Influence of Exogenous 28-Homobrassinolide Optimized Dosage and EDAH Application on Hormone Status, Grain Filling, and Maize Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
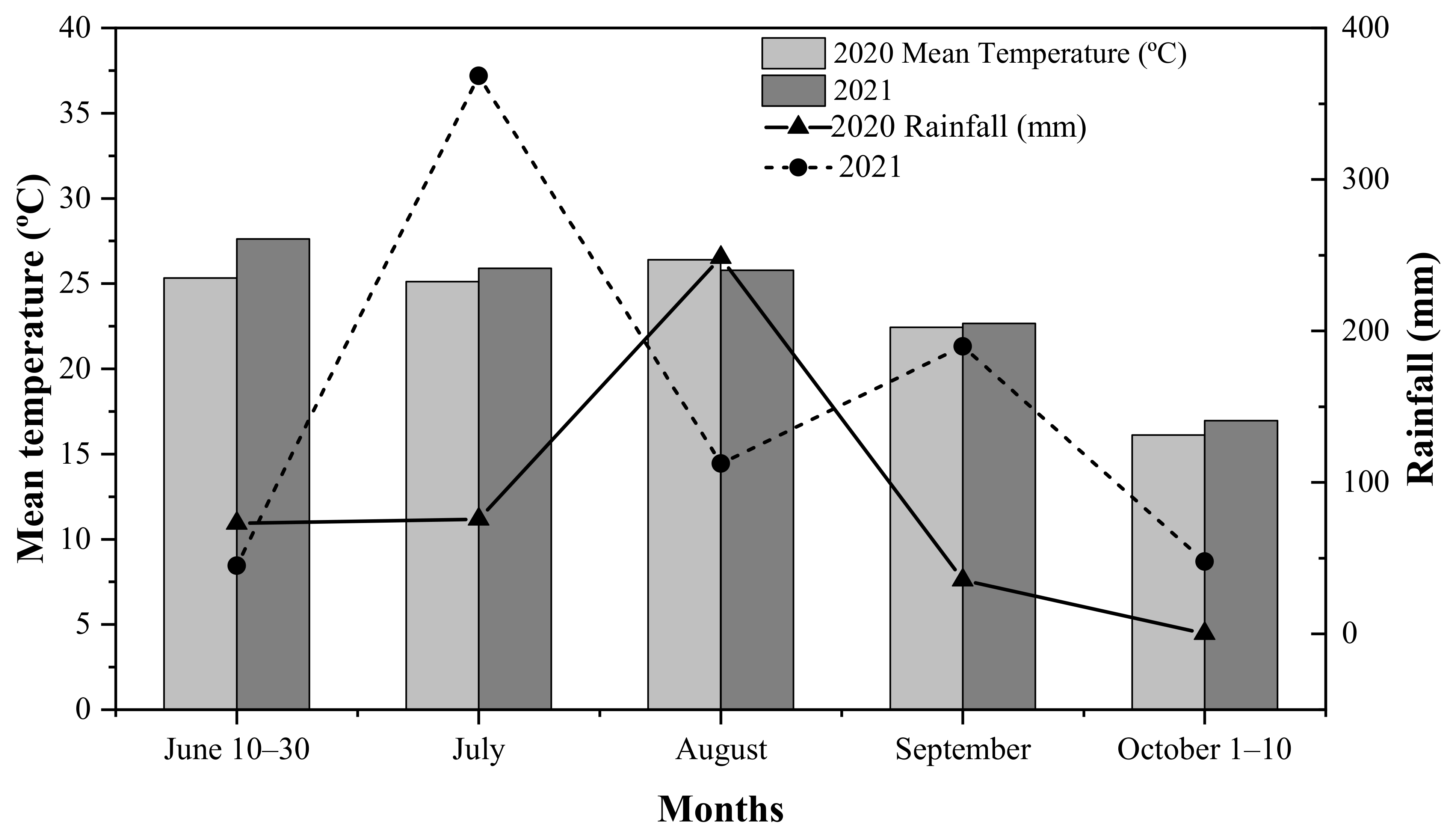
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. Measurement and Sample Collection
2.3.1. The Photosynthetic Attributes and Relative Chlorophyll Content
2.3.2. Leaf Senescence
2.3.3. Grain Filling Rate
2.3.4. Endogenous Hormones
2.3.5. Yield and Yield Components
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
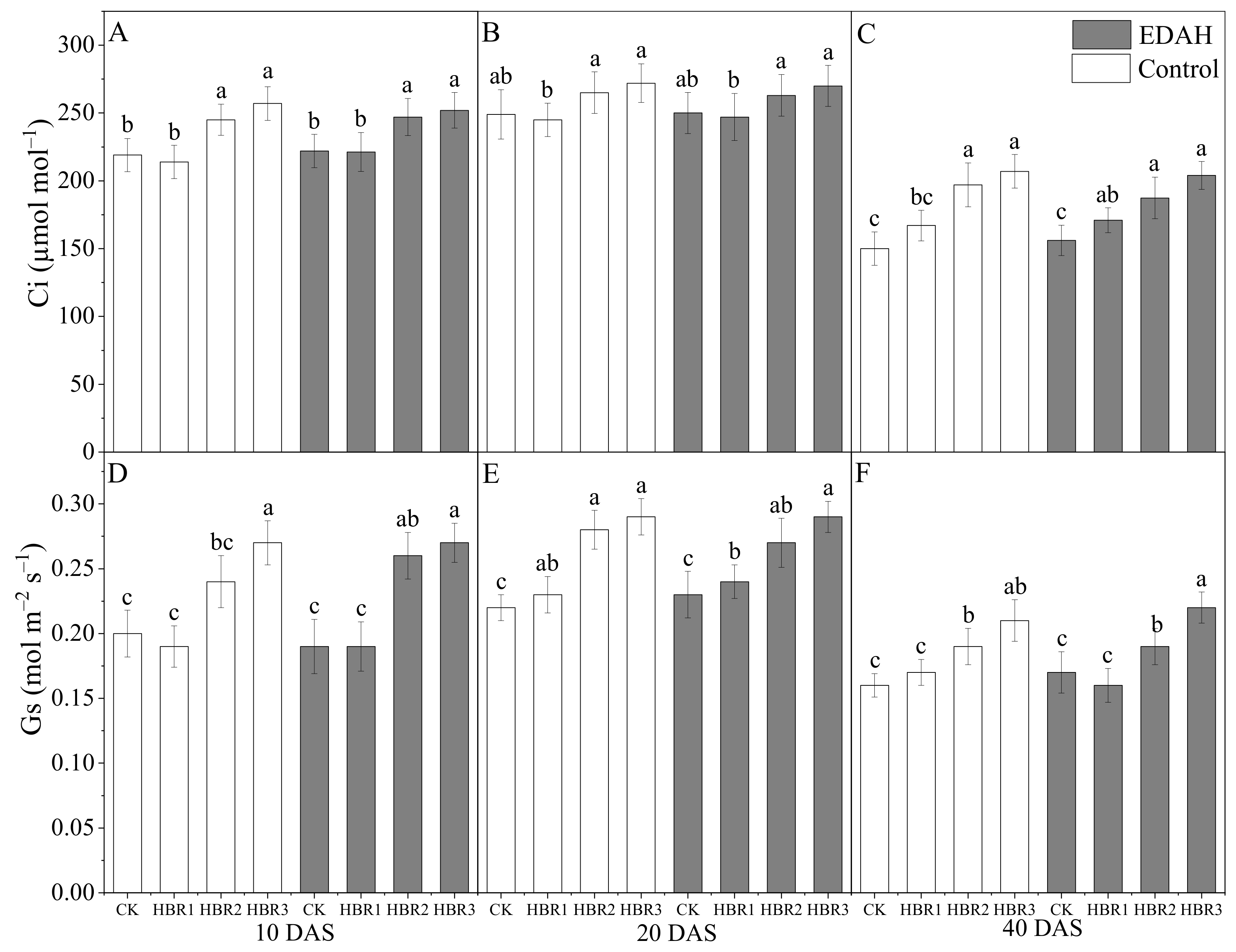
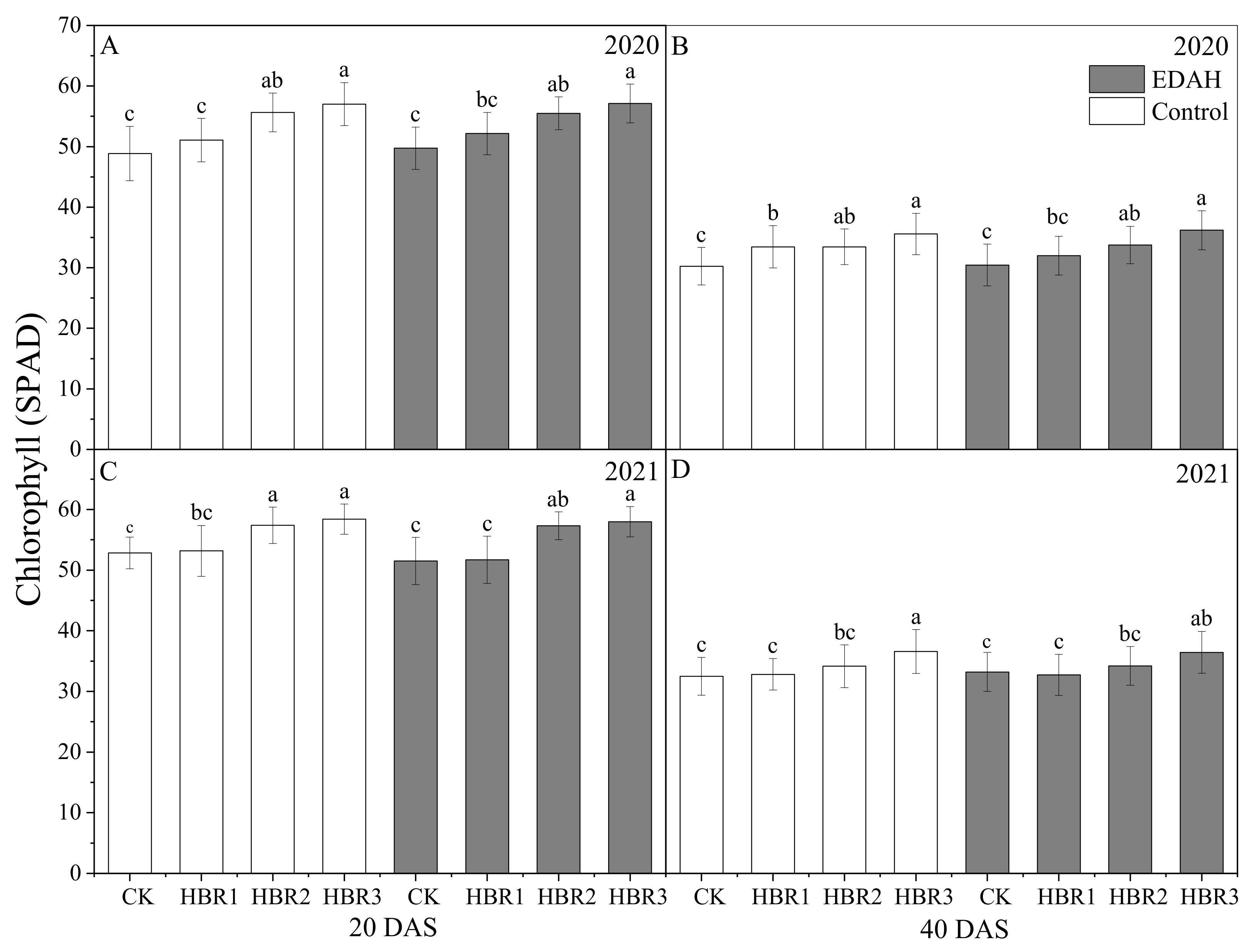
3.1. Photosynthetic Attributes and Relative Chlorophyll Content
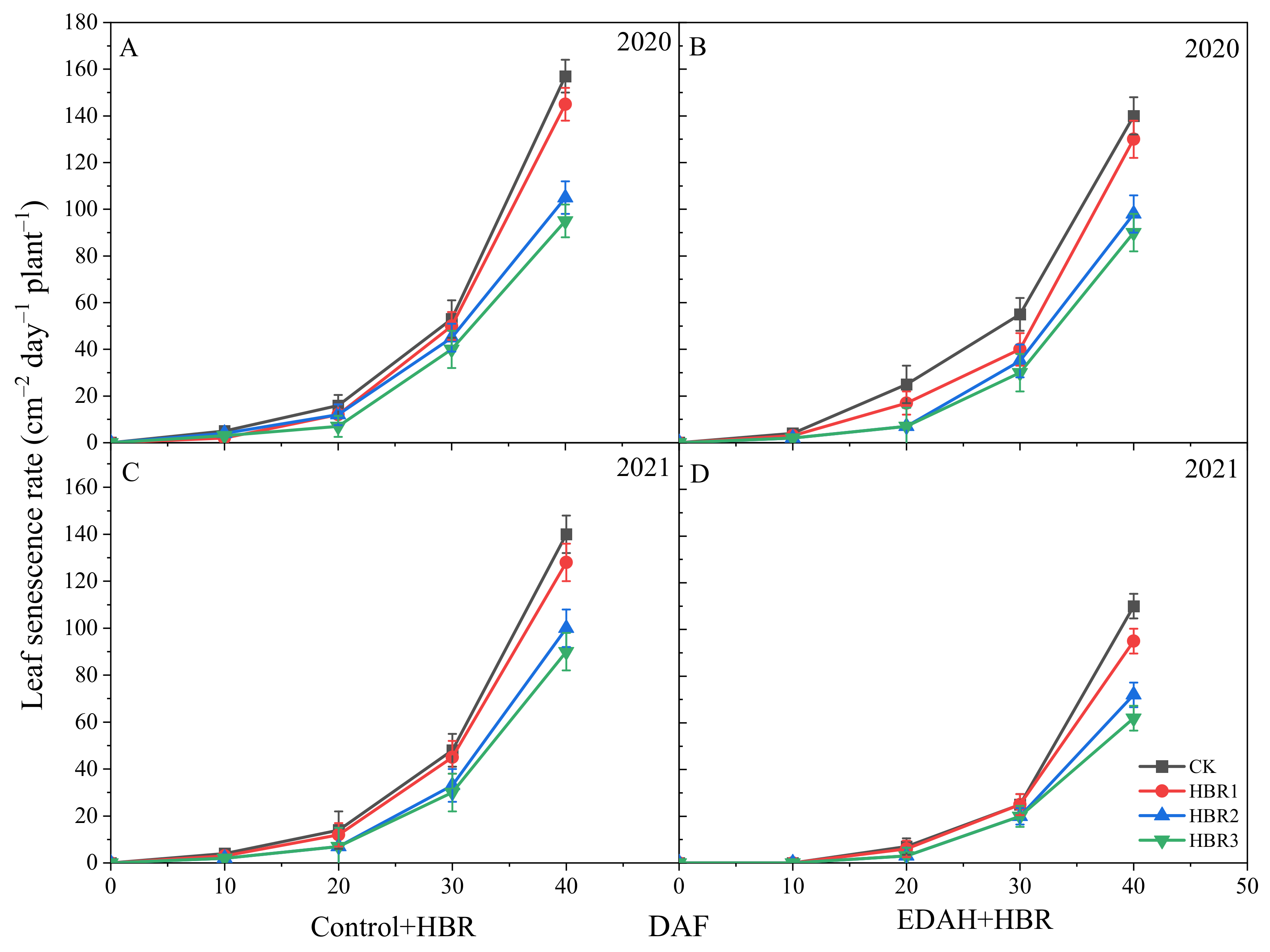
3.2. Leaf Senescence
3.3. Endogenous Hormonal Changes
3.3.1. ABA Contents
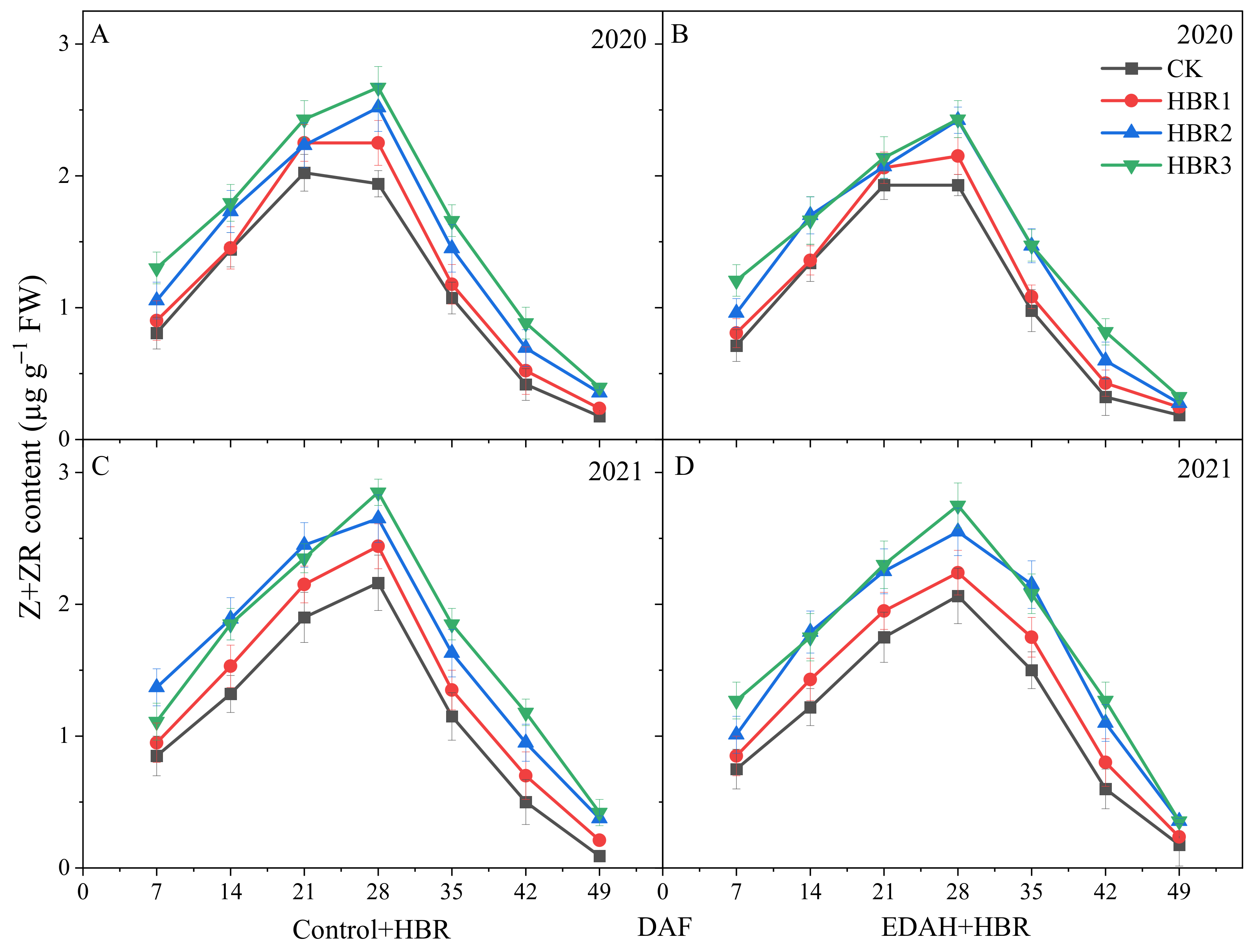
3.3.2. Z+ZR Contents
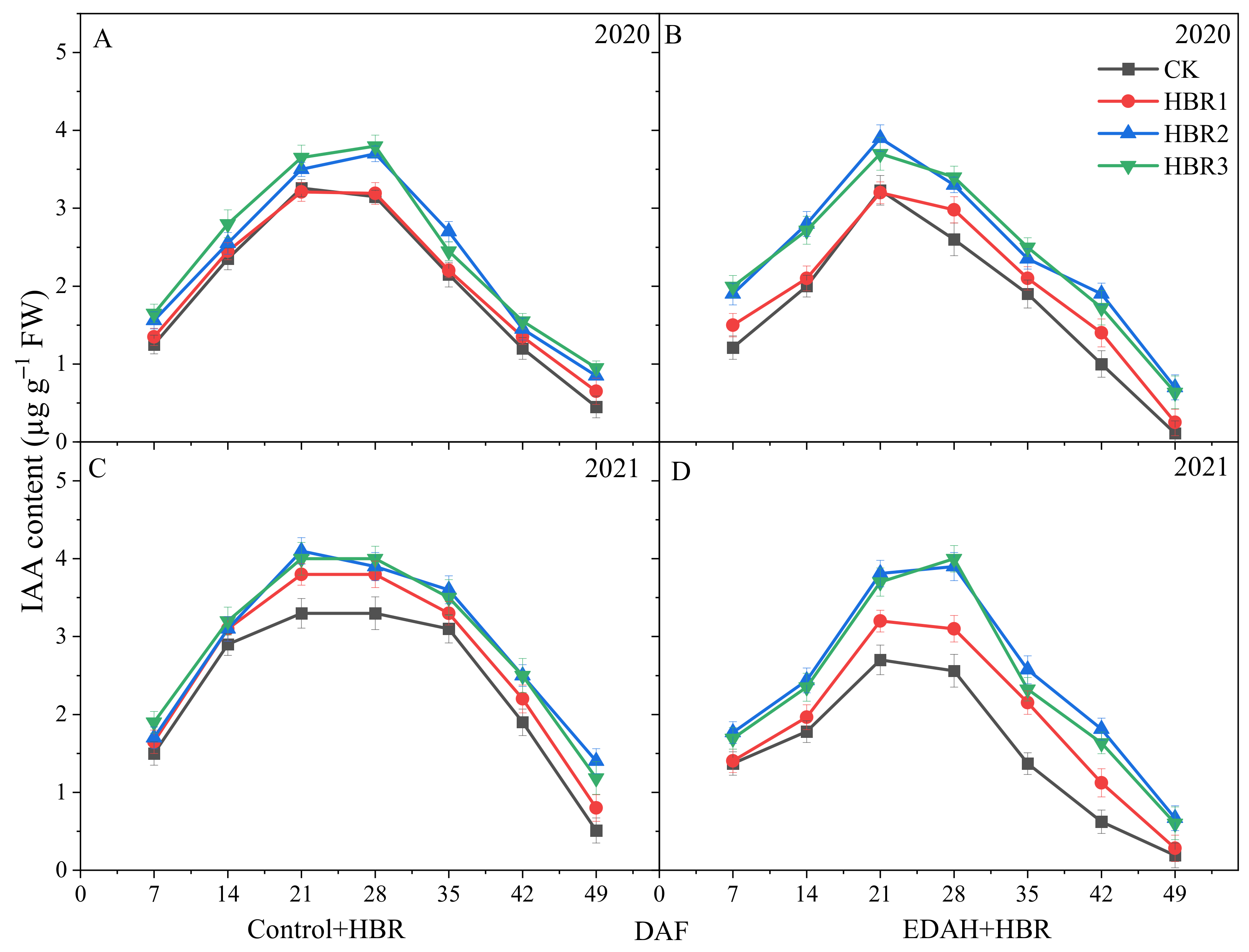
3.3.3. IAA Contents
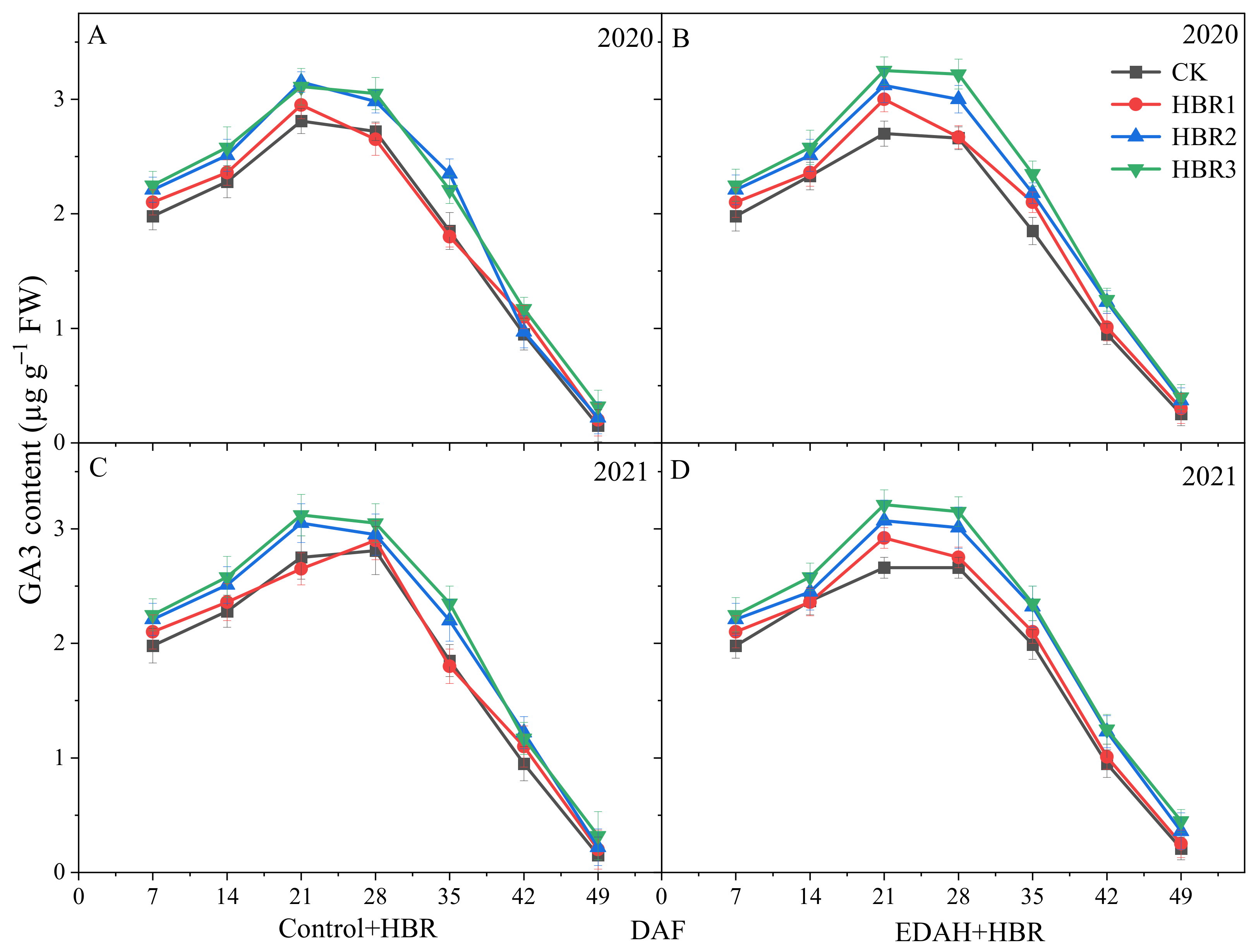
3.3.4. GA3 Contents
3.4. Grain Filling Rate
3.5. Grain Yield and Yield Components
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Irfan, A.R.; Liu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, D. Exogenous Brassinolide Enhances the Growth and Cold Resistance of Maize (Zea mays L.) Seedlings under Chilling Stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, O.P. Nutritive Value of Maize: Improvements, Applications and Constraints. In Maize: Nutrition Dynamics and Novel Uses; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz, E.; Nadeau, E. Effects of Intercropping on Yield, Weed Incidence, Forage Quality and Soil Residual N in Organically Grown Forage Maize (Zea mays L.) and Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). Field Crops Res. 2014, 169, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasensky, J.; Jonak, C. Drought, Salt, and Temperature Stress-Induced Metabolic Rearrangements and Regulatory Networks. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dass, S.; Singh, I.; Chikkappa, G.K.; Parihar, C.M.; Kaul, J.; Singode, A.; Manivannan, A.; Singh, D.K. Abiotic Stresses in Maize: Some Issues and Solutions. Dir. Maize Res. Indian Counc. Agric. Res. 2010, 110012, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Atıcı, Ö.; Nalbantoǧlu, B. Antifreeze Proteins in Higher Plants. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, I.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Bones, A.M.; Hall, R.D. Plant Molecular Stress Responses Face Climate Change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.H.; Mohammed, M.I. Effect of Abiotic Stress on Irrigated Maize Forage Yield as Compared to Sorghum. J. Hort. Plant Res 2019, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M. Frequency of Extreme Precipitation Increases Extensively with Event Rareness under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janowiak, F.; Maas, B.; Dörffling, K. Importance of Abscisic Acid for Chilling Tolerance of Maize Seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Effects of Brassinosteroids on the Plant Responses to Environmental Stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louarn, G.; Chenu, K.; Fournier, C.; Andrieu, B.; Giauffret, C. Relative Contributions of Light Interception and Radiation Use Efficiency to the Reduction of Maize Productivity under Cold Temperatures. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.; Babcock, B.; Peng, Y.; Gassman, P.W.; Campbell, T. Placing Bounds on Extreme Temperature Response of Maize to Improve Crop Model Intercomparison. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–18 December 2015; Volume 2015, p. GC11J-06. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.J.; Babcock, B.A.; Peng, Y.; Gassman, P.W.; Campbell, T.D. Placing Bounds on Extreme Temperature Response of Maize. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Song, F.; Liu, F.; Zhu, X.; Xu, H. Effect of Planting Density on Root Lodging Resistance and Its Relationship to Nodal Root Growth Characteristics in Maize (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rademacher, W. Plant Growth Regulators: Backgrounds and Uses in Plant Production. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 34, 845–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.F.; Hall, M.A.; De Klerk, G.-J. Plant Growth Regulators I: Introduction; Auxins, Their Analogues and Inhibitors. In Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 175–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Qu, S.; Huang, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, L. Improving Maize Grain Yield by Formulating Plant Growth Regulator Strategies in North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gao, Y.; Tian, B.; Ren, J.; Meng, Q.; Wang, P. Effects of EDAH, a Novel Plant Growth Regulator, on Mechanical Strength, Stalk Vascular Bundles and Grain Yield of Summer Maize at High Densities. Field Crops Res. 2017, 200, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, D.; Xing, J.; Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Ethephon-Regulated Maize Internode Elongation Associated with Modulating Auxin and Gibberellin Signal to Alter Cell Wall Biosynthesis and Modification. Plant Sci. 2020, 290, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, C. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Mechanism by Which Spraying Diethyl Aminoethyl Hexanoate after Anthesis Regulates Wheat Grain Filling. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Feng, N.; Zheng, D.; Cui, H.; Sun, F.; Gong, X. Uniconazole and Diethyl Aminoethyl Hexanoate Increase Soybean Pod Setting and Yield by Regulating Sucrose and Starch Content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chai, M.; Yang, D.; van der Werf, W.; Evers, J.; Duan, L. Use of EDAH Improves Maize Morphological and Mechanical Traits Related to Lodging. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, L.; Xu, P.; Jiang, S. Dissipation of the Plant Growth Regulator Hexanoic Acid 2-(Diethylamino) Ethyl Ester in Pakchoi and Soil. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2008, 88, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, H.; Pan, C. Dissipation of Diethyl Aminoethyl Hexanoate (DA-6) Residues in Pakchoi, Cotton Crops and Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.C. Biochemistry and Physiology of Plant Hormones; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 1461236541. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.J. Plant Hormones: Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN 9401104735. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, M.E.; Mioto, P.T.; Mercier, H. Hormonal Interactions Underlying Plant Development under Drought. In Plant Hormones under Challenging Environmental Factors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 51–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Sah, S.K.; Khare, T.; Shriram, V.; Wani, S.H. Engineering Phytohormones for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. In Plant Hormones under Challenging Environmental Factors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid-Mediated Stress Responses. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2003, 22, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaubhadel, S.; Chaudhary, S.; Dobinson, K.F.; Krishna, P. Treatment with 24-Epibrassinolide, a Brassinosteroid, Increases the Basic Thermotolerance of Brassica Napus and Tomato Seedlings. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 40, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaubhadel, S.; Browning, K.S.; Gallie, D.R.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid Functions to Protect the Translational Machinery and Heat-shock Protein Synthesis Following Thermal Stress. Plant J. 2002, 29, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, F.; Bor, M.; Demiral, T.; Türkan, İ. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on Seed Germination, Seedling Growth, Lipid Peroxidation, Proline Content and Antioxidative System of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Salinity Stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2004, 42, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divi, U.K.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroids Confer Stress Tolerance. Plant Stress Biol. Genomics Syst. Biol. 2009, 85, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Díaz, M.; Ulloa-Inostroza, E.M.; González-Villagra, J.; Ivanov, A.G.; Kurepin, L.V. Phytohormonal Responses to Soil Acidity in Plants. In Plant Hormones under Challenging Environmental Factors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 133–155. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, G.J.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, J.-Q. Role of Hormones in Plant Adaptation to Heat Stress. In Plant Hormones under Challenging Environmental Factors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, H.; Hayat, S.; Bajguz, A. Regulation of Photosynthesis by Brassinosteroids in Plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Grain Filling of Cereals under Soil Drying. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Jan, A.; Zhang, P.; Khan, M.N.; Cai, T.; Wei, T.; Ren, X.; Jia, Q.; Han, Q.; Jia, Z. Effects of Ridge-Covering Mulches on Soil Water Storage and Maize Production under Simulated Rainfall in Semiarid Regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, D.; Gu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wen, X. Effect of Plastic Film Mulching on the Grain Filling and Hormonal Changes of Maize under Different Irrigation Conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, P. Post-Anthesis Development of Inferior and Superior Spikelets in Rice in Relation to Abscisic Acid and Ethylene. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Li, T.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of Potassium Foliage Application Post-Anthesis on Grain Filling of Wheat under Drought Stress. Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xu, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Jia, Q.; Fangyuan, H.; Daur, I.; Wei, T.; Cai, T.; Ren, X.; Zhang, P. The Ridge Furrow Cropping Technique Indirectly Improves Seed Filling Endogenous Hormonal Changes and Winter Wheat Production under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verslues, P.E.; Zhu, J.-K. Before and beyond ABA: Upstream Sensing and Internal Signals That Determine ABA Accumulation and Response under Abiotic Stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piotrowska, A.; Bajguz, A. Conjugates of Abscisic Acid, Brassinosteroids, Ethylene, Gibberellins, and Jasmonates. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2097–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, T.; Ren, S.; Su, L.; Li, Z. Abscisic Acid and Aldehyde Oxidase Activity in Maize Ear Leaf and Grain Relative to Post-Flowering Photosynthetic Capacity and Grain-Filling Rate under Different Water/Nitrogen Treatments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, S.; Li, Z.; Cheng, R.; Fang, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, W. Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Determination of ABA’s Effects on Grain-Filling of Oryza sativa L. Inferior Spikelets. Plant Sci. 2012, 185, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Gu, D.J.; Zhang, B.B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C. Hormone Contents in Kernels at Different Positions on an Ear and Their Relationship with Endosperm Development and Kernel Filling in Maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sui, Y.; Gu, D.; Wen, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Liao, Y. Effects of Conservation Tillage on Grain Filling and Hormonal Changes in Wheat under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidadi, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Asahina, M.; Satoh, S. Effects of Shoot-Applied Gibberellin/Gibberellin-Biosynthesis Inhibitors on Root Growth and Expression of Gibberellin Biosynthesis Genes in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Root 2010, 4, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rentzsch, S.; Podzimska, D.; Voegele, A.; Imbeck, M.; Müller, K.; Linkies, A.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Dose-and Tissue-Specific Interaction of Monoterpenes with the Gibberellin-Mediated Release of Potato Tuber Bud Dormancy, Sprout Growth and Induction of α-Amylases and β-Amylases. Planta 2012, 235, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Peng, S.; Visperas, R.M.; Sanico, A.L.; Zhu, Q.; Gu, S. Grain Filling Pattern and Cytokinin Content in the Grains and Roots of Rice Plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2000, 30, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Involvement of Cytokinins in the Grain Filling of Rice under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khripach, V.A.; Zhabinskii, V.N.; Khripach, N.B. New Practical Aspects of Brassinosteroids and Results of Their Ten-Year Agricultural Use in Russia and Belarus. In Brassinosteroids; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 189–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.A.; Hayat, S.; Ali, B.; Ahmad, A. 28-Homobrassinolide Protects Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum) from Cadmium Toxicity by Stimulating Antioxidants. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, S.; Khalique, G.; Wani, A.S.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, A. Protection of Growth in Response to 28-Homobrassinolide under the Stress of Cadmium and Salinity in Wheat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bons, H.K.; Kaur, M. Role of Plant Growth Regulators in Improving Fruit Set, Quality and Yield of Fruit Crops: A Review. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, G.; Mo, Y.; Kaousar, R.; Duan, L.; Tan, W. Comparison of Droplet Deposition, 28-Homobrassinolide Dosage Efficacy and Working Efficiency of the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Knapsack Manual Sprayer in the Maize Field. Agronomy 2022, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hasan, S.A.; Yusuf, M.; Hayat, Q.; Ahmad, A. Effect of 28-Homobrassinolide on Photosynthesis, Fluorescence and Antioxidant System in the Presence or Absence of Salinity and Temperature in Vigna Radiata. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 69, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, F.J. A Flexible Growth Function for Empirical Use. J. Exp. Bot. 1959, 10, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiqi, Z. Growth Analysis on the Process of Grain Filling in Rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 1988, 3, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W. Hormonal Changes in the Grains of Rice Subjected to Water Stress during Grain Filling. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clouse, S.D. Brassinosteroids; The Arabidopsis Book/American Society of Plant Biologists: Rockwille, MD, USA, 2011; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mobin, M.; Fariduddin, Q.; Azam, Z.M. Carbonic Anhydrase, Photosynthesis, and Seed Yield in Mustard Plants Treated with Phytohormones. Photosynthetica 2001, 39, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.A.; Wang, L.C.; Farooq, M.; Hussain, M.; Xue, L.L.; Zou, C.M. Brassinolide Application Improves the Drought Tolerance in Maize through Modulation of Enzymatic Antioxidants and Leaf Gas Exchange. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2011, 197, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liang, X.-G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.-L.; Shen, S.; Zhou, S.-L. Spraying Exogenous 6-Benzyladenine and Brassinolide at Tasseling Increases Maize Yield by Enhancing Source and Sink Capacity. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyemeni, M.N.; Al-Quwaiz, S.M. Effect of 28-Homobrassinolide on the Performance of Sensitive and Resistant Varieties of Vigna Radiata. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.-J.; Huang, L.-F.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Mao, W.-H.; Shi, K.; Wu, J.-X.; Asami, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.-Q. Brassinosteroids Promote Photosynthesis and Growth by Enhancing Activation of Rubisco and Expression of Photosynthetic Genes in Cucumis Sativus. Planta 2009, 230, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalio, R.J.D.; Pinheiro, H.P.; Sodek, L.; Haddad, C.R.B. The Effect of 24-Epibrassinolide and Clotrimazole on the Adaptation of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. to Salinity. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, D. The Brassinosteroid Signaling Pathway—New Key Players and Interconnections with Other Signaling Networks Crucial for Plant Development and Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8740–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badger, M.R.; Price, G.D. The Role of Carbonic Anhydrase in Photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1994, 45, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariduddin, Q.; Hayat, S.; Ali, B.; Ahmad, A. Effect of 28-Homobrassinolide on the Nitrate Reductase, Carbonic Anhydrase Activities and Net Photosynthetic Rate in Vigna Radiata. Acta Bot. Croat. 2006, 65, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Han, J.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of Phosphorus and Potassium Foliage Application Post-Anthesis on Grain Filling and Hormonal Changes of Wheat. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, H.; Lv, X.; Liu, D.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. Effect of Polyamines on the Grain Filling of Wheat under Drought Stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 100, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Main Plots | Treatments | HBR Dosage (mg a. i. ha−1) | Spray Method | Spray Volume (L ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CK | 0 | KMS | 450 |
| HBR1 | 20 | |||
| HBR2 | 25 | |||
| HBR3 | 30 | |||
| EDAH | CK | 0 | ||
| HBR1 | 20 | |||
| HBR2 | 25 | |||
| HBR3 | 30 |
| Year | Jointing Treatment | Silking Treatment | R1 | R2 | R3 | Rmax | Wmax | Tmax | D (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Control | CK | 2.72 c | 10.42 b | 3.06 c | 10.62 c | 102.21 c | 18.50 a | 27.12 b |
| HBR1 | 2.97 bc | 10.76 b | 3.30 bc | 12.42 b | 137.93 bc | 17.21 a | 29.07 b | ||
| HBR2 | 3.45 a | 12.46 a | 3.50 ab | 12.08 b | 190.32 a | 15.46 b | 34.19 a | ||
| HBR3 | 3.52 a | 12.83 a | 3.77 a | 13.97 a | 193.14 a | 15.28 b | 36.83 a | ||
| EDAH | CK | 2.70 c | 10.61 b | 3.12 c | 9.97 c | 116.27 c | 19.16 a | 27.14 b | |
| HBR1 | 2.75 c | 10.89 b | 3.27 bc | 12.42 b | 102.49 c | 18.47 a | 29.00 b | ||
| HBR2 | 3.42 a | 12.46 a | 3.61 ab | 13.65 a | 187.39 ab | 15.52 b | 35.69 a | ||
| HBR3 | 3.31 ab | 12.61 a | 3.70 a | 13.97 a | 189.66 ab | 15.28 b | 36.83 a | ||
| 2021 | Control | CK | 2.62 d | 11.18 c | 3.25 c | 9.13 c | 101.56 c | 23.33 a | 28.40 c |
| HBR1 | 3.05 bc | 11.18 c | 3.50 bc | 9.50 c | 102.49 c | 21.00 ab | 28.11 c | ||
| HBR2 | 3.39 a | 16.09 ab | 3.72 ab | 12.54 a | 167.50 ab | 17.36 b | 33.71 b | ||
| HBR3 | 3.52 a | 16.75 a | 4.00 a | 14.34 a | 174.78 a | 16.88 b | 34.83 a | ||
| EDAH | CtK | 2.70 cd | 11.34 c | 3.31 c | 10.92 c | 104.05 c | 23.33 a | 27.14 c | |
| HBR1 | 2.95 cd | 10.95 c | 3.46 bc | 11.02 bc | 103.67 c | 20.01 ab | 27.71 c | ||
| HBR2 | 3.30 ab | 15.20 b | 3.84 ab | 11.49 ab | 158.70 b | 16.86 b | 33.81 b | ||
| HBR3 | 3.27 ab | 14.74 b | 3.92 a | 12.68 a | 174.78 a | 17.46 b | 34.93 a | ||
| ANOVA | Dosage | ** | * | * | *** | ** | * | ** | |
| EDAH | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Year | NS | * | NS | * | ** | NS | ** | ||
| D×E | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| D×Y | NS | * | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | ||
| E×Y | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| D×E×Y | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Year | Jointing Treatment | Silking Treatment | Grains Number (Ear−1) | Ear Number (m−2) | TGW (g) | Grain Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Control | BK | 482.0 c | 7.47 a | 290.0 c | 9.82 c |
| HBR1 | 498.0 bc | 7.48 a | 299.3 bc | 9.66 bc | ||
| HBR2 | 518.0 ab | 7.51 a | 319.3 ab | 10.90 ab | ||
| HBR3 | 531.0 a | 7.49 a | 345.0 a | 12.20 a | ||
| EDAH | EK | 496.0 c | 7.46 a | 295.0 c | 9.78 c | |
| HBR1 | 502.0 b | 7.48 a | 296.0 c | 9.54 bc | ||
| HBR2 | 509.0 ab | 7.49 a | 326.6 ab | 11.53 ab | ||
| HBR3 | 528.0 a | 7.49 a | 339.0 ab | 12.13 a | ||
| 2021 | Control | BK | 505.6 c | 7.47 a | 288.3 c | 10.05 bc |
| HBR1 | 513.0 c | 7.50 a | 292.6 bc | 10.05 bc | ||
| HBR2 | 534.0 b | 7.53 a | 330.0 ab | 11.71 ab | ||
| HBR3 | 548.0 a | 7.51 a | 349.3 a | 12.40 a | ||
| EDAH | EK | 501.0 c | 7.46 a | 276.6 c | 9.97 c | |
| HBR1 | 505.7 c | 7.47 a | 288.2 bc | 10.39 bc | ||
| HBR2 | 536.0 ab | 7.52 a | 321.6 ab | 11.59 ab | ||
| HBR3 | 543.0 ab | 7.49 a | 342.0 ab | 12.23 a | ||
| ANOVA | Dosage | *** | NS | *** | *** | |
| EDAH | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Year | ** | NS | * | * | ||
| D×E | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| D×Y | NS | NS | NS | * | ||
| E×Y | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| D×E×Y | NS | NS | NS | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.; Wang, Z.; Mo, Y.; Huang, G.; Kaousar, R.; Tan, W. Influence of Exogenous 28-Homobrassinolide Optimized Dosage and EDAH Application on Hormone Status, Grain Filling, and Maize Production. Processes 2022, 10, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061118
Hussain M, Wang Z, Mo Y, Huang G, Kaousar R, Tan W. Influence of Exogenous 28-Homobrassinolide Optimized Dosage and EDAH Application on Hormone Status, Grain Filling, and Maize Production. Processes. 2022; 10(6):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061118
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Mujahid, Zhao Wang, You Mo, Guanmin Huang, Rehana Kaousar, and Weiming Tan. 2022. "Influence of Exogenous 28-Homobrassinolide Optimized Dosage and EDAH Application on Hormone Status, Grain Filling, and Maize Production" Processes 10, no. 6: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061118
APA StyleHussain, M., Wang, Z., Mo, Y., Huang, G., Kaousar, R., & Tan, W. (2022). Influence of Exogenous 28-Homobrassinolide Optimized Dosage and EDAH Application on Hormone Status, Grain Filling, and Maize Production. Processes, 10(6), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061118









