropy in fused filament fabricated parts via macroscopic shape, mesoscopic infill orientation, and infill percentage. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.P.; Velez Cuervo, C.; Arnold, D.P.; Velasquez-Garcia, L.F. Fully 3D-Printed, Monolithic, Mini Magnetic Actuators for Low-Cost, Compact Systems. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2019, 28, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magisetty, R.; Cheekuramelli, N.S. Additive manufacturing technology empowered complex electromechanical energy conversion devices and transformers. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 14, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Zhao, P.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. 3D Printing of Functional Magnetic Materials: From Design to Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipirpiridis, G.; Gervasoni, S.; Fischer, C.; Ergeneman, O.; Pellicer, E.; Nelson, B.J.; Pané, S. 3D Printing of Thermoplastic-Bonded Soft- and Hard-Magnetic Composites: Magnetically Tuneable Architectures and Functional Devices. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Abert, C.; Bruckner, F.; Groenefeld, M.; Schuschnigg, S.; Teliban, I.; Vogler, C.; Wautischer, G.; Windl, R.; Suess, D. 3D Printing of Polymer-Bonded Rare-Earth Magnets with a Variable Magnetic Compound Fraction for a Predefined Stray Field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanemann, T.; Syperek, D.; Nötzel, D. 3D printing of ABS barium ferrite composites. Materials 2020, 13, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, C.; Cano, S.; Teliban, I.; Schuschnigg, S.; Groenefeld, M.; Suess, D. Polymer-bonded anisotropic SrFe12O19 filaments for fused filament fabrication. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 063904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Mao, X.; Jiang, W.; Ge, S.S. Net-shaped barium and strontium ferrites by 3D printing with enhanced magnetic performance from milled powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Goertler, M.; Abert, C.; Bruckner, F.; Groenefeld, M.; Teliban, I.; Suess, D. Additive Manufactured and Topology Optimized Passive Shimming Elements for Permanent Magnetic Systems. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Yuk, H.; Zhao, R.; Chester, S.A.; Zhao, X. Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials. Nature 2018, 558, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapan, Y.; Karacakol, A.C.; Guzelhan, S.N.; Isik, I.; Sitti, M. Reprogrammable shape morphing of magnetic soft machines. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvaro, G.; Omelyanchik, A.; Peddis, D. Ferroic Transition Metal Oxide Nano-heterostructures: From Fundamentals to Applications. In Tailored Functional Oxide Nanomaterials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 405–437. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 12, ISBN 9780470386323. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.L.; Granados-Miralles, C.; Saura-Múzquiz, M.; Stingaciu, M.; Larsen, J.; Søndergaard-Pedersen, F.; Ahlburg, J.V.; Keller, L.; Frandsen, C.; Christensen, M. Enhanced intrinsic saturation magnetization of ZnxCo1−xFe2O4 nanocrystallites with metastable spinel inversion. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Levada, K.; Pshenichnikov, S.; Abdolrahim, M.; Baricic, M.; Kapitunova, A.; Galieva, A.; Sukhikh, S.; Astakhova, L.; Antipov, S.; et al. Green Synthesis of Co-Zn Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles: Magnetic and Intrinsic Antimicrobial Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Jovanović, S.; Vukomanović, M.; Spreitzer, M.; Peddis, D. Zn-doped cobalt ferrite: Tuning the interactions by chemical composition. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 796, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C. Hexagonal ferrites: A review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1191–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikeland, A.Z.; Stingaciu, M.; Mamakhel, A.H.; Saura-Múzquiz, M.; Christensen, M. Enhancement of magnetic properties through morphology control of SrFe12O19 nanocrystallites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maltoni, P.; Sarkar, T.; Barucca, G.; Varvaro, G.; Locardi, F.; Peddis, D.; Mathieu, R. Tuning the magnetic properties of hard-soft SrFe12O19/CoFe2O4 nanostructures via composition/interphase coupling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5927–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannas, C.; Falqui, A.; Musinu, A.; Peddis, D.; Piccaluga, G. CoFe2O4 nanocrystalline powders prepared by citrate-gel methods: Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingaciu, M.; Topole, M.; McGuiness, P.; Christensen, M. Magnetic properties of ball-milled SrFe12O19 particles consolidated by Spark-Plasma Sintering. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batlle, X.; Pérez, N.; Guardia, P.; Iglesias, O.; Labarta, A.; Bartolomé, F.; Garca, L.M.; Bartolomé, J.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; et al. Magnetic nanoparticles with bulklike properties (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07B524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omelyanchik, A.; da Silva, F.G.; Gomide, G.; Kozenkov, I.; Depeyrot, J.; Aquino, R.; Campos, A.F.C.; Fiorani, D.; Peddis, D.; Rodionova, V.; et al. Effect of citric acid on the morpho-structural and magnetic properties of ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Costa, C.M.; Correia, D.M.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Martins, P.; Gonçalves, R.; Cardoso, V.F.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based structures for advanced applications. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 681–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Antipova, V.; Gritsenko, C.; Kolesnikova, V.; Murzin, D.; Han, Y.; Turutin, A.V.; Kubasov, I.V.; Kislyuk, A.M.; Ilina, T.S.; et al. Boosting Magnetoelectric Effect in Polymer-Based Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrish, A.H. The Physical Principles of Magnetism; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1965; Volume 1, ISBN 0-7803-6029-X. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, E.C.; Wohlfarth, E.P. A Mechanism of Magnetic Hysteresis in Heterogeneous Alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1948, 240, 599–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, B.; Lappe, K.; Noetzel, D.; Pursche, K.; Hanemann, T. A 3D-Printable Polymer-Metal Soft-Magnetic Functional Composite—Development and Characterization. Materials 2018, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-García, Á.; Law, J.Y.; Cota, A.; Bellido-Correa, A.; Ramírez-Rico, J.; Schäfer, R.; Franco, V. Novel procedure for laboratory scale production of composite functional filaments for additive manufacturing. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, Á.; Law, J.Y.; Felix, M.; Guerrero, A.; Franco, V. Functional, thermal and rheological properties of polymer-based magnetic composite filaments for additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2022, 219, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashimizu, Y.; Iiyoshi, M. New parameter of roundness R: Circularity corrected by aspect ratio. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Tran, P.; Dickens, T.; Schrand, A. Composite Reinforcement Architectures: A Review of Field-Assisted Additive Manufacturing for Polymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type of Fillers | Mass Fraction, % | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| CFO | 5 | 5CFO/PLA |
| CFO | 10 | 10CFO/PLA |
| CFO/ZCFO | 5 | 5CFO/ZCFO/PLA |
| BaFO | 5 | 5BaFO/PLA |
| Sample | M12kOe | MS | MR/MS | HC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| emu/gfilament | emu/gparticles | emu/gfilament | emu/gparticles | % | kOe | |
| 5CFO/PLA | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 43 ± 4 | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 53 ± 5 | 29 ± 5 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 10CFO/PLA | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 44 ± 4 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 54 ± 5 | 32 ± 5 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| 5CFO/ZCFO/PLA | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 52 ± 5 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 60 ± 6 | 32 ± 5 | 0.55 ± 0.02 |
| 5BaFO/PLA | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 60 ± 6 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 85 ± 8 | 32 ± 5 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | Outer Circle | Inner Circle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D, cm | AR | c | d, cm | AR | c | |
| PLA | 1.66 ± 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.917 | 0.99 * | 1.00 | 0.935 |
| 5CFO/PLA | 1.67 ± 0.03 | 1.03 | 0.919 | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 1.03 | 0.883 |
| 5CFO/ZCFO/PLA | 1.64 ± 0.02 | 1.03 | 0.897 | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 1.05 | 0.910 |
| 5BaFO/PLA | 1.65 ± 0.02 | 1.03 | 0.823 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 1.03 | 0.941 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amirov, A.; Omelyanchik, A.; Murzin, D.; Kolesnikova, V.; Vorontsov, S.; Musov, I.; Musov, K.; Khashirova, S.; Rodionova, V. 3D Printing of PLA/Magnetic Ferrite Composites: Effect of Filler Particles on Magnetic Properties of Filament. Processes 2022, 10, 2412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112412
Amirov A, Omelyanchik A, Murzin D, Kolesnikova V, Vorontsov S, Musov I, Musov K, Khashirova S, Rodionova V. 3D Printing of PLA/Magnetic Ferrite Composites: Effect of Filler Particles on Magnetic Properties of Filament. Processes. 2022; 10(11):2412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112412
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmirov, Abdulkarim, Alexander Omelyanchik, Dmitry Murzin, Valeria Kolesnikova, Stanislav Vorontsov, Ismel Musov, Khasan Musov, Svetlana Khashirova, and Valeria Rodionova. 2022. "3D Printing of PLA/Magnetic Ferrite Composites: Effect of Filler Particles on Magnetic Properties of Filament" Processes 10, no. 11: 2412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112412
APA StyleAmirov, A., Omelyanchik, A., Murzin, D., Kolesnikova, V., Vorontsov, S., Musov, I., Musov, K., Khashirova, S., & Rodionova, V. (2022). 3D Printing of PLA/Magnetic Ferrite Composites: Effect of Filler Particles on Magnetic Properties of Filament. Processes, 10(11), 2412. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112412











