Abstract
The heritage of ancient buildings is an important part of the world’s history and culture, which has extremely rich historical–cultural value and artistic research value. Beijing has a large number of ancient palace buildings, and because of the age of their construction, many of them have problems with varying degrees of peeling and molding on the inner surfaces of the envelope. To solve the problems of damp interiors of palace buildings, a mathematical model of indoor heat and moisture transfer was established based on an ancient wooden palace building in Beijing. The model was validated by fitting the measured and simulated data. And the effects of outdoor relative humidity, soil moisture, wall moisture, and other factors on indoor heat and moisture transfer of ancient buildings were simulated and analyzed via the control variables method. The results showed that the measured and simulated data are within the error range, which verifies the accuracy of the model. And the simulation of indoor humidity matched the measured humidity. Thus, the simulation results were consistent with the actual situation. The variable trend of the relative humidity of the indoor environment with the outdoor humidity is inconsistent from plane to plane, i.e., it increases or remains constant with the increase in the outdoor humidity. Indoor ambient relative humidity increased with increasing wall moisture. And the indoor average temperature is 24.5 °C, and indoor relative humidity ranged between 87.4% and 92.4%. Soil moisture and wall moisture were the main factors affecting indoor relative humidity.
1. Introduction
Ancient buildings are an important part of the world’s historical and cultural heritage, which is an important carrier for inheriting national traditional culture and promoting cultural exchanges among nations and cannot be restored once they are damaged [1]. Nowadays, the protection of cultural relics and ancient buildings is gaining more and more attention. “Preserve the original appearance” is the basic principle for the protection of ancient buildings, so higher requirements for the technology of protection and restoration of ancient buildings have been proposed. With the advancement of technology, the conservation and repair of ancient buildings have gradually incorporated modern simulation and digital means from a purely manual approach [2,3] to seek the root mechanism of problem solving.
To better preserve its original appearance and historical value, revitalize the social value of ancient buildings, and enhance the comfort of visitors, many researchers have been conducting various explorations in recent years [4,5,6,7], such as ancient building wall repair work and ancient architecture of digital protection, etc. The typical problems of ancient building damage are the degradation of the anti-corrosion paint surface and the moldy wood structure. It was found that the deterioration and mold problems of ancient buildings are influenced by the coupling of multiple factors, such as the thermal and humid environment around the building, air flow, underground soil moisture, and the building envelope, etc. [8,9,10]. Exploring the patterns of influence of different factors on the deterioration of ancient buildings is an important prerequisite for taking effective conservation measures. At present, numerical simulation methods investigating the effects of airflow, the envelope structure, soil, precipitation, and other factors on the heat and moisture migration of ancient buildings are a low-cost and highly efficient way to grasp the influence law. And the degree of ancient building damage can put forward effective protection schemes for the problems such as dampness. Therefore, it is especially important to carry out more in-depth research and analysis based on numerical simulation methods for ancient buildings and propose reasonable conservation plans.
Currently, some scholars have conducted single-factor or multi-factor coupled analyses in numerical simulation studies. For ordinary residential buildings, Hong et al. [11] used the software CFD to study the indoor wet environment and linearly fitted the factors affecting humidity and concluded that the predicted humidity distribution was in good agreement with the experiment. Teodosiu et al. [12] investigated numerical models for assessing thermal comfort and developed CFD numerical models for airflow modeling and humidity modeling of indoor air, then analyzed and demonstrated the good potential for correctly estimating the indoor environment under stable and uniform thermal conditions. In addition to the relevant research on heat and humidity transfer in residential buildings, existing literature has also investigated building types such as libraries, temples, churches, grottoes, museums, etc. Liu [13] focused on and studied the insulation technology of ancient buildings in the Amu River basin, using AIRPAK software to simulate and analyze the indoor temperature of ancient buildings and explore the effect of active heating measures. Bi et al. [14] conducted an experimental and numerical analysis of the moisture and heat transfer in the cave walls of the Mogao Caves using a comparison of simulation results with experimental temperature and relative humidity values, finding that temperature changes may lead to condensation of moisture in the air, and the application of the one-dimensional model to simulate the cave wall has limitations. Balocco et al. [15] adopted CFD software to carry out a three-dimensional transient simulation of the natural ventilation system of a historical building library in Italy and explored the operation mode of the natural ventilation system inside the building, which confirmed that the ancient building could create a good natural ventilation environment. Li et al. [16] analyzed the hygrothermal environment of the Luohan Hall of Baosheng Temple located in the southeast of China and concluded that the air temperature near the sculpture had different fluctuation modes in different directions, and the relative air humidity fluctuated violently. Cao et al. [17] used the CFD software Fluent to numerically simulate the air movement, temperature, and relative humidity of the micro-environment in the museum and concluded that the large gradient of temperature and humidity distribution was not conducive to the preservation of artifacts. In addition, some scholars have studied numerical simulations for the cultural heritage of wooden structures. Huijbregts et al. [18] conducted a two-dimensional multi-area building simulation on a wooden cabinet in a Dutch castle to study the influence of indoor climate changes on the heat and humidity of the cabinet and concluded that indoor climate conditions were controlled by humidity rather than restricted by the average water content of the room. Napp et al. [19] studied the different indoor climate control schemes of a church in Estonia via field measurement and simulation and concluded that dehumidification measures could be used to prevent mold growth and protect wood parts from cracking.
Summarizing previous research results, it is known that the wet and cold interior of buildings only takes into account the influence of outdoor climatic conditions without exploring the influence of soil moisture and wall moisture on the situation of large indoor humidity. In this paper, soil moisture and wall moisture added to the influence of indoor humidity in ancient buildings.
The object of this study is the world’s most complete surviving palace-type ancient building with a construction history of 600 years. The three-dimensional heat and moisture transfer characteristics of palace-style wooden ancient buildings in Beijing are studied. A mathematical model of indoor heat and moisture transfer is established, and the accuracy of the model is verified via comparison with simulated data using actual measurements of indoor relative humidity. The influences of outdoor humidity environment, soil moisture, and wall humidity on the indoor heat and moisture transfer characteristics of ancient buildings are analyzed. And the correlation analysis of these three factors and the main protection measures of ancient buildings are proposed. The research results provide effective theoretical guidance for the conservation of palace-style wooden ancient buildings in Beijing.
2. Indoor and Outdoor Heat and Humidity Environment Testing of Ancient Buildings
2.1. Overview of Ancient Buildings
The palace-style buildings in Beijing are one of the largest and best-preserved wooden ancient buildings in the world, which have a variety of architectural structures with more than 70 different building types [20]. In this study, a palace-style wooden ancient building in Beijing is selected as the research object. The building is located on the west side of the palace-style building complex in Beijing, which was built during the Jiajing period of the Ming Dynasty.
2.2. Outdoor Environmental Parameters
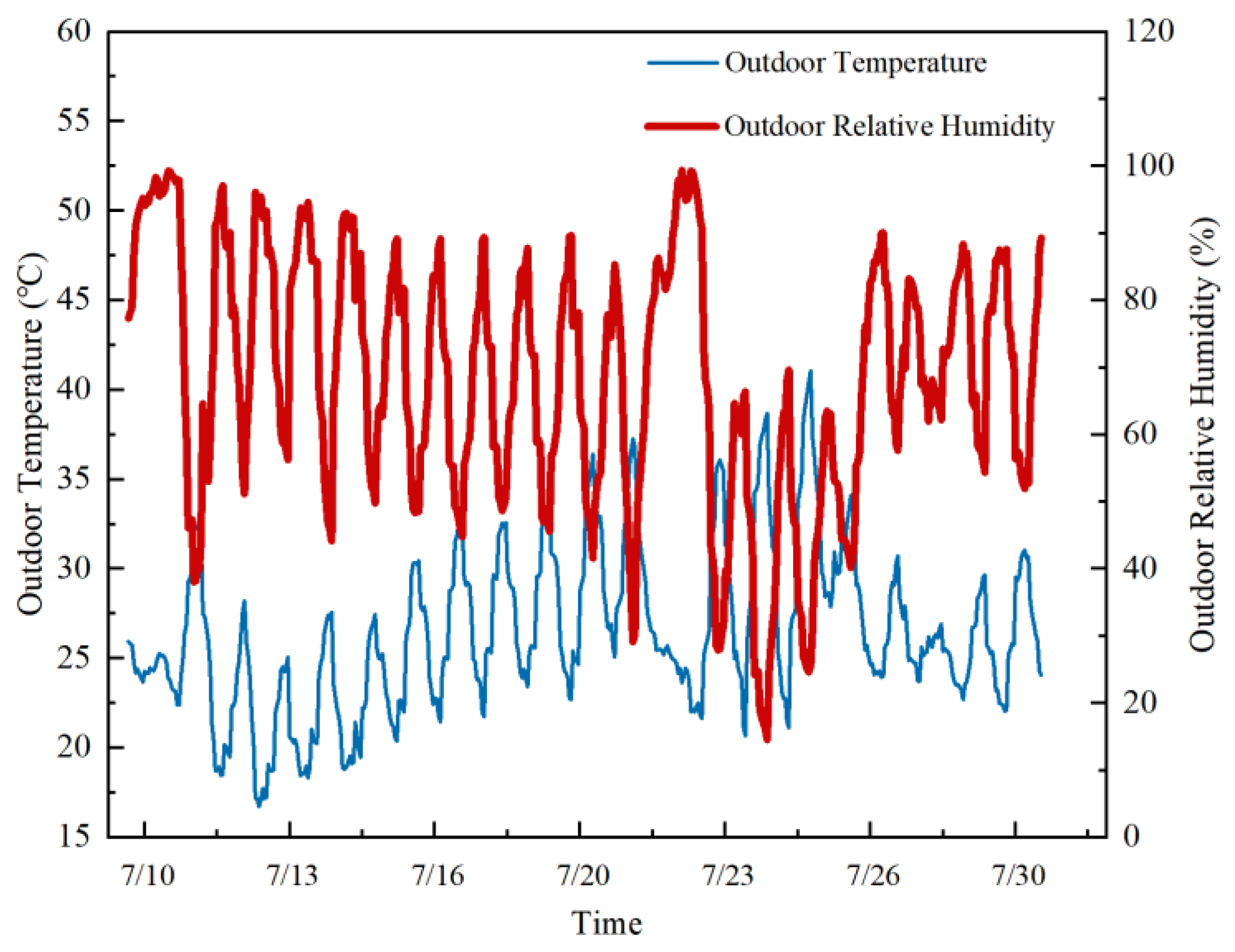
According to the data statistics of a weather station in Beijing (https://www.xihe-energy.com/, accessed on 1 January 2023), the outdoor temperature and humidity change curve of the ancient building is shown in Figure 1. Through the investigation and analysis of the environmental monitoring of ancient buildings, the relative humidity of the indoor environment of the ancient building is high in summer. The original appearance of the building is damaged by the humid indoor environment. Therefore, the outdoor ambient temperature and humidity for the July period from 2020 to 2022 were selected and averaged as the outdoor meteorological parameter of choice. The outdoor temperature is 26.3 °C, the outdoor relative humidity is 67.17%, and the atmospheric pressure is 101.35 kPa. The moisture content is 14.49 g/kg dry air, and the water vapor partial pressure is 2.3073 kPa.
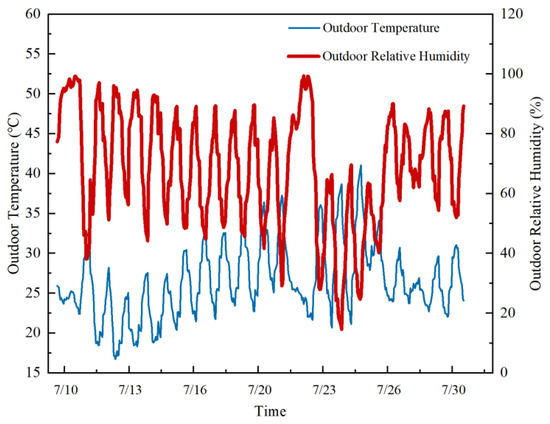
Figure 1.
Outdoor temperature and humidity change curve.
2.3. Indoor Environmental Parameters
Based on the relevant research [21], the indoor air temperature is 24.7 °C, the indoor relative humidity is 75%, the moisture content is 14.67 g/kg dry air, and the water vapor partial pressure is 2.3347 kPa. The indoor relative humidity of the interior walls is 92%, the moisture content is 18.09 g/kg dry air, and the water vapor partial pressure is 2.8639 kPa.
2.4. Indoor Flooring Parameters
Soil temperature and humidity can have an impact on the coupled heat and moisture transfer [22]. The ground temperature is set at 23.3 °C, and the water absorption rate of ancient grey bricks generally ranges from 14% to 25% [23], so the water absorption rate of grey bricks is set at 14% in this work. Beijing, located in the North China Plain, is sandy soil. According to relevant studies [21,24], the soil volumetric moisture content of ancient buildings in the area is 0.09 m3/m3. The field capacity of sandy soils in the North China Plain is 10–14%. The soil bulk density value of this study is selected from the Second National Soil Survey of China (SNSSC), and the reference value is 0.95 g/cm3. The conversion relationship between the soil’s relative humidity and the soil’s volumetric water content is expressed as follows [25]:
where is the soil’s volumetric water content, m3/m3; R is the soil’s relative humidity, %; is the soil’s field capacity (taken as 10%); and is the soil’s bulk density, kg/m3.
Consequently, it is calculated that the soil’s relative humidity of the indoor building ground is 81.5%, the moisture content is 15.97 g/kg dry air, and the water vapor partial pressure is 2.5371 kPa.
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Physical Model
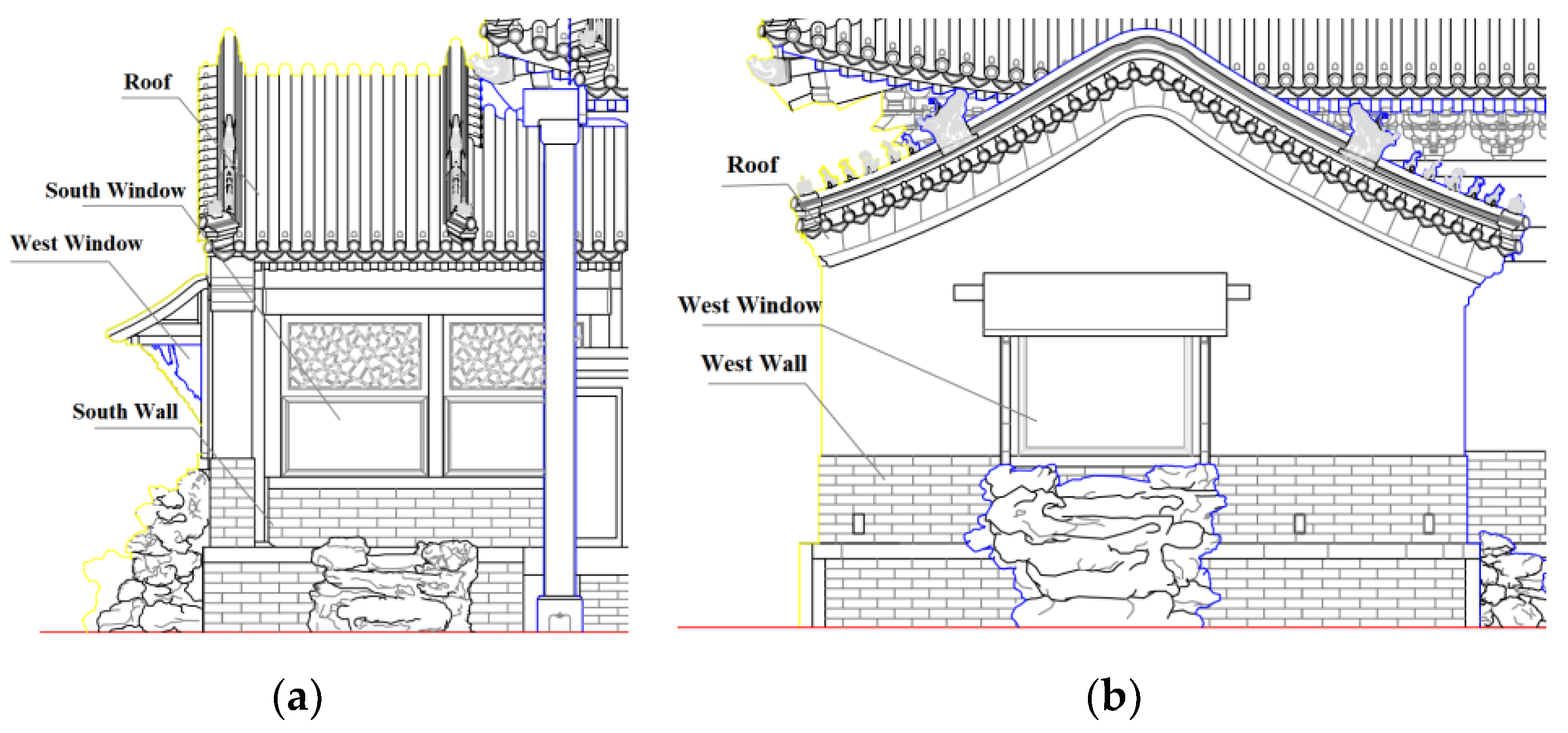
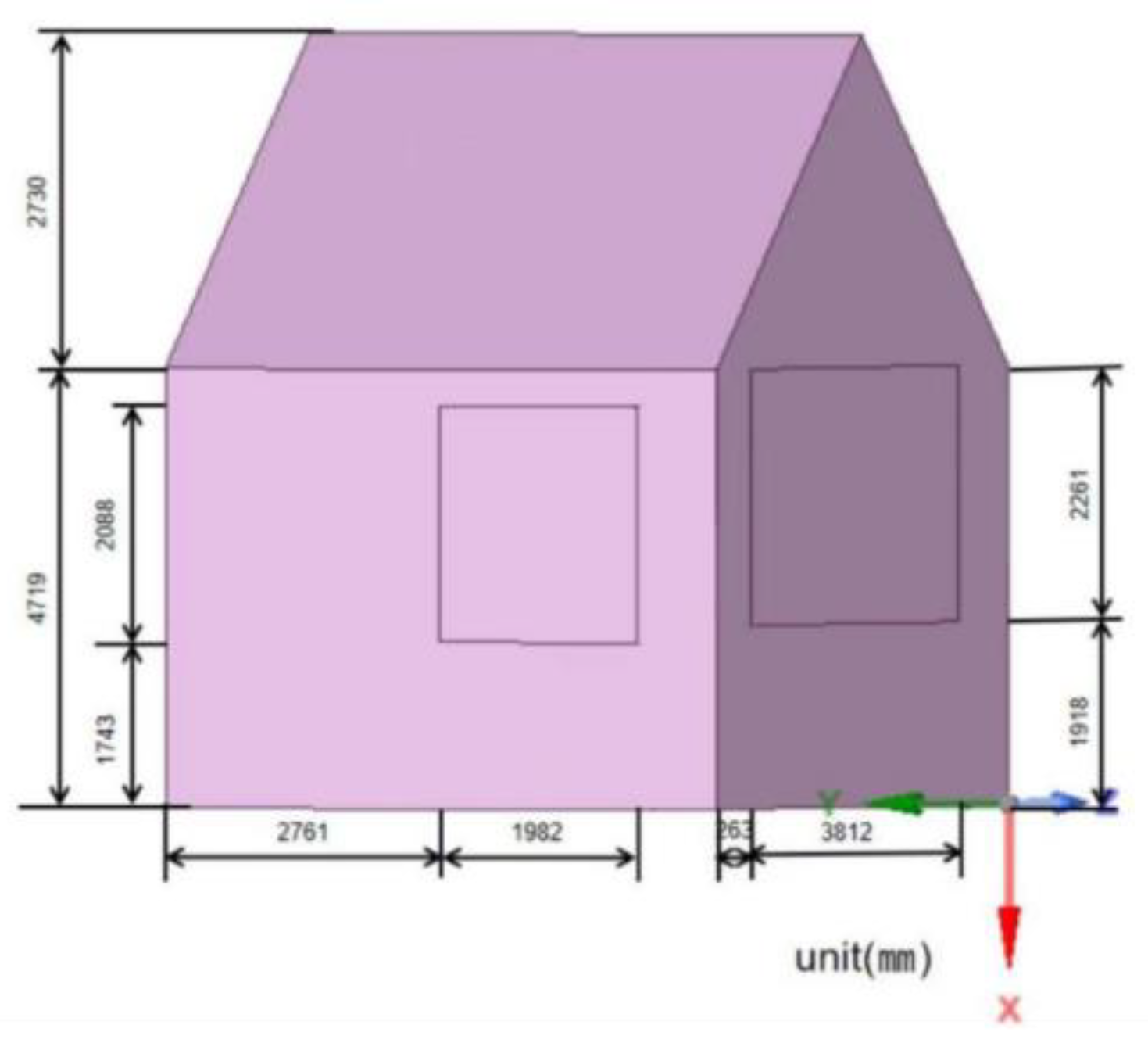
The physical graphic of the ancient building is shown in Figure 2. The main area of the ancient building is 26.63 m2, and the height of the hard roof is 2.73 m. Its building envelope structure mainly includes a roof, walls, doors and windows, and indoor floors composed of a variety of building structures and components of different materials. The specific structure and its adjustment effect on the environment are shown in Table 1. Table 2 shows the dimensions of the ancient building envelope.
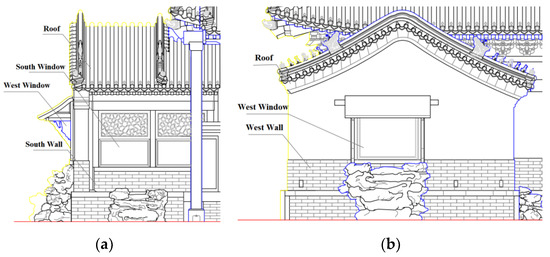
Figure 2.
Elevation of a palace-style wooden ancient building in Beijing: (a) south elevation and (b) west elevation.

Table 1.
Composition and role of the ancient architecture building envelope.

Table 2.
Envelope-sized building table.
In the room, the release of water vapor comes mainly from the ground and walls, and water vapor can be used as a medium between the two. Due to differences in indoor and outdoor pressure and no mechanical equipment, the air is only penetrated by opening the window, and the density of air in and out is small. The wet environment near the window is close to the wet outdoor environment, and the wet air in the room penetrates the outdoors through the window.
After simplifying the physical graphic, the building structure of the physical model is shown in Figure 3.
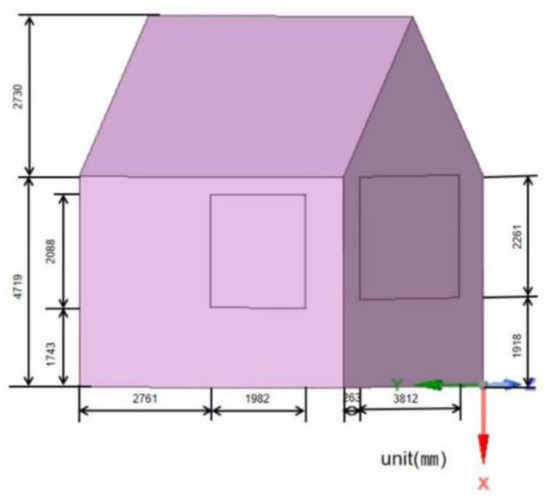
Figure 3.
Structure of a palace-style wooden ancient building in Beijing.
3.2. Mathematical Model
3.2.1. Basic Assumptions
In this study, the ground and wall are set as the wet source, and the effects of ground soil moisture and wall moisture on the relative humidity inside the room are simulated, respectively. To simplify the simulation, the actual physical process is assumed as follows:
- (1)
- The soil and the wall are wet sources;
- (2)
- The ground and the wall are the water vapor flow inlet, and the two windows are the gas outlets;
- (3)
- The building interior is natural convection, and the indoor airflow is a low-speed flow, which is regarded as an incompressible fluid [26], and satisfies the ideal gas equation of state;
- (4)
- The water vapor mass fraction of the windows is set as the outdoor water vapor mass fraction.
3.2.2. Governing Equations
Based on the physical model and basic assumptions, the governing equations in this paper are outlined as follows.
Continuity equation:
Momentum equation:
Energy equation:
The ideal gas equation of state:
where is the fluid density, g/cm3; is the specific heat capacity of fluid, ;
λ is the thermal conductivity; ) and U are the velocity vectors; T is the thermodynamic temperature; K. is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid; m2/s and ST are the viscous dissipation terms.
Due to the existence of the moat, the ground dissipates moisture. The windows of ancient buildings are made of wooden materials, which have poor sealing performance, resulting in a pressure difference between indoors and outdoors, causing some moisture to dissipate and diffuse from the outside to the inside. Therefore, in the simulation procedure, it is considered that the airflow in the ancient building blows upwards from the ground. The standard model is used for simulation analysis [27]. In the near wall region, the flow state is laminar and has a low Reynolds number, with a ground average Reynolds number of 1.2109, which is processed using the wall function method.
The floor and walls are made of grey bricks. The thermal conductivity of grey brick is 0.265 . The water vapor diffusion coefficient is . The heat flux of the building envelope and the parameters of the indoor environment are shown in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Heat flux values of the building envelope.

Table 4.
Indoor environmental parameters table.
3.3. Grid Partitioning and Irrelevance Verification
3.3.1. Grid Division
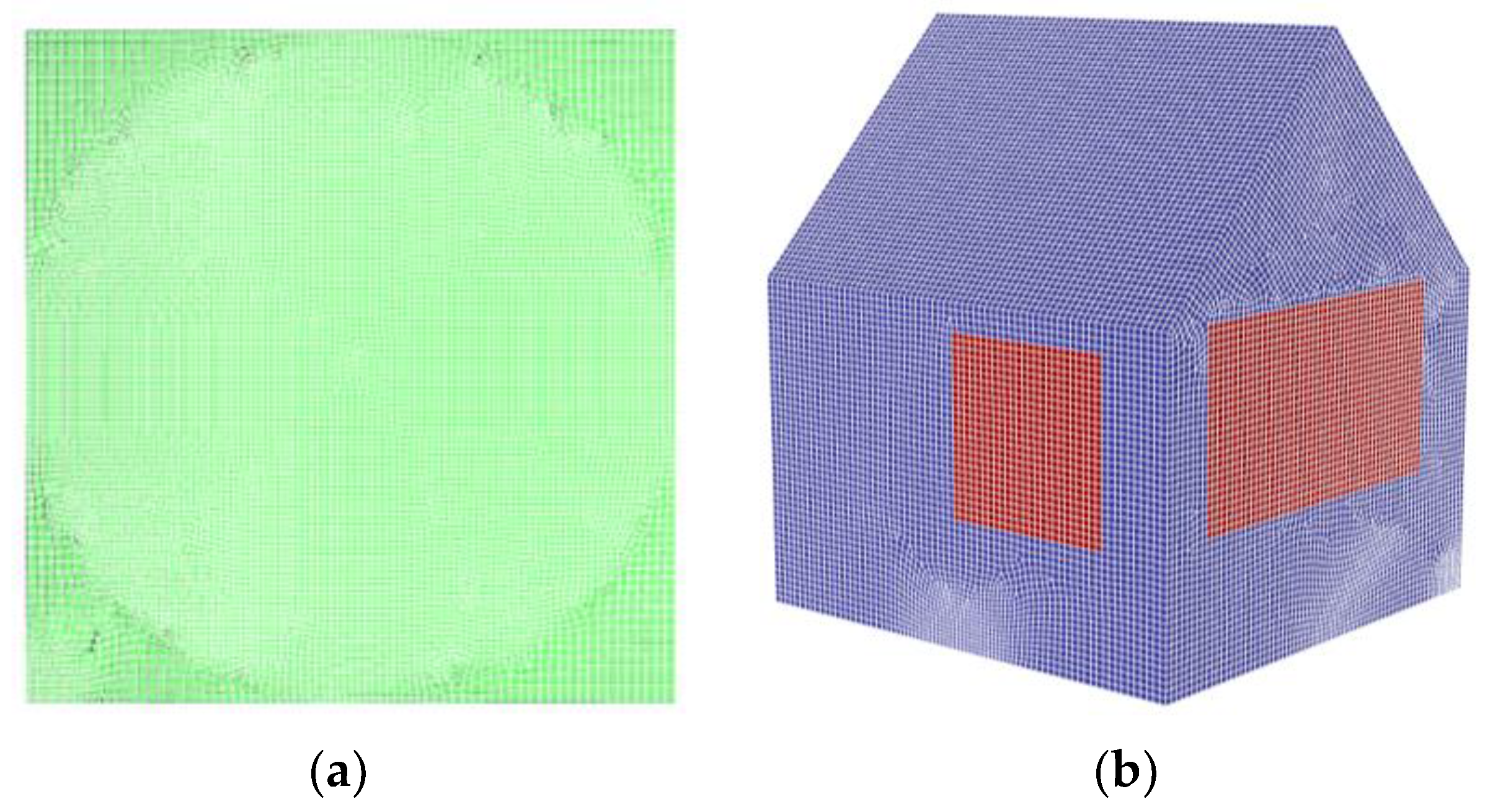
Grid generation is very important in CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulations, which seriously affects the accuracy of CFD simulations by the quality of the generated grid [17]. In this work, a combination of tetrahedral and hexahedral grid types is used to mesh the building. Due to the high accuracy and quality of structural grids, a combination of tetrahedral and hexahedral grids is chosen as the structural grid. The length (X) of the computational region is 6.816 m, the width (Y) is 5.554 m, and the height (Z) is 5.366 m. The number of grids in the X-direction is 97, the number of grids in the Y-direction is 79, and the number of grids in the Z-direction is 77. The average value of this grid quality is 0.77, the grid cell size is 0.07 m, and the number of grids is 1,085,324. At the same time, boundary conditions and local encryption were used. The grids of the ground and the south corner of the palace-style building were encrypted, and the number of grids after encryption is 3,307,497. The results of local encryption are shown in Figure 4a. The results of grid division are shown in Figure 4b.
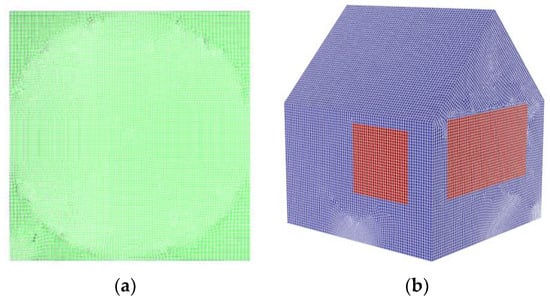
Figure 4.
Grid division of a palace-style ancient building model in Beijing: (a) local encrypted grid division and (b) overall meshing diagram.
3.3.2. Grid Independence Verification
To ensure the accuracy of the calculation results, the generated grids are verified for independence [26]. The following grids all converge monotonically, which are presented in Table 5. Comparing the data in Table 5, the grid independence verification is performed with the value of the average relative humidity on the ground as the reference variable. Grade 3 is closer to grade 1 than the other grades in terms of average relative humidity. In addition, the calculation time of grade 3 is much less than that of grade 1, which can reduce the calculation time to a certain extent. Therefore, grade 3 is selected for the simulation study in this work. At this time, the number of grids is about 1.08 million, the grid cell size is 0.07 m, and the grid quality is good, which can meet the requirements of calculation accuracy.

Table 5.
Data statistics of mesh verification.
3.4. Initial Working Conditions
The outdoor relative humidity range is 45.45% to 87.89%.
The range of relative humidity is simulated by changing the water vapor mass fraction, with a gradient of 0.02%. The effects of ground soil relative humidity, outdoor ambient temperature, and wall relative humidity on indoor relative humidity are investigated. The boundary conditions are set as follows:
- (1)
- The west window and south window are set as the pressure outlets. The outdoor humidity is 67.17%, and the water vapor mass fraction is 0.0142%.
- (2)
- The ground and wall are set as the mass flow inlet, and the mass flow rate is 0.3 m/s.
- (3)
- The wall temperature is set to 26.3 °C, and the ground temperature is 23.3 °C. The water vapor mass fraction of ground and wall are 0.0145% and 0.0167%.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Mathematical Model Accuracy Verification
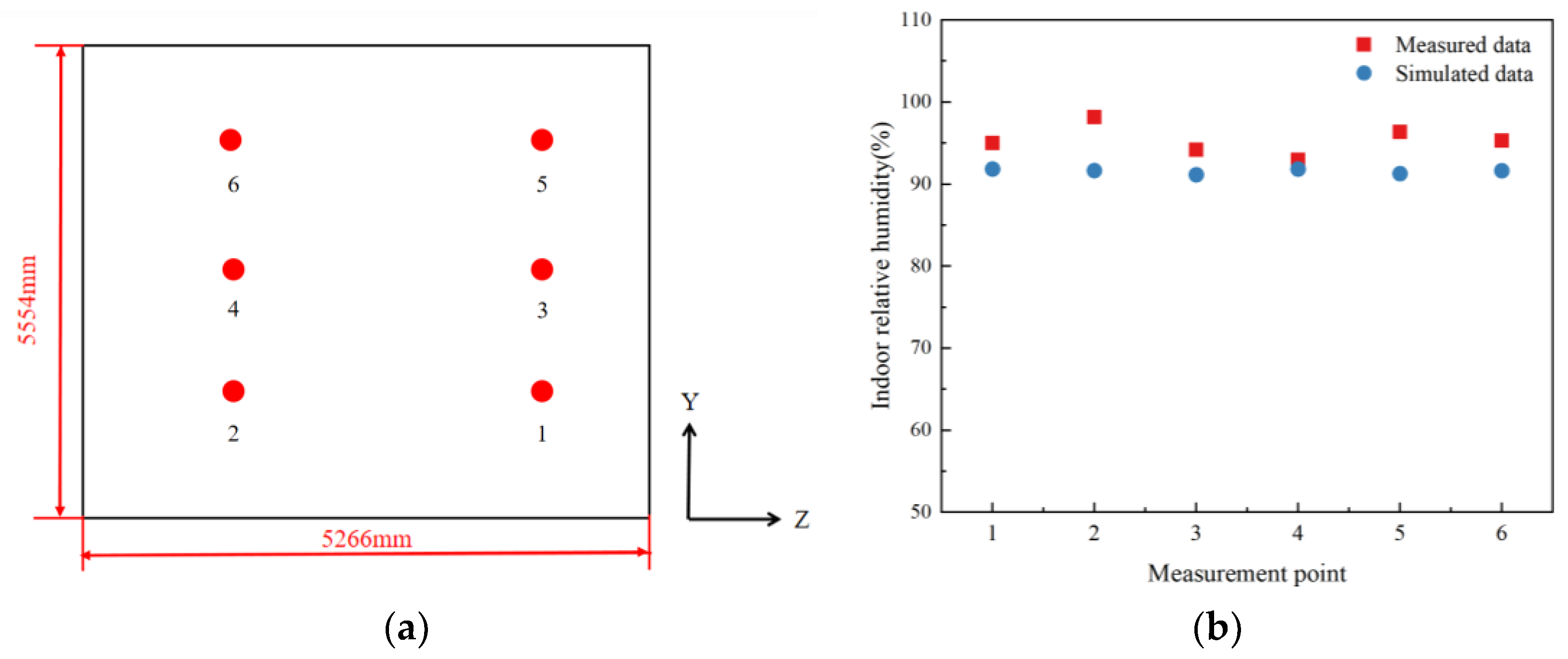
According to the relevant standards [28], the indoor area is less than 30 m2, the measurement points should be placed on a plane of (1.3 ± 0.1) m height, and the humidity measurement points should be no less than three. In this paper, six relative humidity measurement points are set up, and the measurement points are indicated by the numbers 1–6. The locations of the indoor relative humidity measurement points are shown in Figure 5a, and the coordinates of the measurement points are 1 (−1.2 m, −1.6 m, −1.5 m), 2 (−1.2 m, −3.2 m, −1.5 m), 3 (−1.2 m, −1.6 m, −3 m), 4 (−1.2 m, −3.2 m, −3 m), 5 (−1.2 m, −1.6 m, −4.5 m), and 6 (−1.2 m, −1.6 m, −4.5 m). At this point, multiple measurements are taken at each measurement point on a particular day in summer, and the average is taken as the actual indoor RH data. The model’s accuracy is verified by simulating relative humidity at each measurement point. A comparison graph of measured and simulated data is shown in Figure 5b.
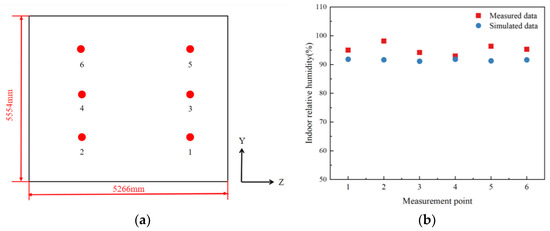
Figure 5.
Location of measurement points and data map. (a) Location of indoor relative humidity measurement points and (b) comparison chart of measured and simulated data.
As seen from Figure 5b, the measured and simulated interior average relative humidity at each measurement point ranged from 90% to 100%. Clearly, the relative humidity is large. The maximum relative error between measured and simulated data was calculated to be 6%, and the minimum relative error was 1.2%. The results show that the data from the simulation are consistent with the measured data. The accuracy of the simulation results is verified based on the comparison of the measured and simulated data.
4.2. The Indoor Temperature and Humidity Distribution in Initial Working Conditions
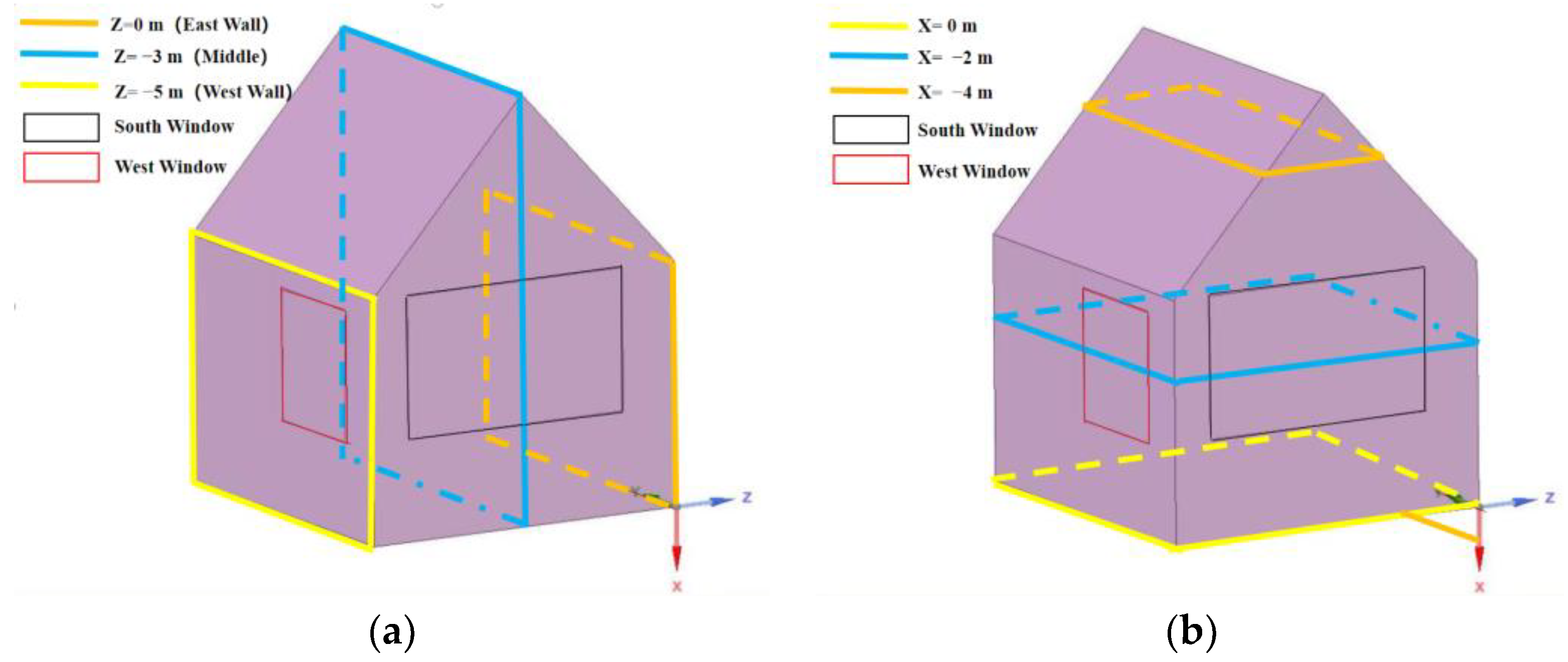
In this work, under the initial working conditions of ancient buildings (outdoor temperature of 26.3 °C and outdoor relative humidity of 67.17%), the indoor temperature and humidity distribution of ancient buildings are simulated. For the purpose of the following analysis, detailed cross-sections in the horizontal and vertical directions are shown in Figure 6 below.
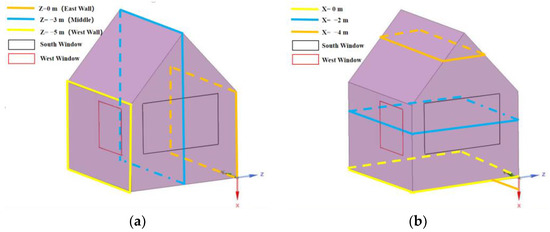
Figure 6.
Cross-sectional view in different directions. (a) Cross-section in the vertical direction and (b) cross-section in the horizontal direction.
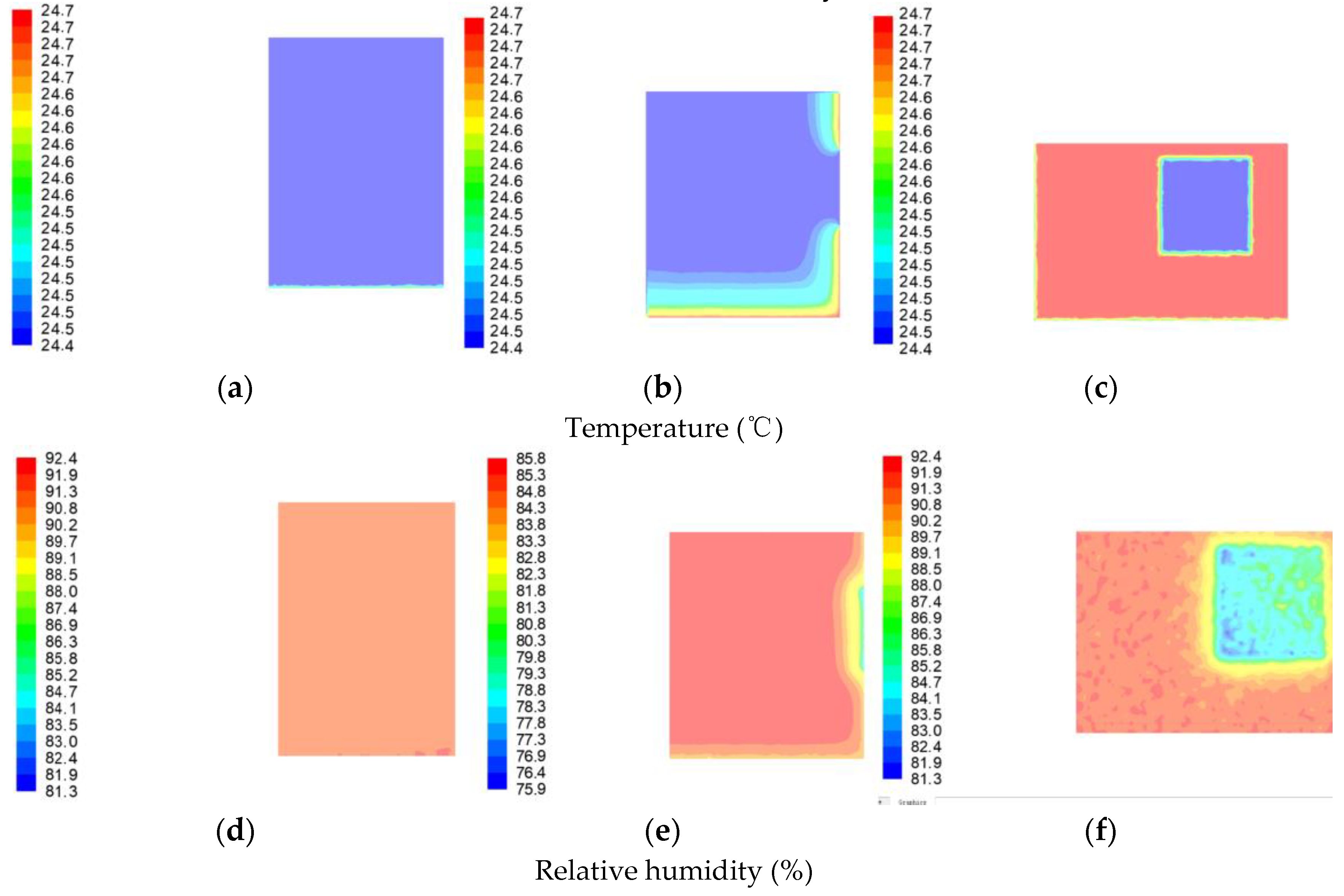
The distribution of temperature and relative humidity at Z = 0 m, Z = −3 m, and Z = −5 m in the vertical direction are shown in Figure 7, respectively. As seen in Figure 7a,d, the temperature and relative humidity distribution at Z = 0 m (east wall) remain essentially constant. This is due to the fact that there are no windows in the east wall, and there is no heat dissipation to dissipate humidity. However, there are smaller temperature and humidity fluctuations at ground level. This is due to the fact that the wall root zone is less exposed to sunlight, which causes its humidity to rise slightly. The temperature was around 24.5 °C, and the relative humidity was 90.2%.
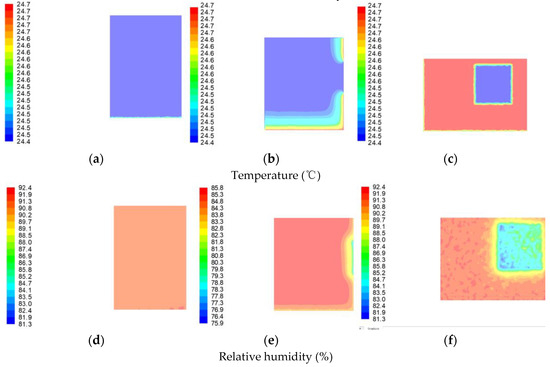
Figure 7.
Indoor temperature and relative humidity distribution in the vertical direction. (a) Indoor temperature distribution at Z = 0 m, (b) indoor temperature distribution at Z = −3 m, (c) indoor temperature distribution at Z = −5 m, (d) indoor relative humidity distribution at Z = 0 m in the vertical direction, (e) indoor relative humidity distribution at Z = −3 m, and (f) indoor relative humidity distribution at Z = −5 m.
As shown in Figure 7b,e, the temperature and relative humidity in the middle part of the room remain more or less constant at Z = −3 m. The temperature is 24.5 °C, and the relative humidity is about 84.3%, mainly due to its more even distribution of moisture content. Fluctuations in temperature and humidity occur on the lower side (floor) and the right side (around the south window). The relative humidity is lower near walls and the ground than inside, mainly because sunlight in summer and poor heat storage capacity of windows can make the part near windows and walls warmer than inside and contain less moisture.
As shown in Figure 7c,f, at Z = −5 m (west wall), fluctuations in temperature and humidity occur mainly in the west window. The temperature and relative humidity at the west window are lower than at the same vertical plane, and the temperature and relative humidity gradually increase from the middle of the window to the surrounding area. This is due to the fact that the windows are wooden and will have gaps, resulting in infiltration and moisture dispersion, resulting in low moisture content. The overall temperature is at 24.4 °C–24.7 °C, and the relative humidity is at 75.9–85.8%.
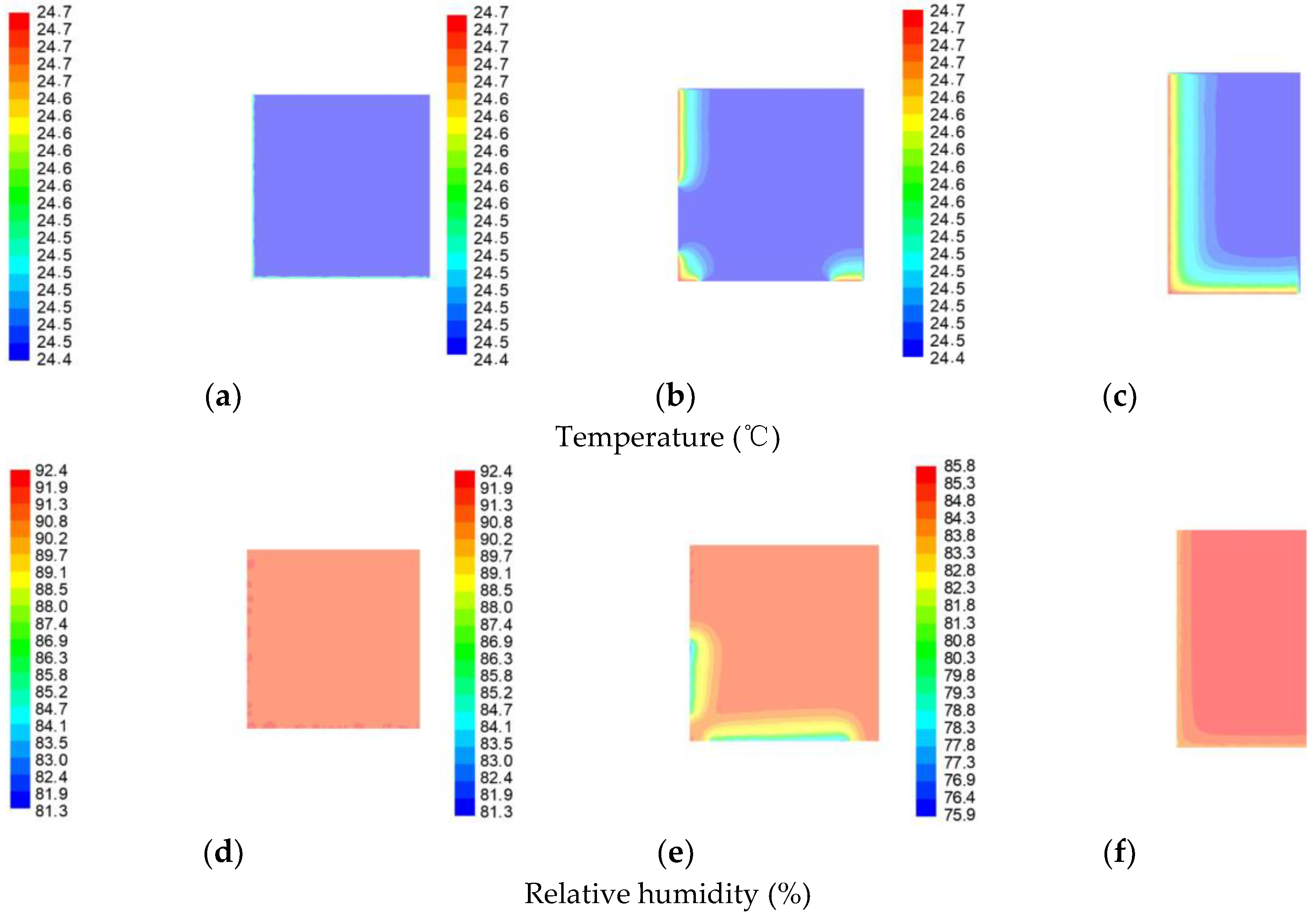
The distribution of temperature and relative humidity in the horizontal direction at X = 0 m, X = −2 m, and X = −4 m are shown in Figure 8, respectively. Analysis of Figure 8a–c above shows that the room temperature is maintained at 23.3 °C and remains the same. From Figure 8d, it can be seen that the relative humidity of the ground remains unchanged at 91.7%. This is mainly due to the presence of a moat on the ground, which makes its moisture content evenly distributed. From Figure 8e, it can be seen that the relative humidity values of the south and west windows are larger than those of the rest of the plane, which is due to the infiltration effect of the windows that makes their humidity greater. From Figure 8f, it can be seen that the relative humidity on the roof remains constant, and the indoor relative humidity value is higher.
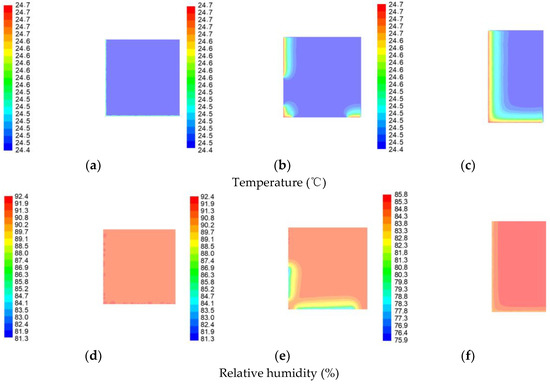
Figure 8.
Indoor temperature and humidity distribution in the horizontal direction. (a) Indoor temperature distribution at X = 0 m, (b) indoor temperature distribution at X = −2 m, (c) indoor temperature distribution at X = −4 m, (d) indoor relative humidity distribution at X = 0 m in the vertical direction, (e) indoor relative humidity distribution at X = −2 m, and (f) indoor relative humidity distribution at X = −4 m.
The comprehensive analysis reveals that the indoor average temperature is 24.5 °C, and the indoor relative humidity range is between 87.4% and 92.4%. Overall, the temperature fluctuations in the interior of the ancient building are small, while the relative humidity fluctuates widely. Therefore, the following section focuses on the effect of each factor on indoor humidity. The control variate method is taken to investigate changes in humidity.
4.3. Effect of Outdoor Humidity on Indoor Moisture Transfer
The humidity of the soil and walls is set as the initial state. With the difference in outdoor humidity, the indoor humidity is shown in Figure 9a,b. Due to the ancient age of this historic building, outdoor air enters the interior through windows, which are made of a paper material and have a significant degree of damage. Thus, the outdoor humid environment is an important factor affecting the indoor humidity of ancient buildings.
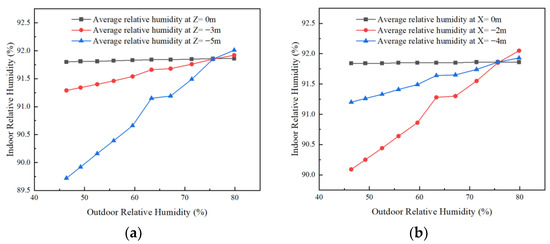
Figure 9.
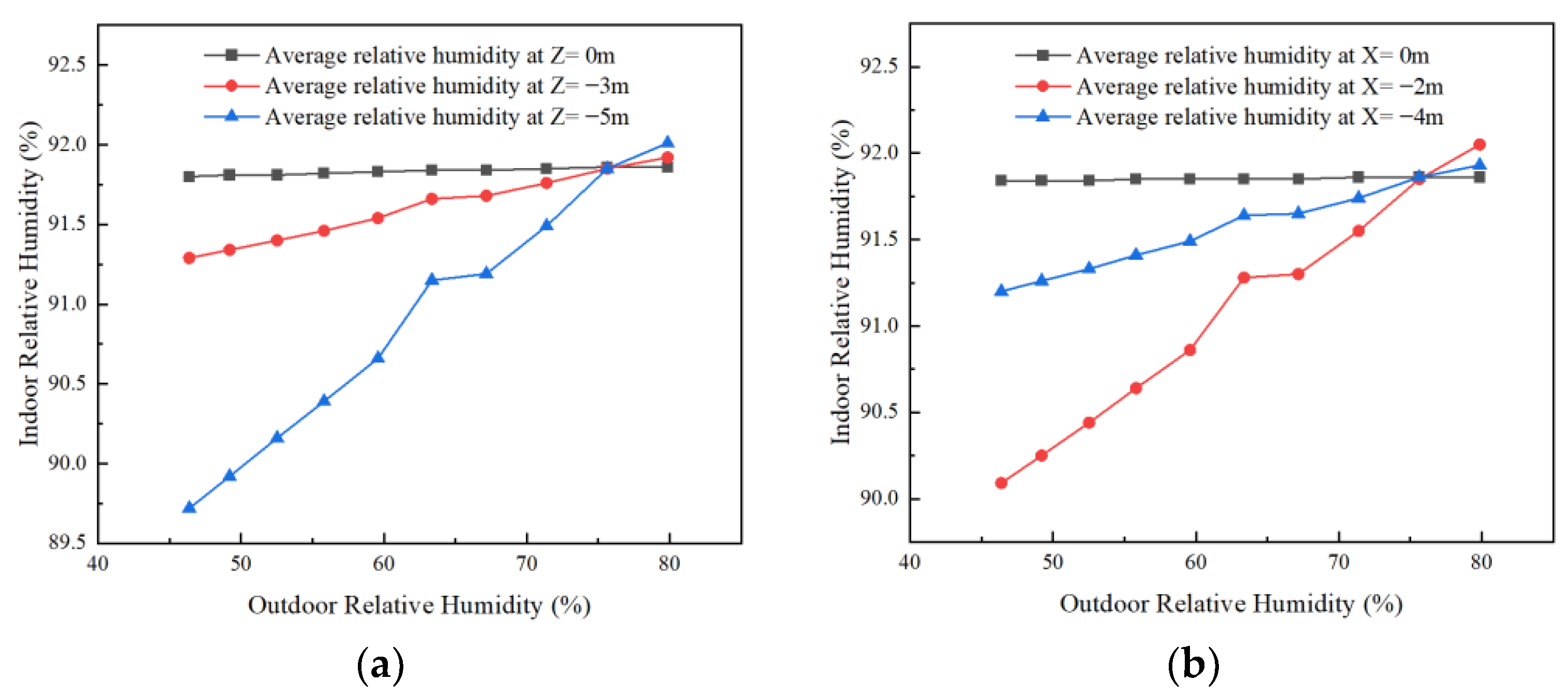
Effect of outdoor humidity on the humidity in the horizontal and vertical direction of the room. (a) Trends in the effect of outdoor ambient relative humidity on average relative humidity in the vertical direction inside the room and (b) trends in the effect of outdoor ambient relative humidity on average relative humidity in the horizontal direction of the room.
As seen from Figure 9a, under a given outdoor humidity, the indoor relative humidity is observed to change in the vertical direction from east to west (Z = 0 m to Z = −5 m). When the outdoor humidity is less than 75.6%, the average indoor relative humidity shows a trend of gradual decrease. And when the outdoor humidity is greater than 75.6%, the average indoor relative humidity shows a gradually increasing trend. When located in the same vertical plane, with the increase in outdoor humidity, the average indoor relative humidity increases significantly at Z = −5 m. At Z = −3 m, the trend of the average indoor relative humidity increases more slowly than that at Z = −5 m. At Z = 0 m, the average indoor relative humidity remains unchanged.
As seen from Figure 9b, under a given outdoor humidity, the change in indoor relative humidity in the horizontal direction from the ground to the roof (X = 0 m to X = −4 m) is observed. When the outdoor humidity is less than 75.6%, the average indoor relative humidity shows a trend of first decreasing and then gradually increasing, and the change in decreasing is larger. At outdoor humidity greater than 75.6%, the average indoor relative humidity showed a trend of first increasing and then gradually decreasing. Therefore, it was concluded that the average relative humidity at ground level was the highest. When located in the same horizontal plane, with the increase in outdoor humidity, the average indoor relative humidity is the highest and remains the same at X = 0 m. At X = −2 m, the average indoor relative humidity increases significantly. At X = −4 m, the average indoor relative humidity shows a slowly increasing trend.
4.4. Effect of Soil Moisture on Moisture Transfer
Xu et al. [22] carried out experiments on the effect of coupled heat and moisture transfer on soil heat storage systems and confirmed that ignoring moisture migration and temperature dependence of soil thermal conductivity would lead to a low predicted value of the numerical model, and the influence of initial soil moisture on coupled heat and moisture transfer should be considered. In this paper, the influence of soil moisture on the humidity in different directions in the room was simulated by changing the mass fraction of groundwater vapor (soil moisture).
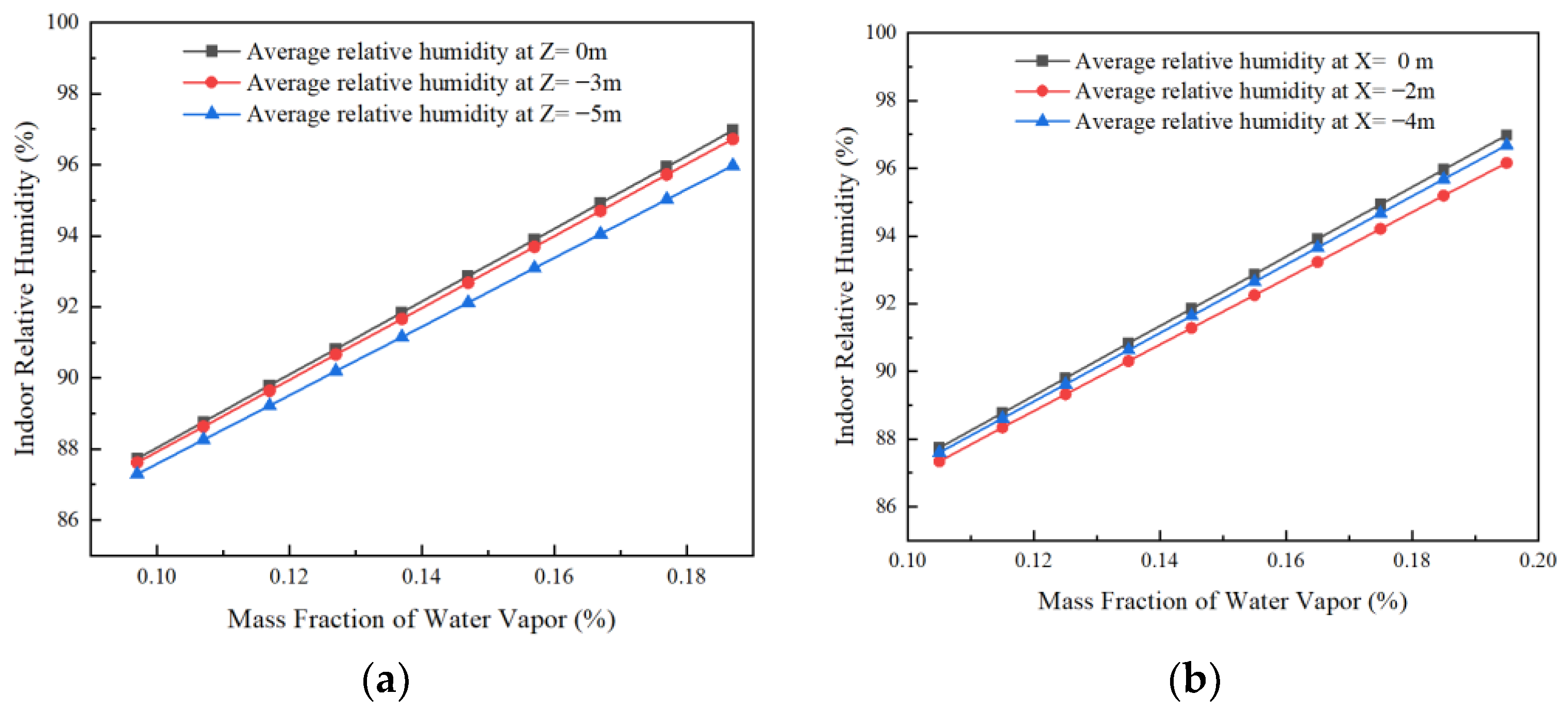
As seen from Figure 10a, under a given soil moisture, changes in indoor relative humidity in the vertical direction from east to west (Z = 0 m to Z = −5 m) are observed. The average indoor relative humidity decreases gradually, but the decrease is small. When located in the same vertical plane, the average indoor relative humidity gradually increased with the increase in soil moisture, and the trend of the increase was almost the same on each plane.
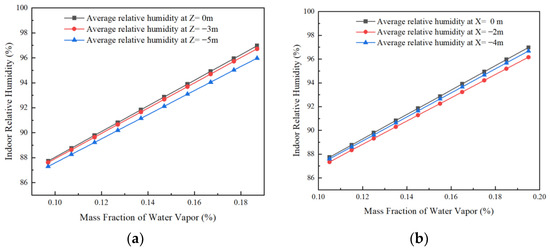
Figure 10.
Effect of soil moisture on the humidity in the horizontal and vertical direction of the room. (a) Trends in the effect of soil moisture on average relative humidity in the vertical direction inside the room and (b) trends in the effect of soil moisture on average relative humidity in the horizontal direction of the room.
As seen from Figure 10b, under a given soil moisture, the average indoor temperature shows a first decreasing and then increasing trend when observing the change in indoor temperature and humidity in the horizontal direction from ground to roof (X = 0 m to X = −4 m), but the change is smaller. When located in the same horizontal plane, the average indoor relative humidity increases gradually with the increase in soil humidity.
4.5. Effect of Wall Moisture on Indoor Humidity Transfer
Over time, the porosity of the ancient building envelope will become larger, and its moisture storage capacity will also be enhanced. In addition, excessive humidity in the building envelope can lead to damage to building materials and mold growth [29]. It is also a factor that produces wall mold, as it migrates into the indoor environment. Therefore, the influence of wall humidity on the humidity in different directions of the room was simulated by changing the water vapor mass fraction (changing wall moisture) of the wall.
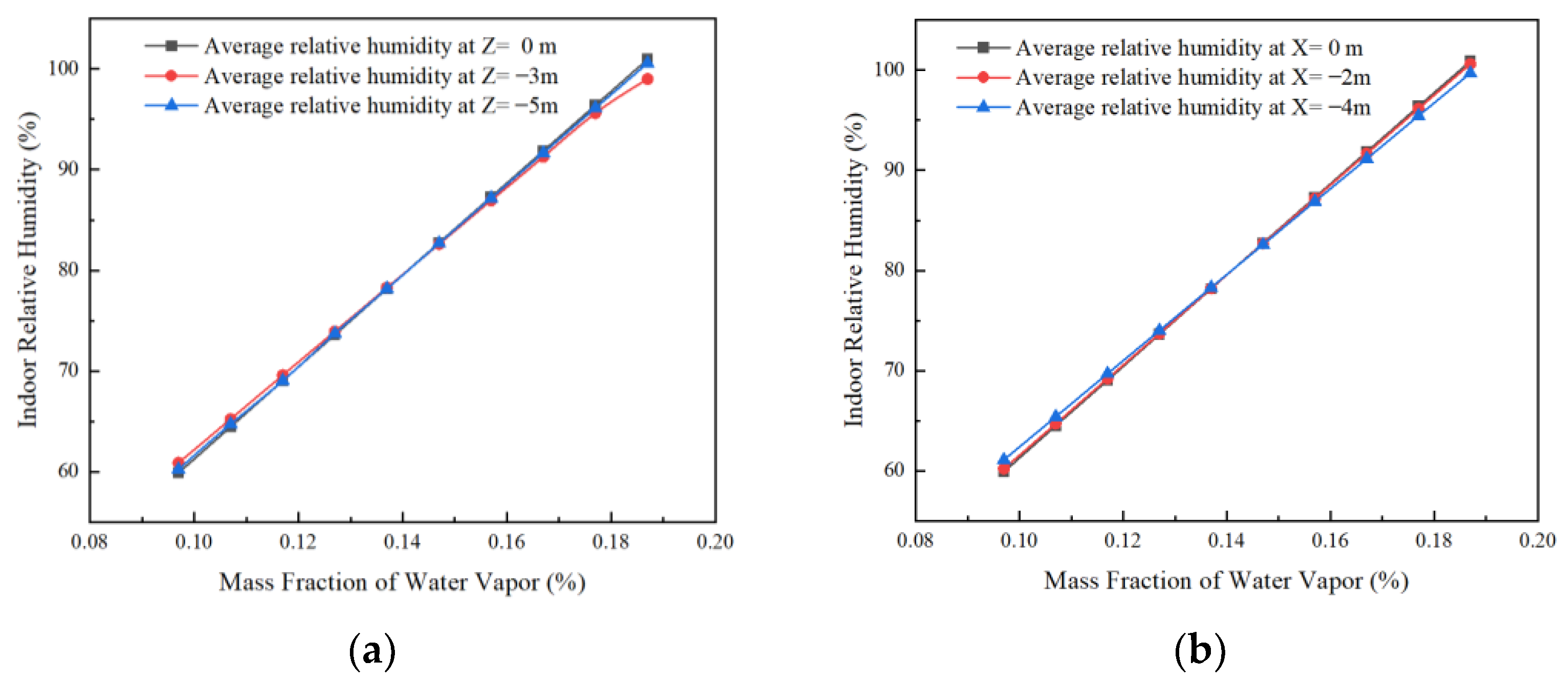
As seen from Figure 11a, the indoor relative humidity values on different planes are the same, so the relative humidity of the whole room can be analyzed by the above figure. From Figure 11a,b, it can be seen that as the humidity of the walls increases, the relative humidity in the room also gradually increases. This is due to the moisture transfer from the walls, which makes the humidity in the room also increase gradually.
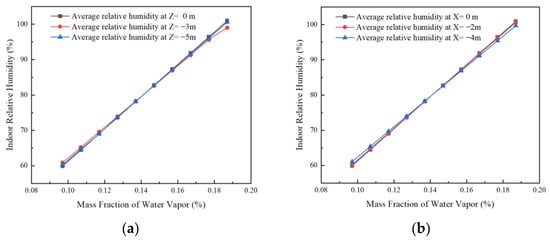
Figure 11.
Effect of wall humidity on the average humidity in the horizontal and vertical direction of the room. (a) Trends in the effect of wall humidity on average relative humidity in the vertical direction inside the room and (b) trends in the effect of wall humidity on average relative humidity in the horizontal direction of the room.
From the analysis of indoor relative humidity law in 4.4 and 4.5, it can be seen that when the ground or wall water vapor mass fraction decreases (ground soil or wall moisture decreases), the average indoor relative humidity decreases when the conditions of building protection and maintaining the original appearance of the building can be met. Therefore, the relative humidity of the indoor environment can be reduced by lowering the ground soil moisture or wall moisture.
4.6. The Sensitivity of Factors
While the effect patterns of outdoor environmental humidity, soil moisture, and wall humidity on indoor relative humidity have been obtained via simulation, the sensitivity of each factor requires correlation analysis that takes statistical methods [30], with indoor relative humidity as the target (significant test level of 0.01). Outdoor ambient relative humidity, soil moisture, and wall moisture are set as the reference series and the indoor ambient relative humidity is set as the comparison series , respectively. Based on the existing correlation empirical equations [31,32], the calculation steps for correlation analysis are as follows.
Relation coefficient:
where is the resolution factor, which usually takes the value of 0.5.
Correlation degree:
From Table 6, it can be seen that the correlation between outdoor ambient humidity to indoor relative humidity is weak; while the correlation between soil humidity and wall humidity to indoor relative humidity is strong, and the correlation between wall and indoor relative humidity is lower than that of soil by 0.002. This paper mainly focuses on the problem of wet building floors and high indoor relative humidity. Therefore, it can be concluded that soil moisture and wall moisture are the main factors affecting indoor relative humidity.

Table 6.
Correlation analysis result.
4.7. Indoor Temperature and Humidity Distribution after Moisture-Proof Treatment
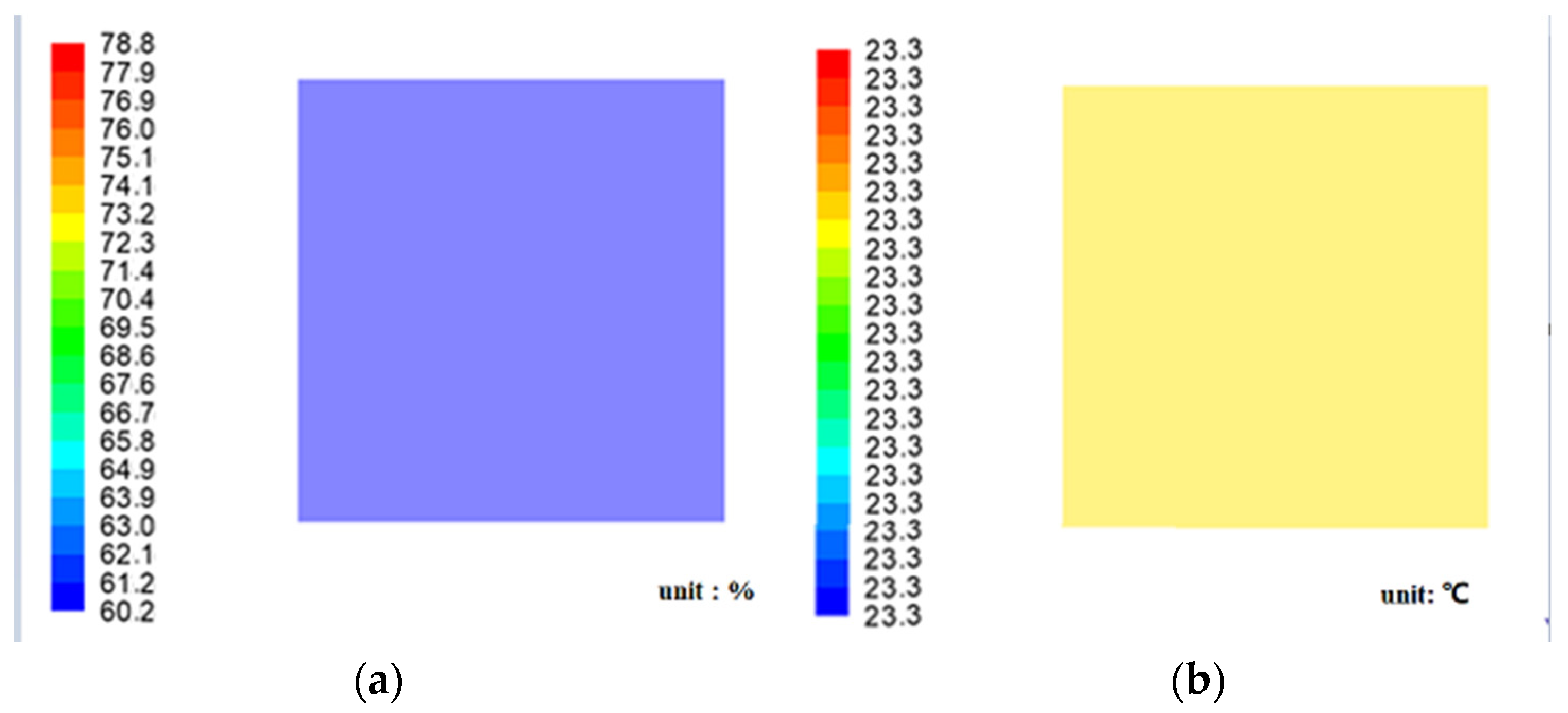
According to related studies [33,34,35], antimicrobial and hydrophobic coatings can be used to reduce room humidity by coating and protecting moldy areas of bricks without affecting the appearance of ancient buildings, such as SiO2-TiO2 hybrid fluorinated B-72, lime putty mortar (ASPL and ASPL/PP series), etc. This coating has better resistance to acid, alkali, salt, and UV light as well as the inhibition of damp proofing. Ground and walls are as examples of wet sources, obtained from Figure 12. When the water vapor mass fraction is 0.0105% (ground soil relative humidity of 59.02%) and the wall water vapor mass fraction is 0.0107% (wall relative humidity of 60%), the relative humidity of the ancient building interior is 60.2% to 78.8%, in line with the requirements of indoor relative humidity under summer working conditions. Indoor ground temperature and humidity distribution are shown in Figure 12, and the temperature at the ground is 23.3 °C, with an average relative humidity of 60.32%. As seen in Figure 12a, after the damp-proofing treatment, the relative humidity of the ancient building interior was reduced from 90.9% to 94.0% to 60.2% to 78.8%, and the relative humidity decreased and met the requirements of indoor relative humidity under summer working conditions.
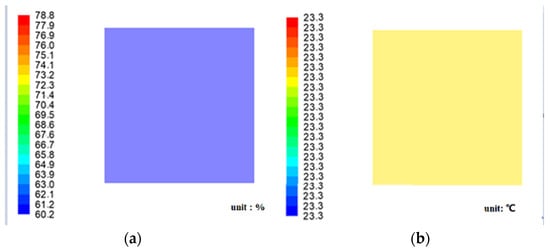
Figure 12.
Indoor ground temperature and humidity distribution picture: (a) Relative humidity distribution at ground level and (b) temperature distribution at ground level.
5. Conclusions
To solve the problem of mold growth causing damage to the architectural style of an ancient palace in Beijing, a simulation study of indoor heat and humidity transfer characteristics of ancient buildings was carried out via an ANSYS numerical simulation research method. The results of the parameters affecting the indoor humidity and the proposed protective measures were obtained as follows.
- (1)
- In the initial state, the overall room temperature varied between 24.4 °C and 24.7 °C, and the relative humidity fluctuated between 87.4% and 92.4%, with high relative humidity.
- (2)
- The indoor relative humidity changes with the outdoor relative humidity and increases with the increase in soil moisture and wall moisture.
- (3)
- Soil moisture and wall moisture are the main factors affecting the change in indoor relative humidity.
- (4)
- By adding hydrophobic coatings to the floor and walls, the room temperature was 23.3 °C, and the relative humidity ranged from 60.2% to 78.8%, which had the effect of reducing humidity.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to this paper. Conceptualization, F.L. and X.Z.; methodology, writing—original draft preparation, resources, supervision, F.L.; software, J.Z.; validation, X.Z. and J.Z.; formal analysis, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, supervision, F.L.; writing—review and editing, G.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
We also would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions that lead to a substantially improved manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wei, K.; Yang, W.Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, K.; Sun, J.Z.; Sun, X.K.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.Q.; Qiu, B.; Wang, W.; et al. The color change analysis of historic wooden remains after fire-suppression by fluorinated chemical gases. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.H. 3D Reconstruction and Intelligent Digital Conservation of Ancient Buildings Based on Laser Point Cloud Data. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7182018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubeis, T.D.; Nardi, I.; Muttilloa, M.; Paoletti, D. The restoration of severely damaged churche-Implications and opportunities on cultural heritage conservation, thermal comfort and energy efficiency. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosuosso, P. A satisfaction-based model for risk indexing in cultural heritage conservation. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 57, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fico, D.; Rizzo, D.; Casciaro, R.; Corcione, C.E. Historically Accurate Reconstruction of the Materials and Conservation Technologies Used on the Facades of the Artistic Buildings in Lecce (Apulia, Italy). Materials 2022, 15, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Sheng, G.H. Experimental and Numerical Simulation Analyses of Flame Spread Behaviour over Wood Treated with Flame Retardant in Ancient Buildings of Fuling Mausoleum, China. Fire. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, C.P.; Xie, J.C.; Liu, F.; Du, J.T.; Chow, D.H.C.; Liu, J.P. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Fire Risk in Historic Chinese Temples: A Case in Beijing. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2022, 16, 1844–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, R.; Picco, M.; Greenfield, D.; Ashton, P.; Arbuthnot, E.; Hashemi, A. Historic Churches and Their Hygrothermal Environment: A Review of Criteria Related to Building Fabric, Artefacts, Artwork and Occupants. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeman, H.J.; Belleghem, M.V.; Janssens, A.; Paepe, M.D. Coupled simulation of heat and moisture transport in air and porous materials for the assessment of moisture related damage. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleghem, M.V.; Steeman, M.; Willockx, A.; Janssens, A.; Paepe, M.D. Benchmark experiments for moisture transfer modelling in air and porous materials. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Kato, S.; Hu, R.; Ishida, Y. Development of new indices to assess the contribution of moisture sources to indoor humidity and application to optimizati-on design: Proposal of CRI(H) and a transient simulation for the prediction of i-ndoor humidity. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodosiu, C.; Hohota, R.; Rusaouën, G.; Woloszyn, M. Numerical prediction of ind-oor air humidity and its effect on indoor environment. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q. The Evolution of Cold Adaptation Technology within Ancient Buildings in Amur River Basin Viewed from Archaeology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.B.; Yan, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yao, S.S.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, X.D. Modeling and numerical simulation of heat and mass transfer in the cave wall of the Mogao -Grottoes in China. Build. Environ. 2021, 201, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balocco, C.; Grazzini, G. Numerical simulation of ancient natural ventilation syste-ms of historical buildings. A case study in Palermo. J. Cult. Herit. 2009, 10, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, H.R.; Ma, Y.; Hokoi, S.C.; Li, Y.H. Assessing the deterioration risk of polychrome clay sculptures based on the hygrothermal environment: A case study of Baosheng temple, China. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.N.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Zhang, Y.W.; Tie, X.X. Numerical Simulation of the Micro Environment in the Han Yang Mausoleum Museum. Aerosol. Air. Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, Z.; Schellen, H.; Schijndel, J.V.; Ankersmit, B. Modelling of heat and moisture induced strain to assess the impact of present and historical indoor climate conditions on mechanical degradation of a wooden cabinet. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 16, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napp, M.; KalameesA, T. Energy use and indoor climate of conservation heating, dehumidification and adaptive ventilation for the climate control of a mediaeval c-hurch in a cold climate. Energy. Build. 2015, 108, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.M.; Ding, J.J.; Jin, G.W.; Gu, A.; Lei, Y. Application of Advanced Analytical Techniques in Organic Cultural Heritage: A Case Study of Ancient Architecture Relics in the Palace Museum (Beijing). Coatings 2022, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.Y. Research and Analysis of the Building Environment in the Conservation of Yang Xin Hall Area in the Palace Museum. Tradit. Chin. Archit. Gard. Prot. Cult. Herit. 2018, 2, 31–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.S.; Zeng, Z.T.; Sun, D.A. Experimental and numerical investigation on the effect of heat and moisture coupling migration of unsaturated lateritic clay for the soil thermal storage system. Energy Build. 2022, 276, 112499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.Z.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhou, L.Z. Conservation of disappearing traditional manufacturing process for Chinese grey brick: Field survey and laboratory study. Constr. Build Mater. 2019, 212, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Ye, J.C.; Lu, G.H.; Qin, F.X. Study on field capacity distribution about soil of China. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2004, 35, 113–116, 119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL 364-2015; Specifications for soil moisture monitoring. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- Xiong, J.; Li, A.G.; Liu, C.P.; Dong, J.G.; Yang, B.; Cao, J.J.; Ren, T. Probing the historic thermal and humid environment in a 2000-year-old ancient underground tomb and enlightenment for cultural heritage protection and preventive conservation. Energy Build. 2021, 251, 111388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, E.; Roels, S. Review of mould prediction models and their influence on mould risk evaluation. Build. Environ. 2011, 51, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 18883-2022.2022-07-11; Standards for indoor air quality. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Li, Y.H.; Kong, Z.Y.; Xie, H.R.; Ma, Y.; Mu, B.G.; Hokoi, S.C. Construction type influences features of rising damp of blue-brick masonry walls, Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 284, 122791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, K.S. Statistical Methods in Psychiatric Research and SPSS. Indian J. Psychiatry 2016, 58, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.; Luo, L.Q.; Anser, M.K. Do BRI policy and institutional quality influence economic growth and environmental quality? An empirical analysis from South Asian- countries affiliated with the Belt and Road Initiative. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 8438–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausam, K.; Pare, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Tiwari, A.K. Thermal performance analysis of hybrid-nanofluid based flat plate collector using Grey relational analysis (GRA): An approach for sustainable energy harvesting. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 37, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, S.; Hernandez, C.; Bärtschi, C.; Poussereau, N. Impact of paint and wall-paper on mould growth on plasterboards and aluminum. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Bu, N.J.; Zhen, Q.; Liu, J.B.; Bashir, S. Modified nano-SiO2/TiO2 hybrid fluorinated B-72 as antimicrobial and hydrophobic coatings for the conservation of ancient bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, F.G.; Belgas, M.D.L.; Mendes, C.; Pereira, L.; Ortega, J.M. Characterization of Fresh and Durability Properties of Different Lime Mortars for Being Used as Masonry Coatings in the Restoration of Ancient Constructions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).