The Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite Ore by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting–Leaching Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
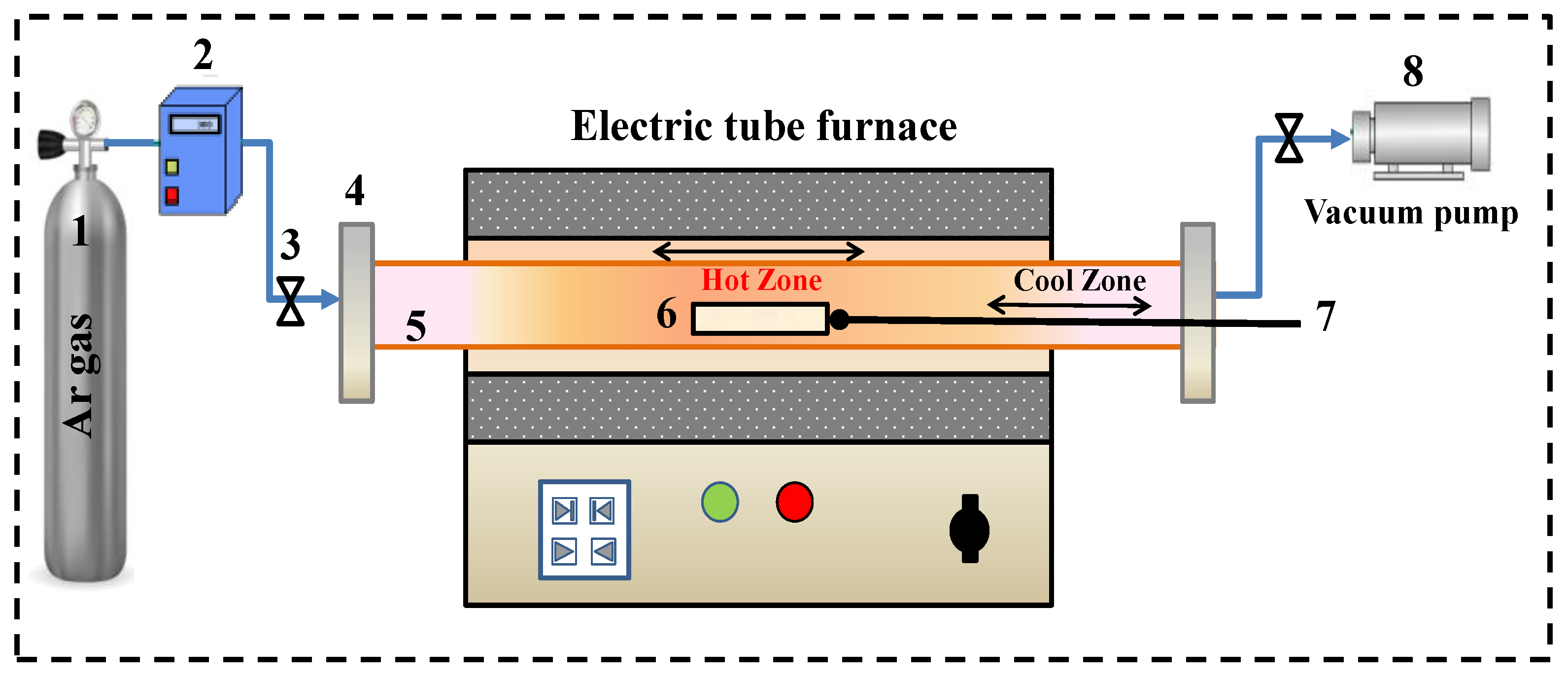
2.2. Methods
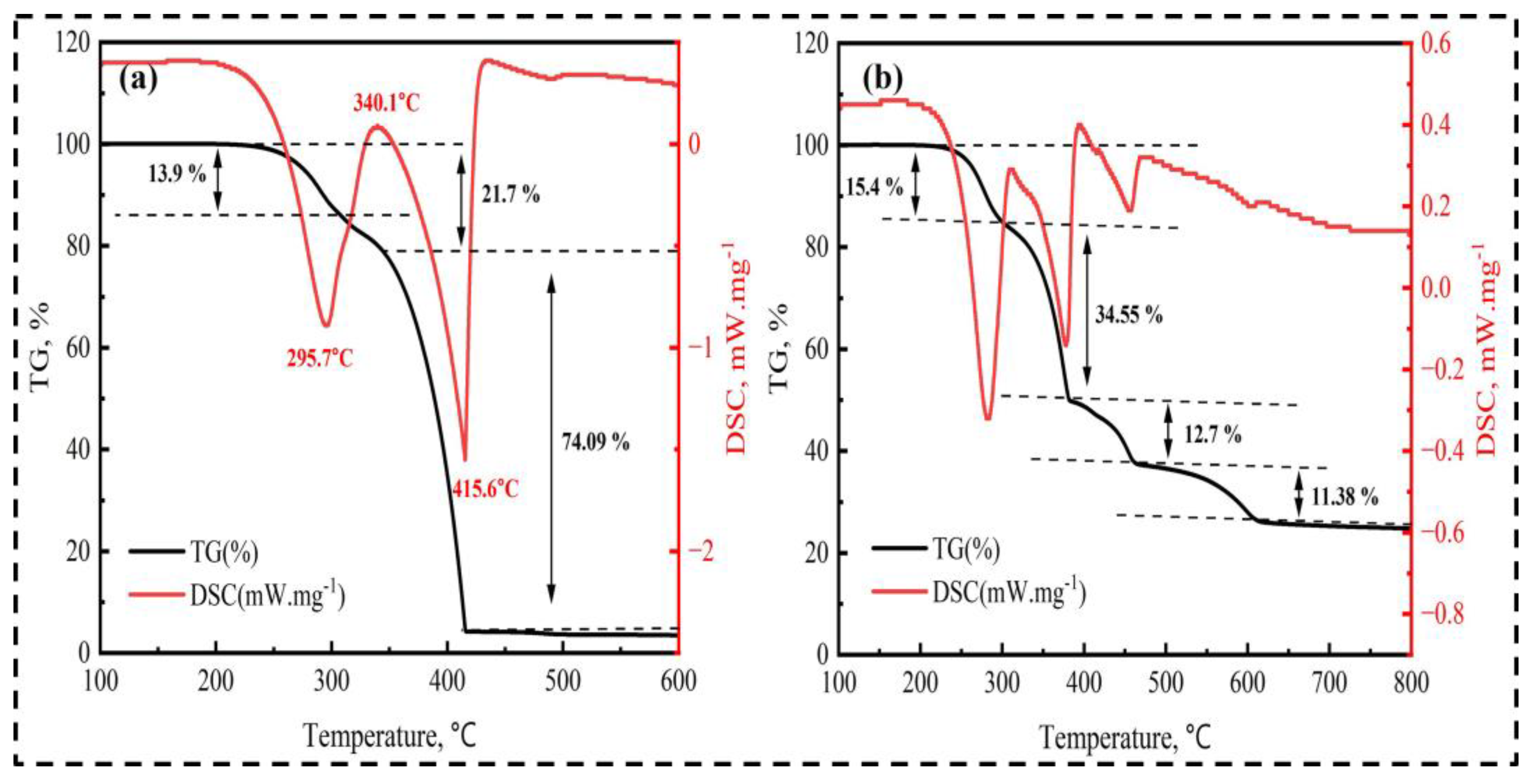
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sulfation Roasting
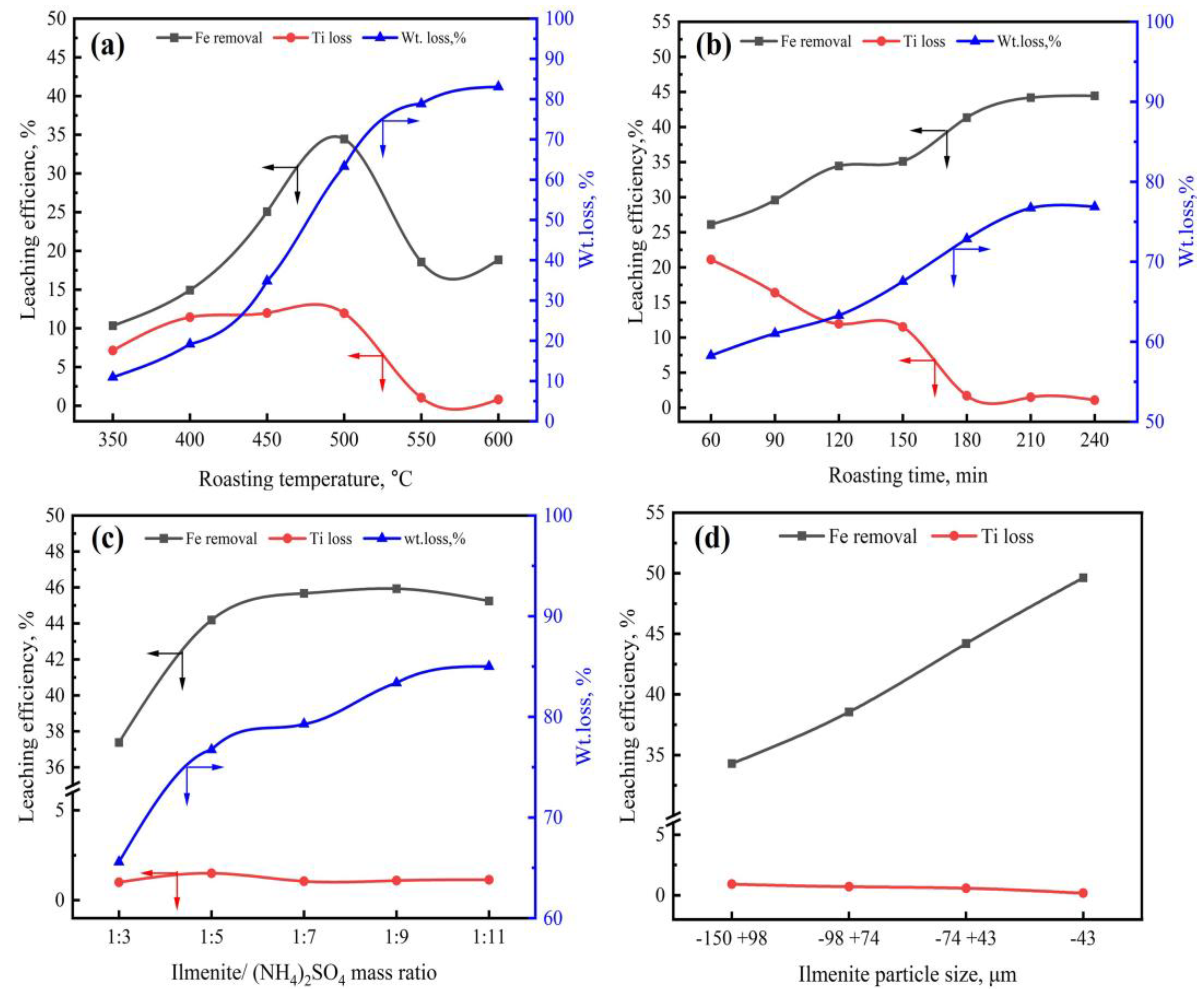
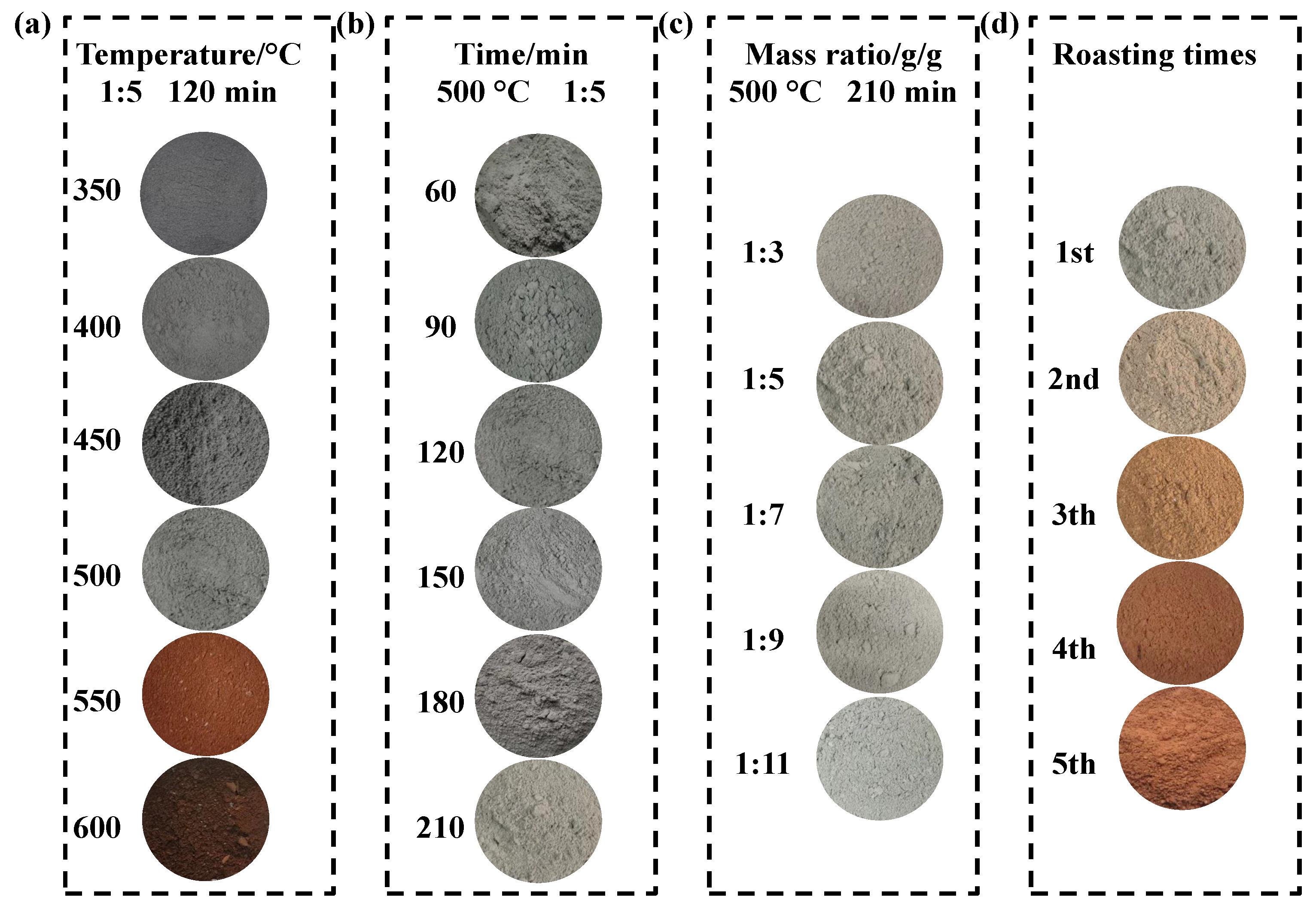
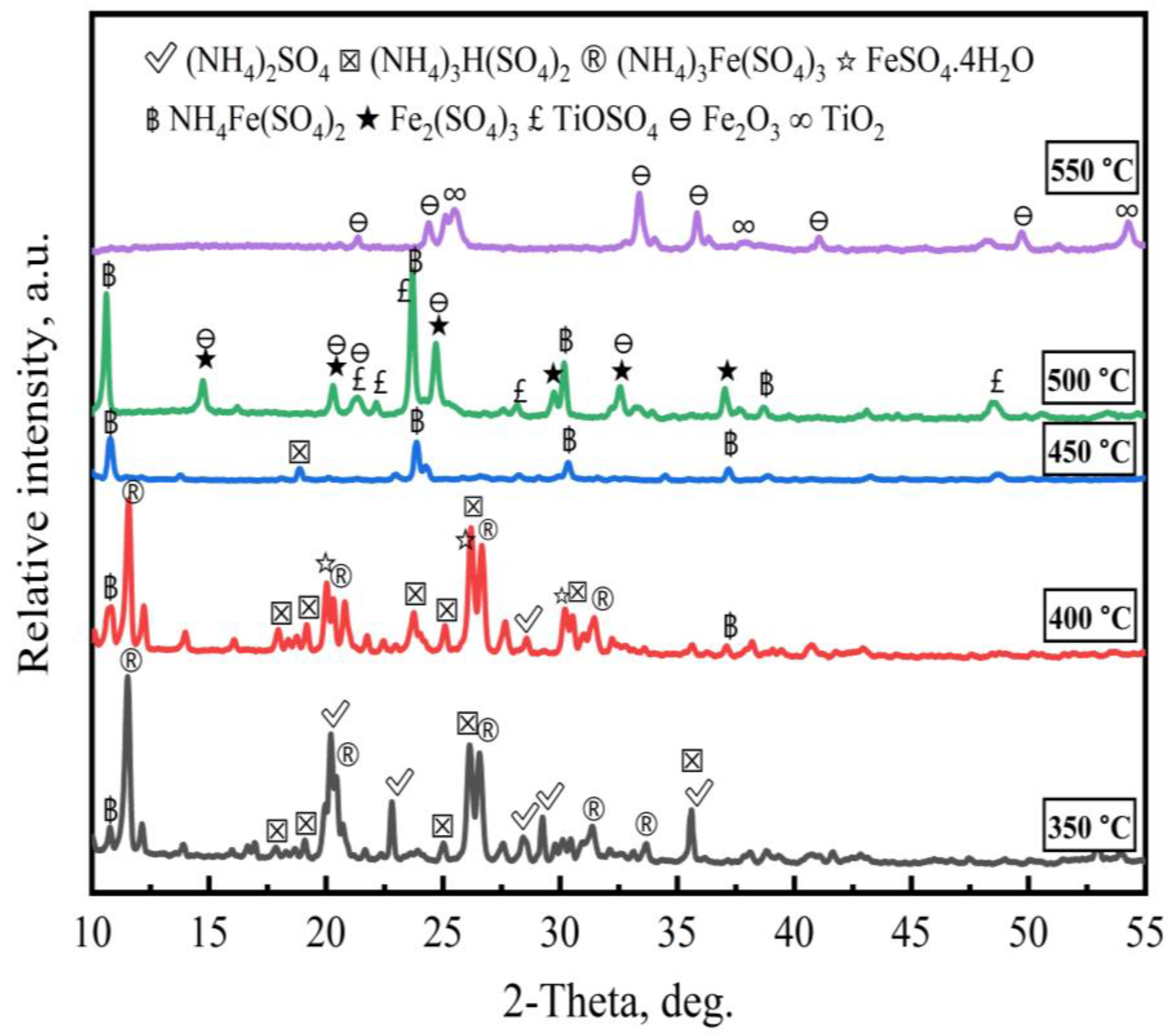
3.1.1. Effect of Roasting Temperature
3.1.2. Effect of Roasting Time
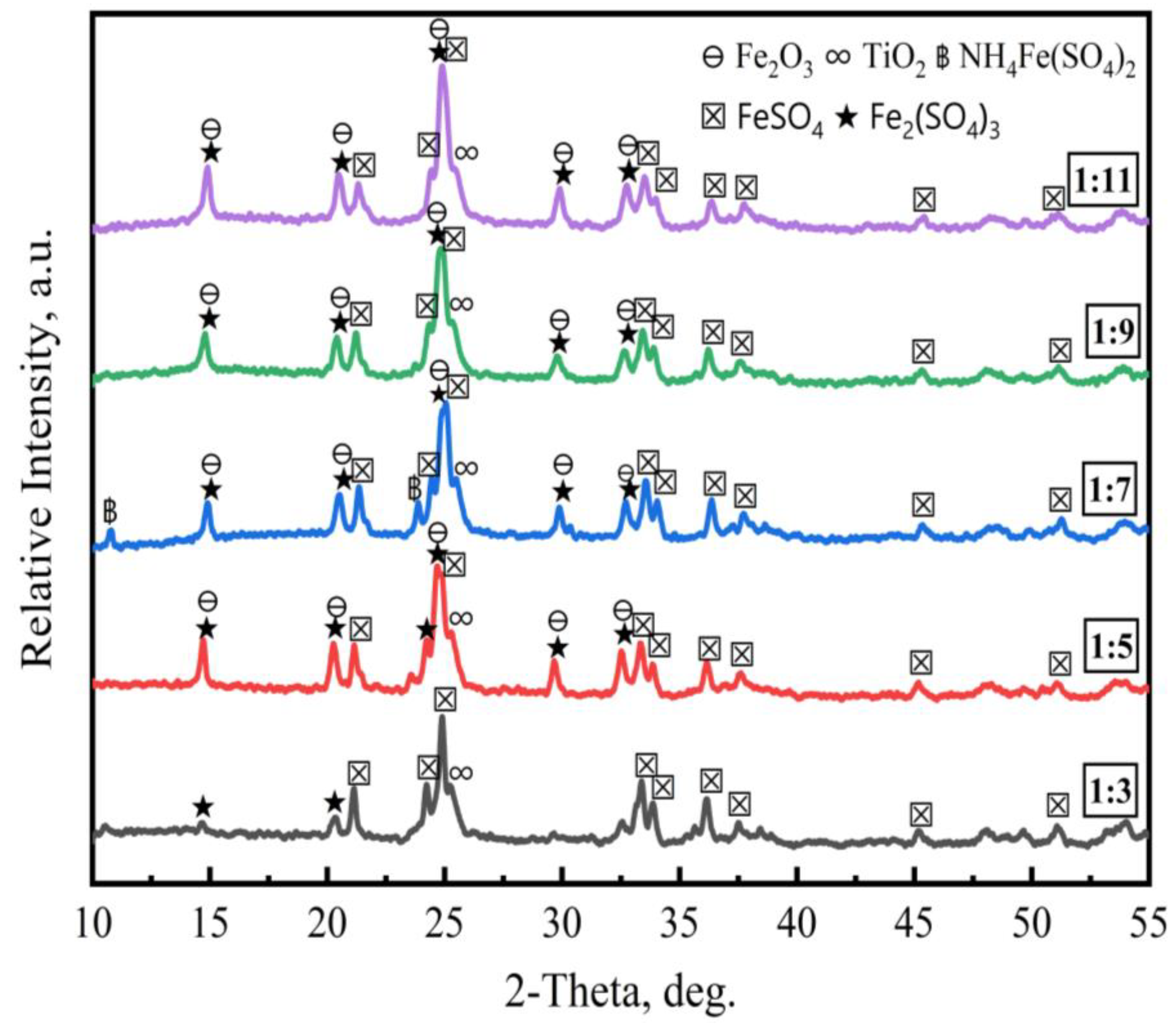
3.1.3. Effect of Ilmenite-to-(NH4)2SO4 Mass Ratio
3.1.4. Effect of Ilmenite Particle Size
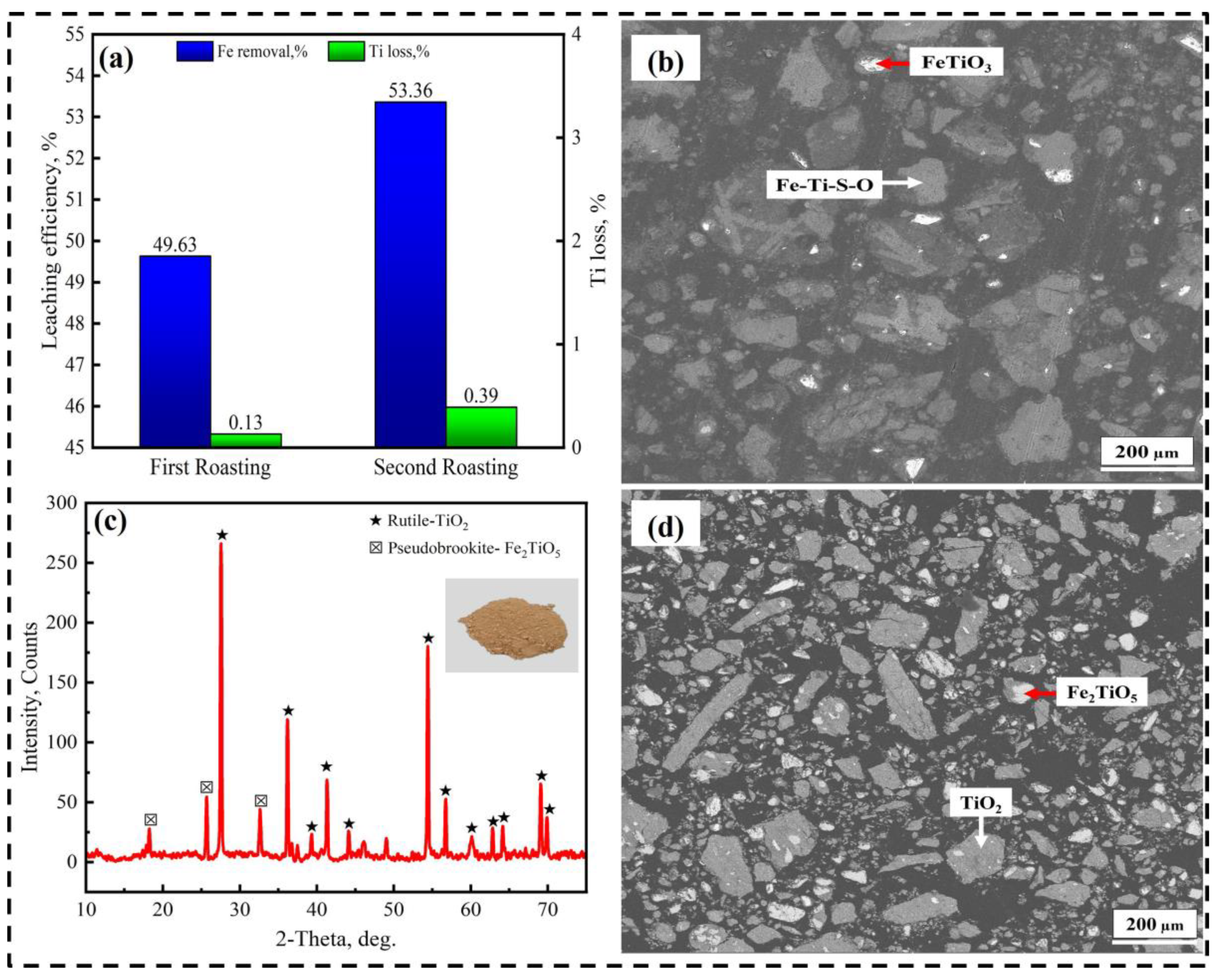
3.2. Effect of Second-Stage Roasting
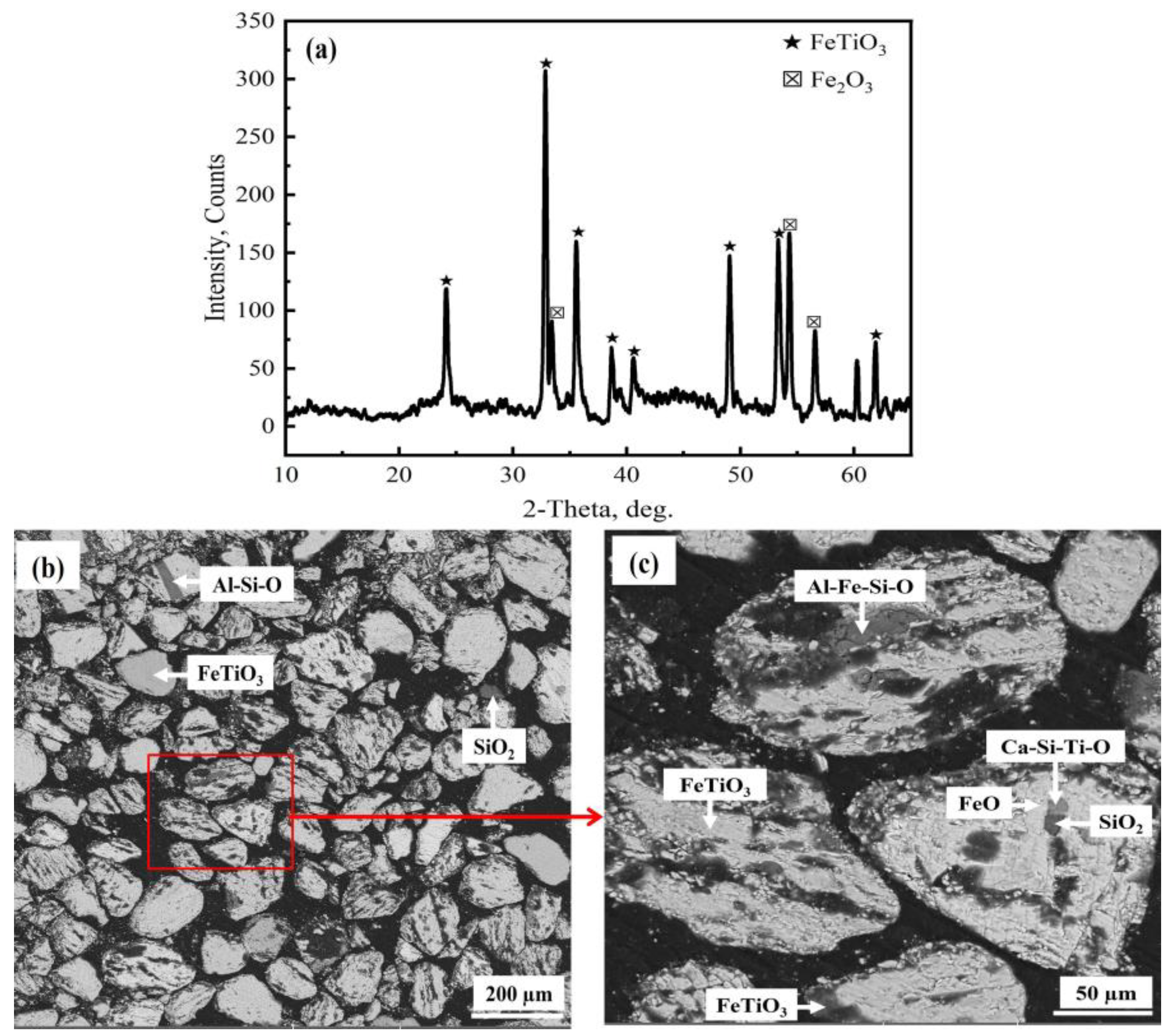
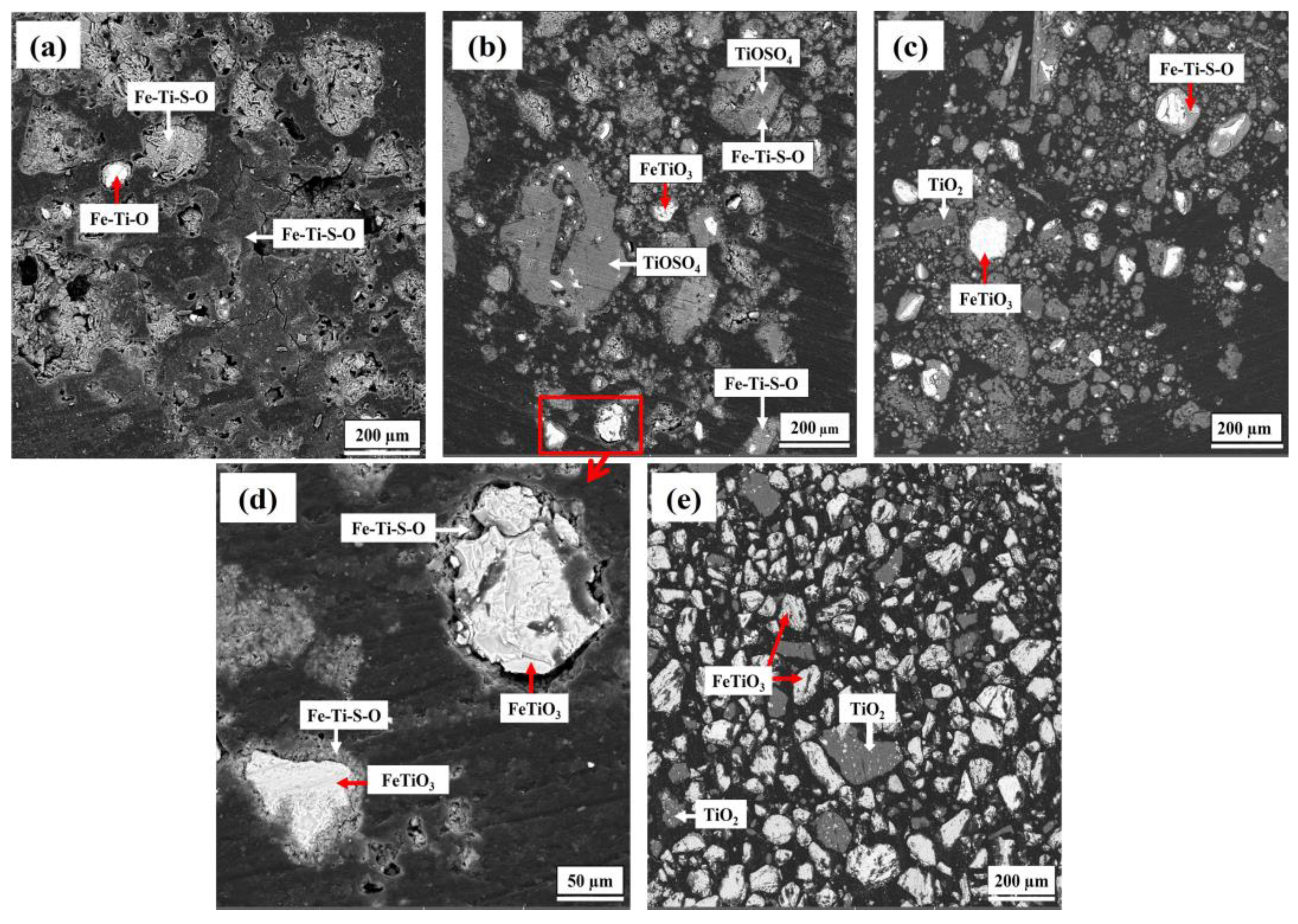
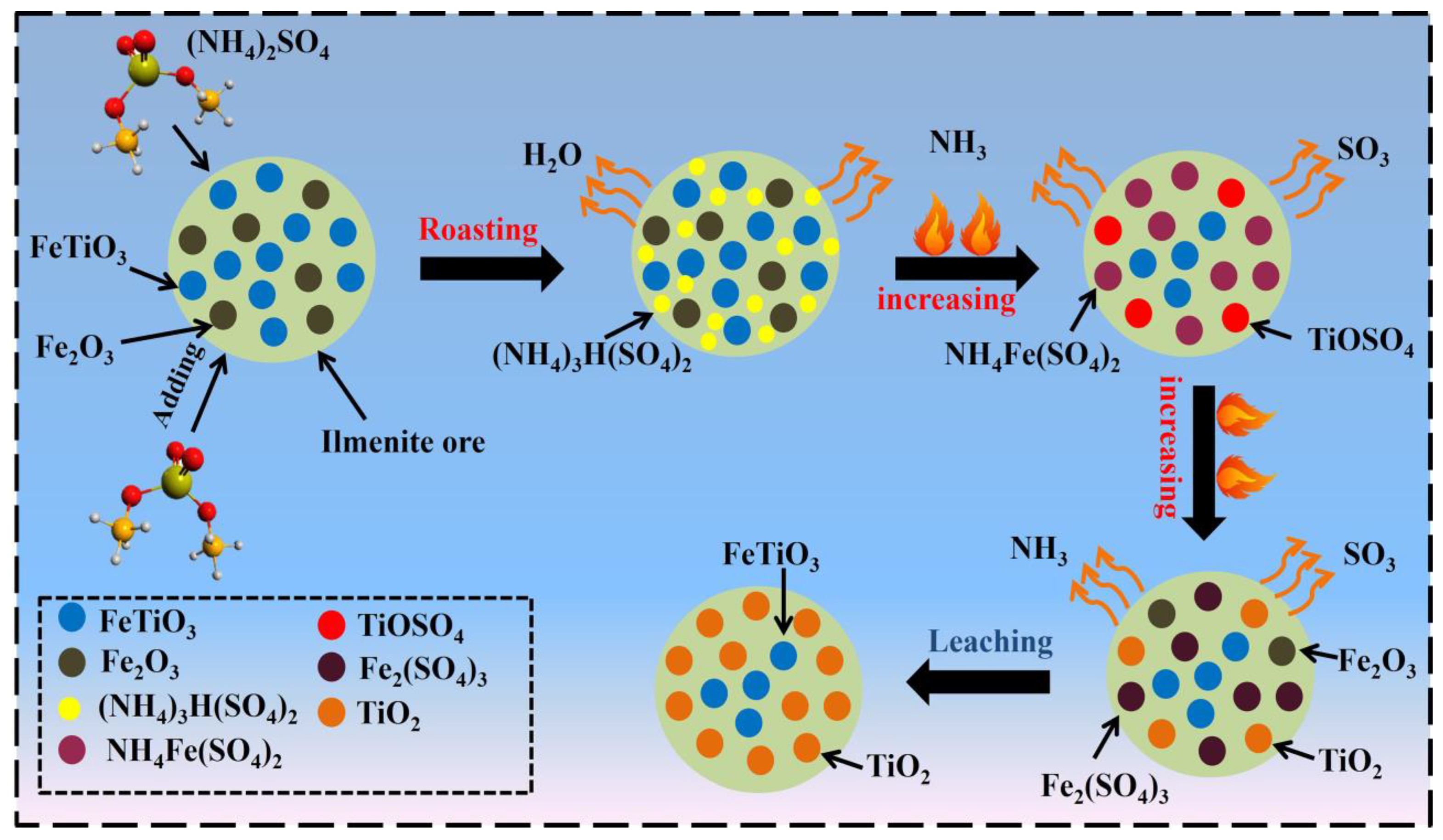
3.3. Reaction Mechanism
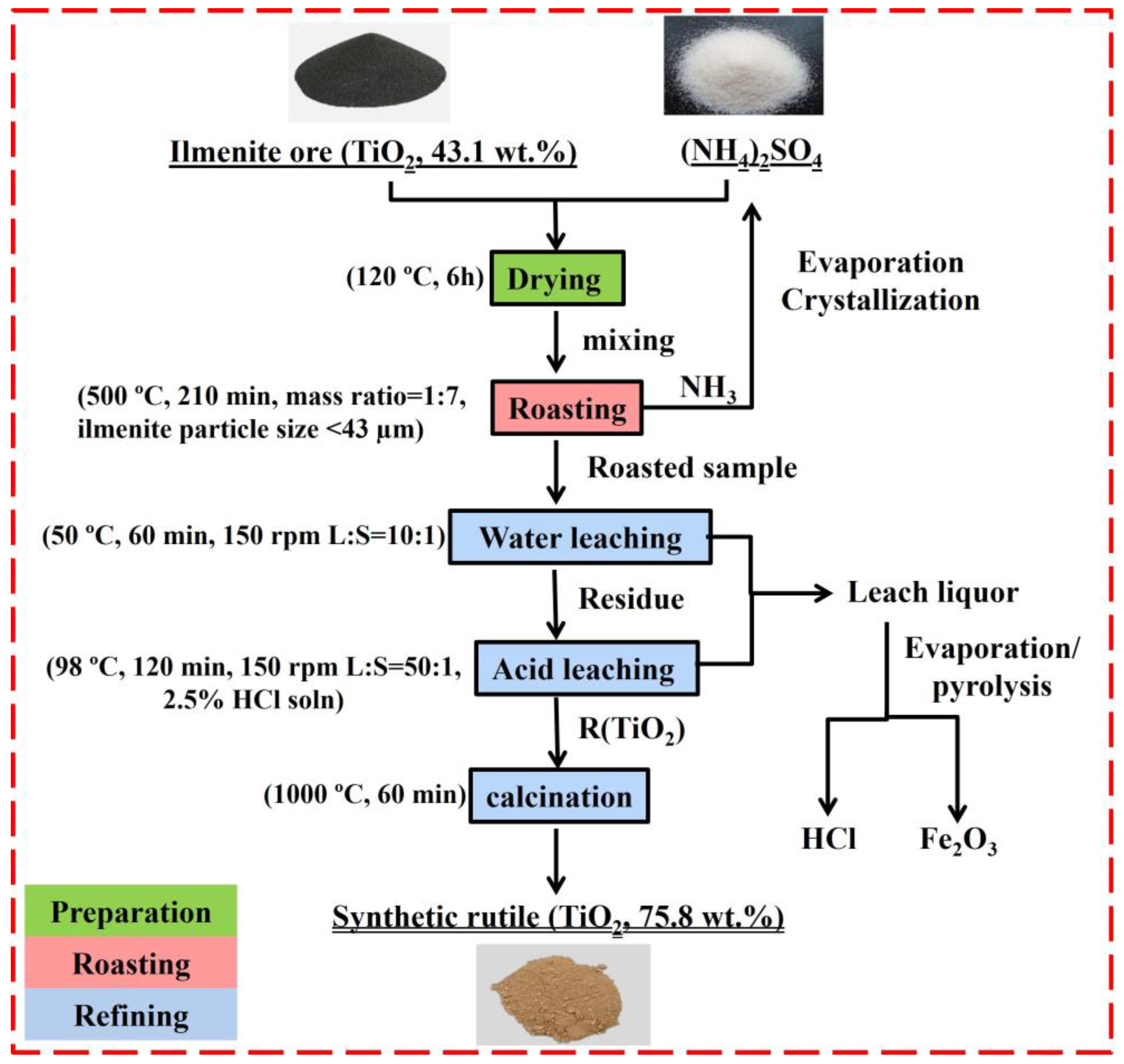
3.4. Flow Sheet
4. Conclusions
- The recovery of TiO2 from titanium ores such as ilmenite via traditional methods like smelting or acid leaching processes has disadvantages. Theses disadvantages include high energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and acid waste emissions. Therefore, there is an urgent need for an efficient, economical, clean, and sustainable technology for the recovery of TiO2 from ilmenite ore.
- An ammonium sulfate roasting method was proven to be an effective way to convert metal oxides in ilmenite ore to soluble sulfates at a low temperature. (NH4)2SO4 acted as a sulfation agent to produce NH4Fe(SO4)2, Fe2(SO4)3, TiOSO4, and Fe2O3 during the roasting process. The roasted products were leached by water, followed by diluted HCl acid.
- The optimal iron leaching efficiency was 49.6% at the following roasting conditions: roasting temperature of 500 °C, roasting time of 210 min, ilmenite-to-(NH4)2SO4 mass ratio of 1:7, and ilmenite particle size of less than 43 µm. The second-stage roasting enhanced the iron leaching efficiency from 49.6% to 53.3%.
- The obtained synthetic rutile after calcination had a TiO2 grade of 75.83 wt.%. According to the XRD analysis, the main phase was rutile-TiO2, with small diffraction peaks of Fe2TiO5. The iron removal efficiency was not high due to the non-sulfated ilmenite particles shown in the XRD and SEM-EDS analysis. These remaining non-sulfated ilmenite particles, which were surrounded by a metal sulfate layer, demonstrate the complexity of the ilmenite ore crystal structure. Therefore, more attention should be paid to the crystal structure breakdown of ilmenite in future studies.
- During this process, ammonium sulfate and hydrochloric acid can be recycled, as well as iron that is wasted in the solution. Therefore, the process is environmentally friendly.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diebold, U. The Surface Science of Titanium Dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Peng, J.H.; Chen, J. Optimizing Conditions for Wet Grinding of Synthetic Rutile Using Response Surface Methodology. Min. Metall. Explor. 2011, 28, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A. Kinetic Extraction of Titanium (IV) from Chloride Solution Containing Fe (III), Cr (III) and V (V) Using the Single Drop Technique. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chai, W.; Han, G.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Liu, J. A Perspective of Stepwise Utilisation of Bayer Red Mud: Step Two—Extracting and Recovering Ti from Ti-Enriched Tailing with Acid Leaching and Precipitate Flotation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.Q. Thermodynamic Analysis of Extraction of Synthetic Rutile from Modified Slag. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4924–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F. Titanium: Physical Metallurgy, Processing, and Applications; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2015; ISBN 1627080805. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liang, B. Study on the Mechanochemical Oxidation of Ilmenite. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 459, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, D.K.; Verhulst, D.; Spitler, T.M.; Sabacky, B.J. Titanium Nanoparticles Move to the Marketplace. Chem. Innov. 2000, 30, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mineral Commodity Summaries 2023; ASM International: Reston, VA, USA, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.A. Non-Rutile Feedstocks for the Production of Titanium. JOM 1984, 36, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Sato, S.; Ono, J.; Okada, H.; Nagasaka, T. Feasibility Study of the New Rutile Extraction Process from Natural Ilmenite Ore Based on the Oxidation Reaction. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2006, 37, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hazek, N.; Lasheen, T.A.; El-Sheikh, R.; Zaki, S.A. Hydrometallurgical Criteria for TiO2 Leaching from Rosetta Ilmenite by Hydrochloric Acid. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 87, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Mohapatra, B.K.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Chatterjee, S.K. Integrated XRD, EPMA and XRF Study of Ilmenite and Titania Slag Used in Pigment Production. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamor, L. Titanium Dioxide Manufacture, a World Source of Ilmenite, Rutile, Monazite and Zircon. In Conference Proceedings; AusIMM: Perth, WA, USA, 1986; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger, R.H.; Elger, G.W. Preparation of Titanium Feedstock from Minnesota Ilmenite by Smelting and Sulfation-Leaching; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Xie, Z. Enhanced Reduction of Ilmenite Ore by Pre-Oxidation in the View of Pore Formation. Powder Technol. 2022, 405, 117539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liang, B.; Lü, L.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Beneficiation of Titania by Sulfuric Acid Pressure Leaching of Panzhihua Ilmenite. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemas, S.; Fang, Z.Z.; Fan, P. A New Method for Production of Titanium Dioxide Pigment. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Liao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Tan, J. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching Behavior of Different Treated Panxi Ilmenite Concentrations. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 107, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Nicol, M.J. An Electrochemical Study of the Reduction and Dissolution of Ilmenite in Sulfuric Acid Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, T.; Qiu, G.; Chen, F. A Process for Producing Synthetic Rutile from Panzhihua Titanium Slag. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 147, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, H.N. Ilmenite Upgrading by the Murso Process; TMS Paper NO A 72-32; AIME: New York, NY, USA, 1972; 14p. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.; Clamp, F.; Mobbs, D.B.; Pearse, R.V. Laporte High-Efficiency Ilmenite Beneficiation Process. Proc. Symp. Adv. Extr. Metall. 1977, 89–96, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, S.; Yamada, S. Acid Leaching Upgrades Ilmenite to Synthetic Rutile. Chem. Eng. 1973, 80, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Walpole, E.A.; Winter, J.D. The Austpac ERMS and EARS Processes for the Manufacture of High-Grade Synthetic Rutile by the Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Ilmenite. In Proceedings of the Chloride Metallurgy 2002-International Conference on the Practice and Theory of Chloride/Metal interaction, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–23 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. A Literature Review of Titanium Metallurgical Processes. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Teng, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Study on the High-Efficiency Separation of Fe and Mn from Low-Grade Pyrolusite and the Preparation of LiMn2O4 Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Che, L.; Wei, L.; Cheng, H.; Zou, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S. Sulfation Roasting of Nickel Oxide–Sulfide Mixed Ore Concentrate in the Presence of Ammonium Sulfate: Experimental and DFT Studies. Metals 2019, 9, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, B. A Sustainable Low-Temperature Roasting and Water Leaching Process for Simultaneously Extracting Mn, Cu, Co, and Ni from Ocean Manganese Nodules. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaishi, T.; Ishiyama, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Yoshinaga, S. Reactions between Ammonium Sulphate and Metal Oxides (Metal = Cr, Mn and Fe) and Thermal Decomposition of the Products. J. Therm. Anal. 1984, 29, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, D.; Deng, C.; Lv, L.; Liang, B.; Li, C. Simultaneous Extraction of Vanadium and Titanium from Vanadium Slag Using Ammonium Sulfate Roasting-Leaching Process. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Shen, X.; Zhai, Y.; Xiao, P.; Webley, P. Extraction of Iron and Aluminum from High-Iron Bauxite by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting and Water Leaching. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, H.; Qu, X.; Xing, P.; Yin, H. Recovery and Regeneration of Lithium Cobalt Oxide from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries through a Low-Temperature Ammonium Sulfate Roasting Approach. J. Power Sources 2020, 474, 228596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Qu, B.; Su, S.-J.; Ding, S.-L.; Sun, W.-Y. Extraction of Iron and Manganese from Pyrolusite Absorption Residue by Ammonium Sulphate Roasting–Leaching Process. Metals 2018, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Cui, F.; Huang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Xu, Q.; Luo, S. Synchronous Extraction of Nickel and Copper from a Mixed Oxide-Sulfide Nickel Ore in a Low-Temperature Roasting System. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Sohn, H.Y. Recovery of Synthetic Rutile and Iron Oxide from Ilmenite Ore by Sulfation with Ammonium Sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 1802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Yue, H.; Liang, B.; Lü, L.; Li, C. Preparation of Synthetic Rutile via Selective Sulfation of Ilmenite with (NH4)2SO4 Followed by Targeted Removal of Impurities. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, W.D. Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Sulphate. J. Appl. Chem. 1970, 20, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoura, R.; Urano, K. Mechanism, Kinetics, and Equilibrium of Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1970, 9, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Hara, Y.; Osada, H. The Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Sulfate and Its Reaction with Iron (III) Oxide. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1980, 5, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-B.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-T.; Ryoo, Y.-H. Sulfidization of Titaniferous Magnetite with Elemental Sulfur. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 1985, 23, 425. [Google Scholar]


| Component | TiO2 | Total Fe | SiO2 | CaO | MnO | MgO | Al2O3 | V2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content wt.% | 43.13 | 36.45 | 2.35 | 1.55 | 1.16 | 1.16 | 0.81 | 0.32 |
| Component | TiO2 | Total Fe | SiO2 | CaO | MnO | MgO | Al2O3 | V2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content wt.% | 75.83 | 16.53 | 4.26 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelgalil, M.S.; El-Barawy, K.; Ge, Y.; Xia, L. The Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite Ore by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting–Leaching Process. Processes 2023, 11, 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092570
Abdelgalil MS, El-Barawy K, Ge Y, Xia L. The Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite Ore by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting–Leaching Process. Processes. 2023; 11(9):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092570
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelgalil, Mahmoud S., K. El-Barawy, Yang Ge, and Longgong Xia. 2023. "The Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite Ore by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting–Leaching Process" Processes 11, no. 9: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092570
APA StyleAbdelgalil, M. S., El-Barawy, K., Ge, Y., & Xia, L. (2023). The Recovery of TiO2 from Ilmenite Ore by Ammonium Sulfate Roasting–Leaching Process. Processes, 11(9), 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092570








