Control Approach of Grid-Connected PV Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
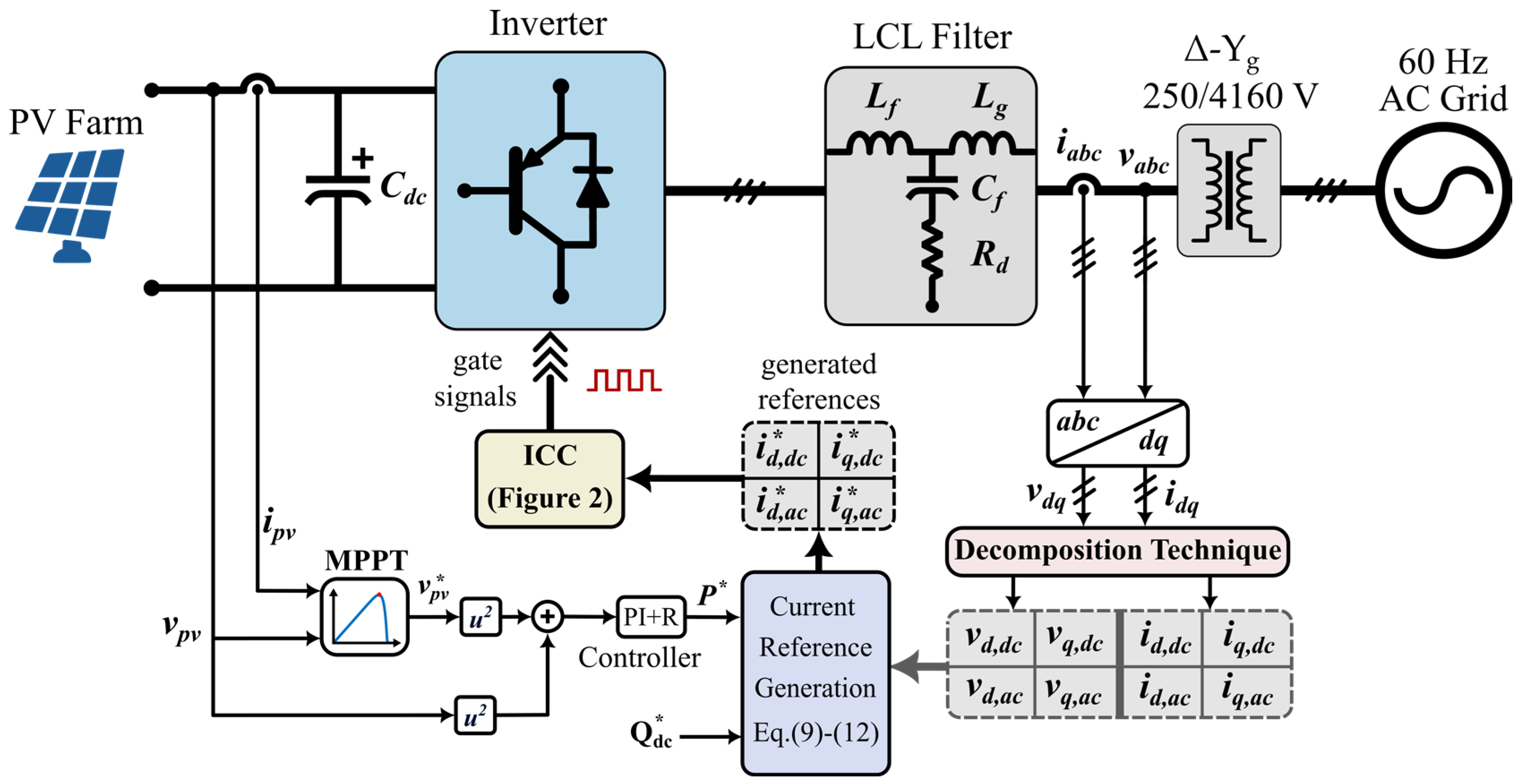
2. System Structure
3. Control Strategy under Unbalanced Grid Conditions
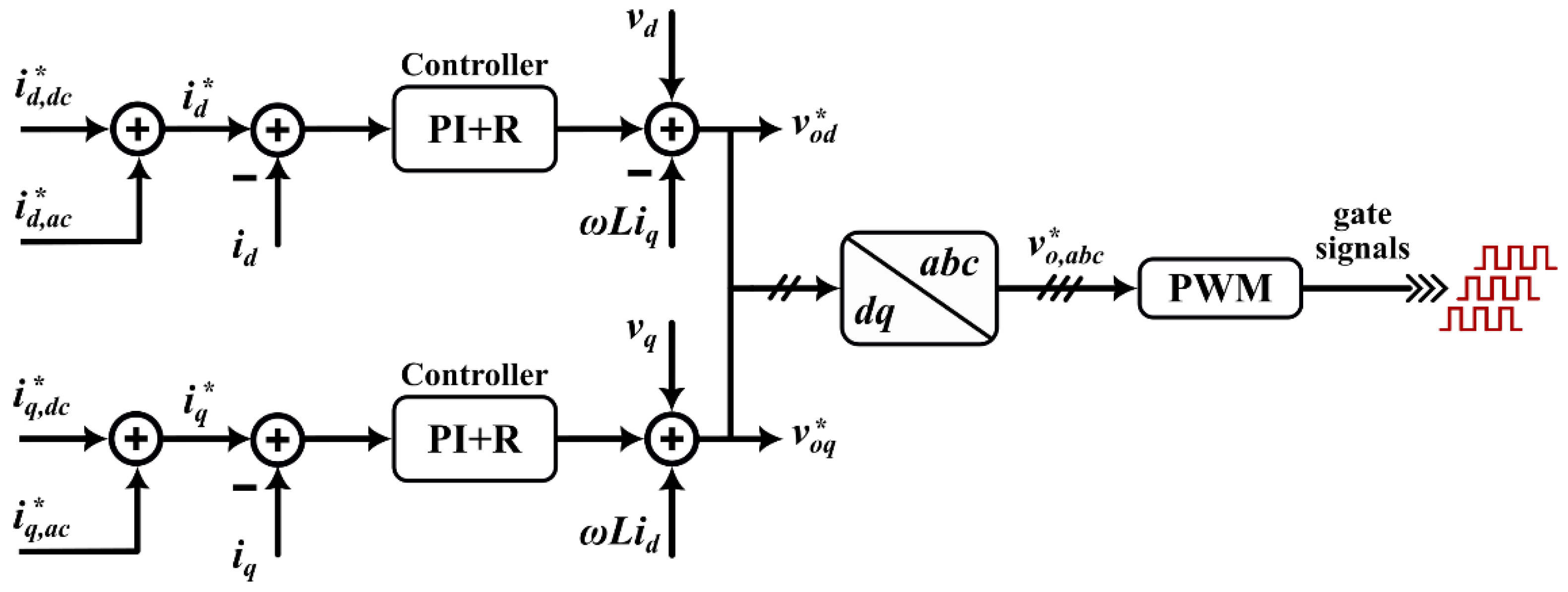
3.1. Current Control System
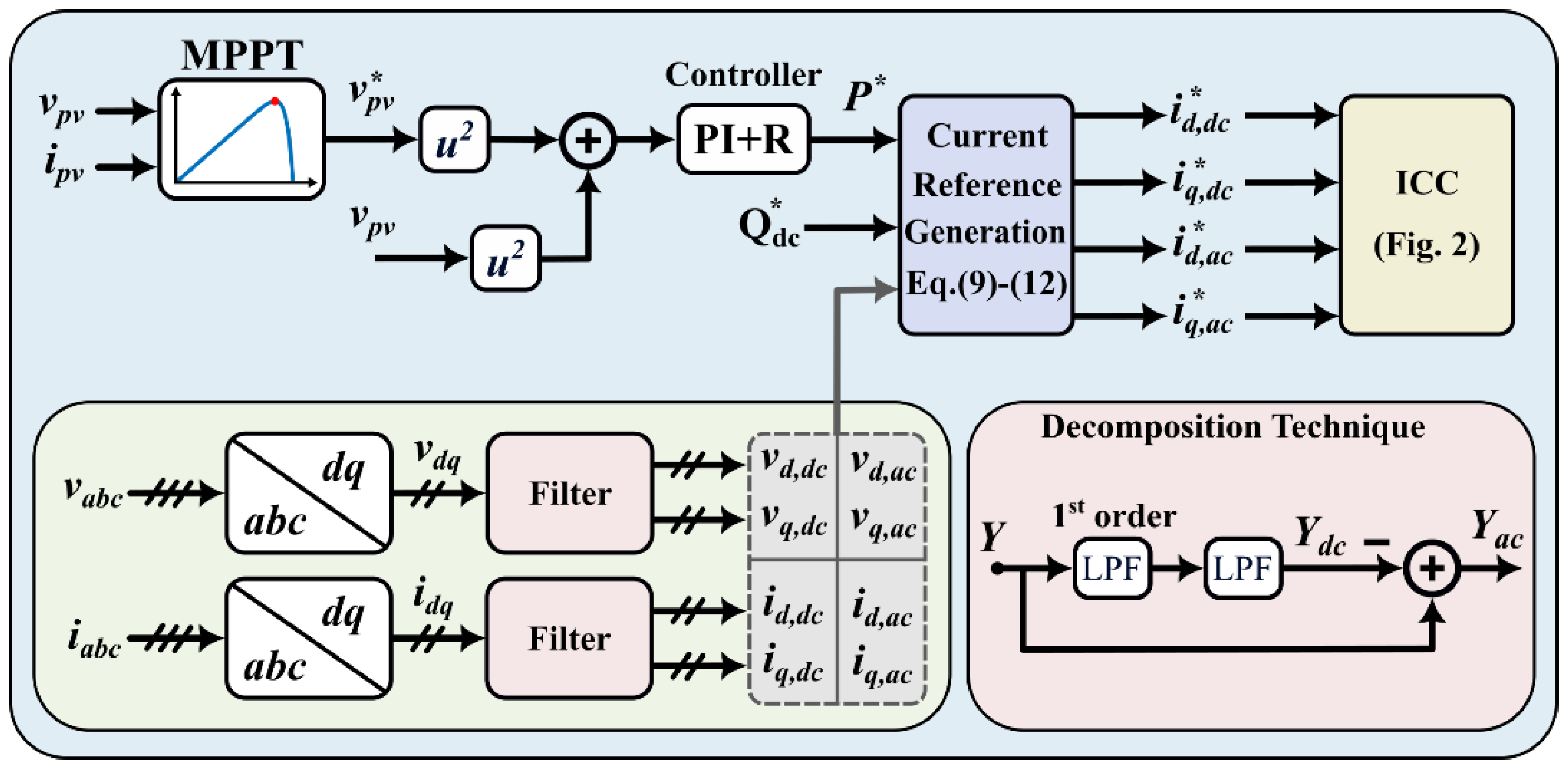
3.2. Constant Power Control
3.3. Constant DC-Link Voltage Control
4. Simulation Results
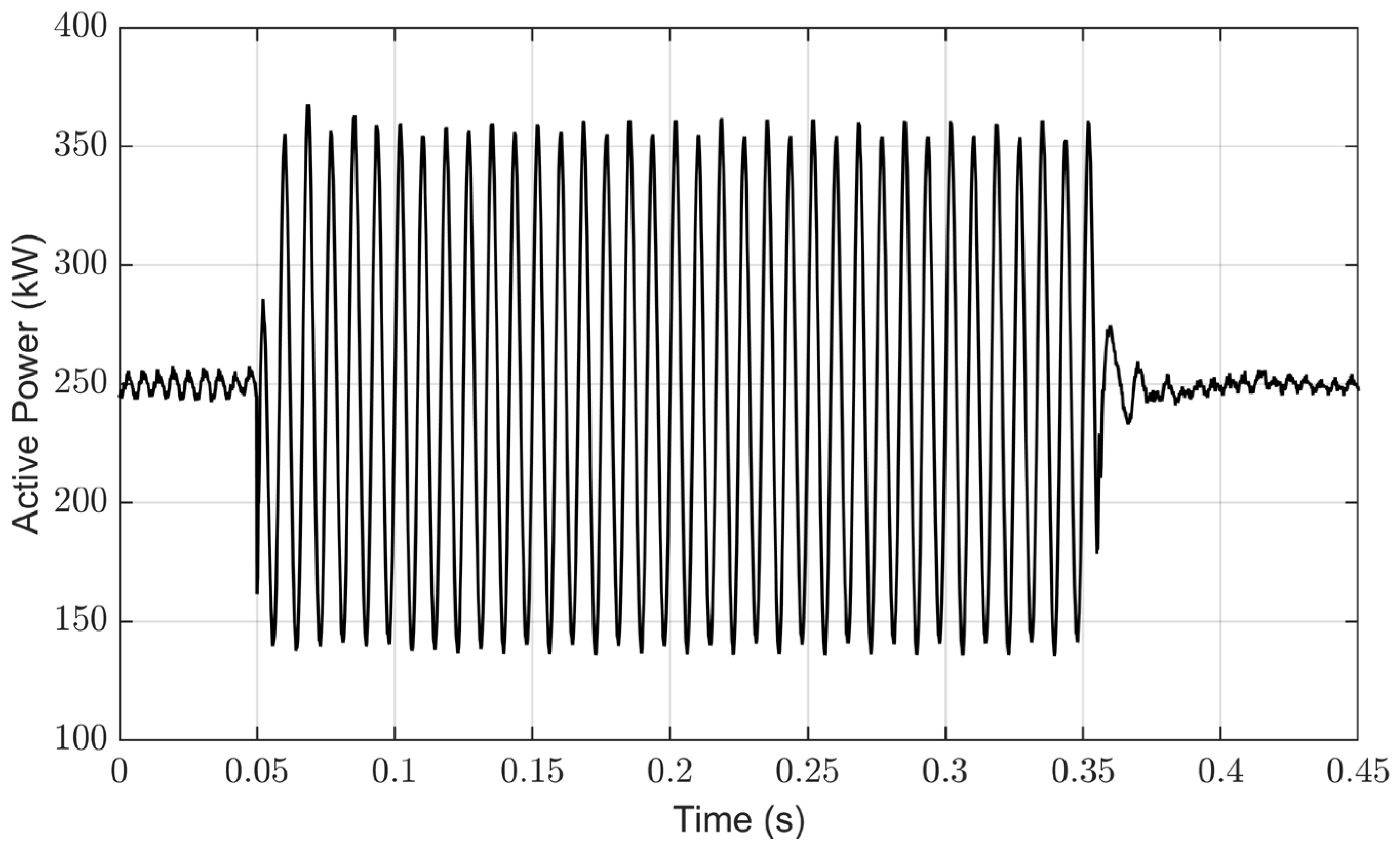
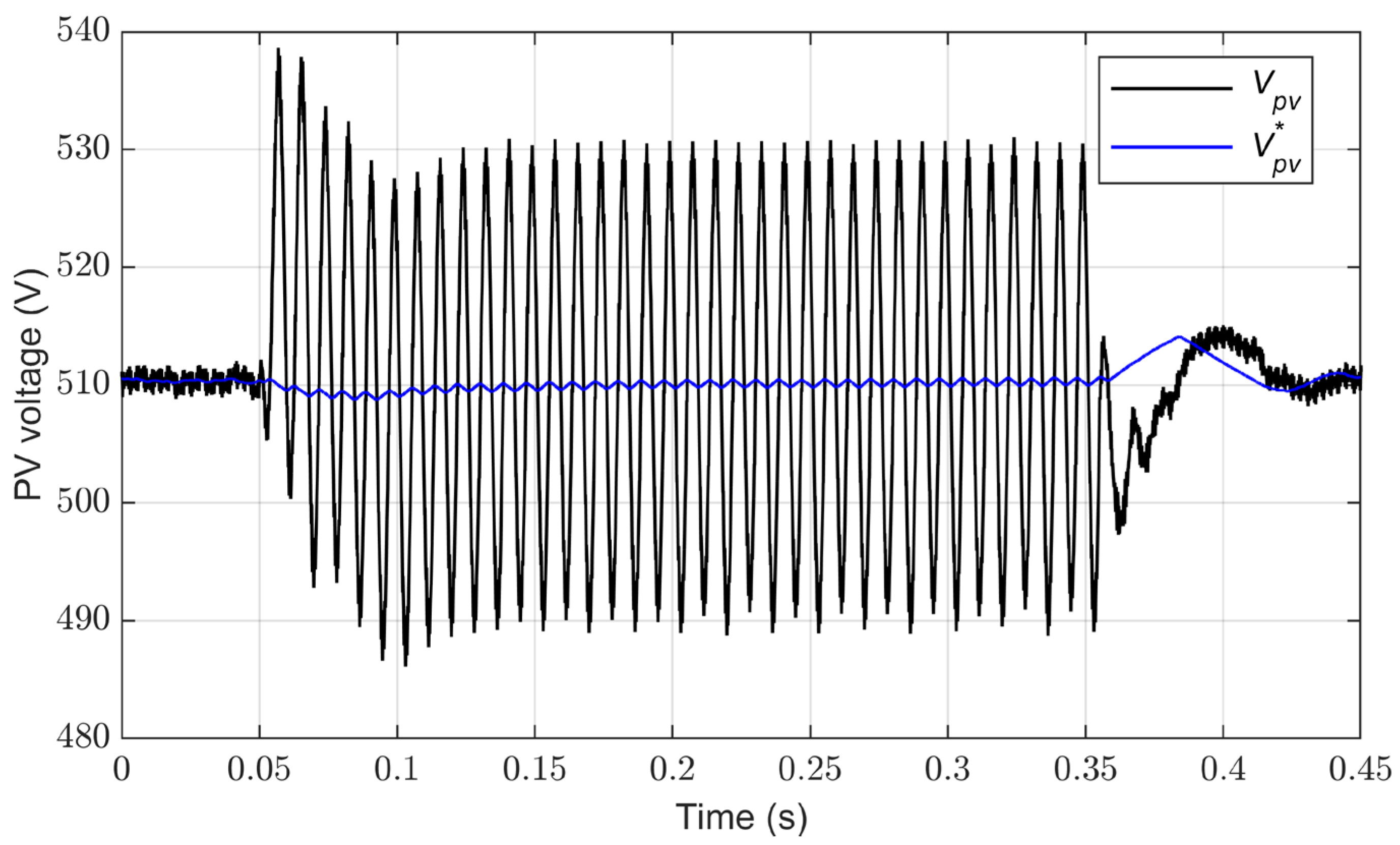
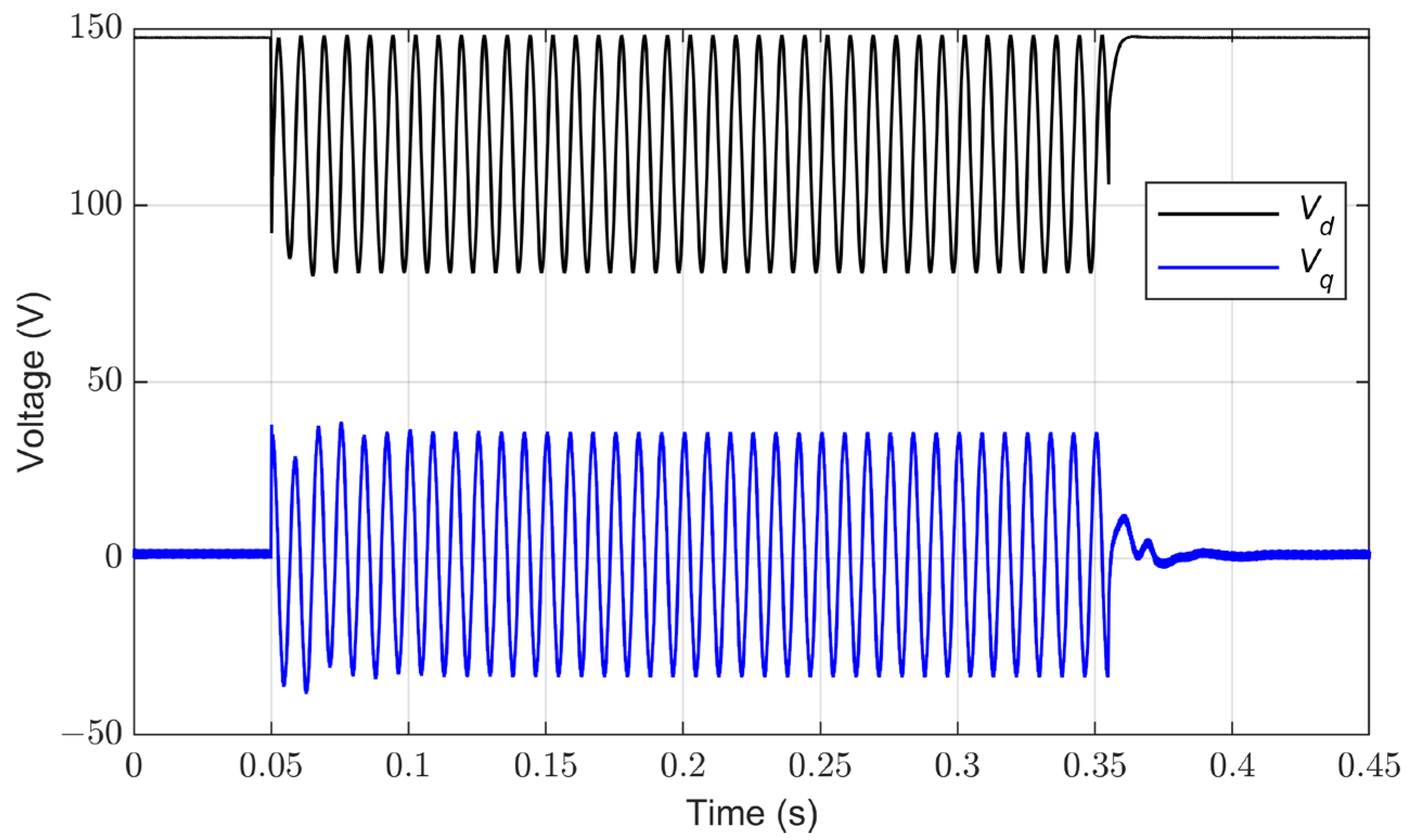
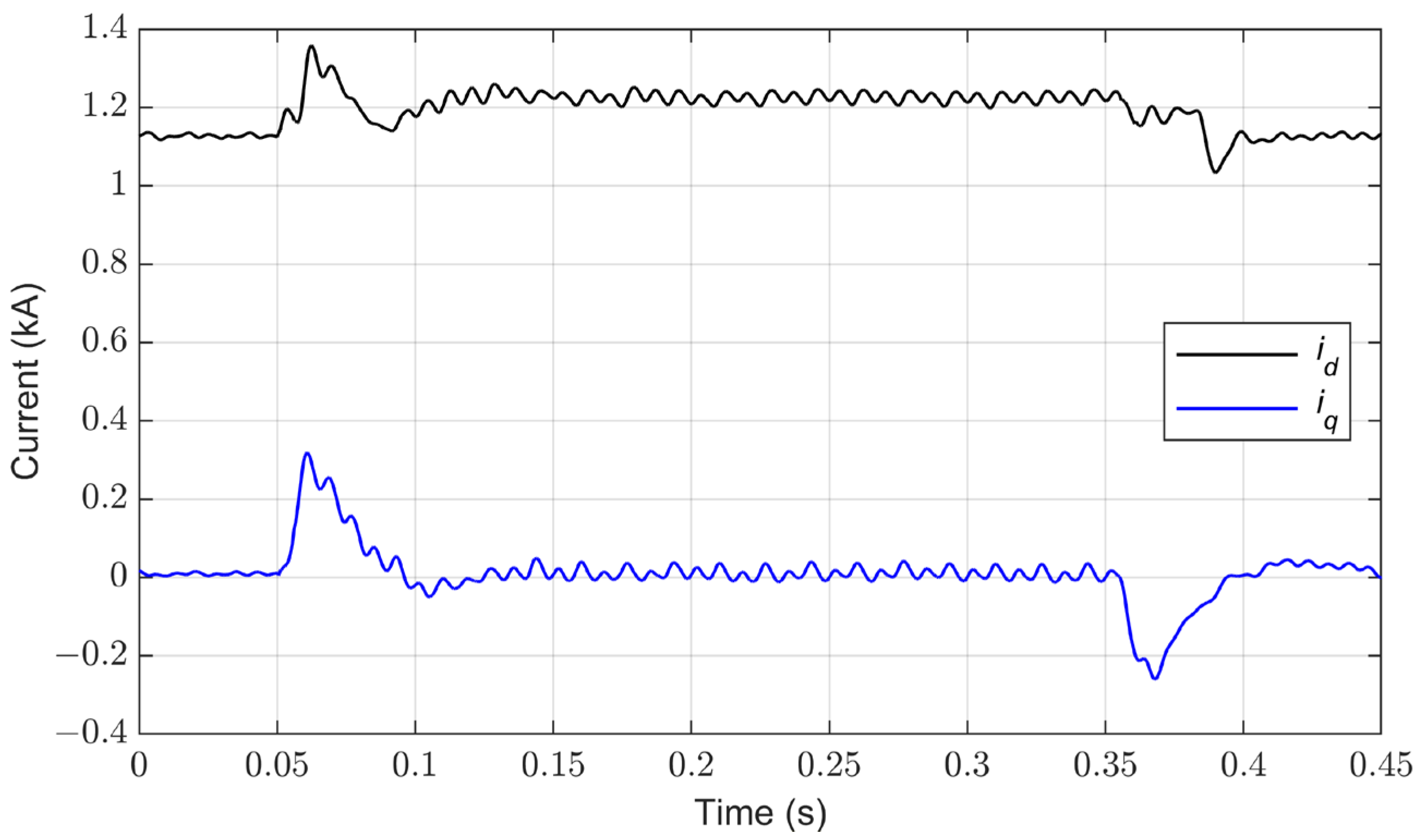
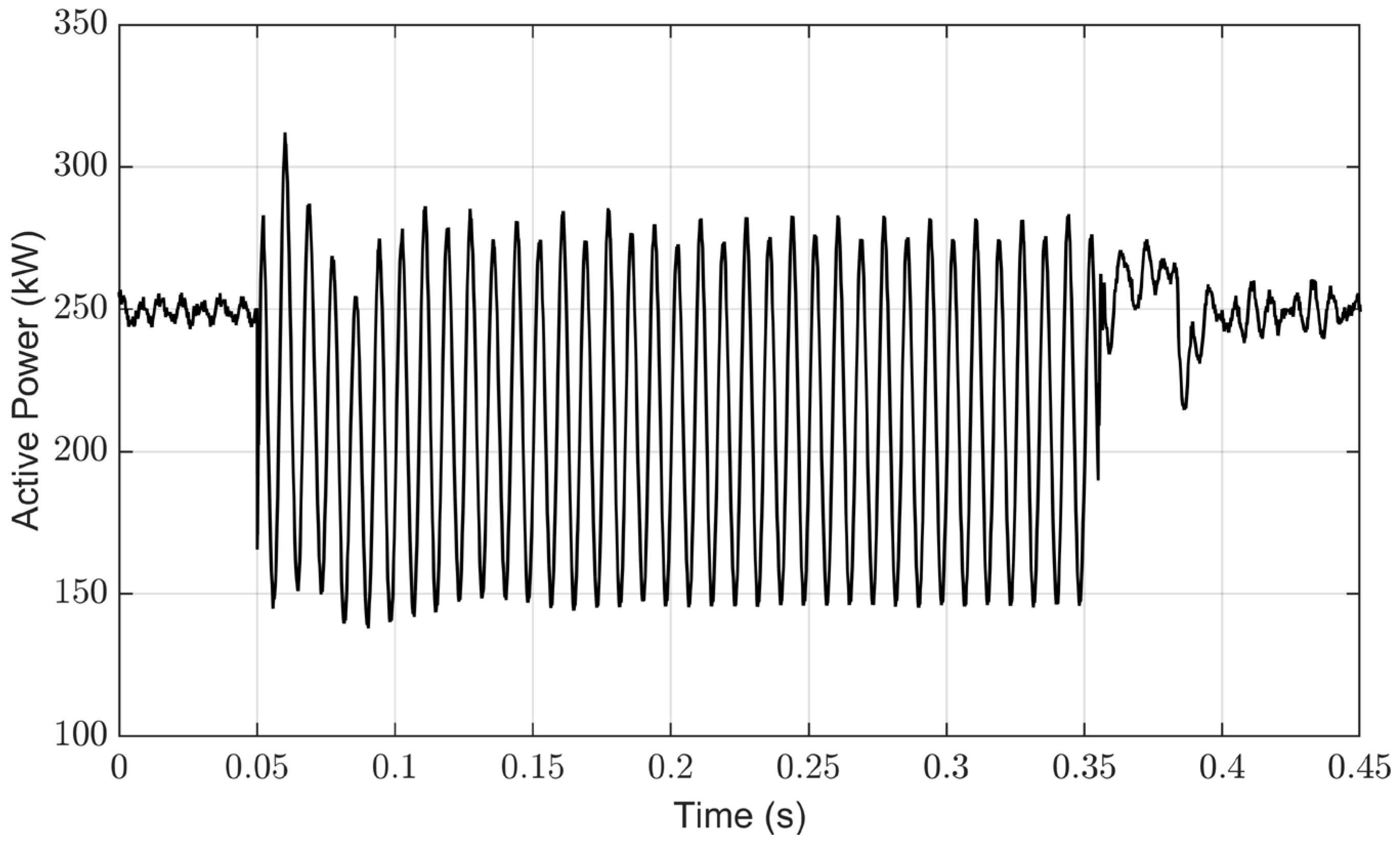
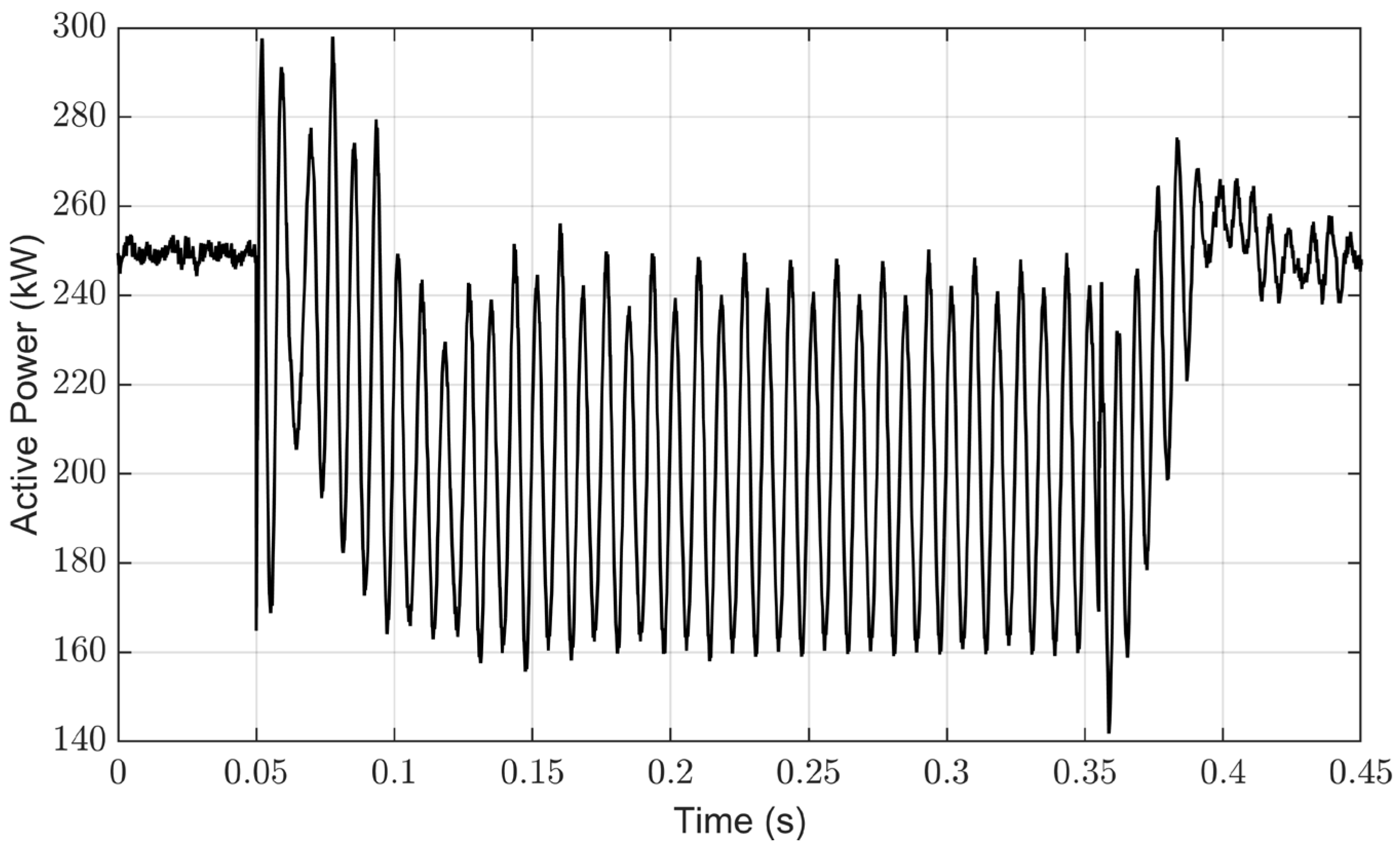
4.1. Performance of Conventional Control under Grid Imbalance
4.2. Performance of Conventional Control for Grid Current Balance
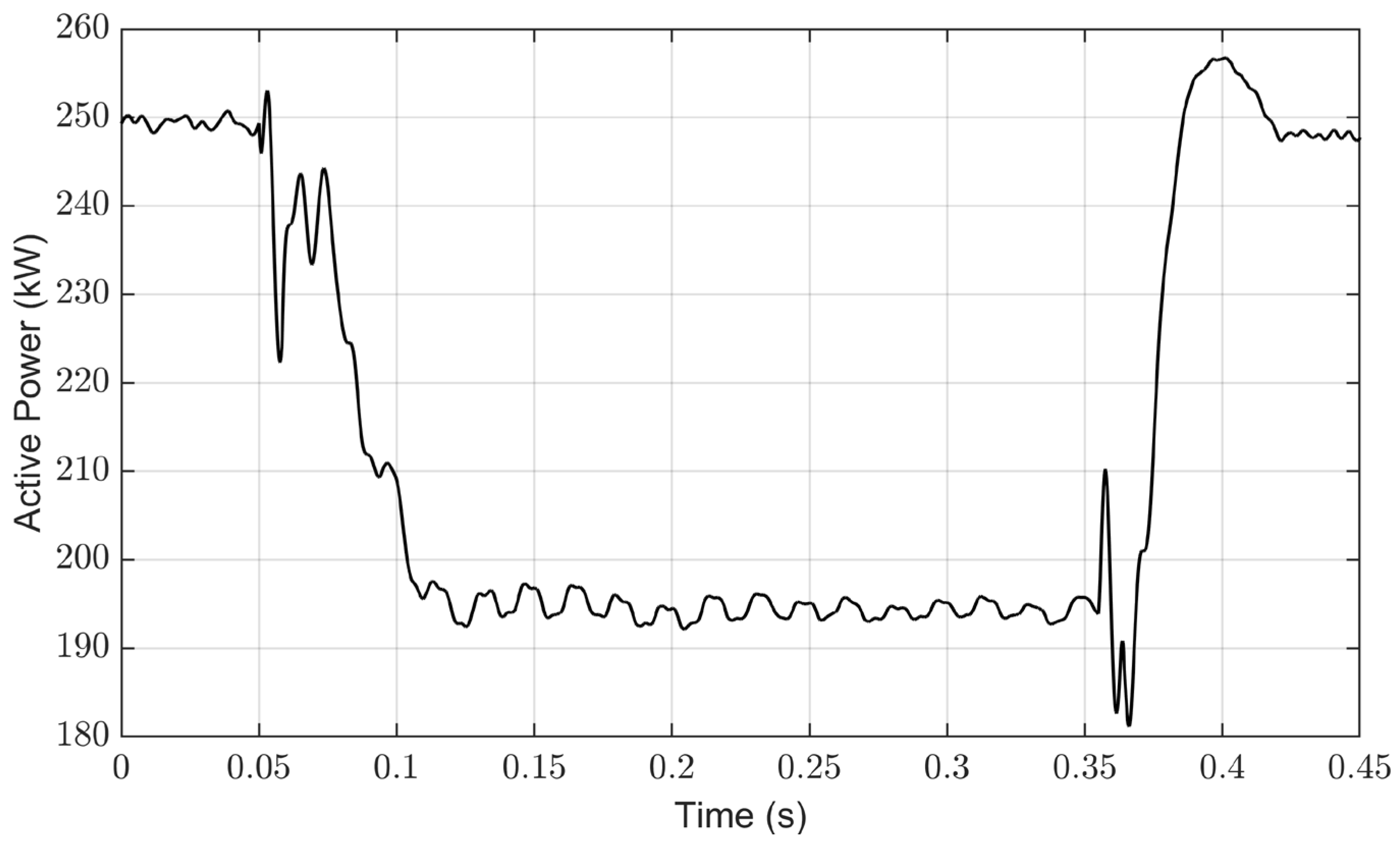
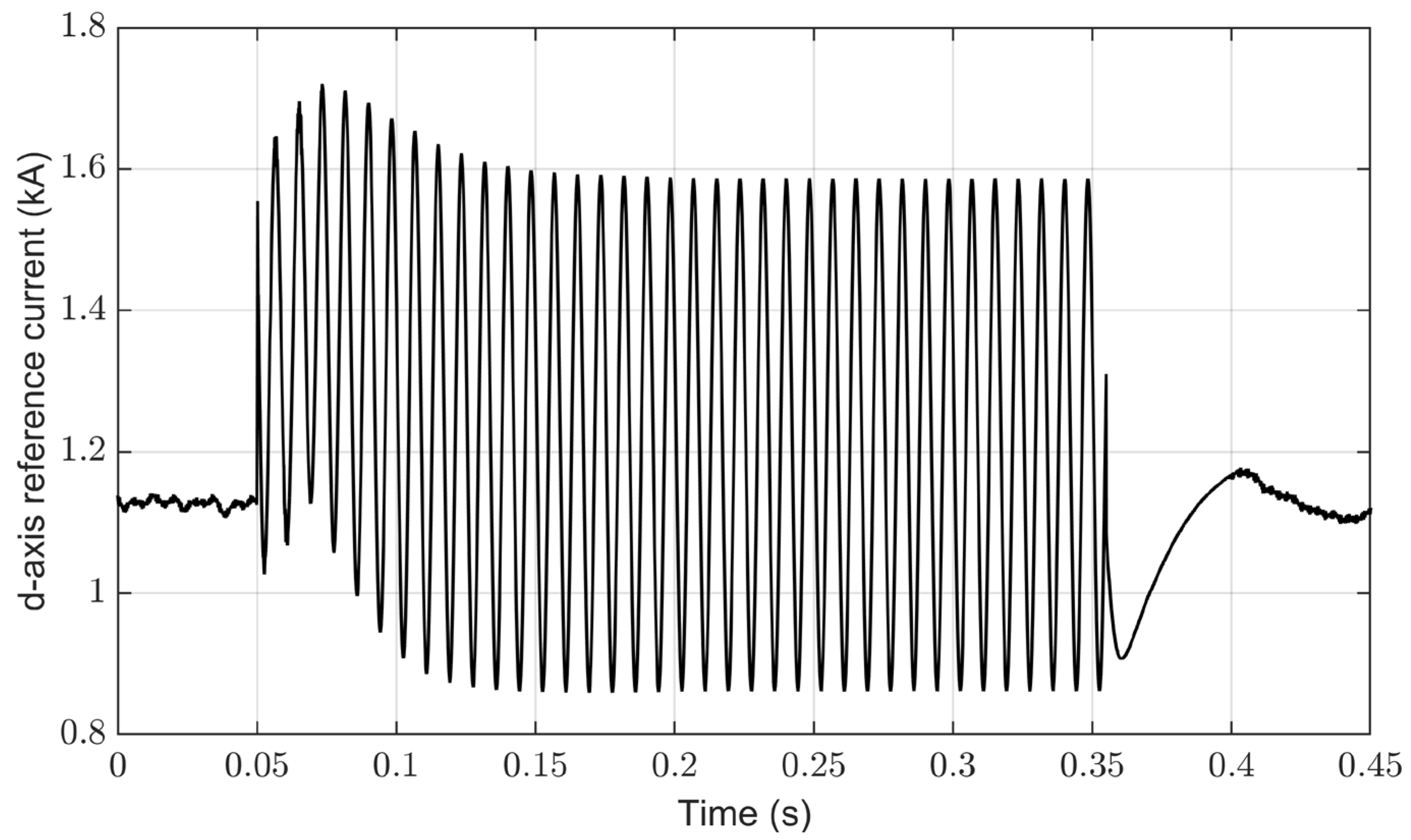
4.3. Implementation of the Control System for Constant Active Power under Unbalanced Conditions
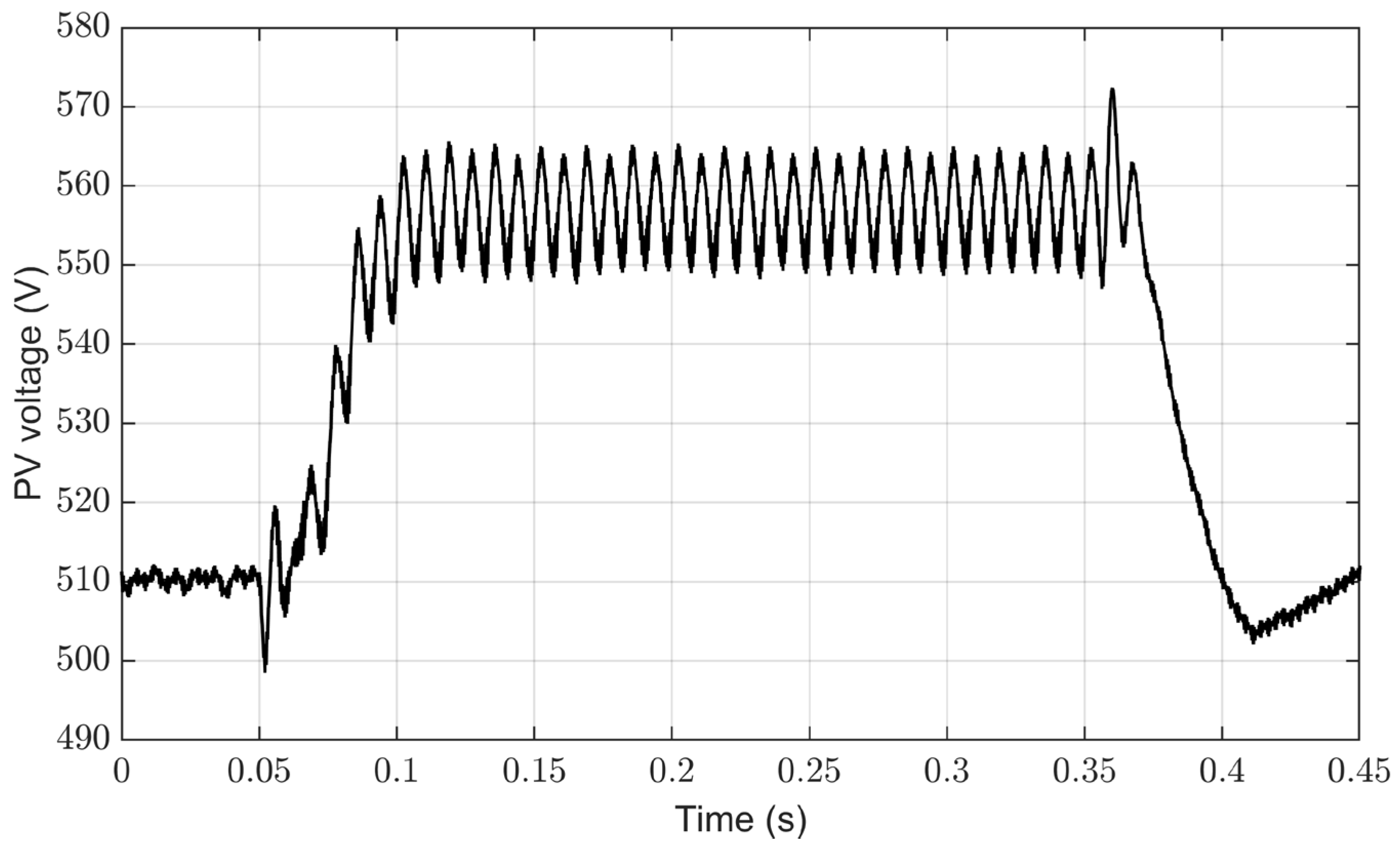
4.4. Implementation of the Control System for Constant DC-Link Voltage under Unbalanced Conditions
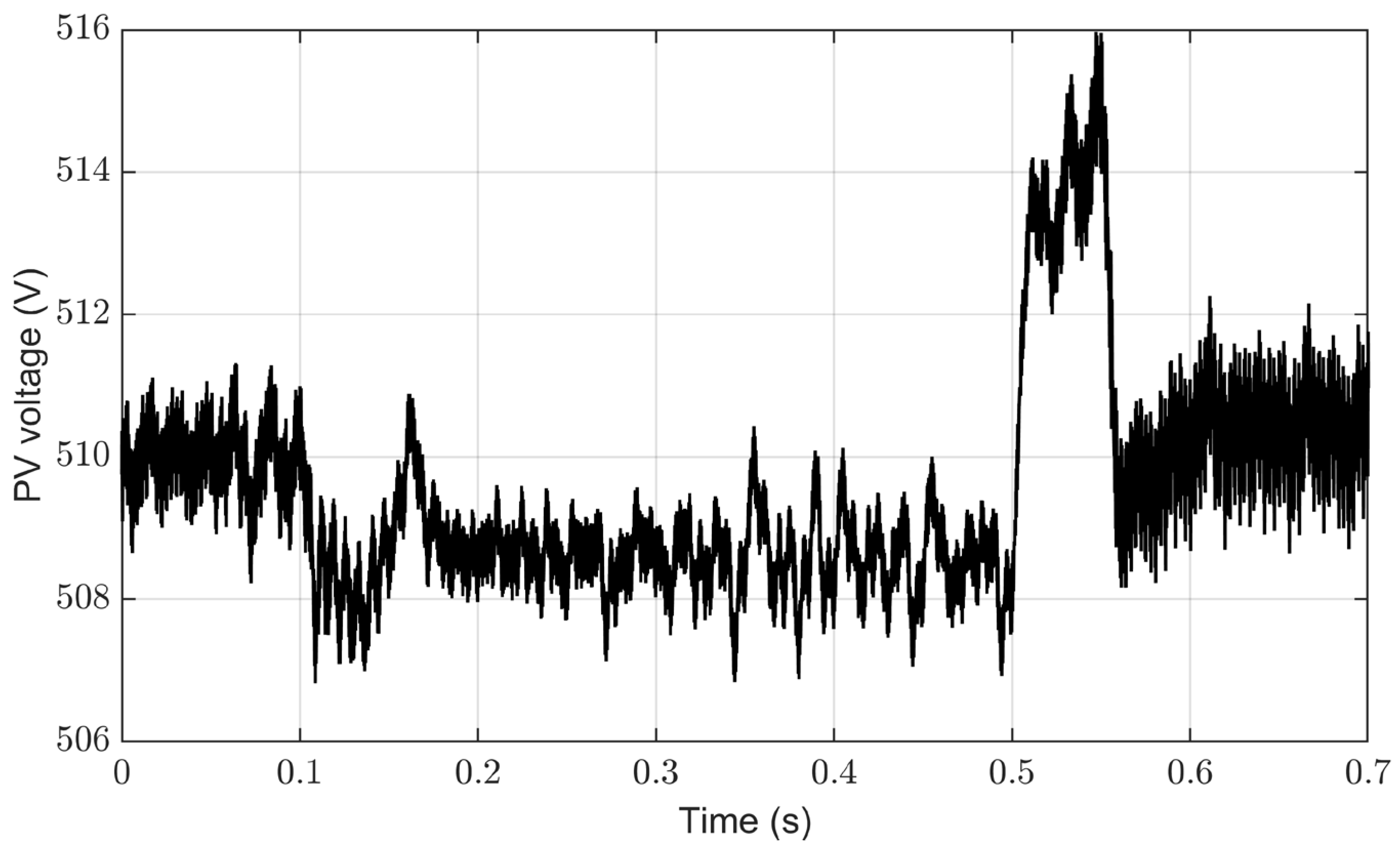
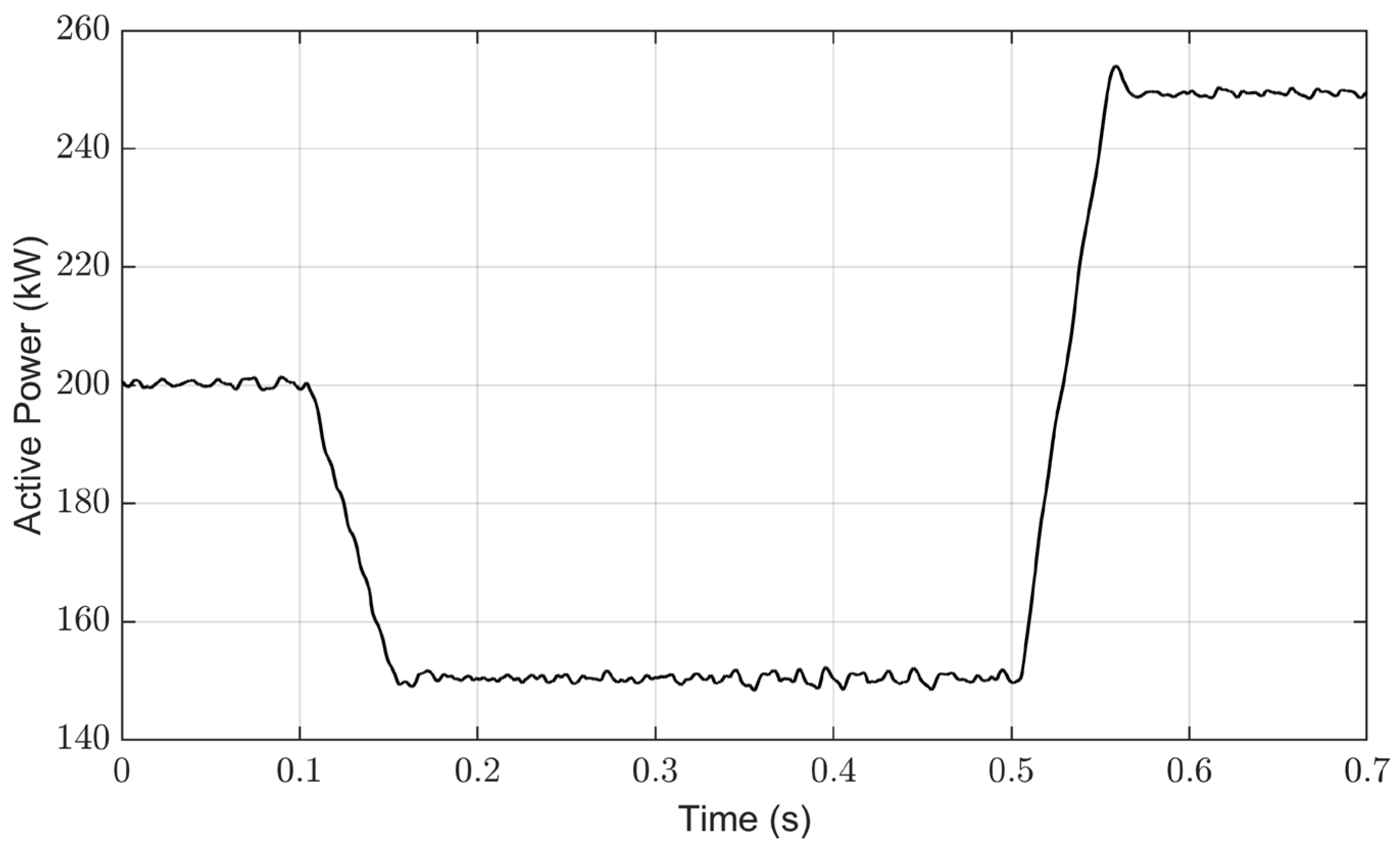
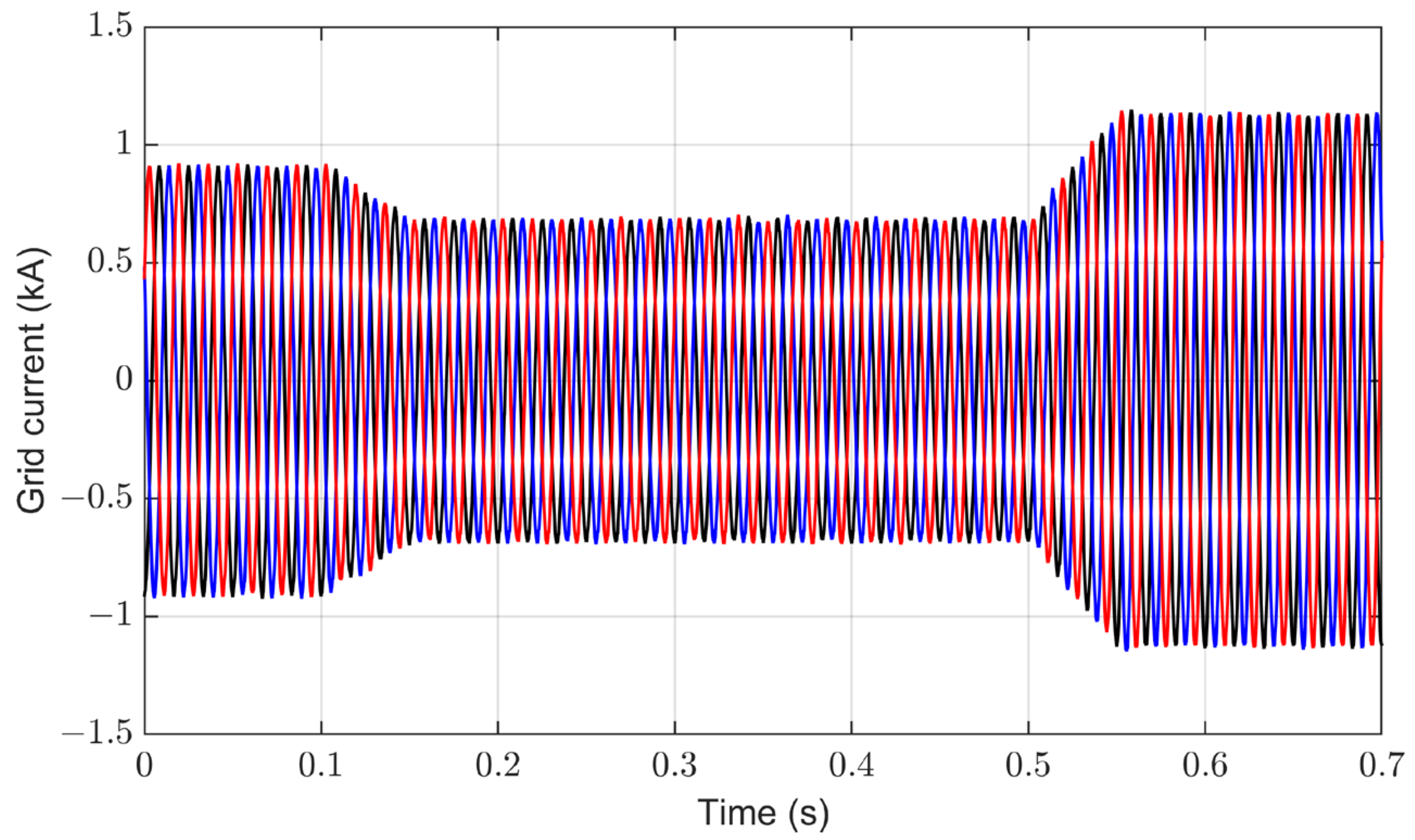
4.5. Performance Evaluation of the Proposed Control System under Irradiance Changes
5. Limitations and Future Research Plans of the Proposed Control Scheme
- Controllers’ Parameters Design Sensitivity: The performance of the control strategy is heavily dependent on the precise tuning of the controllers’ parameters. This sensitivity could lead to challenges in real-world applications, where exact parameter values may not be consistently attainable or where parameters may need to be adjusted to accommodate varying grid conditions;
- Implementation Complexity in Real-World Settings: Although the scheme has shown promising results in simulations, the real-world implementation might encounter complexities due to factors like hardware limitations, environmental variations, and unanticipated grid disturbances. These factors can affect the control strategy’s performance and reliability;
- Scalability and Adaptability Concerns: The current research primarily focuses on specific grid imbalances. Extending the control strategy to various types and scales of PV systems, and under different grid conditions, requires further exploration to establish its scalability and adaptability;
- Dynamic Environmental Response: The control scheme’s responsiveness to a range of dynamic environmental factors, beyond solar irradiance changes, is not fully explored. Understanding the system’s performance under a broader spectrum of environmental conditions is crucial for its application in diverse geographical and climatic settings.
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, J.; Yang, G.; Nielsen, A.H. A Review on Grid-Connected Converter Control for Short-Circuit Power Provision under Grid Unbalanced Faults. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2018, 33, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Boué, A.B.; Guerrero-Rodríguez, N.F.; Stöckl, J.; Strasser, T.I. Frequency- Adaptive Control of a Three-Phase Single-Stage Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System under Grid Voltage Sags. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 125, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Lal, V.N. A Multiobjective Control Strategy for Harmonic Current Mitigation with Enhanced LVRT Operation of a Grid-Tied PV System Without PLL under Abnormal Grid Conditions. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 2164–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.O.M.B.; Torres, A.G.; Cupertino, A.F.; Pereira, H.A. Three-Phase Photovoltaic Inverters during Unbalanced Voltage Sags: Comparison of Control Strategies and Thermal Stress Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON), Curitiba, Brazil, 20–23 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupertino, A.F.; Xavier, L.S.; Brito, E.M.S.; Mendes, V.F.; Pereira, H.A. Benchmarking of Power Control Strategies for Photovoltaic Systems under Unbalanced Conditions. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 106, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, M.E.; Çelik, D. Minimisation of Power Oscillations with a Novel Optimal Control Strategy for Distributed Generation Inverter under Grid Faulty and Harmonic Networks. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, E.; Moradi, G.R.; Rahimi, R.; Farhangi, B.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Farhangi, S. Control Strategy for Three-Phase Grid-Connected PV Inverters Enabling Current Limitation under Unbalanced Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8908–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Lee, C.T.; Cheng, P.T.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. A Low-Voltage Ride-Through Technique for Grid-Connected Converters with Reduced Power Transistors Stress. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8562–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Reliability of Capacitors for DC-Link Applications in Power Electronic Converters—An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3569–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Timbus, A.V.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F. Flexible Active Power Control of Distributed Power Generation Systems during Grid Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; Sosa, J.L.; Matas, J.; Vicuña, L.G. De Grid-Fault Control Scheme for Three-Phase Photovoltaic Inverters with Adjustable Power Quality Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Duarte, J.L.; Hendrix, M.A.M. Pliant Active and Reactive Power Control for Grid-Interactive Converters under Unbalanced Voltage Dips. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, M.; Isik, S.; Alkuhayli, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Power Ripple Control Method for Modular Multilevel Converter under Grid Imbalances. Energies 2022, 15, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Robina, P.; Rouzbehi, K.; Gordillo, F.; Pou, J. Grid-Following Voltage Source Converters: Basic Schemes and Current Control Techniques to Operate with Unbalanced Voltage Conditions. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2021, 2, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; Borrell, A.; De Vicuña, L.G. Active and Reactive Power Strategies with Peak Current Limitation for Distributed Generation Inverters during Unbalanced Grid Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Mohammadi, R. Peak Current Limitation for Grid Side Inverter by Limited Active Power in PMSG-Based Wind Turbines During Different Grid Faults. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alathamneh, M.; Ghanayem, H.; Yang, X.; Nelms, R.M. Three-Phase Grid-Connected Inverter Power Control under Unbalanced Grid Conditions Using a Proportional-Resonant Control Method. Energies 2022, 15, 7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, Z. Flexible Power Regulation and Current-Limited Control of the Grid-Connected Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Voltage Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7425–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Rodríguez, P. Grid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power Systems; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470057513. [Google Scholar]
- El Aamri, F.; Maker, H.; Sera, D.; Spataru, S.V.; Guerrero, J.M.; Mouhsen, A. A Direct Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Single-Phase Grid-Connected PV Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8961–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedari Zare Zadeh, M.; Fathi, S.H. A New Approach for Photovoltaic Arrays Modeling and Maximum Power Point Estimation in Real Operating Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9334–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa De Souza, A.; Cardoso Melo, F.; Lima Oliveira, T.; Eduardo Tavares, C. Performance Analysis of the Computational Implementation of a Simplified PV Model and MPPT Algorithm. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.; Acharya, S.; Hosani, M.A.; Moursi, M.S. El Hill Climbing Power Flow Algorithm for Hybrid DC/AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5532–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.C.; Dunnigan, M.W. Development and Comparison of an Improved Incremental Conductance Algorithm for Tracking the MPP of a Solar PV Panel. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Hussain, I.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Framework of Maximum Power Extraction from Solar PV Panel Using Self Predictive Perturb and Observe Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sera, D.; Mathe, L.; Kerekes, T.; Spataru, S.V.; Teodorescu, R. On the Perturb-and-Observe and Incremental Conductance Mppt Methods for PV Systems. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2013, 3, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanaban, S.; Priyadarshi, N.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Hossain, E. A Hybrid ANFIS-ABC Based MPPT Controller for PV System with Anti-Islanding Grid Protection: Experimental Realization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 103377–103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.Y.; Sarimuthu, C.R.; Lim, J.M.Y. Artificial Intelligence Based MPPT Techniques for Solar Power System: A Review. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, M.; Velasco, M.; Miret, J.; Borrell, A.; Guzman, R. Control Scheme for Negative-Sequence Voltage Compensation and Current Sharing in Inverter-Based Grid-Connected Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 6556–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachi, M.R.K.; Awal, M.A.; Husain, I. Asymmetrical Fault Ride-Through and Power Oscillation Characterization for Grid-Tied Voltage Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 4550–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, I.; Isakov, I.; Grabic, S. Extensive Technique for Grid-Connected Converter Power Generation Maximisation during Asymmetrical Grid Voltages. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Negative Sequence Current Regulation Based Power Control Strategy for Vienna Rectifier Under Unbalanced Grid Voltage Dips. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Hsu, C.W.; Cheng, P.T. A Low-Voltage Ride-through Technique for Grid-Connected Converters of Distributed Energy Resources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Chen, W.; Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F. Power Controllability of a Three-Phase Converter with an Unbalanced AC Source. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, R.; Díaz, M.; Rojas, F.; Clare, J.; Wheeler, P. Resonant Control System for Low-Voltage Ride-through in Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Vu, T.K.; Kim, R.Y. Implemental Control Strategy for Grid Stabilization of Grid-Connected PV System Based on German Grid Code in Symmetrical Low-to-Medium Voltage Network. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.L.; Hu, S.H.; Chan, Y.H. D-STATCOM with Positive-Sequence Admittance and Negative-Sequence Conductance to Mitigate Voltage Fluctuations in High-Level Fenetration of Distributed-Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, S.; Azzouz, M.; Awad, A.S.A.; Sindi, H. Fault Ride-through Strategies for Synchronverter-Interfaced Energy Resources Under Asymmetrical Grid Faults. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L. Different Control Objectives for Grid-Connected Converter under Unbalanced Grid Voltage Using Forgotten Iterative Filter as Phase Lock Loop. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.W.; Nejabatkhah, F.; Mei, Y.; Lu, X. Parallel Operation of Bidirectional Interfacing Converters in a Hybrid AC/DC Microgrid Under Unbalanced Grid Voltage Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Guerrero, J.M. Asymmetrical Grid Fault Ride-through Strategy of Three-Phase Grid-Connected Inverter Considering Network Impedance Impact in Low-Voltage Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, H.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H.; Quan, Y. Flexible Grid Connection Technique of Voltage-Source Inverter Under Unbalanced Grid Conditions Based on Direct Power Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 4041–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, M.E.; Çelik, D. Mitigation of DC-Link Voltage Oscillations to Reduce Size of DC-Side Capacitor and Improve Lifetime of Power Converter. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 194, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Abusorrah, A.M.; Al-Turki, Y. Hybrid Synchronous/Stationary Reference-Frame-Filtering-Based PLL. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5018–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ruan, X.; Bao, C.; Pan, D.; Wang, X. Grid Synchronization Systems of Three-Phase Grid-Connected Power Converters: A Complex-Vector-Filter Perspective. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, Z.; Wei, T. A Novel Phase-Locked Loop with Improved-Dual Adaptive Notch Filter and Multi-Variable Filter. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 176578–176586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









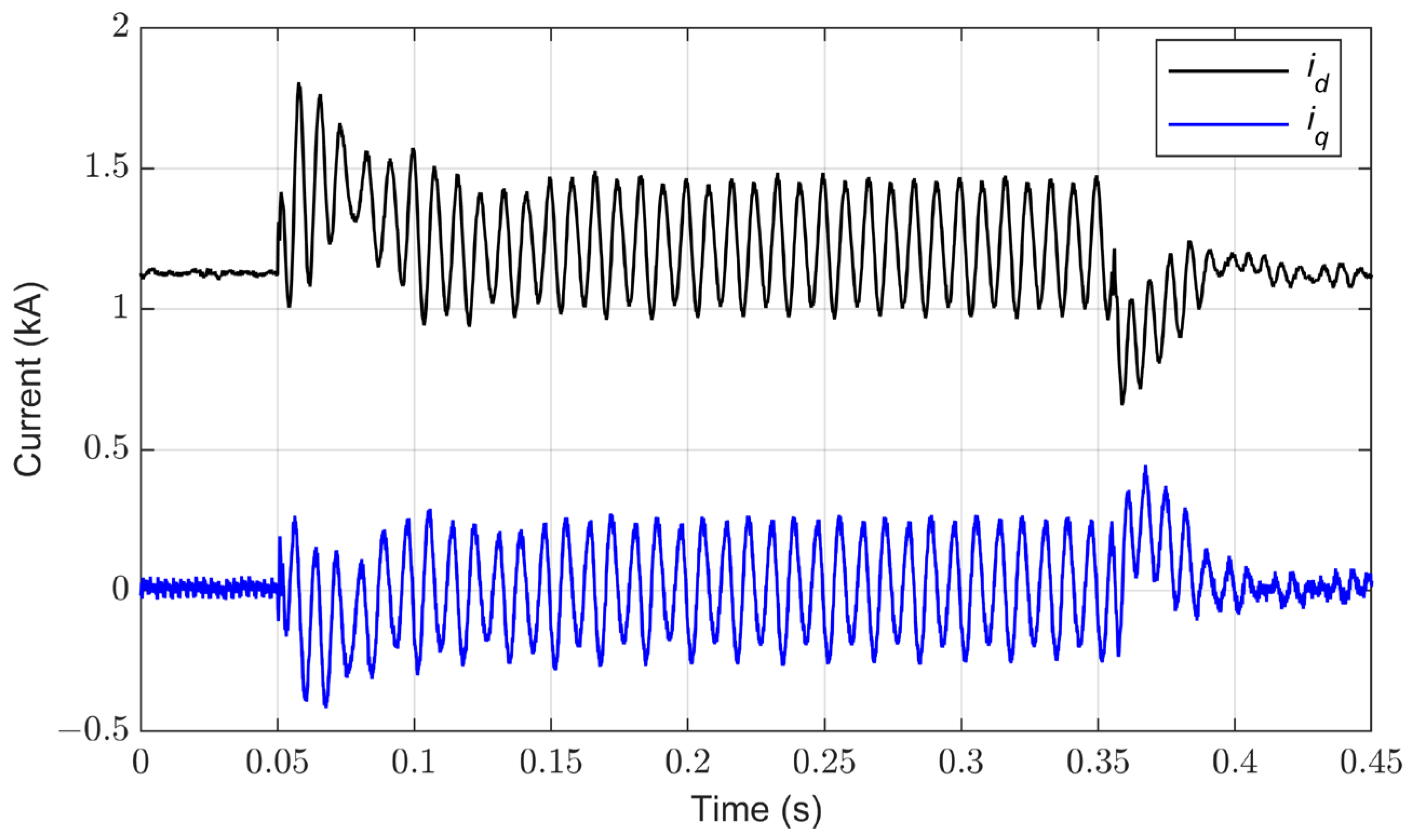
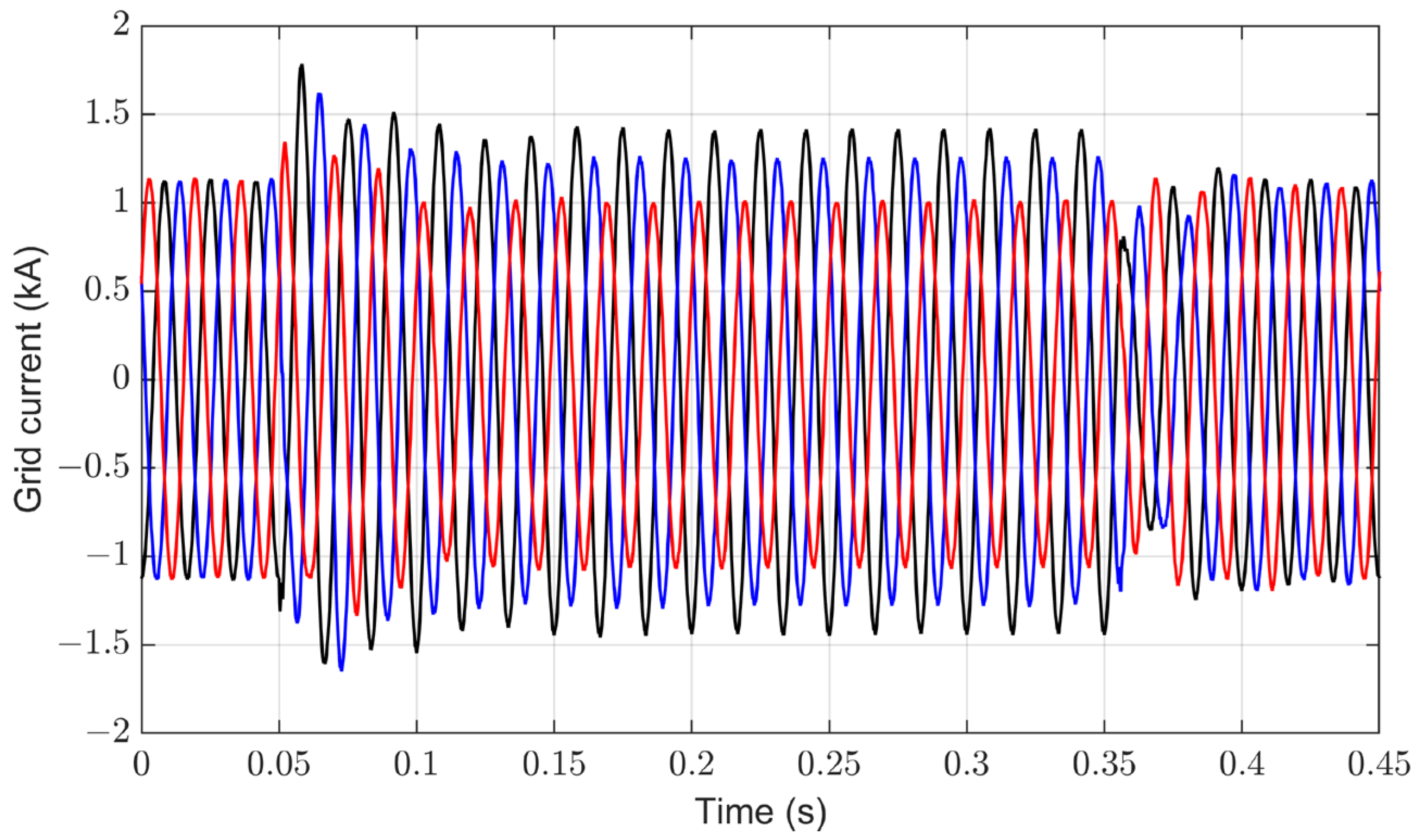
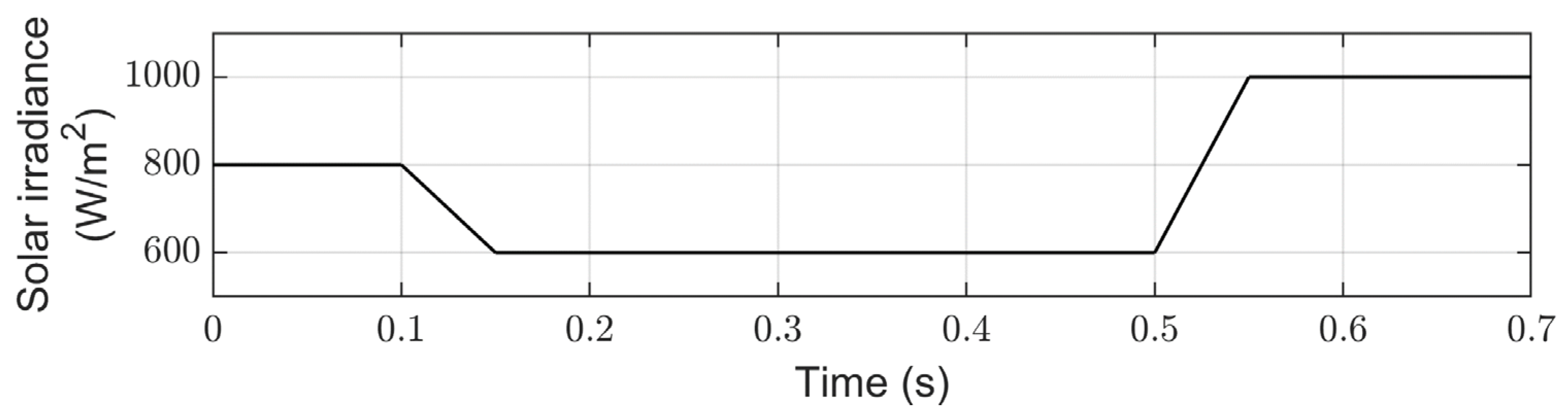
| Symbol | Description | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 280 | kVA | |
| DC-link voltage | 800 | V | |
| Line-to-line grid voltage | 250 | V | |
| T | Transformer (Δ-Yg) | 250/4160 | V |
| f | Fundamental frequency | 60 | Hz |
| LCL filter inductance | 99.35 | µH | |
| LCL filter capacitance | 19.87 | mF | |
| Damping resistor | 2.67 | mΩ | |
| Inverter switching frequency | 1980 | Hz | |
| DC-link capacitance | 13.55 | mF | |
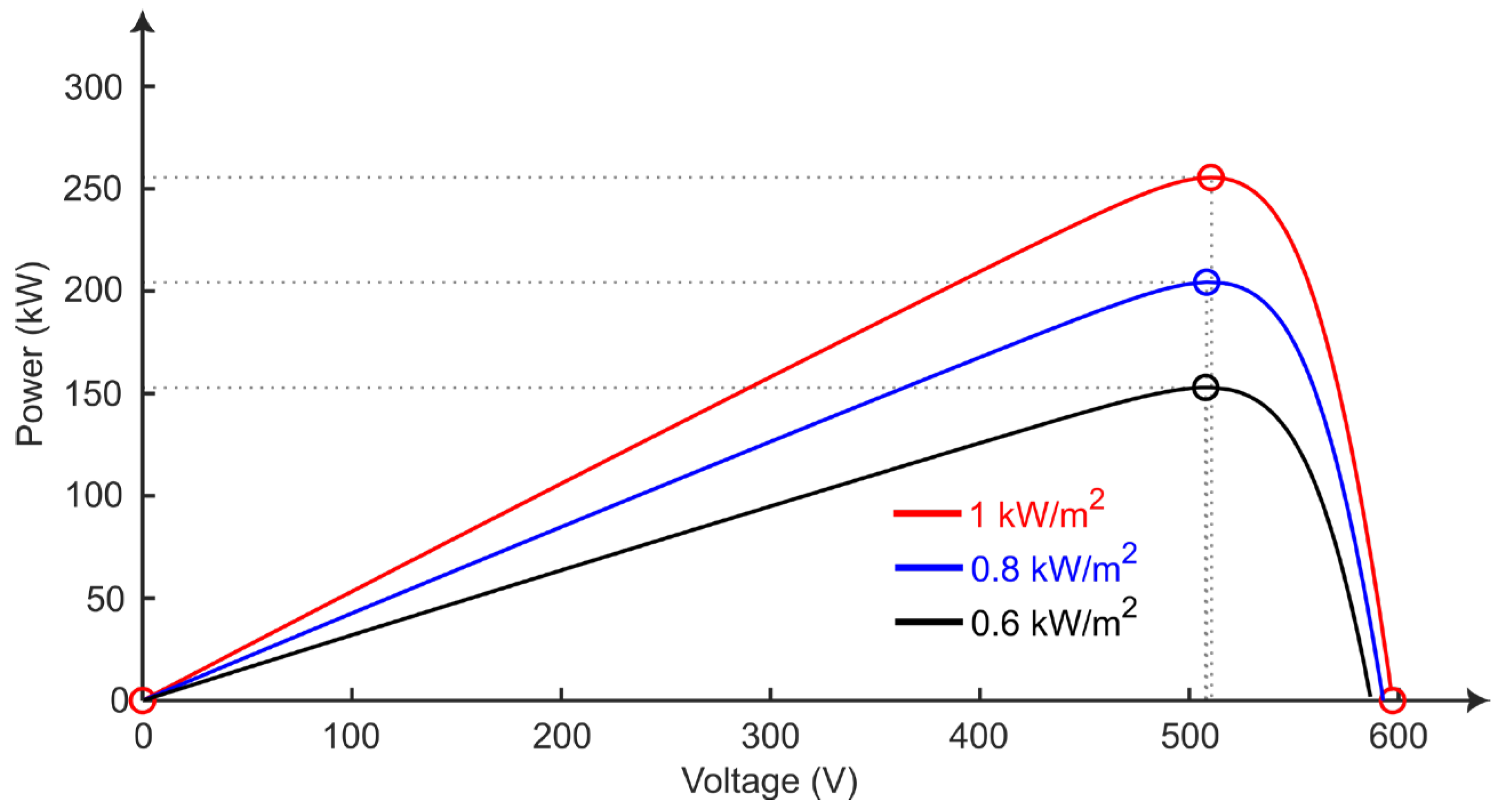
| Maximum power point voltage 1 | 510.3 | V | |
| PV farm maximum power 1 | 255.5 | kW |
| Solar Irradiance | Calculated P-V Characteristics | Simulated PV System | Error (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Power (kW) | Voltage (V) | Power (kW) | Voltage (V) | Power (kW) | |
| 600 W/m2 | 507.8 | 152.9 | 508.5 | 152.7 | 0.14% | 0.13% |
| 800 W/m2 | 508.3 | 204.4 | 510 | 204.2 | 0.33% | 0.10% |
| 1000 W/m2 | 510.3 | 255.5 | 510.2 | 255.1 | 0.02% | 0.16% |
| Parameter\Solar Irradiance | 600 W/m2 | 800 W/m2 | 1000 W/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power of PV Array () | 152.7 kW | 204.2 kW | 255.1 kW |
| Active Power at PCC () | 149.6 kW | 200.9 kW | 249.0 kW |
| Efficiency of PV Inverter () | 98% | 98.4% | 97.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, M. Control Approach of Grid-Connected PV Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Conditions. Processes 2024, 12, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010212
Alharbi M. Control Approach of Grid-Connected PV Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Conditions. Processes. 2024; 12(1):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010212
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Mohammed. 2024. "Control Approach of Grid-Connected PV Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Conditions" Processes 12, no. 1: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010212
APA StyleAlharbi, M. (2024). Control Approach of Grid-Connected PV Inverter under Unbalanced Grid Conditions. Processes, 12(1), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010212










